Identifying the evolution of water balance and influencing factors in the mountainous area of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei
-
摘要:
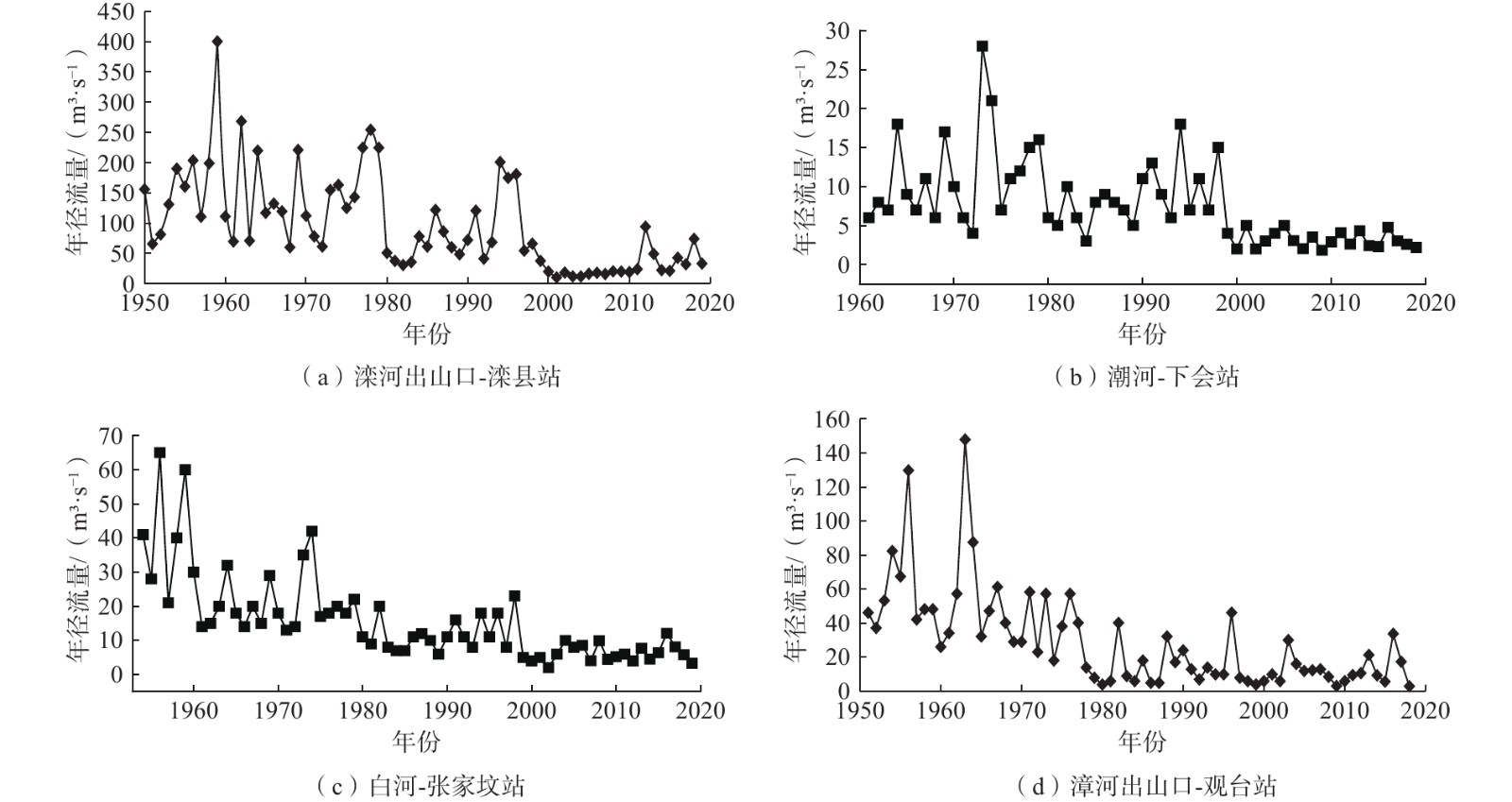
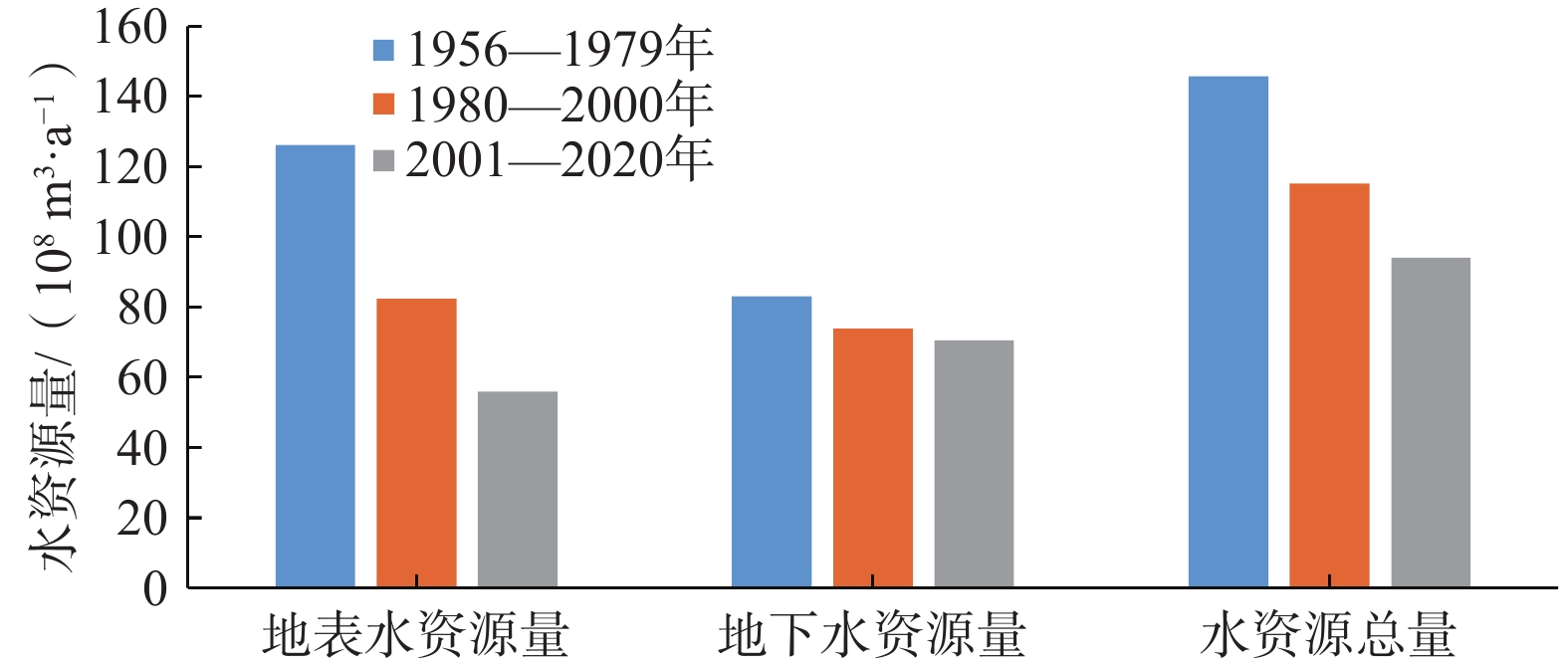
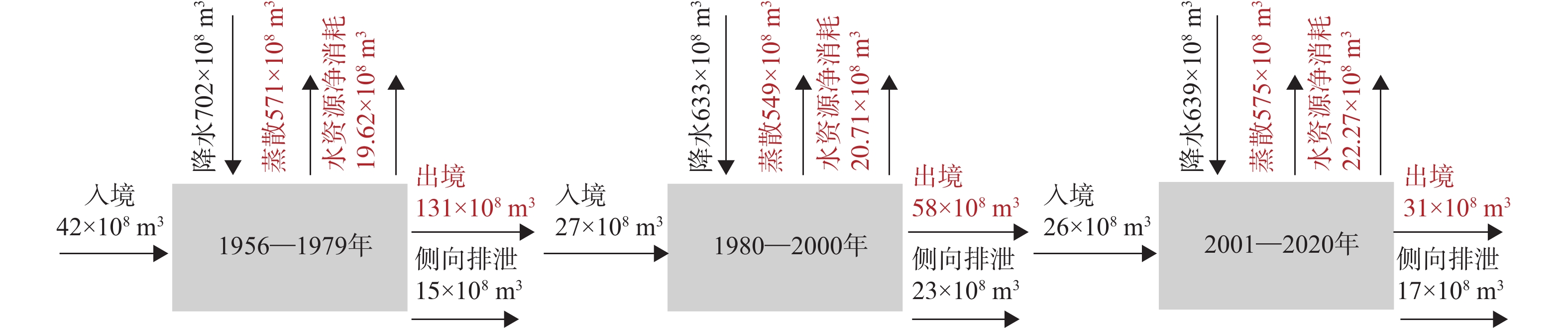
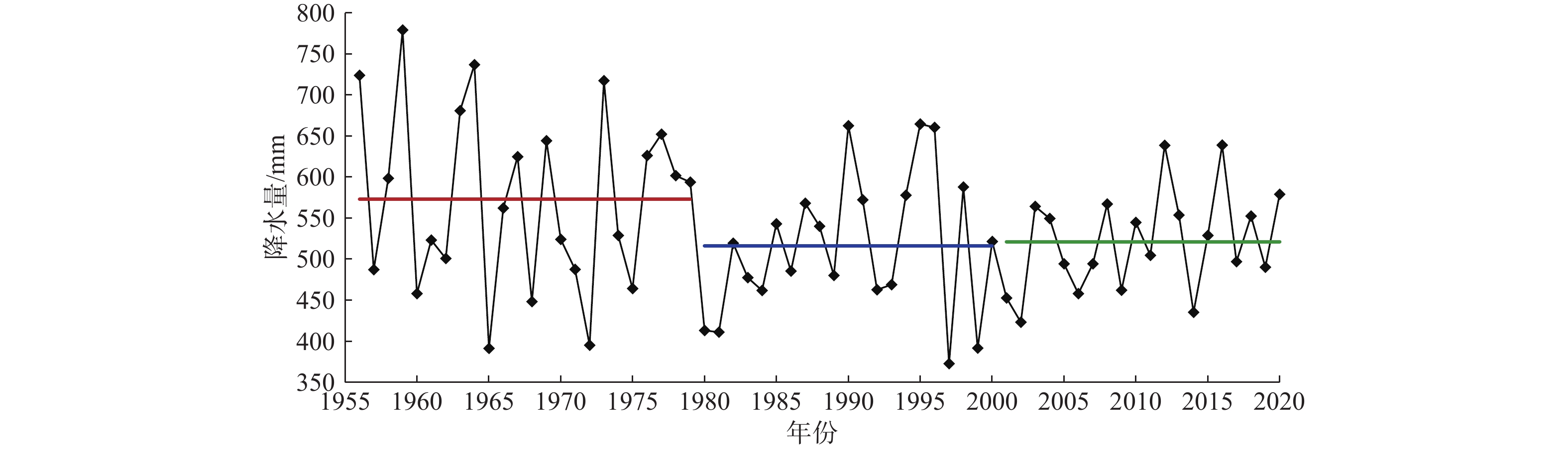
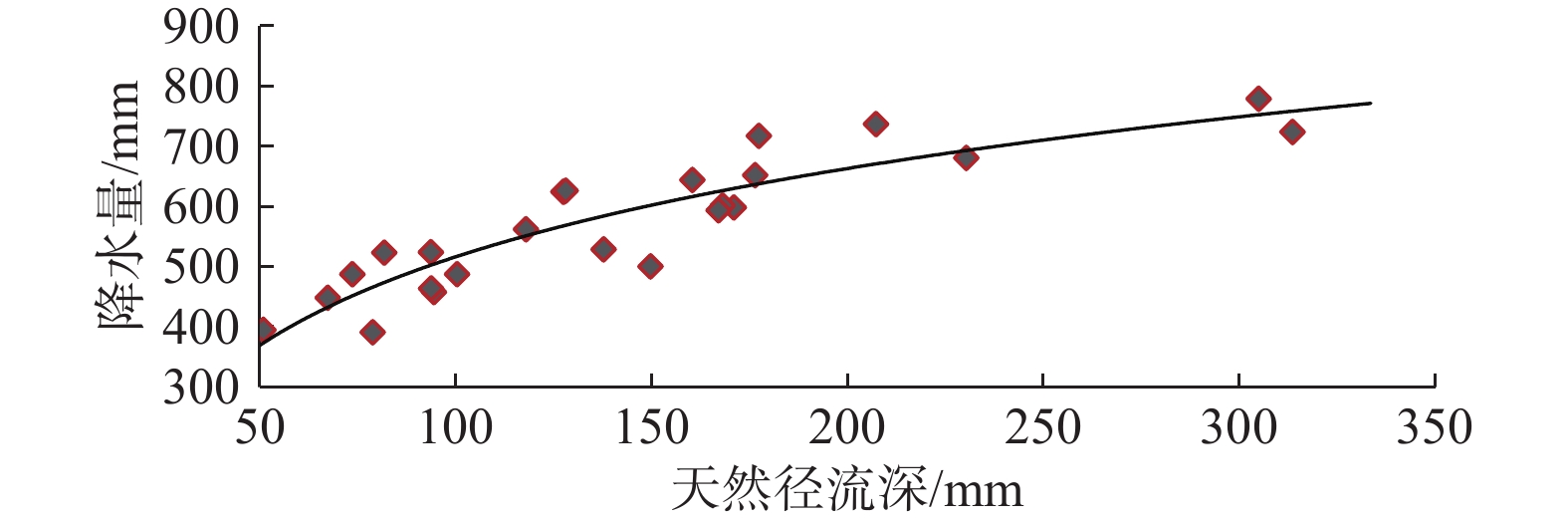
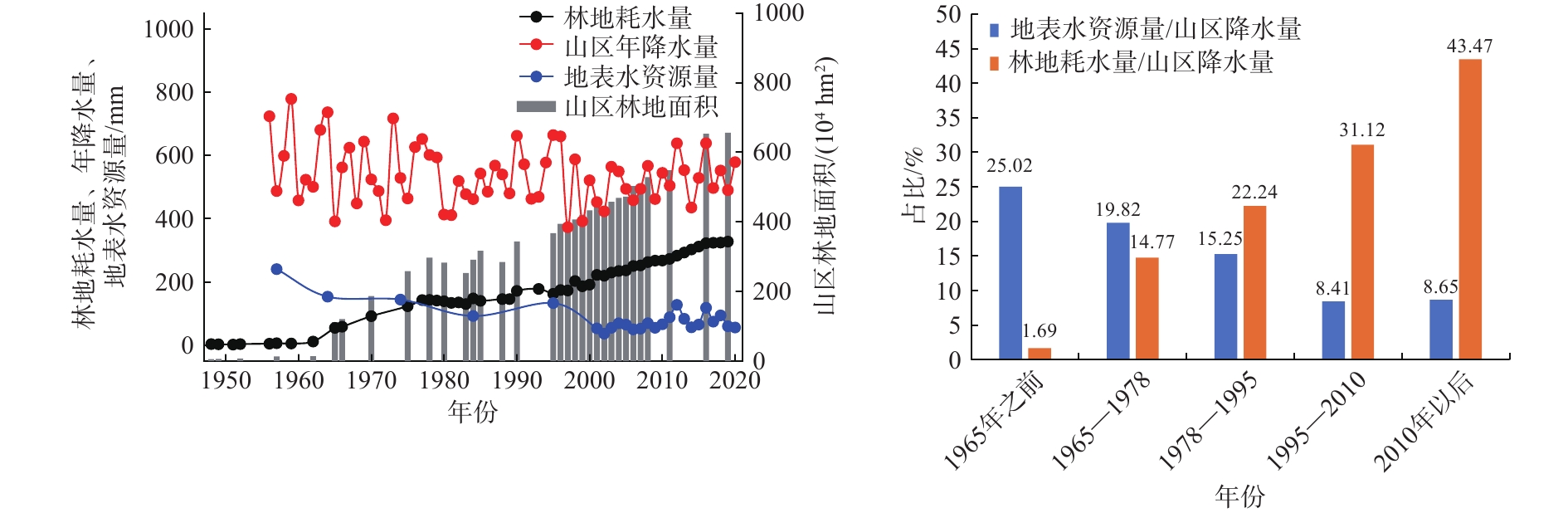
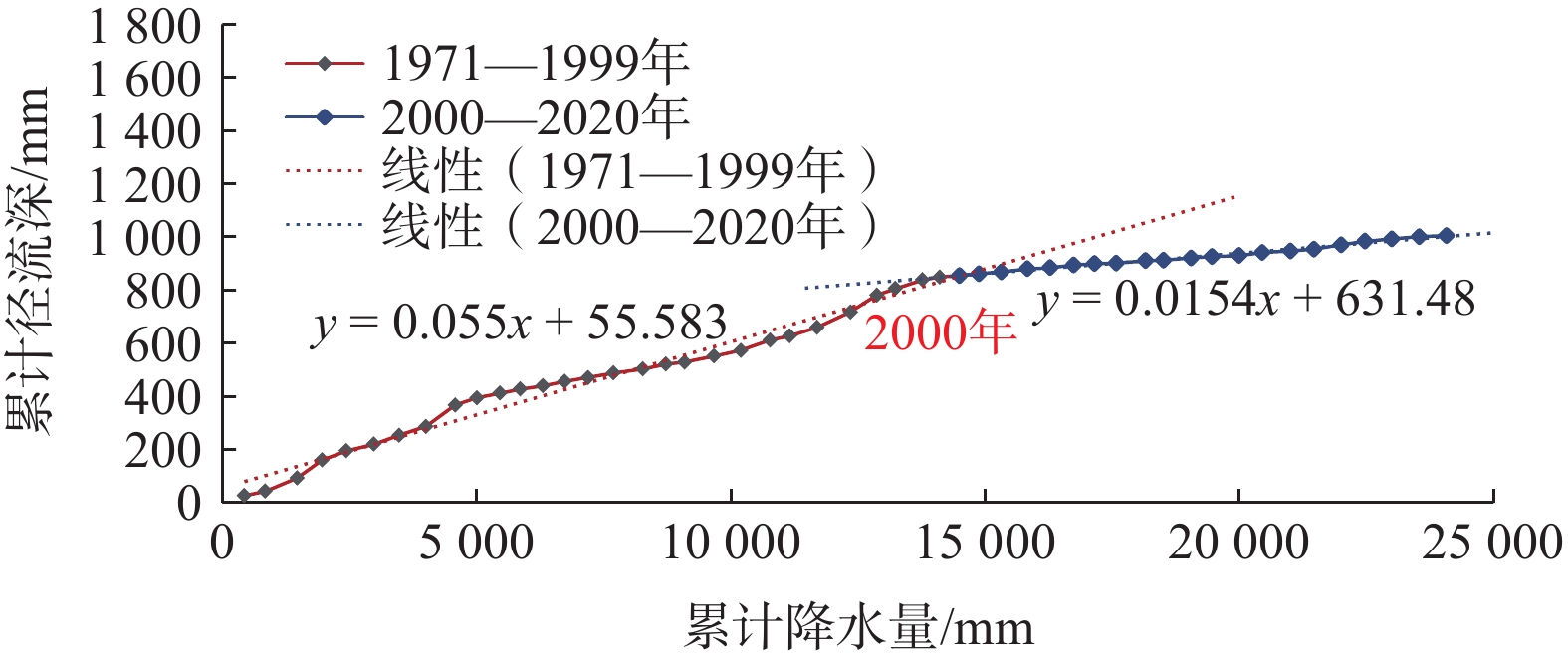
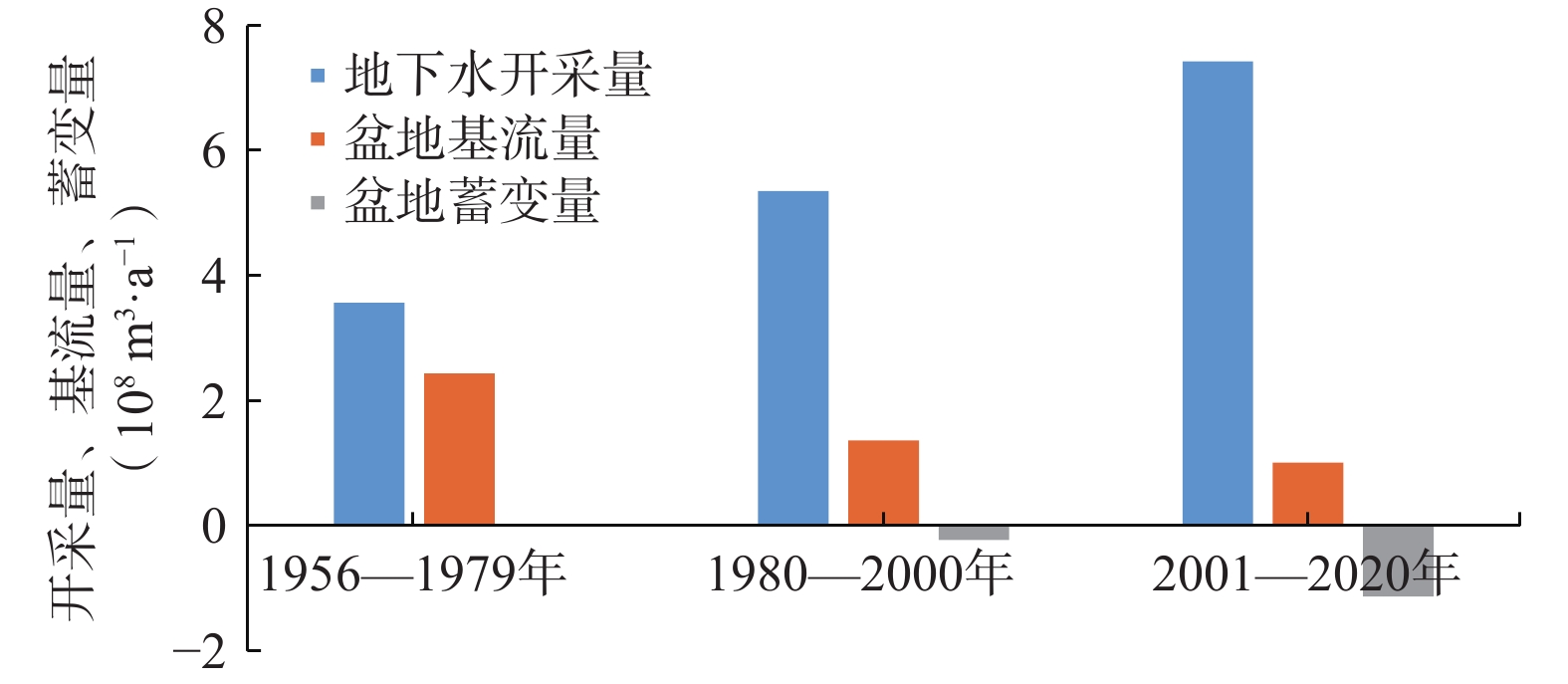
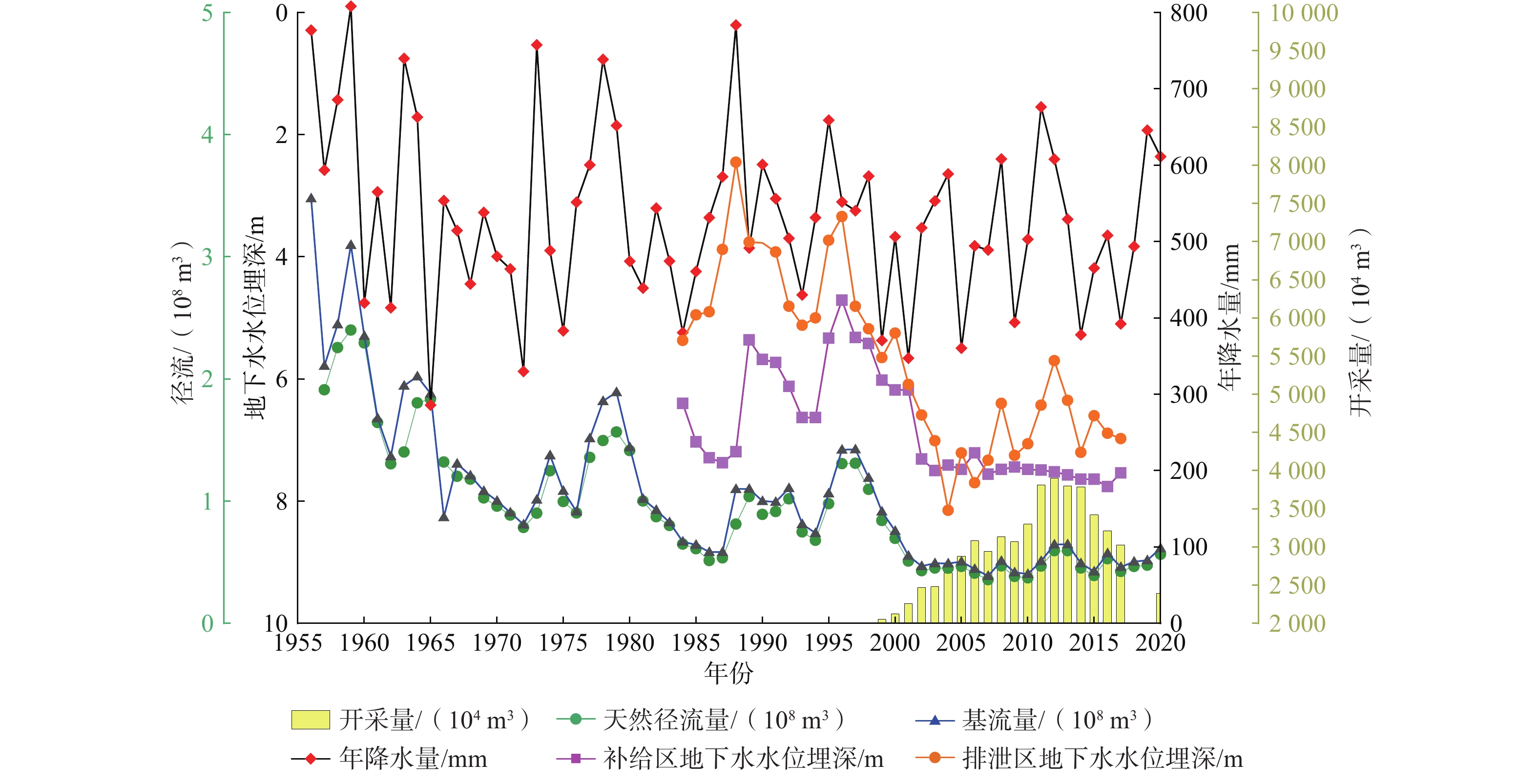
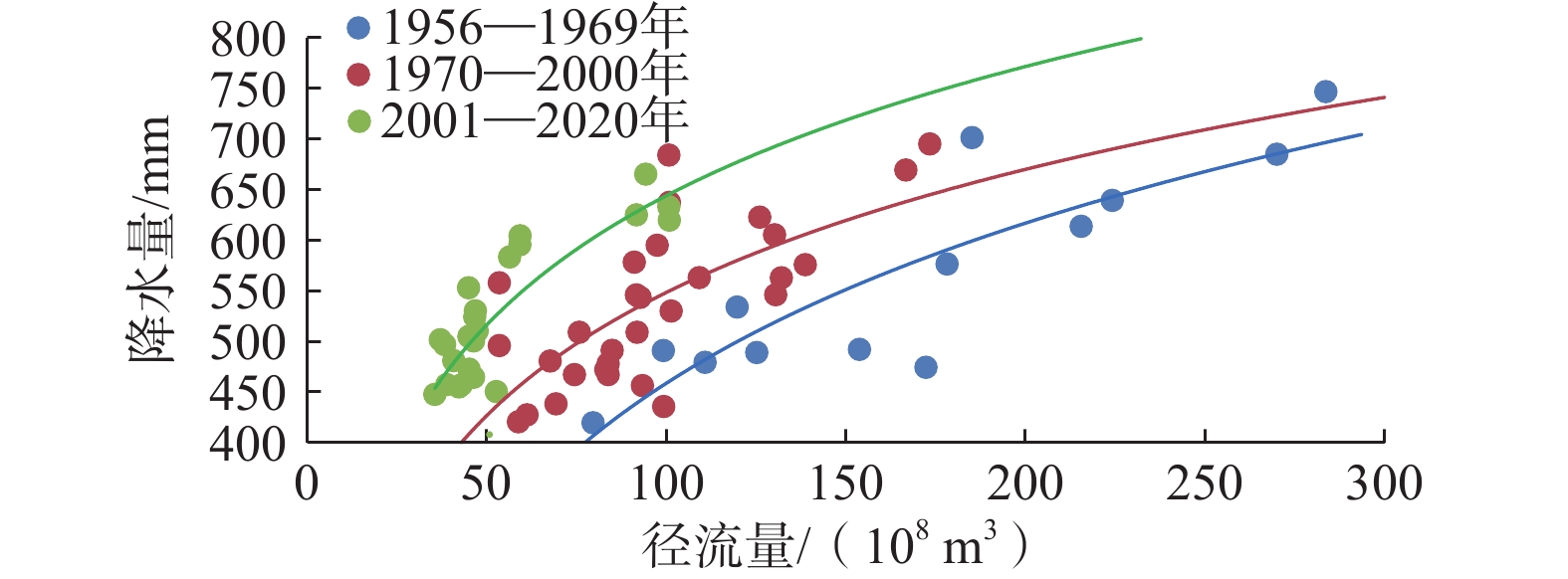
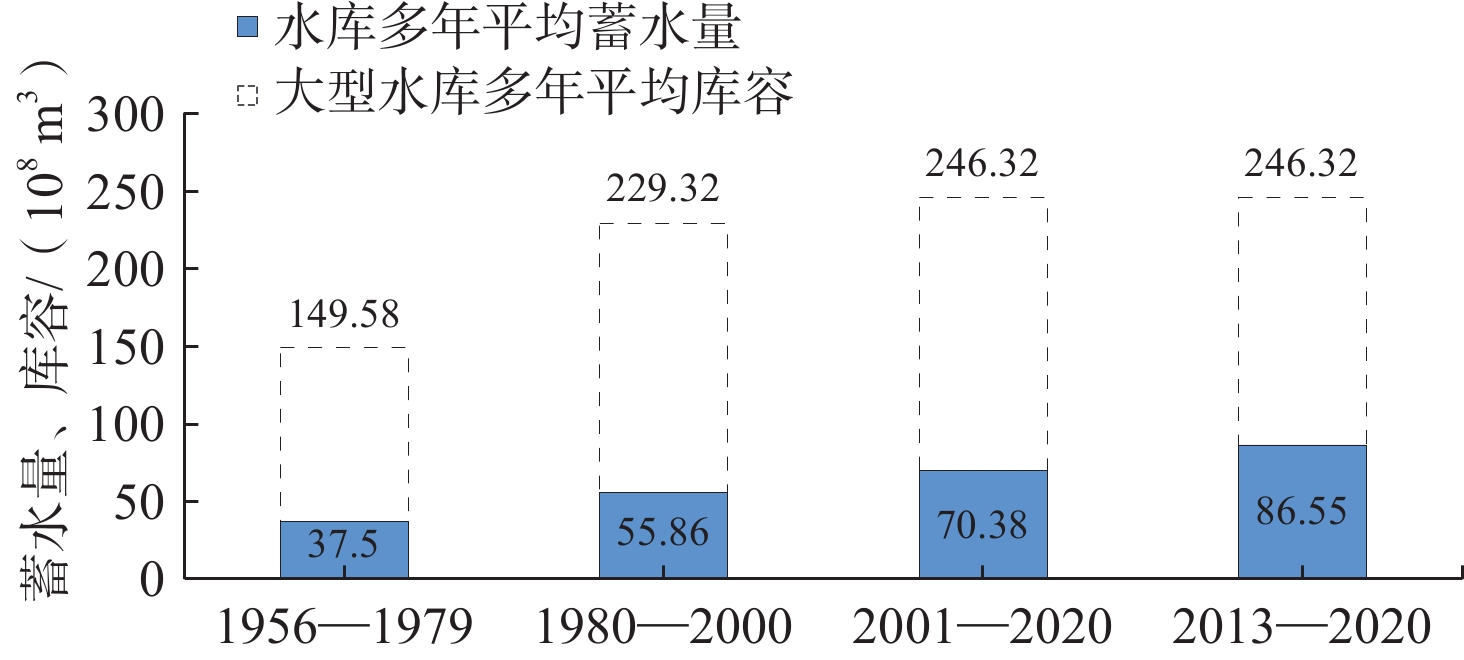
定量识别水平衡演变影响因素及其贡献是开展生态环境保护和水资源科学管理的前提。以往成果对人类活动中不同影响因子的归因识别与定量研究较少。在识别京津冀山区水平衡演变的基础上,采用双累计曲线法、径流变化定量分离法分析了降水变化和人类活动对水平衡演变的影响;分别选择涞源盆地、清水河小流域,分析了用水增加以及林业耗水增加对水平衡演变的影响。结果显示:(1)近65 a来,京津冀山区年降水量总体呈缓慢减少趋势,速率为0.97 mm/a,21世纪以来,年降水量有小幅增加趋势;(2)相比于1956—1979年基准期,1980—2000年降水变化和人类活动对天然径流衰减的影响程度分别为49.25%、50.75%,水土保持和植树造林是影响水平衡变化的主要人类活动因素,2001—2020年天然径流衰减的主要原因为人类活动,影响程度达到68.2%,其中地下水开采增加是主要人类活动因素,林业耗水量增加是重要人类活动因素;(3)山区水库蓄水及用水增加直接造成实际径流衰减,是造成平原区水平衡加剧的主要原因;(4)清水河小流域研究结果表明,在一定规模下,林地耗水增加与山区径流衰减呈正相关关系。林地面积增加对径流衰减的影响存在15~20 a的滞后性。林地面积达到23.48%后,林地耗水增加对天然径流产生了明显负作用,平均每增加1 km2林地,耗水量增加37.25×104 m3/a,天然径流量衰减59×104 m3/a,林地年均耗水增加量占流域天然径流衰减量的63.22%,表明林地面积增加起到水源涵养的作用,同时也造成了有效径流的减少。研究成果对开展京津冀山区生态环境保护、水资源科学管理以及水平衡调控具有重要意义。
Abstract:Quantitatively identifying the effects and contributions on the water balance evolution is the premise of ecological environmental protection and scientific management of water resources. However, most of the previous studies focused on the effects of climate change and human activities on runoff attenuation; few studies paid attention to the attribution and quantitative identification of different factors in human activities. On the basis of identifying the evolution process of water balance in the study area, the effects of precipitation change and human activities on the evolution of water balance at different time periods were analyzed by using the double cumulative curve method and the quantitative separation method of runoff change. The effects of the increase of water resource exploitation and forestry water consumption on water balance evolution were analyzed in the Laiyuan Basin and Qingshuihe Basin, respectively. The results show that: (1) The annual precipitation presented a slightly decreasing trend with a decreasing rate of 0.97 mm/a in the past 65 years; since the 21st century, precipitation has increased slightly. (2) Compared with the period of 1956−1979, the natural runoff attenuation during 1980−2000 was affected by precipitation change and human activities, with corresponding contributions of 49.25% and 50.75%, respectively. Soil and water conservation and afforestation are the main factors of human activity affecting the change of water balance. the decrease in natural runoff was mainly caused by human activities, with the influence contribution of 68.2%. The increase of groundwater exploitation was the main factor of human activity, and the increase of water consumption was the second factor of human activity. (3) The increase in reservoir storage and water consumption in mountainous areas led to the actual runoff attenuation directly, which was the main reason for the intensification of water balance in the plain areas. (4) In the Qingshuihe River Basin, there was a positive correlation between the increase of forest water consumption and the decline of mountain runoff at a certain scale. The effect of runoff attenuation on the increase of forest area was not immediate, with a lag of 15−20 a. As the forest area reached 23.48%, the increase in forest water consumption had a significant negative effect on the natural runoff. An average increase of 1 km2 of forest land led to water consumption being increased by 37.25×104 m3/a, and the natural runoff being decreased by 59×104 m3/a. The increase in annual water consumption of forest land accounted for 63.22% of the natural runoff attenuation. It indicated that the increase in forest area played an important role in water conservation, resulting in a decrease in effective runoff. The results of the study are of great significance for the ecological and environmental protection, scientific management of water resources and regulation of water balance in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei mountain area.
-

-
表 1 京津冀山区天然径流衰减定量分析
Table 1. Quantitative analysis of natural runoff attenuation
阶段 降水量/mm 天然径流深/mm 总变化量/mm 降水变化影响 人类活动影响 数量/mm 比例/% 数量/mm 比例/% 1956—1979 572.96 130.23 1980—2000 516.33 74.24 −56.0 −27.58 49.25 −28.42 50.75 2001—2020 521.44 50.43 −79.80 −25.38 31.81 −54.42 68.19 表 2 京津冀山区土地利用占比
Table 2. The variation of proportion of land use
年份 林地面积占比/% 草地面积占比/% 梯田面积占比/% 1985 35.87 32.22 31.91 1990 36.62 31.79 31.59 2000 40.35 30.77 28.88 2010 43.38 30.79 25.83 2020 46.21 27.62 26.17 表 3 清水河流域现状树种面积及其占比[43]
Table 3. The area and proportion of the tree species in the Qingshuihe River Basin
树种 白桦 华北落叶松 杨树 蒙古栎 白榆 柳 八棱海棠 油松 樟子松 云杉 沙棘 山杏 枸杞 果木类 面积/km2 239.1 178.7 58.3 14.6 22.5 0.2 0.12 35.3 0.55 1.46 1.08 306.2 0.1 18.0 占比/% 27.29 20.40 6.65 1.67 2.57 0.02 0.01 4.03 0.06 0.17 0.12 34.95 0.01 2.05 树种 生长月份 胸径/cm 树高/m 生长季平均耗水量
/(kg·a−1)白桦 4—10 10.2~21.9 9.8~10.6 10743.32 杨树 4—10 15.6~29.5 6.5~12.5 7452.00 蒙古栎 4—10 12.3~25.6 5.5~10.8 207.74 白榆 4—10 4.0~9.5 5.0~10.5 539.41 旱柳 4—10 8.6~15.6 4.5~6.5 1494.00 华北落叶松 4—10 13.5~20.3 9.5~10.8 2455.41 油松 4—11 12.3~21.8 8.6~10.2 2696.08 樟子松 4—11 3.5~7.5 3.5~4.8 132.68 山杏 5—10 3.5~8.3 1.0~2.5 76.60 果木类 4—9 4.5~7.8 2.0~3.5 600.00 表 5 清水河流域林地耗水情况
Table 5. Water consumption of forest land in Qingshui River Basin
年份 林地面积/km2 林地耗水量/108 m3 1985 437.65 1.168 1990 439.12 1.379 1995 460.21 1.561 2000 558.95 1.492 2005 646.15 1.725 2010 663.13 2.083 2015 929.18 2.481 2020 1009.75 3.172 表 6 涞源盆地天然径流衰减贡献分析
Table 6. Analysis on contribution of natural runoff attenuation in the Laiyuan Basin
阶段 降水量/mm 天然径流深度/mm 总变化量/mm 气候变化影响 人类活动影响 地下水开采影响 数量/mm 占比/% 数量/mm 占比/% 数量/mm 占比/% 1956—1969 560.36 142.15 1970—2000 523.91 88.61 −53.54 −25.09 47 −28.44 53 2001—2020 508.21 46.08 −96.06 −34.55 36 −61.51 64 −26.96 28 -
[1] 王佰伟,张存龙,刘诗剑. 海河流域水资源量演变分析研究[J]. 上海国土资源,2022,43(3):15 − 18. [WANG Baiwei,ZHANG Cunlong,LIU Shijian. Study on the situation of water resource quantity change in the Haihe River Basin[J]. Shanghai Land & Resources,2022,43(3):15 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Baiwei, ZHANG Cunlong, LIU Shijian . Study on the situation of water resource quantity change in the Haihe River Basin[J]. Shanghai Land & Resources,2022 ,43 (3 ):15 −18 . (in Chinese with English abstract).[2] 任宪韶. 海河流域水资源评价[M]. 北京:中国水利水电出版社,2007. [REN Xianshao. Evaluation of water resources in Haihe River Basin[M]. Beijing:China Water & Power Press,2007. (in Chinese)
REN Xianshao. Evaluation of water resources in Haihe River Basin[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2007. (in Chinese) [3] 夏军. 变化环境下中国北方水循环与水安全研究面临的问题与展望——以华北地区水问题为例[C]//中国自然资源学会土地资源研究专业委员会. 中国土地资源态势与持续利用研究. 2004:45 − 52. [XIA Jun. Problems and perspective of water security to change environment in North China[C]//Land Resources Research Committee of China Society of Natural Resources. Research on the situation and sustainable utilization of land resources in China. 2004:45 − 52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XIA Jun. Problems and perspective of water security to change environment in North China[C]//Land Resources Research Committee of China Society of Natural Resources. Research on the situation and sustainable utilization of land resources in China. 2004: 45 − 52. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] 张兆吉,雒国中,王昭,等. 华北平原地下水资源可持续利用研究[J]. 资源科学,2009,31(3):355 − 360. [ZHANG Zhaoji,LUO Guozhong,WANG Zhao,et al. Study on sustainable utilization of groundwater in North China plain[J]. Resources Science,2009,31(3):355 − 360. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Zhaoji, LUO Guozhong, WANG Zhao, et al . Study on sustainable utilization of groundwater in North China plain[J]. Resources Science,2009 ,31 (3 ):355 −360 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[5] 郭海朋,李文鹏,王丽亚,等. 华北平原地下水位驱动下的地面沉降现状与研究展望[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(3):162 − 171. [GUO Haipeng,LI Wenpeng,WANG Liya,et al. Present situation and research prospects of the land subsidence driven by groundwater levels in the North China Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(3):162 − 171. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GUO Haipeng, LI Wenpeng, WANG Liya, et al . Present situation and research prospects of the land subsidence driven by groundwater levels in the North China Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021 ,48 (3 ):162 −171 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[6] 栗士棋,刘颖,程芳芳,等. 环境变化对水资源影响研究进展及其借鉴与启示[J]. 水利科学与寒区工程,2020,3(5):1 − 6. [LI Shiqi,LIU Ying,CHENG Fangfang,et al. Research progress and reference for the impact of environmental change on water resources[J]. Hydro Science and Cold Zone Engineering,2020,3(5):1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Shiqi, LIU Ying, CHENG Fangfang, et al . Research progress and reference for the impact of environmental change on water resources[J]. Hydro Science and Cold Zone Engineering,2020 ,3 (5 ):1 −6 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[7] 夏军,刘春蓁,任国玉. 气候变化对我国水资源影响研究面临的机遇与挑战[J]. 地球科学进展,2011,26(1):1 − 12. [XIA Jun,LIU Chunzhen,REN Guoyu. Opportunity and challenge of the climate change impact on the water resource of China[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2011,26(1):1 − 12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XIA Jun, LIU Chunzhen, REN Guoyu . Opportunity and challenge of the climate change impact on the water resource of China[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2011 ,26 (1 ):1 −12 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[8] 张士锋,贾绍凤. 降水不均匀性对黄河天然径流量的影响[J]. 地理科学进展,2001,20(4):355 − 363. [ZHANG Shifeng,JIA Shaofeng. A research of the impacts of uneven precipitation on the natural runoff in the Yellow River[J]. Progress in Geography,2001,20(4):355 − 363. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Shifeng, JIA Shaofeng . A research of the impacts of uneven precipitation on the natural runoff in the Yellow River[J]. Progress in Geography,2001 ,20 (4 ):355 −363 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[9] 王乐扬,李清洲,王金星,等. 变化环境下近60年来中国北方江河实测径流量及其年内分配变化特征[J]. 华北水利水电大学学报(自然科学版),2020,41(2):36 − 42. [WANG Yueyang,LI Qingzhou,WANG Jinxing,et al. The variation characteristics of recorded runoff and its annual distribution in North China during the recent 60 years in the context of environment change[J]. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (Natural Science Edition),2020,41(2):36 − 42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Yueyang, LI Qingzhou, WANG Jinxing, et al . The variation characteristics of recorded runoff and its annual distribution in North China during the recent 60 years in the context of environment change[J]. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (Natural Science Edition),2020 ,41 (2 ):36 −42 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[10] 师忱,袁士保,史常青,等. 滦河流域气候变化与人类活动对径流的影响[J]. 水土保持学报,2018,32(2):264 − 269. [SHI Chen,YUAN Shibao,SHI Changqing,et al. Effects of climate change and human activities on runoff in Luanhe Basin[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2018,32(2):264 − 269. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SHI Chen, YUAN Shibao, SHI Changqing, et al . Effects of climate change and human activities on runoff in Luanhe Basin[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2018 ,32 (2 ):264 −269 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[11] 王国庆,张建云,管晓祥,等. 中国主要江河径流变化成因定量分析[J]. 水科学进展,2020,31(3):313 − 323. [WANG Guoqing,ZHANG Jianyun,GUAN Xiaoxiang,et al. Quantifying attribution of runoff change for major rivers in China[J]. Advances in Water Science,2020,31(3):313 − 323. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Guoqing, ZHANG Jianyun, GUAN Xiaoxiang, et al . Quantifying attribution of runoff change for major rivers in China[J]. Advances in Water Science,2020 ,31 (3 ):313 −323 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[12] 秦鹏程,刘敏,夏智宏,等. 气候变化对我国水资源和重大水利工程影响研究进展[J]. 气象科技进展,2022,12(6):7 − 15. [QIN Pengcheng,LIU Min,XIA Zhihong,et al. Progress in assessing the impacts of climate change on China’s water resources and major water conservancy projects[J]. Advances in Meteorological Science and Technology,2022,12(6):7 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
QIN Pengcheng, LIU Min, XIA Zhihong, et al . Progress in assessing the impacts of climate change on China’s water resources and major water conservancy projects[J]. Advances in Meteorological Science and Technology,2022 ,12 (6 ):7 −15 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[13] 杨永辉,任丹丹,杨艳敏,等. 海河流域水资源演变与驱动机制[J]. 中国生态农业学报,2018,26(10):1443 − 1453. [YANG Yonghui,REN Dandan,YANG Yanmin,et al. Advances in clarification of the driving forces of water shortage in Haihe River Catchment[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture,2018,26(10):1443 − 1453. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YANG Yonghui, REN Dandan, YANG Yanmin, et al . Advances in clarification of the driving forces of water shortage in Haihe River Catchment[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture,2018 ,26 (10 ):1443 −1453 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[14] LIU Lüliu,DU Jianjun. Documented changes in annual runoff and attribution since the 1950s within selected rivers in China[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research,2017,8(1):37 − 47. doi: 10.1016/j.accre.2017.03.005
[15] 曾卉洁. 海河流域水资源衰减机理与演变预测[J]. 高科技与产业化,2022,28(5):30 − 35. [ZENG Huijie. Attenuation mechanism and evolution prediction of water resources in the Haihe River Basin[J]. High-Technology & Commercialization,2022,28(5):30 − 35. (in Chinese)
ZENG Huijie . Attenuation mechanism and evolution prediction of water resources in the Haihe River Basin[J]. High-Technology & Commercialization,2022 ,28 (5 ):30 −35 . (in Chinese)[16] 水利部水利水电规划设计总院. 中国水资源及其开发利用调查评价[M]. 北京:中国水利水电出版社,2014. [Investigation and evaluation of water resources and their development and utilization in China[M]. Beijing:China Water & Power Press,2014. (in Chinese)
Investigation and evaluation of water resources and their development and utilization in China[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2014. (in Chinese) [17] 姜萍. 1982-2015年中国植被覆盖变化及其对气候变化的敏感性分析[D]. 兰州:兰州大学,2022. [JIANG Ping. Analysis of vegetation change in China and its sensitivity to climate variability from 1982 to 2015[D]. Lanzhou:Lanzhou University,2022. (in Chinese with English abstract)
JIANG Ping. Analysis of vegetation change in China and its sensitivity to climate variability from 1982 to 2015[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] HUA Wenjian,CHEN Haishan,ZHU Siguang,et al. Hotspots of the sensitivity of the land surface hydrological cycle to climate change[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2013,58(30):3682 − 3688. doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5846-7
[19] 陈军锋,李秀彬. 森林植被变化对流域水文影响的争论[J]. 自然资源学报,2001,16(5):474 − 480. [CHEN Junfeng,LI Xiubin. The impact of forest change on watershed hydrology:Discussing some controversies on forest hydrology[J]. Journal of Natural Resources,2001,16(5):474 − 480. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHEN Junfeng, LI Xiubin . The impact of forest change on watershed hydrology: Discussing some controversies on forest hydrology[J]. Journal of Natural Resources,2001 ,16 (5 ):474 −480 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[20] 周金星,彭镇华,李世东. 森林生态工程建设对水资源的影响[J]. 世界林业研究,2002,15(6):54 − 60. [ZHOU Jinxing,PENG Zhenhua,LI Shidong. The relationship between forestry eco-engineering and water resource exploitation and utilization[J]. World Forestry Research,2002,15(6):54 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHOU Jinxing, PENG Zhenhua, LI Shidong . The relationship between forestry eco-engineering and water resource exploitation and utilization[J]. World Forestry Research,2002 ,15 (6 ):54 −60 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[21] 王礼先,张志强. 森林植被变化的水文生态效应研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究,1998,11(6):14 − 23. [WANG Lixian,ZHANG Zhiqiang. Advances in the study of ecohydrological effects from vegetation changes[J]. World Forestry Research,1998,11(6):14 − 23. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Lixian, ZHANG Zhiqiang . Advances in the study of ecohydrological effects from vegetation changes[J]. World Forestry Research,1998 ,11 (6 ):14 −23 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[22] 吕一河,胡健,孙飞翔,等. 水源涵养与水文调节:和而不同的陆地生态系统水文服务[J]. 生态学报,2015,35(15):5191 − 5196. [LÜ Yihe,HU Jian,SUN Feixiang,et al. Water retention and hydrological regulation:Harmony but not the same in terrestrial hydrological ecosystem services[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2015,35(15):5191 − 5196. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LÜ Yihe, HU Jian, SUN Feixiang, et al . Water retention and hydrological regulation: Harmony but not the same in terrestrial hydrological ecosystem services[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2015 ,35 (15 ):5191 −5196 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[23] 王新峰,刘蕴,李伟,等. 涞源盆地水文地质特征及缺水现状分析[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2012,10(6):74 − 78. [WANG Xinfeng,LIU Yun,LI Wei,et al. Analysis of hydrogeological conditions and water shortage status in the Laiyuan Basin[J]. South-to-North Water Diversion and Water Science & Technology,2012,10(6):74 − 78. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Xinfeng, LIU Yun, LI Wei, et al . Analysis of hydrogeological conditions and water shortage status in the Laiyuan Basin[J]. South-to-North Water Diversion and Water Science & Technology,2012 ,10 (6 ):74 −78 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[24] 杜兵建. 拒马河流域水文地质环境现状与思考[C]//京津冀六区市县协同发展研讨会论文集(地质水利篇). 2015. [DU Bingjian. Current situation and consideration of hydrogeological environment in Juma River Basin[C]//Proceedings of the Seminar on Coordinated Development of Cities and Counties in the Six Districts of Beijing,Tianjin and Hebei (Geology and Water Resources). 2015. (in Chinese)
DU Bingjian. Current situation and consideration of hydrogeological environment in Juma River Basin[C]//Proceedings of the Seminar on Coordinated Development of Cities and Counties in the Six Districts of Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei (Geology and Water Resources). 2015. (in Chinese) [25] 国家林业局. 中国林业年鉴[M]. 北京:中国林业出版社,1949 − 2020. [National Forestry Administration. China forestry yearbook [M]. Beijing:China Forestry Publishing House,1949 − 2020. (in Chinese)
National Forestry Administration. China forestry yearbook [M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 1949 − 2020. (in Chinese) [26] 河北省统计局. 河北省统计年鉴[M]. 北京:中国统计出版社,1985 − 2020. [Hebei Provincial Bureau of Statistics. Hebei statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing:China Statistics Press,1985 − 2020. (in Chinese)
Hebei Provincial Bureau of Statistics. Hebei statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 1985 − 2020. (in Chinese) [27] 北京市统计局. 北京市统计年鉴[M]北京:中国统计出版社,1980 − 2020. [Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Beijing statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing:China Statistics Press,1980 − 2020. (in Chinese)
Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Beijing statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 1980 − 2020. (in Chinese) [28] 天津市统计局,国家统计局天津调查总队. 天津市统计年鉴[M]. 北京:中国统计出版社,2002 − 2020. [Tianjin Bureau of Statistics,National Bureau of Statistics Tianjin Survey Team. Tianjin statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing:China Statistics Press,2002 − 2020. (in Chinese)
Tianjin Bureau of Statistics, National Bureau of Statistics Tianjin Survey Team. Tianjin statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2002 − 2020. (in Chinese) [29] 孟瑞芳,杨会峰,白华,等. 华北地区地下水资源评价[R]. 石家庄:中国地质科学院水文地质环境地质研究所,2021. [MENG Ruifang,YANG Huifeng,BAI Hua et al. Evaluation of groundwater resources in North China[R]. Shijiazhuang:Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology,Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences,2021. (in Chinese)
MENG Ruifang, YANG Huifeng, BAI Hua et al. Evaluation of groundwater resources in North China[R]. Shijiazhuang: Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2021. (in Chinese) [30] 杨会峰,白华. 京津冀地区地表水及浅层地下水资源调查评价[R]. 石家庄:中国地质科学院水文地质环境地质研究所,2020. [YANG Huifeng,BAI Hua. Investigation and evaluation of surface water and shallow groundwater resources in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region[R]. Shijiazhuang:Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology,Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences,2020. (in Chinese)
YANG Huifeng, BAI Hua. Investigation and evaluation of surface water and shallow groundwater resources in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region[R]. Shijiazhuang: Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2020. (in Chinese) [31] 杨会峰,孟瑞芳,白华,等. 海河流域地下水资源调查评价[R]. 石家庄:中国地质科学院水文地质环境地质研究所,2023. [YANG Huifeng,MENG Ruifang,BAI Hua,et al. Investigation and evaluation of groundwater resources in Haihe River Basin[R]. Shijiazhuang:Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology,Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences,2023. (in Chinese)
YANG Huifeng, MENG Ruifang, BAI Hua, et al. Investigation and evaluation of groundwater resources in Haihe River Basin[R]. Shijiazhuang: Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2023. (in Chinese) [32] 张家口市人民政府. 张家口经济年鉴[M]. 北京:中国统计出版社,1999 − 2019. [The People’s Government of Zhangjiakou Municipality. Zhangjiakou economy year book [M]. Beijing:China Statistics Press,1999 − 2019. (in Chinese)
The People’s Government of Zhangjiakou Municipality. Zhangjiakou economy year book [M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 1999 − 2019. (in Chinese) [33] 张家口统计局. 张家口市国民经济和社会发展统计公报[R]. 1999 − 2021. [Zhangjiakou Municipal Bureau of Statistics. National economic and social development statistical bulletin of Zhangjiakou[R]. 1999 − 2021. (in Chinese)
Zhangjiakou Municipal Bureau of Statistics. National economic and social development statistical bulletin of Zhangjiakou[R]. 1999 − 2021. (in Chinese) [34] 张家口崇礼区国民经济和社会发展统计公报[R]. 2020 − 2021. [National Economic and Social Development. Statistical bulletin of Chongli district of Zhangjiakou[R]. 2020 − 2021. (in Chinese)
National Economic and Social Development. Statistical bulletin of Chongli district of Zhangjiakou[R]. 2020 − 2021. (in Chinese) [35] 张立彬,王印肖. 河北林木种质资源[M]. 北京:中国林业出版社,2015. [ZHANG Libin,WANG Yinxiao. Tree germplasm resources in Hebei[M]. Beijing:China Forestry Publishing House,2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Libin, WANG Yinxiao. Tree germplasm resources in Hebei[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract) [36] 保定市地质环境监测报告[R]. 石家庄:河北省地质环境监测总站,1987 − 2020. [Geo-environment monitoring report of Baoding city[R]. Shijiazhuang:Geological Environment Monitoring Institute of Hebei Province,1987 − 2020. (in Chinese)
Geo-environment monitoring report of Baoding city[R]. Shijiazhuang: Geological Environment Monitoring Institute of Hebei Province, 1987 − 2020. (in Chinese) [37] 河北省保定水文勘测研究中心/保定市人民政府水资源办. 保定市水资源公报[R]. 保定:保定市水利局,2000 − 2020. [Hydrology Survey and Research Center of Baoding/ the Water Resource Administration Office of Baoding Municipality,Hebei Province. Water resources bulletin of Baoding city[R]. Baoding:Baoding Water Authority,2000 − 2020. (in Chinese)
Hydrology Survey and Research Center of Baoding/ the Water Resource Administration Office of Baoding Municipality, Hebei Province. Water resources bulletin of Baoding city[R]. Baoding: Baoding Water Authority, 2000 − 2020. (in Chinese) [38] 张磊,孙运芳,宋金玲,等. 河北省水利年鉴[M]. 石家庄:河北省水利厅,2002 − 2020. [ZHANG Lei,SUN yunfang,SONG,jinling,et al. Hebei water statistical yearbook[M]. Shijiazhuang:Department of Water Resources of Hebei Province,2002 − 2020. (in Chinese)
ZHANG Lei, SUN yunfang, SONG, jinling, et al. Hebei water statistical yearbook[M]. Shijiazhuang: Department of Water Resources of Hebei Province, 2002 − 2020. (in Chinese) [39] 杨继翔. 基于Mann-Kendall检验对近10年滨州市全年降水量的探究[J]. 农业灾害研究,2022,12(5):42 − 44. [YANG Jixiang. Research on annual precipitation of Binzhou city in recent ten years based on mann-kendall test[J]. Journal of Agricultural Catastrophology,2022,12(5):42 − 44. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YANG Jixiang . Research on annual precipitation of Binzhou city in recent ten years based on mann-kendall test[J]. Journal of Agricultural Catastrophology,2022 ,12 (5 ):42 −44 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[40] 曹洁萍,迟道才,武立强,等. Mann-Kendall检验方法在降水趋势分析中的应用研究[J]. 农业科技与装备,2008(5):35 − 37. [CAO Jieping,CHI Daocai,WU Liqiang,et al. Mann-kendall examination and application in the analysis of precipitation trend[J]. Agricultural Science & Technology and Equipment,2008(5):35 − 37. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CAO Jieping, CHI Daocai, WU Liqiang, et al . Mann-kendall examination and application in the analysis of precipitation trend[J]. Agricultural Science & Technology and Equipment,2008 (5 ):35 −37 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[41] LI Qiang,WEI Xiaohua,ZHANG Mingfang,et al. The cumulative effects of forest disturbance and climate variability on streamflow components in a large forest-dominated watershed[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2018,557:448 − 459. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.12.056
[42] 海、滦河流域水资源调查评价初步分析报告[R]. 天津:水利电力部天津勘测设计院,1982. [Preliminary analysis report on investigation and evaluation of water resources in Haihe and Luanhe River Basin [R]. Tianjin:Tianjin Survey and Design Institute and Research Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower,1982. (in Chinese)
Preliminary analysis report on investigation and evaluation of water resources in Haihe and Luanhe River Basin [R]. Tianjin: Tianjin Survey and Design Institute and Research Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower, 1982. (in Chinese)
[43] 孙鹏森,马履一. 水源保护树种耗水特性研究与应用[M]. 北京:中国环境科学出版社,2002. [SUN Pengsen,MA Lvyi. Study and application of water consumption characteristics of water source protection tree species[M]. Beijing:China Environmental Science Press,2002. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SUN Pengsen, MA Lvyi. Study and application of water consumption characteristics of water source protection tree species[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2002. (in Chinese with English abstract) [44] 桂云鹏. 区域耗水核算方法与演变驱动研究——以京津冀地区为例[D]. 北京:中国水利水电科学研究院,2018. [GUI Yunpeng. Research on regional water consumption accounting method and evolution drive[D]. Beijing:China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research,2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GUI Yunpeng. Research on regional water consumption accounting method and evolution drive[D]. Beijing: China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract) [45] 李洁,任启文,孙杰肖. 张家口崇礼区3种优势树种蒸腾耗水特征研究[J]. 西北林学院学报,2018,33(6):40 − 46. [LI Jie,REN Qiwen,SUN Jiexiao. Water consumption of three dominant tree species at Qingshuihe watershed of Chongli district in Zhangjiakou[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University,2018,33(6):40 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Jie, REN Qiwen, SUN Jiexiao . Water consumption of three dominant tree species at Qingshuihe watershed of Chongli district in Zhangjiakou[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University,2018 ,33 (6 ):40 −46 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[46] 杨良辰,张健强,杨新兵,等. 华北土石山区7种优势乔木树种耗水分析[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报,2019,39(3):69 − 75. [YANG Liangchen,ZHANG Jianqiang,YANG Xinbing,et al. Water consumption analysis on seven dominant arbor tree species in earth and rock mountains in Northern China[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology,2019,39(3):69 − 75. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YANG Liangchen, ZHANG Jianqiang, YANG Xinbing, et al . Water consumption analysis on seven dominant arbor tree species in earth and rock mountains in Northern China[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology,2019 ,39 (3 ):69 −75 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[47] 任启文,忻富宁,李联地,等. 冀北山地华北落叶松全生长季树干液流及蒸腾耗水特征[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报,2018,38(5):91 − 97. [REN Qiwen,XIN Funing,LI Liandi,et al. Stem sap flow and water consumption of Larix principis-rupprechtii during growth season in northern mountain areas of Hebei Province[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology,2018,38(5):91 − 97. (in Chinese with English abstract)
REN Qiwen, XIN Funing, LI Liandi, et al . Stem sap flow and water consumption of Larix principis-rupprechtii during growth season in northern mountain areas of Hebei Province[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology,2018 ,38 (5 ):91 −97 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[48] 刘春鹏. 河北省平山县石质山区主要造林树种耗水特征研究[D]. 保定:河北农业大学,2011. [LIU Chunpeng. Water-consumption characteristics of main planting tree species in the rocky mountainous area of Pingshan County,Hebei Province[D]. Baoding:Hebei Agricultural University,2011. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Chunpeng. Water-consumption characteristics of main planting tree species in the rocky mountainous area of Pingshan County, Hebei Province[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract) [49] 河北省森林规划设计调查操作细则[M]. 石家庄:河北省林业调查规划设计院,2015. [Operation detailed rules of forest planning and design and survey of Hebei Province[M]. Shijiazhuang:Forestry Survey and Planning and Design Institute of Hebei Province,2015. (in Chinese)
Operation detailed rules of forest planning and design and survey of Hebei Province[M]. Shijiazhuang: Forestry Survey and Planning and Design Institute of Hebei Province, 2015. (in Chinese) [50] 田菲,韩淑敏,胡玉昆. 海河流域典型山区子流域近34年气候及径流变化趋势[J]. 中国农业气象,2009,30(1):60 − 65. [TIAN Fei,HAN Shumin,HU Yukun. Variance tendency of precipitation and runoff in mountain watershed of Hai River Basin in recent 34 years[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology,2009,30(1):60 − 65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
TIAN Fei, HAN Shumin, HU Yukun . Variance tendency of precipitation and runoff in mountain watershed of Hai River Basin in recent 34 years[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology,2009 ,30 (1 ):60 −65 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[51] 王海宁,乔光建. 涞源岩溶地下水系统泉水量变化特征分析[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2011,9(6):54 − 57. [WANG Haining,QIAO Guangjian. Variations of spring volume of the Karst groundwater system in the Laiyuan region[J]. South-to-North Water Diversion and Water Science & Technology,2011,9(6):54 − 57. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Haining, QIAO Guangjian . Variations of spring volume of the Karst groundwater system in the Laiyuan region[J]. South-to-North Water Diversion and Water Science & Technology,2011 ,9 (6 ):54 −57 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[52] 李志先. 利用降水量推算涞源泉流量方法的探讨[J]. 水文地质工程地质,1984,11(2):48 − 50. [LI Zhixian. Discussion on the method of calculating the flow rate of Laiyuan spring by precipitation[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,1984,11(2):48 − 50. (in Chinese)
LI Zhixian . Discussion on the method of calculating the flow rate of Laiyuan spring by precipitation[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,1984 ,11 (2 ):48 −50 . (in Chinese)[53] 张彪,李文华,谢高地,等. 森林生态系统的水源涵养功能及其计量方法[J]. 生态学杂志,2009,28(3):529 − 534. [ZHANG Biao,LI Wenhua,XIE Gaodi,et al. Water conservation function and its measurement methods of forest ecosystem[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2009,28(3):529 − 534. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Biao, LI Wenhua, XIE Gaodi, et al . Water conservation function and its measurement methods of forest ecosystem[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2009 ,28 (3 ):529 −534 . (in Chinese with English abstract) -




 下载:
下载: