Analytical solution of formation temperature distribution under dynamic heat load of borehole heat exchangers
-
摘要:
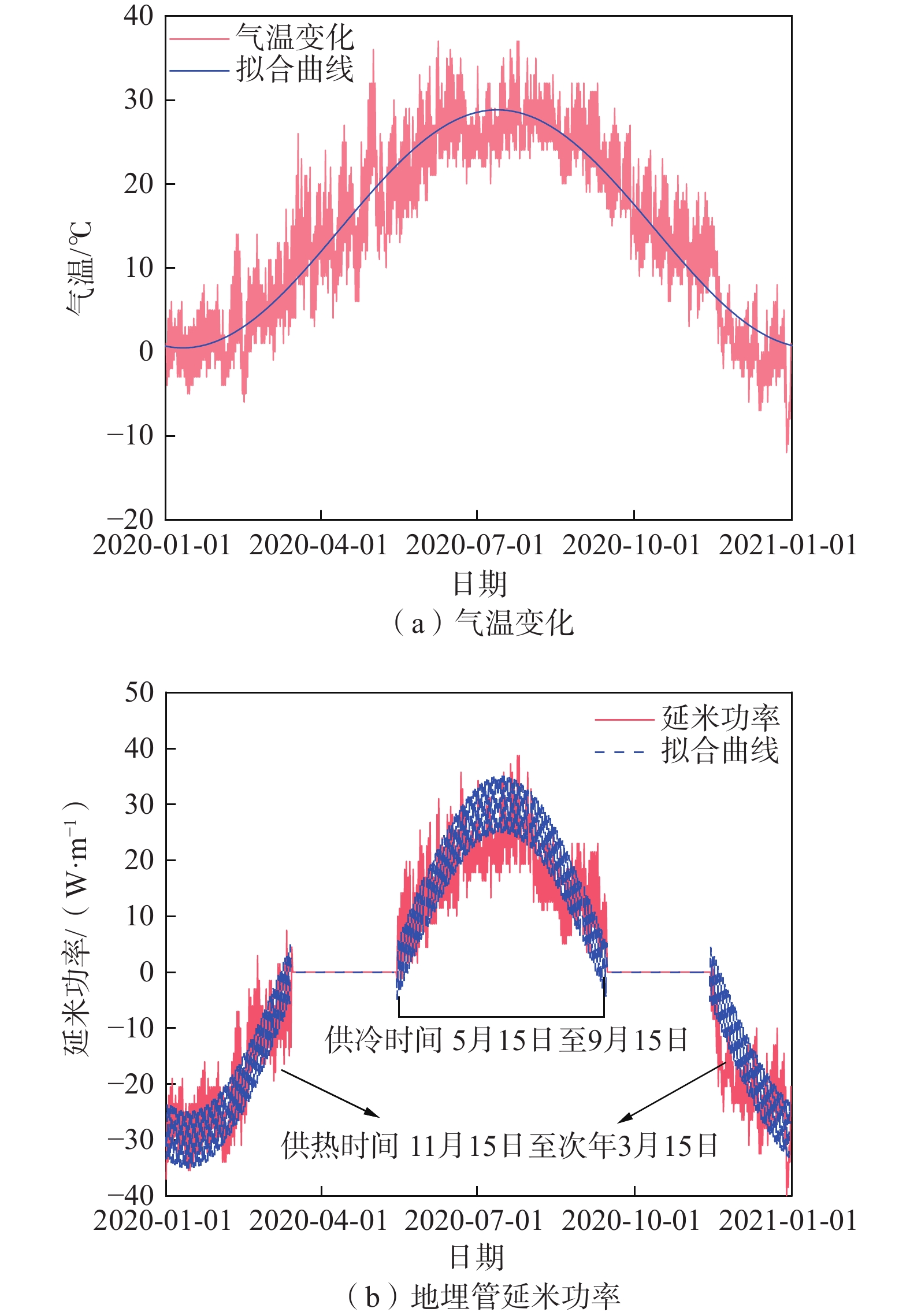
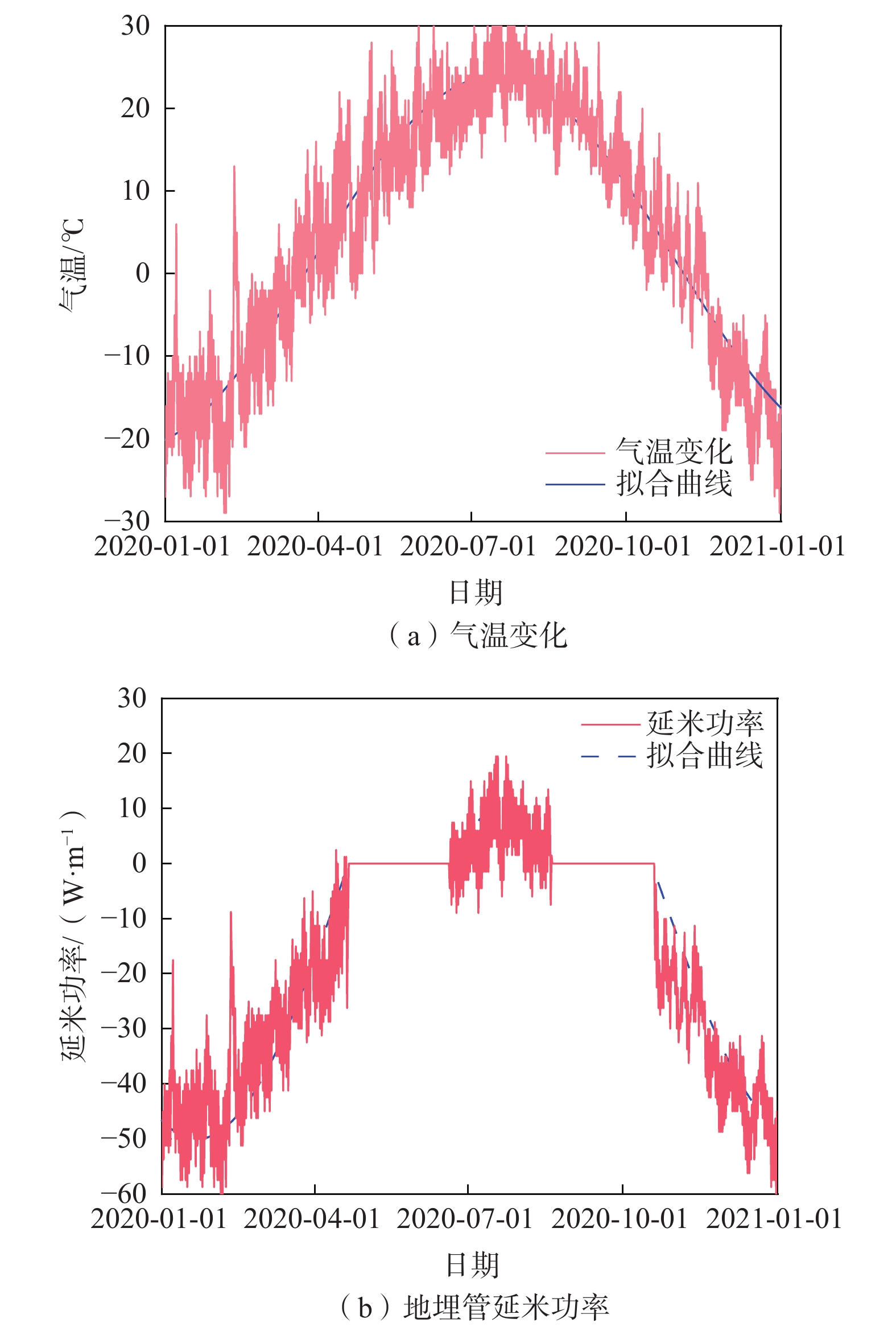
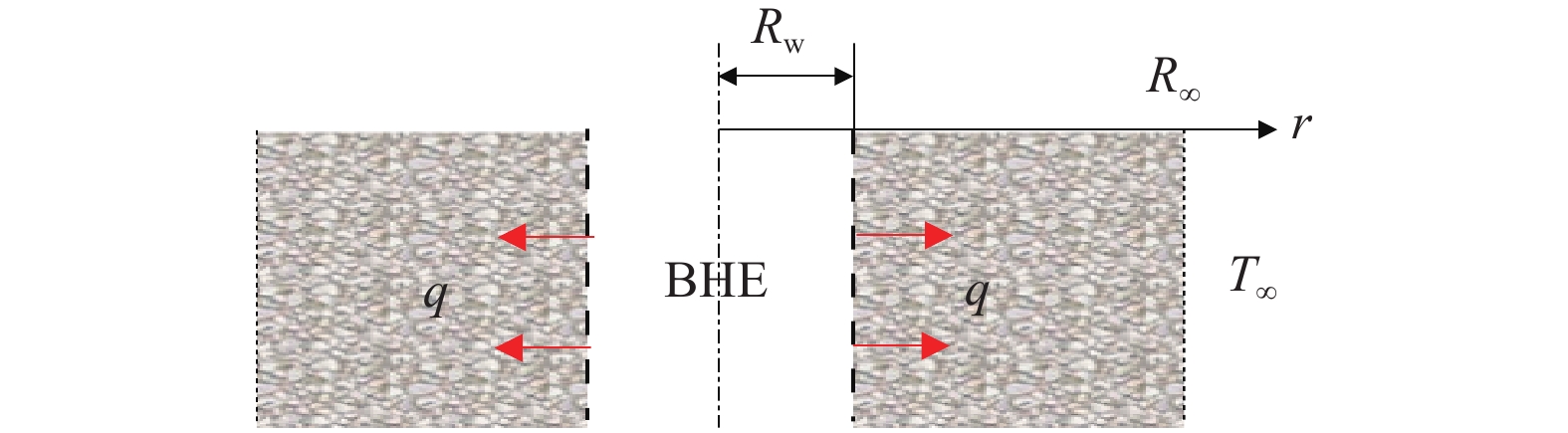
垂直地埋管换热器(borehole heat exchanger,BHE)是利用浅层地热能的主要换热装置,如何确定合理的地埋管间距对地源热泵系统(ground source heat pump system,GSHPs)的传热性能与经济性影响很大。以往工程应用中未考虑地埋管热负荷的动态变化,常采用最大延米热/冷负荷(即最不利情况下)的影响半径作为设计依据,使设计参数趋于保守,很难实现地源热泵系统的技术和经济优化,而考虑负荷变化的数值模拟方法耗时复杂,不便于工程应用。文章提出了一种在地埋管实际热冷负荷动态变化条件下,计算地埋管换热器影响半径的简单数学方法。该法首先推导了地埋管换热器在周期性热流边界条件下,井筒周围地层温度场的解析解,在此基础上将地面建筑物全年周期下的实际波动热冷负荷进行傅里叶级数近似展开,最后通过线性叠加每个周期函数对应的解析解,得到建筑物实际动态热冷负荷下的地层温度动态分布。提出的解析解实时耦合了地面建筑动态热冷负荷,计算结果接近实际应用,具有计算精度高、简单方便快捷的优点,便于在工程实际中推广应用。
Abstract:The borehole heat exchanger (BHE) is a key component using shallow geothermal energy in ground source heat pump systems (GSHPS), and reasonable pipe spacing design has a great impact on the heat transfer performance and economy of the GSHPs. In most of real applications, the thermal disturbance radius of the maximum heat load per unit length (that is, the most unfavorable case) is often used as the design basis, and this makes it difficult to achieve the technical and economic optimization of the ground source heat pump system. This paper proposes a simple but more practical mathematical method to obtain the thermal disturbance radius of the borehole heat exchanger. The method first derives an analytical solution of the formation temperature distribution around the borehole under the boundary condition of periodic heat flow. On this basis, the actual dynamic building heating and cooling load is approximately expanded into a finite of sine and cosine periodic functions with the Fourier series. By superimposing the analytical solution corresponding to each periodic function obtained by Fourier series expansion of the original dynamic load, the variation of formation temperature distribution under the actual dynamic heating and cooling load conditions can be obtained.
-

-
表 1 地埋管几何与地层物性参数
Table 1. Geometrical and physical parameters given in the simulation
参数名称 值 参数名称 值 Rw /mm 55 T0/°C 15 λs/(W·m−1·K−1) 2.2 (ρCp)s/(J·m−3·K−1) 2.16×106 tm
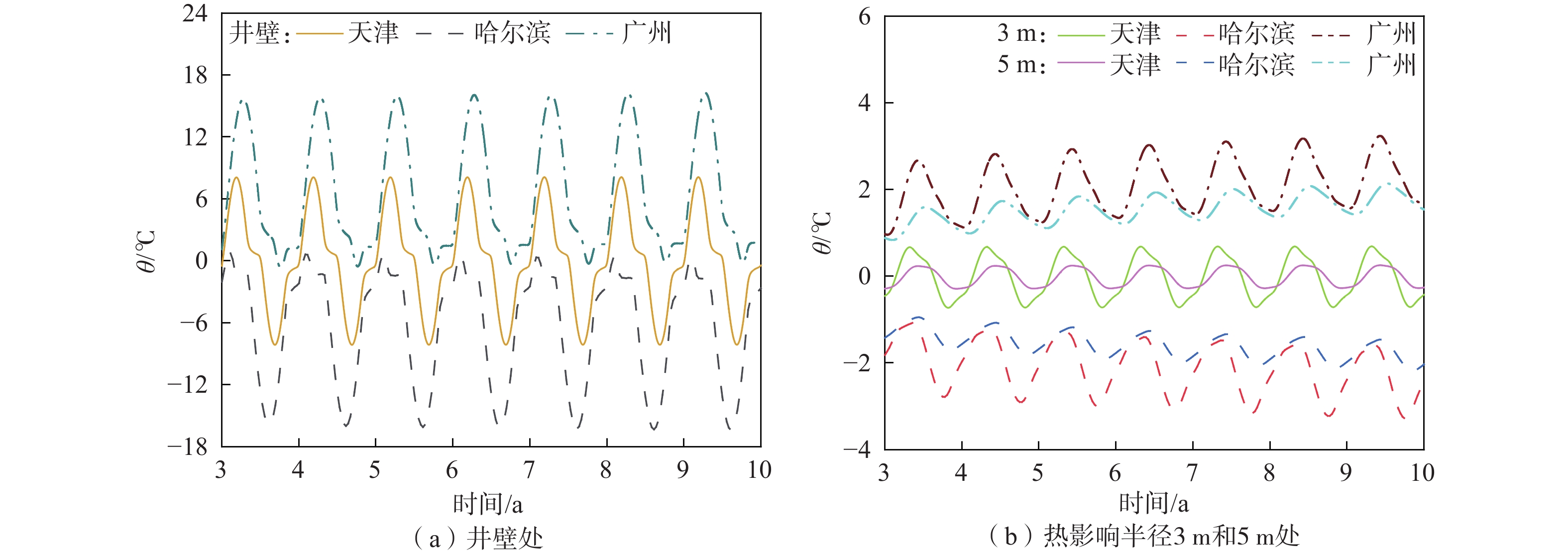
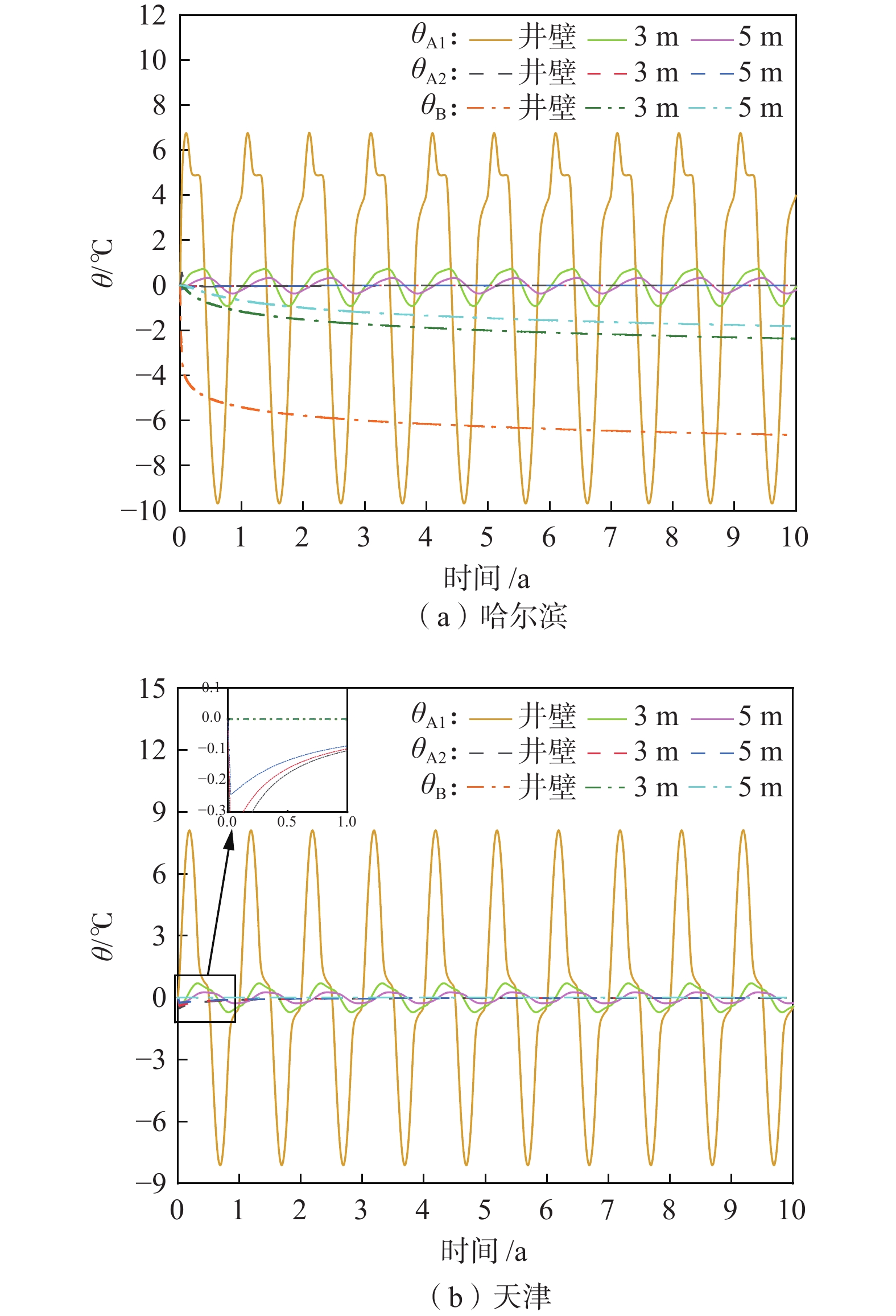
(2L)/月12 t/a 10 nm 20 nh 500 注:nm、nh为年、天周期傅里叶展开级数。 表 2 不同地区的傅里叶展开级数
Table 2. Fourier expansion series in different areas
地区 


天津 


哈尔滨 


天津年周期负荷: 
哈尔滨年周期负荷:
傅里叶展开公式:
-
[1] LUND J W,TOTH A N. Direct utilization of geothermal energy 2020 worldwide review[J]. Geothermics,2021,90:101915. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2020.101915
[2] GAO Qing,LI Ming,YU Ming. Experiment and simulation of temperature characteristics of intermittently-controlled ground heat exchanges[J]. Renewable Energy,2010,35(6):1169 − 1174. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2009.10.039
[3] NIU Fuxin, NI Long, YAO Yang, et al. Thermal accumulation effect of ground-coupled heat pump system[C]//2011 International Conference on Electric Technology and Civil Engineering (ICETCE). IEEE, 2011: 1805-1807.
[4] CAO Xiaoling,YUAN Yanping,SUN Liangliang,et al. Restoration performance of vertical ground heat exchanger with various intermittent ratios[J]. Geothermics,2015,54:115 − 121. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2014.12.005
[5] BIGLARIAN H,ABBASPOUR M,SAIDI M H. Evaluation of a transient borehole heat exchanger model in dynamic simulation of a ground source heat pump system[J]. Energy,2018,147:81 − 93. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2018.01.031
[6] BAEK S H,YEO M S,KIM K W. Effects of the geothermal load on the ground temperature recovery in a ground heat exchanger[J]. Energy and Buildings,2017,136:63 − 72. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2016.11.056
[7] 官燕玲,江超,黄雪婷,等. 地源热泵竖直地埋管动态负荷下换热特性解析分析方法[J]. 暖通空调,2013,43(11):87 − 91. [GUAN Yanling,JIANG Chao,HUANG Xueting,et al. Analytical method for heat transfer characteristics of vertical ground heat exchangers in ground-source heat pump under dynamic load[J]. Heating Ventilating & Air Conditioning,2013,43(11):87 − 91. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 柳晓雷,王德林,方肇洪. 垂直埋管地源热泵的圆柱面传热模型及简化计算[J]. 山东建筑工程学院学报,2001,16(1):47 − 51. [LIU Xiaolei,WANG Delin,FANG Zhaohong. Modeling of heat transfer of a vertical bore in ground-source heat pumps[J]. Journal of Shandong Institute of Architecture and Engineering,2001,16(1):47 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] CARSLAW H S, JAEGER J C. Conduction of Heat in Solids[M]. 2nd ed. London: Oxford University Press, 1959.
[10] ZENG H Y,DIAO N R,FANG Z H. A finite line-source model for boreholes in geothermal heat exchangers[J]. Heat Transfer—Asian Research:Co-sponsored by the Society of Chemical Engineers of Japan and the Heat Transfer Division of ASME,2002,31(7):558 − 567.
[11] MAN Yi,YANG Hongxing,DIAO Nairen,et al. A new model and analytical solutions for borehole and pile ground heat exchangers[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2010,53(13/14):2593 − 2601.
[12] ESKILSON P. Thermal analysis of heat extraction boreholes[D]. Lund: University of Lund, 1987.
[13] BERNIER M A. Ground-coupled heat pump system simulation[J]. ASHRAE Transactions,2001,107(1):605 − 616.
[14] BERNIER M A,PINEL P,LABIB R,et al. A multiple load aggregation algorithm for annual hourly simulations of GCHP systems[J]. HVAC& R Research,2004,10(4):471 − 487.
[15] MARCOTTE D,PASQUIER P. Fast fluid and ground temperature computation for geothermal ground-loop heat exchanger systems[J]. Geothermics,2008,37(6):651 − 665. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2008.08.003
[16] MAN Yi,YANG Hongxing,WANG Jinggang,et al. Operation performance investigation of ground-coupled heat-pump system for temperate region[J]. International Journal of Low-Carbon Technologies,2011,6(2):107 − 118. doi: 10.1093/ijlct/ctq047
[17] ZHANG Linfeng,ZHANG Quan,LI Min,et al. A new analytical model for the underground temperature profile under the intermittent operation for ground-coupled heat pump systems[J]. Energy Procedia,2015,75:840 − 846. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2015.07.170
[18] ZHANG Linlin,ZHAO Lei,YANG Liu,et al. Analyses on soil temperature responses to intermittent heat rejection from BHEs in soils with groundwater advection[J]. Energy and Buildings,2015,107:355 − 365. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2015.08.040
[19] WANG Enqi,ZHANG Fangfang,ZHANG Yuanyuan,et al. Influence investigation of thermal load imbalance on geothermal heat exchanger[J]. Procedia Engineering,2017,205:3846 − 3851. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2017.10.072
[20] 杨露梅,鄂建,朱明君,等. 典型地埋管系统模拟工况地温场特征研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(2):178 − 183. [YANG Lumei,E Jian,ZHU Mingjun,et al. Characteristics of the ground temperature of the typical Ground-Source heat pumps system in Nanjing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(2):178 − 183. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2017.02.27
[21] 刘爱华,佟红兵,冉伟彦. 北京某垂直地埋管区地温场变化规律研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(4):165 − 170. [LIU Aihua,TONG Hongbing,RAN Weiyan. A study of ground temperature changes in a vertical heat exchanger area of Beijing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(4):165 − 170. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 杨卫波,张来军,汪峰. 桩埋管参数对渗流下能量桩热-力耦合特性的影响[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(5):176 − 185. [YANG Weibo,ZHANG Laijun,WANG Feng. Effects of the pile buried pipe parameters on the thermal-mechanical coupling characteristics of energy pile under the groundwater seepage[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(5):176 − 185. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 陈宝义,岳韬,曹品鲁,等. 挤密条件下U型地埋管换热器换热效率的理论分析及数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2016,46(6):1808 − 1814. [CHEN Baoyi,YUE Tao,CAO Pinlu,et al. Theoretical analysis and numerical simulation of heat exchange efficiency of U-tube ground heat exchanger under the condition of soil compaction[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2016,46(6):1808 − 1814. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 张延军, 张通, 殷仁朝, 等. 基于2 m测温法的地热异常区探测及地温预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2017, 47(1): 189−196
ZHANG Yanjun, ZHANG Tong, YIN Renchao, et al. Geothermal anomaly areas exploration and ground temperature prediction based on 2-meter temperature survey[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2017, 47(1): 189−196. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 赵德印,范宏武,潘黎. 气象参数与建筑冷热负荷相关性分析[J]. 绿色建筑,2019,11(1):47 − 50. [ZHAO Deyin,FAN Hongwu,PAN Li. Relevance between climate parameter and building heating & cooling load[J]. Green Building,2019,11(1):47 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1672.2019.01.017
-



 下载:
下载: