Experimental study on engineering properties of red clay modified by sodium polyacrylate
-
摘要:
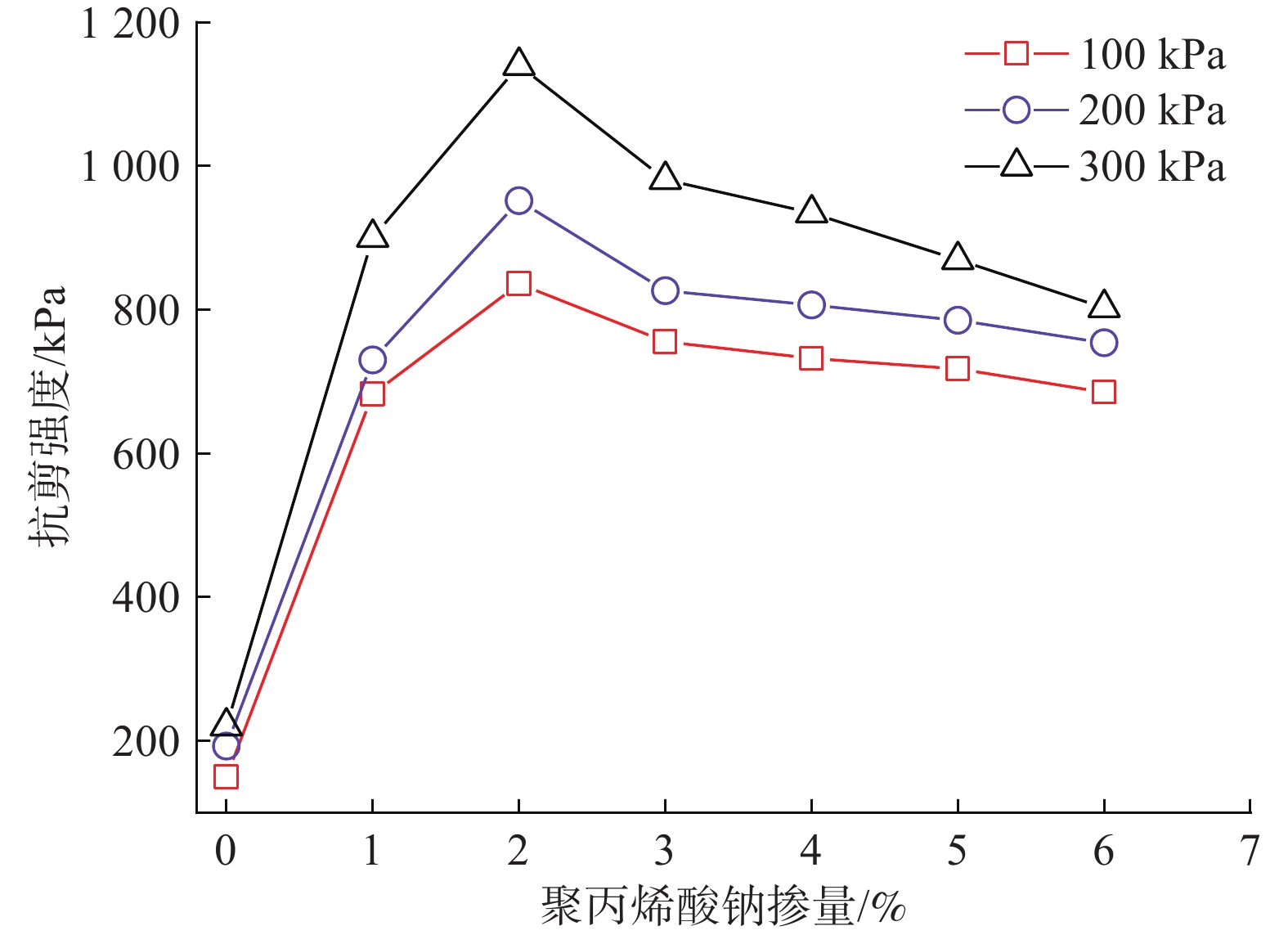
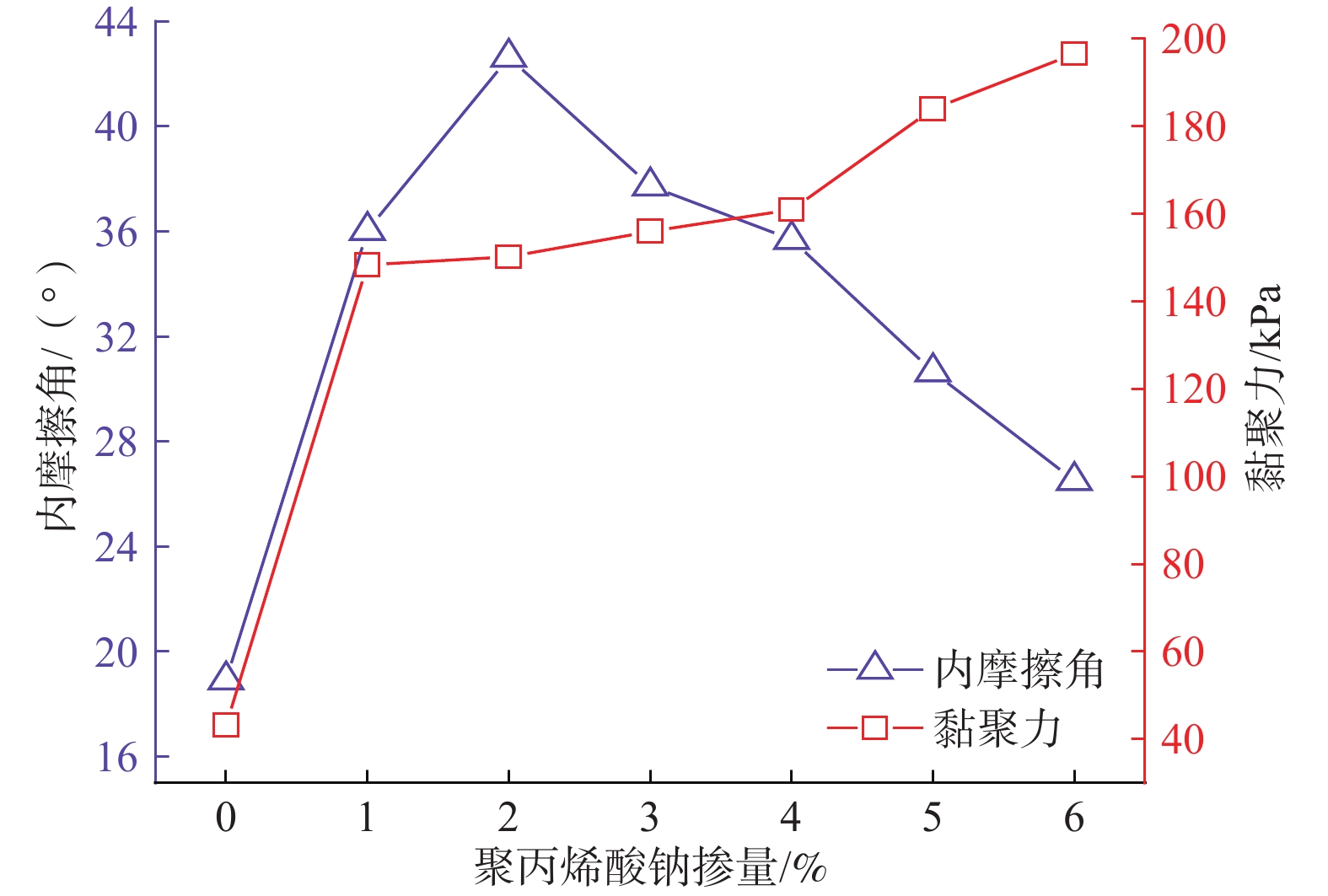
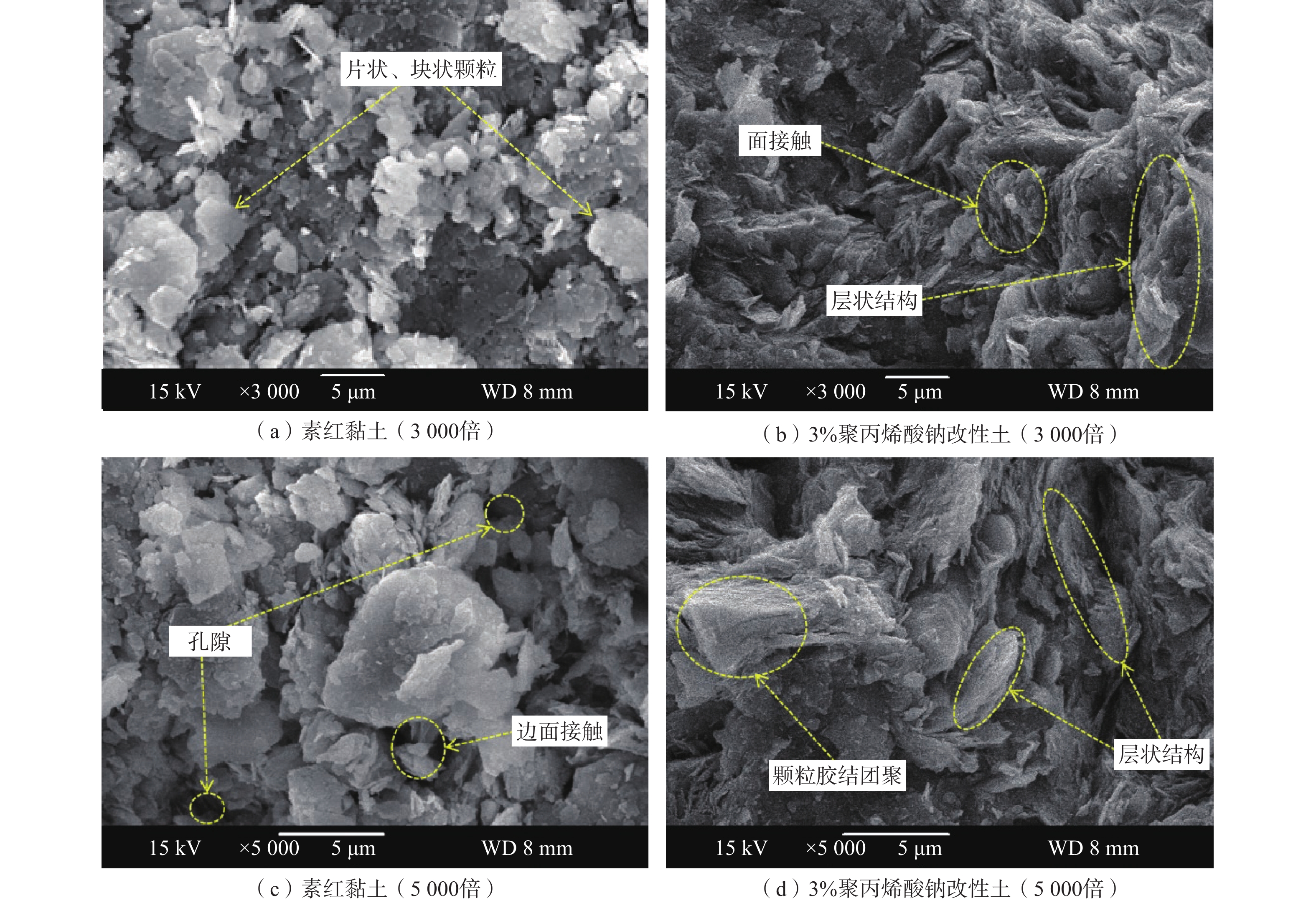
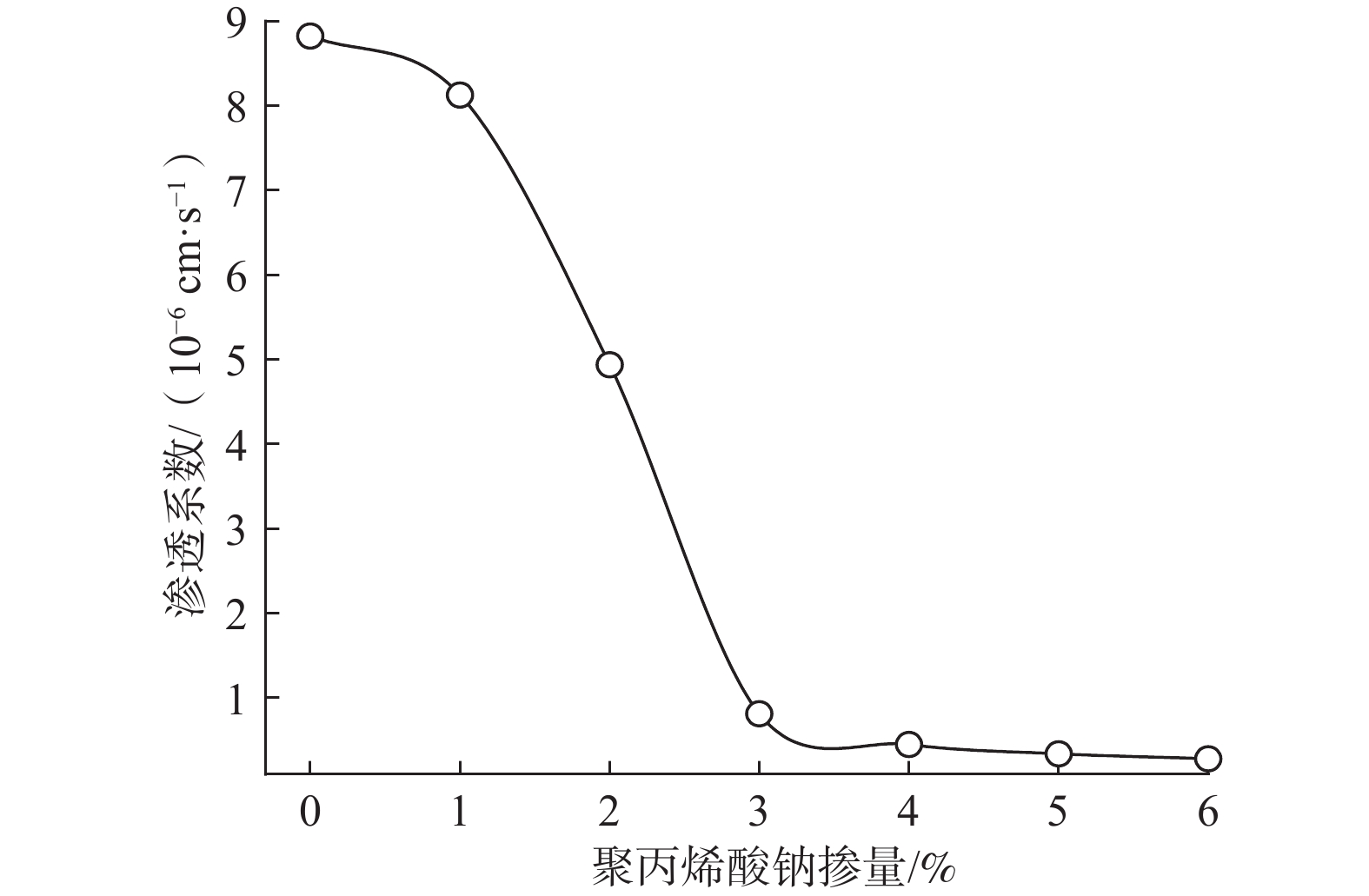
为研究聚丙烯酸钠改性红黏土的工程特性,利用聚丙烯酸钠对柳州重塑红黏土进行固化处理,开展变水头渗透试验和三轴剪切试验,分析改性红黏土的渗透特性和力学性能,确定聚丙烯酸钠的最适掺量,并通过对最适改性土开展崩解试验和扫描电镜试验,确定改性红黏土的抗崩解性能,揭示聚丙烯酸钠改性红黏土的微观作用机理。结果表明:随聚丙烯酸钠掺量的增加,改性土的渗透系数呈现逐步下降的趋势,并在达到3%后逐渐趋于稳定,此时渗透系数为8.1379×10−7 cm/s,相对素红黏土降低了90.78%;而改性红黏土的抗剪强度呈现先增大后减小的趋势,并在2%时达到峰值,相对素红黏土提高了394.21%。综上确定聚丙烯酸钠的最适掺量为3%,此掺量下改性土的抗崩解性能提高了42.86%,土颗粒间的孔隙被聚合物链所填充,碎散的颗粒状红黏土变为连续状,排列结构与致密程度均优于素红黏土。经聚丙烯酸钠改性后,红黏土的防渗性能、力学性能与抗崩解性均存在明显提高,可以为实际工程提供理论指导。
Abstract:To study the engineering properties of red clay modified by sodium polyacrylate, the Liuzhou remodeled red clay cured by sodium polyacrylate was selected for the permeability test with variable head and triaxial shear test to analyze the permeability and mechanical properties of the modified red clay and to determine the optimum amount of sodium polyacrylate. The disintegration resistance and microscopic mechanism of the modified red clay were determined by the disintegration test and scanning electron microscope test, respectively. The results show that the permeability coefficient of the modified soil decreases gradually with the increase of sodium polyacrylate, and gradually stabilizes after reaching 3% with the permeability coefficient of 8.1379×10−7 cm/s, 90.78% lower than that of the plain soil. In contrast, the shear strength of the modified red clay shows an increasing trend firstly, then decreases, and then keeps stable at at 2%, which is 394.21% higher than that of the plain soil. The optimal dosage is 3%, and in such situation, the anti-disintegration performance of the modified soil is improved by 42.86%. The pores between the soil particles filled by polymer chains lead to the continuous fragmented granular red clay . The arrangement structure and denseness are better than those of the plain red clay. The impermeability, mechanical properties, and disintegration resistance of the red clay modified by sodium polyacrylate are significantly improved. This study can provide theoretical information for the practical engineering.
-
Key words:
- sodium polyacrylate /
- red clay /
- permeability /
- shear strength /
- disintegration resistance /
- microscopic mechanism
-

-
表 1 崩解过程
Table 1. Disintegration process
掺量
/%浸泡时间 5 s 5 min 20 min 1 h 2 h 3 h 4 h 5 h 0 吸水 吸水+
土颗粒剥落吸水+土颗粒剥落+
裂隙形成吸水+裂隙数量骤增+
大量崩解吸水+崩解加剧 几乎崩解完毕+
崩解减缓完全崩解 完全崩解 3 吸水 吸水 吸水速率减缓 吸水+土颗粒剥落 吸水+裂隙形成+稳定崩解 吸水+裂隙发展+稳定崩解 吸水+裂隙发展+崩解减缓 完全崩解 -
[1] 穆锐,黄质宏,姚未来,等. 分级循环荷载下原状红黏土动力特性试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(3):94 − 102. [MU Rui,HUANG Zhihong,YAO Weilai,et al. An experimental study of the dynamic characteristics of the undisturbed laterite under graded cyclic loading[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(3):94 − 102. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
MU Rui, HUANG Zhihong, YAO Weilai, et al. An experimental study of the dynamic characteristics of the undisturbed laterite under graded cyclic loading[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(3): 94 − 102. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 陈佳雨,刘之葵,陈永国,等. 纤维红黏土强度的正交试验及多元非线性回归分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(1):117 − 124. [CHEN Jiayu,LIU Zhikui,CHEN Yongguo,et al. Orthogonal test and multivariate nonlinear regression analyses of strength of the fiber red clay[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(1):117 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Jiayu, LIU Zhikui, CHEN Yongguo, et al. Orthogonal test and multivariate nonlinear regression analyses of strength of the fiber red clay[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(1): 117 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 蒋文宇. 广西红黏土土质特征及土性改良研究[D]. 南宁:广西大学,2015. [JIANG Wenyu. Study on soil characteristics and filling performance of Guangxi red clay[D]. Nanning:Guangxi University,2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
JIANG Wenyu. Study on soil characteristics and filling performance of Guangxi red clay[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 王泽成,李栋伟,张潮潮,等. 考虑含水率对人工冻结红黏土力学特性的影响[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(6):287 − 293. [WANG Zecheng,LI Dongwei,ZHANG Chaochao,et al. Effect of water content on the mechanical properties of artificially frozen red clay[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(6):287 − 293.(in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Zecheng, LI Dongwei, ZHANG Chaochao, et al. Effect of water content on the mechanical properties of artificially frozen red clay[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(6): 287 − 293.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 侯正伟,李建宏,李财生,等. 椰纤维生物炭及其硝酸改性对稻田土壤中Pb钝化的影响[J]. 环境科学,2023,44(8):4497 − 4506. [HOU Zhengwei,LI Jianhong,LI Caisheng,et al. Effect of coconut fiber biochar and its nitrate modification on Pb passivation in paddy soils[J]. Environmental Science,2023,44(8):4497 − 4506. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HOU Zhengwei, LI Jianhong, LI Caisheng, et al. Effect of coconut fiber biochar and its nitrate modification on Pb passivation in paddy soils[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(8): 4497 − 4506. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] TAMASSOKI S,DAUD N N N,JAKARNI F M,et al. Compressive and shear strengths of coir fibre reinforced activated carbon stabilised lateritic soil[J]. Sustainability,2022,14(15):9100. doi: 10.3390/su14159100
[7] ALMAJED A,LATEEF M A,ALI BAIG MOGHAL A,et al. State-of-the-art review of the applicability and challenges of microbial-induced calcite precipitation (MICP) and enzyme-induced calcite precipitation (EICP) techniques for geotechnical and geoenvironmental applications[J]. Crystals,2021,11(4):370. doi: 10.3390/cryst11040370
[8] AHENKORAH I,RAHMAN M M,KARIM M R,et al. Enzyme induced calcium carbonate precipitation and its engineering application:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,308:125000. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125000
[9] 余梦,张家铭,周杨,等. MICP技术改性膨胀土试验研究[J]. 长江科学院院报,2021,38(5):103 − 108. [YU Meng,ZHANG Jiaming,ZHOU Yang,et al. Experimental study on modifying expansive soil by MICP technology[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2021,38(5):103 − 108. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YU Meng, ZHANG Jiaming, ZHOU Yang, et al. Experimental study on modifying expansive soil by MICP technology[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2021, 38(5): 103 − 108. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 张茜,叶为民,刘樟荣,等. 基于生物诱导碳酸钙沉淀的土体固化研究进展[J]. 岩土力学,2022,43(2):345 − 357. [ZHANG Qian,YE Weimin,LIU Zhangrong,et al. Advances in soil cementation by biologically induced calcium carbonate precipitation[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2022,43(2):345 − 357. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Qian, YE Weimin, LIU Zhangrong, et al. Advances in soil cementation by biologically induced calcium carbonate precipitation[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2022, 43(2): 345 − 357. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] POONI J,GIUSTOZZI F,ROBERT D,et al. Durability of enzyme stabilized expansive soil in road pavements subjected to moisture degradation[J]. Transportation Geotechnics,2019,21:100255. doi: 10.1016/j.trgeo.2019.100255
[12] 裴向军,杨晴雯,许强,等. 改性钠羧甲基纤维素胶结固化土质边坡机制与抗冲蚀特性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(11):2316 − 2327. [PEI Xiangjun,YANG Qingwen,XU Qiang,et al. Research on glue reinforcement mechanism and scouring resistant properties of soil slopes by modified carboxymethyl cellulose[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(11):2316 − 2327. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
PEI Xiangjun, YANG Qingwen, XU Qiang, et al. Research on glue reinforcement mechanism and scouring resistant properties of soil slopes by modified carboxymethyl cellulose[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(11): 2316 − 2327. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] SOLDO A,MILETIĆ M. Study on shear strength of xanthan gum-amended soil[J]. Sustainability,2019,11(21):6142. doi: 10.3390/su11216142
[14] KARIMI S,LASHKAR-ARA B,NAJAFI L. Influence of sugarcane molasses addition on the shear strength properties of slightly plastic loamy soils[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2022,15(9):903. doi: 10.1007/s12517-021-09395-z
[15] 杨万里,石玉玲,穆鹏雪,等. 瓜尔豆胶固化黄土的工程特性及抗冲蚀试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(4):117 − 124. [YANG Wanli,SHI Yuling,MU Pengxue,et al. An experimental study of the engineering properties and erosion resistance of guar gum-reinforced loess[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(4):117 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YANG Wanli, SHI Yuling, MU Pengxue, et al. An experimental study of the engineering properties and erosion resistance of guar gum-reinforced loess[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(4): 117 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 王章琼,高云,沈雷,等. 石灰改性红砂岩残积土工程性质试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(2):416 − 421. [WANG Zhangqiong,GAO Yun,SHEN Lei,et al. Engineering properties of lime-modifiedred sandstone residual soil[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(2):416 − 421. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Zhangqiong, GAO Yun, SHEN Lei, et al. Engineering properties of lime-modifiedred sandstone residual soil[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(2): 416 − 421. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] YANG Wenrui,ZHOU Feng,ZHU Rui,et al. Strength performance of mucky silty clay modified using early-age fly ash-based curing agent[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials,2022,17:e01595. doi: 10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e01595
[18] 易富,管茂成,李军,等. 稻壳灰-地聚物固化土力学特性及机理分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(2):94 − 101. [YI Fu,GUAN Maocheng,LI Jun,et al. Mechanical properties and mechanism analyses of rice husk ash geopolymer solidified soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(2):94 − 101. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YI Fu, GUAN Maocheng, LI Jun, et al. Mechanical properties and mechanism analyses of rice husk ash geopolymer solidified soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(2): 94 − 101. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 吴雪婷,项伟,王臻华,等. 离子土固化剂固化淤泥的微观机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(5):1285 − 1291. [WU Xueting,XIANG Wei,WANG Zhenhua,et al. Microscopic mechanism of solidified silt with ionic soil stabilizer[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(5):1285 − 1291. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WU Xueting, XIANG Wei, WANG Zhenhua, et al. Microscopic mechanism of solidified silt with ionic soil stabilizer[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(5): 1285 − 1291. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 游庆龙,邱欣,杨青,等. 离子土壤固化剂固化红黏土强度特性[J]. 中国公路学报,2019,32(5):64 − 71. [YOU Qinglong,QIU Xin,YANG Qing,et al. Strength properties of ionic soil stabilizer treated red soil[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport,2019,32(5):64 − 71. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YOU Qinglong, QIU Xin, YANG Qing, et al. Strength properties of ionic soil stabilizer treated red soil[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(5): 64 − 71. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 牛鹏尧,庄建琦,贾珂程,等. 聚丙烯酸钠混合剂固化黄土特性研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(4):1028 − 1035. [NIU Pengyao,ZHUANG Jianqi,JIA Kecheng,et al. Study on properties of loess solidified by polyacrylate sodium[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(4):1028 − 1035. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
NIU Pengyao, ZHUANG Jianqi, JIA Kecheng, et al. Study on properties of loess solidified by polyacrylate sodium[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2022, 30(4): 1028 − 1035. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] BIAN Xia,ZENG Lingling,LI Xiaozhao,et al. Fabric changes induced by super-absorbent polymer on cement–lime stabilized excavated clayey soil[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering,2021,13(5):1124 − 1135.
[23] BIAN Xia,DING Guoquan,WANG Zhifeng,et al. Compression and strength behavior of cement–lime–polymer-solidified dredged material at high water content[J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology,2017,35(6):840 − 846.
[24] BIAN Xia,WANG Zhifeng,DING Guoquan,et al. Compressibility of cemented dredged clay at high water content with super-absorbent polymer[J]. Engineering Geology,2016,208:198 − 205. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.04.036
[25] BIAN Xia,ZENG Lingling,DENG Yongfeng,et al. The role of superabsorbent polymer on strength and microstructure development in cemented dredged clay with high water content[J]. Polymers,2018,10(10):1069. doi: 10.3390/polym10101069
[26] 康祺祯,李静静,李育超,等. PAA-Na改性膨润土在酸碱盐溶液中的渗透性[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版),2021,55(10):1877 − 1884. [KANG Qizhen,LI Jingjing,LI Yuchao,et al. Permeability of sodium polyacrylate modified calcium bentonite in acid-base salt solution[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science),2021,55(10):1877 − 1884. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
KANG Qizhen, LI Jingjing, LI Yuchao, et al. Permeability of sodium polyacrylate modified calcium bentonite in acid-base salt solution[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2021, 55(10): 1877 − 1884. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 王玲玲,隋雪,谢宇航,等. 聚丙烯酸钠对透水混凝土物理力学性能影响研究[J]. 混凝土,2020(2):57 − 60. [WANG Lingling,SUI Xue,XIE Yuhang,et al. Effects of sodium polyacrylate on physical properties and mechanical behaviors of pervious concrete[J]. Concrete,2020(2):57 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Lingling, SUI Xue, XIE Yuhang, et al. Effects of sodium polyacrylate on physical properties and mechanical behaviors of pervious concrete[J]. Concrete, 2020(2): 57 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] AZARIJAFARI H,KAZEMIAN A,RAHIMI M,et al. Effects of pre-soaked super absorbent polymers on fresh and hardened properties of self-consolidating lightweight concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2016,113:215 − 220. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.03.010
[29] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 土工试验方法标准:GB/T 50123—2019[S]. 北京:中国计划出版社,2019. [Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for soil test methods:GB/T 50123—2019[S]. Beijing:China Planning Press,2019. (in Chinese)]
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for soil test methods: GB/T 50123—2019[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2019. (in Chinese)
[30] TIAN Kuo,LIKOS W J,BENSON C H. Pore-scale imaging of polymer-modified bentonite in saline solutions[C]//Geo-Chicago 2016. Chicago,Illinois. Reston,VA:American Society of Civil Engineers,2016:468 − 477.
[31] GEORGEES R N,HASSAN R A,EVANS R P,et al. Effect of the use of a polymeric stabilizing additive on unconfined compressive strength of soils[J]. Transportation Research Record:Journal of the Transportation Research Board,2015,2473(1):200 − 208. doi: 10.3141/2473-23
-



 下载:
下载: