An attribution analysis of land subsidence features in the city of Bayannur in Inner Mongolia based on InSAR
-
摘要:
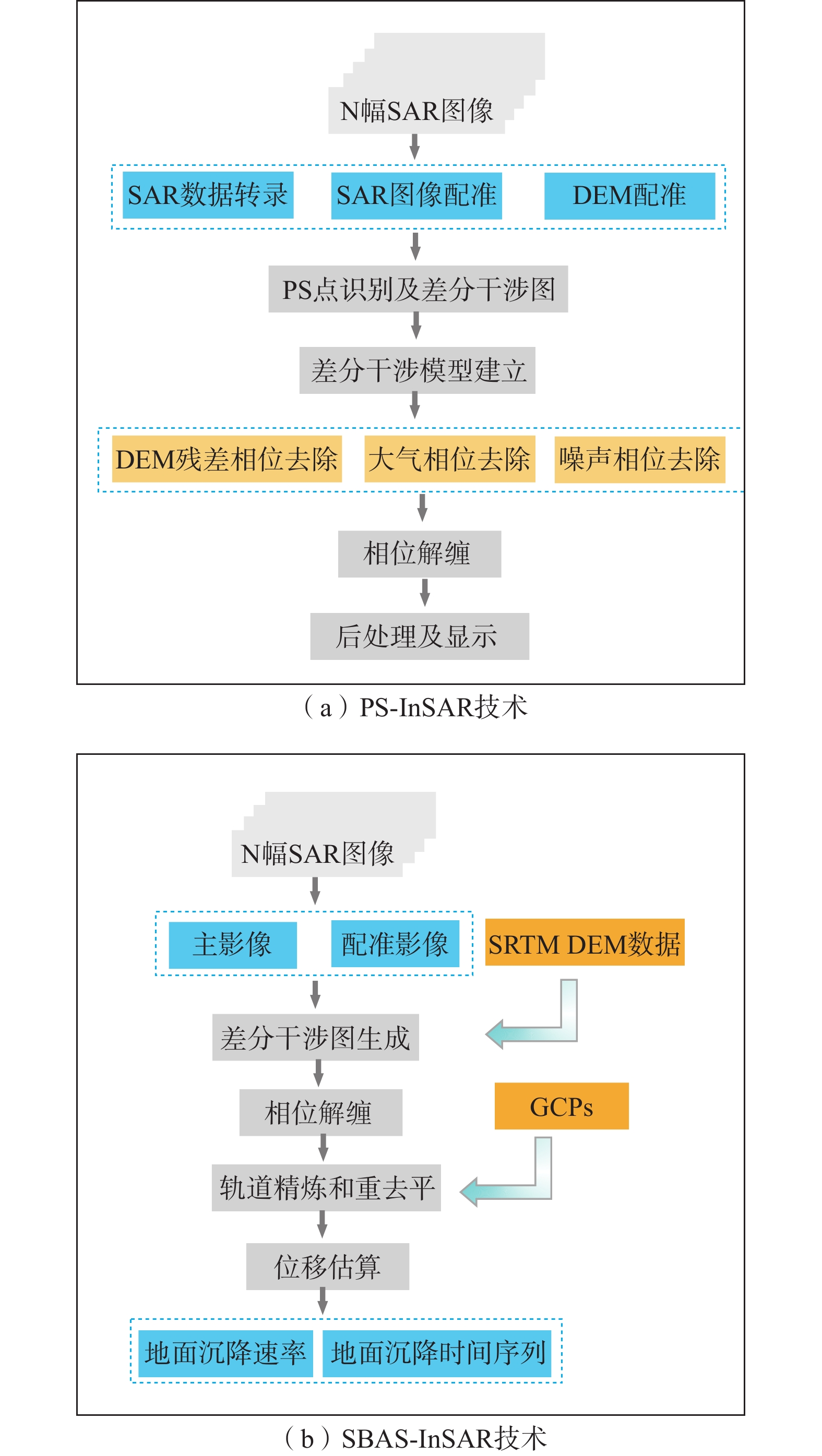
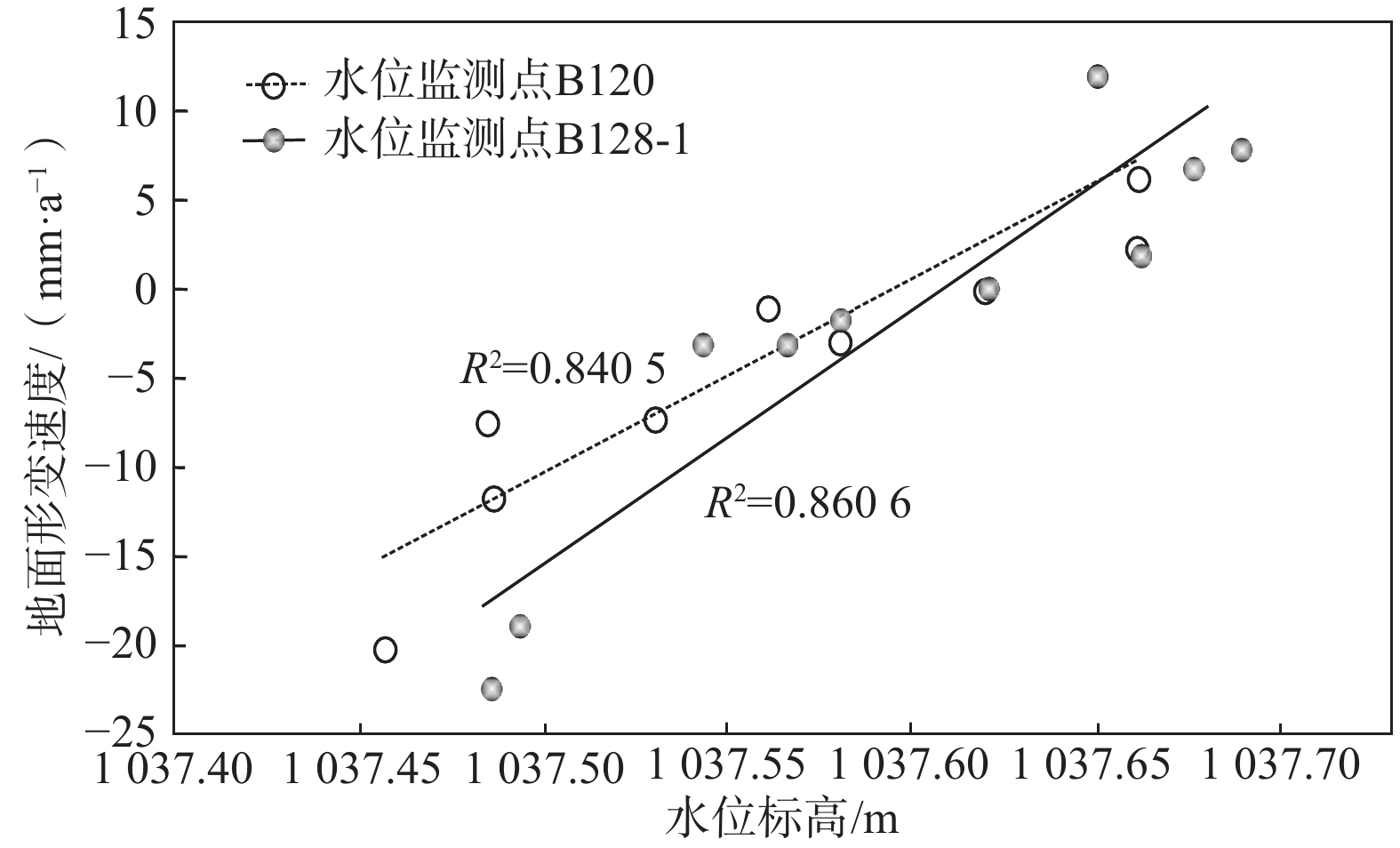
巴彦淖尔市位于内蒙古自治区西部,区内第四系松散沉积层厚度大,具有发育地面沉降的基础条件。为填补该地区地面沉降研究的空白,利用PS-InSAR和SBAS-InSAR技术分别对巴彦淖尔市2007—2011年(ALOS PALSAR数据,98景)和2015—2016年(Radarsat-2数据,10景)的地面沉降情况进行定量分析,并现场实地调查验证了InSAR技术监测结果的可靠性,以分析探讨该区域地面沉降成因及发展趋势。研究结果表明:(1)巴彦淖尔市地面沉降属于缓慢性沉降,沉降严重程度为低级,处于发生阶段;(2)2007—2011年沉降速率主要集中在0~10 mm/a,存在3处地面沉降集中区,即杭锦后旗沉降区(A)、临河区沉降区(B)、开发区水源地及北部沉降区(C);(3)2015—2016年沉降速率主要集中在0~2.6 mm/a,存在1处地面沉降区,即临河区及北部沉降区(D),该沉降区是在B区的基础上继续向周边及北部扩展形成的;(4)巴彦淖尔市地面沉降的主要影响因素为地下水开发利用引起的地下水位下降,沉积层固结压实是重要因素,地表荷载的增加也产生了一定推动作用。
-
关键词:
- PS-InSAR /
- SBAS-InSAR /
- 巴彦淖尔市 /
- 地面沉降 /
- 地下水位下降
Abstract:The thickness of Quaternary loose sediments in the city of Bayannur in the west of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region is large, which provides basic conditions for the development of land subsidence. ALOS PALSAR (98 frames from 2007 to 2011) and RADARSAT-2 (10 frames from 2015 to 2016) are extracted to quantitatively analyze the land subsidence in the city of Bayannur, respectively, by using the PS-InSAR and SBAS-InSAR method for the first time, and field investigation is carried out to verify the reliability of InSAR monitoring results. The causes and development trend of land subsidence in this area are further analyzed, and important technical support for land subsidence disaster prevention and reduction are provided. The results indicate that (1) the land subsidence in the city of Bayannur exhibites a slow trend. The severity of subsidence is low and belongs to the stage of occurrence. (2) The subsidence rate was mainly concentrated in 0−10 mm/a from 2007 to 2011, and three concentrated land subsidence areas were observed: the Hanggin Rear Banner subsidence area (A), Linhe district subsidence area (B), and the water source area of development zone subsidence area (C). (3) From 2015 to 2016, the subsidence rate was mainly concentrated in 0−2.6 mm/a, and one concentrated land subsidence area was detected, that is, the Linhe district and north subsidence area (D), where the land subsidence is based on the Linhe district subsidence area (B), and continues to expand to the surrounding areas and the north. (4) The main influencing factor of land subsidence in the city of Bayannur is the groundwater level drop caused by the development and utilization of groundwater. Besides, the consolidation and compaction of the sediments is also an essential factor for the land subsidence in this area, and the increase in surface load has a certain promoting effect on the land subsidence.
-
Key words:
- PS-InSAR /
- SBAS-InSAR /
- Bayannur /
- land subsidence /
- groundwater level drop
-

-
表 1 巴彦淖尔市ALOS PALSAR 和Radarsat-2 数据参数
Table 1. Parameters of ALOS PALSAR data and Radarsat-2 SAR data in the city of Bayannur
传感器 ALOS PALSAR Radarsat-2 卫星高度/km 691.65 798 波段(波长/cm) L(23.6) C(5.6) 空间分辨率/m 4.684(FBS)/9.368(FBD) 5 图幅范围/km 30×70 125×125 影像数/景 98 10 时间跨度 2007-01-13—2011-03-11 2015-06-02—2016-12-31 表 2 巴彦淖尔市地面沉降集中区特征
Table 2. Characteristics of land subsidence concentration area in the city of Bayannur
编号 地面沉降区 最大沉降
速率/(mm·a−1)沉降区面积
/km2时间段 A 杭锦后旗 7.285 33.04 2007—2011 B 临河区 8.336 139.98 2007—2011 C 开发区水源地及北部 4.615 51.51 2007—2011 D 临河区及北部 5.634 221.43 2015—2016 -
[1] DU Z Y, GE L L, NG A H, et al. Correlating the subsidence pattern and land use in Bandung, Indonesia with both Sentinel-1/2 and Alos-2 satellite images[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation,2018,67:54 − 68. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2018.01.001
[2] LIU Y Y, ZHAO C Y, ZHANG Q, et al. Complex surface deformation monitoring and mechanism inversion over Qingxu-Jiaocheng, China with multi-sensor SAR images[J]. Journal of Geodynamics,2018,114:41 − 52. doi: 10.1016/j.jog.2018.01.016
[3] KIM S W, WDOWINSKI S, DIXON T H, et al. InSAR-based mapping of surface subsidence in Mokpo City, Korea, using JERS-1 and ENVISAT SAR data[J]. Earth, Planets and Space,2008,60(5):453 − 461. doi: 10.1186/BF03352812
[4] KARIMZADEH S. Characterization of land subsidence in Tabriz Basin (NW Iran) using InSAR and watershed analyses[J]. Acta Geodaetica Et Geophysica,2016,51(2):181 − 195. doi: 10.1007/s40328-015-0118-4
[5] 殷跃平, 张作辰, 张开军. 我国地面沉降现状及防治对策研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2005,16(2):1 − 8. [YIN Yueping, ZHANG Zuochen, ZHANG Kaijun. Land subsidence and countermeasures for its prevention in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2005,16(2):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2005.02.001
YIN Yueping, ZHANG Zuochen, ZHANG Kaijun. Land subsidence and countermeasures for its prevention in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2005, 16(2): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2005.02.001
[6] BELL J W, AMELUNG F, FERRETTI A, et al. Permanent scatterer InSAR reveals seasonal and long-term aquifer-system response to groundwater pumping and artificial recharge[J]. Water Resources Research,2008,44(2):W02407.
[7] 房浩, 何庆成, 徐斌, 等. 沧州地区地面沉降灾害风险评价研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(4):159 − 164. [FANG Hao, HE Qingcheng, XU Bin, et al. A study of risk assessment of the land subsidence in Cangzhou[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(4):159 − 164. (in Chinese with English abstract)
FANG Hao, HE Qingcheng, XU Bin, et al. A study of risk assessment of the land subsidence in Cangzhou[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(4): 159-164. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 张剑, 柯宝贵, 刘同木, 等. 利用时序InSAR监测兰州市中心城区地面沉降[J]. 测绘科学,2021,46(1):99 − 107. [ZHANG Jian, KE Baogui, LIU Tongmu, et al. Surface subsidence monitoring of Lanzhou downtown area based on time series InSAR technology[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping,2021,46(1):99 − 107. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Jian, KE Baogui, LIU Tongmu, et al. Surface subsidence monitoring of Lanzhou downtown area based on time series InSAR technology[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2021, 46(1): 99-107. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] ZHAO C Y, ZHANG Q, YANG C S, et al. Integration of MODIS data and short baseline subset (SBAS) technique for land subsidence monitoring in Datong, China[J]. Journal of Geodynamics,2011,52(1):16 − 23. doi: 10.1016/j.jog.2010.11.004
[10] ZHU W, ZHANG Q, DING X L, et al. Recent ground deformation of Taiyuan Basin (China) investigated with C-, L-, and X-bands SAR images[J]. Journal of Geodynamics,2013,70:28 − 35. doi: 10.1016/j.jog.2013.06.003
[11] NIKOS S, LOANNIS P, CONSTANTINOS L, et al. Land subsidence rebound detected via multi-temporal InSAR and ground truth data in Kalochori and Sindos regions, Northern Greece[J]. Engineering Geology,2016,209:175 − 186. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.05.017
[12] 刘一霖, 黄海军, 刘艳霞, 等. 短基线集InSAR技术用于黄河三角洲地面沉降监测与人为因素影响[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2016,36(5):173 − 180. [LIU Yilin, HUANG Haijun, LIU Yanxia, et al. Monitoring of land subsidence and impacts of human activities in the Yellow River Delta using the small baseline subset method[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2016,36(5):173 − 180. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Yilin, HUANG Haijun, LIU Yanxia, et al. Monitoring of land subsidence and impacts of human activities in the Yellow River Delta using the small baseline subset method[J]. Marine geolog & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(5): 173-180. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] CASTELLAZZI P, ARROYO-DOMÍNGUEZ N, MARTEL R, et al. Land subsidence in major cities of Central Mexico:Interpreting InSAR-derived land subsidence mapping with hydrogeological data[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation,2016,47:102 − 111. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2015.12.002
[14] AIMAITI Y, YAMAZAKI F, LIU W. Multi-sensor InSAR analysis of progressive land subsidence over the Coastal City of Urayasu, Japan[J]. Remote Sensing,2018,10(8):1304. doi: 10.3390/rs10081304
[15] 杨志岩, 孙标, 李元杰, 等. 内蒙古临河区地下水补径排特征及动态变化规律[J]. 中国地质调查,2016,3(6):63 − 67. [YANG Zhiyan, SUN Biao, LI Yuanjie, et al. Characterization of groundwater recharge, runoff and drainage and their dynamic changes in Linhe, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Survey of China,2016,3(6):63 − 67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YANG Zhiyan, SUN Biao, LI Yuanjie, et al. Characterization of groundwater recharge, runoff and drainage and their dynamic changes in Linhe, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2016, 3(6): 63-67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 李元杰, 杨志岩, 丁慧君. 内蒙古自治区巴彦淖尔市临河区地下水资源综合评价(1∶50 000)[R]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古自治区地质环境监测院, 2014
LI Yuanjie, YANG Zhiyan, DING Huijun. Comprehensive evaluation of groundwater resources in Langhe District, Bayannur City, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (1∶50 000)[R]. Huhhot: Inner Mongolia Geological Environmental Monitoring Institute, 2014. (in Chinese)
[17] 石建省, 张翼龙, 刘银虎. 河套平原地下水资源及其环境问题调查评价[R]. 石家庄: 中国地质科学院水文地质环境地质研究, 2013
SHI Jiansheng, ZHANG Yilong, LIU Yinhu. Investigation and evaluation of groundwater resources and environmental problems in Hetao Plain[R]. Shijiazhuang: Research of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2013. (in Chinese)
[18] 张金芝, 黄海军, 刘艳霞, 等. 基于PSInSAR技术的现代黄河三角洲地面沉降监测与分析[J]. 地理科学,2013,33(7):831 − 836. [ZHANG Jinzhi, HUANG Haijun, LIU Yanxia, et al. Monitoring and analysis of ground subsidence in the modern Yellow River Delta area based on PSInSAR technique[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica,2013,33(7):831 − 836. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Jinzhi, HUANG Haijun, LIU Yanxia, et al. Monitoring and analysis of ground subsidence in the modern Yellow River Delta Area based on PSInSAR Technique[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2013, 33(7): 831-836. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 王彩会, 陈杰, 朱锦旗. 开采浅层地下水对地面沉降影响的探讨[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2004,15(4):79 − 81. [WANG Caihui, CHEN Jie, ZHU Jinqi. Inquiring into the influence of shallow groundwater exploitation on land subsidence in Suzhou, Wuxi and Changzhou area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2004,15(4):79 − 81. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2004.04.017
WANG Caihui, CHEN Jie, ZHU Jinqi. Inquiring into the influence of shallow groundwater exploitation on land subsidence in Suzhou, Wuxi and Changzhou area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2004, 15(4): 79-81. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2004.04.017
[20] 池永翔. 福州温泉区地面沉降特点及影响因素分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2009,36(6):131 − 133. [CHI Yongxiang. Analysis of influence factors for land subsidence in Fuzhou[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2009,36(6):131 − 133. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2009.06.029
CHI Yongxiang. Analysis of influence factors for land subsidence in Fuzhou[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2009, 36(6): 131-133. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2009.06.029
[21] 陈崇希, 裴顺平. 地下水开采-地面沉降模型研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2001,28(2):5 − 8. [CHEN Chongxi, PEI Shunping. Research on groundwater exploitation-land subsidence model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2001,28(2):5 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2001.02.002
CHEN Chongxi, PEI Shunping. Research on groundwater exploitation-land subsidence model[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2001, 28 (2): 5-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2001.02.002
[22] 雷坤超, 陈蓓蓓, 宫辉力, 等. 基于PS-InSAR技术的天津地面沉降研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2013,40(6):106 − 111. [LEI Kunchao, CHEN Beibei, GONG Huili, et al. Detection of land subsidence in Tianjin based on PS-InSAR technology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2013,40(6):106 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LEI Kunchao, CHEN Beibei, GONG Huili, et al. Detection of land subsidence in Tianjin based on PS-InSAR technology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2013, 40(6): 106-111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 全国国土资源标准化技术委员会. 地面沉降调查监测规范: DZ/T0283—2015[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015: 16 − 17
National Technical Committee of Land and Resources Standardization. Code for investigation and monitoring of land subsidence: DZ/T0283—2015[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2015: 16 − 17. (in Chinese)
-




 下载:
下载: