Landslide susceptibility assessment based on K-means cluster information model in Wenchuan and two neighboring counties, China
-
摘要:
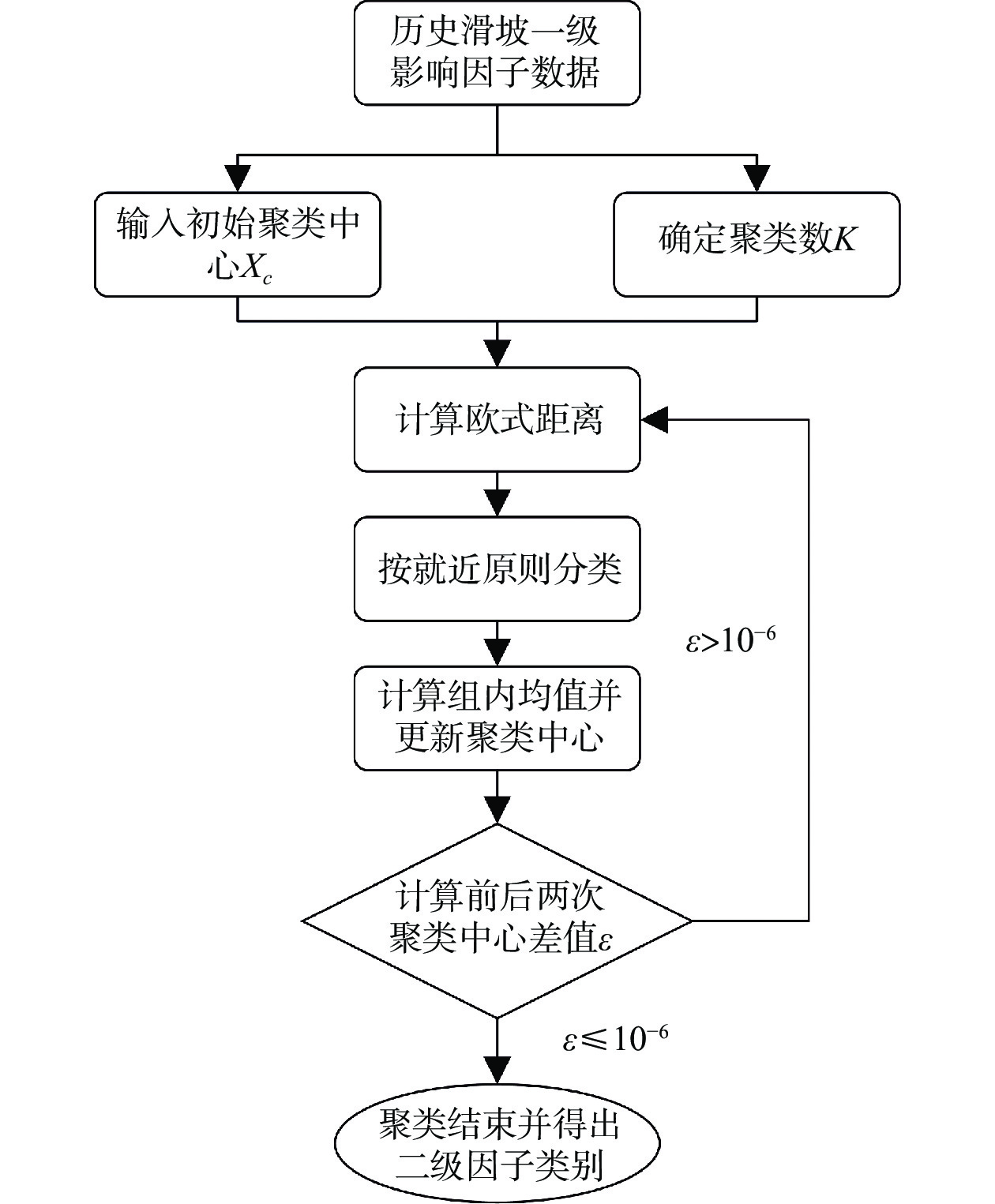
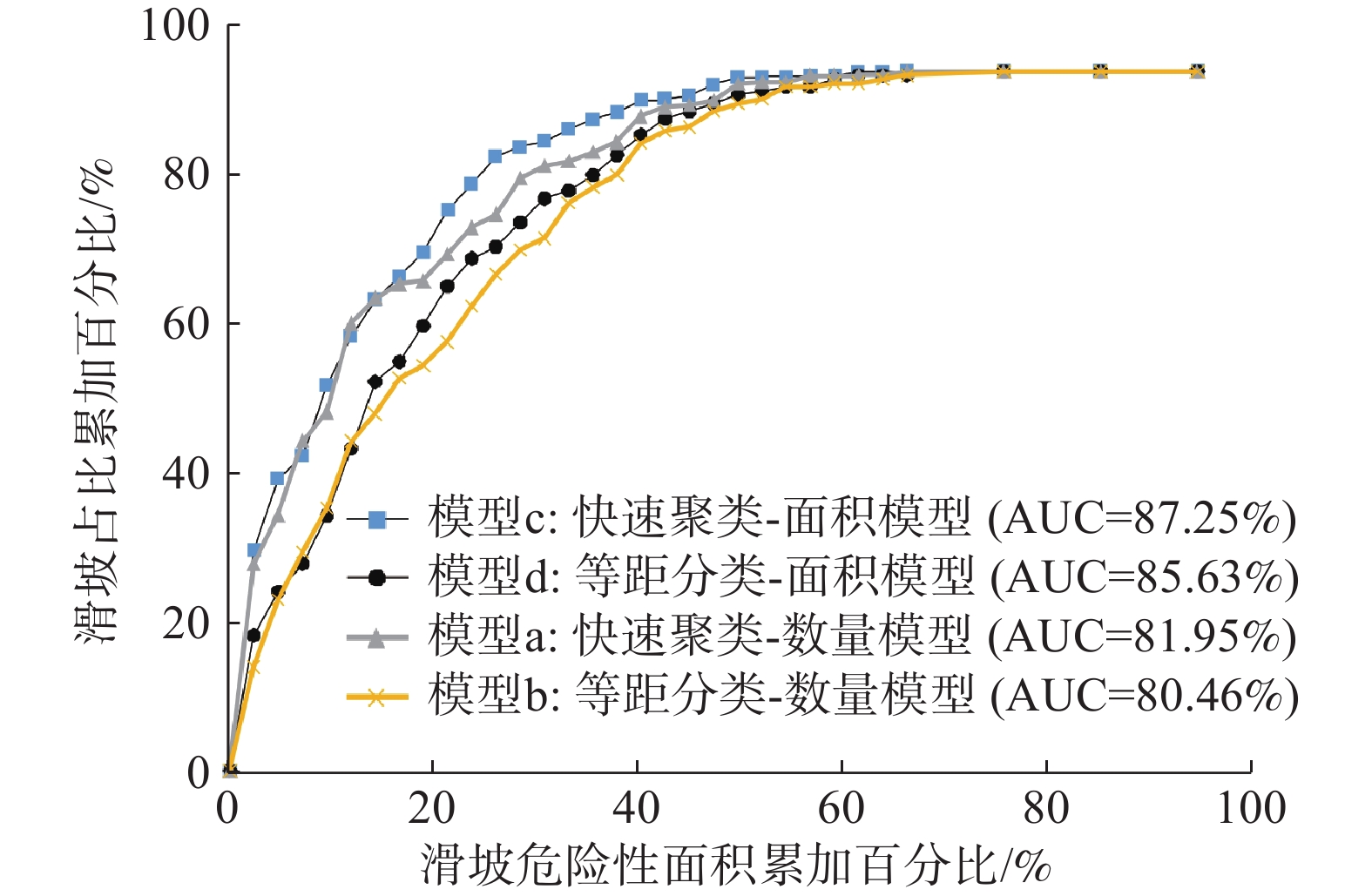
滑坡灾害易发性评价研究对规划灾害区域、制定防灾策略等方面具有十分重要的意义。以滑坡灾害频发的汶川及周边两县(理县和茂县)为例,提出滑坡灾害易发性评价的快速聚类-信息量模型。选取坡度、高程、坡向、距构造的距离、距水系的距离、地层岩性和土地利用情况为对滑坡有重要影响的7个影响因子,并在二级因子的分类上,对上述前5个影响因子依据159处滑坡样本分别开展快速聚类分析,同时也给出了传统的等距分类法,以便与快速聚类方法形成对比,对后2个影响因子则以定性方法分类。根据上述二级分类方法的不同,以及滑坡样本是否考虑面积因素,将信息量模型细分为四类(模型a:快速聚类-数量模型、模型b:等距分类-数量模型、模型c:快速聚类-面积模型、模型d:等距分类-面积模型),分别计算各二级指标信息量,并通过ArcGIS空间叠加分析得到研究区域信息量分布,然后通过自然断点法将研究区滑坡易发性划分为五个等级。以易发性递增原则和线下面积(Area Under Curve,AUC)作为精度评价指标,结果表明:①快速聚类模型(模型a和模型c)整体效果优于等距分类模型(模型b和模型d);②相同分类方法下,面积模型(模型c与模型d)整体优于数量模型(模型a和模型b);③在上述两项优势的加持下,模型c相较于模型b,评价精度明显提升,其AUC值从80.46%提高到87.25%。
Abstract:The study of landslide susceptibility evaluation is of great significance to both zoning of geological disasters and disaster prevention strategies. Taking Wenchuan and two surrounding counties (Li County and Mao County), which are prone to landslides, as an example, K-means cluster information model for landslide susceptibility mapping is proposed. After seven impact factors, i.e., slope angle, elevation, aspect, distance from the structure, distance from the water system, formation lithology and the land usage, are selected, the secondary classification for factors is carried out. The former five impact factors mentioned above were classified separately by K-means cluster analysis according to 159 landslide samples. At the sametime, the traditional isometric classification was also presented to compare with the K-means clustering method. The latter two impact factors were classified qualitatively. According to the differences of the above secondary classification methods and whether the landslide sample considers the area factor, the information model is subdivided into four categories (model a: K-means clustering quantitative model, model b: isometric classification quantitative model, model c: K-means clustering area model, and model d: isometric classification area model). The information of each secondary index was calculated separately, and the information distribution of the study area was obtained through spatial overlay analysis of ArcGIS. Then, the landslide susceptibility of the study area was divided into five grades by natural breakpoint method. Taking the principle of increasing susceptibility and Area Under Curve (AUC) as the accuracy evaluation indicators, three results were obtained. First, the overall effect of K-means clustering models (model a and model c) is better than that of isometric classification models (model b and model d). Second, the area models (model c and model d) are generally better than the quantitative models (model a and model b) under the same classification method. Third, With the above two advantages, the evaluation accuracy of model c is significantly improved compared with model b, and its AUC value is increased from 80.46% to 87.25%.
-
Key words:
- landslide susceptibility assessment /
- K-means cluster /
- information model /
- GIS
-

-
表 1 影响因子选择
Table 1. Selection of impact factors
表 2 基于滑坡样本点数的信息量表
Table 2. Information table based on landslide sample points
快速聚类 等距分类 影响因子 类别 Ni/个 Si/km2 信息量 信息量排序 类别 Ni/个 Si/km2 信息量 信息量
排序坡度/(°) 0~11 7 511.43 0.0537 19 0~10 6 421.68 0.0925 18 11~16 6 628.12 −0.3060 31 10~20 19 1 487.20 −0.0152 26 16~23.5 23 1 675.49 0.0566 18 20~30 37 3 152.83 −0.1001 28 23.5~31 29 2 644.01 −0.1678 27 30~40 43 4 006.00 −0.1893 33 31~37.1 29 2 505.85 −0.1141 24 40~50 35 2 442.66 0.0995 17 37.1~42.3 20 1 869.38 −0.1926 29 50~60 17 649.38 0.7022 4 42.3~48 19 1 371.03 0.0661 17 60~70 2 82.78 0.6220 6 48~55 18 766.38 0.5937 9 70~80 0 11.90 0.0000 20 >55 8 285.93 0.7687 4 80~90 0 3.20 0.0000 21 坡向/(°) 平地 0 16.21 0.0000 21 平地 0 16.21 0.0000 22 0~73 28 2 408.54 −0.1096 23 北 34 2 900.44 −0.1013 29 73~165 52 3 433.19 0.1550 16 东 53 3 370.65 0.1924 16 165~273 30 3 452.58 −0.4007 33 南 21 2 916.79 −0.5887 37 273~360 49 2 947.11 0.2482 12 西 51 3 053.54 0.2528 11 高程/m 0~1 560 31 457.67 1.6528 1 0~1 000 2 36.59 1.4385 2 1 560~2 141 38 1 171.89 0.9162 3 1 000~2 000 53 1 235.36 1.1962 3 2 141~2 647 42 1 653.95 0.6717 6 2 000~3 000 79 3 466.41 0.5636 9 2 647~3 196 37 2 335.66 0.1999 15 3 000~4 000 24 4 719.42 −0.9364 40 3 196~3 805 10 2 958.07 −1.3447 39 4 000~5 000 1 2 719.74 −3.5633 42 >3 805 1 3 680.40 −3.8658 42 5 000~6 000 0 80.12 0.0000 23 距水系的距离/m 0~375 88 3 712.72 0.6028 8 0~600 106 5 734.40 0.3542 10 375~858 37 4 024.04 −0.3441 32 600~1 200 32 4 003.87 −0.4843 36 858~1373 23 2 728.73 −0.4311 34 1 200~1 800 18 1 836.15 −0.2801 34 1 373~1 972 10 1 352.43 −0.5621 35 1 800~2 400 3 555.91 −0.8770 39 >1 972 1 439.71 −1.7411 40 >2 400 0 127.30 0.0000 24 距构造的距离/m 0~912 50 2 130.68 0.5928 10 0~1 000 53 2 316.74 0.5674 8 912~2137 39 2 268.16 0.2818 11 1 000~2 000 31 1 866.78 0.2470 12 2 137~3 705 25 1 897.92 0.0154 20 2 000~3 000 19 1 367.60 0.0686 19 3 705~5 592 26 1 615.25 0.2159 13 3 000~4 000 12 1 030.66 −0.1080 30 5 592~7 350 12 1 120.21 −0.1914 28 4 000~5 000 14 877.28 0.2072 15 7 350~8 689 3 615.83 −0.9794 37 5 000~6 000 12 742.27 0.2202 13 8 689~11 039 3 741.00 −1.1644 38 6 000~7 000 8 634.16 −0.0279 27 >11 039 1 1 868.59 −3.1879 41 >7 000 10 3 422.15 −1.4904 41 岩性 坚硬岩石 3 531.70 −0.8325 36 坚硬岩石 3 531.70 −0.8325 38 较硬岩石 58 5 964.50 −0.2881 30 较硬岩石 58 5 964.50 −0.2881 35 较软岩石 37 3 226.83 −0.1233 25 较软岩石 37 3 226.83 −0.1233 31 软硬相间岩石 55 2 299.43 0.6119 7 软硬相间岩石 55 2 299.43 0.6119 7 软岩 6 235.17 0.6765 5 软岩 6 235.17 0.6765 5 土地利用 耕地 24 421.85 1.4784 2 耕地 24 421.85 1.4784 1 林地 134 11 766.00 −0.1301 26 林地 134 11 766.00 −0.1301 32 人类活动 0 7.15 0.0000 22 人类活动 0 7.15 0.0000 25 其他用地 1 62.64 0.2077 14 其他用地 1 62.64 0.2077 14 表 3 基于滑坡样本面积的信息量表
Table 3. Information table based on landslide sample area
快速聚类 等距分类 影响因子 类别 Ai/km2 Si/km2 信息量 信息量排序 类别 Ai/km2 Si/km2 信息量 信息量排序 坡度/(°) 0~11 0.0053 511.43 −2.1677 39 0~10 0.0049 421.68 −2.0431 40 11~16 0.0267 628.12 −0.7512 31 10~20 0.0460 1 487.20 −1.0677 36 16~23.5 0.1035 1 675.49 −0.3766 28 20~30 0.3476 3 152.83 0.2026 15 23.5~31 0.3189 2 644.01 0.2923 11 30~40 0.3695 4 006.00 0.0242 20 31~37.1 0.1896 2 505.85 −0.1739 23 40~50 0.2291 2 442.66 0.0407 18 37.1~42.3 0.1544 1 869.38 −0.0862 21 50~60 0.0938 649.38 0.4724 8 42.3~48 0.1237 1 371.03 0.0021 17 60~70 0.0127 82.78 0.5321 7 48~55 0.1519 766.38 0.7891 4 70~80 0.0000 11.90 0.0000 21 >55 0.0297 285.93 0.1422 16 80~90 0.0000 3.20 0.0000 22 坡向/(°) 平地 0.0000 16.21 0.0000 18 平地 0.0000 16.21 0.0000 23 0~73 0.1839 2 408.54 −0.1651 22 北 0.1600 2 900.44 −0.4901 32 73~165 0.5009 3 433.19 0.4826 9 东 0.5816 3 370.65 0.6504 5 165~273 0.0719 3 452.58 −1.4646 35 南 0.0606 2 916.79 −1.4667 38 273~360 0.3471 2 947.11 0.2684 12 西 0.3015 3 053.54 0.0923 16 高程/m 0~1 560 0.3770 457.67 2.2135 1 0~1 000 0.0587 36.59 2.8806 1 1 560~2 141 0.1873 1 171.89 0.5739 7 1 000~2 000 0.4482 1 235.36 1.3937 3 2 141~2 647 0.3084 1 653.95 0.7280 5 2 000~3 000 0.4682 3 466.41 0.4056 9 2 647~3 196 0.1977 2 335.66 −0.0620 20 3 000~4 000 0.1277 4 719.42 −1.2024 37 3 196~3 805 0.0325 2 958.07 −2.1033 38 4 000~5 000 0.0008 2 719.74 −5.7310 42 >3 805 0.0008 3 680.40 −6.0335 42 5 000~6 000 0.0000 80.12 0.0000 24 距水系的距离/m 0~375 0.6835 3 712.72 0.7153 6 0~600 0.7637 5 734.40 0.3915 10 375~858 0.2641 4 024.04 −0.3162 27 600~1 200 0.2228 4 003.87 −0.4812 31 858~1 373 0.0973 2 728.73 −0.9261 33 1 200~1 800 0.0761 1 836.15 −0.7759 33 1 373~1 972 0.0575 1 352.43 −0.7509 30 1 800~2 400 0.0411 555.91 −0.1982 27 >1 972 0.0012 439.71 −3.4659 41 >2 400 0.0000 127.30 0.0000 25 距构造的距离/m 0~912 0.4494 2 130.68 0.8512 3 0~1 000 0.4571 2 316.74 0.7844 4 912~2 137 0.1493 2 268.16 −0.3136 26 1 000~2 000 0.1180 1 866.78 −0.3534 30 2 137~3 705 0.2212 1 897.92 0.2580 13 2 000~3 000 0.1266 1 367.60 0.0275 19 3 705~5 592 0.1791 1 615.25 0.2081 15 3 000~4 000 0.1194 1 030.66 0.2519 14 5 592~7 350 0.0379 1 120.21 −0.9782 34 4 000~5 000 0.1140 877.28 0.3672 11 7 350~8 689 0.0276 615.83 −0.6976 29 5 000~6 000 0.0720 742.27 0.0750 17 8 689~11 039 0.0100 741.00 −1.8935 37 6 000~7 000 0.0262 634.16 −0.7775 34 >11 039 0.0292 1 868.59 −1.7520 36 >7 000 0.0703 3 422.15 −1.4778 39 岩性 坚硬岩石 0.0380 531.70 −0.2312 24 坚硬岩石 0.0380 531.70 −0.2312 28 较硬岩石 0.2407 5 964.50 −0.8024 32 较硬岩石 0.2407 5 964.50 −0.8024 35 较软岩石 0.5088 3 226.83 0.5603 8 较软岩石 0.5088 3 226.83 0.5603 6 软硬相间岩石 0.2888 2 299.43 0.3327 10 软硬相间岩石 0.2888 2 299.43 0.3327 12 软岩 0.0274 235.17 0.2565 14 软岩 0.0274 235.17 0.2565 13 土地利用 耕地 0.2865 421.85 2.0207 2 耕地 0.2865 421.85 2.0207 2 林地 0.8168 11 766.00 −0.2601 25 林地 0.8168 11 766.00 −0.2601 29 人类活动 0.0000 7.15 0.0000 19 人类活动 0.0000 7.15 0.0000 26 其他用地 0.0003 62.64 −2.7848 40 其他用地 0.0003 62.64 −2.7848 41 -
[1] 高华喜. 滑坡灾害风险区划与预测研究综述[J]. 灾害学,2010,25(2):124 − 128. [GAO Huaxi. Overview on landslide risk zoning and prediction research[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2010,25(2):124 − 128. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2010.02.025
[2] LEE S, PRADHAN B. Landslide hazard mapping at Selangor, Malaysia using frequency ratio and logistic regression models[J]. Landslides,2007,4(1):33 − 41. doi: 10.1007/s10346-006-0047-y
[3] POURGHASEMI H R, JIRANDEH A G, PRADHAN B, et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping using support vector machine and GIS at the Golestan Province, Iran[J]. Journal of Earth System Science,2013,122(2):349 − 369. doi: 10.1007/s12040-013-0282-2
[4] DU J, GLADE T, WOLDAI T, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on an incomplete landslide inventory in the Jilong Valley, Xizang, Chinese Himalayas[J]. Engineering Geology,2020,270:105572. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105572
[5] 高克昌, 崔鹏, 赵纯勇, 等. 基于地理信息系统和信息量模型的滑坡危险性评价: 以重庆万州为例[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2006,25(5):991 − 996. [GAO Kechang, CUI Peng, ZHAO Chunyong, et al. Landslide hazard evaluation of Wanzhou based on GIS information value method in the Three Gorges reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2006,25(5):991 − 996. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.05.020
[6] 刘艺梁, 殷坤龙, 刘斌. 逻辑回归和人工神经网络模型在滑坡灾害空间预测中的应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2010,37(5):92 − 96. [LIU Yiliang, YIN Kunlong, LIU Bin. Application of logistic regression and artificial neural networks in spatial assessment of landslide hazards[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2010,37(5):92 − 96. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.05.017
[7] JIANG L, LIU D S, JIANG Y H, et al. Landside susceptibility assessment based on weighted information value model: A case study of Wenchuan earthquake 10 degree region[C]//2014 The Third International Conference on Agro-Geoinformatics. Beijing: IEEE, 2014: 1-4.
[8] 马国超. 强震区汶川县地质灾害危险性评价研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2015.
MA Guochao. The geological hazard assessment and mapping study of Wenchuan in meizoseismal area[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 王磊. 基于GIS的理县滑坡地质灾害风险性评价[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2013.
WANG Lei. Risk assessment of landslide in Li County based on GIS[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 崔志超, 王俊豪, 崔传峰, 等. 基于层次分析法和模糊数学相结合的甘肃东乡八丹沟泥石流易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(1):44 − 50. [CUI Zhichao, WANG Junhao, CUI Chuanfeng, et al. Evaluation of the susceptibility of debris flow in Badan gully of Dongxiang County of Gansu based on AHP and fuzzy mathematics[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(1):44 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 孙长明, 马润勇, 尚合欣, 等. 基于滑坡分类的西宁市滑坡易发性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):173 − 181. [SUN Changming, MA Runyong, SHANG Hexin, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment in Xining based on landslide classification[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):173 − 181. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 方然可, 刘艳辉, 苏永超, 等. 基于逻辑回归的四川青川县区域滑坡灾害预警模型[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):181 − 187. [FANG Ranke, LIU Yanhui, SU Yongchao, et al. A early warning model of regional landslide in Qingchuan County,Sichuan Province based on logistic regression[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):181 − 187. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 韩蓓. 基于GIS的岷江上游汶川—叠溪河段滑坡灾害危险性评价[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2014.
HAN Bei. Landslide geological disaster hazard assessment in Minjiang river from Wenchuan to diexi based on GIS[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 王雷, 吴君平, 赵冰雪, 等. 基于GIS和信息量模型的安徽池州地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(3):96 − 103. [WANG Lei, WU Junping, ZHAO Bingxue, et al. Susceptibility assessment of geohazards in Chizhou City of Anhui Province based on GIS and informative model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(3):96 − 103. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 冯超. K-means聚类算法的研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2007.
FENG Chao. Research of K-means clustering algorithm[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 吴夙慧, 成颖, 郑彦宁, 等. K-means算法研究综述[J]. 现代图书情报技术,2011(5):28 − 35. [WU Suhui, CHENG Ying, ZHENG Yanning, et al. Survey on K-means algorithm[J]. New Technology of Library and Information Service,2011(5):28 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 李军, 周成虎. 基于栅格GIS滑坡风险评价方法中格网大小选取分析[J]. 遥感学报,2003,7(2):86 − 92. [LI Jun, ZHOU Chenghu. Appropriate grid size for terrain based landslide risk assessment in lantau island, Hong Kong[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing,2003,7(2):86 − 92. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11834/jrs.20030202
[18] 王帅永. 县域地质灾害风险评价研究: 以四川省汶川县为例[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2016.
WANG Shuaiyong. Geohazard risk assessment at the county-level: A case study of Wenchuan County, Sichuan Province[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] YANG J T, SONG C, YANG Y, et al. New method for landslide susceptibility mapping supported by spatial logistic regression and GeoDetector: A case study of Duwen Highway Basin, Sichuan Province, China[J]. Geomorphology,2019,324:62 − 71. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.09.019
[20] 吴志宇, 刘齐建. SH波作用下边坡地形的地面运动分析[J]. 公路工程,2019,44(3):80 − 84. [WU Zhiyu, LIU Qijian. Surface motion of a slope on half space to SH waves[J]. Highway Engineering,2019,44(3):80 − 84. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 王智伟, 王利, 黄观文, 等. 基于BP神经网络的滑坡监测多源异构数据融合算法研究[J]. 地质力学学报,2020,26(4):575 − 582. [WANG Zhiwei, WANG Li, HUANG Guanwen, et al. Research on multi-source heterogeneous data fusion algorithm of landslide monitoring based on BP neural network[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2020,26(4):575 − 582. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 樊晓一, 张睿骁, 胡晓波. 沟谷地形参数对滑坡运动距离的影响研究[J]. 地质力学学报,2020,26(1):106 − 114. [FAN Xiaoyi, ZHANG Ruixiao, HU Xiaobo. Study on the influence of valley topographic parameter on the moving distance of landslide[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2020,26(1):106 − 114. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: