A discussion of the cause of land subsidence in the northeast of the Xiongan New Area
-
摘要:
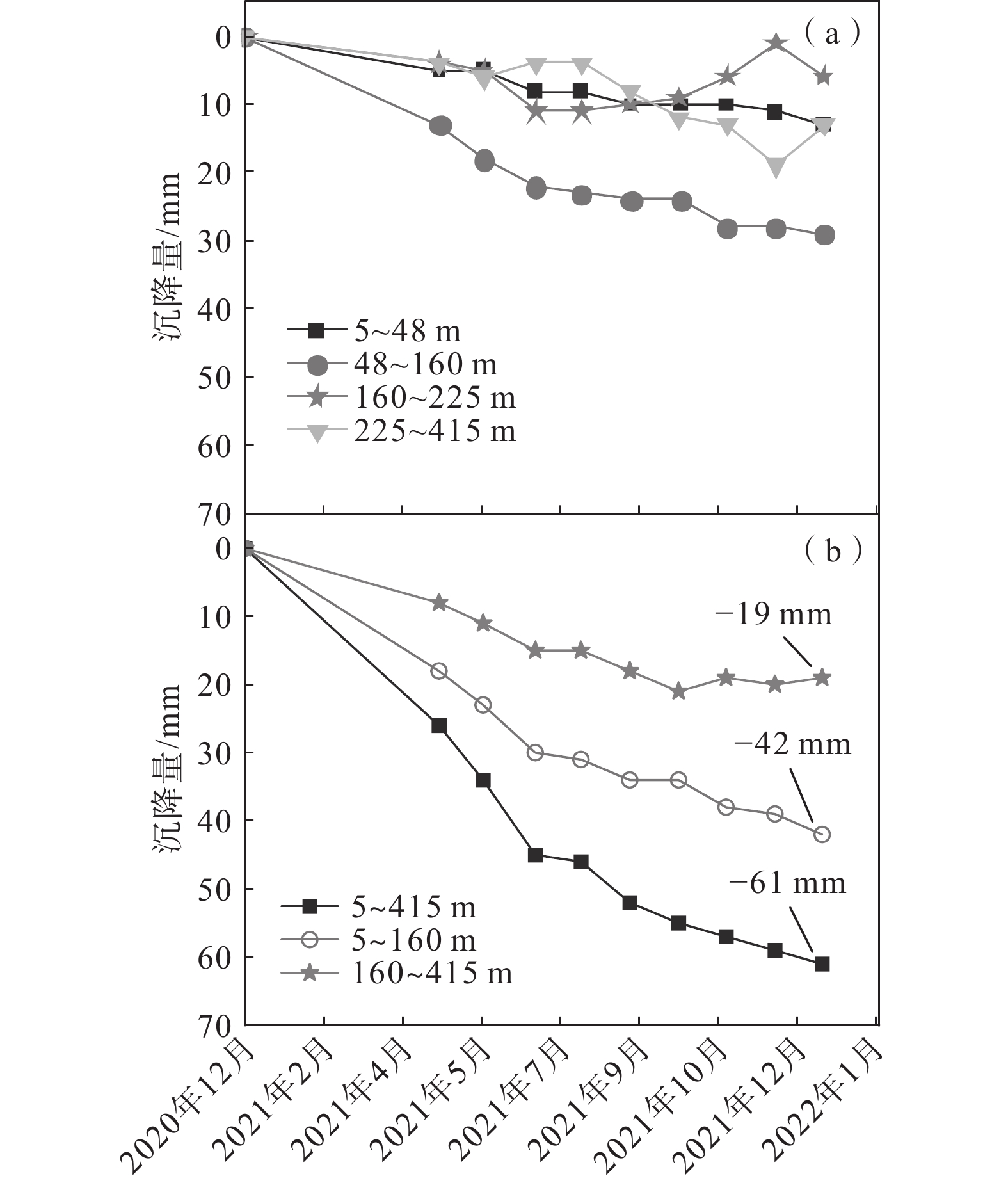
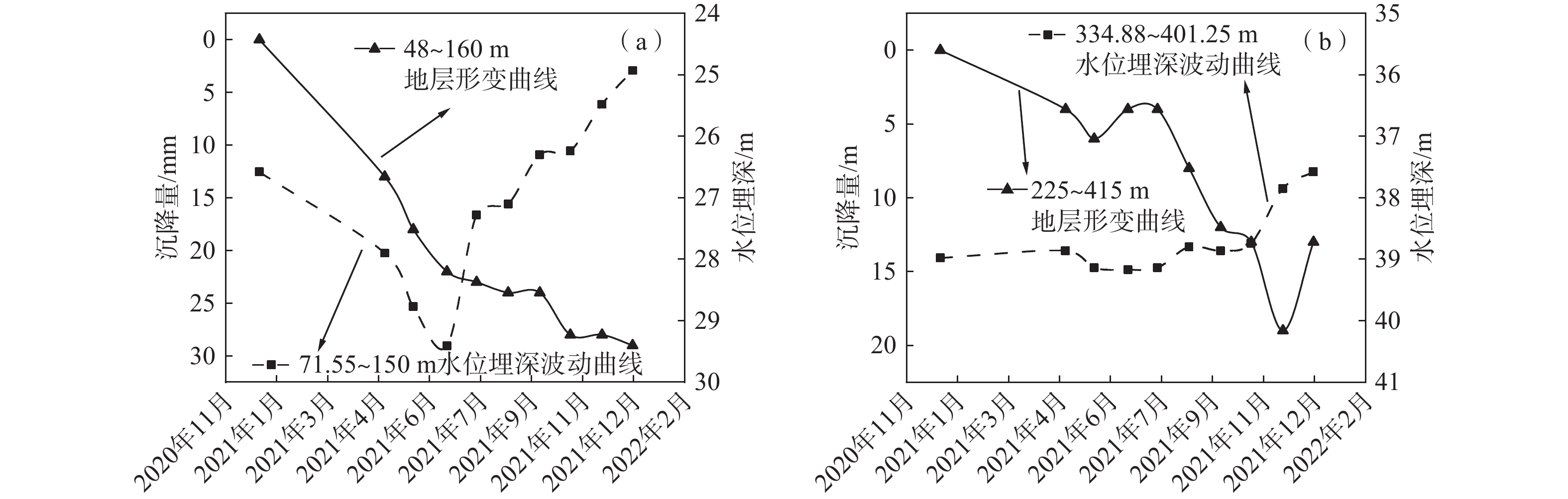
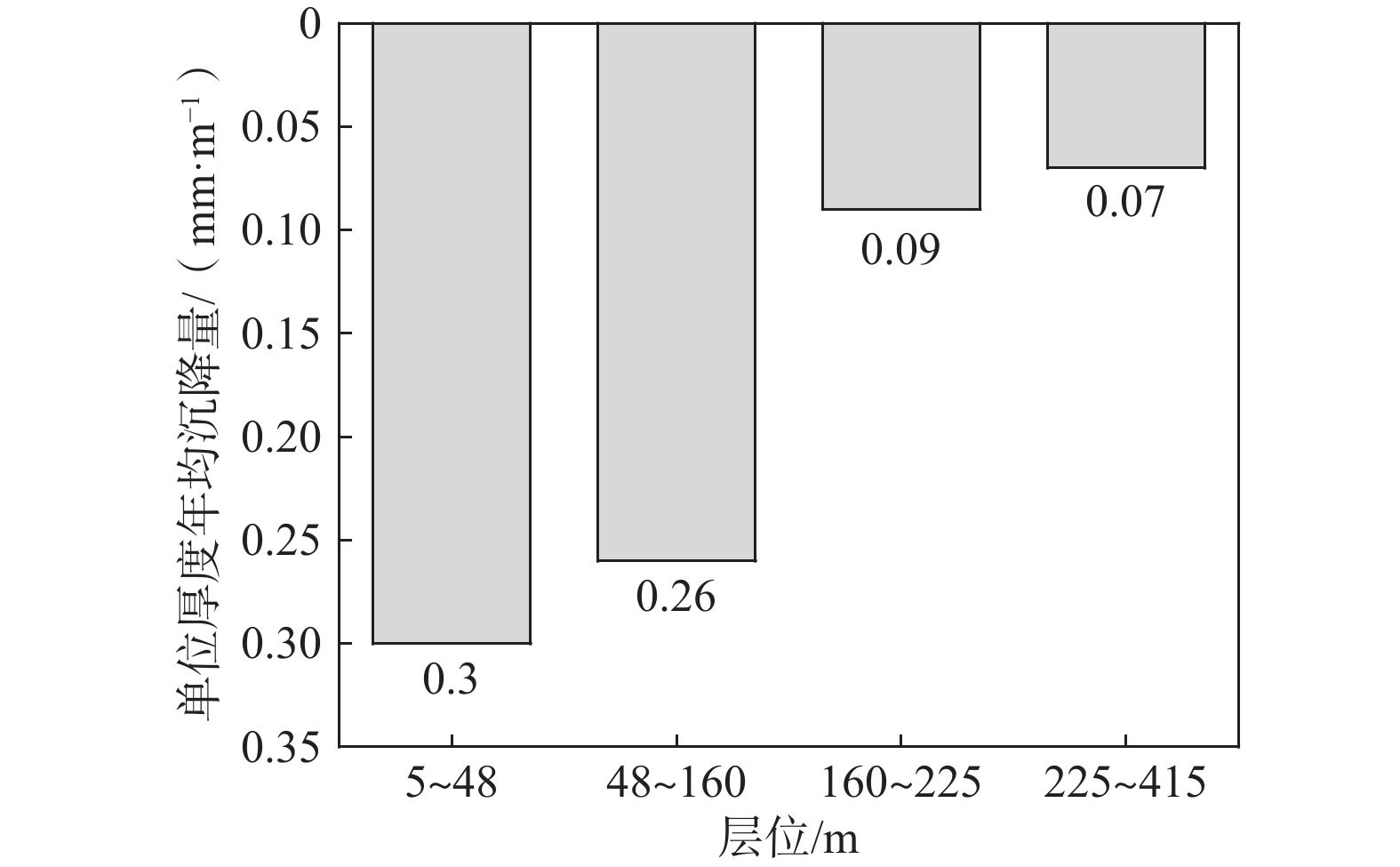
为深入研究雄安新区东北部地面沉降主控因素,以大营镇分层标组为研究对象,利用常规土工试验、高压固结试验与分层沉降观测数据,结合前人研究成果对地面沉降成因进行探讨。结果表明:大营镇分层标组G1孔内第四系松散层总厚度412 m,其中浅部地层(第I、II含水组)厚度约170 m,黏性土占比66.4%~80.2%,结构松散,砂黏互层交替频繁,释水条件较好。浅部黏性土颗粒较细、分选性好、孔隙度大,液性指数多大于0.25,呈软塑、可塑态,自重压缩系数为0.03~0.43,均值0.08,与深部相比压缩性较强。浅部黏性土层以欠固结、正常固结夹欠固结状态为主,0~90 m超固结比均值为0.55,90~280 m超固结比均值为0.89,易于发生塑性变形,形成永久性沉降。雄安新区主要开采浅层地下水,地面沉降与地下水关系密切。2020年12月—2021年12月,大营镇分层标组监测结果显示,第四系松散层总沉降量为61 mm。其中,5~160 m第四系松散层沉降贡献量最大,为42 mm,表现为塑性形变特征;160~415 m第四系地层沉降贡献量小,为19 mm,表现为黏弹塑性形变特征。过量开采浅层地下水引起浅部固结程度低、压缩性高的黏性土层发生塑性变形是发生严重沉降的主要原因。
Abstract:In order to deeply study the main controlling factors of land subsidence in the northeast of the Xiongan New Area, the layered monitoring points of Daying Town are taken as the research object, and the causes of land subsidence are discussed based on the conventional soil test, high pressure consolidation test and layered settlement observation data combined with previous research results. The results show that the total thickness of the Quaternary loose layer in the layered monitoring points of G1 hole in Daying Town is 412 m, and the thickness of the shallow layer is 170 m. The viscous soil accounts for 66.4%−80.2%. The structure is loose and the sand-clay interlayer alternates frequently, and the water release condition is good. The shallow viscous soil has finer particles, good sortability, large porosity, and more than 0.25 liquid index, showing a soft plastic and plasticable state. The dead weight compression coefficient ranges from 0.03 to 0.43, with an average value of 0.07. Compared with the deep soil, the shallow viscous soil is of stronger compressibility. The shallow cohesive soil layer is dominated by underconsolidation, normal consolidation and underconsolidation. The average OCR of a depth of 0−90 m is 0.55, and that of 90-280 m is 0.89. Plastic deformation and permanent settlement are easy to occur. Xiongan New Area mainly exploits shallow groundwater, which is closely related to land subsidence. From December 2020 to December 2021, the monitoring results of the layered monitoring points of Daying Town show that the total settlement of the Quaternary loose layer is 61 mm. Among them, the subsidence contribution of the shallow Quaternary unconsolidated layer at a depth of 5−160 m is the largest, which is 42 mm, showing the characteristics of plastic deformation. The subsidence contribution of the deep Quaternary strata at 160−415 m is 19 mm, which shows the characteristics of viscoelastic-plastic deformation. The plastic deformation of cohesive soil layer with low consolidation and high compressibility caused by the excessive exploitation of shallow groundwater is the main cause of serious settlement.
-

-
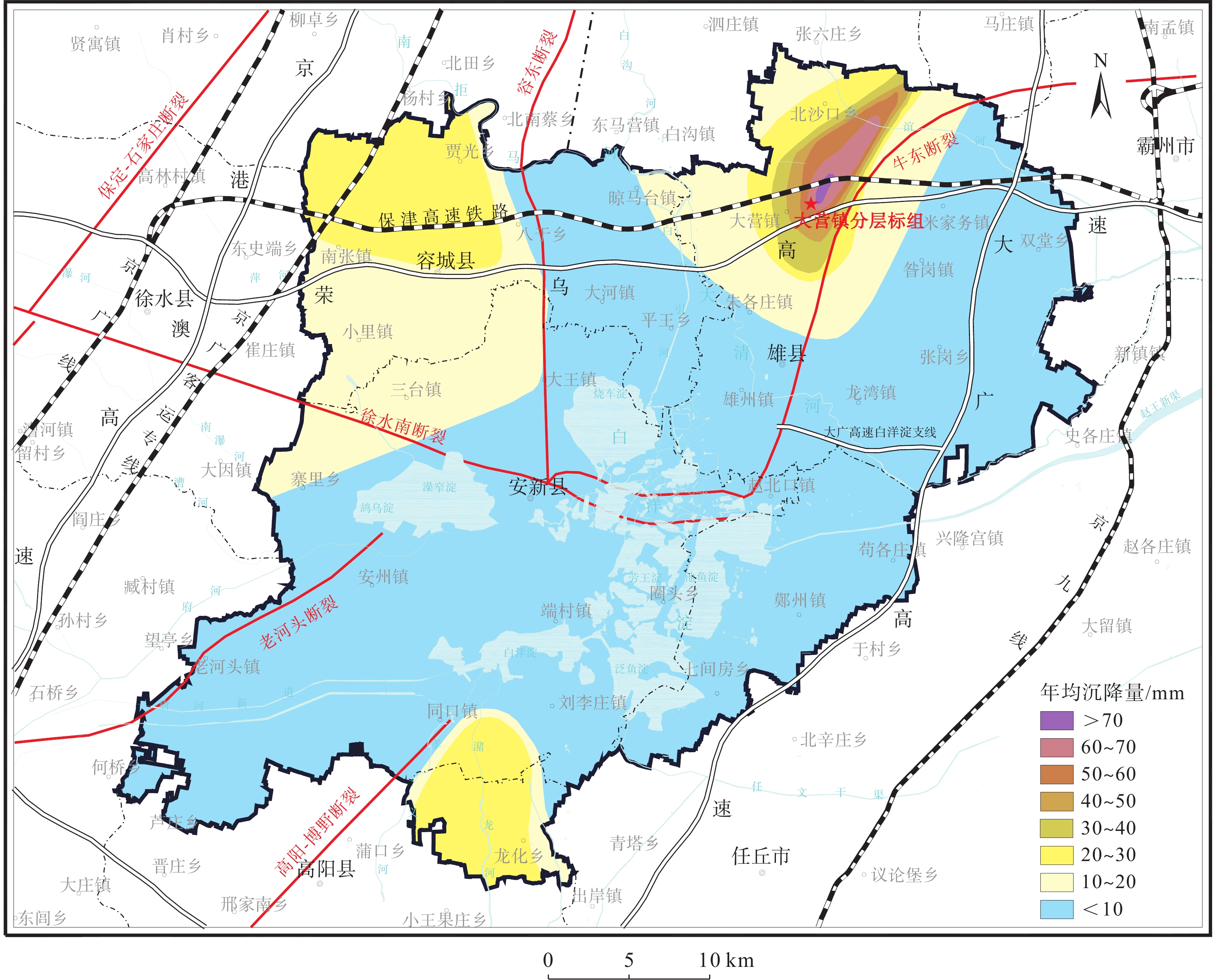
图 1 雄安新区地面沉降平均速率图(据文献[24]改编)
Figure 1.
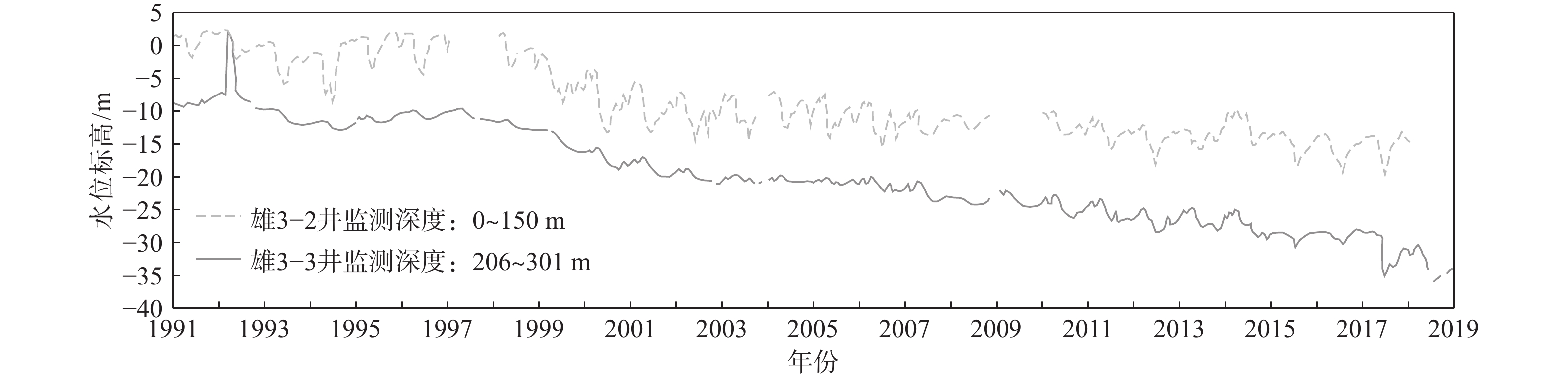
图 12 雄安新区浅层、深层地下水水位历时曲线(据文献[23]修改)
Figure 12.
-
[1] XUE Yuqun,ZHANG Yun,YE Shujun,et al. Land subsidence in China[J]. Environmental Geology,2005,48(6):713 − 720. doi: 10.1007/s00254-005-0010-6
[2] HSU W C,CHANG H C,CHANG K C,et al. Observing Land Subsidence and Revealing the Factors That Influence It Using a Multi-Sensor Approach in Yunlin County,Taiwan[J]. Remote Sensing,2015,7(6):8202 − 8223. doi: 10.3390/rs70608202
[3] 李红,肖国强,杨吉龙,等. 天津滨海新区地面沉降层位的精准识别与沉降过程重建[J]. 地质通报,2016,35(10):1646 − 1652. [LI Hong,XIAO Guoqiang,YANG Jilong,et al. Precise identification of land-subsiding layers and reconstruction of subsidence process in Tianjin Binhai New Area[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2016,35(10):1646 − 1652. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Hong, XIAO Guoqiang, YANG Jilong, et al. Precise identification of land-subsiding layers and reconstruction of subsidence process in Tianjin Binhai New Area[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2016, 35(10): 1646-1652. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 赵慧. 地面沉降的人为主控因素研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2005
ZHAO Hui. The research of land subsidence’s master-control factor created by men[D]. Xi'an: Changan University, 2005. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] ABIDIN H Z,ANDREAS H,GUMILAR I,et al. Land subsidence in coastal city of Semarang (Indonesia):characteristics,impacts and causes[J]. Geomatics,Natural Hazards and Risk,2013,4(3):226 − 240. doi: 10.1080/19475705.2012.692336
[6] 龚士良. 上海城市建设对地面沉降的影响[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,1998,9(2):108 − 111. [GONG Shiliang. Effects of urban construction on the land subsidence in Shanghai[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,1998,9(2):108 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GONG Shiliang. Effects of urban construction on the land subsidence in Shanghai[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 1998, 9(2): 108-111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 胡彩萍,张景燕,郝梦圆,等. 黄河三角洲生态区孔隙热储地热开发对地面沉降的影响分析[J]. 山东国土资源,2017,33(2):39 − 42. [HU Caiping,ZHANG Jingyan,HAO Mengyuan,et al. Impact analysis of geothermal development on land subsidence in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Shandong Land and Resources,2017,33(2):39 − 42. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2017.02.007
HU Caiping, ZHANG Jingyan, HAO Mengyuan, et al. Impact analysis of geothermal development on land subsidence in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2017, 33(2): 39-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2017.02.007
[8] 姚书灵,高金川,容姣. 几种典型成因类型的地面沉降机理分析及其防治对策[J]. 台声 新视角,2006(1):243 − 244. [YAO Shuling,GAO Jinchuan,RONG Jiao. Mechanism analysis and prevention measures of several typical causes of land subsidence[J]. New Angle of View,2006(1):243 − 244. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YAO Shuling, GAO Jinchuan, RONG Jiao. Mechanism analysis and prevention measures of several typical causes of land subsidence[J]. New Angle of View, 2006(1): 243-244. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] AL-MAHBASHI A M,AL-SHAMRANI M A,ABBAS M F. Hydromechanical behavior of unsaturated expansive clay under repetitive loading[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering,2021,13(5):1136 − 1146. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2021.05.002
[10] ZHANG Yun,WU Jichun,XUE Yuqun,et al. Land subsidence and uplift due to long-term groundwater extraction and artificial recharge in Shanghai,China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2015,23(8):1851 − 1866. doi: 10.1007/s10040-015-1302-x
[11] SUDDEEPONG A,CHAI Jinchun,SHEN Shuilong,et al. Deformation behaviour of clay under repeated one-dimensional unloading-reloading[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2015,52(8):1035 − 1044. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2014-0216
[12] 肖国强. 深部粘性土高压固结机理与地面沉降过程研究——以天津滨海新区G2孔为例[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2014
XIAO Guoqiang. Study on mechanism of clayey soil by high pressure consolidation and process of land subsidence: A case study of the G2 geologic drill-hole in Tianjin Binhai New Area[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 郭海朋,丁国平,朱菊艳,等. 沧州地面沉降区粘土压缩变形和渗透特征研究[J]. 武汉理工大学学报,2014,36(5):111 − 117. [GUO Haipeng,DING Guoping,ZHU Juyan,et al. Compression deformation and permeability characteristics of clay in land subsidence area of Cangzhou[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology,2014,36(5):111 − 117. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GUO Haipeng, DING Guoping, ZHU Juyan, et al. Compression deformation and permeability characteristics of clay in land subsidence area of Cangzhou[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2014, 36(5): 111-117. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 杨吉龙,袁海帆,胡云壮,等. 天津滨海地区深部黏土层弹塑性变形特征与地面沉降关系研究[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(10):3763 − 3772. [YANG Jilong,YUAN Haifan,HU Yunzhuang,et al. Relationship between elastoplastic deformation of deep clay and land subsidence in Tianjin coastal area[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2018,39(10):3763 − 3772. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YANG Jilong, YUAN Haifan, HU Yunzhuang, et al. Relationship between elastoplastic deformation of deep clay and land subsidence in Tianjin coastal area[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(10): 3763-3772. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 田芳,郭萌,罗勇,等. 北京地面沉降区土体变形特征[J]. 中国地质,2012,39(1):236 − 242. [TIAN Fang,GUO Meng,LUO Yong,et al. The deformation behavior of soil mass in the subsidence area of Beijing[J]. Geology in China,2012,39(1):236 − 242. (in Chinese with English abstract)
TIAN Fang, GUO Meng, LUO Yong, et al. The deformation behavior of soil mass in the subsidence area of Beijing[J]. Geology in China, 2012, 39(1): 236-242. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 雷坤超,马凤山,罗勇,等. 北京平原区现阶段主要沉降层位与土层变形特征[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(2):442 − 458. [LEI Kunchao,MA Fengshan,LUO Yong,et al. Main subsidence layers and deformation characteristics in Beijing plain at present[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(2):442 − 458. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2021-0238
LEI Kunchao, MA Fengshan, LUO Yong, et al. Main subsidence layers and deformation characteristics in Beijing plain at present[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2022, 30(2): 442-458. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2021-0238
[17] 朱利民,沙志华,段晓飞,等. 基于分层标监测的德州城区地面沉降分层沉降特征浅析[J]. 山东国土资源,2020,36(8):32 − 39. [ZHU Limin,SHA Zhihua,DUAN Xiaofei,et al. Analysis on characteristics of layered settlement of land subsidence in urban area of Dezhou city based on layering marks monitoring[J]. Shandong Land and Resources,2020,36(8):32 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHU Limin, SHA Zhihua, DUAN Xiaofei, et al. Analysis on characteristics of layered settlement of land subsidence in urban area of Dezhou city based on layering marks monitoring[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2020, 36(8): 32-39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 何健辉,张进才,陈勇,等. 基于弱光栅技术的地面沉降自动化监测系统[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):146 − 153. [HE Jianhui,ZHANG Jincai,CHEN Yong,et al. Automatic land subsidence monitoring system based on weak-reflection fiber gratings[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):146 − 153. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HE Jianhui, ZHANG Jincai, CHEN Yong, et al. Automatic land subsidence monitoring system based on weak-reflection fiber gratings[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(1): 146-153. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 林良俊,韩博,马震,等. 雄安多要素城市地质标准体系研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(2):152 − 156. [LIN Liangjun,HAN Bo,MA Zhen,et al. A study of the multi-factor urban geology standard system in Xiongan New Area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(2):152 − 156. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIN Liangjun, HAN Bo, MA Zhen, et al. A study of the multi-factor urban geology standard system in Xiongan New Area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(2): 152-156. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 张永红,刘冰,吴宏安,等. 雄安新区2012—2016年地面沉降InSAR监测[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2018,40(5):652 − 662. [ZHANG Yonghong,LIU Bing,WU Hongan,et al. Ground subsidence in Xiong’an new area from 2012 to 2016 monitored by InSAR technique[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,2018,40(5):652 − 662. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Yonghong, LIU Bing, WU Hongan, et al. Ground subsidence in Xiong’an new area from 2012 to 2016 monitored by InSAR technique[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2018, 40(5): 652-662. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] DAI Keren,RAN Peilian,LI Zhenhong,et al. Land subsidence in Xiong’an New Area,China revealed by InSAR observations[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geoinformation Science,2021,4(1):70 − 76.
[22] 冉培廉,李少达,戴可人,等. 雄安新区2017—2019年地面沉降SBAS-InSAR监测与分析[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2022,41(3):66 − 73. [RAN Peilian,LI Shaoda,DAI Keren,et al. SBAS-InSAR monitoring and analysis of land subsidence in Xiongan New Area from 2017 to 2019[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Natural Science),2022,41(3):66 − 73. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9787.2022.3.jzgxyxb202203009
RAN Peilian, LI Shaoda, DAI Keren, et al. SBAS-InSAR monitoring and analysis of land subsidence in Xiongan New Area from 2017 to 2019[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Natural Science), 2022, 41(3): 66-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9787.2022.3.jzgxyxb202203009
[23] 马震,夏雨波,李海涛,等. 雄安新区自然资源与环境-生态地质条件分析[J]. 中国地质,2021,48(3):677 − 696. [MA Zhen,XIA Yubo,LI Haitao,et al. Analysis of natural resources and environment eco-geological conditions in the Xiong’an New Area[J]. Geology in China,2021,48(3):677 − 696. (in Chinese with English abstract)
MA Zhen, XIA Yubo, LI Haitao, et al. Analysis of natural resources and environment eco-geological conditions in the Xiong’an New Area[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(3): 677-696. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 马峰,王贵玲,张薇,等. 古潜山热储开发对地面沉降的影响机制研究[J]. 中国地质,2021,48(1):40 − 51. [MA Feng,WANG Guiling,ZHANG Wei,et al. Influence mechanism of ancient buried hill geothermal development on land subsidence[J]. Geology in China,2021,48(1):40 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[MA Feng, WANG Guiling, ZHANG Wei, et al. Influence mechanism of ancient buried hill geothermal development on land subsidence[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(1): 40-51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 何登发,单帅强,张煜颖,等. 雄安新区的三维地质结构:来自反射地震资料的约束[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2018,48(9):1207 − 1222. [HE Dengfa,SHAN Shuaiqiang,ZHANG Yuying,et al. Geologic architecture of Xiong’an New Area:Constraints from seismic reflection data[J]. Science China Earth Sciences,2018,48(9):1207 − 1222. (in Chinese)
HE Dengfa, SHAN Shuaiqiang, ZHANG Yuying, et al. Geologic architecture of Xiong’an New Area: Constraints from seismic reflection data[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2018, 48(9): 1207-1222. (in Chinese)
[26] 李海涛,凤蔚,王凯霖,等. 雄安新区地下水资源概况、特征及可开采潜力[J]. 中国地质,2021,48(4):1112 − 1126. [LI Haitao,FENG Wei,WANG Kailin,et al. Groundwater resources in Xiong’an New Area and its exploitation potential[J]. Geology in China,2021,48(4):1112 − 1126. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Haitao, FENG Wei, WANG Kailin, et al. Groundwater resources in Xiong’an New Area and its exploitation potential[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(4): 1112-1126. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 苏永强,李郡. 雄安新区地热资源评价与开发应用潜力分析[J]. 河北工业大学学报,2018,47(4):62 − 67. [SU Yongqiang,LI Jun. Evaluation of geothermal resources and their potential utilization in Xiongan New Area[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Technology,2018,47(4):62 − 67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SU Yongqiang, LI Jun. Evaluation of geothermal resources and their potential utilization in Xiongan New Area[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Technology, 2018, 47(4): 62-67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 土工试验方法标准: GB/T 50123—2019[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2019.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for geotechnical testing method: GB/T 50123—2019[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2019. (in Chinese)
[29] 中华人民共和国自然资源部. 地面沉降测量规范: DZ/T 0154—2020[S].
Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Land subsidence measurement specification: DZ/T 0154—2020[S]. (in Chinese)
[30] 中华人民共和国国土资源部. 地面沉降调查与监测规范: DZ/T 0283—2015[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015.
Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Specification for survey and monitoring of land subsidence: DZ/T 0283—2015[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2015. (in Chinese)
[31] 郭海朋,白晋斌,张有全,等. 华北平原典型地段地面沉降演化特征与机理研究[J]. 中国地质,2017,44(6):1115 − 1127. [GUO Haipeng,BAI Jinbin,ZHANG Youquan,et al. The evolution characteristics and mechanism of the land subsidence in typical areas of the North China Plain[J]. Geology in China,2017,44(6):1115 − 1127. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GUO Haipeng, BAI Jinbin, ZHANG Youquan, et al. The evolution characteristics and mechanism of the land subsidence in typical areas of the North China Plain[J]. Geology in China, 2017, 44(6): 1115-1127. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 薛禹群. 论地下水超采与地面沉降[J]. 地下水,2012,34(6):1 − 5. [XUE Yuqun. Discussion on groundwater overexploitation and ground settlement[J]. Ground Water,2012,34(6):1 − 5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XUE Yuqun. Discussion on groundwater overexploitation and ground settlement[J]. Ground Water, 2012, 34(6): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 郭海朋,李文鹏,王丽亚,等. 华北平原地下水位驱动下的地面沉降现状与研究展望[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(3):162 − 171. [GUO Haipeng,LI Wenpeng,WANG Liya,et al. Present situation and research prospects of the land subsidence driven by groundwater levels in the North China Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(3):162 − 171. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GUO Haipeng, LI Wenpeng, WANG Liya, et al. Present situation and research prospects of the land subsidence driven by groundwater levels in the North China Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(3): 162-171. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] GUO Haipeng,ZHANG Zuochen,CHENG Guoming,et al. Groundwater-derived land subsidence in the North China Plain[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2015,74(2):1415 − 1427. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4131-2
[35] 张永伟. 华北平原德州地面沉降成生机理、监测预警与可控性研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2014
ZHANG Yongwei. Formation mechanism, monitoring and warning, controlling research of subsidence of Dezhou in North China plain[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[36] ABIDIN H Z,GUMILAR I,ANDREAS H,et al. On causes and impacts of land subsidence in Bandung Basin,Indonesia[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2013,68(6):1545 − 1553. doi: 10.1007/s12665-012-1848-z
[37] 薛传东,刘星,李保珠,等. 昆明市区地面沉降的机理分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2004,15(3):47 − 54. [XUE Chuandong,LIU Xing,LI Baozhu,et al. Mechanism analysis of land subsidence in Kunming City area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2004,15(3):47 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2004.03.011
XUE Chuandong, LIU Xing, LI Baozhu, et al. Mechanism analysis of land subsidence in Kunming City area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2004, 15(3): 47-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2004.03.011
-



 下载:
下载: