Emergency rapid assessment of landslides induced by the Luding MS6.8 earthquake in Sichuan of China
-
摘要:
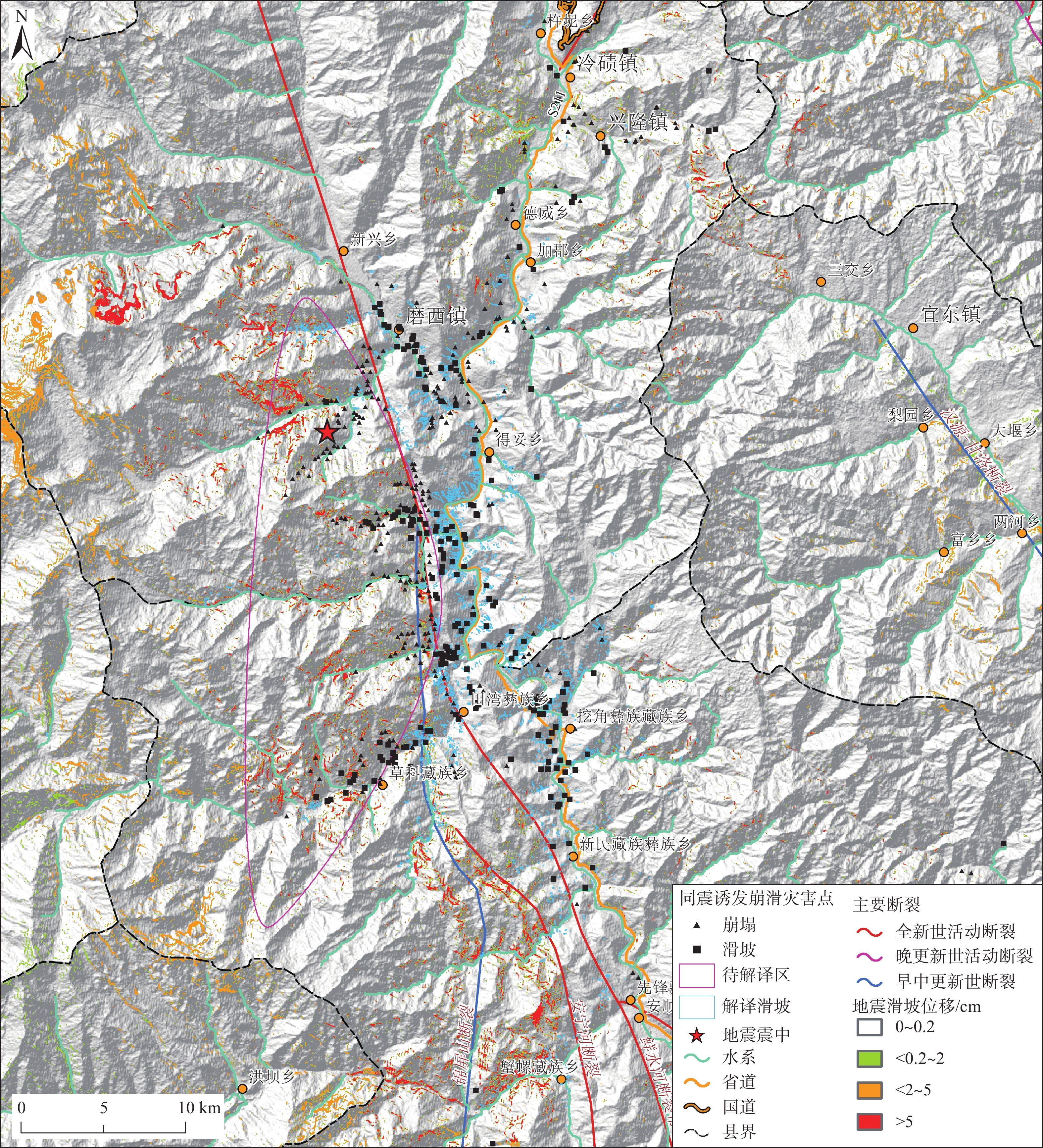
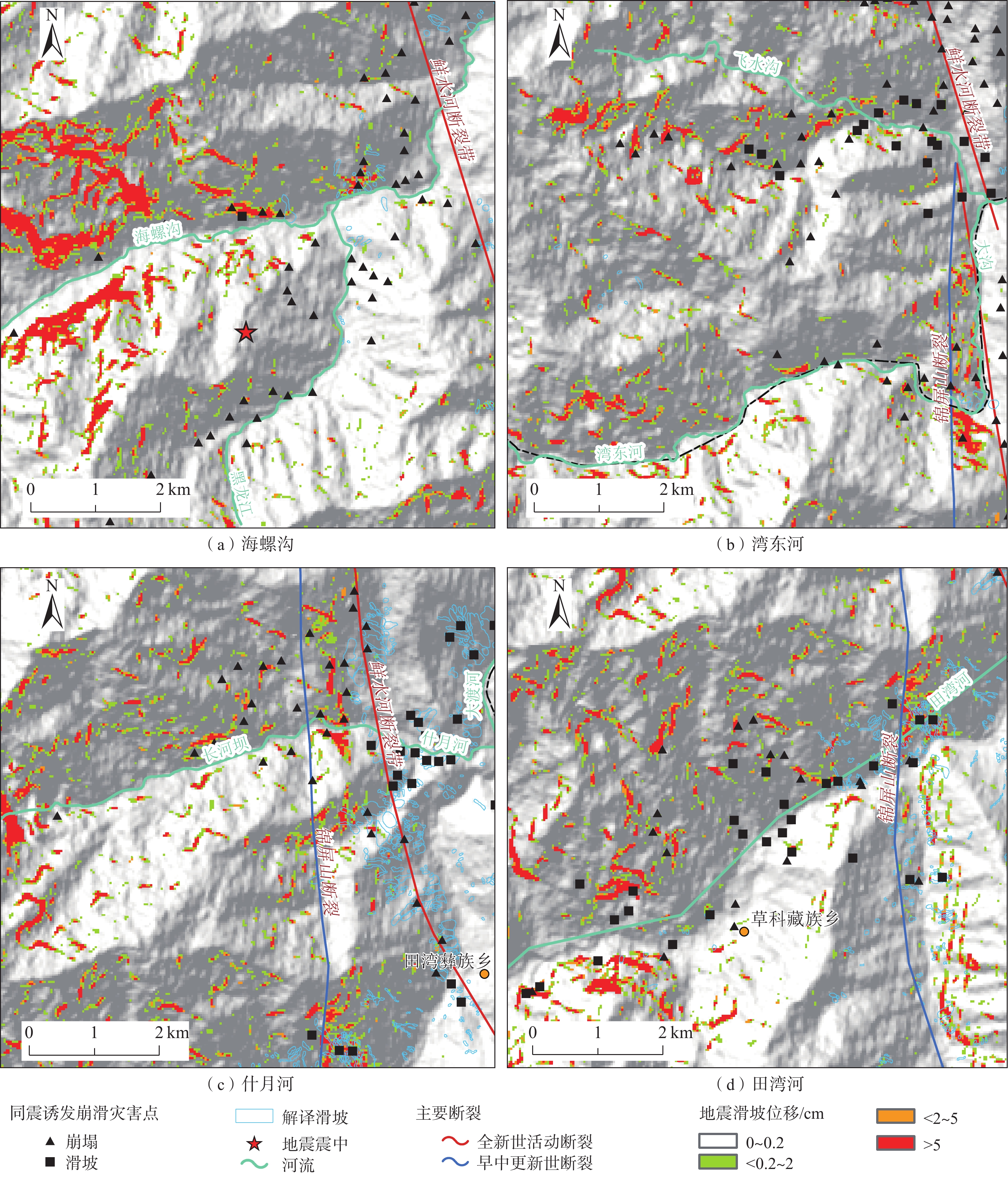
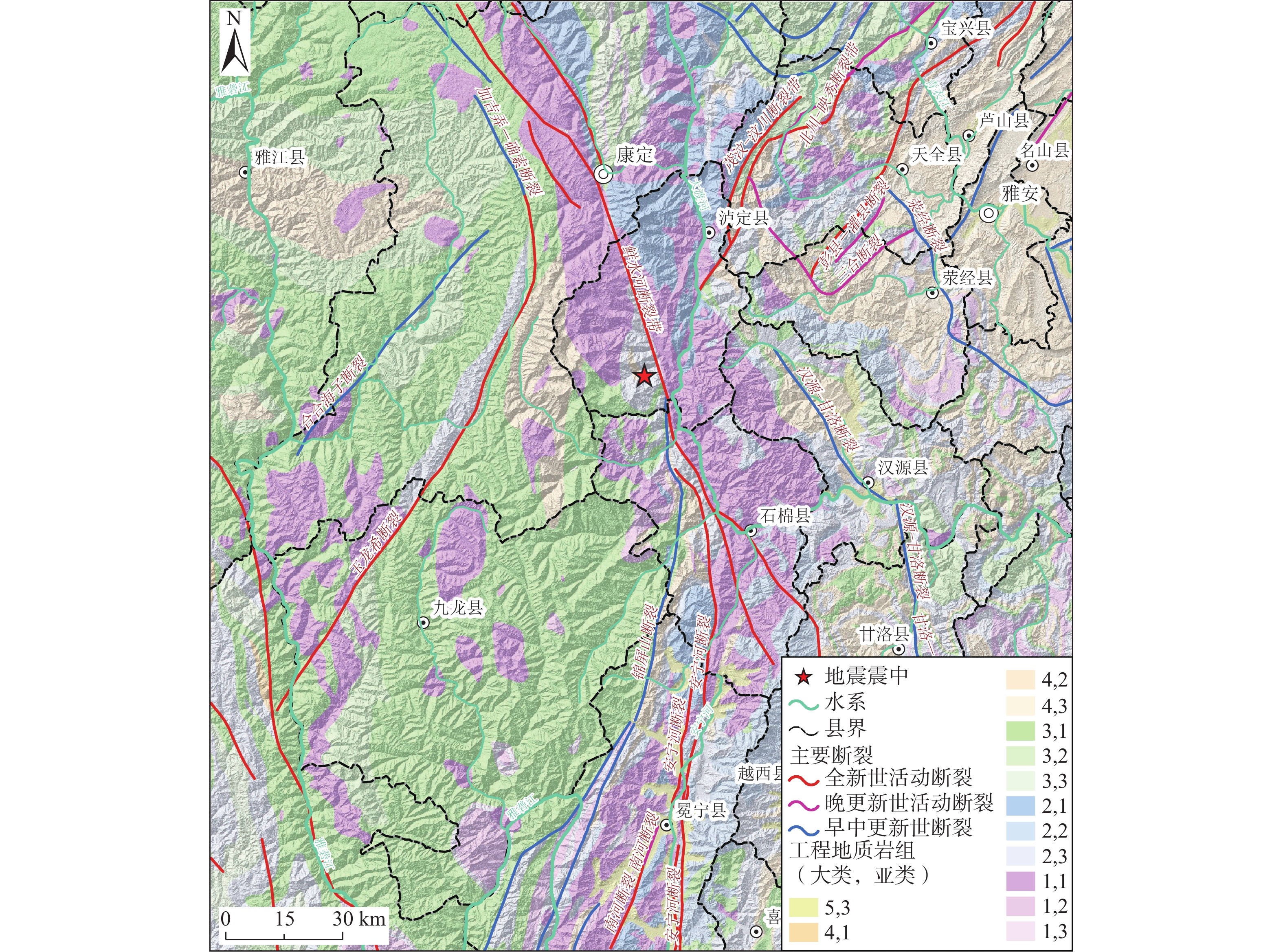
强震诱发崩滑灾害可严重加剧地震灾害损失,快速评估地震诱发崩滑分布对于应急救灾工作部署具有重要意义。利用2022年9月5日泸定MS6.8级地震震前30 m分辨率地形数据结合1∶50万比例尺地质图,采用Newmark累积位移方法开展了泸定地震诱发崩滑灾害快速评估。结果显示:(1)地震诱发崩滑灾害较为严重,崩滑高危险区面积约为45 km2,主要分布在鲜水河断裂以西大渡河西岸近东西向支沟两岸,其中以燕子沟、磨子沟、海螺沟、飞水沟、湾东河、什月河、田湾河等崩滑危险性较高,对沟内居民及游客生命安全威胁较大,沟内公路受崩滑阻断风险较高,局部河道有被崩滑堵塞风险;(2)泸定县冷碛镇、兴隆镇、磨西镇、得妥乡等4个乡镇及石棉县田湾乡、草科乡、新民乡、先锋乡、蟹螺乡、挖角乡等6个乡镇崩滑危险性较高;(3)震中附近地区大渡河沿线省道S434和S211受崩滑阻断可能性较大;(4)贡嘎雪山一带预测地震崩滑危险性为中等,但需关注冰崩型、岩崩型高位远程灾害(链)风险。通过与震后应急排查、遥感解译等获取的地震Ⅷ度、Ⅸ度区内发生的崩滑分布对比,表明在大渡河西岸各支沟滑坡位移分析结果能够较好地反映同震滑坡的宏观分布特征,但在磨西台地边缘、大渡河干流两岸吻合程度欠佳,后续将通过提升岩性和地形等数据质量进行改进。有关成果可为震后重建规划、震后长期灾害效应分析等提供参考,同时深化了地震崩滑快速评估技术方法,地震崩滑快速评估的可靠性。
-
关键词:
- 泸定地震 /
- 地震崩滑危险性 /
- 应急快速评估 /
- Newmark累积位移模型
Abstract:Seismic landslides can seriously aggravate the losses of earthquake disasters. Therefore, it is of great significance to assessment the distribution of earthquake induced landslides for emergency relief. In this paper, based on the 30 m resolution DEM and regional geologic data with a scale of 1∶500 000, emergency rapid assessment of earthquake induced landslides is carried out using the Newmark cumulative displacement model for the 5 September 2022 Luding MS6.8 earthquake, China. The results show that the earthquake induced landslides are relatively serious in this earthquake. The high hazard zones of the coseismic landslides are about 45 km2, which is mainly distributed on the two banks of the nearly east-west tributaries on the west bank of the Dadu River and the west of the Xianshuihe fault, especially along the Yanzigou, Mozigou, Hailuogou, Feishuigou gullies and the Wandong, Shiyue, Tianwan rivers, posing a great threat to the lives of residents and tourists. The rivers and roads in these tributaries are at high risk of being blocked by landslides. The Lengqi, Xinglong, Moxi and Detuo towns in Luding County and Tianwan, Caoke, Xinmin, Xianfeng, Xieluo and Wajiao towns in Shimian County are at high risk of landslides. The S434 Provincial Road and S211 Provincial Road along the Dadu River near the epicenter are more likely to be blocked by landslides. The predicted earthquake landslide hazard in the Gongga Snow Mountain area is medium, but it is necessary to pay attention to the risks of long range and high position landslide disaster (chain), such as ice avalanche and rock avalanche. Comparison between the distribution of induced landslides in zones with intensity VIII and IX obtained from post-earthquake emergency investigation and remote sensing interpretation shows that the obtained displacements can well reflect the macro distribution of coseismic landslides along the tributaries on the west bank of the Dadu River, but cannot be exerted effectively around the edge of the Moxi platform and the banks of the main stream of Dadu River, which can be enhanced through the improvement of large scale of geologic maps and high quality topography data. The results can provide reference for valuable timely reference information on post-earthquake reconstruction planning and long-time activity of post-earthquake geohazard and risk recognition of landslide disaster chains.
-

-
表 1 泸定地震峰值加速度预测值与断层距50 km以内强震台站观测值对比
Table 1. Comparison between the predicted and the observed PGA values of stations with rupture distance less than 50 km
台站编码 观测值/g 预测值/g 相对误差(绝对值)/% CNXJ 0.76 0.69 9.35 VL002 0.42 0.40 4.78 V2203 0.19 0.23 16.33 T2471 0.65 0.48 26.51 T2307 0.16 0.17 2.77 T2371 0.18 0.18 1.12 HYYD 0.05 0.07 38.66 VL001 0.16 0.16 2.30 TS003 0.19 0.22 13.24 T2405 0.19 0.22 15.33 T2311 0.11 0.12 11.78 T2408 0.11 0.16 45.96 T2406 0.39 0.36 8.35 TT001 0.11 0.13 16.57 V0172 0.04 0.05 26.06 TY001 0.18 0.17 5.56 SMML 0.17 0.20 18.65 平均值 15.49 -
[1] 丁彦慧,王余庆,孙进忠,等. 地震崩滑预测方法及其工程应用研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2000,8(4):475 − 480. [DING Yanhui,WANG Yuqing,SUN Jinzhong,et al. Research on the method for prediction of earthquake-induced landslides and its application to engineering projects[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2000,8(4):475 − 480. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2000.04.016
[2] 陈晓利,单新建,张凌,等. 地震诱发滑坡的快速评估方法研究—以2017年MS7.0级九寨沟地震为例[J]. 地学前缘,2019,26(2):312 − 320. [CHEN Xiaoli,SHAN Xinjian,ZHANG Ling,et al. Quick assessment of earthquake-triggered landslide hazards:A case study of the 2017 MS7.0 Jiuzhaigou earthquake[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2019,26(2):312 − 320. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] WEN Baoping,WANG Sijing,WANG Enzhi,et al. Characteristics of rapid giant landslides in China[J]. Landslides,2004,1(4):247 − 261. doi: 10.1007/s10346-004-0022-4
[4] 许冲,田颖颖,马思远,等. 1920年海原8.5级地震高烈度区滑坡编录与分布规律[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(5):1188 − 1195. [XU Chong,TIAN Yingying,MA Siyuan,et al. Inventory and spatial distribution of landslides in IX-XI high intensity areas of 1920 Haiyuan (China) MS8.5 earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(5):1188 − 1195. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 原廷宏, 冯希杰. 一五五六年华县特大地震[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 2010
YUAN Tinghong, FENG Xijie. In 1566, the great earthquake in Nianhua County[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 徐岳仁,张伟恒,李文巧,等. 1556年华县地震同震黄土滑坡密集区的发现及意义[J]. 地震地质,2018,40(4):721 − 737. [XU Yueren,ZHANG Weiheng,LI Wenqiao,et al. Distribution characteristics of the ad 1556 Huaxian earthquake triggered disasters and its implications[J]. Seismology and Geology,2018,40(4):721 − 737. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 许冲, 徐锡伟, 吴熙彦, 等. 2008年汶川地震滑坡详细编目及其空间分布规律分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2013, 21(1): 25 − 44
XU Chong, XU Xiwei, WU Xiyan, et al. Detailed catalog of landslides triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake and statistical analyses of their spatial distribution[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2013, 21(1): 25 − 44. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 殷跃平. 汶川八级地震滑坡高速远程特征分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2009,17(2):153 − 166. [YIN Yueping. Rapid and long run-out features of landslides triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2009,17(2):153 − 166. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.02.002
[9] 庄建琦,崔鹏,葛永刚,等. “5·12”汶川地震崩塌滑坡危险性评价—以都汶公路沿线为例[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2010,29(增刊 2):3735 − 3742. [ZHUANG Jianqi,CUI Peng,GE Yonggang,et al. Risk assessment of collapses and landslides caused by 5·12 Wenchuan earthquake:A case study of Dujiangyan—Wenchuan highway[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2010,29(Sup 2):3735 − 3742. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 许冲,徐锡伟,于贵华. 玉树地震滑坡分布调查及其特征与形成机制[J]. 地震地质,2012,34(1):47 − 62. [XU Chong,XU Xiwei,YU Guihua. Study on the characteristics,mechanism,and spatial distribution of Yushu earthquake triggered landslides[J]. Seismology and Geology,2012,34(1):47 − 62. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2012.01.006
[11] 许冲,徐锡伟,郑文俊,等. 2013年四川省芦山“4·20” 7.0级强烈地震触发滑坡[J]. 地震地质,2013,35(3):641 − 660. [XU Chong,XU Xiwei,ZHENG Wenjun,et al. Landslides triggered by the April 20,2013 Lushan,Sichuan Province MS7.0 strong earthquake of China[J]. Seismology and Geology,2013,35(3):641 − 660. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2013.03.018
[12] 殷志强,赵无忌,褚宏亮,等. “4·20”芦山地震诱发地质灾害基本特征及与“5·12”汶川地震对比分析[J]. 地质学报,2014,88(6):1145 − 1156. [YIN Zhiqiang,ZHAO Wuji,CHU Hongliang,et al. Basic characteristics of geohazards induced by Lushan earthquake and compare to them of Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2014,88(6):1145 − 1156. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 许冲,徐锡伟,沈玲玲,等. 2014年鲁甸MS6.5地震触发滑坡编录及其对一些地震参数的指示[J]. 地震地质,2014,36(4):1186 − 1203. [XU Chong,XU Xiwei,SHEN Lingling,et al. Inventory of landslides triggered by the 2014 MS6.5 Ludian earthquake and its implications on several earthquake parameters[J]. Seismology and Geology,2014,36(4):1186 − 1203. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.04.020
[14] 陈晓利,常祖峰,王昆. 云南鲁甸MS6.5地震红石岩滑坡稳定性的数值模拟[J]. 地震地质,2015,37(1):279 − 290. [CHEN Xiaoli,CHANG Zufeng,WANG Kun. Numerical simulation study of Hongshiyan landslide triggered by the MS6.5 Ludian earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology,2015,37(1):279 − 290. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.01.022
[15] 刘甲美,王涛,石菊松,等. 四川九寨沟MS7.0级地震滑坡应急快速评估[J]. 地质力学学报,2017,23(5):639 − 645. [LIU Jiamei,WANG Tao,SHI Jusong,et al. Emergency rapid assessment of landslides induced by the Jiuzhaigou MS7.0 earthquake,Sichuan,China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2017,23(5):639 − 645. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2017.05.001
[16] 李强,张景发. 高分三号卫星全极化SAR影像九寨沟地震滑坡普查[J]. 遥感学报,2019,23(5):883 − 891. [LI Qiang,ZHANG Jingfa. Investigation on earthquake-induced landslide in Jiuzhaigou using fully polarimetric GF-3 SAR images[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing,2019,23(5):883 − 891. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 范宣梅,方成勇,戴岚欣,等. 地震诱发滑坡空间分布概率近实时预测研究—以2022年6月1日四川芦山地震为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(3):729 − 739. [FAN Xuanmei,FANG Chengyong,DAI Lanxin,et al. Near real time prediction of spatial distribution probability of earthquake-induced landslides:Take the Lushan earthquake on June 1,2022 as an example[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(3):729 − 739. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] NOWICKI JESSEE M A,HAMBURGER M W,ALLSTADT K,et al. A global empirical model for near-real-time assessment of seismically induced landslides[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Earth Surface,2018,123(8):1835 − 1859. doi: 10.1029/2017JF004494
[19] 刘甲美,王涛,石菊松,等. 基于不同位移预测模型的地震滑坡危险性评估研究—以天水地区为例[J]. 地质力学学报,2018,24(1):87 − 95. [LIU Jiamei,WANG Tao,SHI Jusong,et al. The influence of different newmark displacement models on seismic landslide hazard assessment:A case study of Tianshui area,China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2018,24(1):87 − 95. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2018.24.01.010
[20] 范宣梅,王欣,戴岚欣,等. 2022年MS6.8级泸定地震诱发地质灾害特征与空间分布规律研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(5):1504 − 1516. [FAN Xuanmei,WANG Xin,DAI Lanxin,et al. Characteristics and spatial distribution pattern of MS6.8 Luding earthquake occurred on September 5,2022[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(5):1504 − 1516. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 铁永波,张宪政,卢佳燕,等. 四川省泸定县MS6.8级地震地质灾害发育规律与减灾对策[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(6):1 − 12. [TIE Yongbo,ZHANG Xianzheng,LU Jiayan,et al. Characteristics of geological hazards and it’s mitigations of the MS6.8 earthquake in Luding County,Sichuan Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(6):1 − 12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] YANG Zhigao,DAI Danqing,ZHANG Yong,et al. Rupture process and aftershock mechanisms of the 2022 Luding MS6.8 earthquake in Sichuan,China[J]. Earthquake Science,2022,35:1 − 2. doi: 10.1016/j.eqs.2022.01.020
[23] 白明坤,CHEVALIER M L,李海兵,等. 鲜水河断裂带乾宁段晚第四纪走滑速率及区域强震危险性研究[J]. 地质学报,2022,96(7):2312 − 2332. [BAI Mingkun,CHEVALIER M L,LI Haibing,et al. Late Quaternary slip rate and earthquake hazard along the Qianning segment,Xianshuihe fault[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2022,96(7):2312 − 2332. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.07.005
[24] 陈桂华,闵伟,宋方敏,等. 从1786年磨西地震看地震地表破裂带在不同地貌区的保存[J]. 地震地质,2011,33(4):804 − 817. [CHEN Guihua,MIN Wei,SONG Fangmin,et al. Preservation of co-seismic surface rupture in different geomorphological settings from the study of the 1786 Moxi earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology,2011,33(4):804 − 817. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2011.04.006
[25] 周洪福,韦玉婷,王运生,等. 1786年磨西地震触发的摩岗岭滑坡演化过程与成因机理[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2017,44(6):649 − 658. [ZHOU Hongfu,WEI Yuting,WANG Yunsheng,et al. Discussion on the formation evolution and genetic mechanism of Mogangling landslide triggered by Moxi earthquake,Sichuan,China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition),2017,44(6):649 − 658. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2017.06.02
[26] NEWMARK N M. Effects of earthquakes on dams and embankments[J]. Géotechnique,1965,15(2):139 − 160.
[27] JIBSON R W,HARP E L,MICHAEL J A. A method for producing digital probabilistic seismic landslide hazard maps[J]. Engineering Geology,2000,58(3/4):271 − 289.
[28] 王涛,刘甲美,栗泽桐,等. 中国地震滑坡危险性评估及其对国土空间规划的影响研究[J]. 中国地质,2021,48(1):21 − 39. [WANG Tao,LIU Jiamei,LI Zetong,et al. Seismic landslide hazard assessment of China and its impact on national territory spatial planning[J]. Geology in China,2021,48(1):21 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12029/gc20210102
[29] 肖亮. 水平向基岩强地面运动参数衰减关系研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地球物理研究所, 2011
XIAO Liang. Study on the attenuation relationships of horizontal groundmotion parameters near the sourse of rock site[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 陈鲲,俞言祥,高孟潭. 基于地震记录的震动图校正方法研究[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报,2013,21(4):679 − 691. [CHEN Kun,YU Yanxiang,GAO Mengtan. Research on correction method for ShakeMap based on seismic data[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering,2013,21(4):679 − 691. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0930.2013.04.010
[31] 陈鲲,俞言祥,高孟潭. 考虑场地效应的ShakeMap系统研究[J]. 中国地震,2010,26(1):92 − 102. [CHEN Kun,YU Yanxiang,GAO Mengtan. Research on ShakeMap system in terms of the site effect[J]. Earthquake Research in China,2010,26(1):92 − 102. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2010.01.009
[32] AMBRASEYS N N,MENU J M. Earthquake-induced ground displacements[J]. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics,1988,16(7):985 − 1006.
[33] WIECZOREK G F, WILSON R C, HARP E L. Map showing slope stability during earthquake in San Mateo County, California[R]. Miscellaneous Investigation Series, MAP I-1257-E. Virginia: United States Geological Survey, 1985.
[34] 王秀英,聂高众,王松. 汶川地震诱发滑坡的地震动加速度评判标准[J]. 地震学报,2011,33(1):82 − 90. [WANG Xiuying,NIE Gaozhong,WANG Song. Ground motion acceleration criterion for judging landslide induced by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,2011,33(1):82 − 90. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-3782.2011.01.007
[35] HUANG Yuandong,XIE Chenchen,LI Tao,et al. An open-accessed inventory of landslides triggered by the MS6.8 Luding earthquake,China on September 5,2022[J]. Earthquake Research Advances,2022:100181.
[36] 王欣,方成勇,唐小川,等. 泸定MS6.8级地震诱发滑坡应急评价研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2023,48(1):25 − 35. [WANG Xin,FANG Chengyong,TANG Xiaochuan,et al. Research on emergency evaluation of landslides induced by Luding MS6.8 earthquake[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2023,48(1):25 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: