Application of the grey theory to dynamic analyses of the Baiquan Spring flow rate in Xinxiang
-
摘要:
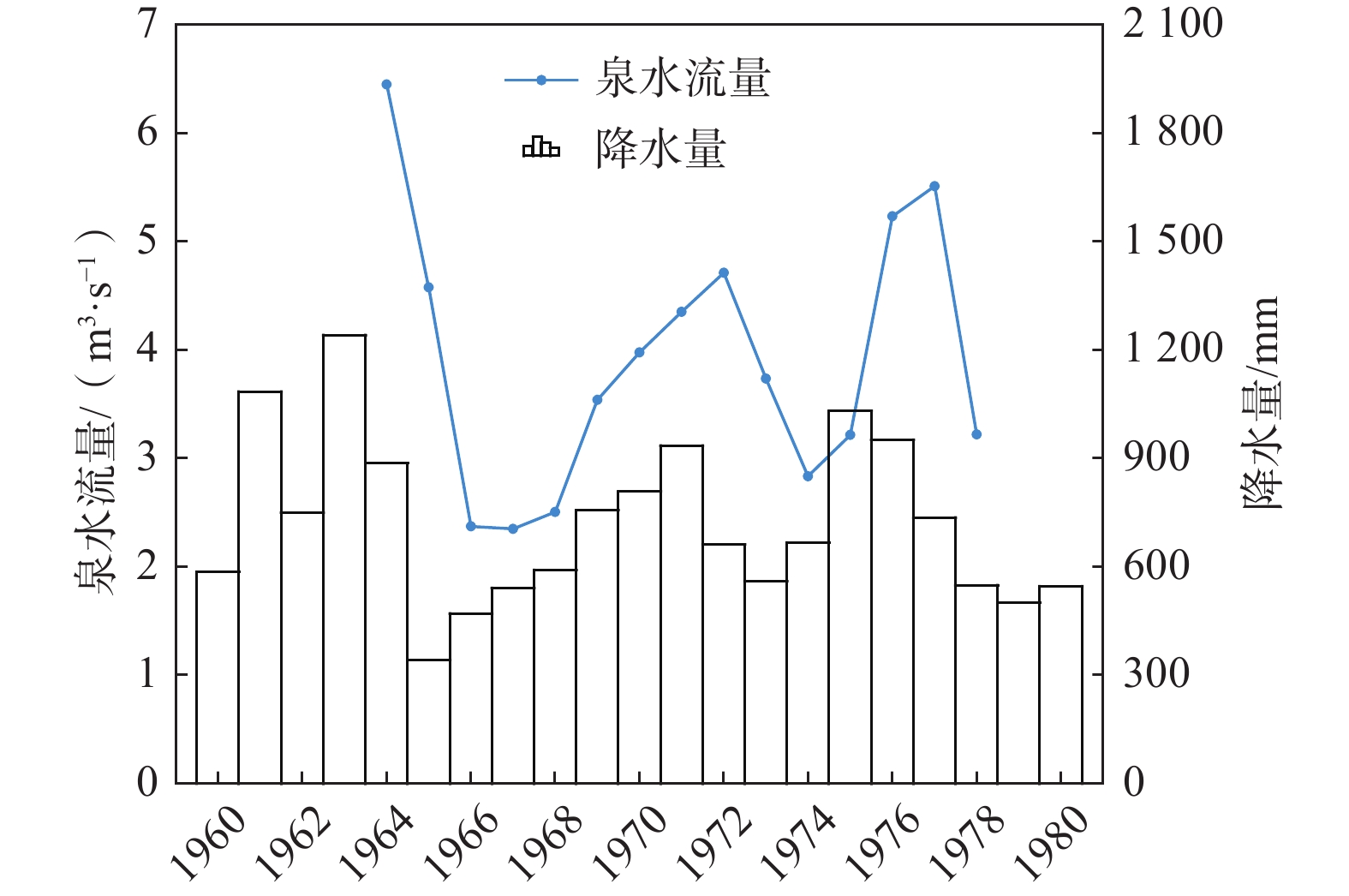
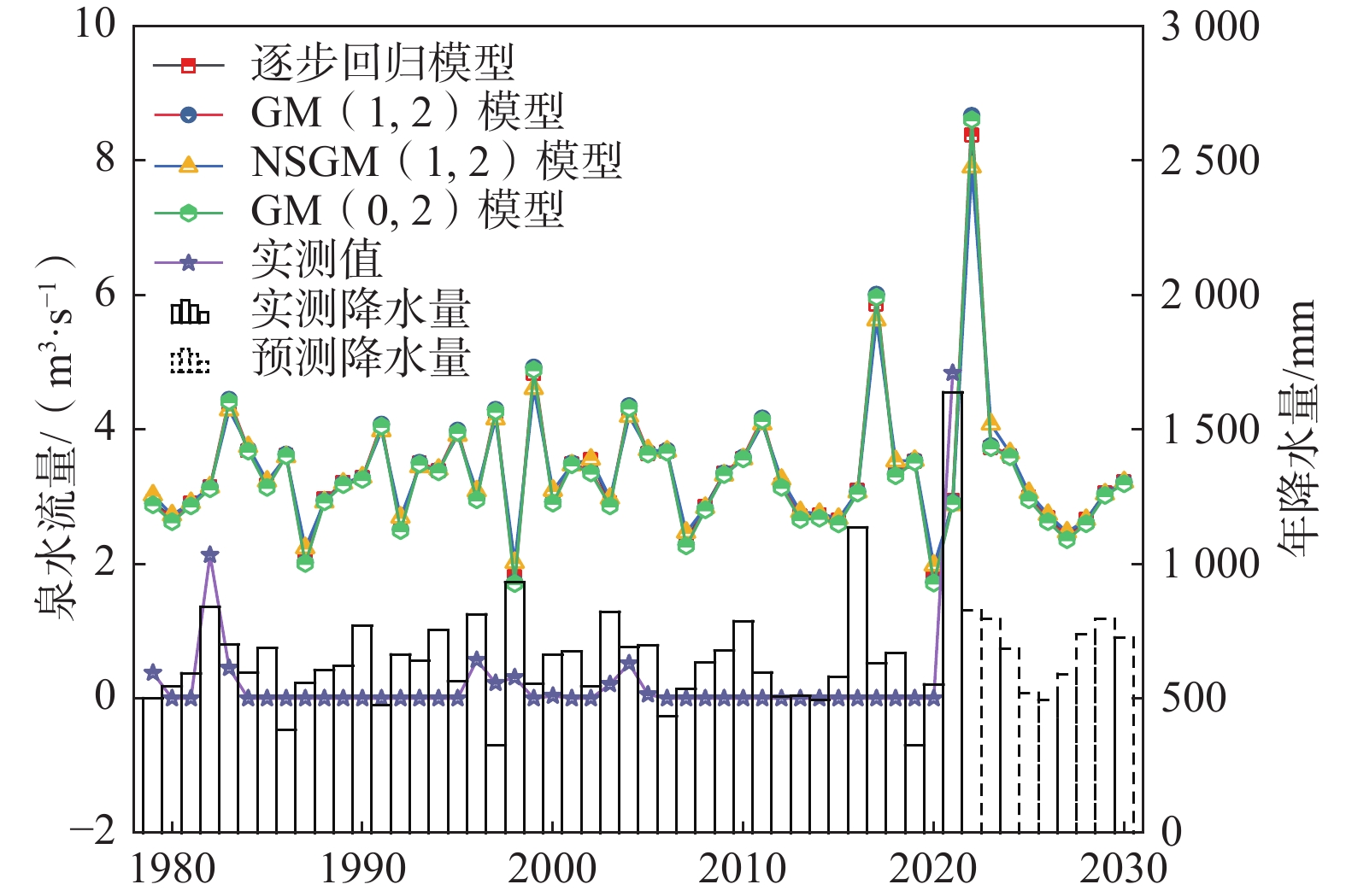
新乡百泉具有供水、农灌、人文、旅游及生态等多种功能,研究其泉水流量动态,建立泉水流量动态预测模型,对泉域水资源评价和泉水资源保护具有重要意义。为了进一步研究新乡百泉天然状态下泉水流量动态特征、评价泉域岩溶水资源,基于1964—1978年泉水年均实测流量和泉域年均降水量资料,通过逐步回归分析,确定泉水流量的主要影响因素为前1年降水量,并建立了逐步回归模型,其回归效果显著;在逐步回归分析的基础上建立了泉水流量动态预测的GM(1, 2)模型、NSGM(1, 2)模型和GM(0, 2)模型。结果表明:1964—1978年百泉泉水流量动态主要受泉域降水控制,且泉水流量滞后降水1年,反映了天然状态下泉水动态特征。3种灰色模型的精度等级均为最高级(优)。1964—1978年百泉泉水实测流量为2.347~6.448 m³/s,平均为3.904 m3/s;逐步回归模型预测值为1.882~6.383 m3/s,平均为3.904 m3/s;GM(1,2)模型预测值为2.327~6.448 m3/s,平均为3.939 m3/s;NSGM(1,2)模型预测值为2.133~6.448 m3/s,平均为3.927 m3/s;GM(0,2)模型预测值为1.787~6.448 m3/s,平均为3.907 m3/s。逐步回归模型和前述3种灰色模型的平均相对误差分别为7.794%、7.292%、7.122%、7.797%,均<10%,可用于泉水流量动态预测;其中NSGM(1,2)模型精度更高、对曲线“拐点”的拟合更好。根据4种模型预测的1964—2030年泉水流量,从保泉角度评价百泉泉域岩溶水的开采资源量不得超过1.69 m3/s。研究成果可为泉水流量动态预测和泉域水资源评价提供科学依据,也可为类似地区地下水动态研究提供参考。
-
关键词:
- 新乡百泉 /
- 逐步回归分析 /
- GM(1, N)模型 /
- NSGM(1, N)模型 /
- GM(0, N)模型 /
- P-Ⅲ型曲线
Abstract:The Baiquan Spring in Xinxiang has many functions, such as water supply, agricultural irrigation, humanities, tourism and ecology. It is of great significance to study the dynamics of the spring flow rate and establish a dynamic prediction model for the spring water resources evaluation and protection. In order to further study the dynamic characteristics of the Baiquan Spring flow rate in Xinxiang and evaluate karst water resources in the spring area, based on the data of annually measured spring flow rate and annual average precipitation in the spring area from 1964 to 1978, the main influencing factors of the spring flow rate are determined by using the stepwise regression analysis, and a stepwise regression model is established, with remarkable regression effect. On the basis of the stepwise regression analysis, this paper establishes the GM(1, 2) model, NSGM(1, 2) model and GM(0, 2) model for the dynamic prediction of the spring flow rate. The results show that (1) from 1964 to 1978, the Baiquan spring flow rate was mainly controlled by the precipitation in the spring area, and the spring flow rate lagged behind the precipitation for one year, reflecting the dynamic characteristics of the spring water in the natural state. (2) The accuracy levels of the three grey models are the highest (excellent). (3) From 1964 to 1978, the measured discharge of the Baiquan spring ranged from 2.347 to 6.448 m3/s, with an average of 3.904 m3/s. The predicted values of the stepwise regression model range from 1.882 to 6.383 m3/s, with an average of 3.904 m3/s. The predicted value of the GM(1, 2) model varies between 2.327 and 6.448 m3/s, with an average of 3.939 m3/s. The predicted values of the NSGM(1, 2) model range from 2.133 to 6.448 m3/s, with an average of 3.927 m3/s. The predicted values of the GM(0, 2) model range from 1.787 to 6.448 m3/s, with an average of 3.907 m3/s. (4) The average relative errors of the stepwise regression model and the three grey models mentioned above are 7.794%, 7.292%, 7.122% and 7.797% respectively, all of which are less than 10%, indicating that they can be used for dynamic prediction of the spring water. Among them, the NSGM(1, 2) model has a higher accuracy and better fitting to the inflection point of the curve. (5) According to the spring flow rate from 1964 to 2030 predicted by the four models, the exploitation resources of the karst water in the Baiquan spring area should not exceed 1.69 m3/s from the angle of spring protection. The research results can not only provide scientific basis for spring flow dynamic prediction and spring area water resources evaluation, but also provide reference for the study of groundwater dynamics in similar areas.
-

-
表 1 1979—2021年百泉泉水复流情况
Table 1. Statistics of re-flow of the Baiquan Spring from 1979 to 2021
复流年份 复流情况 1982 8月15日复流至次年5月断流,最大出水量为6.65 m3/s 1988 8月中旬复流,次年断流(断流日期不详),最大出水量约为5 m3/s 1996 8月3日复流,次年4月17日断流,最大出水量为3.10 m3/s 1998 9月2日复流,次年1月8日断流,最大出水量为1.91 m3/s 2000 9月21复流,10月26日断流,最高湖水位仅为40 cm 2003 10月26复流,次年3月28日断流,最大出水量为2.35 m3/s 2004 8月28日复流,次年1月31断流,最大出水量为1.40 m3/s 2021 百泉泉域遭遇有气象记录以来的特大降雨,7月23日复流,最大出水量为10 m3/s。2022年7月,仍有近4 m3/s 表 2 灰色模型精度等级评价
Table 2. Evaluation of the accuracy grade of the grey model
精度等级 P C 
优 0.95<P≤1.00 0.00<C≤0.35 0.90<  ≤1.00
≤1.00良 0.80<P≤0.95 0.35<C≤0.50 0.80<  ≤0.90
≤0.90中 0.70<P≤0.80 0.50<C≤ 0.65 0.70<  ≤0.80
≤0.80差 0.00<P≤0.70 0.65<C≤1.00 0.00<  ≤0.70
≤0.70表 3 1964—1978年泉水流量预测值与实测值对比结果
Table 3. Comparison results between the predicted and measured values of the spring flow rate from 1964 to 1978
年份 年均降水量
/mm实测值
/(m³·s−1)逐步回归模型 GM(1, 2)模型 NSGM(1, 2)模型 GM(0. 2)模型 预测值/ (m³·s−1) 相对误差/% 预测值/ (m³·s−1) 相对误差/% 预测值/(m³·s−1) 相对误差/% 预测值/(m³·s−1) 相对误差/% 1963 1240.0 — — — — — — — — — 1964 886.0 6.448 6.383 1.016 6.448 0.000 6.448 0.000 6.448 0.000 1965 340.0 4.575 4.612 0.817 4.156 9.158 4.678 2.251 4.656 1.770 1966 470.0 2.370 1.882 20.583 2.327 1.814 2.133 10.000 1.787 24.599 1967 540.0 2.347 2.532 7.892 2.585 10.141 2.520 7.371 2.470 5.241 1968 590.0 2.504 2.882 15.016 2.876 14.856 2.870 14.617 2.838 13.339 1969 755.0 3.537 3.132 11.443 3.126 11.620 3.126 11.620 3.101 12.327 1970 807.0 3.976 3.957 0.469 3.996 0.503 3.899 1.937 3.968 0.201 1971 935.0 4.349 4.217 3.027 4.271 1.794 4.198 3.472 4.241 2.483 1972 660.0 4.711 4.857 3.108 4.948 5.031 4.806 2.017 4.914 4.309 1973 560.0 3.733 3.482 6.716 3.493 6.429 3.602 3.509 3.468 7.099 1974 666.0 2.833 2.982 5.269 2.964 4.624 3.049 7.624 2.943 3.883 1975 1030.0 3.215 3.512 9.247 3.525 9.642 3.487 8.460 3.500 8.865 1976 950.0 5.232 5.332 1.920 5.451 4.186 5.181 0.975 5.413 3.459 1977 735.0 5.509 4.932 10.466 5.028 8.731 4.954 10.074 4.993 9.366 1978 548.0 3.219 3.857 19.830 3.890 20.845 3.956 22.895 3.863 20.006 最大值 1240.0 6.448 6.383 19.830 6.448 20.845 6.448 22.895 6.448 20.006 最小值 340.0 2.347 1.882 0.469 2.327 0.000 2.133 0.000 1.787 0.000 平均值 732.0 3.904 3.904 7.794 3.939 7.292 3.927 7.122 3.907 7.797 表 4 灰色模型检验指标计算结果
Table 4. Calculation results of the grey model test index
模型 P C 
GM(1, 2) 1.0000 0.2653 0.9974 NSGM(1, 2) 1.0000 0.2004 0.9997 GM(0, 2) 1.0000 0.2747 0.9963 表 5 不同保证率泉水流量
Table 5. Spring flow rate with different guarantee rates
保证率/% 泉水流量/ (m³·s−1) 逐步回归 GM(1, 2) NSGM(1, 2) GM(0, 2) 平均 10 4.91 4.94 4.94 4.94 4.93 20 4.35 4.38 4.37 4.37 4.37 50 3.42 3.44 3.43 3.41 3.43 75 2.80 2.81 2.81 2.77 2.80 95 2.08 2.09 2.11 2.02 2.08 99 1.69 1.69 1.74 1.62 1.69 -
[1] LIANG Yongping,GAO Xubo,ZHAO Chunhong,et al. Review:Characterization,evolution,and environmental issues of Karst water systems in Northern China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2018,26(5):1371 − 1385. doi: 10.1007/s10040-018-1792-4
[2] 梁永平,王维泰,赵春红,等. 中国北方岩溶水变化特征及其环境问题[J]. 中国岩溶,2013,32(1):34 − 42. [LIANG Yongping,WANG Weitai,ZHAO Chunhong,et al. Variations of Karst water and environmental problems in North China[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2013,32(1):34 − 42. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2013.01.006
[3] 梁永平,申豪勇,赵春红,等. 对中国北方岩溶水研究方向的思考与实践[J]. 中国岩溶,2021,40(3):363 − 380. [LIANG Yongping,SHEN Haoyong,ZHAO Chunhong,et al. Thinking and practice on the research direction of Karst water in Northern China[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2021,40(3):363 − 380. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 王志恒, 梁永平, 申豪勇, 等. 自然与人类活动叠加影响下晋祠泉域岩溶地下水动态特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2021,51(6):1823 − 1837. [WANG Zhiheng,LIANG Yongping,SHEN Haoyong,et al. Dynamic characteristics of karst groundwater in Jinci Spring under superimposed influence of natural and human activities[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2021,51(6):1823 − 1837. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] HAO Yonghong,ZHANG Juan,WANG Jiaojiao,et al. How does the anthropogenic activity affect the spring discharge?[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2016,540:1053 − 1065. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.07.024
[6] 王大伟,乔小娟,高波,等. 山西龙子祠岩溶泉流量动态特征与影响因素分析[J]. 中国岩溶,2021,40(3):420 − 429. [WANG Dawei,QIAO Xiaojuan,GAO Bo,et al. Dynamic characteristics and influence factors of discharge of the Longzici Karst spring in Shanxi Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2021,40(3):420 − 429. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] LIU Y,WANG B,ZHAN H,et al. Simulation of nonstationary spring discharge using time series models[J]. Water Resources Management,2017,31(15):4875 − 4890. doi: 10.1007/s11269-017-1783-6
[8] 茅伟绩,王锦国. 云南鹤庆县蝙蝠洞泉流量衰减分析[J]. 中国煤炭地质,2021,33(11):47 − 50. [MAO Weiji,WANG Jinguo. Analysis of Bianfudong spring flow attenuation in Heqing County,Yunnan Province[J]. Coal Geology of China,2021,33(11):47 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2021.11.09
[9] 梁日胜,曾成,闫志为,等. 贵州印江朗溪岩溶槽谷龙洞湾泉流量衰减分析[J]. 中国岩溶,2019,38(1):10 − 18. [LIANG Risheng,ZENG Cheng,YAN Zhiwei,et al. Recession flow analysis for Longdongwan spring at Langxi Karst valley in Yinjiang County,Guizhou Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2019,38(1):10 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] WU Xiancang,LI Changsuo,SUN Bin,et al. Groundwater hydrogeochemical formation and evolution in a Karst aquifer system affected by anthropogenic impacts[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health,2020,42(9):2609 − 2626. doi: 10.1007/s10653-019-00450-z
[11] NUNNO D F,GRANATA F. Groundwater level prediction in Apulia region (Southern Italy) using NARX neural network[J]. Environmental Research,2020,190:110062. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.110062
[12] HAO Yonghong,YEH T C J,GAO Zongqiang,et al. A gray system model for studying the response to climatic change:The Liulin Karst springs,China[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2006,328(3/4):668 − 676.
[13] HAO Yonghong,CAO Bibo,CHEN Xiang,et al. A piecewise grey system model for study the effects of anthropogenic activities on Karst hydrological processes[J]. Water Resources Management,2013,27(5):1207 − 1220. doi: 10.1007/s11269-012-0231-x
[14] LIU Peigui,GAO Yang,SHANG Manting,et al. Predicting water level rises and their effects on surrounding Karst water in an abandoned mine in Shandong,China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2020,79(1):1 − 10. doi: 10.1007/s12665-019-8746-6
[15] AN Lixing,HAO Yonghong,YEH T C J,et al. Simulation of Karst spring discharge using a combination of time-frequency analysis methods and long short-term memory neural networks[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2020,589:125320. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125320
[16] CHENG Shu,QIAO Xiaojun,SHI Yaolin,et al. Machine learning for predicting discharge fluctuation of a karst spring in North China[J]. Acta Geophysica,2021,69:257 − 270.
[17] 林云,曲鹏冲,吕海新,等. 太行山东缘典型岩溶泉流量变化特征及规律分析[J]. 中国岩溶,2018,37(5):671 − 679. [LIN Yun,QU Pengchong,LV Haixin,et al. Variation characteristics of typical karst springs in the eastern margin of the Taihang Mountains[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2018,37(5):671 − 679. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 卢丽,邹胜章,赵一,等. 桂林会仙湿地狮子岩地下河系统水循环对降水的响应[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(5):63 − 72. [LU Li,ZHOU Shengzhang,ZHAO Yi,et al. Response of water cycle to precipitation in Shizhiyan underground river system in Huixian wetland of Guilin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(5):63 − 72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 郭艺,王枫,甘甫平,等. 基于移动平均模型和指数平滑模型的岩溶泉泉流量预测[J]. 河北地质大学学报,2020,43(4):19 − 25. [GUO Yi,WANG Feng,GAN Fuping,et al. Forecasting of spring flow based on moving average model and exponential smoothing model[J]. Journal of Hebei GEO University,2020,43(4):19 − 25. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 姜宝良,付北锋,赵延涛. 泉水动态分析预测和资源评价:以辉县百泉为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2002,29(3):43 − 46. [JIANG Baoliang,FU Beifeng,ZHAO Yantao. Analysis prediction and resources evaluation of spring dynamic:A case study of Bai spring in Hui County[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2002,29(3):43 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2002.03.013
[21] 姜宝良, 赵贵章, 于怀昌, 等. 河南新乡百泉供水研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2012
JIANG Baoliang, ZHAO Guizhang, YU Huaichang, et al. Study on water supply of Baiquan in Xinxiang, Henan [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2012. (in Chinese)
[22] 姜宝良,许来慧,崔江利,等. 新乡市百泉泉水流量动态预测与资源评价[J]. 人民黄河,2013,35(12):71 − 72. [JIANG Baoliang,XU Laihui,CUI Jiangli,et al. Dynamic prediction of spring flow and resources evaluation of Baiquan at Xinxiang[J]. Yellow River,2013,35(12):71 − 72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 肖荣鸽,靳帅帅,庄琦,等. 基于灰色理论的油气管道腐蚀速率预测[J]. 热加工工艺,2022,51(18):53 − 57. [XIAO Rongge,JIN Shuaishuai,ZHUANG Qi,et al. Prediction of corrosion rate of oil and gas pipeline based on grey theory[J]. Hot Working Technology,2022,51(18):53 − 57. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 曾波, 李树良, 孟伟. 灰色预测理论及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020
ZENG Bo, LI Shuliang, MENG Wei. Grey prediction theory and its applications[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2020. (in Chinese)
[25] 吴磊, 陶忠, 赵志曼, 等. 基于NSGM(1, 3)模型的短切聚丙烯纤维-磷建筑石膏复合材料强度预测[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(增刊2): 655 − 659
WU Lei, TAO Zhong, ZHAO Zhiman, et al. Strength prediction of short-cut PP fiber-phosphorus building gypsum composites based on NSGM(1, 3) model[J]. Materials Reports, 2021, 35(Sup 2): 655 − 659. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 穆奎,马崇启. 梳棉工艺对单纱强力影响的灰色GM(0,N)预测模型[J]. 纺织学报,2011,32(6):34 − 38. [MU Kui,MA Chongqi. Grey GM(0,N) prediction model of influence of carding process on yarn strength[J]. Journal of Textile Research,2011,32(6):34 − 38. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 刘思峰. 灰色系统理论及其应用[M]. 9版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021.
LIU Sifeng. The grey system theory and its application[M]. 9th ed. Beijing: Science Press, 2021. (in Chinese)
[28] 姜宝良,陈宁宁,李小建,等. 河南某大型裂隙岩溶水源地地下水位动态分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(2):37 − 43. [JIANG Baoliang,CHEN Ningning,LI Xiaojian,et al. A dynamic analysis of groundwater levels in a large fractured-Karst groundwater wellfield in Henan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(2):37 − 43. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 刘德林. 郑州市年降水量的ARIMA模型预测[J]. 水土保持研究,2011,18(6):249 − 251. [LIU Delin. Annual precipitation forecasting of Zhengzhou City based on ARIMA model[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2011,18(6):249 − 251. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 张浪,贺中华,夏传花,等. 基于河流出水量的区域水文干旱特征及其水文频率分析—以黔中水利枢纽工程区为例[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021,21(27):11480 − 11489. [ZHANG Lang,HE Zhonghua,XIA Chuanhua,et al. Analysis of regional hydrological drought characteristics and hydrological frequency based on river water output:Taking Qianzhong water conservancy project area as an example[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2021,21(27):11480 − 11489. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.27.005
-




 下载:
下载: