The development characteristics of geological hazards in Gansu segment of the Yellow River basin
-
摘要:
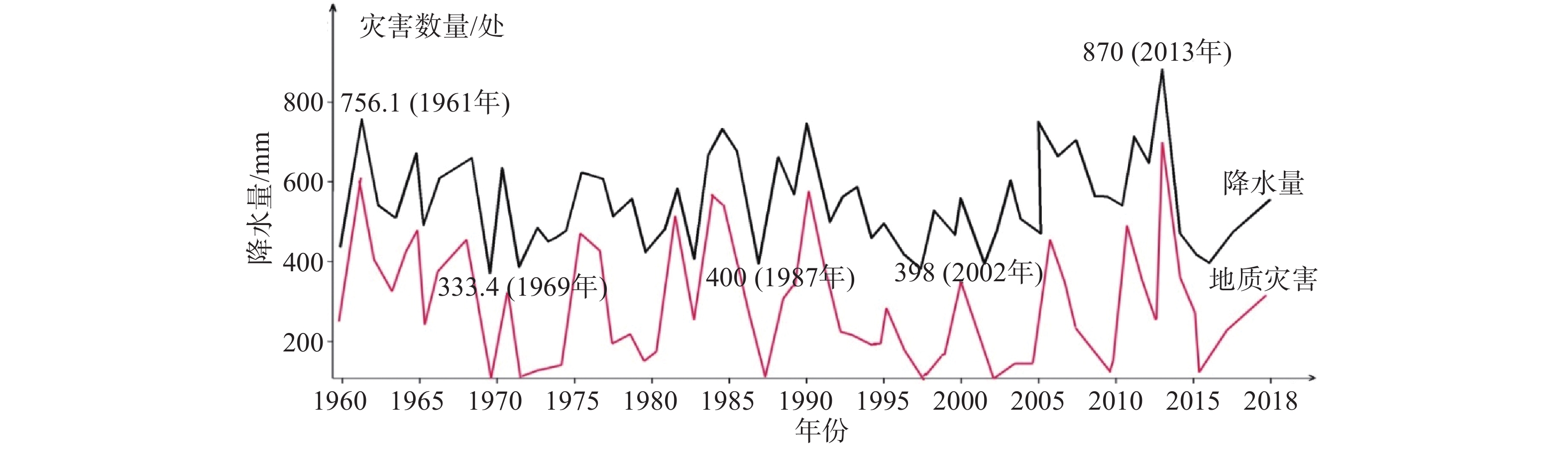
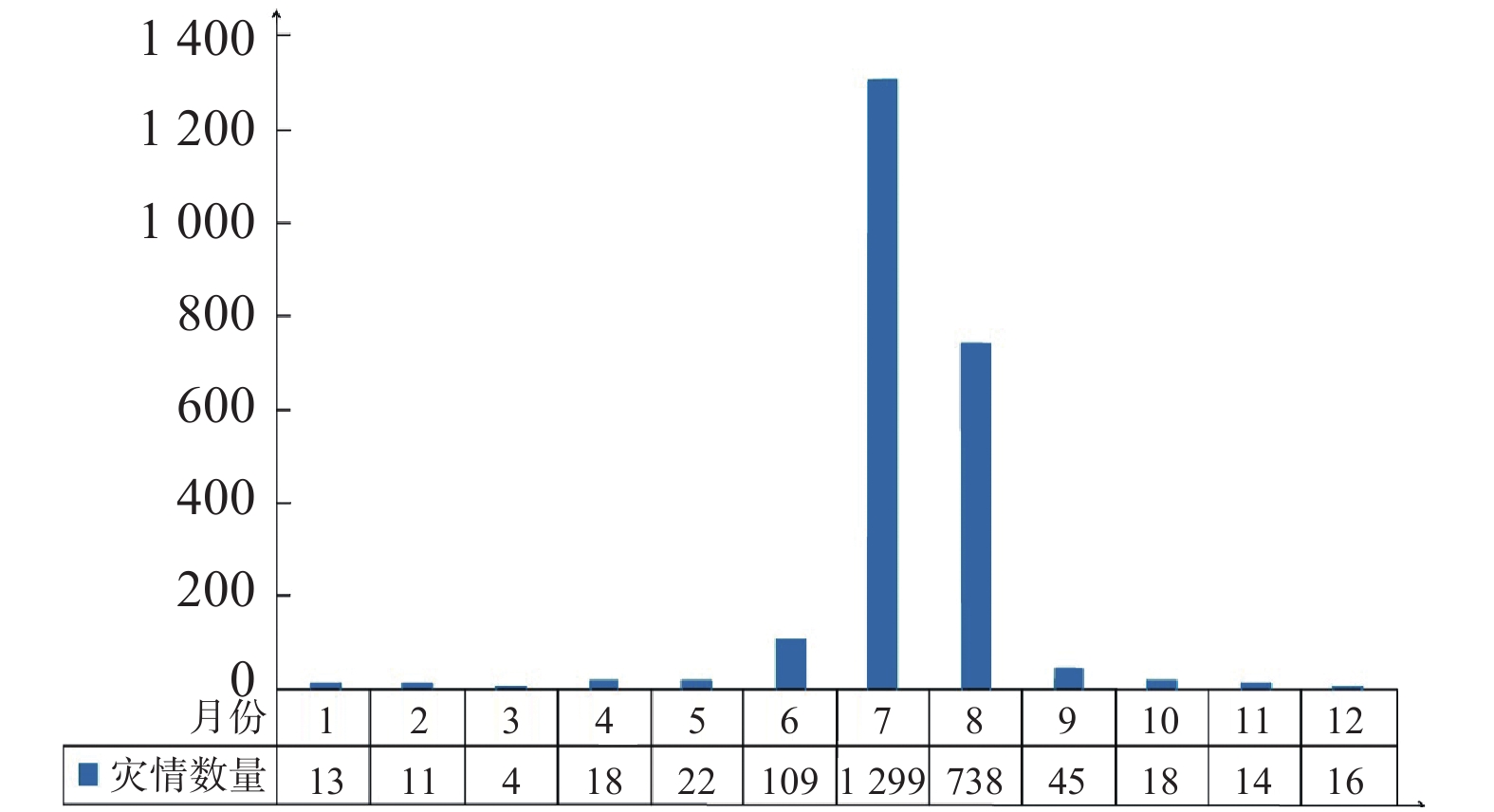
黄河流域甘肃段是甘肃省地质灾害最为集中的区域。截止2019年底,查明地质灾害点共12829处,占全省灾害总量的70.83%。按照水系分布划分,以渭河流域、泾河流域、黄河干流流域最为发育,其他水系次之。依据空间分布特征,划分为永登—靖远等北部泥石流灾害为主的区段、中部崩塌滑坡泥石流集中区段、南部崩塌滑坡泥石流为主的区段和玛曲—碌曲地质灾害轻微发育区段。依据时间分布特征,具有2—5月冻融期、7—9月主汛期两个高发时段。地质灾害具有小灾巨损、群发巨损和链式巨损等致灾特征。单体灾害易形成巨大损失,降雨、地震引发的群发性地质灾害往往损失巨大,同时崩滑流阻断河道形成的堰塞湖风险也常有发生。
Abstract:Gansu section of the Yellow River basin is the most concentrated area of geological disasters in Gansu Province. By the end of 2019, 12829 potential geological hazard points have been identified, accounting for 70.83% of the total number of disasters in Gansu Province. According to the distribution characteristics of water system, Weihe River basin, Jinghe River basin and the Yellow River basin are the most developed, followed by other water systems. According to the spatial distribution characteristics, it can be divided into three sections: the northern Yongdeng—Jingyuan debris flow area, the central and northern landslide debris flow concentrated section, the central and southern collapse landslide debris flow section, and the southern Maqu—Luqu geological disaster development section. In terms of time distribution, there are two high frequency periods: freezing and thawing period from February to May and main flood season from July to September. Geological disasters have the characteristics of small disaster and huge loss, mass damage and chain type huge loss. Single disaster is easy to form huge loss. The mass geological disaster caused by rainfall and earthquake often causes huge loss. At the same time, the risk of dammed lake formed by landslide flow blocking river channel often occurs.
-

-
表 1 黄河流域不同水系地质灾害分布数量一览表
Table 1. List of distribution quantity of geological hazards in different water systems in the Yellow River basin
水系名称 滑坡 崩塌 泥石流 地裂缝 地面塌陷 合计 湟水河流域 187 29 71 0 6 293 黄河干流流域 1952 300 565 87 19 2923 洮河流域 1444 87 910 0 3 2444 渭河流域 2676 239 1004 8 3 3930 泾河流域 2493 188 382 81 21 3165 北洛河流域 55 8 11 0 0 74 合计 8807 851 2943 176 52 12829 表 2 黄河流域不同水系地质灾害人员伤亡及经济损失一览表
Table 2. List of casualties and property losses caused by geological disasters in different water systems in the Yellow River basin
水系名称 受灾人口/人 人员伤亡/人 直接经济损失/万元 黄河干流流域 1131 21 7718.34 洮河流域 5889 11 24442.00 渭河流域 294747 60 419777.20 泾河流域 4448 16 17337.70 合计 306215 108 469275.24 表 3 地震引发崩塌、滑坡数量表
Table 3. Quantity of collapse and landslide caused by earthquake
名称 震级 烈度 区域 引发加剧灾害 海原地震 8.0 6~11 陇东南区域 大型657滑坡处,中小型上万处 漳县岷县地震 6.6 6~8 岷县漳县 289处滑坡,崩塌1000多处 临洮地震 4.5 6 临洮辛店镇 通渭地震 5.5 6~7 通渭县一带 大于500 m3的滑坡337处 永登祁山地震 5.9 6~7 永登景泰 大小黄土滑坡150多处 表 4 黄河流域甘肃段不同水系地质灾害点面积比统计表
Table 4. Statistical table of area ratio of geological hazard of different water systems in Gansu section of the Yellow River basin
水系 滑坡 崩塌 泥石流 地裂缝 地面塌陷 总面积比/
(10−3个·km−2)渭河水系 102.77 9.18 38.55 0.31 0.12 150.90 泾河水系 80.53 6.07 12.33 2.62 0.68 102.19 洮河水系 59.8 3.61 37.71 0 0.12 101.28 湟水河水系 49.31 7.65 18.74 0 1.58 77.33 黄河干流水系 35.36 5.43 10.23 1.58 0.34 52.94 北洛河水系 24.13 3.51 4.83 0 0 32.47 -
[1] 曲雪妍, 李媛, 杨旭东, 等. 中国地质灾害总体特征与形势分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2016,27(4):109 − 113. [QU Xueyan, LI Yuan, YANG Xudong, et al. The general characteristics and situation analysis of geo-hazards in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2016,27(4):109 − 113. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 李媛, 孟晖, 董颖, 等. 中国地质灾害类型及其特征: 基于全国县市地质灾害调查成果分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2004, 15(2): 29−34.
LI Yuan, MENG Hui, DONG Ying, et al. Main types and characterisitics of geo-hazard in China—Based on the results of geo-hazard survey in 290 counties[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2004, 15(2): 29−34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 赵成, 施孝. 甘肃省地质灾害发育特征及防治对策[J]. 甘肃科学学报,2003,15(增刊1):23 − 29. [ZHAO Cheng, SHI Xiao. The development characteristic and prevention and treatment of geologic hazard in Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Gansu Sciences,2003,15(Sup1):23 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 孙建中. 黄土学(上篇)[M]. 香港: 香港考古学会, 2005.
SUN Jianzhong. Loessology (Vol. 1)[M]. Hong Kong: Hong Kong Archaeological Society, 2005. (in Chinese).
[5] 孙於春. 黄河上游甘南地区地质灾害形成条件及防治对策[J]. 甘肃地质,2016,25(4):69 − 73. [SUN Yuchun. Development condition of geological disasters at the upper reaches of the Yellow River in Gannan area and its control measures[J]. Gansu Geology,2016,25(4):69 − 73. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 吕鸿图, 杨双庆, 艾南山. 洒勒山滑坡与新构造应力场关系的探讨[J]. 兰州大学学报,1984,20(4):96 − 104. [LYU Hongtu, YANG Shuangqing, AI Nanshan. On the connection between the landslide at Sale mountain and the neotectonic stress field [J]. Journal of Lanzhou University,1984,20(4):96 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 王家鼎, 惠泱河. 黑方台台缘灌溉水诱发黄土滑坡群的系统分析[J]. 水土保持通报,2001,21(3):10 − 13. [WANG Jiading, HUI Yanghe. Systems analysis on Heifangtai loess landslide in crows induced by irrigated water[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2001,21(3):10 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-288X.2001.03.003
[8] 苏人琼, 杨勤业. 黄河流域灾害环境综合治理对策[J]. 人民黄河,1996,18(11):16 − 20. [SU Renqiong, YANG Qinye. Treatment policy to comprehensively harness the disaster environment in the Yellow River basin[J]. Yellow River,1996,18(11):16 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 姜程, 霍艾迪, 朱兴华, 等. 黄土水力侵蚀-滑坡-泥流灾害链的研究现状[J]. 自然灾害学报,2019,28(1):38 − 43. [JIANG Cheng, HUO Aidi, ZHU Xinghua, et al. Research status of loess hydraulic erosion-landslide-mudflow chain[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2019,28(1):38 − 43. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 马润勇, 彭建兵, 袁志东, 等. 青藏高原隆升的黄土高原构造侵蚀效应[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2007,29(3):289 − 293. [MA Runyong, PENG Jianbing, YUAN Zhidong, et al. Geological hazard effect in loess plateau due to Qinghai-Xizang plateau uplift[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,2007,29(3):289 − 293. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2007.03.013
[11] 郭富赟, 孟兴民, 黎志恒, 等. 天水市“7·25”群发性地质灾害特征及成因[J]. 山地学报,2015,33(1):100 − 107. [GUO Fuyun, MENG Xingmin, LI Zhiheng, et al. Characteristics and causes of assembled geo-hazards induced by the rainstorm on 25th July 2013 in Tianshui City, Gansu, China[J]. Mountain Research,2015,33(1):100 − 107. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 许冲, 吴熙彦, 徐锡伟. 黄土高原及邻区的地震滑坡[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(增刊1):260 − 273. [XU Chong, WU Xiyan, XU Xiwei. Earth earthouake-triggered landslides in the loess platsau and its adjacent areas[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(Sup1):260 − 273. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 王兰民, 蒲小武, 陈金昌. 黄土高原地震诱发滑坡分布特征与灾害风险[J]. 城市与减灾,2019(3):33 − 40. [WANG Lanmin, PU Xiaowu, CHEN Jinchang. Distribution feature and disaster risk of earthquake-induced landslide in loess plateau[J]. City and Disaster Reduction,2019(3):33 − 40. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0495.2019.03.009
[14] 郭富赟, 宋晓玲, 谢煜, 等. 甘肃地质灾害气象预警技术方法探讨[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2015,26(1):127 − 133. [GUO Fuyun, SONG Xiaoling, XIE Yu, et al. A discussion on the geological hazards meteorological warning system in Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2015,26(1):127 − 133. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 张茂省, 李同录. 黄土滑坡诱发因素及其形成机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2011,19(4):530 − 540. [ZHANG Maosheng, LI Tonglu. Triggering factors and forming mechanism of loess landslides[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2011,19(4):530 − 540. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2011.04.014
[16] 郭富赟. 兰州市地质灾害特征与风险管控对策[J]. 城市与减灾,2019(3):59 − 63. [GUO Fubin. Feature of geological disaster in Lanzhou City and its counter measures of management and control[J]. City and Disaster Reduction,2019(3):59 − 63. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0495.2019.03.013
[17] 廖红建, 赵树德, 高小育, 等. 西部黄土高原窑洞民居发展中的环境工程问题[J]. 西安交通大学学报(社会科学版),2000,20(3):7 − 10. [LIAO Hongjian, ZHAO Shude, GAO Xiaoyu, et al. Environmental engineering problems in developing loess plateau cave dwellings in western areas[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University (Social Sciences Edition),2000,20(3):7 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 雷祥义. 黄土高原地质灾害与人类活动[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2001.
LEI Xiangyi. Geological disasters and human activities on the loess plateau of China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2001. (in Chinese).
[19] 罗守敬, 王珊珊, 付德奎, 等. 北京山区突发性地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(4):126 − 133. [LUO Shoujing, WANG Shanshan, FU Dekui, et al. Assessment on the susceptibility of sudden geological hazaeds in mountainous areas of Beijing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(4):126 − 133. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 樊晓一, 张睿骁, 胡晓波. 沟谷地形参数对滑坡运动距离的影响研究[J]. 地质力学学报,2020,26(1):106 − 114. [FAN Xiaoyi, ZHANG Ruixiao, HU Xiaobo. Study on the influence of valley topographic parameter on the moving distance of landslide[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2020,26(1):106 − 114. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 彭建兵, 王启耀, 庄建琦, 等. 黄土高原滑坡灾害形成动力学机制[J]. 地质力学学报,2020,26(5):714 − 730. [PENG Jianbing, WANG Qiyao, ZHUANG Jianqi, et al. Dynamic formation mechanism of landslide disaster on the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2020,26(5):714 − 730. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 祁小军. 公路工程环境的岩土勘察与地质灾害评估技术研究[J]. 公路工程,2019,44(1):115 − 119. [QI Xiaojun. Geotechnical investigation and geological hazard assessment technology for highway engineering environment[J]. Highway Engineering,2019,44(1):115 − 119. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 李滨, 殷跃平, 高杨, 等. 西南岩溶山区大型崩滑灾害研究的关键问题[J]. 水文地质工程质,2020,47(4):5 − 13. [LI Bin, YING Yueping, GAO Yang, et al. Critical issues in rock avanlanches in the karst mountain areas of southwest China[J]. Hydrogelogy & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):5 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 李明威, 唐川, 陈明, 等. 汶川震区北川县泥石流流域崩滑体时空演变特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):182 − 190. [LI Mingwei, TANG Chuan, CHEN Ming, et al. Spatio-temporal evolution characteristics of landslides in debris flow catchment in Beichuan County in the Wenchuan earthquake zone[J]. Hydrogelogy & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):182 − 190. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 陈冠, 孟兴民, 乔良, 等. “7·22”岷县漳县地震地质灾害分布、特征及与影响因子间关系分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2013,21(5):750 − 760. [CHEN Guan, MENG Xingmin, QIAO Liang, et al. Distribution, characteristics, and associated influencial factors of the geohazards induced by Minxian-Zhangxian earthquake on 22 July, 2013, Gansu, China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2013,21(5):750 − 760. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2013.05.011
[26] 费杰, 何洪鸣, 杨帅, 等. 公元前221年—公元1911年陕甘地区堰塞湖成因浅析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(6):117 − 125. [FEI Jie, HE Hongming, YANG Shuai, et al. Landslide lakes in Shaanxi and Gansu Provinces in the period between BC 221 and AD 1911[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(6):117 − 125. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: