A study of the critical groundwater level related to soil consolidation characteristics of land subsidence in Cangzhou
-
摘要:
沧州市长期以来面临严重的地面沉降问题,在控制沉降发展的前提下,为合理利用地下水资源,需要确立开采水位埋深警戒线。针对地面沉降综合防治如何确定临界水位这一科学问题,以沧州3个典型沉降区土样为研究对象,分析了地层固结特征,通过关联地层厚度的方式改进了以先期固结压力求解临界水位的方法,结合多年来地面沉降与地下水水位监测数据,对沧州市临界水位进行了综合定量评估。研究表明:沧州地区0 ~150 m以内多为正常固结或欠固结土,150 m以下普遍为超固结土,非弹性释水变形是影响该地区地面沉降速率变化的重要因素。运用改进后的方法计算出沧州市区、肃宁县及东光县的临界水位埋深分别为66.8 ,67.5 ,67.8 m。综合分析沧州市区累计地面沉降与地下水水位变化资料,得出两者之间的指数函数关系,并以沉降速率为指标,求得65~70 m为沧州市区临界水位区间范围。在验证了两种方法计算结果一致性的基础上,最终将65 m作为沧州市区采取地面沉降防控措施的参考临界水位,为地方政府制定合理的地下水开采方案提供可靠依据。
Abstract:Land subsidence has become a serious issue in Cangzhou for a long time. In order to make reasonable use of groundwater resources, it is necessary to establish a warning groundwater level under the premise of controlling the development of land subsidence. How to quantitatively determine the critical gorundwater level (CWL) for comprehensive control of land subsidence? In allusion to this scientific problem, this paper takes the soil samples of three typical settlement areas in Cangzhou as the research object, and analyzes the formation consolidation characteristics. By correlating the stratum thickness, we improve the method of calculating the CWL with the previous consolidation pressure. Based on the monitoring data of land subsidence and groundwater level in Cangzhou for many years, the comprehensive quantitative evaluation of the CWL in Cangzhou are carried out. The results show that the soil within a depth ranging from 0 to 150 m in Cangzhou is normally consolidated or under-consolidated, and the soil below the depth of 150 m is generally over-consolidated. The inelastic water release deformation is an important factor affecting the change of land subsidence rate in this area. Using the improved method, the CWL in Cangzhou, Suning and Dongguang is 66.8 m, 67.5 m and 67.8 m, respectively. Based on the data of the cumulative land subsidence and groundwater level change in the urban of Cangzhou, we obtain the exponential function relationship between the cumulative land subsidence and groundwater level. The subsidence rate is taken as the index, and the critical groundwater level in the urban of Cangzhou ranges from 65 to 70 m. On the basis of verifying the consistency of the calculation results of the two methods, we determined 65 m as the critical groundwater level for the prevention and control measures of land subsidence in Cangzhou. The results provide a reliable basis for the local government to formulate a reasonable groundwater exploitation plan.
-

-
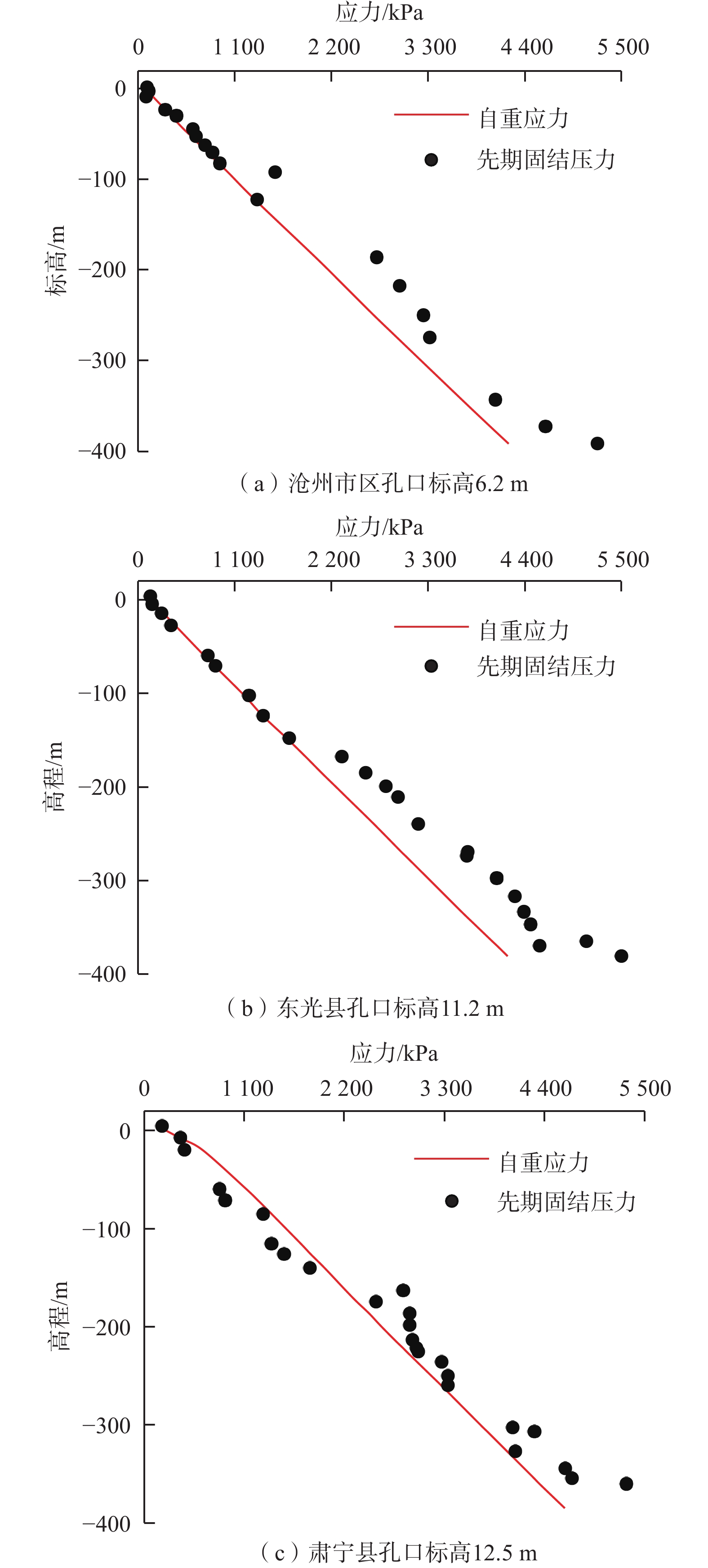
表 1 沧州地区第Ⅲ含水层组土样基本情况及临界水位降深统计表
Table 1. Statistics of critical groundwater level drawdown and basic information of soil samples from the third aquifer group in Cangzhou
地名 土层 层厚/m 取样与测试 临界水位降深/m 取样点高程/m 前期固结压力/MPa 超固结比 压缩指数 回弹指数 沧州市区 C1 22.0 −186.1 2.72 1.35 0.1 0.03 71.3 C2 31.1 −217.2 2.98 1.27 0.3 0.04 64.8 C3 32.6 −249.8 3.25 1.21 0.3 0.03 57.9 C4 25.1 −274.9 3.32 1.12 0.2 0.05 37.6 C5 40.0 −314.9 4.36 1.29 0.2 0.05 99.9 C6 28.3 −343.1 4.07 1.10 0.3 0.03 39.2 肃宁县 S1 16.8 −175.6 2.55 1.22 0.4 0.05 21.3 S2 12.0 −187.6 2.92 1.31 0.2 0.03 44.6 S3 11.8 −199.4 2.92 1.24 0.2 0.05 32.7 S4 15.2 −214.6 2.95 1.17 0.3 0.05 19.6 S5 12.0 −226.6 3.01 1.14 0.3 0.03 12.4 S6 10.3 −236.9 3.27 1.19 0.3 0.03 27.1 S7 14.5 −251.4 3.34 1.14 0.3 0.04 18.0 S8 52.2 −303.6 4.05 1.16 0.3 0.04 32.8 S9 4.5 −308.1 4.29 1.21 0.2 0.04 51.7 东光县 D1 9.0 −166.5 2.32 1.22 0.2 0.03 41.2 D2 17.3 −183.8 2.59 1.24 0.2 0.03 50.0 D3 14.4 −198.2 2.82 1.25 0.2 0.02 57.3 D4 11.3 −209.5 2.96 1.25 0.2 0.03 59.0 D5 29.0 −238.5 3.19 1.19 0.3 0.03 50.5 D6 30.0 −268.5 3.75 1.25 0.2 0.03 75.1 D7 28.0 −296.5 4.08 1.24 0.3 0.03 78.0 D8 19.5 −316 4.29 1.22 0.3 0.03 78.3 D9 16.7 −332.7 4.39 1.19 0.3 0.03 70.5 表 2 沧州地区第Ⅲ含水层组临界水位埋深表
Table 2. The critical groundwater level depths of the third aquifer group in Cangzhou
地区 临界水位
降深/m观测水位
埋深/m观测孔地面
高程/m临界水位埋深
(高程)/m沧州市区 64.3 2.5 6.2 66.8(−60.6) 肃宁县 28.2 39.3 12.5 67.5(−54.7) 东光县 64.7 3.1 11.2 67.8(−56.6) -
[1] 房浩,何庆成,徐斌,等. 沧州地区地面沉降灾害风险评价研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(4):159 − 164. [FANG Hao,HE Qingcheng,XU Bin,et al. A study of risk assessment of the land subsidence in Cangzhou[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(4):159 − 164. (in Chinese with English abstract)
FANG Hao, HE Qingcheng, XU Bin, et al. A study of risk assessment of the land subsidence in Cangzhou[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(4): 159-164. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] PHIEN-WEJ N,GIAO P H,NUTALAYA P. Land subsidence in Bangkok,Thailand[J]. Engineering Geology,2006,82(4):187 − 201. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2005.10.004
[3] MADANI K,AGHAKOUCHAK A,MIRCHI A. Iran’s socio-economic drought:challenges of a water-bankrupt nation[J]. Iranian Studies,2016,49(6):997 − 1016. doi: 10.1080/00210862.2016.1259286
[4] FAUNT C C,SNEED M,TRAUM J,et al. Water availability and land subsidence in the Central Valley,California,USA[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2016,24(3):675 − 684. doi: 10.1007/s10040-015-1339-x
[5] 马峰,王贵玲,张薇,等. 古潜山热储开发对地面沉降的影响机制研究[J]. 中国地质,2021,48(1):40 − 51. [MA Feng,WANG Guiling,ZHANG Wei,et al. Influence mechanism of ancient buried hill geothermal development on land subsidence[J]. Geology in China,2021,48(1):40 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
MA Feng, WANG Guiling, ZHANG Wei, et al. Influence mechanism of ancient buried hill geothermal development on land subsidence[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(1): 40-51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] CONWAY B D. Land subsidence and earth fissures in south-central and southern Arizona,USA[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2016,24(3):649 − 655. doi: 10.1007/s10040-015-1329-z
[7] MILLER M M,SHIRZAEI M,ARGUS D. Aquifer mechanical properties and decelerated compaction in Tucson,Arizona[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,2017,122(10):8402 − 8416. doi: 10.1002/2017JB014531
[8] 袁伟民,张金平. 地面沉降成灾临界水位的识别及意义[J]. 灾害学,2007,22(2):67 − 69. [YUAN Weimin,ZHANG Jinping. Identification of disaster-causal critical water table of land subsidence and its significance[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2007,22(2):67 − 69. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YUAN Weimin, ZHANG Jinping. Identification of disaster-causal critical water table of land subsidence and its significance[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2007, 22(2): 67-69. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 牛修俊. 地层的固结特性与地面沉降临界水位控沉[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,1998,9(2):68 − 74. [NIU Xiujun. Characteristics of strata consolidation and land subsidence controlling by critical water level[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,1998,9(2):68 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract)
NIU Xiujun. Characteristics of strata consolidation and land subsidence controlling by critical water level[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 1998, 9(2): 68-74. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 白晋斌,牛修俊. 天津新生界固结特征与地面沉降[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2010,21(1):42 − 46. [BAI Jinbin,NIU Xiujun. Cenozoic consolidation characteristics and land subsidence in Tianjin[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2010,21(1):42 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract)
BAI Jinbin, NIU Xiujun. Cenozoic consolidation characteristics and land subsidence in Tianjin[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2010, 21(1): 42-46.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 王家兵,李平. 天津平原地面沉降条件下的深层地下水资源组成[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2004,31(5):35 − 37. [WANG Jiabing,LI Ping. Composition of groundwater resources in deep-seated aquifers under the condition of land subsidence in Tianjin Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2004,31(5):35 − 37. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Jiabing, LI Ping. Composition of groundwater resources in deep-seated aquifers under the condition of land subsidence in Tianjin Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2004, 31(5): 35-37.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 赵慧,钱会,彭建兵. 超固结土层垂向形变机理及临界水位控沉分析—以西安南郊钻孔土样研究为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2008,19(1):124 − 127. [ZHAO Hui,QIAN Hui,PENG Jianbing. Deformation mechanism of over-consolidation soil and land subsidence controlled by critical water-level[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2008,19(1):124 − 127. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2008.01.027
ZHAO Hui, QIAN Hui, PENG Jianbing. Deformation mechanism of over-consolidation soil and land subsidence controlled by critical water-level[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2008, 19(1): 124-127. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2008.01.027
[13] 赵慧,冉兴龙,李渊. 根据地面沉降与地下水头的关系求地面沉降临界水位[J]. 勘察科学技术,2005(2):19 − 23. [ZHAO Hui,RAN Xinglong,LI Yuan. To determine critical water level by correlation between land subsidence and groundwater drawdown[J]. Site Investigation Science and Technology,2005(2):19 − 23. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3946.2005.02.006
ZHAO Hui, RAN Xinglong, LI Yuan. To determine critical water level by correlation between land subsidence and groundwater drawdown[J]. Site Investigation Science and Technology, 2005(2): 19-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3946.2005.02.006
[14] 李国和,荆志东,许再良. 京沪高速铁路沿线地面沉降与地下水位变化关系探讨[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2008,35(6):90 − 94. [LI Guohe,JING Zhidong,XU Zailiang. A discussion of the correlation between land subsidence and groundwater level variation along the Jinghu high speed railway[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2008,35(6):90 − 94. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Guohe, JING Zhidong, XU Zailiang. A discussion of the correlation between land subsidence and groundwater level variation along the Jinghu high speed railway[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2008, 35(6): 90-94. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 姜媛,田芳,罗勇,等. 北京地区基于不同地面沉降阈值的地下水位控制分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2015,26(1):37 − 42. [JIANG Yuan,TIAN Fang,LUO Yong,et al. Groundwater control target under different threshold of land subsidence in Beijing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2015,26(1):37 − 42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
JIANG Yuan, TIAN Fang, LUO Yong, et al. Groundwater control target under different threshold of land subsidence in Beijing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2015, 26(1): 37-42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 张文杰. 沧州市地面沉降与开采地下水关系初探[J]. 地下水,2010,32(6):41 − 42. [ZHANG Wenjie. Preliminary study on the relationship between land subsidence and groundwater exploitation in Cangzhou City[J]. Ground Water,2010,32(6):41 − 42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Wenjie. Preliminary study on the relationship between land subsidence and groundwater exploitation in Cangzhou City[J]. Ground Water, 2010, 32(6): 41-42.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 邢忠信,李和学,张熟,等. 沧州市地面沉降研究及防治对策[J]. 地质调查与研究,2004,27(3):157 − 163. [XING Zhongxin,LI Hexue,ZHANG Shu,et al. Surface subsidence and its countermeasures in Cangzhou city[J]. Geological Survey and Research,2004,27(3):157 − 163. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XING Zhongxin, LI Hexue, ZHANG Shu, et al. Surface subsidence and its countermeasures in Cangzhou city[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2004, 27(3): 157-163. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] POLAND J F, DAVIS G H. Land subsidence due to withdrawal of fluids[C]//Reviews in Engineering Geology. Boulder: Geological Society of America, 1969: 187 − 270.
[19] GALLOWAY D L,BURBEY T J. Review:Regional land subsidence accompanying groundwater extraction[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2011,19(8):1459 − 1486. doi: 10.1007/s10040-011-0775-5
[20] GAO Mingliang, GONG Huili, CHEN Beibei,et al. Regional land subsidence analysis in eastern Beijing plain by InSAR time series and wavelet transforms[J]. Remote Sensing,2018,10(3):365. doi: 10.3390/rs10030365
-



 下载:
下载: