Rainfall thresholds of typhoon rainstorm induce landslides: A case study over Taishun County
-
摘要:
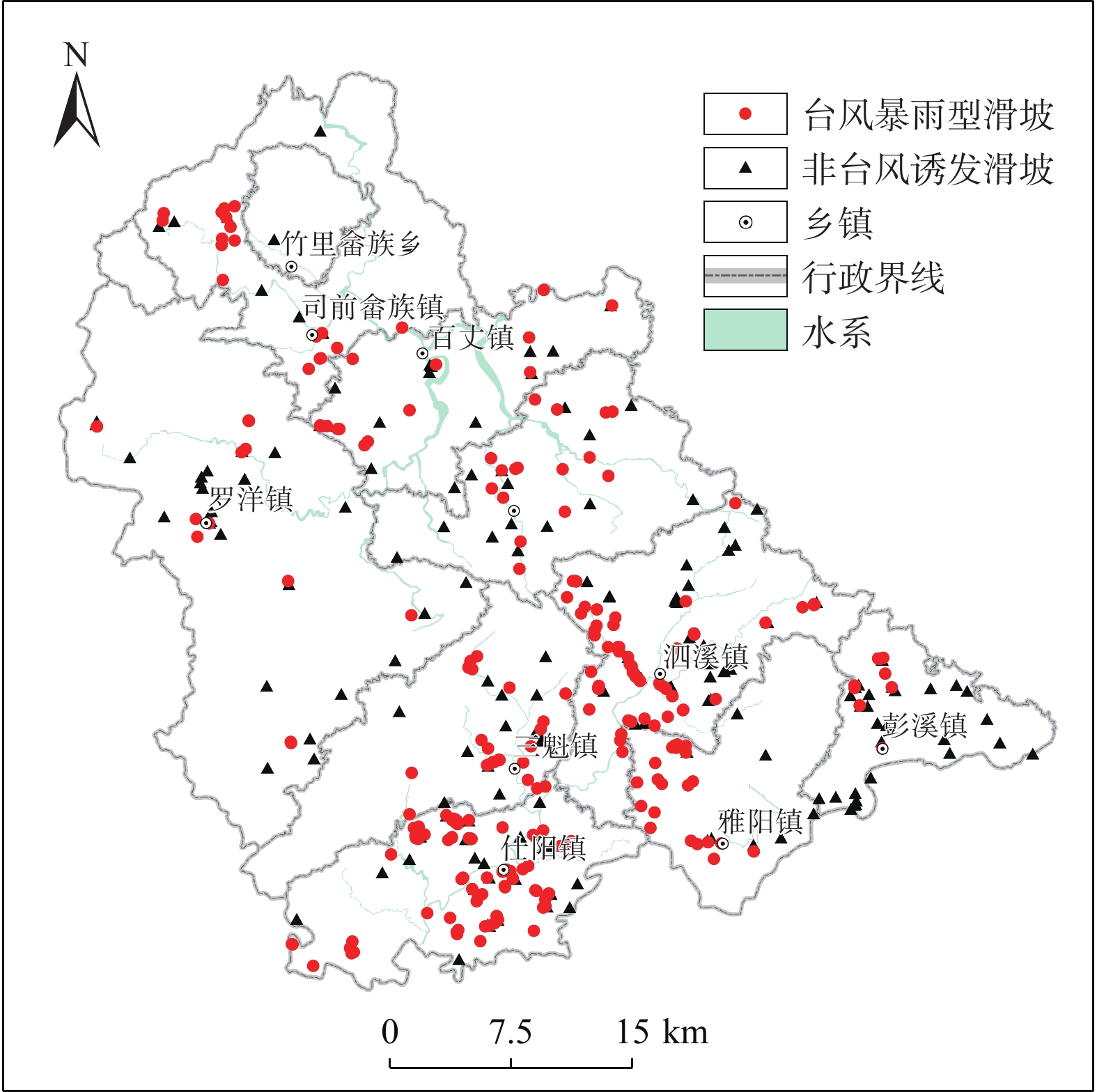
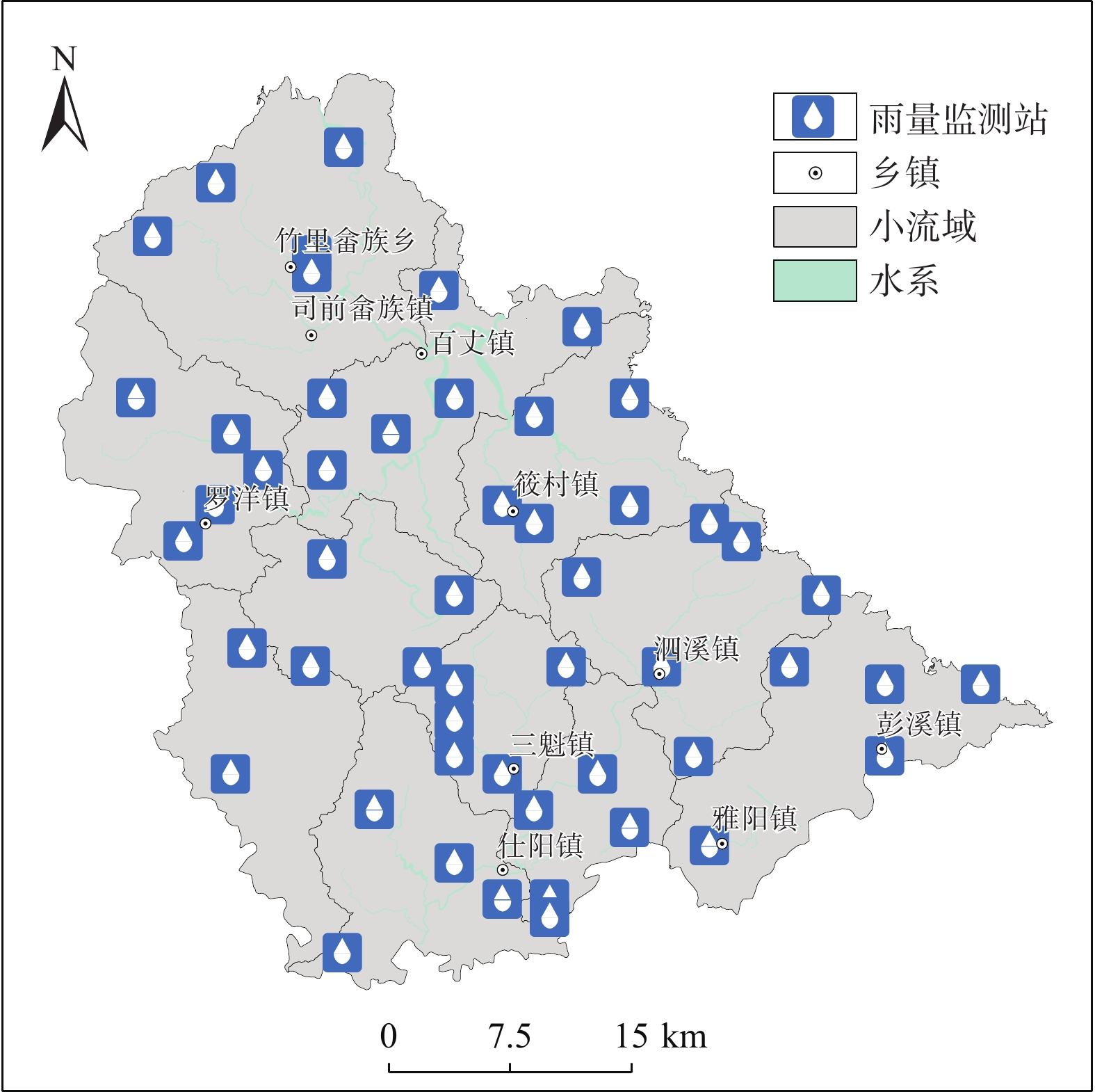
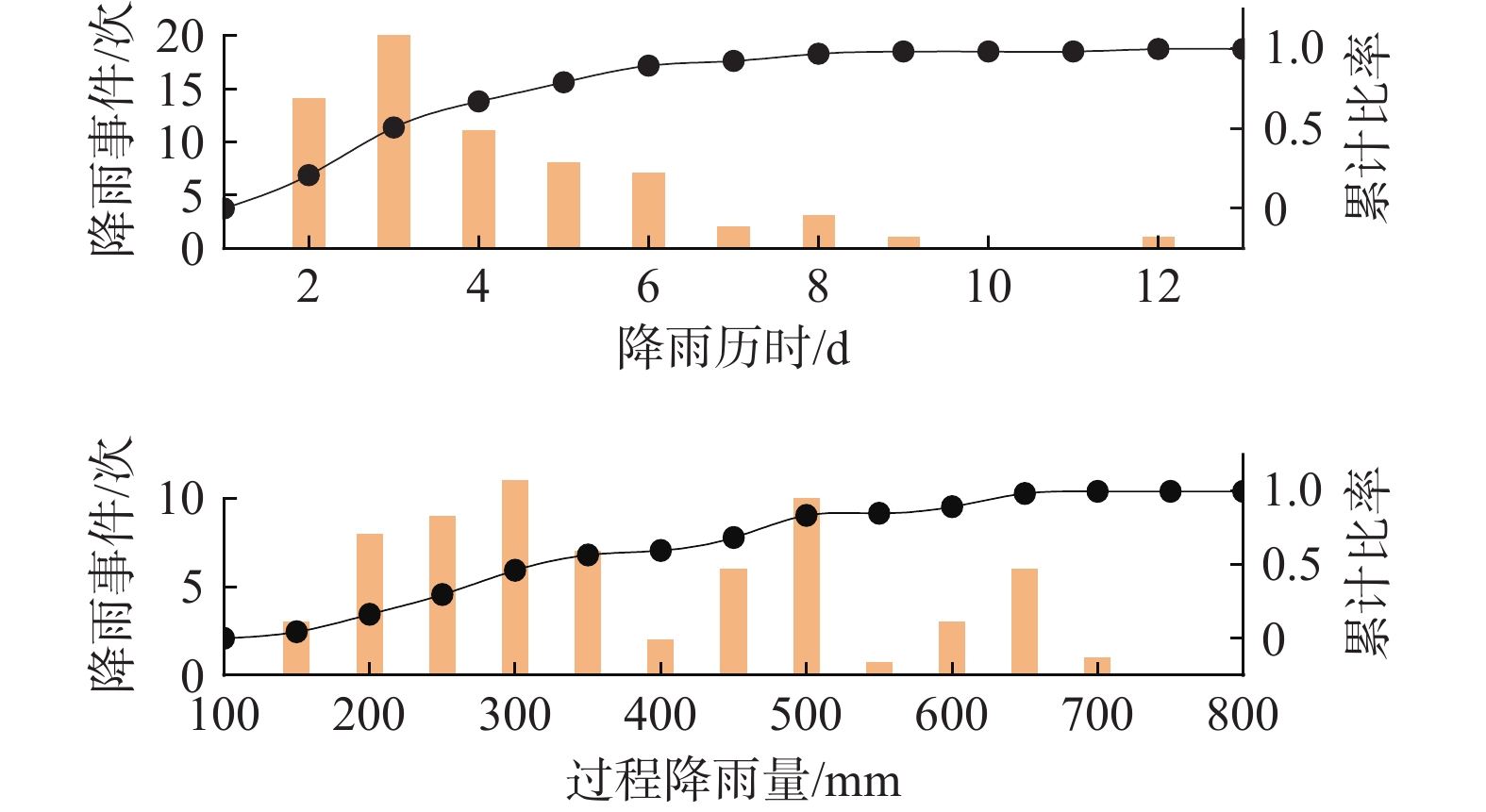
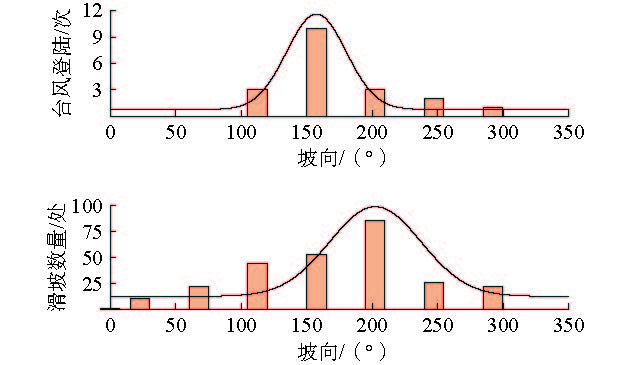
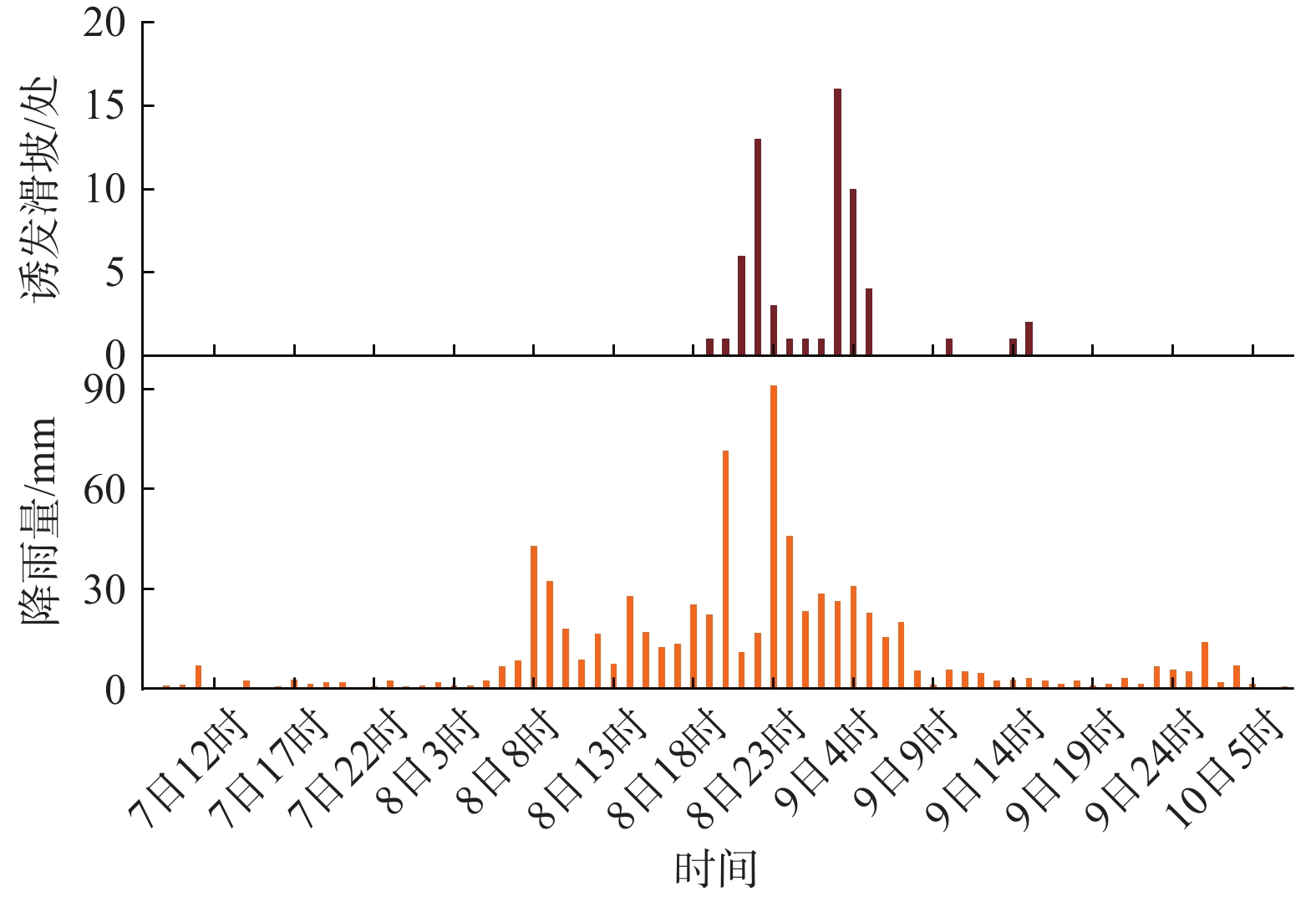
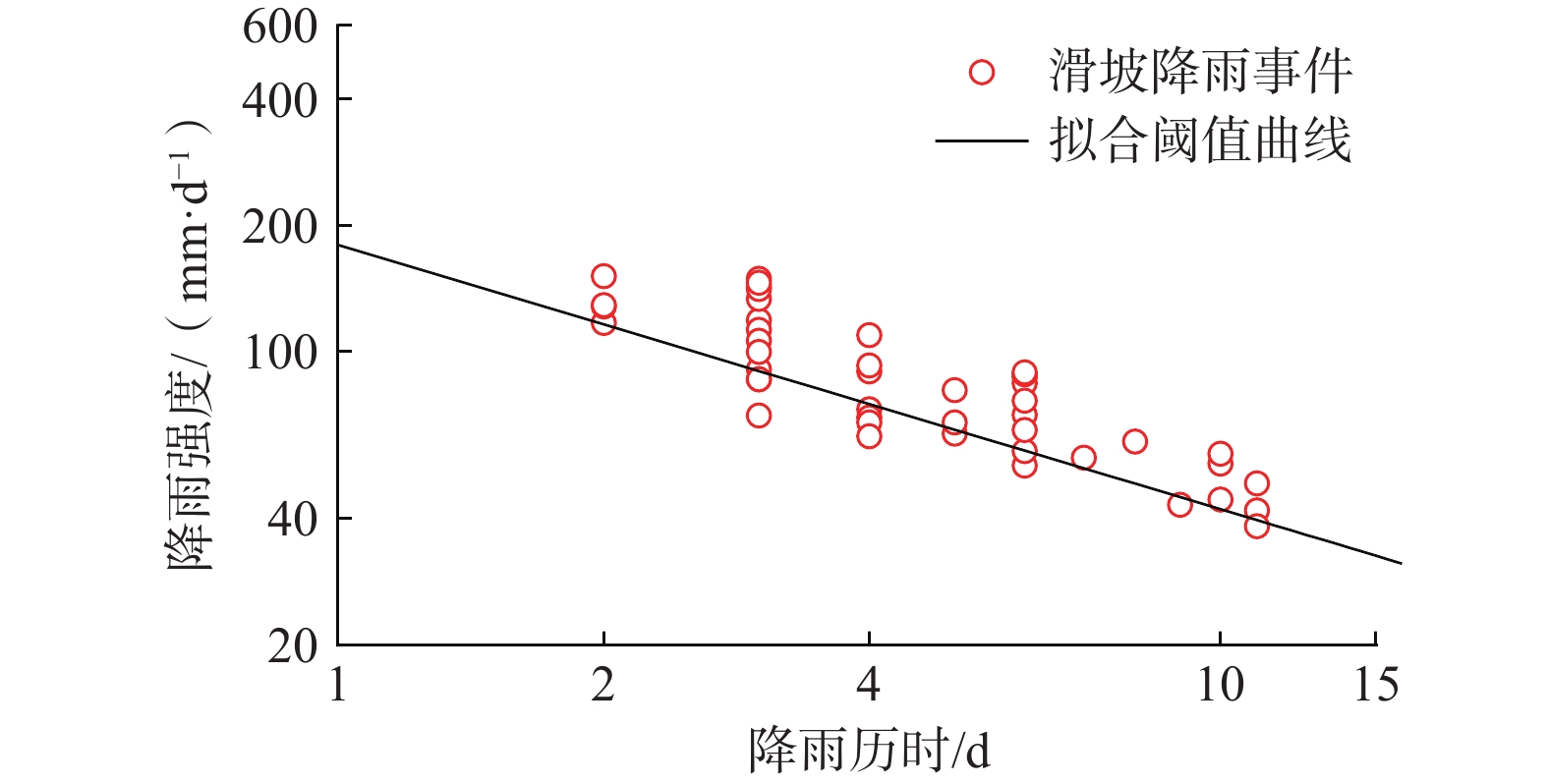
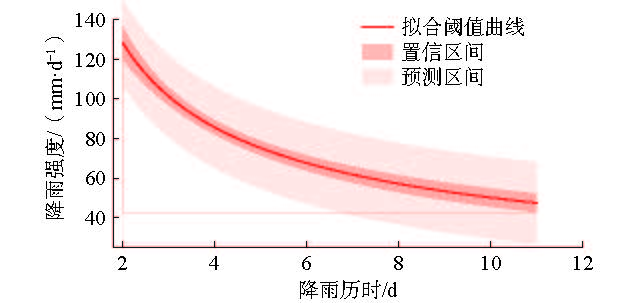
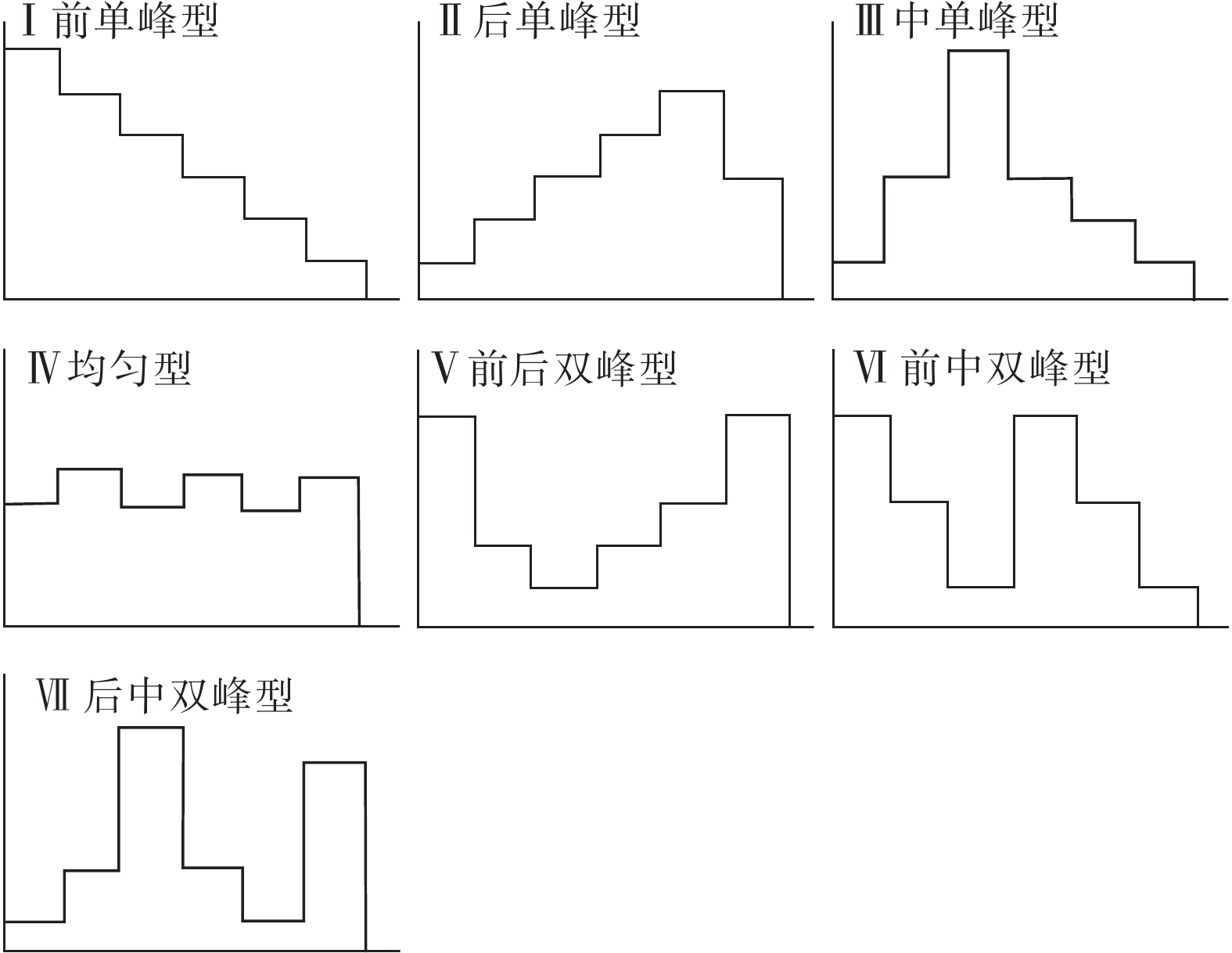
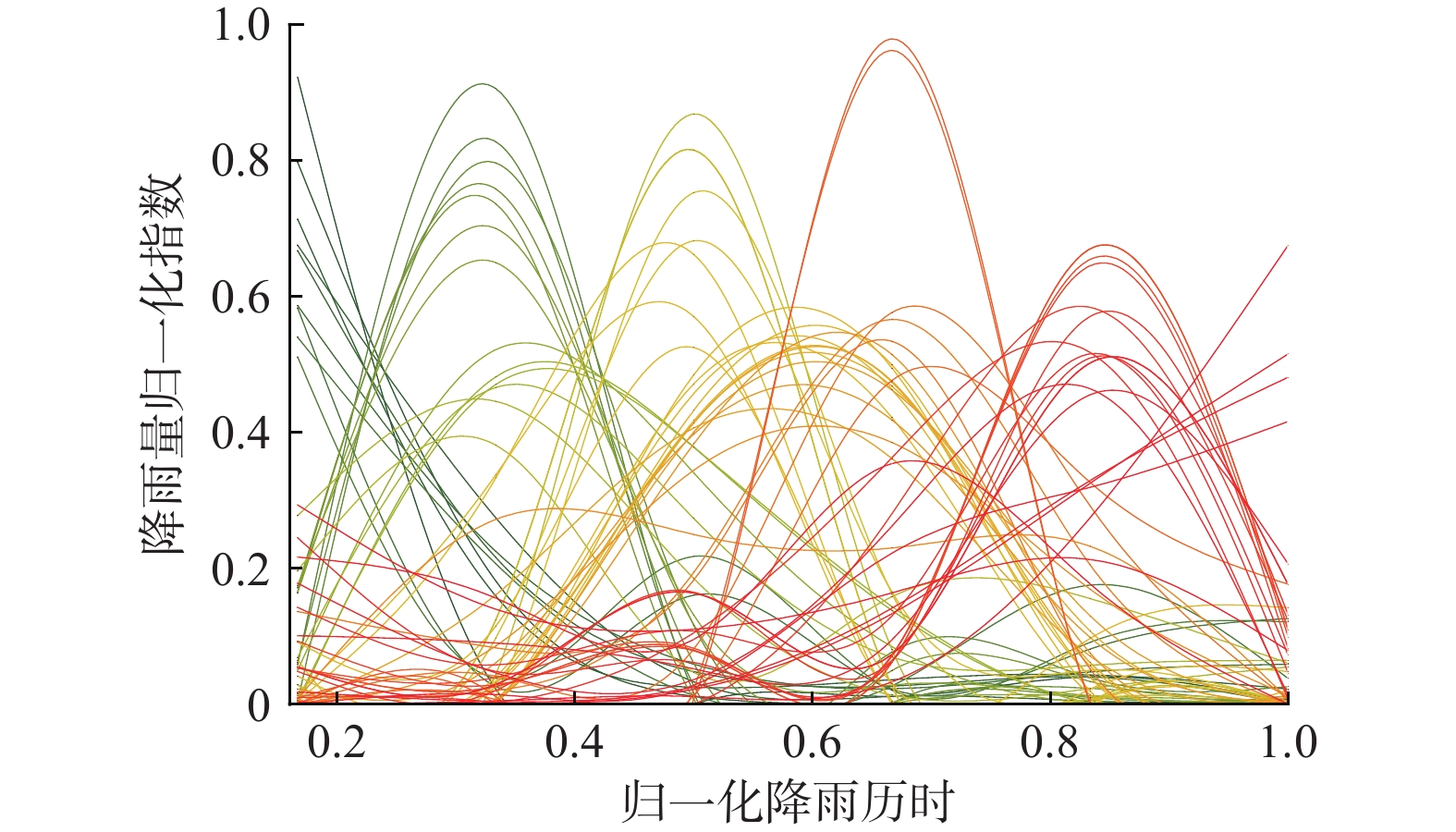
在我国东南沿海地区,台风暴雨诱发了大量山体滑坡。建立诱发台风暴雨型滑坡的降雨阈值模型,可为该地区的滑坡预警提供参考依据。基于浙江省泰顺县2007—2022年以来发生的滑坡信息和日降雨量数据,进行了诱发滑坡的台风暴雨事件编目,初步揭示了台风暴雨型滑坡的发育规律和触发降雨特征,通过降雨强度(I)、降雨历时(D)的幂律关系构建了滑坡临界降雨阈值模型,并开展了不同台风降雨雨型的阈值模型对比。结果表明:台风暴雨型滑坡大量发生在与台风登陆方向接近的迎风坡,坡表植被多为乔木和竹林;诱发滑坡的台风降雨一般持续2~3 d,且降雨过程集中,降雨雨型以单峰型为主,总降雨量一般在200 mm以上;台风暴雨诱发滑坡的降雨阈值显著高于一般性的降雨,这种差异与台风降雨模式及大尺度气候环境有关;雨型也会显著影响降雨阈值,随着降雨峰值的后移,阈值逐渐降低,表明台风暴雨型滑坡对长时间降雨后出现的强降雨事件更加敏感。通过降雨阈值模型对9次台风降雨事件是否诱发滑坡进行了预测,预测结果与实际情况比较吻合,证明该模型及研究思路对台汛期东南沿海的滑坡监测预警有较强的参考价值。
Abstract:In the southeast coast of China, typhoon rainstorms resulted in lots of landslides. Investigating rainfall thresholds and patterns of typhoons is of great importance for the early warning of landslides. In this study, the landslide information obtained from multiple sources and typhoon rainstorm data were used to analyze landslide and rainfall characteristics in Taishun 2007 to 2022; the rainfall threshold of typhoon rainstorm-induce landslides was defined for Taishun area based on the rainfall intensity–duration (I-D) model. It finds that a large number of typhoon rainstorm landslides occur at the windward slope close to the landing direction of the typhoon, where the main vegetation types of the landslide are arbors and herbs with tall trunks and shallow roots. The duration of rainfall events inducing landslides is usually 2~3 days, with concentrated rainfall and total rainfall more than 200 mm. The threshold of typhoon rainstorm-induced landslides is significantly higher than that of rainfall-induced landslides in other regions. With the backward position of rainfall peak in rainfall process, the thresholds become lower and steeper, indicating that more rainfall is needed to trigger landslides when the rainfall peak appears earlier than when it is late. Typhoon rainstorm-induced landslides are more sensitive to the heavy rainfall event after a long rainfall. The threshold model established in this study is consistent with the observation, indicating that it is effective for landslide monitoring during the typhoon season.
-
Key words:
- typhoon rainstorm /
- landslide /
- rainfall thresholds /
- rainfall patterns /
- cluster analysis
-

-
表 1 泰顺县2007—2020年台风暴雨诱发滑坡数量
Table 1. Typhoon rainstorm-induced landslides in Taishun from 2007 to 2020
年份 台风 诱发滑坡/处 累计降雨量/mm 2007 罗莎 2 348.0 圣帕 13 511.8 蝴蝶 1 98.7 2009 莫拉克 6 1240.7 2010 南川 1 88.6 2011 南玛都 1 575.7 2012 苏拉 2 154.5 2013 菲特 7 372.9 2015 苏迪罗 90 780.3 2016 莫兰蒂 82 390.1 鲇鱼 54 575.3 2017 纳沙 3 202.1 海棠 2 232.1 2018 玛莉亚 2 236.4 2020 黑格比 3 132.1 表 2 不同地区诱发滑坡降雨阈值
Table 2. Rainfall I-D thresholds for landslides in different areas
表 3 不同雨型降雨阈值的拟合曲线方程
Table 3. Rainfall I-D thresholds of different rain patterns
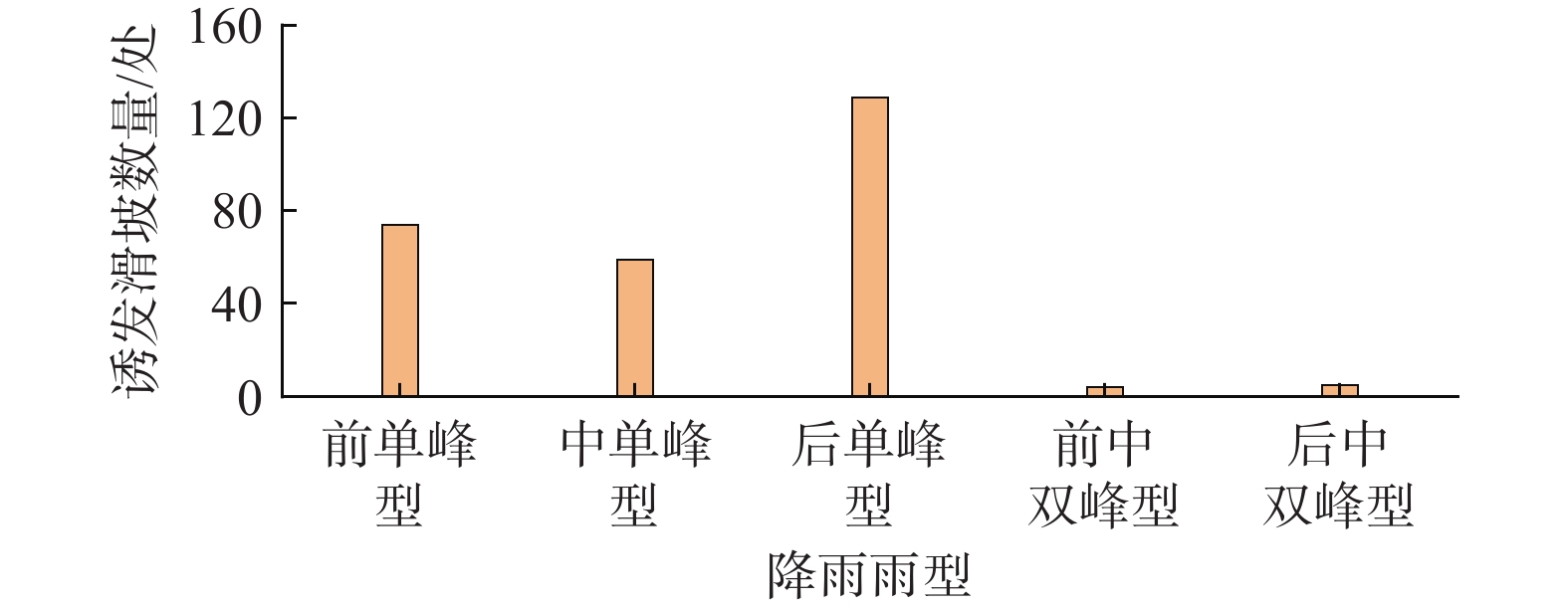
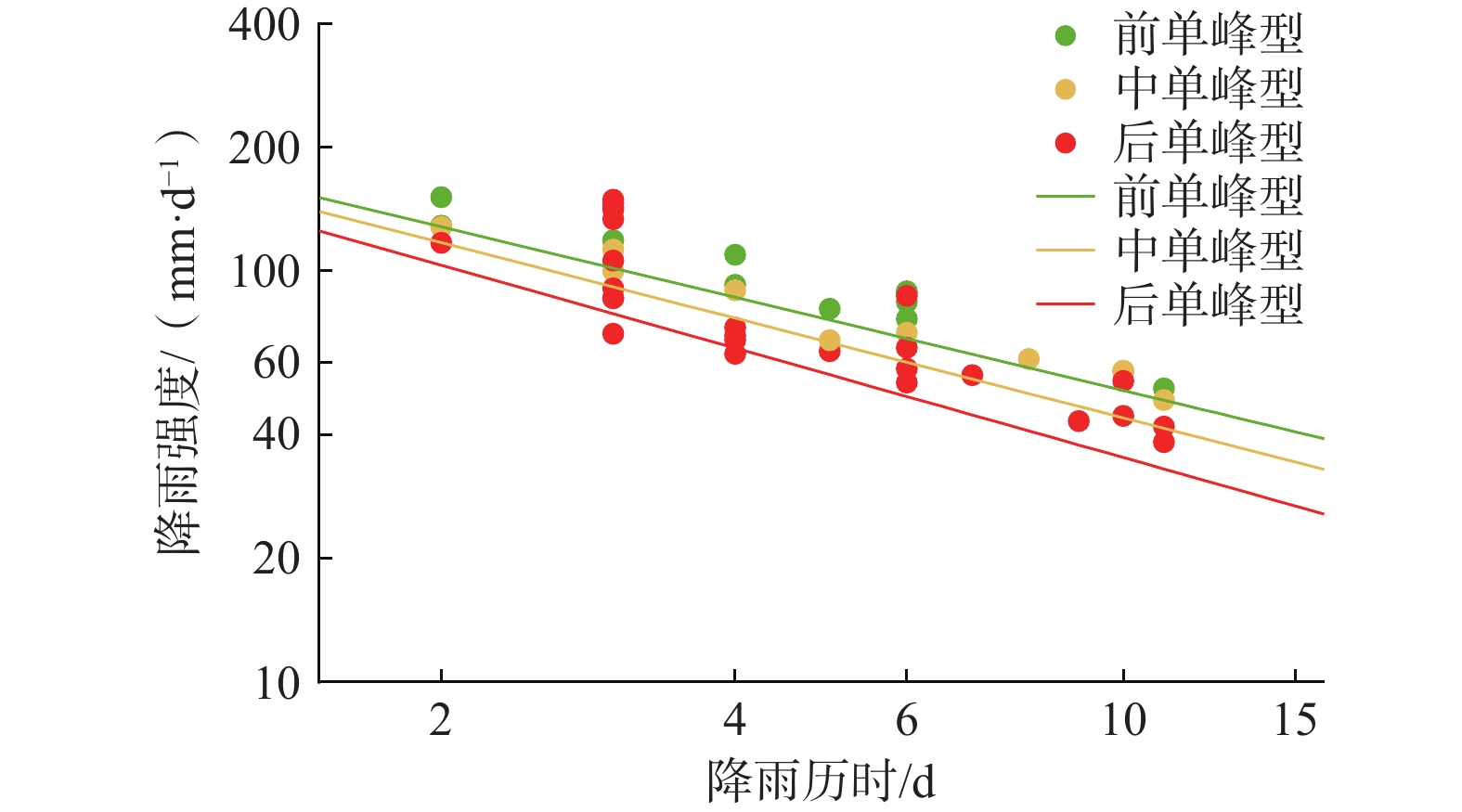
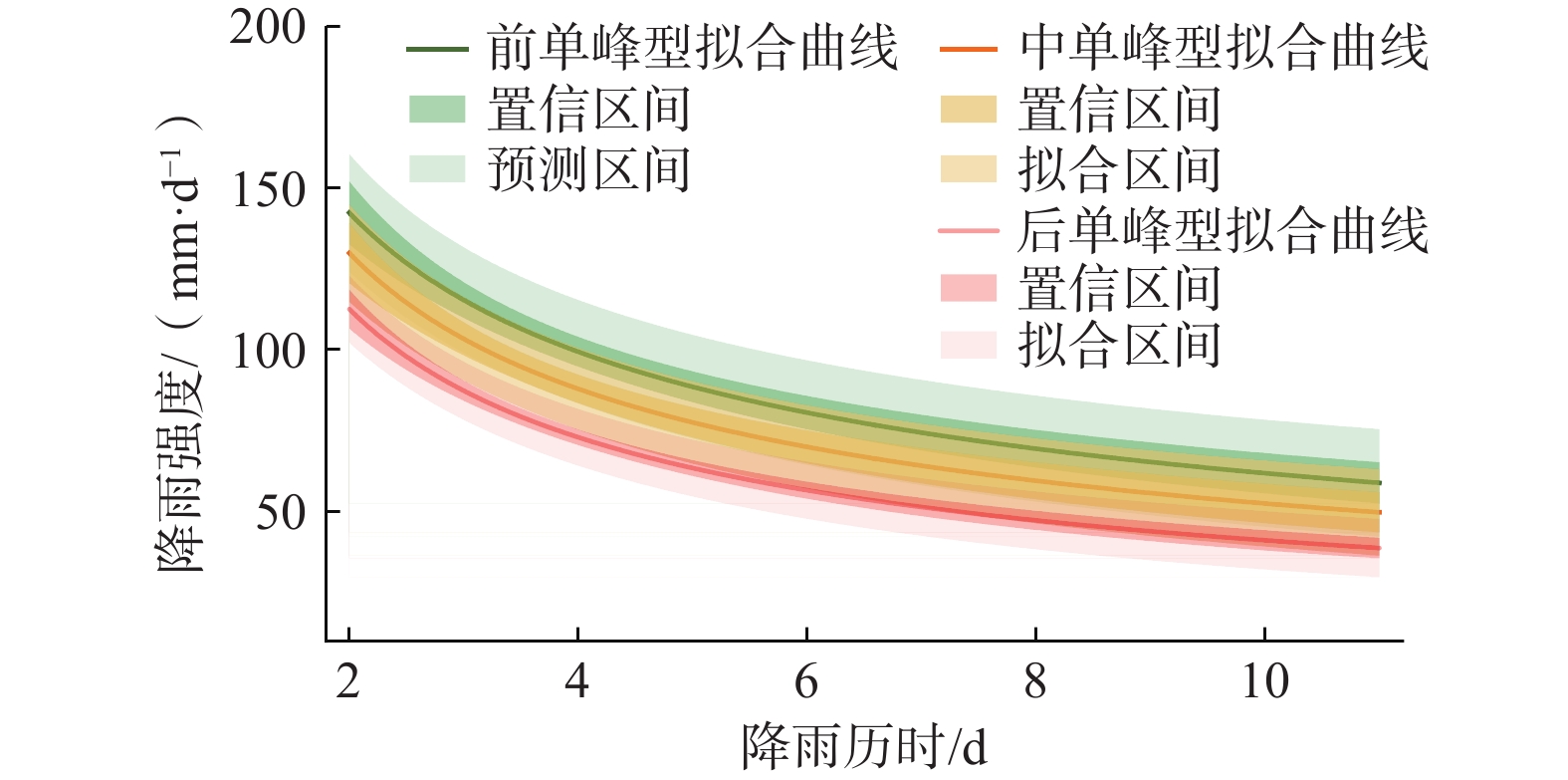
雨型 滑坡数量 I/(mm·d−1) D/d 最小值 均值 最大值 最小值 均值 最大值 前单峰 74 76.5 109.7 154.4 2 4.2 6 中单峰 55 48.5 93.9 142.9 2 4.8 11 后单峰 124 38.3 68.0 117.1 2 6.1 11 拟合曲线方程 前单峰 $ I=(203.89\pm 13.58)\times {D}^{(-0.52\pm 0.05)} $ 中单峰 $ I=(189.24\pm 9.50)\times {D}^{(-0.55\pm 0.04)} $ 后单峰 $ I=(165.53\pm 9.08)\times {D}^{(-0.59\pm 0.04)} $ 表 4 阈值模型预测情况
Table 4. Rainfall I-D thresholds prediction
年份 台风 诱发滑坡 D/d I/(mm·d−1) 雨型 模型阈值/(mm·d−1) 预测滑坡 2017 纳沙 是 5 63.82 中单峰 69.54 否 2017 海棠 是 3 112.70 中单峰 94.00 是 2018 玛莉亚 是 6 87.10 后单峰 50.53 是 2018 山竹 否 2 60.70 中单峰 100.97 否 2019 利奇马 否 1 98.77 中单峰 179.74 否 2020 黑格比 是 3 85.87 后单峰 78.20 是 2021 烟花 否 5 36.22 中单峰 69.54 否 2022 轩岚诺 否 5 62.90 中单峰 69.54 否 2022 梅花 否 3 75.22 后单峰 94.00 否 -
[1] 宋琨,陈伦怡,刘艺梁,等. 降雨诱发深层老滑坡复活变形的动态作用机制[J]. 地球科学,2022,47(10):3665 − 3676. [SONG Kun,CHEN Lunyi,LIU Yiliang,et al. Dynamic mechanism of rain infiltration in deep-seated landslide reactivate deformation[J]. Earth Science,2022,47(10):3665 − 3676. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SONG Kun, CHEN Lunyi, LIU Yiliang, et al. Dynamic mechanism of rain infiltration in deep-seated landslide reactivate deformation[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(10): 3665 − 3676. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 代贞伟,李滨,陈云霞,等. 三峡大树场镇堆积层滑坡暴雨失稳机理研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(1):149 − 156. [DAI Zhenwei,LI Bin,CHEN Yunxia,et al. A study of the failure mechanism of rainfall-induced accumulation landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(1):149 − 156. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
DAI Zhenwei, LI Bin, CHEN Yunxia, et al. A study of the failure mechanism of rainfall-induced accumulation landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(1): 149 − 156. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 孙强,张泰丽,伍剑波,等. SHALSTAB模型在浙南林溪流域滑坡预测中的应用[J]. 华东地质,2021,42(4):383 − 389. [SUN Qiang,ZHANG Taili,WU Jianbo,et al. Application of shallow landslide stability model to landslide prediction in the Linxi River Basin of southern Zhejiang[J]. East China Geology,2021,42(4):383 − 389. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SUN Qiang, ZHANG Taili, WU Jianbo, et al. Application of shallow landslide stability model to landslide prediction in the Linxi River Basin of southern Zhejiang[J]. East China Geology, 2021, 42(4): 383 − 389. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 盛逸凡,李远耀,徐勇,等. 基于有效降雨强度和逻辑回归的降雨型滑坡预测模型[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(1):156 − 162. [SHENG Yifan,LI Yuanyao,XU Yong,et al. Prediction of rainfall-type landslides based on effective rainfall intensity and logistic regression[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(1):156 − 162. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SHENG Yifan, LI Yuanyao, XU Yong, et al. Prediction of rainfall-type landslides based on effective rainfall intensity and logistic regression[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(1): 156 − 162. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] PERUCCACCI S,BRUNETTI M T,GARIANO S L,et al. Rainfall thresholds for possible landslide occurrence in Italy[J]. Geomorphology,2017,290:39 − 57. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.03.031
[6] CHANG J M,CHEN H,JOU B J D,et al. Characteristics of rainfall intensity,duration,and kinetic energy for landslide triggering in Taiwan[J]. Engineering Geology,2017,231:81 − 87.
[7] 张泰丽,周爱国,孙强,等. 台风暴雨条件下滑坡地下水渗流特征及成因机制[J]. 地球科学,2017,42(12):2354 − 2362. [ZHANG Taili,ZHOU Aiguo,SUN Qiang,et al. Characteristics of the groundwater seepage and failure mechanisms of landslide induced by typhoon rainstorm[J]. Earth Science,2017,42(12):2354 − 2362. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Taili, ZHOU Aiguo, SUN Qiang, et al. Characteristics of the groundwater seepage and failure mechanisms of landslide induced by typhoon rainstorm[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(12): 2354 − 2362. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 刘艳辉,温铭生,苏永超,等. 台风暴雨型地质灾害时空特征及预警效果分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(5):119 − 126. [LIU Yanhui,WEN Mingsheng,SU Yongchao,et al. Characteristics of geo-hazards induced by typhoon rainstorm and evaluation of geo-hazards early warning[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(5):119 − 126. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Yanhui, WEN Mingsheng, SU Yongchao, et al. Characteristics of geo-hazards induced by typhoon rainstorm and evaluation of geo-hazards early warning[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(5): 119 − 126. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 栗倩倩,史绪山,柴波,等. 台风-非台风降雨型滑坡的多时段临界雨量值预测模型[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(2):267 − 273. [LI Qianqian,SHI Xushan,CHAI Bo,et al. Multiduration critical rainfall prediction model for typhoons and non-typhoon rainfall landslides[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(2):267 − 273. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Qianqian, SHI Xushan, CHAI Bo, et al. Multiduration critical rainfall prediction model for typhoons and non-typhoon rainfall landslides[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 267 − 273. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 刘明军,王邦贤. 浙江省泰顺县地质灾害成因及分布特征浅析[J]. 地下水,2017,39(1):148 − 150. [LIU Mingjun,WANG Bangxian. Analysis on the causes and distribution characteristics of geological disasters in Taishun County,Zhejiang Province[J]. Ground Water,2017,39(1):148 − 150. (in Chinese)]
LIU Mingjun, WANG Bangxian. Analysis on the causes and distribution characteristics of geological disasters in Taishun County, Zhejiang Province[J]. Ground Water, 2017, 39(1): 148 − 150. (in Chinese)
[11] 姜建丰,余霖枫,戴益斌. 泰顺县台风灾害统计分析[J]. 山西农经,2019(12):112. [JIANG Jianfeng,YU Linfeng,DAI Yibin. Statistical analysis of typhoon disaster in Taishun County[J]. Shanxi Agricultural Economy,2019(12):112. (in Chinese)]
JIANG Jianfeng, YU Linfeng, DAI Yibin. Statistical analysis of typhoon disaster in Taishun County[J]. Shanxi Agricultural Economy, 2019(12): 112. (in Chinese)
[12] 赵阳,倪化勇,伍剑波,等. 基于AHP-CF模型的地质灾害易发性评价——以泰顺县仕阳镇为例[J]. 华东地质,2021,42(1):66 − 75. [ZHAO Yang,NI Huayong,WU Jianbo,et al. Evaluation of geological hazard vulnerability based on AHP-CF model:take Shiyang Town of Taishun County as an example[J]. East China Geology,2021,42(1):66 − 75. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHAO Yang, NI Huayong, WU Jianbo, et al. Evaluation of geological hazard vulnerability based on AHP-CF model: take Shiyang Town of Taishun County as an example[J]. East China Geology, 2021, 42(1): 66 − 75. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 王凯,齐铎,高丽,等. 浙东地形对台风“利奇马” 极端降水的影响分析[J]. 气象科学,2021,41(2):162 − 171. [WANG Kai,QI Duo,GAO Li,et al. Analysis of the effects of the topography of eastern Zhejiang on the extreme precipitation of typhoon “Lekima”[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Sciences,2021,41(2):162 − 171. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Kai, QI Duo, GAO Li, et al. Analysis of the effects of the topography of eastern Zhejiang on the extreme precipitation of typhoon “Lekima”[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Sciences, 2021, 41(2): 162 − 171. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] GLADE T,CROZIER M,SMITH P. Applying probability determination to refine landslide-triggering rainfall thresholds using an empirical “antecedent daily rainfall model”[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics,2000,157(6):1059 − 1079.
[15] 刘艳辉,刘丽楠. 基于诱发机理的降雨型滑坡预警研究——以花岗岩风化壳二元结构斜坡为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2016,24(4):542 − 549. [LIU Yanhui,LIU Linan. Rainfall-induced mechanism based early warning model for slopes of dualistic layers in weathered granitic area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2016,24(4):542 − 549. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Yanhui, LIU Linan. Rainfall-induced mechanism based early warning model for slopes of dualistic layers in weathered granitic area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2016, 24(4): 542 − 549. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 孙强,张泰丽,张沙莎,等. 基于ARDL模型的滑坡地下水水位预测[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(2):147 − 152. [SUN Qiang,ZHANG Taili,ZHANG Shasha,et al. Prediction of the landslide water table based on ARDL model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(2):147 − 152. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SUN Qiang, ZHANG Taili, ZHANG Shasha, et al. Prediction of the landslide water table based on ARDL model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(2): 147 − 152. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] SUN Q,WU J B,ZHANG T L,et al. Promoting effect of vegetation onthe initiation of landslides induced by typhoon rainstorms[J]. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science,2021,861(6):062005. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/861/6/062005
[18] CAINE N. The rainfall intensity - duration control of shallow landslides and debris flows[J]. Geografiska Annaler:Series A,Physical Geography,1980,62(1/2):23 − 27.
[19] 伍宇明,兰恒星,高星,等. 台风暴雨型滑坡降雨阈值曲线研究——以福建地区为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2014,22(2):255 − 262. [WU Yuming,LAN Hengxing,GAO Xing,et al. Rainfall threshold of storm-induced landslides in typhoon areas:a case study of Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2014,22(2):255 − 262. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WU Yuming, LAN Hengxing, GAO Xing, et al. Rainfall threshold of storm-induced landslides in typhoon areas: a case study of Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2014, 22(2): 255 − 262. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 张勇,温智,程英建. 四川巴中市滑坡灾害与降雨雨型关系探讨[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(2):178 − 182. [ZHANG Yong,WEN Zhi,CHENG Yingjian. A discussion of the relationship between landslide disaster and rainfall types in Bazhong of Sichuan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(2):178 − 182. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Yong, WEN Zhi, CHENG Yingjian. A discussion of the relationship between landslide disaster and rainfall types in Bazhong of Sichuan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(2): 178 − 182. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 刘樱,杨明,徐集云. 杭州市城市暴雨雨型分析研究[J]. 科技通报,2021,37(4):15 − 22. [LIU Ying,YANG Ming,XU Jiyun. Analysis and study of rainstorm pattern in Hangzhou[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology,2021,37(4):15 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Ying, YANG Ming, XU Jiyun. Analysis and study of rainstorm pattern in Hangzhou[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2021, 37(4): 15 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: