Discrete element analysis of torpedo anchor penetration into calcareous sands considering particle breakage
-
摘要:
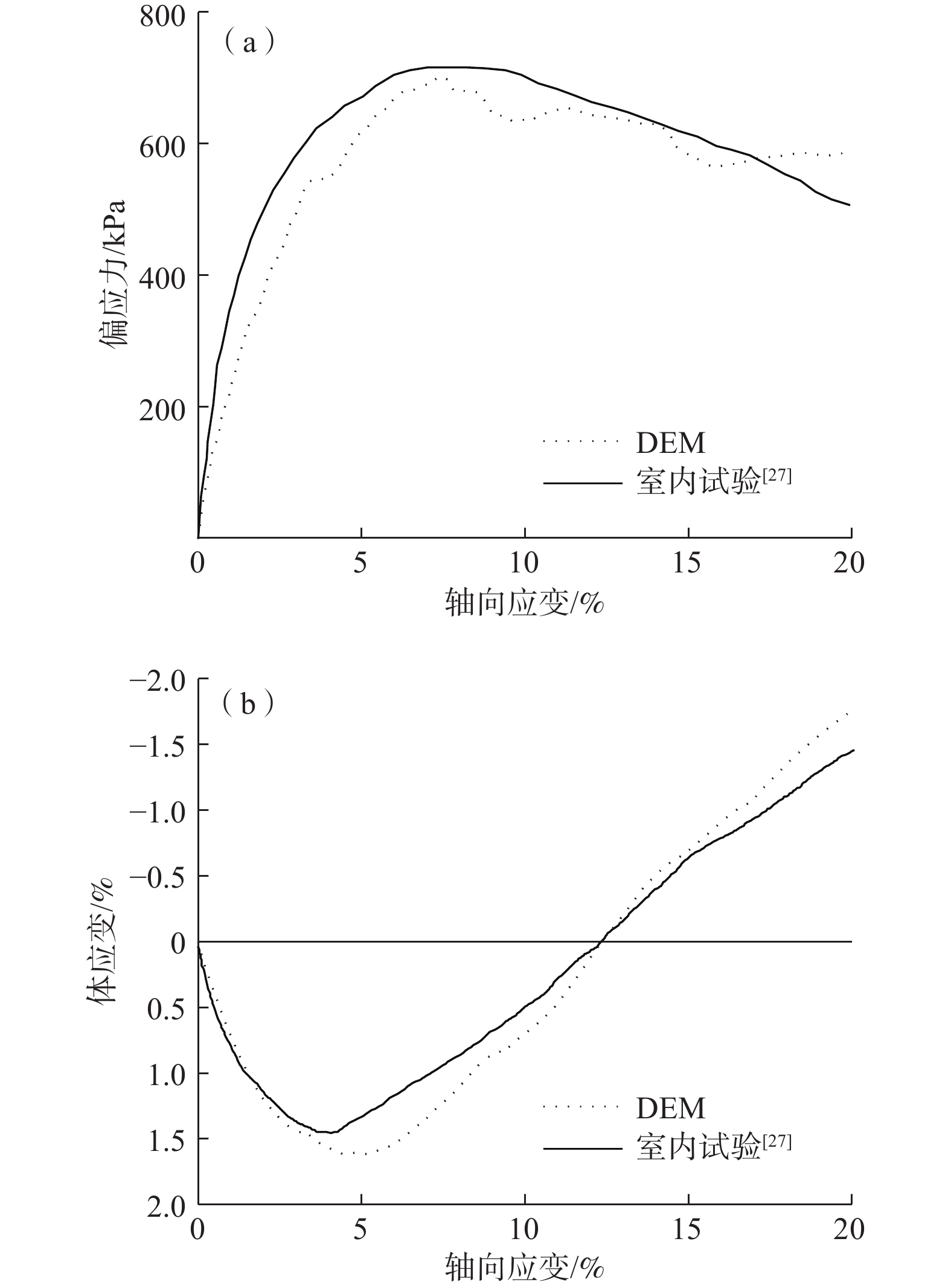
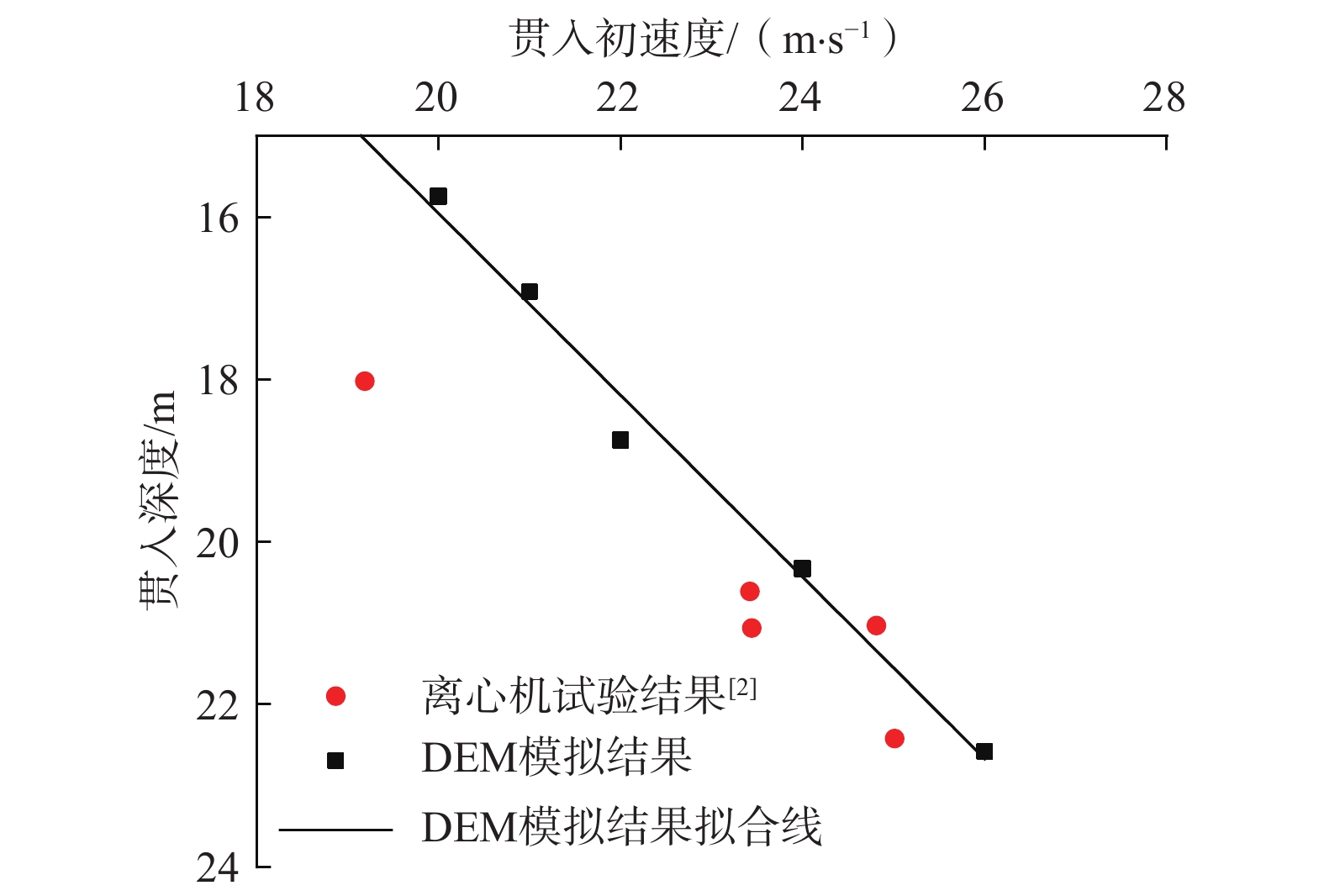
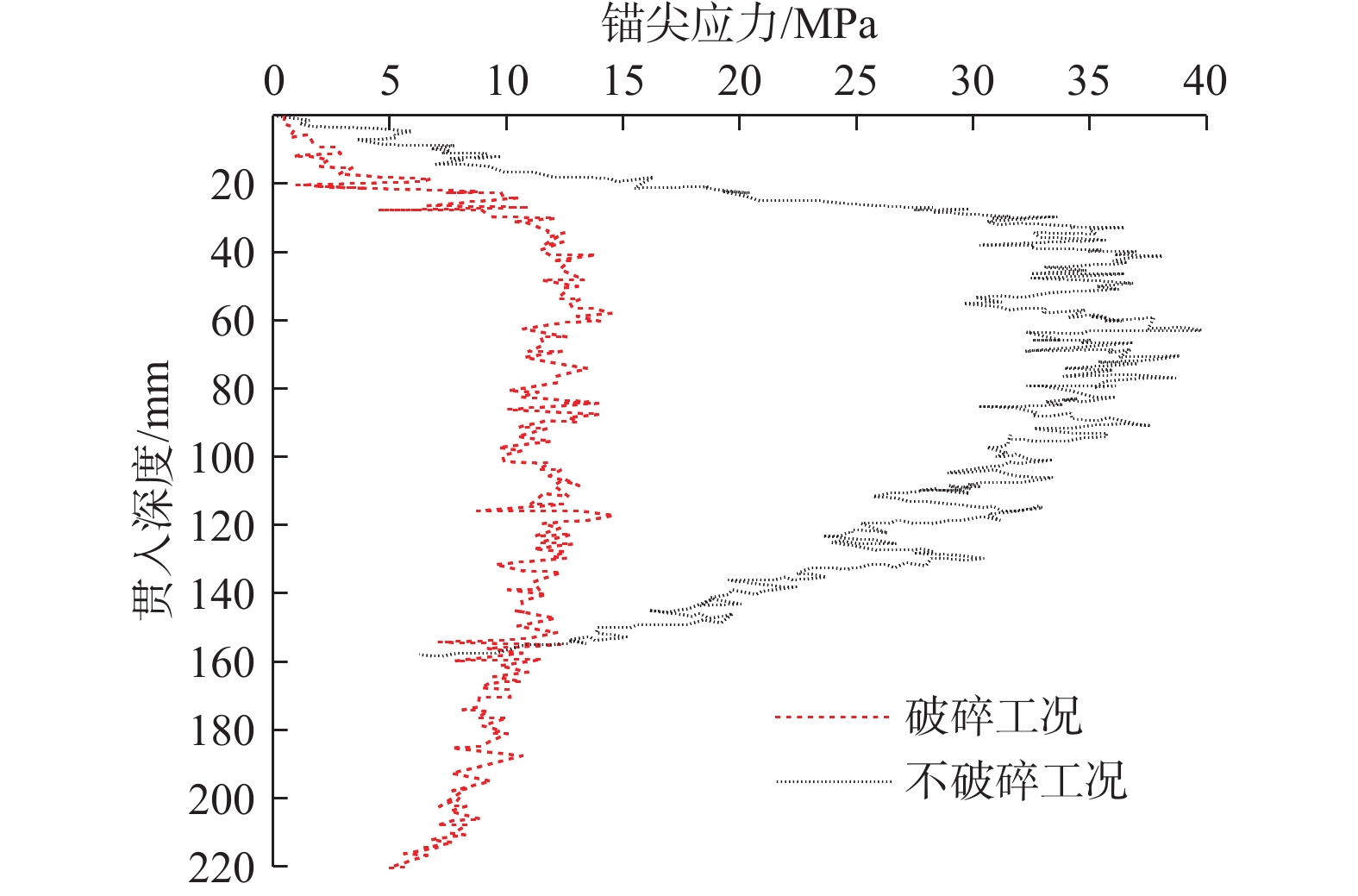
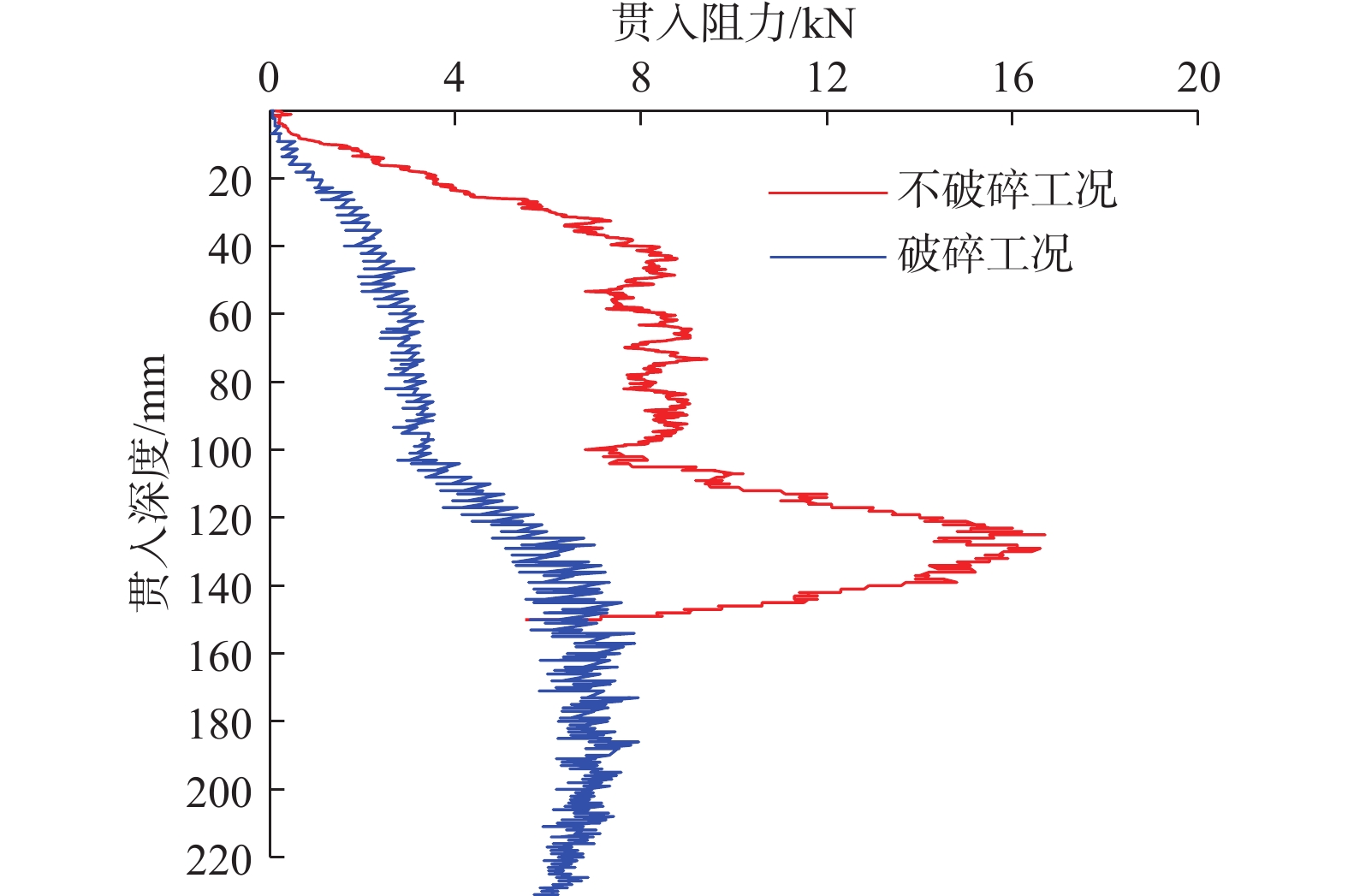
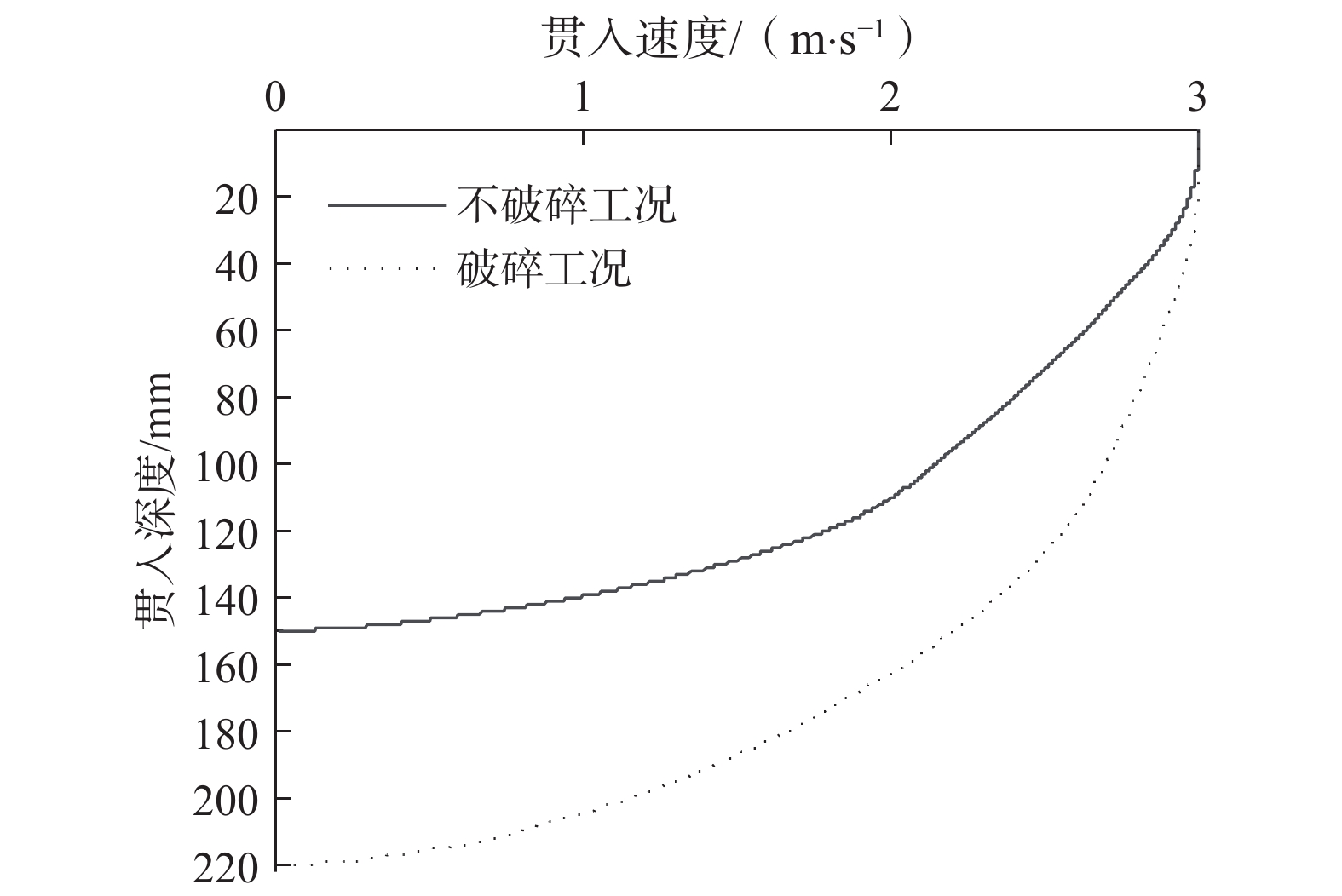
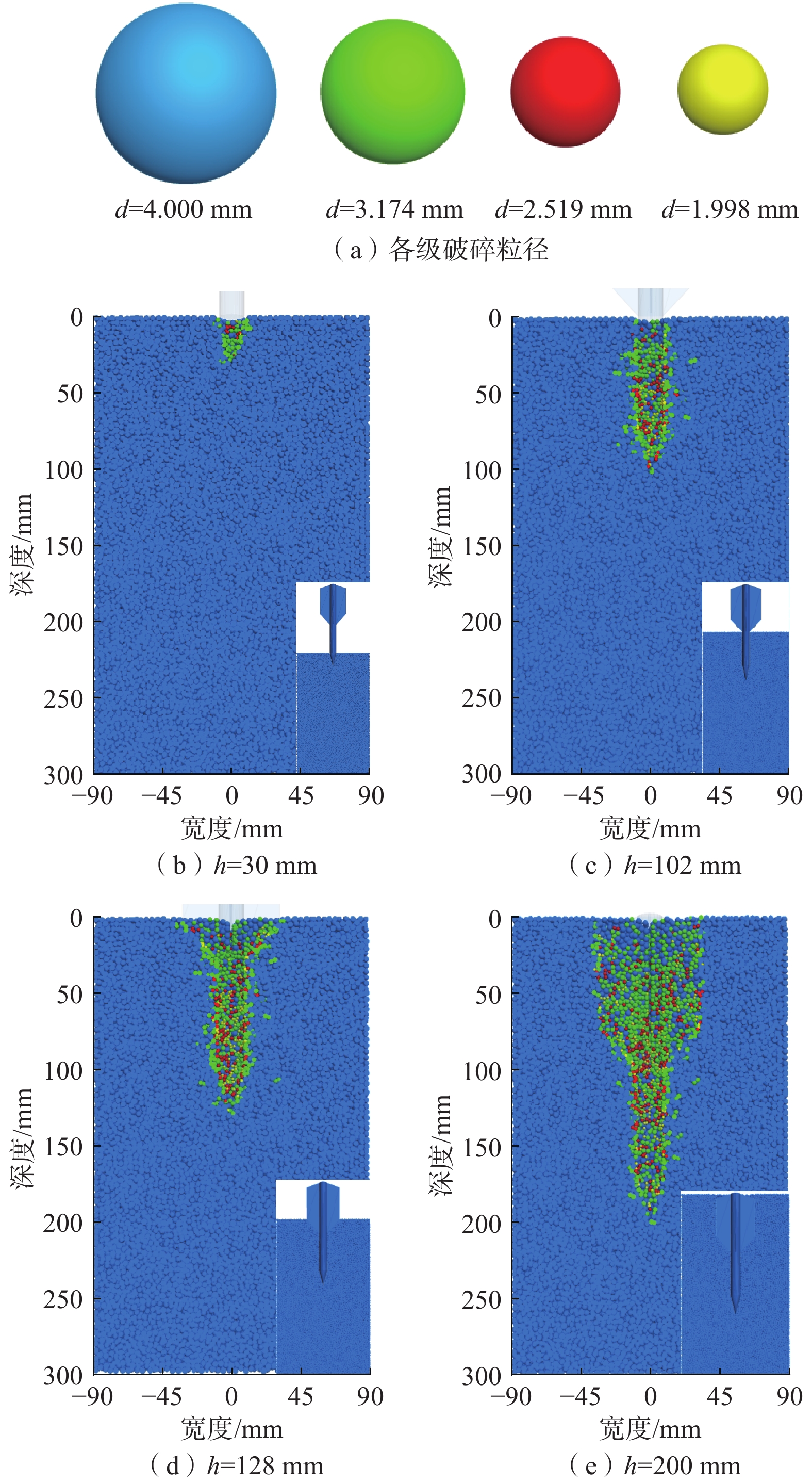
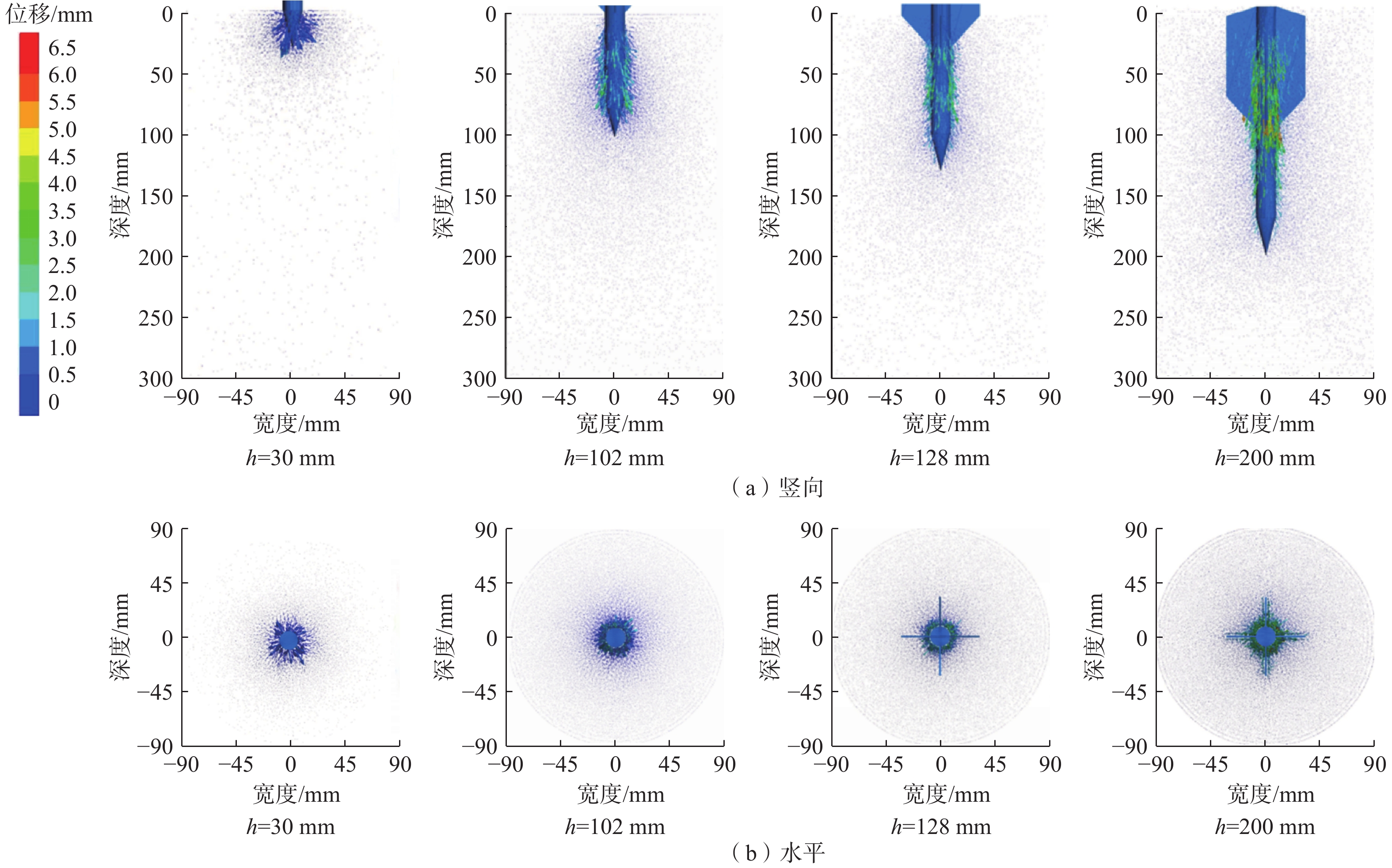
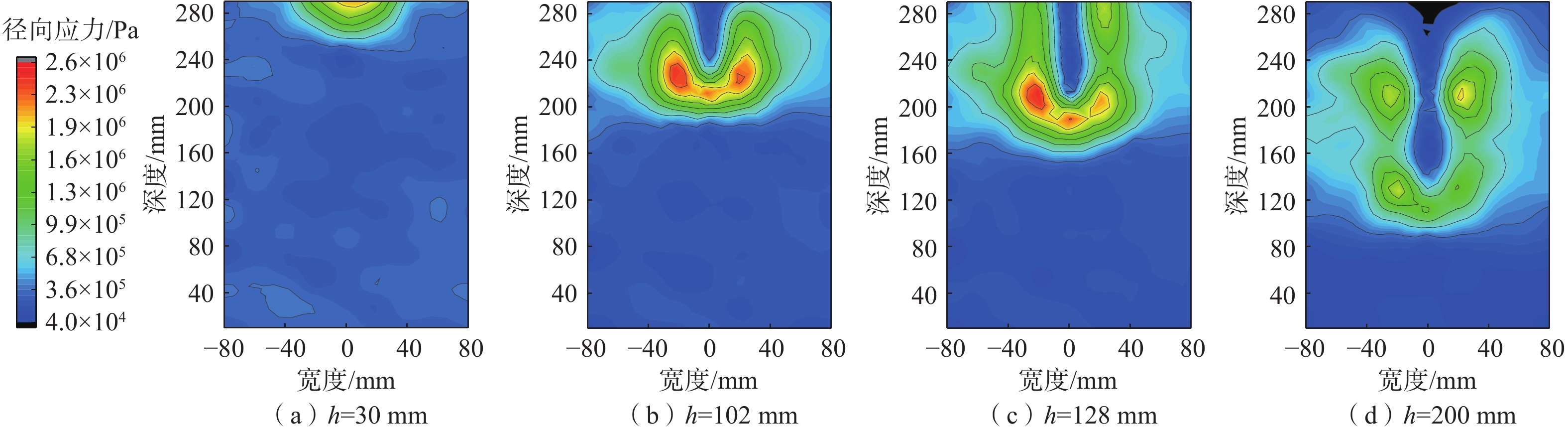
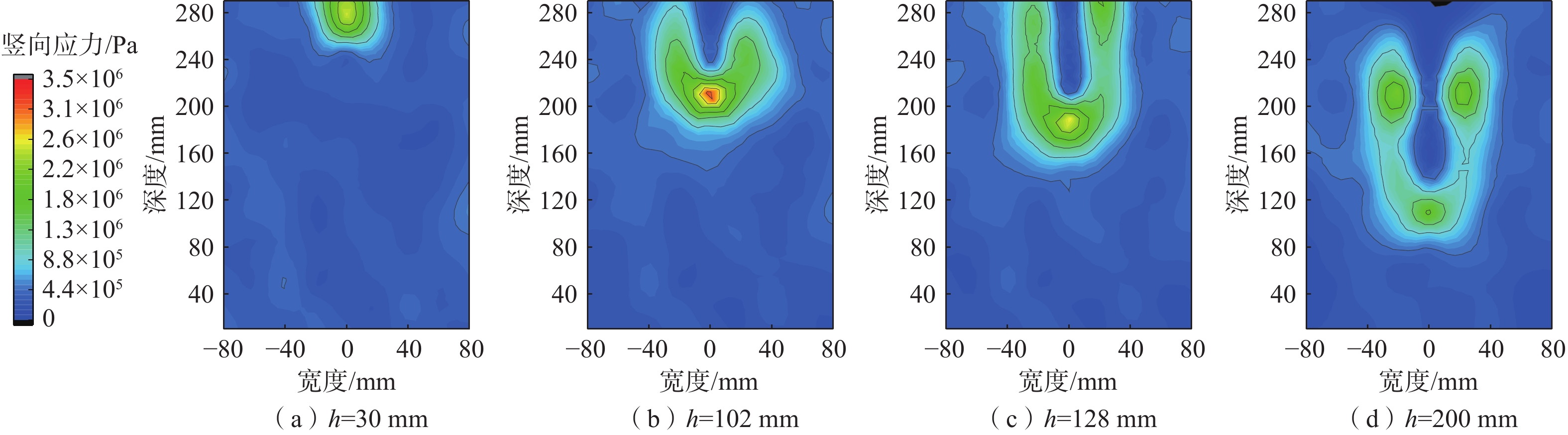
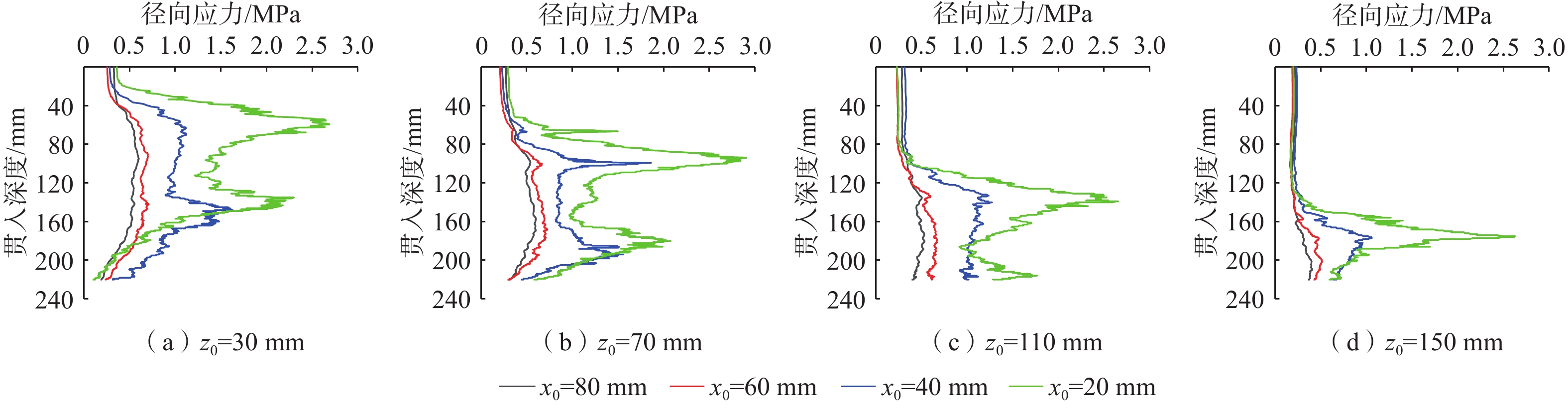
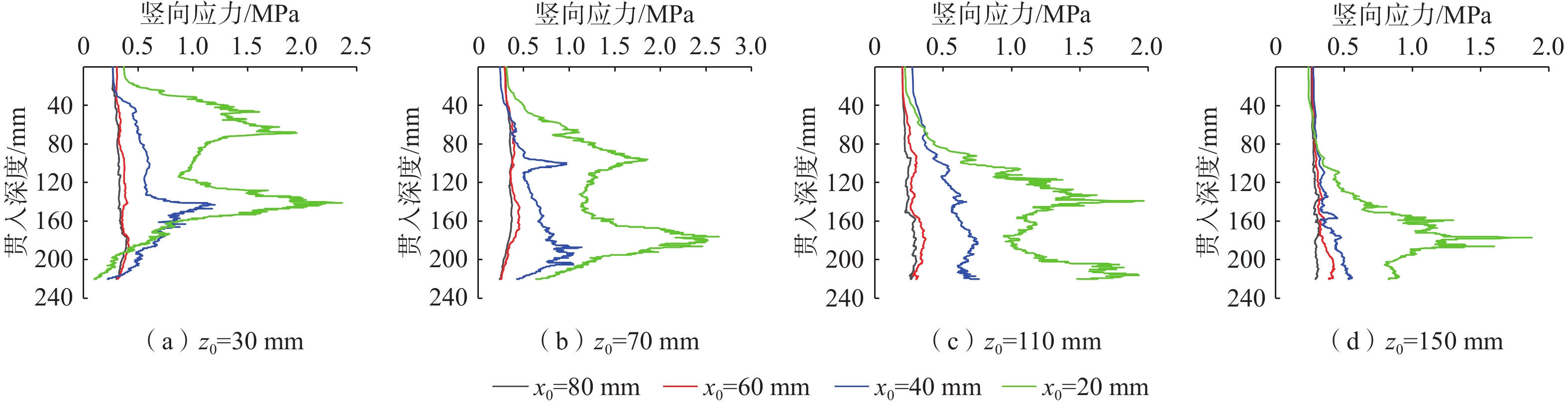
鱼雷锚作为一种新型深海锚固装置,在海洋油气开发等工程中应用广泛,但目前关于钙质砂海床中鱼雷锚贯入特性的研究较为匮乏。基于离散元方法,对钙质砂地基中的鱼雷锚贯入过程进行了数值分析,通过与已有室内试验结果的对比验证了数值模型的可靠性,数值模拟重点分析了鱼雷锚贯入过程中锚周土体颗粒破碎的演化规律及其对锚体贯入特性的宏细观影响。结果表明:在鱼雷锚贯入过程中,锚尖及锚端周围土体破碎严重,锚侧颗粒破碎相对较弱,颗粒破碎数量随着贯入深度的增加而增加;颗粒速度场分布基于锚体中心轴基本对称,随着贯入深度的增加,颗粒速度场分布范围扩大,颗粒运动速度峰值在贯入过程中先增加后下降;随着贯入深度增加,应力峰值先增加后逐渐减少,在翼板开始接触土体后,应力峰值达到最大值。研究结果可为岛礁工程动力锚贯入设计提供参考。
Abstract:As a new type of deep-sea anchorage device, the torpedo anchor is widely used in deep-sea oil and gas exploitation projects, but few attentions have been paid to the torpedo anchor penetrating into coral deposits. Based on the discrete element method, the penetration process of torpedo anchor into calcareous sands is numerically analyzed. The reliability of the numerical model is verified by comparing with the existing indoor test results. The numerical simulation focuses on the evolution of particle breakage of soils around the anchor during the penetration process, and its macro and micro effects on the anchor penetration characteristics are also discussed. The results show that in the process of torpedo anchor penetration, the soil around the anchor tip is seriously broken, while the particle breakage at the anchor side is relatively weak. The particle breakage quantity increases with the increase of penetration depth, and the distribution of particle velocity field is basically symmetrical along the central axis of the anchor body. With the increase of penetration depth, the distribution range of particle velocity field expands, and the peak particle velocity first increases and then decreases during the penetration process. The peak value in the stress concentration area first increases and then decreases, when the penetration depth increases. After the flange starts to contact the soil, the stress within the soil reaches the maximum. The research results can provide references for the design of dynamic anchor penetration in island and reef engineering.
-
Key words:
- calcareous sand /
- particle breakage /
- torpedo anchor /
- penetration characteristics /
- DEM analysis
-

-
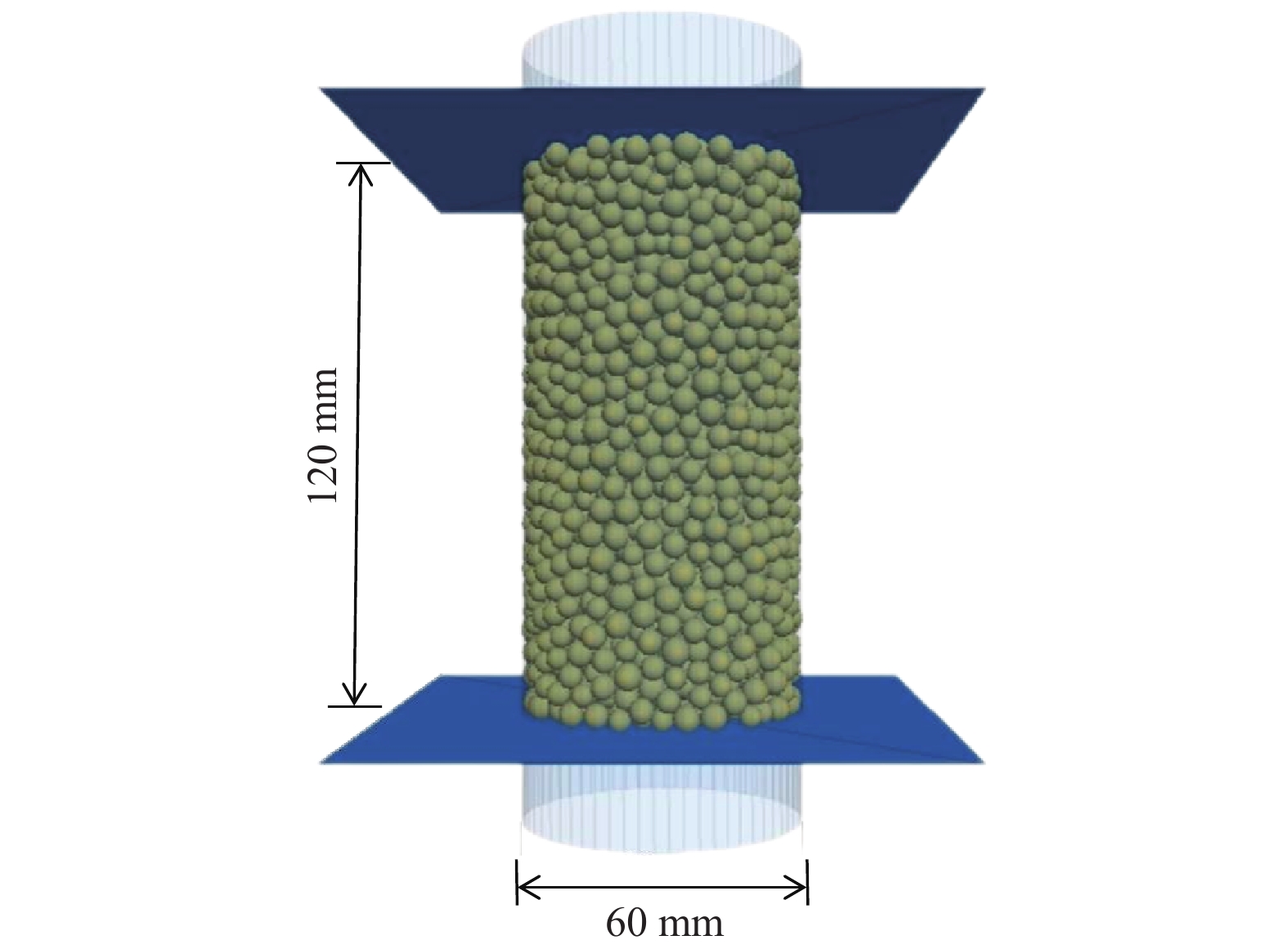
表 1 模型细观参数
Table 1. Micromechanical parameters of the model
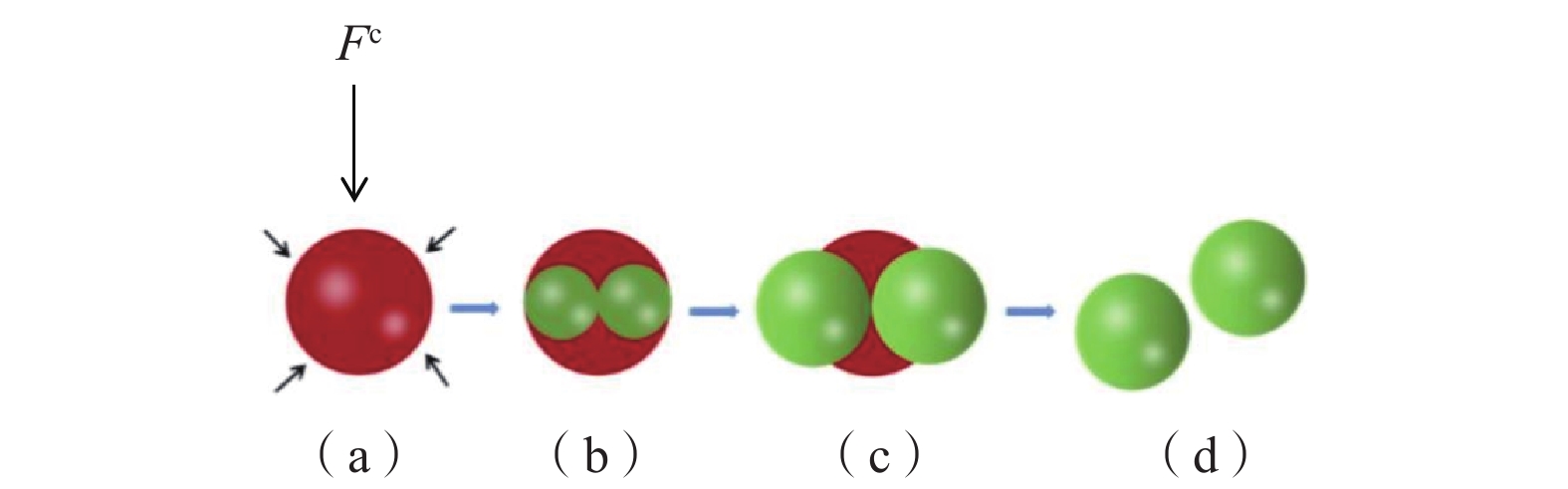
细观参数 数值 颗粒间接触刚度/(N·m−1) 2×106 颗粒与墙体间接触刚度/(N·m−1) 4×106 颗粒与锚之间的摩擦系数 0.5 颗粒之间的摩擦系数 0.5 颗粒特征粒径/mm 4 颗粒特征抗拉强度/MPa 5.67 韦伯模量 2.56 表 2 鱼雷锚模型参数
Table 2. Dimensions of torpedo anchor
相关参数 原始模型 缩尺模型 l/m 15 0.200 0 l1/m 0.600 0 0.008 0 l2/m 4.800 0 0.064 0 l3/m 2.000 0 0.027 0 l4/m 2.280 0 0.030 4 w1/m 1.800 0 0.024 0 w2/m 0.082 5 0.001 1 dt/m 1.200 0 0.016 0 落距/m 34.5 0.460 0 贯入初速度/(m·s−1) 26 3.000 0 锚重/kN 1.22×103 2.880 0 表 3 不同贯入深度时颗粒数量统计
Table 3. Statistical table of particle quantity at different penetration depth
颗粒破碎等级 颗粒数量 h=0 mm h=30 mm h=102 mm h=128 mm h=200 mm 初始颗粒 145 392 145 333 144 994 144 768 144 099 一级破碎 0 104 670 1 048 2 116 二级破碎 0 24 176 282 666 三级破碎 0 8 152 236 548 总计 145 392 145 469 145 992 146 334 147 429 -
[1] MEDEIROS C J. Low cost anchor system for flexible risers in deep waters[M]. Houston:Offshore Technology Conference,2002:OTC14151.
[2] RICHARDSON M D. Dynamically installed anchors for floating offshore structures[D]. Perth:University of Western Australia,2008.
[3] YU Lu,YANG Qing. The penetration resistance of the elliptical tip of torpedo anchors in cohesive soil[J]. Ocean Engineering,2020,218:1 − 14.
[4] 喻国良,王闻恺,王呈. 动力型鱼雷锚基本结构与特性[J]. 海洋工程,2018,36(2):143 − 148. [YU Guoliang,WANG Wenkai,WANG Cheng. Basic structure and characteristics of power torpedo anchor[J]. The Ocean Engineering,2018,36(2):143 − 148. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16483/j.issn.1005-9865.2018.02.017
YU Guoliang, WANG Wenkai, WANG Cheng . Basic structure and characteristics of power torpedo anchor[J]. The Ocean Engineering,2018 ,36 (2 ):143 −148 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[5] 瑜璐,杨庆,杨钢,等. 塑性极限分析鱼雷锚锚尖贯入阻力[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(6):1953 − 1962. [YU Lu,YANG Qing,YANG Gang,et al. Plastic limit analysis of penetration resistance of torpedo anchor tip[J]. Rock and soil Mechanics,2020,41(6):1953 − 1962. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2019.1182
YU Lu, YANG Qing, YANG Gang, et al . Plastic limit analysis of penetration resistance of torpedo anchor tip[J]. Rock and soil Mechanics,2020 ,41 (6 ):1953 −1962 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[6] 程钰,邱长林. 鱼雷锚上拔承载力的物质点法数值分析[J]. 水道港口,2021,42:114 − 122. [CHENG Yu,QIU Changlin. Numerical analysis of torpedo anchor’s uplift bearing capacity by material point method[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor,2021,42:114 − 122. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2021.01.017
CHENG Yu, QIU Changlin . Numerical analysis of torpedo anchor’s uplift bearing capacity by material point method[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor,2021 ,42 :114 −122 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[7] HAN Congcong,LIU Jun,ZHANG Yuqin,et al. An innovative booster for dynamic installation of OMNI-Max anchors in clay:Physical modeling[J]. Ocean Engineering,2019,171:345 − 360. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.10.029
[8] 韩聪聪,沈侃敏,李炜,等. 新型组合动力锚安装性能现场试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2021,43(9):1657 − 1665. [HAN Congcong,SHEN Kanmin,LI Wei,et al. Field tests on installation performance of a new hybrid dynamically installed anchor[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2021,43(9):1657 − 1665. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11779/CJGE202109010
HAN Congcong, SHEN Kanmin, LI Wei, et al . Field tests on installation performance of a new hybrid dynamically installed anchor[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2021 ,43 (9 ):1657 −1665 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[9] 马露. 无黏性土的压缩特性及模型[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(4):72 − 77. [MA Lu. Compression characteristics and models of cohesionless soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(4):72 − 77. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202010014
MA Lu . Compression characteristics and models of cohesionless soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021 ,48 (4 ):72 −77 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[10] HOSSAIN M S,O’LOUGHLIN C D,KIM Y. Dynamic installation and monotonic pullout of a torpedo anchor in calcareous silt[J]. Géotechnique,2015,65(2):77 − 90.
[11] LI Gang,ZHANG Jinli,LIU Jia. Model test of the pullout bearing capacity of end-bearing torpedo anchors[J]. Marine Science and Engineering,2022,728(10):1 − 12.
[12] 王呈,陈晓辉,喻国良. 鱼雷锚在钙质砂床中的贯入深度研究[J]. 浙江大学学报(理学版),2020,47(2):253 − 260. [WANG Cheng,CHEN Xiaohui,YU Guoliang. Study on penetration depth of torpedo anchor in calcareous sand bed[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Science Edition),2020,47(2):253 − 260. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9497.2020.02.016
WANG Cheng, CHEN Xiaohui, YU Guoliang . Study on penetration depth of torpedo anchor in calcareous sand bed[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Science Edition),2020 ,47 (2 ):253 −260 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[13] CHANG Kuntan,Hossain M S,WANG Dong,et al. Performance of a novel dynamically installed fish anchor in calcareous silt[J]. Geotechnical and Geoeniveronmental Engineering,2019,145(6):1 − 14.
[14] KIM Y H,HOSSAIN M S,CHANG Kuntan. Numerical investigation of novel dynamic installed fish anchors in clay and calcareous silt[J]. Ocean Engineering,2018,163:29 − 39. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.05.051
[15] 苏永华,王栋. 基于离散元法的砂石混合体直剪试验结果分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):97 − 104. [SU Yonghua,WANG Dong. An analysis of direct shear test results of sand - gravel mixture based on the discrete element method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):97 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202012029
SU Yonghua, WANG Dong . An analysis of direct shear test results of sand - gravel mixture based on the discrete element method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021 ,48 (6 ):97 −104 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[16] 张恩铭,程谦恭,林棋文,等. 岩体结构对岩质滑坡运动过程和堆积特征的影响研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(3):125 − 135. [ZHANG Enming,CHENG Qiangong,LIN Qiwen,et al. A study of the influence of rock mass structure on the propagation processes and deposit characteristics of rockslides[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(3):125 − 135. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202107001
ZHANG Enming, CHENG Qiangong, LIN Qiwen, et al . A study of the influence of rock mass structure on the propagation processes and deposit characteristics of rockslides[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022 ,49 (3 ):125 −135 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[17] ZHANG Nan,EVANS T M. Offshore anchor penetration in sands-granular simulations[J]. Geotechnical Frontiers,2017,279:132 − 142.
[18] ZHANG Nan,EVANS T M. Discrete numerical simulations of torpedo anchor installation in granular soils[J]. Computers and Geotechnics,2019,108:40 − 52. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2018.12.013
[19] MCDOWELL G R,YU Haishui. Discrete element modeling of cone penetration tests incorporating particle shape and crushing[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics,2015,15(6):1 − 14.
[20] 张家铭,邵晓泉,王霄龙,等. 沉桩过程中钙质砂颗粒破碎特性模拟研究[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36:272 − 278. [ZHANG Jiaming,SHAO Xiaoquan,WANG Xiaolong,et al. Simulation study on the crushing characteristics of calcareous sand particles during pile sinking[J]. Rock and soil Mechanics,2015,36:272 − 278. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2015.01.037
ZHANG Jiaming, SHAO Xiaoquan, WANG Xiaolong, et al . Simulation study on the crushing characteristics of calcareous sand particles during pile sinking[J]. Rock and soil Mechanics,2015 ,36 :272 −278 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[21] 和睿,曹冬,史旦达. 可破碎颗粒材料中螺旋桩贯入特性的离散元模拟[J]. 长江科学院院报,2021,38(3):128 − 136. [HE Rui,CAO Dong,SHI Danda. Discrete element simulations of screw pile drilling in crushable granular materials[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2021,38(3):128 − 136. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.202000532021
HE Rui, CAO Dong, SHI Danda . Discrete element simulations of screw pile drilling in crushable granular materials[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2021 ,38 (3 ):128 −136 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[22] MCDOWELL G R,DE BONO J P. On the micro mechanics of one-dimensional normal compression[J]. Géotechnique,2013(63):895 − 908.
[23] WEIBULL W. A statistical distribution function of wide applicability[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics,1951,18:293 − 297. doi: 10.1115/1.4010337
[24] NAKATA Y,KATO Y,HYODO M,et al. One-dimensional compression behavior of uniformly graded sand related to single particle crushing strengthen[J]. Soils and Foundations,2001,41(2):39 − 51. doi: 10.3208/sandf.41.2_39
[25] ÅSTRÖM J A,HERRMANN H J. Fragmentation of grains in a two-dimensional packing[J]. European Physical Journal B,1998,5(3):551 − 554. doi: 10.1007/s100510050476
[26] MA Linjian,LI Zeng,WANG Mingyang,et al. Effects of size and loading rate on the mechanical properties of single coral particles[J]. Powder Technology,2019,342:961 − 971. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2018.10.037
[27] 汪轶群. 钙质砂宏细观力学特性试验及离散元模拟[D]. 杭州:浙江大学,2016. [WANG Yiqun. Experiment and discrete element simulation of macro meso mechanical properties of calcareous sand[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University,2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Yiqun. Experiment and discrete element simulation of macro meso mechanical properties of calcareous sand[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) [28] HARDIN B O. Crushing of soil particles[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1985,111(10):1177 − 1192. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1985)111:10(1177)
[29] KIM Y H,HOSSAIN M S,WANG D,et al. Numerical investigation of dynamic installation of torpedo anchors in clay[J]. Ocean Engineering,2015,108:820 − 832.
-



 下载:
下载: