Characterizing fracture networks by integrating hydrogeophysical data based on the ESMDA-DS method
-
摘要:
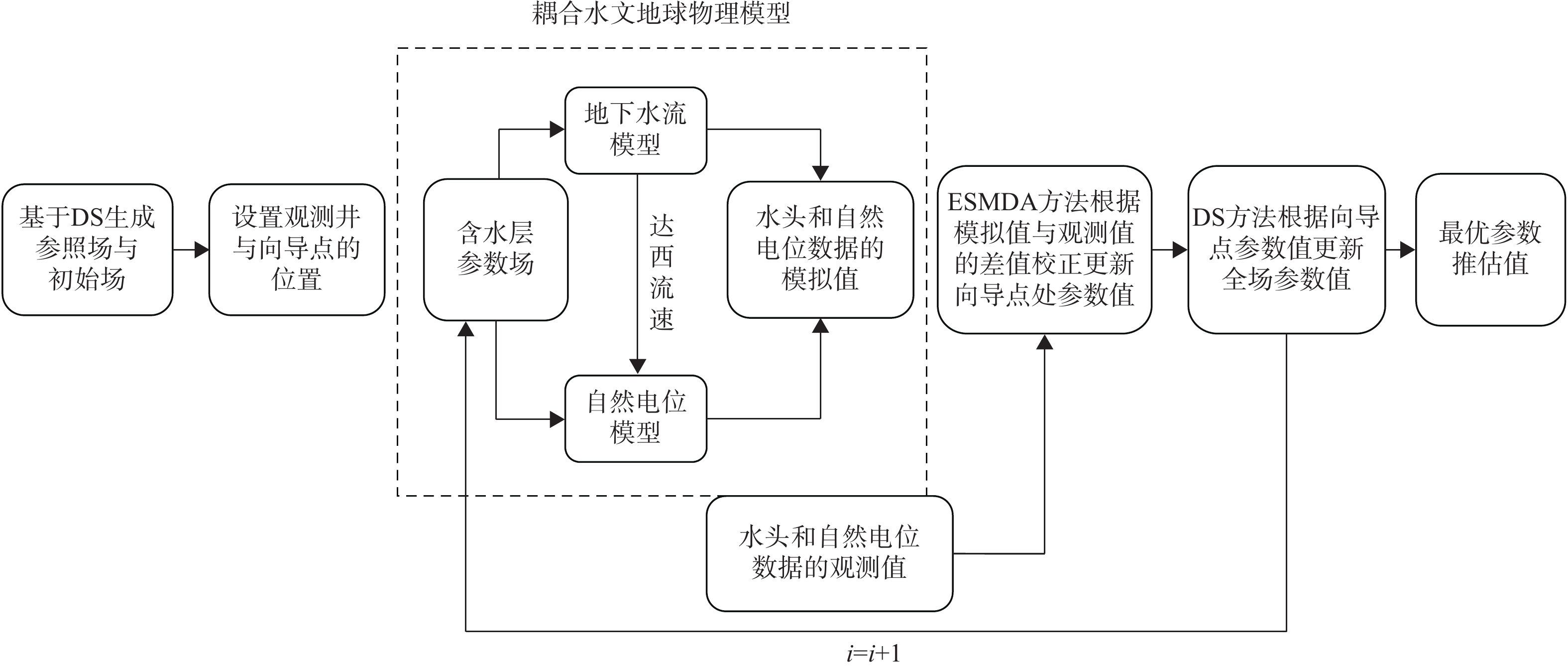
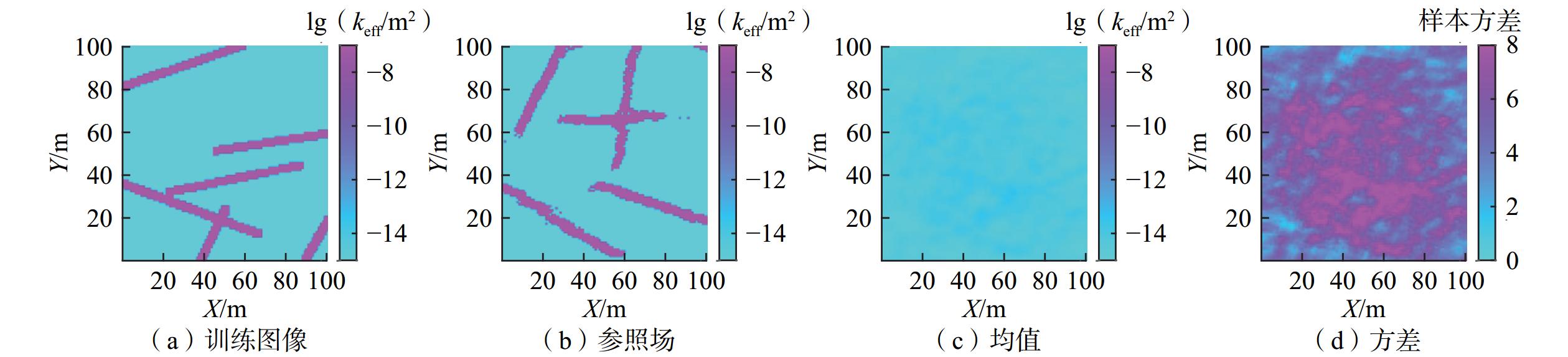
刻画裂隙含水层在地下水污染、地热、油气资源开采等研究中起关键作用。由于裂隙介质的强非均质性,其渗透率场一般呈现出显著的非高斯特性,该特性给水文地质参数的推估带来了极大的困难与挑战。为解决裂隙介质参数推估难的问题,本研究利用集合平滑数据同化与直接采样法融合水文地球物理数据推估裂隙介质参数场,设计多个数值算例,探究该数据同化框架刻画裂隙介质参数场的有效性,分析同化3种不同类型的观测数据对参数推估结果的影响,并探讨裂隙密度以及观测井的数量对参数推估效果的影响。研究结果表明:(1)基于集合平滑数据同化与直接采样法融合水文地球物理数据的方法,可有效地推估裂隙介质水文地质参数空间分布;(2)对比3种类型的观测数据推估结果,可知同时融合水头和自然电位观测数据(水文地球物理数据)的参数推估效果最佳;(3)研究区的裂隙密度以及观测井的数量同样对数据同化结果产生影响,因此建议在实际应用中应选择合理的观测井数量从而获得最优的参数推估方案。该研究可为裂隙介质参数场的刻画提供一种有效的方法,进一步为裂隙水资源的开发和管理提供可靠的理论依据。
Abstract:Characterizing fractured aquifers plays a crucial role in the issues related to groundwater contamination, and geothermal and hydrocarbon resource exploitation. Due to the heterogeneity of the fractured medium, the permeability of fractured medium generally exhibits significant non-Gaussian characteristics, leading to difficulties and challenges in the estimation of hydrogeological parameters. This study used the ESMDA-DS (ensemble smoother with multiple data assimilation-direct sampling) integrating hydrogeophysical data to explore the effectiveness of the data assimilation framework in portraying the parameter field of the fractured medium and to analyze the influences of assimilating three different types of observation data, the fracture density, and the number of observation wells on the parameter estimation. The results show that the method of ESMDA-DS integrating hydrogeophysical data can estimate the spatial distribution of hydrogeological parameters in the fractured medium effectively. Comparing the estimated results from three types of observation, it finds that fusing the hydraulic head and the self-potential observational data (hydrogeophysical data) has the best effect. The fracture density in the study area and the number of observation wells also affect the data assimilation results. A reasonable number of observation wells is suggested to obtain the optimal parameter estimation scheme in practical applications. This study can provide an effective method for characterizing the parameter field of the fractured medium and a reliable theoretical basis for the development and management of fractured water resources.
-

-
表 1 地下水流模型和自然电位模型主要参数
Table 1. Parameters in the groundwater flow model and self-potential model
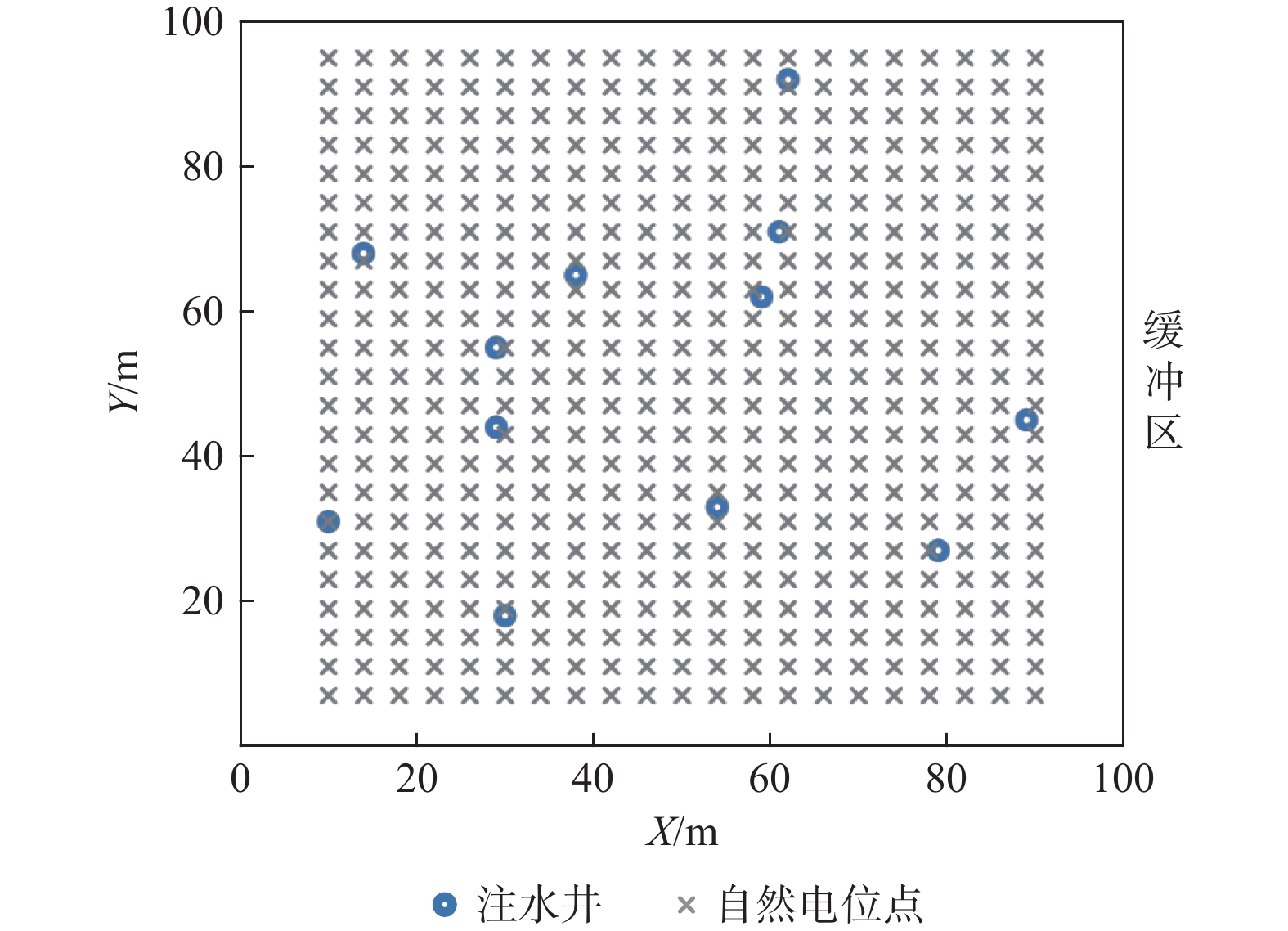
参数 参数值 参数 参数值 网格边长/m 1×1 基质的渗透率/m2 10−15 模型尺寸/m 100×100 缓冲区的渗透率/m2 10−15 初始水头/m 5 初始电位/V 0 流场模拟时间/d 35 电场模拟时间/d 15 流场时间步长/d 5 电场时间步长/d 5 储水系数/Pa−1 6×10−5 裂隙水的电导率/(S∙m−1) 0.1 裂隙孔隙度 1 基质的电导率/(S∙m−1) 7.5×10−6 基质孔隙度 0.15 裂隙的相对介电常数 80 裂隙的渗透率/m2 10−7 基质的相对介电常数 7 表 2 算例设置
Table 2. The setting of cases
向导点
数量观测井
数量注水井
数量裂隙密度 观测数据
类型观测
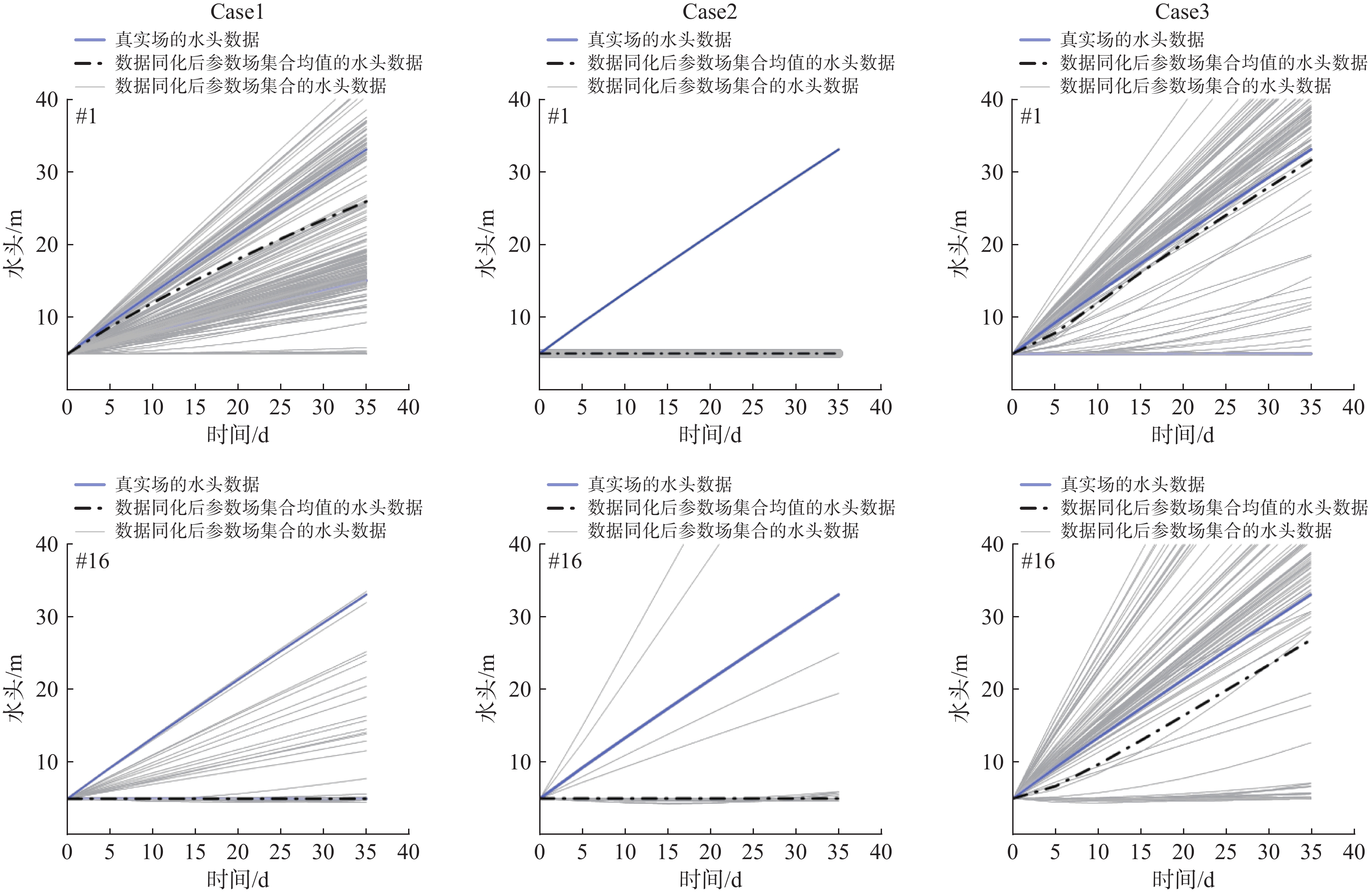
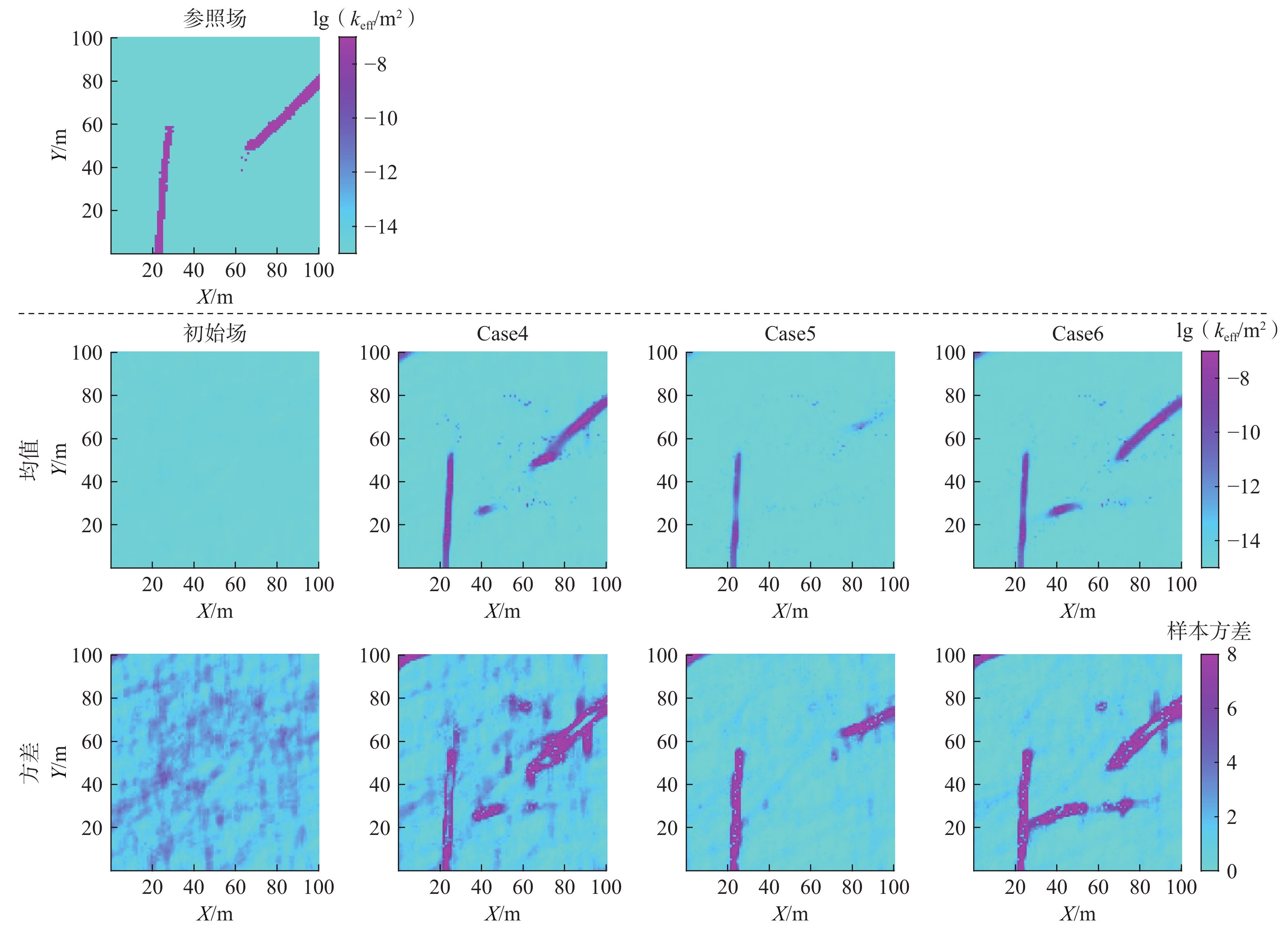
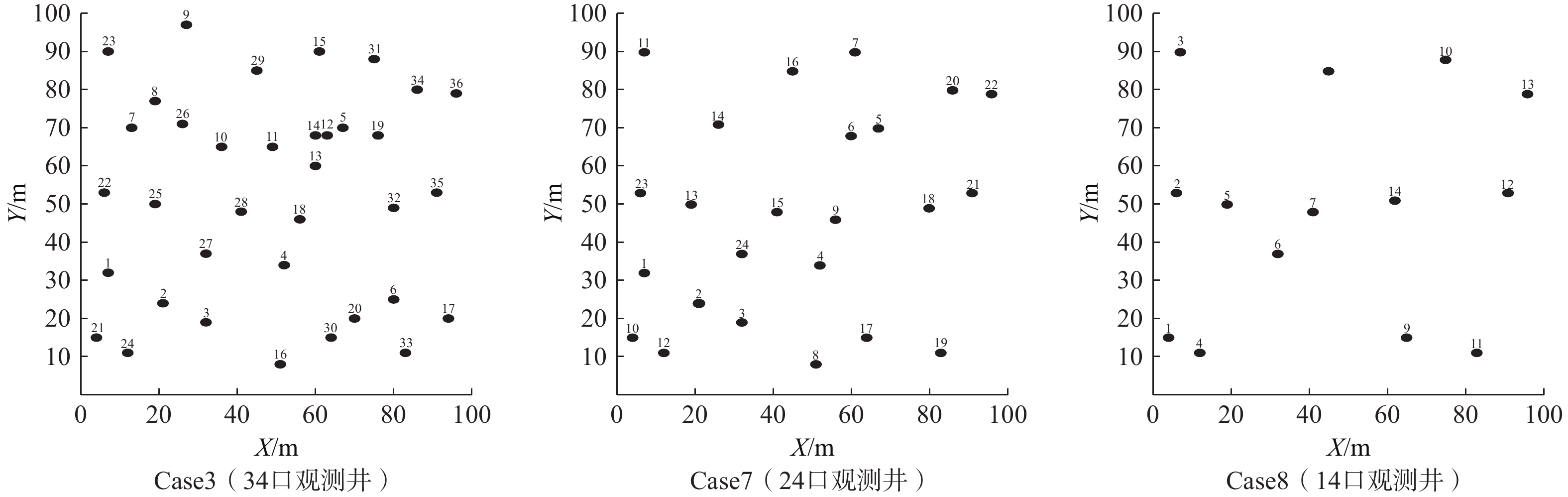
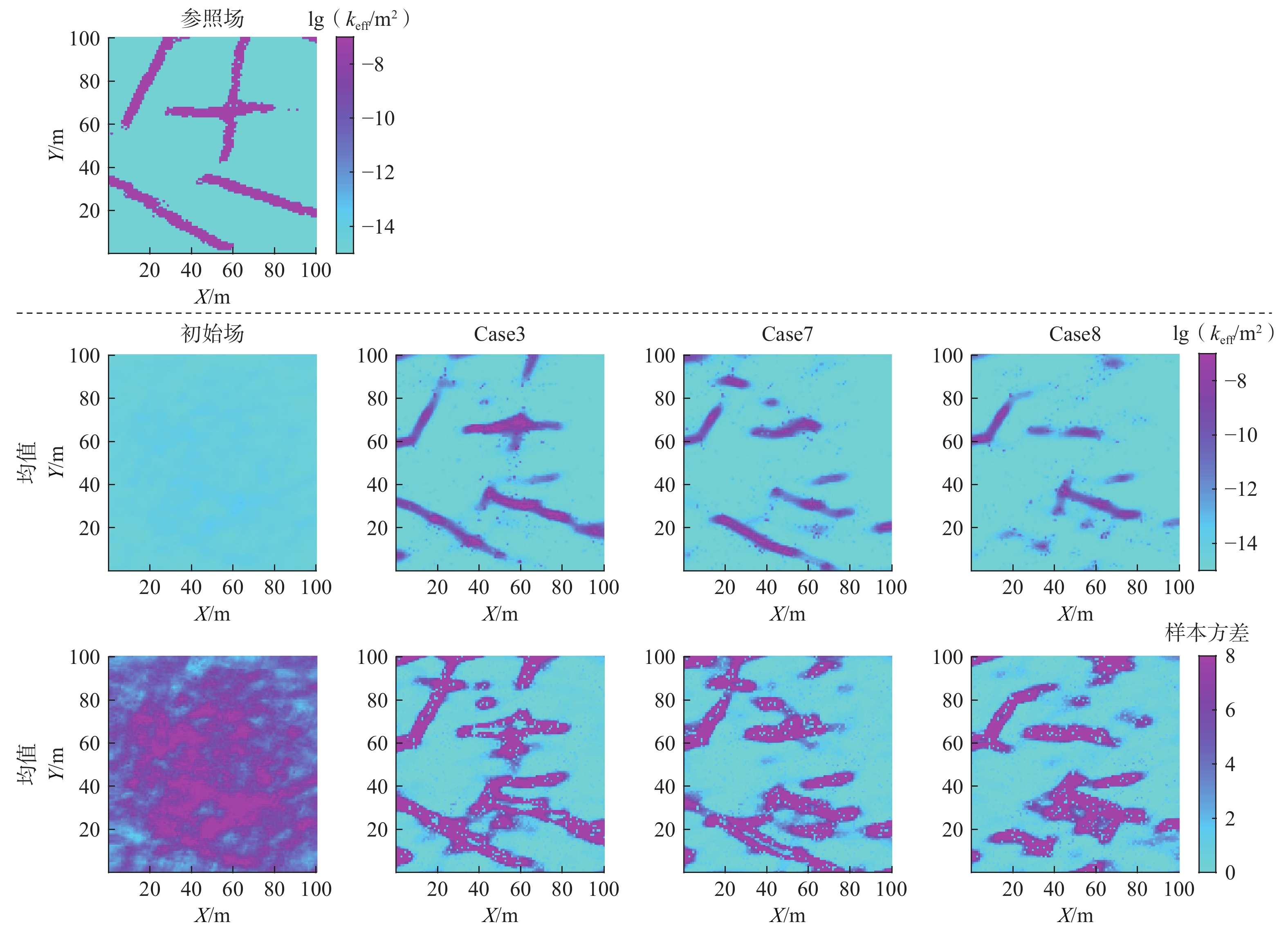
数据量Case1 1000 34 12 0.00560 H 2856 Case2 1000 34 12 0.00560 SP 17388 Case3 1000 34 12 0.00560 H+SP 20244 Case4 1000 13 10 0.00125 H 910 Case5 1000 13 10 0.00125 SP 14490 Case6 1000 13 10 0.00125 H+SP 15400 Case7 1000 24 12 0.00560 H+SP 19404 Case8 1000 14 12 0.00560 H+SP 18564 表 3 Case1、Case2及Case3 lgkeff场的均方根误差
Table 3. Values of RMSE for Case1, Case2, and Case3 lgkeff fields
裂隙密度 融合数据类型 IRMSE Case1 0.0056 H 2.3377 Case2 0.0056 SP 2.2192 Case3 0.0056 H+SP 1.9712 表 4 Case4、Case5及Case6 lgkeff场的均方根误差
Table 4. Values of RMSE for Case4, Case5, and Case6 lgkeff fields
裂隙密度 融合数据类型 IRMSE Case4 0.00125 H 1.1621 Case5 0.00125 SP 1.3648 Case6 0.00125 H+SP 1.1488 表 5 Case3、Case7及Case8 lgkeff场的均方根误差
Table 5. Values of RMSE for Case3, Case7, and Case8 lgkeff fields
观测井数量 融合数据类型 IRMSE Case3 34 H+SP 1.9712 Case7 24 H+SP 2.3435 Case8 14 H+SP 2.5092 -
[1] LIU Longcheng,MENG Shuo,LI Chunguang. A new analytical solution of contaminant transport along a single fracture connected with porous matrix and its time domain random walk algorithm[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2022,610(1):127828.
[2] JI Jiayan,SONG Xianzhi,SONG Guofeng,et al. Study on fracture evolution model of the enhanced geothermal system under thermal-hydraulic-chemical-deformation coupling[J]. Energy,2023,269:126604. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2022.126604
[3] 张烈辉,贾鸣,张芮菡,等. 裂缝性油藏离散裂缝网络模型与数值模拟[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2017,39(3):121 − 127. [ZHANG Liehui,JIA Ming,ZHANG Ruihan,et al. Discrete fracture network modeling and numerical simulation of fractured reservoirs[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition),2017,39(3):121 − 127. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Liehui, JIA Ming, ZHANG Ruihan, et al. Discrete fracture network modeling and numerical simulation of fractured reservoirs[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2017, 39(3): 121 − 127. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 石鸿蕾,郝奇琛,邵景力,等. 基于多源数据的弱透水层水文地质参数反演研究——以呼和浩特盆地某淤泥层为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(2):1 − 7. [SHI Honglei,HAO Qichen,SHAO Jingli,et al. Research on hydrogeological parameter inversion of an aquitard based on multi-source data:A case study of a silt layer in the Hohhot Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(2):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SHI Honglei, HAO Qichen, SHAO Jingli, et al. Research on hydrogeological parameter inversion of an aquitard based on multi-source data: A case study of a silt layer in the Hohhot Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(2): 1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 吴延浩,江思珉,吴自军. 地下水污染强度及渗透系数场的反演识别研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(4):193 − 203. [WU Yanhao,JIANG Simin,WU Zijun. Identification of groundwater pollution intensity and hydraulic conductivity field[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(4):193 − 203. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WU Yanhao, JIANG Simin, WU Zijun. Identification of groundwater pollution intensity and hydraulic conductivity field[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(4): 193 − 203. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 陈梦迪,姜振蛟,霍晨琛. 考虑矿层渗透系数非均质性和不确定性的砂岩型铀矿地浸采铀过程随机模拟与分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(2):63 − 72. [CHEN Mengdi,JIANG Zhenjiao,HUO Chenchen. Stochastic modeling of in situ sandstone-type uranium leaching in response to uncertain and heterogeneous hydraulic conductivity[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(2):63 − 72. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Mengdi, JIANG Zhenjiao, HUO Chenchen. Stochastic modeling of in situ sandstone-type uranium leaching in response to uncertain and heterogeneous hydraulic conductivity[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(2): 63 − 72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] KALMAN R E. A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems[J]. Journal of Basic Engineering,1960,82(1):35 − 45. doi: 10.1115/1.3662552
[8] VAN LEEUWEN P J,EVENSEN G. Data assimilation and inverse methods in terms of a probabilistic formulation[J]. Monthly Weather Review,1996,124(12):2898 − 2913. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1996)124<2898:DAAIMI>2.0.CO;2
[9] ZHANG Jiangjiang,LIN Guang,LI Weixuan,et al. An iterative local updating ensemble smoother for estimation and uncertainty assessment of hydrologic model parameters with multimodal distributions[J]. Water Resources Research,2018,54(3):1716 − 1733. doi: 10.1002/2017WR020906
[10] EVENSEN G. The Ensemble Kalman Filter:Theoretical formulation and practical implementation[J]. Ocean Dynamics,2003,53(4):343 − 367. doi: 10.1007/s10236-003-0036-9
[11] 康学远,施小清,邓亚平,等. 基于EnKF融合地球物理数据刻画含水层非均质性[J]. 水科学进展,2018,29(1):40 − 49. [KANG Xueyuan,SHI Xiaoqing,DENG Yaping,et al. Assimilation of hydrogeophysical data for the characterization of subsurface heterogeneity using Ensemble Kalman Filter (EnKF)[J]. Advances in Water Science,2018,29(1):40 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
KANG Xueyuan, SHI Xiaoqing, DENG Yaping, et al. Assimilation of hydrogeophysical data for the characterization of subsurface heterogeneity using Ensemble Kalman Filter (EnKF)[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2018, 29(1): 40 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 兰天,康学远,施小清,等. 基于EnKF综合水头和浓度观测数据推估地下水流模型参数[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(5):6 − 13. [LAN Tian,KANG Xueyuan,SHI Xiaoqing,et al. Joint assimilation of heads and concentrations for estimating parameters of groundwater flow models using the Ensemble Kalman Filter[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(5):6 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LAN Tian, KANG Xueyuan, SHI Xiaoqing, et al. Joint assimilation of heads and concentrations for estimating parameters of groundwater flow models using the Ensemble Kalman Filter[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2017, 44(5): 6 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] CHEN Yan,OLIVER D S. Ensemble randomized maximum likelihood method as an iterative ensemble smoother[J]. Mathematical Geosciences,2012,44(1):1 − 26. doi: 10.1007/s11004-011-9376-z
[14] 夏传安,王浩,简文彬. 基于相关性局域化迭代集合平滑反演渗透系数场[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2024,51(1):12 − 21. [XIA Chuanan,WANG Hao,JIAN Wenbin. Estimation of conductivity fields by using a correlation-based localization scheme of iterative ensemble smoother[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2024,51(1):12 − 21. (in Chinese)]
XIA Chuanan, WANG Hao, JIAN Wenbin. Estimation of conductivity fields by using a correlation-based localization scheme of iterative ensemble smoother[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2024, 51(1): 12 − 21. (in Chinese)
[15] EMERICK A,REYNOLDS A. Ensemble smoother with multiple data assimilation[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2013,55(3):3 − 15.
[16] 周念清,张瑞城,江思珉,等. ES-MDA算法融合ERT数据联合反演地下水污染源与含水层参数[J]. 南水北调与水利科技(中英文),2022,20(3):478 − 486. [ZHOU Nianqing,ZHANG Ruicheng,JIANG Simin,et al. Joint inversion of contaminant source and aquifer parameters by assimilating ERT data with the ES-MDA algorithm[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2022,20(3):478 − 486. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHOU Nianqing, ZHANG Ruicheng, JIANG Simin, et al. Joint inversion of contaminant source and aquifer parameters by assimilating ERT data with the ES-MDA algorithm[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2022, 20(3): 478 − 486. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] HAN Zheng,KANG Xueyuan,WU Jichun,et al. Characterization of the non-Gaussian hydraulic conductivity field via deep learning-based inversion of hydraulic-head and self-potential data[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2022,610(11):127830.
[18] CUI Fan,BAO Jichao,CAO Zhendan,et al. Soil hydraulic parameters estimation using ground penetrating radar data via ensemble smoother with multiple data assimilation[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2020,583(12):124552.
[19] CAMPORESE M,CASSIANI G,DEIANA R,et al. Coupled and uncoupled hydrogeophysical inversions using ensemble Kalman filter assimilation of ERT-monitored tracer test data[J]. Water Resources Research,2015,51(5):3277 − 3291. doi: 10.1002/2014WR016017
[20] JARDANI A,REVIL A,BOLÈVE A,et al. Tomography of the Darcy velocity from self-potential measurements[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2007,34(12):L24403.
[21] STREBELLE S,JOURNEL A. Reservoir modeling using multiple-point statistics[C]//Proceedings of SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. Society of Petroleum Engineers,2001:1-11.
[22] STREBELLE S. Conditional simulation of complex geological structures using multiple-point statistics[J]. Mathematical Geology,2002,34(1):1 − 21. doi: 10.1023/A:1014009426274
[23] ARPAT G B,CAERS J. Conditional simulation with patterns[J]. Mathematical Geology,2007,39(2):177 − 203. doi: 10.1007/s11004-006-9075-3
[24] ZHANG Tuanfeng,SWITZER P,JOURNEL A. Filter-based classification of training image patterns for spatial simulation[J]. Mathematical Geology,2006,38(1):63 − 80. doi: 10.1007/s11004-005-9004-x
[25] MARIETHOZ G,RENARD P,STRAUBHAAR J. The direct sampling method to perform multiple-point geostatistical simulations[J]. Water Resources Research,2010,46(11):W11536.
[26] CAO Zhendan,LI Liangping,CHEN Kang. Bridging iterative Ensemble Smoother and multiple-point geostatistics for better flow and transport modeling[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2018,565:411 − 421. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.08.023
[27] 宗成元,康学远,施小清,等. 基于多点地质统计与集合平滑数据同化方法识别非高斯渗透系数场[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(2):1 − 8. [ZONG Chengyuan,KANG Xueyuan,SHI Xiaoqing,et al. Characterization of non-Gaussian hydraulic conductivity fields using multiple-point geostatistics and ensemble smoother with multiple data assimilation method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(2):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZONG Chengyuan, KANG Xueyuan, SHI Xiaoqing, et al. Characterization of non-Gaussian hydraulic conductivity fields using multiple-point geostatistics and ensemble smoother with multiple data assimilation method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(2): 1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] JOUGNOT D,LINDE N,REVIL A,et al. Derivation of soil-specific streaming potential electrical parameters from hydrodynamic characteristics of partially saturated soils[J]. Vadose Zone Journal,2012,11(1):272 − 286.
[29] REVIL A. Transport of water and ions in partially water-saturated porous media. Part 1. Constitutive equations[J]. Advances in Water Resources,2017,103:119 − 138. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2016.02.006
[30] 李华,王东辉,张伟,等. 地球物理探测技术在成都市浅表地质结构调查中的应用研究[J]. 中国地质,2022,49(5):1438 − 1457. [LI Hua,WANG Donghui,ZHANG Wei,et al. Application research of geophysical exploration technology in the investigation of shallow geological structure in Chengdu[J]. Geology in China,2022,49(5):1438 − 1457. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Hua, WANG Donghui, ZHANG Wei, et al. Application research of geophysical exploration technology in the investigation of shallow geological structure in Chengdu[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(5): 1438 − 1457. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 赵全升,孔智涵,胡舒娅,等. 柴达木盆地马海盐湖地下卤水地球物理探测及应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2023,53(5):1560 − 1572. [Zhao Quansheng,Kong Zhihan,Hu Shuya, et al. Geophysical exploration and application of underground brine of Mahai Salt Lake in Qaidam Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2023,53(5):1560 − 1572. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
Zhao Quansheng, Kong Zhihan, Hu Shuya, et al. Geophysical exploration and application of underground brine of Mahai Salt Lake in Qaidam Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1560 − 1572. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 丁万奇,马振乾,祖自银,等. 基于分形维数的巷道围岩裂隙演化规律研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2021,49(3):167 − 174. [DING Wanqi,MA Zhenqian,ZU Ziyin,et al. Research on the evolution law of roadway surrounding rock fissure based on fractal dimension[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2021,49(3):167 − 174. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
DING Wanqi, MA Zhenqian, ZU Ziyin, et al. Research on the evolution law of roadway surrounding rock fissure based on fractal dimension[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2021, 49(3): 167 − 174. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] WANG Libing. Modeling complex reservoir geometries with multiple-point statistics[J]. Mathematical Geology,1996,28(7):895 − 907. doi: 10.1007/BF02066007
[34] ZHANG Dailu,ZHANG Hongbing,REN Quan,et al. A modified method of multiple point geostatistics for spatial simulation of sedimentary facies for carbonate reservoirs[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics,2023,215:105112. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2023.105112
[35] 王鸣川,商晓飞,段太忠. 多点地质统计学建模中训练图像建立方法综述[J]. 高校地质学报,2022,28(1):96 − 103. [WANG Mingchuan,SHANG Xiaofei,DUAN Taizhong. A review of the establishment methods of training image in multiple-point statistics modeling[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2022,28(1):96 − 103. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Mingchuan, SHANG Xiaofei, DUAN Taizhong. A review of the establishment methods of training image in multiple-point statistics modeling[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2022, 28(1): 96 − 103. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[36] NAN Tongchao,WU Jichun. Groundwater parameter estimation using the ensemble Kalman filter with localization[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2011,19(3):547 − 561. doi: 10.1007/s10040-010-0679-9
[37] LEE J,KITANIDIS P K. Large-scale hydraulic tomography and joint inversion of head and tracer data using the Principal Component Geostatistical Approach (PCGA)[J]. Water Resources Research,2014,50(7):5410 − 5427. doi: 10.1002/2014WR015483
[38] 兰天. 基于改进PCM方法反演非高斯水文地质参数[D]. 南京:南京大学,2020. [LAN Tian. Inversion of Non-Gaussian Hydrogeological Parameters by Modified Probability Conditioning Method[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing University,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LAN Tian. Inversion of Non-Gaussian Hydrogeological Parameters by Modified Probability Conditioning Method[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[39] HUANG Xiang,ANDREWS C B,LIU Jie,et al. Assimilation of temperature and hydraulic gradients for quantifying the spatial variability of streambed hydraulics[J]. Water Resources Research,2016,52(8):6419 − 6439. doi: 10.1002/2015WR018408
[40] ZHAN Chuanjun,DAI Zhenxue,SOLTANIAN M R,et al. Data-worth analysis for heterogeneous subsurface structure identification with a stochastic deep learning framework[J]. Water Resources Research,2022,58(11):e2022WR033241. doi: 10.1029/2022WR033241
-



 下载:
下载: