Analysis on association rules of multi-field information of Baishuihe landslide based on the data mining
-
摘要:
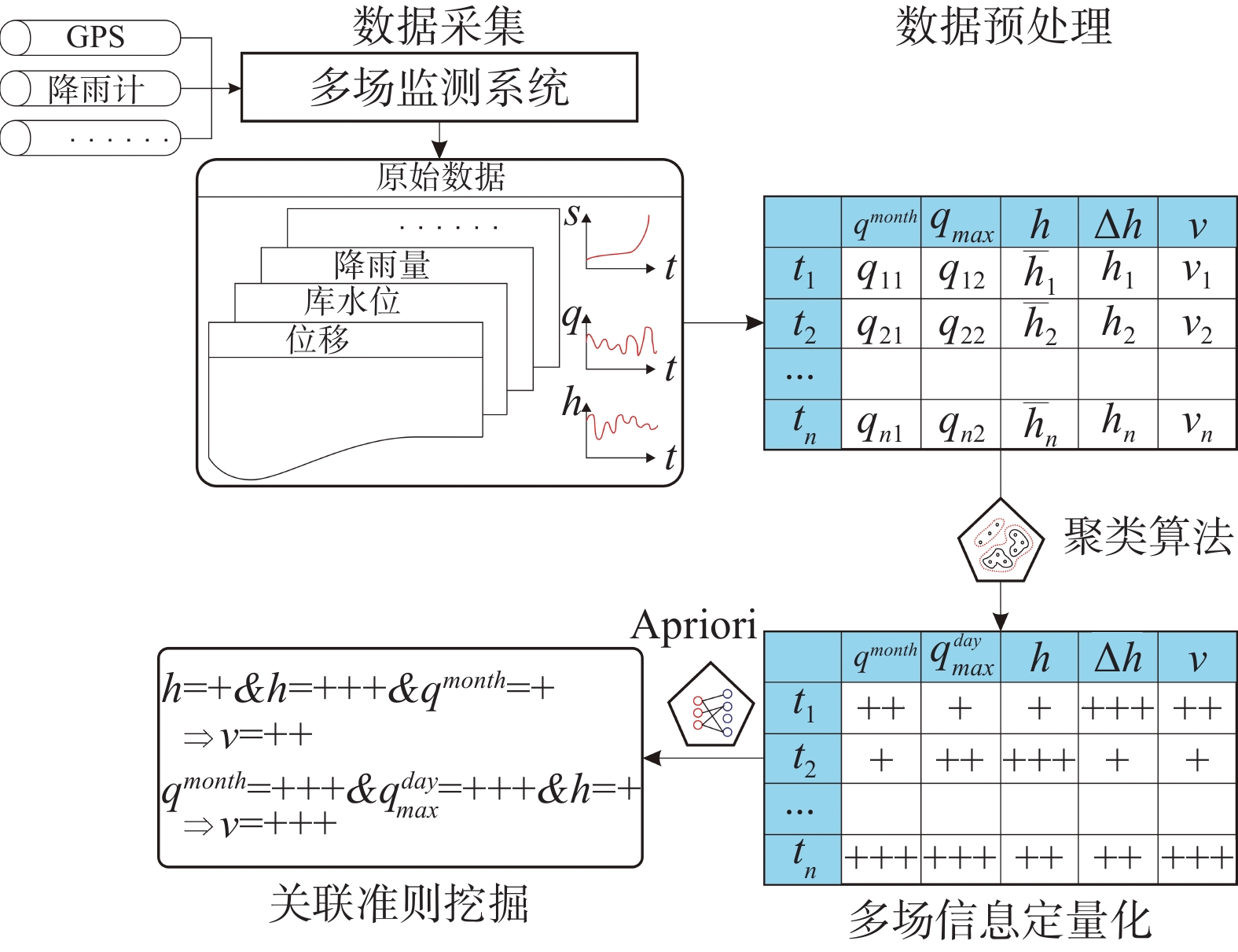
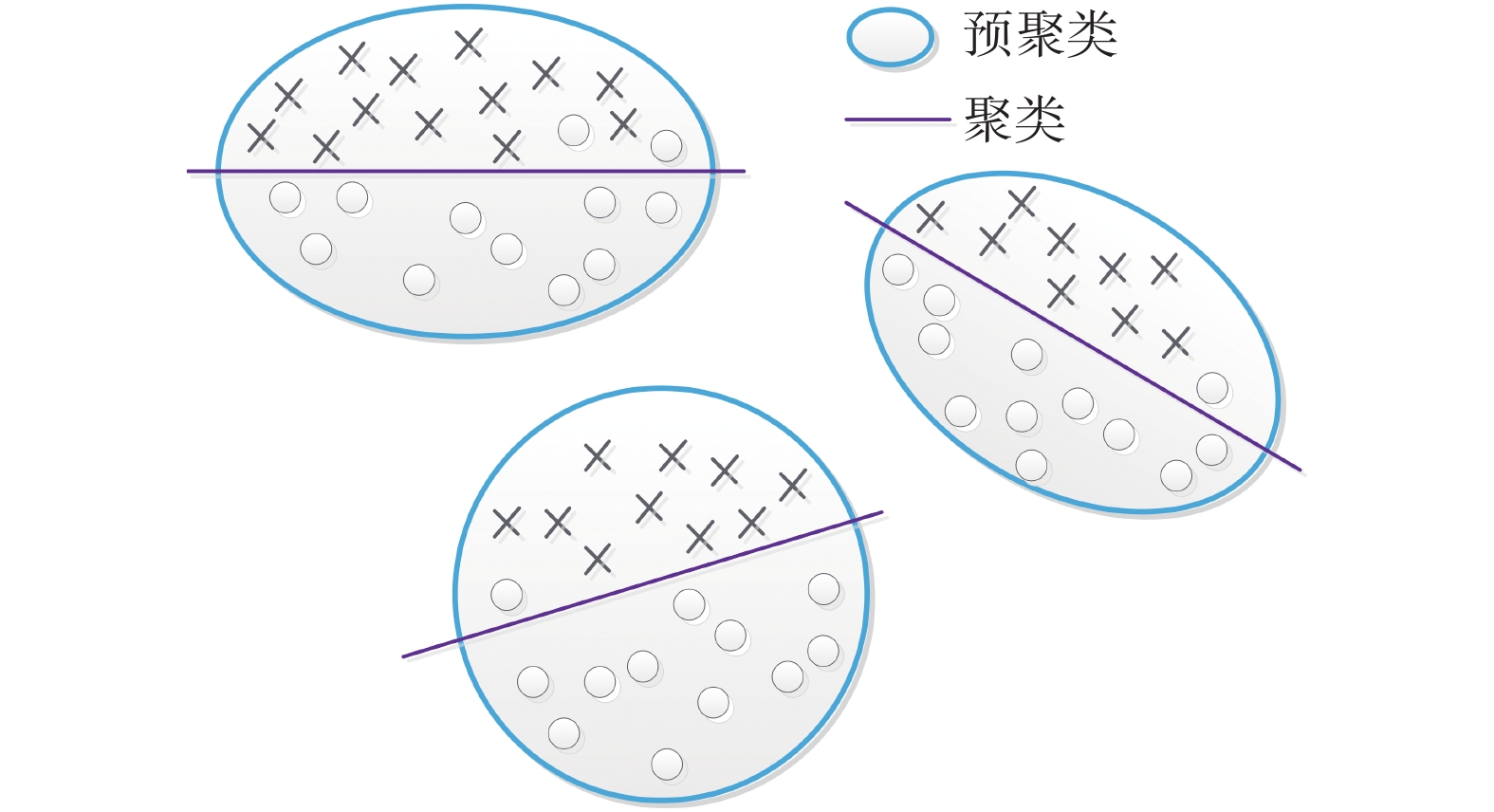
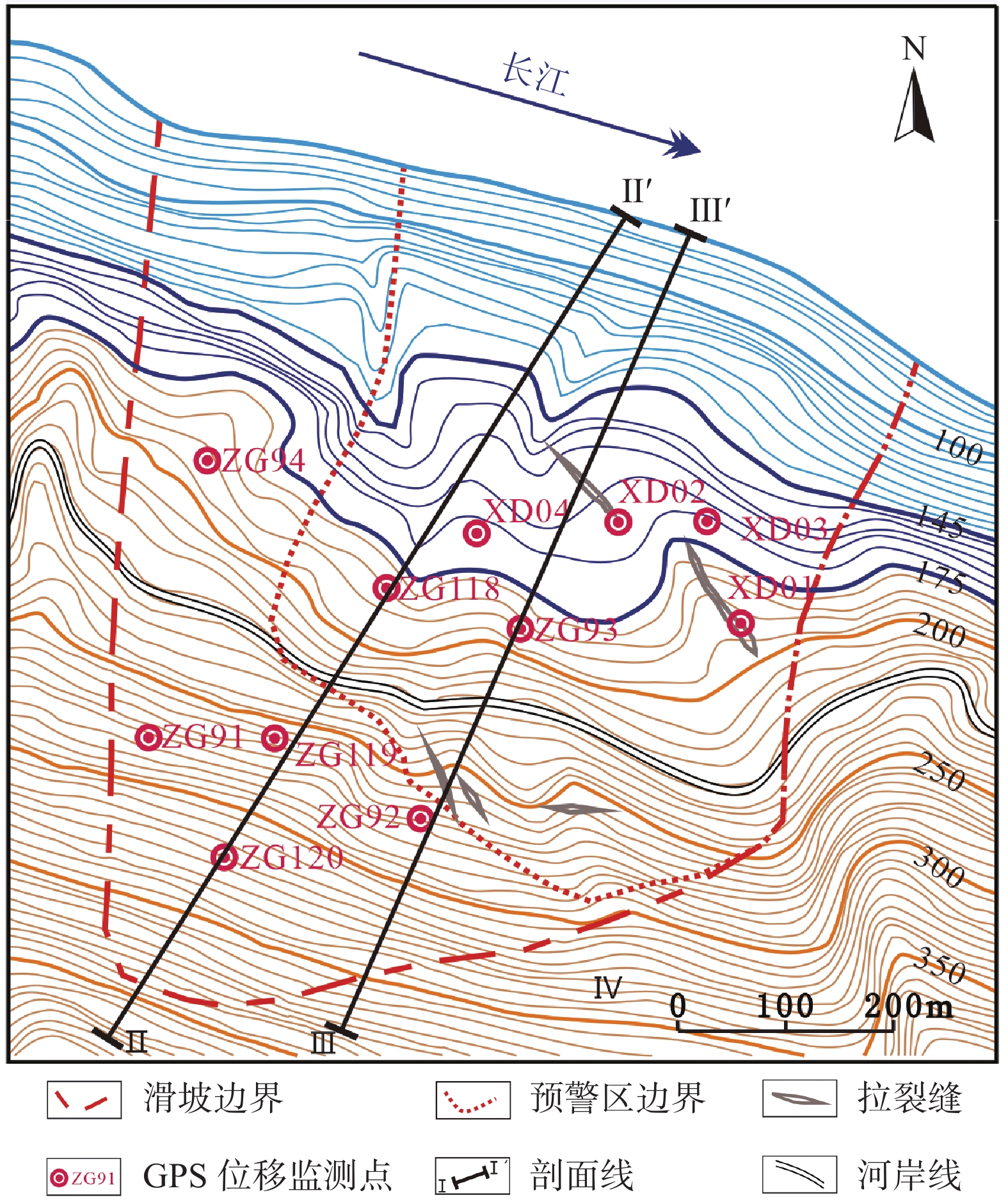
为探究滑坡多场监测数据间的关联准则,采用数据挖掘技术中的两步聚类法与Apriori算法,开展滑坡多场信息关联准则研究。以三峡库区白水河滑坡为例,分析ZG93监测点于2003年6月—2016年12月期间的监测数据,选取影响滑坡变形的主要诱发因子,采用两步聚类法对不同的影响因子进行预聚类和聚类,将数值型变量转化为离散型变量后,应用Apriori算法进行处理,生成满足最小置信度的关联准则,建立白水河滑坡多场耦合作用模式下的影响因子与滑坡位移变形关联准则判据。研究表明,关联准则对于滑坡灾害的变形分析具有重要的意义,数据挖掘技术可较好地应用于三峡库区地质灾害位移预测预报中。
Abstract:In order to explore the association criteria of landslide multi-field monitoring data, we have adopted the two-step clustering method and Apriori algorithm, which belong to the classical data mining method, and we have also proposed the process of landslide monitoring data mining. Based on the Baishuihe landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, we analyzed the monitoring data of ZG93 from June 2003 to June 2016. The main inducing factors of the landslide displacement were selected, and the two-step clustering method was used to pre-cluster and cluster the different influence factors. We used Apriori algorithm to deal with the classified variables to generate frequent item sets that satisfy the minimum support degree. The association rules between the precipitating factors and the landslide deformation are established under the multi-field coupling mode of Baishuihe landslide. The results show that the correlation criterion is of great significance to the deformation analysis of landslide hazards and the data mining technology can be applied to the displacement prediction of geological hazards in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area.
-
Key words:
- reservoir landslide /
- data mining /
- two-step clustering method /
- Apriori algorithm /
- association rules
-

-
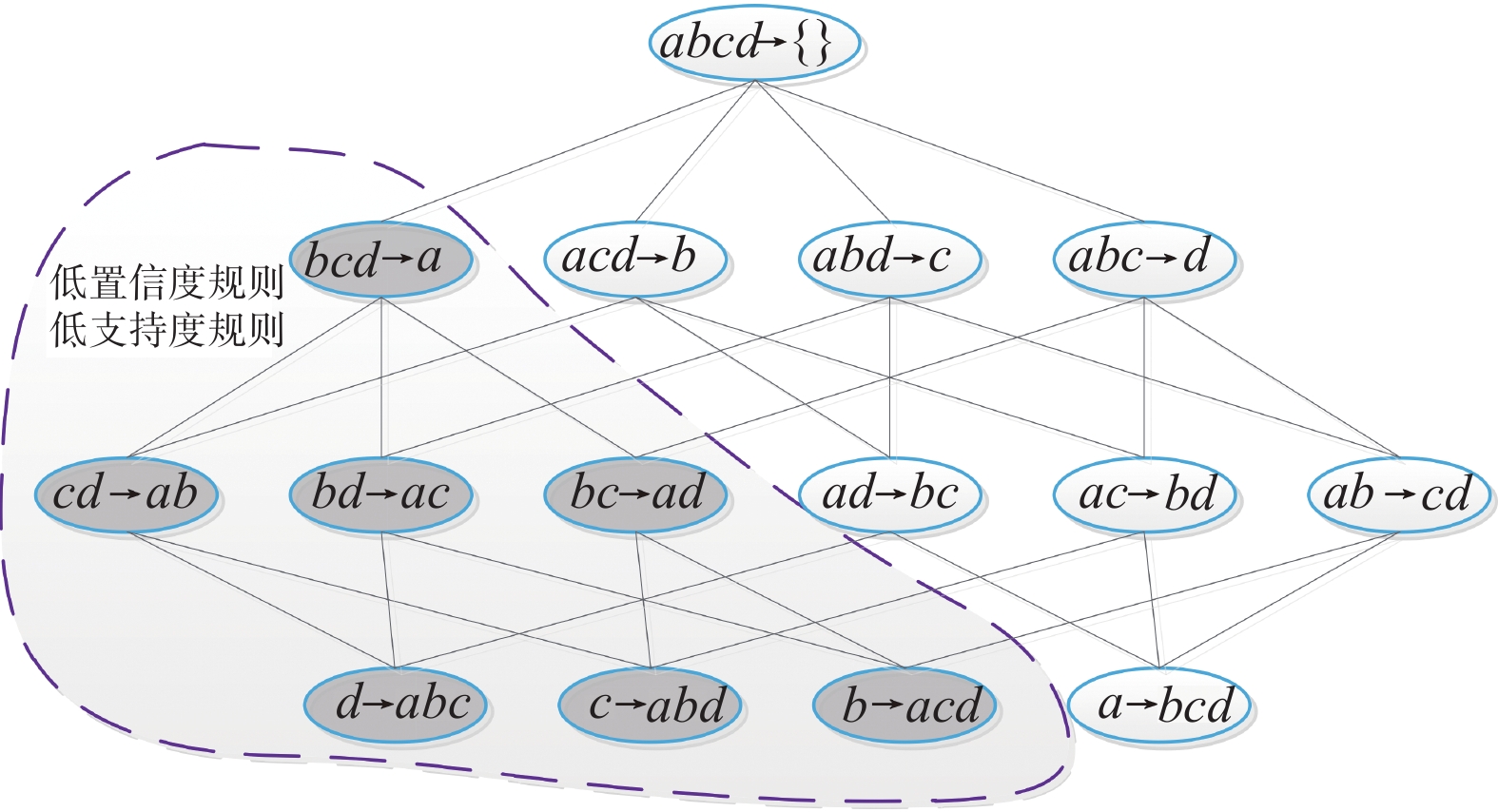
表 7 白水河滑坡月位移速度定性化成果
Table 7. Qualitative results of monthly displacement rate of Baishuihe landslide
月位移速度 v/(mm·mon-1) 定性化值 (1.042,10.669) Ⅲ (0.092,0.939) Ⅱ (−0.195,0.078) Ⅰ 表 1 白水河滑坡月累计降雨量定性化成果
Table 1. Qualitative results of monthly accumulated rainfall of Baishuihe landslide
月累计降雨量 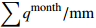
定性化值 (183.5,517.6) Heavy_Rainfall (69.9,179.8) Moderate_Rainfall (3.1,66.1) Light_Rainfall 表 2 白水河滑坡日降雨量月度最大值定性化成果
Table 2. Qualitative results of monthly maximum rainfall of Baishuihe landslide
日降雨量月度最大值 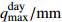
定性化值 (55.9,160.7) Heavy_Rain_Shower (26.5,55.2) Medium_Rain_Shower (1.3,25.6) Light_Rain_Shower 表 3 白水河滑坡库水位月平均值定性化成果
Table 3. Qualitative results of monthly average water level of Baishuihe landslide reservoir
库水位月度平均值 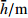
定性化值 (160.14,174.74) High_Water_Level (144.21,158.47) Medium_Water_Level (135.13,138.95) Low_Water_Level 表 4 白水河滑坡月库水位波动速度定性化成果
Table 4. Qualitative results of water level fluctuation rate of Baishuihe landslide monthly reservoir
月库水位波动速度 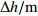
定性化值 (13.26,17.35) Sharply_Rise (7.23,11.36) Medium_Rise (1.57,5.89) Slowly_Rise (-1.56,1.31) Smooth Fluctuation (-7.09,-3.41) Medium_Drop (-13.02,-8.59) Sharply_Drop 表 5 白水河滑坡单月最大有效连续降雨量定性化成果
Table 5. Qualitative results of maximum effective continuous rainfall in a single month of Baishuihe landslide
单月最大有效连续降雨量 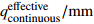
定性化值 (110.5,239.4) High_Effective Rainfall (36.6,109.8) Medium_Effective Rainfall (1.5,36.1) Low_Effective Rainfall 表 6 白水河滑坡单月库水位日浮动最大值定性化成果
Table 6. Qualitative results of the maximum daily fluctuation of the water level in a single month of Baishuihe landslide
单月库水位日浮动最大值  /m
/m定性化值 (1.66,3.223) Sharply_Rise_Water (0.744,1.513) Medium_Rise_Water (0.063,0.63) Slowly_Rise_Water (−0.414,0) Slowly_Drop_Water (−1.697,−0.49) Medium_Drop_Water 表 8 白水河滑坡多场信息关联准则
Table 8. Multi field information association criterion of Baishuihe landslide
规则 ID 规则 支持度/% 置信度/% 提升度 1  = High_Water_Level &
= High_Water_Level &  =Low_Effective Rainfall
=Low_Effective Rainfall Ⅰ
Ⅰ25.77 85.71 2.02 2  =High_Water_Leve &
=High_Water_Leve &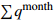 =Light_Rainfall &
=Light_Rainfall & 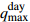 =Light_Rain_Shower
=Light_Rain_Shower Ⅰ
Ⅰ25.15 85.37 2.02 3  = High_Water_Level &
= High_Water_Level & 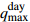 =Light_Rain_Shower
=Light_Rain_Shower Ⅰ
Ⅰ28.22 86.96 2.05 4  = Low_Effective Rainfall &
= Low_Effective Rainfall & = Slowly_Rise_Water &
= Slowly_Rise_Water &  = Low_Water_Level
= Low_Water_Level  Ⅱ
Ⅱ8.42 100.00 4.13 5  = Low_Effective Rainfall &
= Low_Effective Rainfall &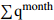 = Moderate_Rainfall &
= Moderate_Rainfall & 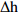 =Slowly_Rise &
=Slowly_Rise &  =Slowly_Rise_Water
=Slowly_Rise_Water Ⅱ
Ⅱ7.56 100.00 4.58 6 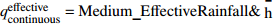 = Low_Water_Level &
= Low_Water_Level &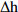 =Slowly_Rise
=Slowly_Rise Ⅱ
Ⅱ7.56 100.00 4.58 7  = High_Effective Rainfall &
= High_Effective Rainfall &  = Medium_Water_Level
= Medium_Water_Level Ⅲ
Ⅲ6.13 90.00 5.24 8  = High_Effective Rainfall &
= High_Effective Rainfall & 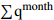 = Heavy_Rainfall &
= Heavy_Rainfall &  = Medium_Water_Level
= Medium_Water_Level Ⅲ
Ⅲ5.52 88.89 5.17 9  = High_Effective Rainfall &
= High_Effective Rainfall & 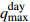 =Heavy_Rain_Shower &
=Heavy_Rain_Shower & 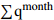 = Heavy_Rainfall &
= Heavy_Rainfall &  = Medium_Water_Level
= Medium_Water_Level Ⅲ
Ⅲ5.52 88.89 5.17 10 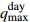 = Heavy_Rain_Shower &
= Heavy_Rain_Shower & 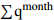 = Heavy_Rainfall &
= Heavy_Rainfall &  = Medium_Water_Level
= Medium_Water_Level Ⅲ
Ⅲ6.13 80.00 4.66 -
[1] 王树良, 王新洲, 曾旭平, 等. 滑坡监测数据挖掘视角[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2004,29(7):608 − 610. [WANG Shuliang, WANG Xinzhou, ZENG Xuping, et al. View angle of landslide-monitoring data mining[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2004,29(7):608 − 610. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 张纯志. 滑坡监测数据处理回归模型分析及探讨[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息,2016,39(8):214 − 217. [ZHANG Chunzhi. Landslide monitoring data processing regression model analysis and discussion[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology,2016,39(8):214 − 217. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2016.08.064
[3] 徐峰, 汪洋, 杜娟, 等. 基于时间序列分析的滑坡位移预测模型研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2011,30(4):746 − 751. [XU Feng, WANG Yang, DU Juan, et al. Study of displacement prediction model of landslide based on time series analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2011,30(4):746 − 751. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] MA J W, TANG H M, LIU X, et al. Establishment of a deformation forecasting model for a step-like landslide based on decision tree C5.0 and two-step cluster algorithms: a case study in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China[J]. Landslides,2017,14(3):1275 − 1281. doi: 10.1007/s10346-017-0804-0
[5] MA J W, TANG H M, HU X L, et al. Identification of causal factors for the Majiagou landslide using modern data mining methods[J]. Landslides,2017,14(1):311 − 322. doi: 10.1007/s10346-016-0693-7
[6] 亓呈明, 崔守梅, 陈辉, 等. 滑坡成因决策树挖掘[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2006,17(1):73 − 76. [QI Chengming, CUI Shoumei, CHEN Hui, et al. Decision-making tree for analysis of landslide causes[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2006,17(1):73 − 76. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2006.01.017
[7] 何少其, 刘元雪, 梁叶, 等. “阶跃式”滑坡突变预测与核心因子提取的平衡集成树模型[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(5):27 − 36. [HE Shaoqi, LIU Yuanxue, LIANG Ye, et al. Balanced decision tree ensemble model for catastrophe prediction and key factors' extraction of step-like landslides[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(5):27 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 马水山, 王志旺, 张漫. 基于关联规则挖掘的滑坡监测资料分析[J]. 长江科学院院报,2004,21(5):48 − 51. [MA Shuishan, WANG Zhiwang, ZHANG Man. Analysis on monitoring data of landslide based on associative data mining[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2004,21(5):48 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5485.2004.05.014
[9] 段功豪. 三峡库区堆积层滑坡预报判据的动态挖掘研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2013.
DUAN Gonghao. Study on prediction criteria of accumulated layer landslide in Three Gorges reservoir using dynamic data mining[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] HUANG H F, YI W, LU S Q, et al. Use of monitoring data to interpret active landslide movements and hydrological triggers in Three Gorges reservoir[J]. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities,2016,30(1):C4014005. doi: 10.1061/(asce)cf.1943-5509.0000682
[11] 孙义杰. 库岸边坡多场光纤监测技术与稳定性评价研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2015.
SUN Yijie. Bank slope multi-fields monitoring based on fiber optic sensing technologies and stability evaluation study[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] TSAI F, LAI J S, CHEN W W, et al. Analysis of topographic and vegetative factors with data mining for landslide verification[J]. Ecological Engineering,2013,61:669 − 677. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013.07.070
[13] 马俊伟. 渐进式滑坡多场信息演化特征与数据挖掘研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2016.
MA Junwei. Evolution characteristics of multiple physics-based parameters and data mining technology for progressive landslides[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] SUN G H, ZHENG H, HUANG Y Y, et al. Parameter inversion and deformation mechanism of Sanmendong landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir region under the combined effect of reservoir water level fluctuation and rainfall[J]. Engineering Geology,2016,205:133 − 145. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.10.014
[15] 李麟玮, 吴益平, 苗发盛, 等. 考虑变形状态动态切换的阶跃型滑坡位移区间预测方法[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2019,38(11):2272 − 2287. [LI Linwei, WU Yiping, MIAO Fasheng, et al. Displacement interval prediction method for step-like landslides considering deformation state dynamic switching[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2019,38(11):2272 − 2287. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 易庆林, 张明玉, 文凯, 等. 三峡库区白水河滑坡变形特征及影响因素的阶段分析[J]. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版),2017,39(1):38 − 42. [YI Qinglin, ZHANG Mingyu, WEN Kai, et al. Periodic analysis of deformation characteristics and influential factors of Baishuihe landslide in Three Gorges reservoir area[J]. Journal of China Three Gorges University (Natural Sciences),2017,39(1):38 − 42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] CHIU T, FANG D P, CHEN J, et al. A robust and scalable clustering algorithm for mixed type attributes in large database environment[C]//Proceedings of the seventh ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining - KDD '01. August 26-29, 2001. San Francisco, California. New York: ACM Press, 2001: 263-268.
[18] AGRAWAL R, IMIELIŃSKI T, SWAMI A. Mining association rules between sets of items in large databases[C]//Proceedings of the 1993 ACM SIGMOD international conference on Management of data - SIGMOD '93. May 25-28, 1993. Washington, D. C. , USA. New York: ACM Press, 1993: 207-216.
[19] WU X L, BENJAMIN ZHAN F, ZHANG K X, et al. Application of a two-step cluster analysis and the Apriori algorithm to classify the deformation states of two typical colluvial landslides in the Three Gorges, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2016,75(2):1 − 16.
[20] LI D Y, SUN Y Q, YIN K L, et al. Displacement characteristics and prediction of Baishuihe landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2019,16(9):2203 − 2214. doi: 10.1007/s11629-019-5470-3
-



 下载:
下载: