Simulation of surface water - groundwater interaction in the plain area of the Poyang Lake considering the change of water body area
-
摘要:
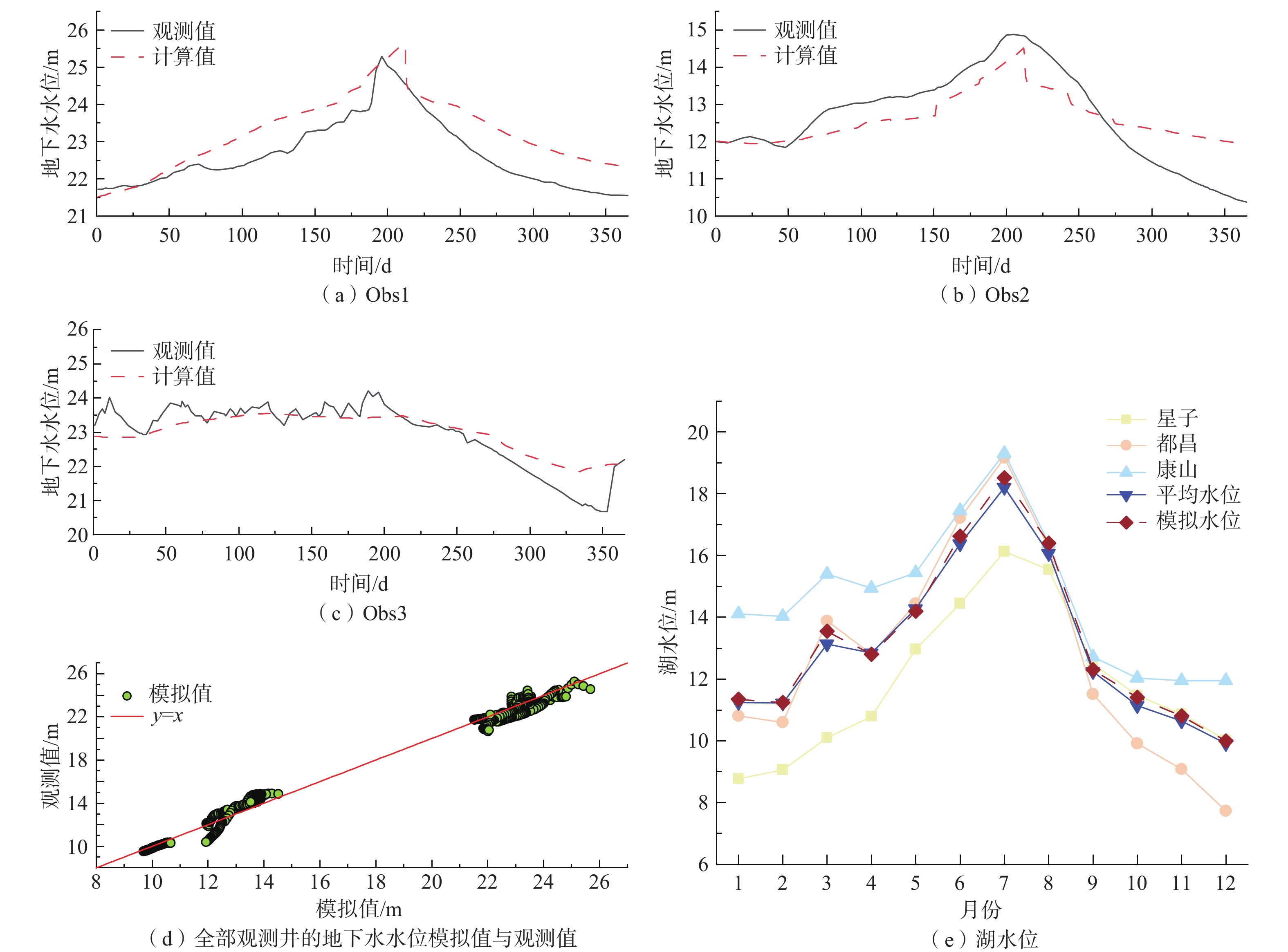
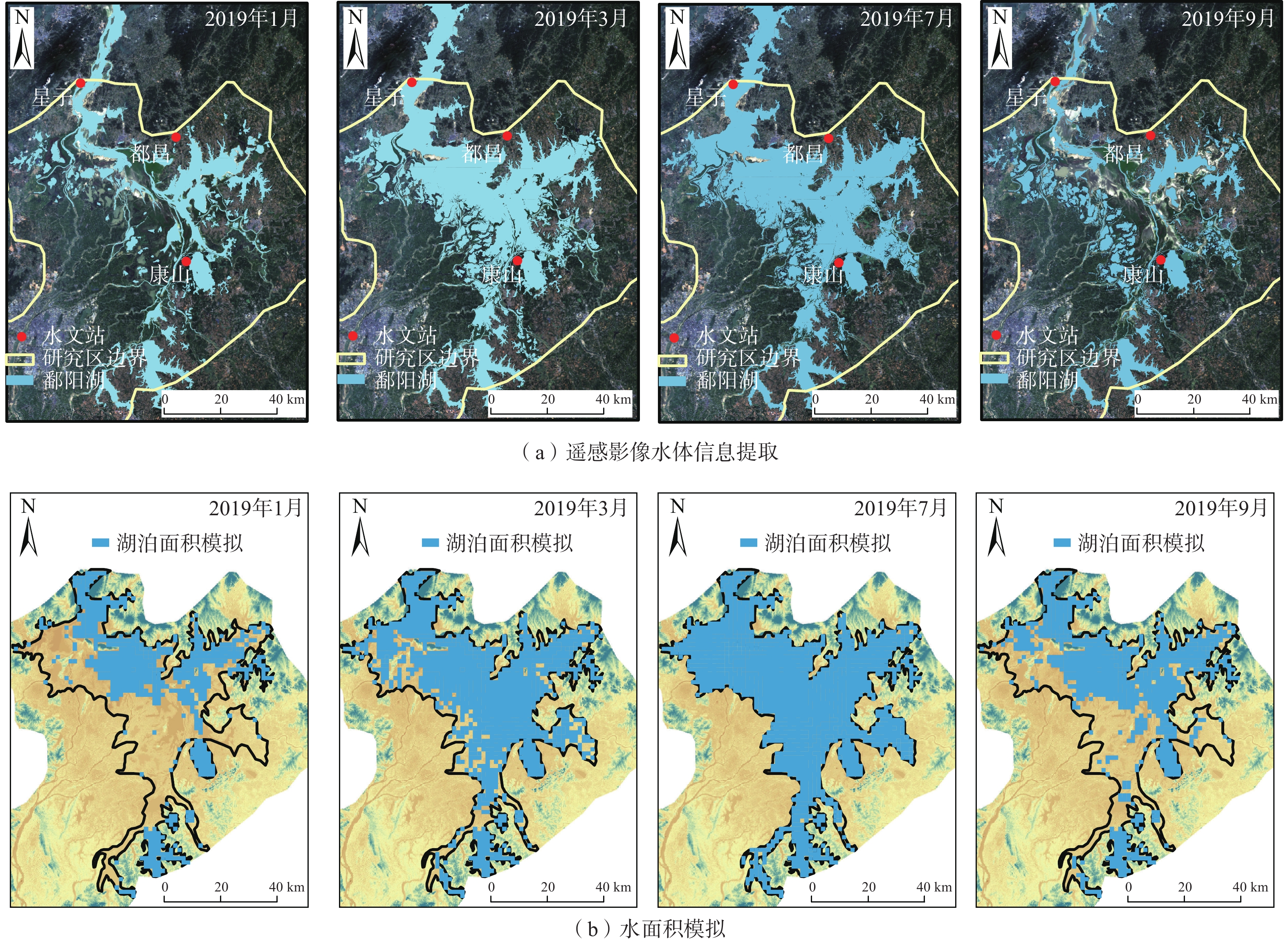
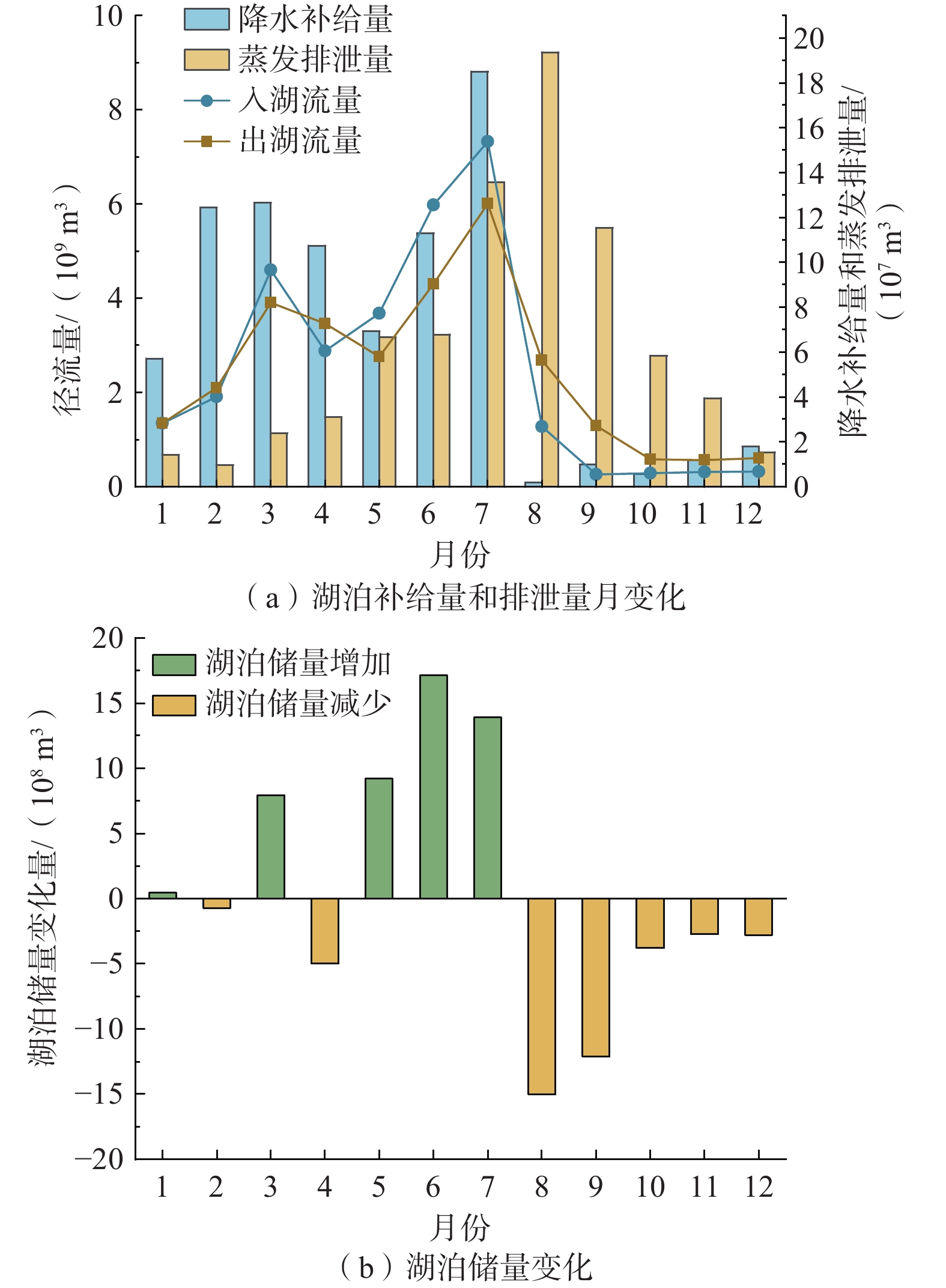
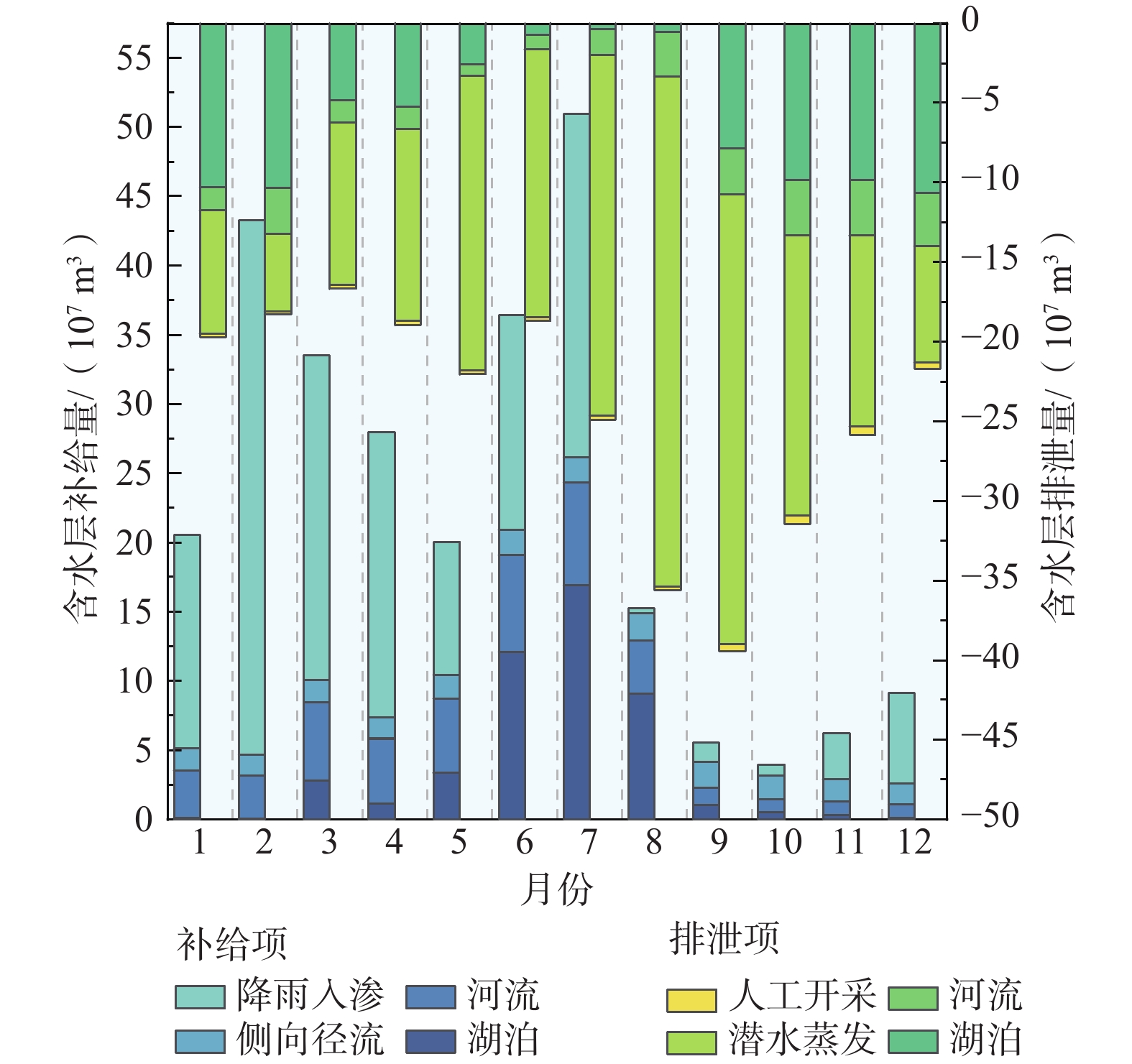
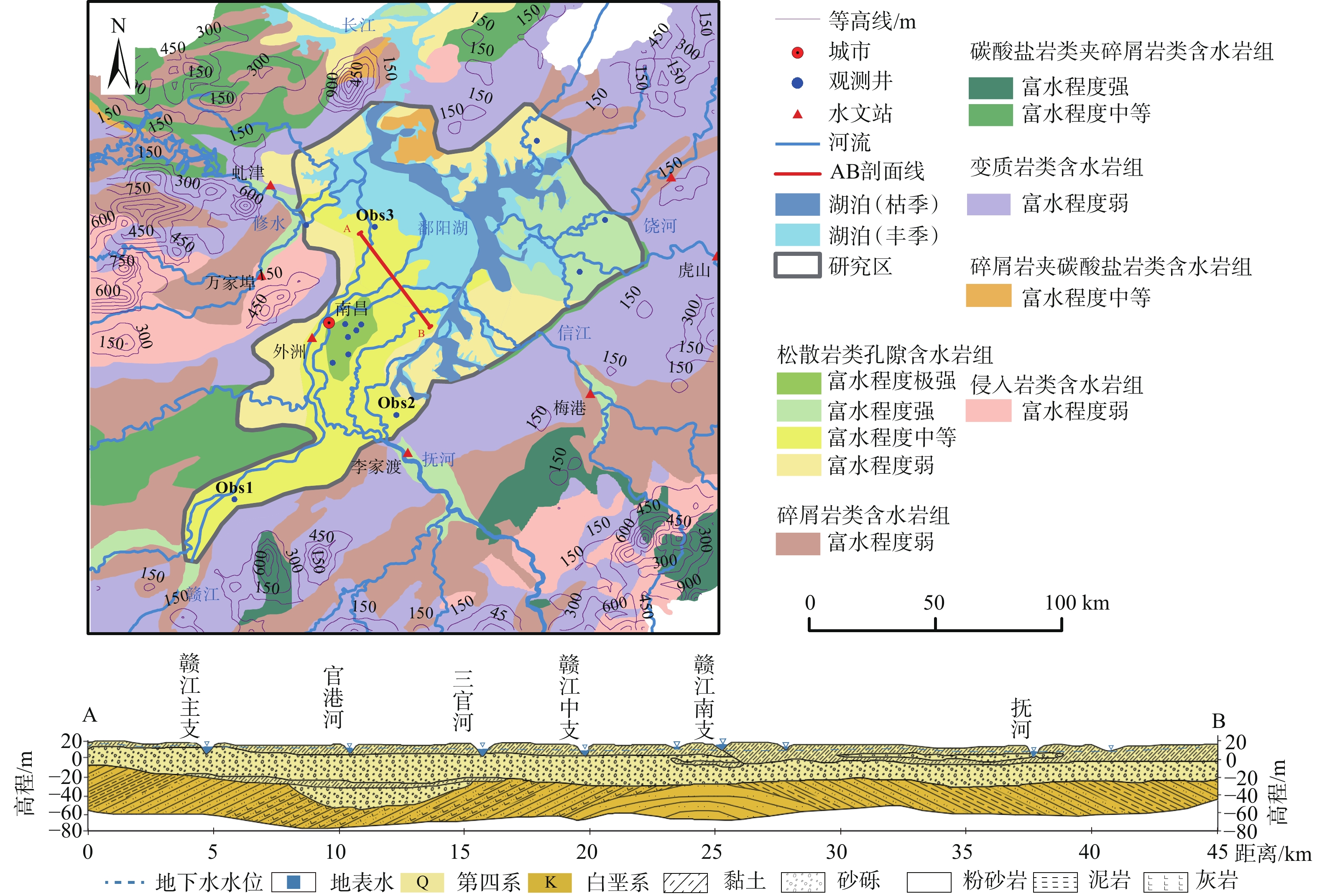
湖泊的水情变化会影响其与地下水之间的物理水文过程和生态行为,鄱阳湖独特的“河湖相”转换特征使得该地区地表-地下水交换过程更加复杂。采用Visual MODFLOW构建三维非稳定流地下水流数值模型,利用LAK3子程序模块,通过输入五河入湖以及鄱阳湖流入长江的水量,实现湖水面积的动态模拟。结果表明,2019年湖水位模拟值与实测值的均方根误差为0.225 m,地下水水位模拟值与实测值的均方根误差为0.571 m;模型模拟鄱阳湖水面积环比变幅−41%~83%,与遥感影像结论吻合。该模型减少了湖泊作为边界条件的约束,可以有效刻画鄱阳湖频繁变化的湖水位和水体面积,准确模拟地下水流场和地表-地下水相互作用关系对湖泊水体高度动态变化的响应。枯水期主要由地下水补给湖水,交换量为2.03×107~10.58×107 m3/mon;丰水期湖水补给地下水,交换量为2.04×107~16.53×107 m3/mon,湖区及周边地下水水位相比枯水期平均抬升2~3 m,地下水由湖区流向周边地区。本研究为地表水体剧烈变化地区提供了有效的数值模拟方法,研究结果可为鄱阳湖平原区未来水资源管理和环境评价提供基础。
-
关键词:
- 鄱阳湖 /
- 湖水-地下水转换关系 /
- 数值模型 /
- LAK3 /
- 水体面积变化
Abstract:Water changing conditions of a lake will affect the physical and hydrological conditions and ecology of the lake and groundwater. The unique "river-lake phase" transition of the Poyang Lake complicates the surface water-groundwater exchange process in the area. Therefore, this study uses Visual MODFLOW to build a 3D numerical model of groundwater transient flow and uses the LAK3 module to realize the dynamic simulation of the lake water area by inputting the runoff from five rivers into the lake and the Poyang Lake into the Yangtze River. The RMSE between the simulated and measured values of lake water level is 0.225 m, and between the simulated and measured values of groundwater level is 0.571 m. The month-on-month ratio variation of the Poyang Lake area simulated by the model ranges from −41% to 83%, consistent with the remote sensing images. This model reduces the constraint of lakes as boundary conditions, can effectively depict the frequently-changing water level and lake area, and accurately simulate the response of groundwater flow field and surface water-groundwater interaction relationship to the height dynamics of lake water. During the dry season, the lake is mainly recharged by groundwater, with an exchange flux ranging from 2.03×107 to 10.58×107 m3/mon. During the wet season, the lake water discharges into groundwater with an exchange flux ranging from 2.04×107 to 16.53×107 m3/mon, with the average groundwater level rise in the lake region and surrounding areas by 2~3 m compared to the dry season. The groundwater flows from the lake region to the surrounding areas. This study contributes an effective numerical simulation method for areas with dramatic changes in surface water bodies. The results can provide a basis for future water resources management and environmental assessment in the Poyang Lake Plain.
-

-
表 1 研究区各分区渗透系数取值
Table 1. The hydraulic conductivity values in each subdomain of the study area
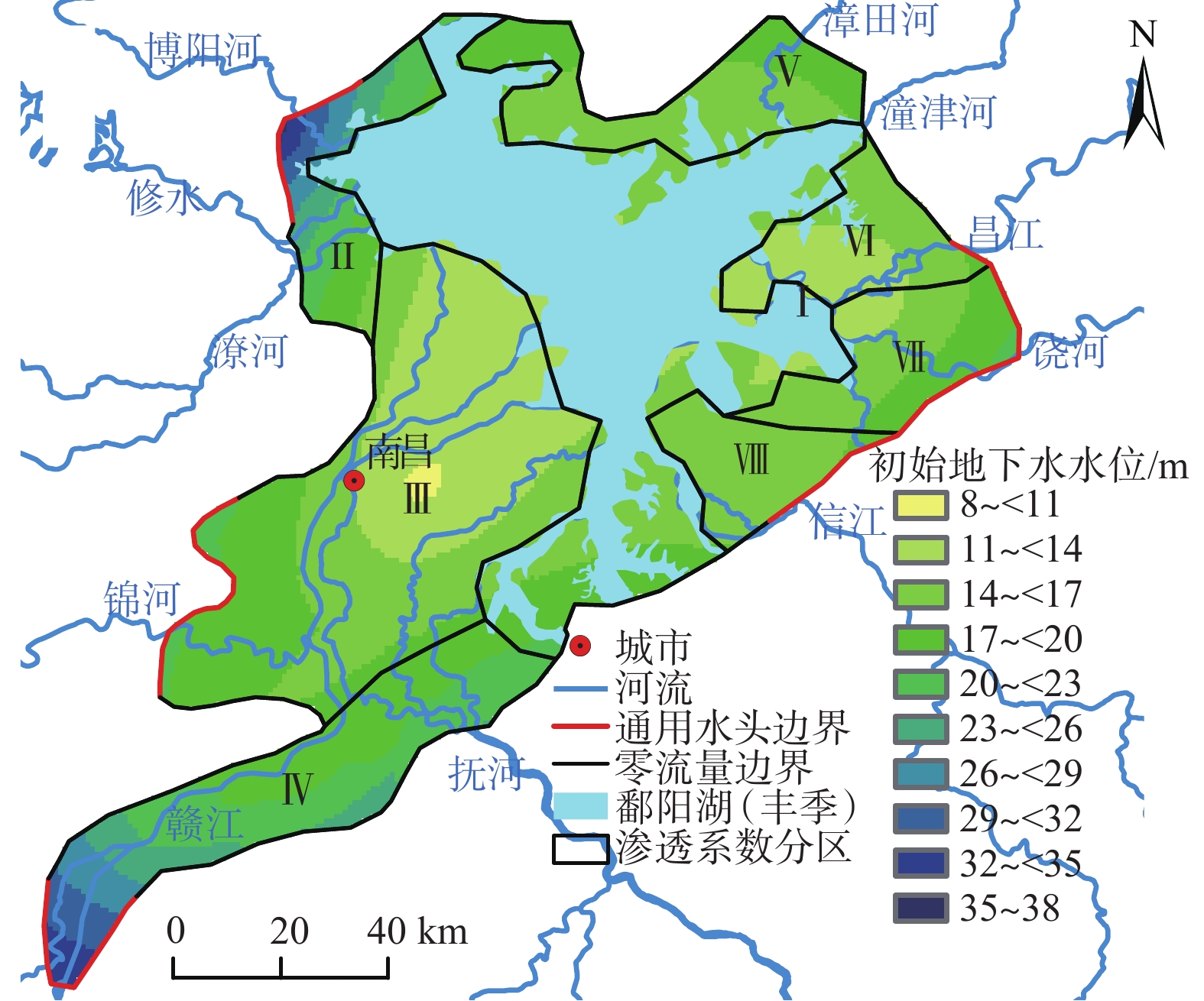
/ (m·d−1) 参数区编号 Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ Ⅴ Ⅵ Ⅶ Ⅷ 第1~3层渗透系数 0.1 5 15 20 35 15 25 5 第4层渗透系数 10 10 20 25 35 20 25 15 -
[1] 杨中华,朱政涛,槐文信,等. 鄱阳湖水利调控对湖区典型丰枯水年水动力水质影响研究[J]. 水利学报,2018,49(2):156 − 167. [YANG Zhonghua,ZHU Zhengtao,HUAI Wenxin,et al. Study on the influence of Poyang Lake Hydraulic Project on hydrodynamics and water-quality in wet and dry year[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2018,49(2):156 − 167. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YANG Zhonghua, ZHU Zhengtao, HUAI Wenxin, et al. Study on the influence of Poyang Lake Hydraulic Project on hydrodynamics and water-quality in wet and dry year[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2018, 49(2): 156–167. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 李刚,马佰衡,周仰效,等. 白洋淀湖岸带地表水与地下水垂向交换研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(4):48 − 54. [LI Gang,MA Baiheng,ZHOU Yangxiao,et al. A study of vertical exchange between surface water and groundwater around the banks of Baiyangdian Lake[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(4):48 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Gang, MA Baiheng, ZHOU Yangxiao, et al. A study of vertical exchange between surface water and groundwater around the banks of Baiyangdian Lake[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(4): 48–54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] PARIZI E,HOSSEINI S M,ATAIE-ASHTIANI B,et al. Quantifying lake–aquifer water exchange:The case of lake urmia,iran[J]. Hydrological Sciences Journal,2022,67(5):725 − 740. doi: 10.1080/02626667.2022.2044044
[4] 束龙仓,栾佳文,宫荣,等. 傍河地下水位监测断面的优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2023,53(2):555 − 565. [SHU Longcang, LUAN Jiawen, GONG Rong, et al. Optimal design of monitoring section for groundwater level beside the river[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2023,53(2):555 − 565. (in Chinese)
[SHU Longcang, LUAN Jiawen, GONG Rong, et al. Optimal design of monitoring section for groundwater level beside the river[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2023,53(2):555-565.(in Chinese)
[5] 龙爱华,邓铭江,谢蕾,等. 巴尔喀什湖水量平衡研究[J]. 冰川冻土,2011,36(6):1341 − 1352. [LONG Aihua,DENG Mingjiang,XIE Lei,et al. A study of the water balance of lake Balkhash[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2011,36(6):1341 − 1352. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LONG Aihua, DENG Mingjiang, XIE Lei, et al. A study of the water balance of lake Balkhash[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2011, 36(6): 1341–1352. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] JAVADZADEH H,ATAIE-ASHTIANI B,HOSSEINI S M,et al. Interaction of lake-groundwater levels using cross-correlation analysis:A case study of Lake Urmia Basin,Iran[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,729:138822. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138822
[7] XU S,FREY S K,ERLER A R,et al. Investigating groundwater-lake interactions in the Laurentian Great Lakes with a fully-integrated surface water-groundwater model[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2021,594:125911. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125911
[8] 陈静,李云良,周俊锋,等. 鄱阳湖洪泛区碟形湖湿地系统地表地下水交互作用[J]. 湖泊科学,2021,33(3):842 − 853. [CHEN Jing,LI Yunliang,ZHOU Junfeng,et al. Assessing surface water-groundwater interactions in the seasonal lake-wetland system of Lake Poyang[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2021,33(3):842 − 853. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18307/2021.0317
CHEN Jing, LI Yunliang, ZHOU Junfeng, et al. Assessing surface water-groundwater interactions in the seasonal lake-wetland system of Lake Poyang [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2021, 33(3): 842–853. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18307/2021.0317
[9] 李云良,姚静,谭志强,等. 鄱阳湖洪泛区碟形湖域与地下水转化关系分析[J]. 水文,2019,39(5):1 − 7. [LI Yunliang,YAO Jing,TAN Zhiqiang,et al. Interactions between typical sublakes and groundwater in floodplains of Poyang Lake[J]. Journal of China Hydrology,2019,39(5):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Yunliang, YAO Jing, TAN Zhiqiang, et al. Interactions between typical sub—lakes and groundwater in floodplains of Poyang Lake [J]. Journal of China Hydrology, 2019, 39(5): 1–7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] LIAO Fu,WANG Guangcai,YI Lixin,et al. Applying radium isotopes to estimate groundwater discharge into Poyang Lake,the largest freshwater lake in China[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2020,585:124782. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124782
[11] LI Yunliang,ZHANG Qi,LU Jianrong,et al. Assessing surface water-groundwater interactions in a complex river‐floodplain wetland‐isolated lake system[J]. River Research and Applications,2019,35(1):25 − 36. doi: 10.1002/rra.3389
[12] 吴雯倩,靳孟贵. 淮北市地下水流数值模拟及水文地质参数不确定性分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2014,41(3):21 − 28. [WU Wenqian,JIN Menggui. Numerical simulation of groundwater flow near Huaibei and uncertainty analysis of the hydrogeological parameters[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2014,41(3):21 − 28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WU Wenqian, JIN Menggui. Numerical simulation of groundwater flow near Huaibei and uncertainty analysis of the hydrogeological parameters [J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2014, 41(3): 21–28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 兰盈盈,曾马荪,靳孟贵,等. 基于GMS鄱阳湖拟建枢纽对地下水影响探讨[J]. 水文,2015,35(6):37 − 41. [LAN Yingying,ZENG Masun,JIN Menggui,et al. Discussion on effects of proposed water structure on poyang lake groundwater using GMS[J]. Journal of China Hydrology,2015,35(6):37 − 41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LAN Yingying, ZENG Masun, JIN Menggui, et al. Discussion on effects of proposed water structure on poyang lake groundwater using GMS[J]. Journal of China Hydrology, 2015, 35(6): 37-41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 宋炎炎,张奇,姜三元,等. 鄱阳湖湿地地下水埋深及其与典型植被群落分布的关系[J]. 应用生态学报,2021,32(1):123 − 133. [SONG Yanyan,ZHANG Qi,JIANG Sanyuan,et al. Groundwater depth and its relation with typical vegetation distribution in the Poyang Lake wetland,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2021,32(1):123 − 133. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202101.018
SONG Yanyan, ZHANG Qi, JIANG Sanyuan, et al. Groundwater depth and its relation with typical vegetation distribution in the Poyang Lake wetland, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(1): 123–133. (in Chinese with English abstract)]. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202101.018
[15] WANG Zhenchen,YANG Y,CHEN G,et al. Variation of lake-river-aquifer interactions induced by human activity and climatic condition in Poyang Lake Basin,china[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2021,595:126058. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126058
[16] ZHOU Pengpeng, WANG Guangcai, MAO Hairu,et al. Numerical modeling for the temporal variations of the water interchange between groundwater and surface water in a regional great lake (Poyang Lake,China)[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2022,610:127827. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127827
[17] 郭云彤,周妍,崔亚莉,等. 基于GSFLOW的青土湖生态输水量-湖水面积关系研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(5):32 − 41. [GUO Yuntong,ZHOU Yan,CUI Yali,et al. A study of the relationship between ecological water conveyance and water surface area of the Qingtu Lake based on GSFLOW[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(5):32 − 41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GUO Yuntong, ZHOU Yan, CUI Yali, et al. A study of the relationship between ecological water conveyance and water surface area of the Qingtu Lake based on GSFLOW[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(5): 32–41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] HUNT R J,HAITJEMA H M,KROHELSKI J T,et al. Simulating ground water-lake interactions:approaches and insights[J]. Ground Water,2003,41(2):227 − 237. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2003.tb02586.x
[19] MERRITT L M, KONIKOW L F. Documentation of a computer program to simulate lake-aquifer interaction using the modflow ground water flow model and the moc3d solute-transport model[R/OL]. http://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/wri004167.
[20] 王亚琴,杨军耀,刘庆,等. 基于Modflow和LAK3的三泉水库渗漏量研究[J]. 人民黄河,2019,41(2):59 − 63. [WANG Yaqin,YANG Junyao,LIU Qing,et al. Research on leakage of Sanquan Reservoir based on modflow and LAK3[J]. Yellow River,2019,41(2):59 − 63. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2019.02.013
WANG Yaqin, YANG Junyao, LIU Qing, et al. Research on leakage of Sanquan Reservoir based on modflow and LAK3 [J]. Yellow River, 2019, 41(2): 59–63. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2019.02.013
[21] YIHDEGO Y,RETA G,BECHT R. Human impact assessment through a transient numerical modeling on the UNESCO World Heritage Site,Lake Naivasha,Kenya[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2017,76(1):9. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-6301-2
[22] ZHANG Bo,ZHENG Xilai,ZHENG Tianyuan,et al. The influence of slope collapse on water exchange between a pit lake and a heterogeneous aquifer[J]. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering,2019,13(2):1 − 9.
[23] FENG Lian,HU C,CHEN X,et al. Assessment of inundation changes of Poyang Lake using modis observations between 2000 and 2010[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2012,121:80 − 92. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2012.01.014
[24] 中国水利水电科学研究院. 江西省鄱阳湖水利枢纽工程环境影响报告书[R/OL]. http://slt.jiangxi.gov.cn/art/2022/5/9/art_28230_3948434.html
China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower. Environmental impact report of Poyang Lake water conservancy hub project in Jiangxi Province[R/OL]. (in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载: