A model of capillary water rise based on fractal theory and experimental validation
-
摘要:
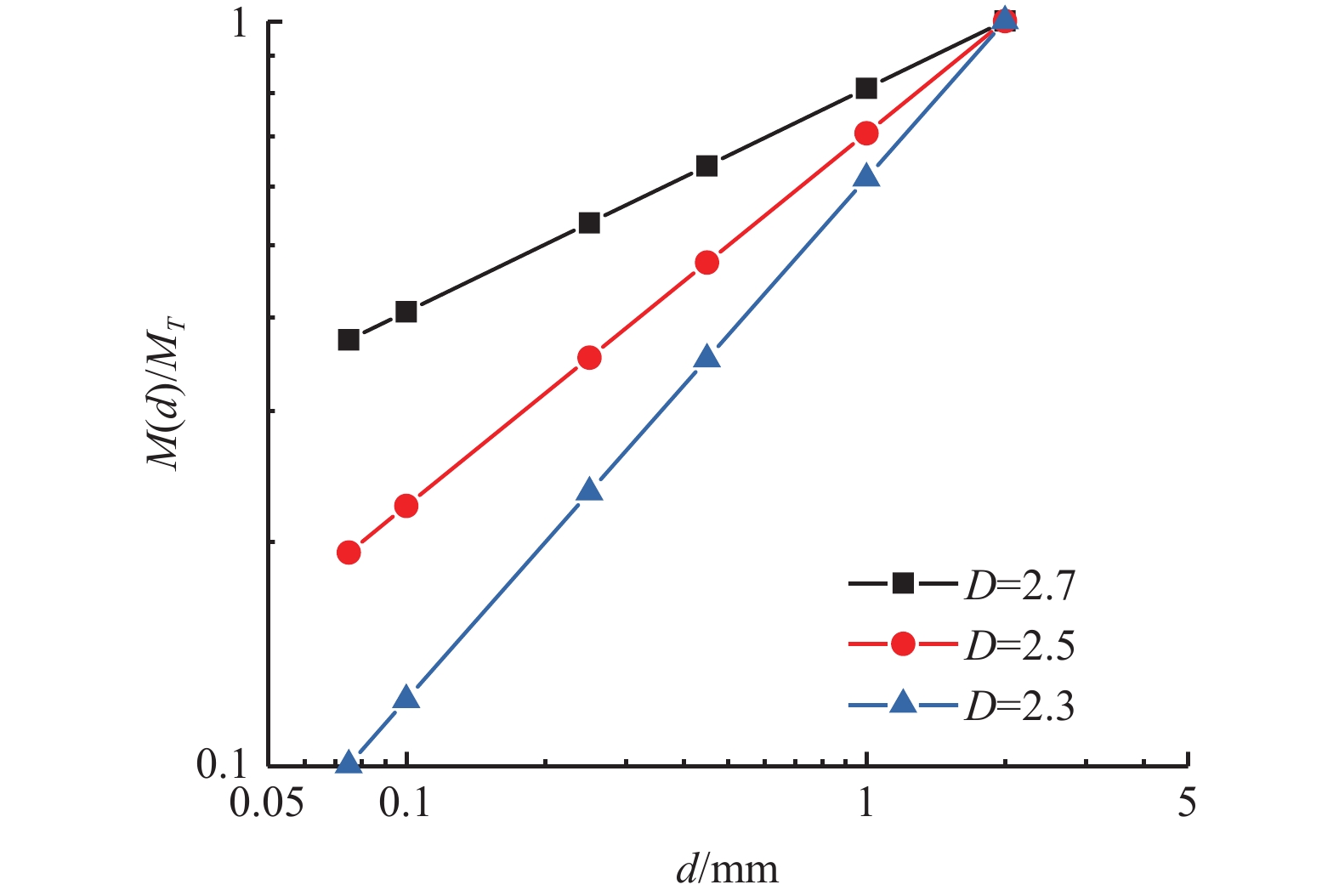
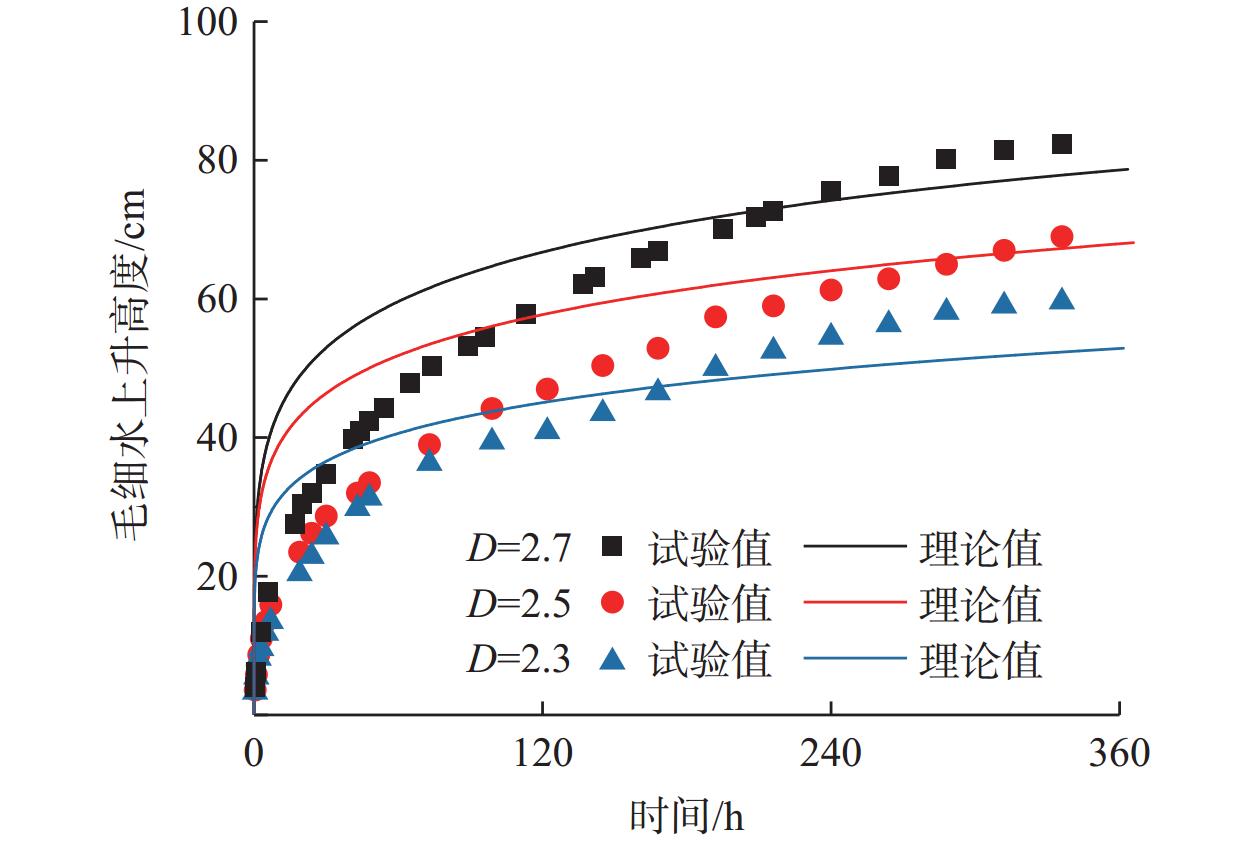
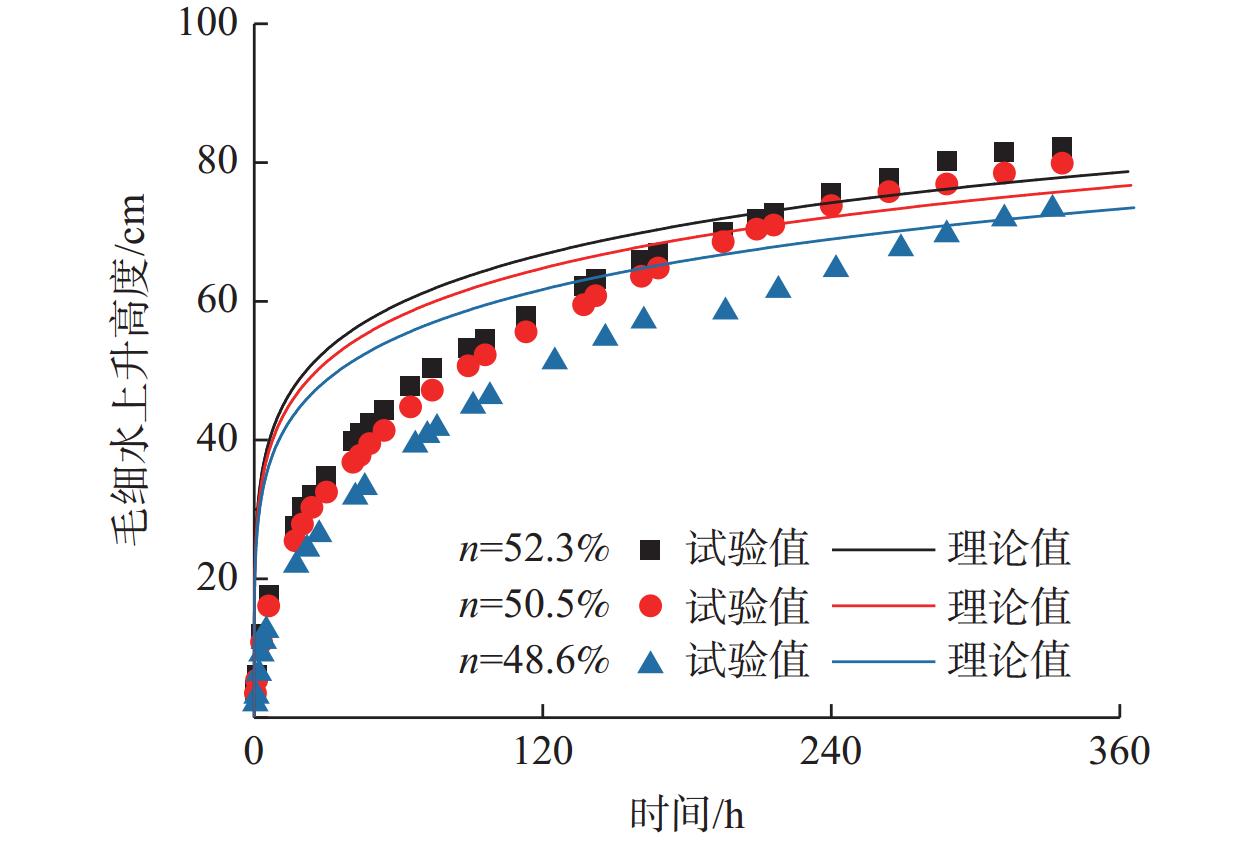
沿海地区的路基工程中,毛细水上升会产生路基病害,影响道路运营的安全性和耐久性,因此研究毛细水上升高度尤为重要。文章视毛细水上升为一种非饱和土的渗流现象,引入分形维数对非饱和土渗透系数进行修正,进而提出了基于分形理论的毛细水上升高度模型,得到了毛细水上升高度随时间变化的曲线;而后对南通某干线公路路基土样进行竖管法毛细水上升高度试验,改变土样的干密度及初始粒径的分形维数分布做对照组试验。研究结果表明:毛细水上升呈现初期先快速增加,然后缓慢增加,最终趋于稳定的趋势;土样颗粒粒径分布的分形维数越大,得到的毛细水上升高度越大;土样的干密度越小,即孔隙率越大,得到的毛细水上升高度越大。文章提出的毛细水上升高度模型中,毛细水上升高度与试样孔隙率、饱和渗透系数、进气值对应的毛细水上升高度、分形维数等参数相关。在模型理论值计算中认为分形维数变化仅改变进气值对应的毛细水高度,不改变饱和渗透系数,而干密度变化即孔隙率变化仅导致饱和渗透系数变化,不改变进气值对应的毛细水高度,由此得到的模型计算结果与试验结果趋势一致,验证了理论模型的正确性,可以为公路路基毛细水病害防治提供理论指导。
Abstract:As to the roadbed projects in coastal areas, capillary water rise can produce roadbed diseases and affect the safety and durability of road operation. It is important to study the capillary water rise height. The article regards capillary water rise as a kind of unsaturated soil seepage phenomenon, and introduces fractal dimension to unsaturated soil permeability coefficient modification. A capillary water rise height model based on fractal theory is proposed to obtain the capillary water rise height curve with time. Then a vertical tube method capillary water rise height test was conducted on a mainline roadbed soil sample in Nantong, with the control test of changes in the dry density of the soil sample and the fractal dimension of the initial particle size distribution. The results show that: the capillary water rise presents a rapid increase at the beginning, and then slowly increases, and finally stabilizes. The larger the fractal dimension of the particle size distribution of soil sample, the greater the capillary water rise height; the smaller the dry density of the soil sample, that is, the greater the porosity, the greater the capillary water rise height. In the capillary water rise height model, the capillary water rise height is related to the sample porosity, saturated permeability coefficient, capillary water rise height corresponding to the inlet value, fractal dimension, etc. In the theoretical model, the variation of fractal dimension only changes the capillary water height corresponding to the inlet value, not the saturated permeability coefficient; while the dry density change, i.e., the porosity change, only leads to the saturated permeability coefficient change, does not affect the intake value corresponding to the height of capillary water, the results from theoretical model are consistent with those from the test, verifying the effectiveness of the theoretical model. This study provides theoretical guidance for the prevention and control of road-base capillary water disease.
-
Key words:
- capillary water /
- particle distribution /
- fractal theory /
- Darcy law /
- dry density
-

-
表 1 试验土样基本物理指标
Table 1. Basic physical properties of soil samples
参数 液限/% 塑限/% 塑性指数 比重 取值 35.01 18.82 16.21 2.73 表 2 试验方案
Table 2. Experimental schemes
组号 干密度/(g·cm−3) 分形维数 1 1.30 2.7 2 1.30 2.5 3 1.30 2.3 4 1.35 2.7 5 1.40 2.7 表 3 理论参数取值
Table 3. Theoretical parameter values
组号 孔隙率/% ks/(cm·s−1) D ha/cm 1 52.3 3.5×10−5 2.7 60 2 52.3 3.5×10−5 2.5 45 3 52.3 3.5×10−5 2.3 30 4 50.5 2.8×10−5 2.7 60 5 48.6 2.0×10−5 2.7 60 -
[1] 刘建强,许强,郑光,等. 贵州省鸡场滑坡地下水化学特征反映的水-岩(土)作用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(2):132 − 140. [LIU Jianqiang,XU Qiang,ZHENG Guang,et al. Water-rock/soil interaction reflected by the chemical characteristics of groundwater of Jichang landslide in Guizhou Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(2):132 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Jianqiang, XU Qiang, ZHENG Guang, et al. Water-rock/soil interaction reflected by the chemical characteristics of groundwater of Jichang landslide in Guizhou Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(2): 132 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 赵明华,刘小平,陈安. 非饱和土路基毛细作用分析[J]. 公路交通科技,2008,25(8):26 − 30. [ZHAO Minghua,LIU Xiaoping,CHEN An. Analysis of capillary effect in unsaturated roadbed[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development,2008,25(8):26 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHAO Minghua, LIU Xiaoping, CHEN An. Analysis of capillary effect in unsaturated roadbed[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2008, 25(8): 26 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 黄晓明. 路基路面工程[M]. 北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2014. [HUANG Xiaoming. Subgrade and pavement engineering[M]. Beijing:China Architecture & Building Press,2014. (in Chinese)]
HUANG Xiaoming. Subgrade and pavement engineering[M]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2014. (in Chinese)
[4] 汤明高,吴川,吴辉隆,等. 水库滑坡地下水动态响应规律及浸润线计算模型——以石榴树包滑坡为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(2):115 − 125. [TANG Minggao,WU Chuan,WU Huilong,et al. Dynamic response and phreatic line calculation model of groundwater in a reservoir landslide:Exemplified by the Shiliushubao landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(2):115 − 125. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
TANG Minggao, WU Chuan, WU Huilong, et al. Dynamic response and phreatic line calculation model of groundwater in a reservoir landslide: Exemplified by the Shiliushubao landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(2): 115 − 125. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 李强,李同录,李华,等. 毛细水作用下非饱和土压缩过程的微观非连续变形数值分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(4):135 − 143. [LI Qiang,LI Tonglu,LI Hua,et al. Numerical analysis of evolution of the unsaturated soil micro-structure with capillary action during compression[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(4):135 − 143. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Qiang, LI Tonglu, LI Hua, et al. Numerical analysis of evolution of the unsaturated soil micro-structure with capillary action during compression[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(4): 135 − 143. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 肖红宇,刘明寿,彭鹏程,等. 基于黏性土分形特征的毛细水上升高度研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(6):48 − 52. [XIAO Hongyu,LIU Mingshou,PENG Pengcheng,et al. A study of the height of capillary water rise based on fractal characteristics of cohesive soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(6):48 − 52. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XIAO Hongyu, LIU Mingshou, PENG Pengcheng, et al. A study of the height of capillary water rise based on fractal characteristics of cohesive soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(6): 48 − 52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 胡明鉴,张晨阳,崔翔,等. 钙质砂中毛细水高度与影响因素试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(11):4157 − 4164. [HU Mingjian,ZHANG Chenyang,CUI Xiang,et al. Experimental study on capillary rise and influencing factors in calcareous sand[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2019,40(11):4157 − 4164. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HU Mingjian, ZHANG Chenyang, CUI Xiang, et al. Experimental study on capillary rise and influencing factors in calcareous sand[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(11): 4157 − 4164. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 邓改革,何建国,康宁波. 基于多物理场耦合的毛细水高度研究[J]. 水土保持研究,2021,28(4):136 − 141. [DENG Gaige,HE Jianguo,KANG Ningbo. Research on capillary water height based on multi-physical field coupling[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2021,28(4):136 − 141. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
DENG Gaige, HE Jianguo, KANG Ningbo. Research on capillary water height based on multi-physical field coupling[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 28(4): 136 − 141. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 吕秋丽,杨海华. 不同土质孔隙结构特点及其毛细水上升规律分析[J]. 能源与环保,2019,41(5):102 − 106. [LÜ Qiuli,YANG Haihua. Pore structure characteristics of different soils and analysis of capillary water rising law[J]. China Energy and Environmental Protection,2019,41(5):102 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LÜ Qiuli, YANG Haihua. Pore structure characteristics of different soils and analysis of capillary water rising law[J]. China Energy and Environmental Protection, 2019, 41(5): 102 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 杨海华,吕秋丽,杨武,等. 利用柱状换土毛细作用提升地下水实现胡杨自我恢复的探索研究[J]. 节水灌溉,2020(12):51 − 56. [YANG Haihua,LÜ Qiuli,YANG Wu,et al. Study on self recovery of populus euphratica using capillary action of column soil exchange to enhance groundwater[J]. Water Saving Irrigation,2020(12):51 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YANG Haihua, LÜ Qiuli, YANG Wu, et al. Study on self recovery of populus euphratica using capillary action of column soil exchange to enhance groundwater[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2020(12): 51 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 刘杰,姚海林,卢正,等. 非饱和土路基毛细作用的数值与解析方法研究[J]. 岩土力学,2013,34(增刊2):421 − 427. [LIU Jie,YAO Hailin,LU Zheng,et al. Study of analytic and numerical methods for capillary action of unsaturated soil subgrade[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2013,34(Sup 2):421 − 427. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Jie, YAO Hailin, LU Zheng, et al. Study of analytic and numerical methods for capillary action of unsaturated soil subgrade[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(Sup 2): 421 − 427. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 朱志铎,彭宇一,张文超,等. 高等级公路粉土路基毛细水处治的试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2011,33(增刊1):52 − 55. [ZHU Zhiduo,PENG Yuyi,ZHANG Wenchao,et al. Experimental study on capillary water in silty subgrade of highway[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2011,33(Sup 1):52 − 55. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHU Zhiduo, PENG Yuyi, ZHANG Wenchao, et al. Experimental study on capillary water in silty subgrade of highway[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2011, 33(Sup 1): 52 − 55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] HIRD R,BOLTON M D. Clarification of capillary rise in dry sand[J]. Engineering Geology,2017,230:77 − 83. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.09.023
[14] 高大钊,袁聚云. 土质学与土力学[M]. 3版. 北京:人民交通出版社,2001. [GAO Dazhao,YUAN Juyun. Soil science and soil mechanics[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing:China Communications Press,2001. (in Chinese)]
GAO Dazhao, YUAN Juyun. Soil science and soil mechanics[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2001. (in Chinese)
[15] 董斌,张喜发,李欣,等. 毛细水上升高度综合试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2008,30(10):1569 − 1574. [DONG Bin,ZHANG Xifa,LI Xin,et al. Comprehensive tests on rising height of capillary water[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2008,30(10):1569 − 1574. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
DONG Bin, ZHANG Xifa, LI Xin, et al. Comprehensive tests on rising height of capillary water[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2008, 30(10): 1569 − 1574. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 杜红普,刘波,王华军,等. 基于土水特征曲线预测多孔介质毛细上升过程[J]. 工程地质学报,2013,21(3):345 − 350. [DU Hongpu,LIU Bo,WANG Huajun,et al. Prediction of capillary rise in porous media based on soil water characteristic curve[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2013,21(3):345 − 350. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2013.03.002
DU Hongpu, LIU Bo, WANG Huajun, et al. Prediction of capillary rise in porous media based on soil water characteristic curve[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2013, 21(3): 345 − 350. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2013.03.002
[17] LU Ning,LIKOS W J. Rate of capillary rise in soil[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2004,130(6):646 − 650. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2004)130:6(646)
[18] MANDELBROT,BENOIT B. The fractal geometry of nature[J]. American Journal of Physics,1984,91(9):594 − 598.
[19] 刘松玉,方磊,陈浩东. 论我国特殊土粒度分布的分形结构[J]. 岩土工程学报,1993,15(1):23 − 30. [LIU Songyu,FANG Lei,CHEN Haodong. Fractal structure of granularity distribution of regional soils in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1993,15(1):23 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Songyu, FANG Lei, CHEN Haodong. Fractal structure of granularity distribution of regional soils in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1993, 15(1): 23 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] TERZAGHI K. Theoretical soil mechanics[M]. New York:Wiley,1943.
[21] 徐永福,叶翠明,赵书权,等. 压应力对非饱和土渗透系数的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报,2004,38(6):982 − 986. [XU Yongfu,YE Cuiming,ZHAO Shuquan,et al. Effect of compressive stress on hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University,2004,38(6):982 − 986. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XU Yongfu, YE Cuiming, ZHAO Shuquan, et al. Effect of compressive stress on hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2004, 38(6): 982 − 986. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 中华人民共和国建设部. 岩土工程勘察规范:GB 50021—2001[S]. 北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2004. [Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China. Code for investigation of geotechnical engineering:GB 50021—2001[S]. Beijing:China Architecture & Building Press,2004. (in Chinese)]
Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China. Code for investigation of geotechnical engineering: GB 50021—2001[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2004. (in Chinese)
[23] 交通运输部公路科学研究院. 公路土工试验规程:JTG 3430—2020[S]. 北京:人民交通出版社,2020. [Research Institute of Highway Ministry of Transport. Test methods of soils for highway engineering:JTG 3430—2020[S]. Beijing:China Communication Press,2020. (in Chinese)]
Research Institute of Highway Ministry of Transport. Test methods of soils for highway engineering: JTG 3430—2020[S]. Beijing: China Communication Press, 2020. (in Chinese)
[24] 徐永福,董 平. 非饱和土的水分特征曲线的分形模型[J]. 岩土力学,2002,23(4):400 − 405. [XU Yongfu,DONG Ping. Fractal models for the soil-water characteristics of unsaturated soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2002,23(4):400 − 405. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XU Yongfu, DONG Ping. Fractal models for the soil-water characteristics of unsaturated soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2002, 23(4): 400 − 405. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 陶高梁. 岩土多孔介质孔隙结构的分形研究及其应用[D]. 武汉:武汉理工大学,2010. [TAO Gaoliang. Fractal approach on pore structure of rock and soil porous media and its applications[D]. Wuhan:Wuhan University of Technology,2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
TAO Gaoliang. Fractal approach on pore structure of rock and soil porous media and its applications[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] ZHOU Annan,FAN Yang,CHENG W C,et al. A fractal model to interpret porosity-dependent hydraulic properties for unsaturated soils[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering,2019,2019:3965803.
[27] LEROUEIL S,BOUCLIN G,TAVENAS F,et al. Permeability anisotropy of natural clays as a function of strain[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1990,27(5):568 − 579. doi: 10.1139/t90-072
[28] TAVENAS F,JEAN P,LEBLOND P,et al. The permeability of natural soft clays. Part II:Permeability characteristics[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1983,20(4):645 − 660. doi: 10.1139/t83-073
-




 下载:
下载: