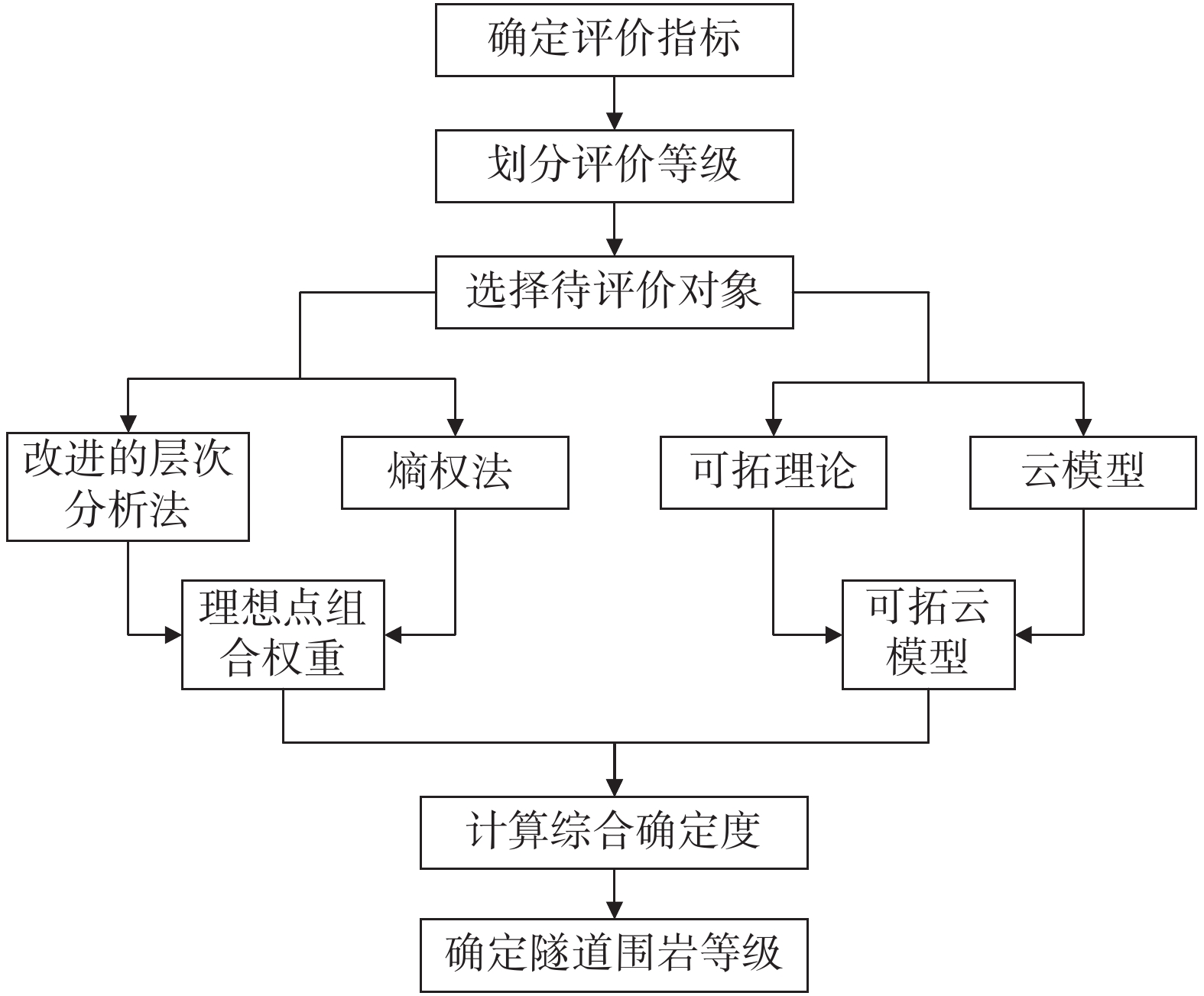
Stability evaluation of tunnel surrounding rock based on ideal point-extension cloud model
-
摘要:
为了对隧道围岩稳定性进行准确评价并解决研究过程中存在的模糊性和随机性以及评价指标不相容的问题,减少单一的主客观赋权法所带来的误差,将云模型引入可拓理论中,利用可拓理论能够实现矛盾问题向相容问题转化的特点和云模型具有处理事物双重不确定性的优势并结合理想点组合赋权法对隧道围岩进行稳定性评价研究。通过文献调研、数据统计的方式,选取具有代表性的6个指标组成隧道围岩评价指标体系,用理想点法赋予评价指标组合权重,并构建可拓云模型对隧道围岩稳定性进行综合评价。通过将此方法应用于工程实例并与其他方法对比,结果表明:基于理想点-可拓云模型的隧道围岩稳定性评价方法能够减少评价过程中存在的不确定性问题,克服单一赋权方法的不足,具有良好的适用性,可以应用于实际工程中。
Abstract:In order to accurately assess the stability of the tunnel surrounding rock and solve the problems of ambiguity and randomness in the research process and the incompatibility of evaluation indicators, reduce the error caused by the single subjective and objective weighting method, and introduce the cloud model into the In the extension theory, the extension theory can be used to realize the conversion of contradictory problems to compatible problems, and the cloud model has the advantage of dealing with the double uncertainty of things. Combined with the ideal point combination weighting method, the stability evaluation of the tunnel surrounding rock is studied. Through literature survey and data statistics, select 6 representative indexes to form the tunnel surrounding rock evaluation index system, use the ideal point method to give the evaluation index combination weight, and construct an extension cloud model to comprehensively evaluate the tunnel surrounding rock stability. By applying this method to engineering examples and comparing with other methods, the results show that the method of tunnel surrounding rock stability evaluation based on the ideal point-extension cloud model can reduce the uncertainty in the evaluation process and overcome the single weighting method. The shortcomings have good applicability and can be applied to actual projects.
-
Key words:
- ideal point /
- weight /
- extension cloud model /
- tunnel surrounding rock /
- evaluation of stability
-

-
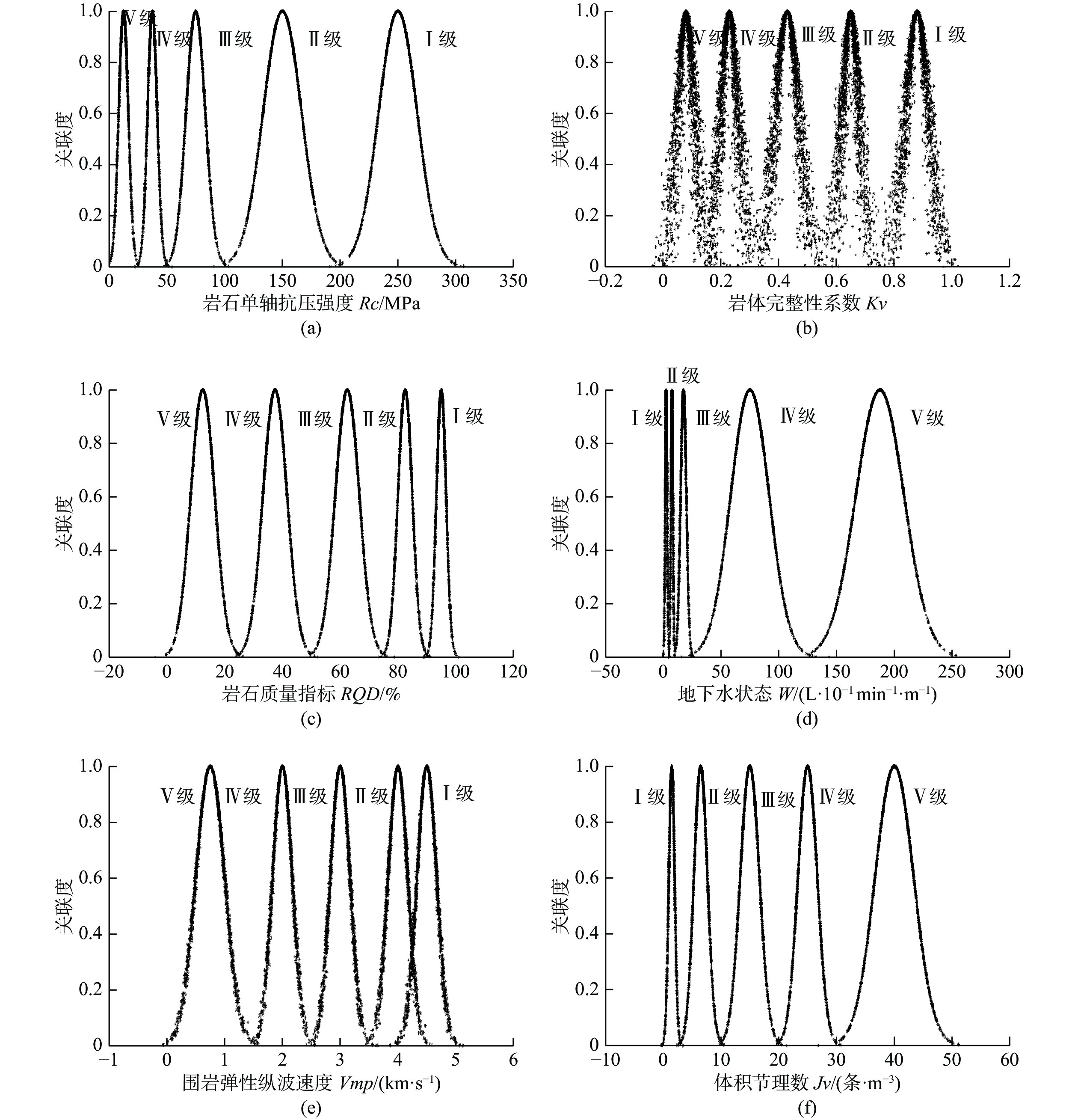
表 1 隧道围岩稳定性评价指标分类标准
Table 1. Classification criteria of tunnel surrounding rock stability evaluation index
类别 岩石单轴抗压强度
Rc/MPa岩体完整性系数
Kv岩石质量指标
RQD/%地下水状态
W/(L·10−1 min−1·m−1)围岩弹性纵波速度
Vmp/(km·s−1)体积节理数
Jv/(条·m−3)稳定Ⅰ 200~300 0.75~1 90~100 0~5 >4.5 0~3 基本稳定Ⅱ 100~200 0.55~0.75 75~90 5~10 3.5~4.5 3~10 稳定性差Ⅲ 50.0~100 0.30~0.55 50~75 10~25 2.5~3.5 10~20 不稳定Ⅳ 25.0~50.0 0.15~0.30 25~50 25~125 1.5~2.5 20~30 极不稳定Ⅴ 0.00~25.0 0.00~0.15 0~25 125~250 0~1.5 30~50 表 2 样本指标实测值
Table 2. Sample index measured value
样本 岩石单轴抗压强度
Rc/MPa岩体完整性系数
Kv岩石质量指标
RQD/%地下水状态
W/(L·10-1 min−1·m−1)声波纵波速度值
Vmp/(km·s−1)体积节理数
Jv/(条·m−3)1 28.76 0.18 36 107.46 1.95 26 2 58.16 0.39 62 21.73 2.83 17 3 12.84 0.14 15 136.95 1.36 39 4 32.52 0.26 41 85.57 2.13 22 5 17.93 0.12 19 127.34 1.25 43 表 3 隧道围岩等级标准云模型
Table 3. Standard cloud model of tunnel surrounding rock grade
类别 岩石单轴抗压强度 岩体完整性系数 岩石质量指标 地下水状态 围岩弹性纵波速度 体积节理数 稳定Ⅰ (250,16.67,0.01) (0.88,0.04,0.01) (95,1.67,0.01) (2.5,0.83,0.01) (4.5,0.17,0.01) (1.5,0.5,0.01) 基本稳定Ⅱ (150,16.67,0.01) (0.65,0.03,0.01) (82.5,2.5,0.01) (7.5,0.83,0.01) (4,0.17,0.01) (6.5,1.17,0.01) 稳定性差Ⅲ (75,8.33,0.01) (0.43,0.04,0.01) (62.5,4.17,0.01) (17.5,2.5,0.01) (3,0.17,0.01) (15,1.67,0.01) 不稳定Ⅳ (37.5,4.17,0.01) (0.23,0.03,0.01) (37.5,4.17,0.01) (75,16.67,0.01) (2,0.17,0.01) (25,1.67,0.01) 极不稳定Ⅴ (12.5,4.17,0.01) (0.08,0.03,0.01) (12.5,4.17,0.01) (187.5,20.83,0.01) (0.75,0.25,0.01) (40,3.33,0.01) 表 4 样本评价结果及对比
Table 4. Sample evaluation results and comparison
样本 综合确定度 本文方法 熵权-云模型 可拓理论 — U(Ⅰ) U(Ⅱ) U(Ⅲ) U(Ⅳ) U(Ⅴ) — — — 1 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.475234 0.000804 Ⅳ Ⅳ Ⅳ 2 0.000000 0.000000 0.459271 0.001137 0.000000 Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ 3 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.001861 0.536067 Ⅴ Ⅴ Ⅳ 4 0.000000 0.000000 0.000038 0.597523 0.000004 Ⅳ Ⅳ Ⅳ 5 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.001542 0.318828 Ⅴ Ⅴ Ⅴ -
[1] 曹文贵, 翟友成, 王江营. 基于漂移度的隧道围岩质量分级组合评价方法[J]. 岩土工程学报,2012,34(6):978 − 984. [CAO Wengui, ZHAI Youcheng, WANG Jiangying. Combination evaluation method for classification of surrounding rock quality of tunnel based on drifting degree[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2012,34(6):978 − 984. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 盛继亮. 地下工程围岩稳定性模糊综合评价模型研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2003,22(增刊1):2418 − 2421. [SHENG Jiliang. Research on fuzzy synthetic evaluation model for the stability of surrounding rocks of underground project[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2003,22(Sup1):2418 − 2421. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 郭磊, 傅鹤林. 基于人工神经网络的梅关隧道围岩级别判别[J]. 现代隧道技术,2010,47(3):13 − 17. [GUO Lei, FU Helin. Rockmass classification for Meiguan tunnel based on artifical neural net[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology,2010,47(3):13 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6582.2010.03.003
[4] 许才仗. 复杂地层大断面隧道围岩分级研究及施工参数优化[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2014.
XU Caizhang. Study on rockmass classification of large cross tunnel in complex formation and construction parameter optimization[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 牛文林, 李天斌, 熊国斌, 等. 基于支持向量机的围岩定性智能分级研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2011,19(1):88 − 92. [NIU Wenlin, LI Tianbin, XIONG Guobin, et al. Support vector machines based intelligent rock mass classification method[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2011,19(1):88 − 92. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2011.01.014
[6] 汪明武, 李丽, 金菊良. 围岩稳定性集对分析-可变模糊集综合评价模型[J]. 岩土工程学报,2008,30(6):941 − 944. [WANG Mingwu, LI Li, JIN Juliang. Set pair analysis-variable fuzzy set model for evaluation of stability of surrounding rock[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2008,30(6):941 − 944. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2008.06.026
[7] 王洪德, 曹英浩. 基于改进变权物元可拓模型的围岩稳定性评价[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2013,23(8):23 − 29. [WANG Hongde, CAO Yinghao. Evaluation of surrounding rock stability based on improved matter-element extension model with variable weight[J]. China Safety Science Journal,2013,23(8):23 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2013.08.004
[8] 李健, 汪明武, 徐鹏, 等. 基于云模型的围岩稳定性分类[J]. 岩土工程学报,2014,36(1):83 − 87. [LI Jian, WANG Mingwu, XU Peng, et al. Classification of stability of surrounding rock using cloud model[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2014,36(1):83 − 87. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201401006
[9] 周麟. 地下工程围岩稳定性评价的物元模型及其应用[J]. 金属矿山,1998(9):9 − 12. [ZHOU Lin. Matter element model for the stability evaluation of adjoining rock of underground construction and its application[J]. Metal Mine,1998(9):9 − 12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 梁桂兰, 徐卫亚, 谈小龙. 基于熵权的可拓理论在岩体质量评价中的应用[J]. 岩土力学,2010,31(2):535 − 540. [LIANG Guilan, XU Weiya, TAN Xiaolong. Application of extension theory based on entropy weight to rock quality evaluation[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2010,31(2):535 − 540. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.02.033
[11] 陈丹, 冯东梅, 邵良杉. 采用AHP-可拓学的地下工程围岩稳定性预测模型[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版),2016,35(1):32 − 36. [CHEN Dan, FENG Dongmei, SHAO Liangshan. AHP-extenics model for stability classification of underground engineering surrounding rock[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University (Natural Science Edition),2016,35(1):32 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11956/j.issn.1008-0562.2016.01.007
[12] 杨春燕, 蔡文. 可拓工程研究[J]. 中国工程科学,2000(12):90 − 96. [YANG Chunyan, CAI Wen. Extension engineering research[J]. Strategic Study of CAE,2000(12):90 − 96. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2000.12.015
[13] 李德毅, 刘常昱. 论正态云模型的普适性[J]. 中国工程科学,2004,6(8):28 − 34. [LI Deyi, LIU Changyu. Study on the universality of the normal cloud model[J]. Engineering Science,2004,6(8):28 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2004.08.006
[14] LI D, CHEUNG D, SHI X M, et al. Uncertainty reasoning based on cloud models in controllers[J]. Computers & Mathematics with Applications,1998,35(3):99 − 123.
[15] 李如琦, 苏浩益. 基于可拓云理论的电能质量综合评估模型[J]. 电力系统自动化,2012,36(1):66 − 70. [LI Ruqi, SU Haoyi. A synthetic power quality evaluation model based on extension cloud theory[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems,2012,36(1):66 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 崔志超, 王俊豪, 崔传峰, 等. 基于层次分析法和模糊数学相结合的甘肃东乡八丹沟泥石流易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(1):44 − 50. [CUI Zhichao, WANG Junhao, CUI Chuanfeng, et al. Evaluation of the susceptibility of debris flow in Badan Gully of Dongxiang County of Gansu based on AHP and Fuzzy mathematics[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(1):44 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 潘国营, 杜鹏卓, 陈国胜. 基于EW-FAHP的煤层底板承压水突水危险评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(1):131 − 136. [PAN Guoying, DU Pengzhuo, CHEN Guosheng. Risk evaluation of confined water-inrush from coal seam floor based on EW-FAHP[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(1):131 − 136. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 江强强, 方堃, 章广成. 基于新组合赋权法的地质灾害危险性评价[J]. 自然灾害学报,2015,24(3):28 − 36. [JIANG Qiangqiang, FANG Kun, ZHANG Guangcheng. Assessment of geohazards risk based on new combined weight method[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2015,24(3):28 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 工程岩体分级标准: GB/T 50218—2014[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2015.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Standard for engineering classification of rock mass: GB/T 50218—2014[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2015. (in Chinese)
[20] 汪明武, 朱其坤, 赵奎元, 等. 基于有限区间联系云的围岩稳定性评价模型[J]. 岩土力学,2016,37(增刊1):140 − 144. [WANG Mingwu, ZHU Qikun, ZHAO Kuiyuan, et al. A novel cloud model coupled with connection number based on finite intervals for evaluation of surrounding rock stability[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2016,37(Sup1):140 − 144. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 王凤山, 何雷, 刘猛. 基于改进可拓方法的地下工程围岩稳定性风险分析[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2011,7(6):1263 − 1268. [WANG Fengshan, HE Lei, LIU Meng. Risk analysis on surrounding rock stability of underground engineering with improved extension method[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering,2011,7(6):1263 − 1268. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 李科. 基于熵权—云模型的隧道围岩分级方法研究[J]. 现代隧道技术,2018,55(4):69 − 75. [LI Ke. Classification method for tunnel surrounding rock based on the Entropy Cloud model[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology,2018,55(4):69 − 75. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 魏新江, 张阳, 陈浙江, 等. 基于GIS的隧道洞口边坡的稳定性分析[J]. 公路工程,2020,45(6):165 − 172. [WEI Xinjiang, ZHANG Yang, CHEN Zhejiang, et al. Stability Analysis of Tunnel Portal Slope Based on GIS[J]. Highway Engineering,2020,45(6):165 − 172. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 刘国伟. 山西白龙山隧道地应力场分布规律分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(3):110 − 116. [LIU Guowei. Analysis on in-situ geo-stress field of Bailong Mountain Tunnel[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(3):110 − 116. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 胡炜, 谭信荣, 蒋尧, 等. 深埋顺层偏压隧道围岩破坏机理及规律研究—以郑万线某隧道为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):60 − 68. [HU Wei, TAN Xinrong, JIANG Yao, et al. A study of the mechanism and regularity of failures in the surrounding rock of a deep buried bias tunnel embedded in geologically bedding strata: Taking one tunnel of the Zhengwan line as an example[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):60 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: