A preliminary study on evaluation of rock slope stability based on index variable weight compound cloud model
-
摘要:
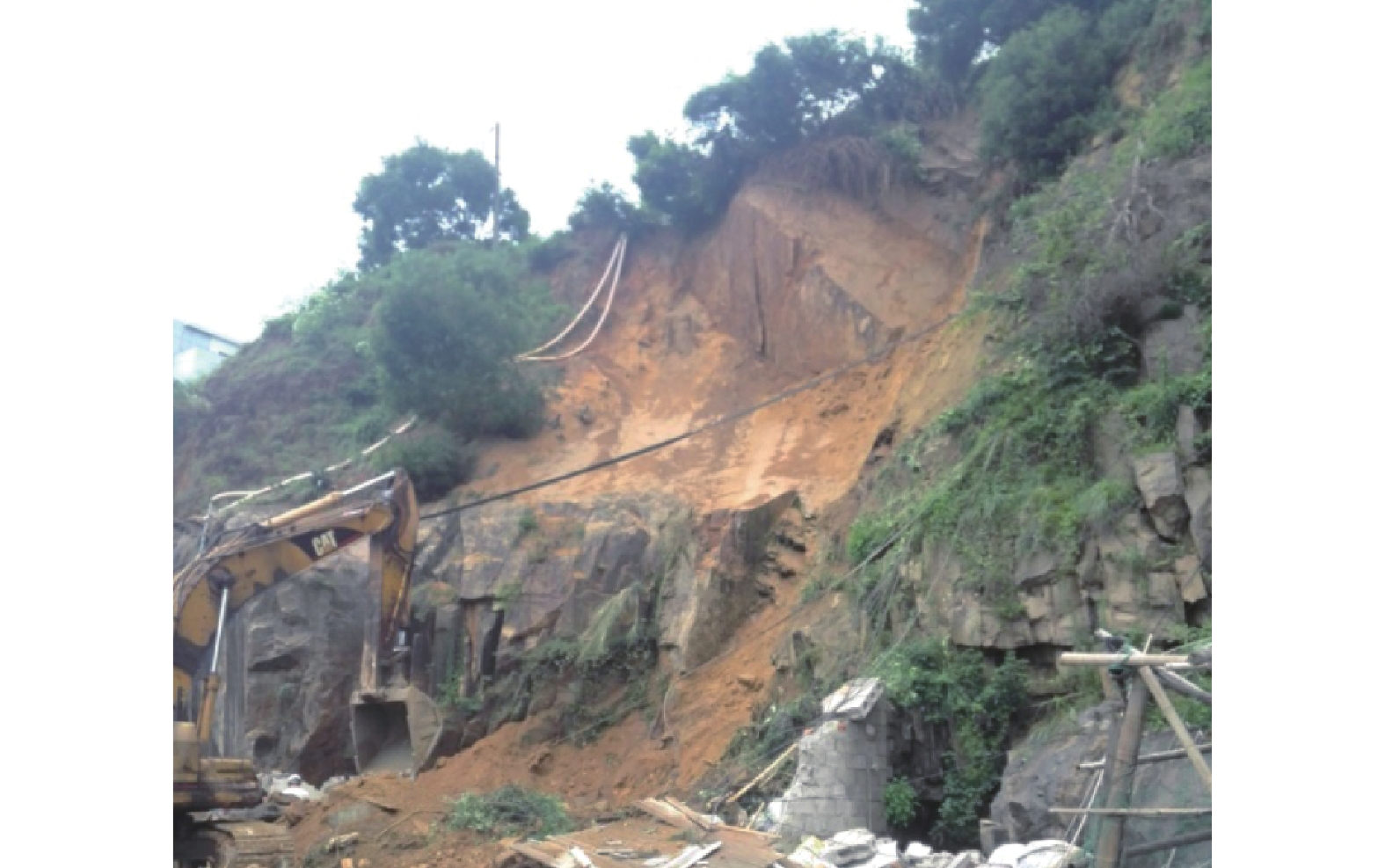
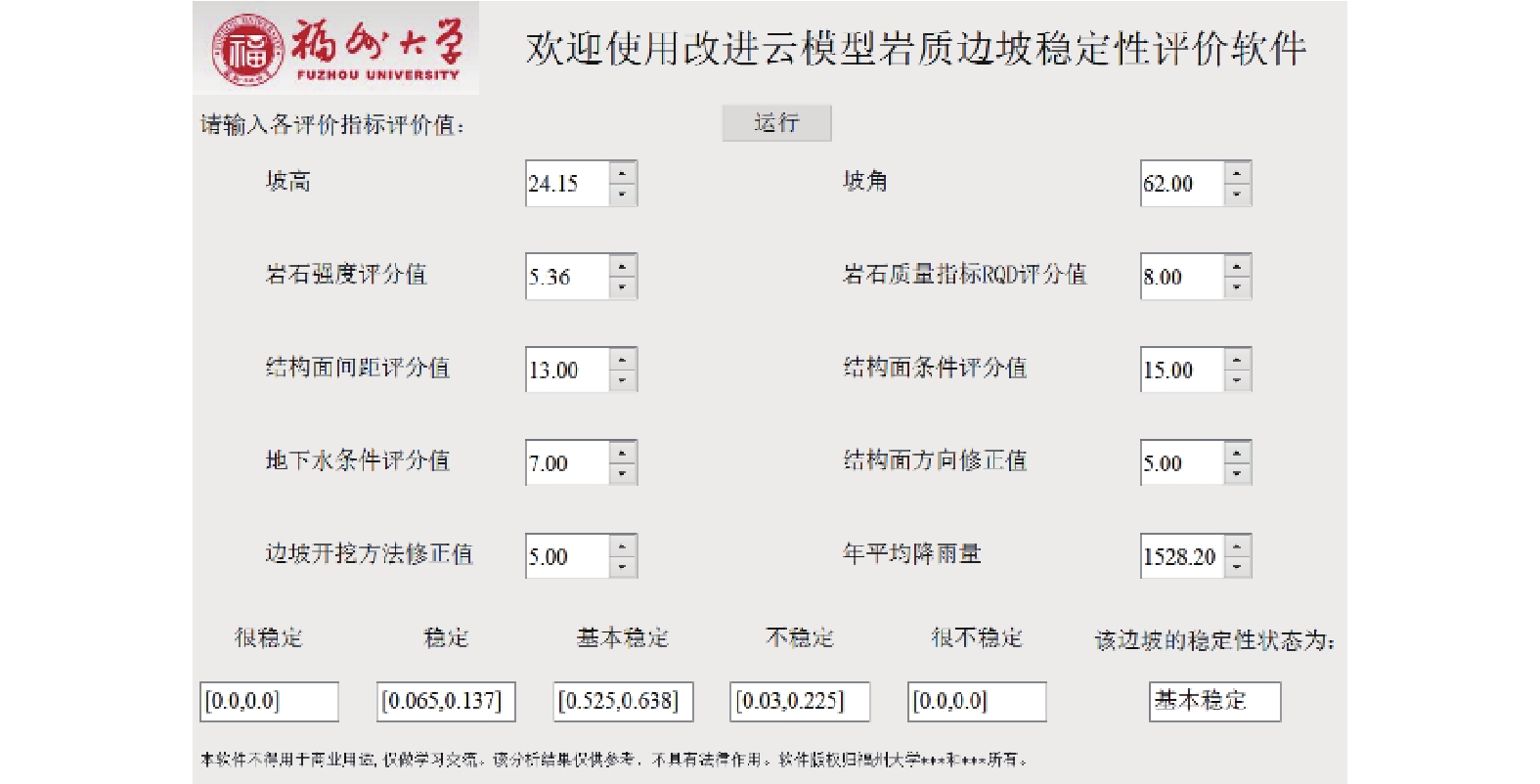
近年来,云模型评价方法在边坡的稳定性评价中得到了较深入的应用。但目前评价指标的权重多为某一精确值,没有考虑指标权重的不确定性和模糊性。为解决这一问题,尝试用指标变权重云模型表示各指标的权重,并引入权重范围系数以调整指标的权重变化幅度。参照《水电水利边坡工程地质勘察技术规程》和《地质灾害调查技术要求》对评价指标进行选取。参考行业规范、学者们的研究经验以及福建省的实际情况,采用等间距法对各评价指标相应的稳定分级区间进行划分。根据上述方法在MATLAB程序中编写算法,得到了基于指标变权重的复合云模型,并开发了相应的应用程序。通过对福建省连江县黄岐镇边坡的分析,认为该边坡总体处于基本稳定状态,但仍存在转化为不稳定的可能性。根据勘察报告,该坡段于2016年6月17日曾因强降雨发生崩塌,初步验证了本方法的分析结果。
Abstract:In recent years, cloud model evaluation methods has been deeply applied in slope stability evaluation. However, the current evaluation index weight was a precise value, which has not take uncertainty and ambiguity of the index weight into consideration. In order to solve this problem, the paper tried to using the index variable weight cloud model, and introduced the weight range coefficient to adjust the change range of the index. The evaluation indexes were selected by referring to "Technical Regulations for Hydropower and Water Conservancy Slope Engineering Geological Survey" and "Technical Requirements for Geological Hazard Survey". With reference to industry standards, the research experience of scholars and the actual situation in Fujian Province, the equidistant method was used to divide the stable grading intervals of each evaluation index. According to the above method, the algorithm was developed in the MATLAB program. The compound cloud model based on the variable weight of the index and the corresponding application program were developed. Based on the analysis of the slope of Huangqi Town, Lianjiang County, Fujian Province, it was believed that the slope was generally stable, but there still has the possibility of turning into instability. According to the survey report, the slope section collapsed due to heavy rainfall on June 17, 2016, which preliminarily verified the analysis results of this method.
-
Key words:
- index variable weight /
- compound cloud model /
- rock slope /
- weight range coefficient
-

-
表 1 评价指标评分标准表
Table 1. Scoring standard table of evaluation indexes
参数 评分标准 岩石强度 /MPa 点荷载 >10 4~10 2~4 1~2 <1不宜采用 单轴抗压强度 250~100 100~60 60~30 30~15 15~5 评分 15~10 8 5 3 2~0 岩石质量指标RQD /% 250~100 100~60 60~30 30~15 15~5 评分 20 17 13 8 3 结构面间距 /cm 200~100 100~50 50~30 30~5 <5 评分 20~15 13 10 8 5 结构面条件 粗糙度 很粗糙 粗糙 较粗糙 光滑 擦痕、镜面 评分 6 4 2 1 0 充填物 /mm 无 <5(硬) >5(硬) <5(软) >5(软) 评分 6 4 2 2 0 张开度 /mm 未张开 <0.1 0.1 ~1 1 ~5 >5 评分 6 5 4 1 0 结构面长度 /m <1 1~3 3~10 10~20 >20 评分 6 4 2 1 0 岩石风化程度 未风化 微风化 弱风化 强风化 全风化 评分 6 5 3 1 0 地下水条件 状态 干燥 湿润 潮湿 滴水 流水 透水率(Lu) <0.1 0.1~1 1~10 10~100 >100 评分 15 10 7 4 0 表 2 结构面方位系数取值
Table 2. Orientation coefficient of structural plane
破坏机制 情况 非常有利 有利 一般 不利 非常不利 滑动 γ1=ǀαj-αsǀ >30° 30°~20° 20°~10° 10°~5° <5° 倾倒 γ1=ǀαj−αs−180°ǀ 滑动,倾倒 F1 0.15 0.4 0.7 0.85 1 滑动 γ2=ǀβjǀ <20° 20°~30° 30°~35° 35°~45° >45° 滑动 F2 0.15 0.4 0.7 0.85 1 倾倒 F2 1 1 1 1 1 滑动 γ3=βj−βs >10° 10°~0° 0° 0°~−10° <−10° 倾倒 γ3=βj+βs <110° 110°~120° >120° —— —— 滑动,倾倒 F3 0 5 25 50 60 注:αs为边坡倾向;αj为结构面倾向;βs为边坡倾角;βj为结构面倾角。 表 3 岩质边坡稳定性评价指标及其各分级区间
Table 3. Stability evaluation index of rock slope and its grade intervals
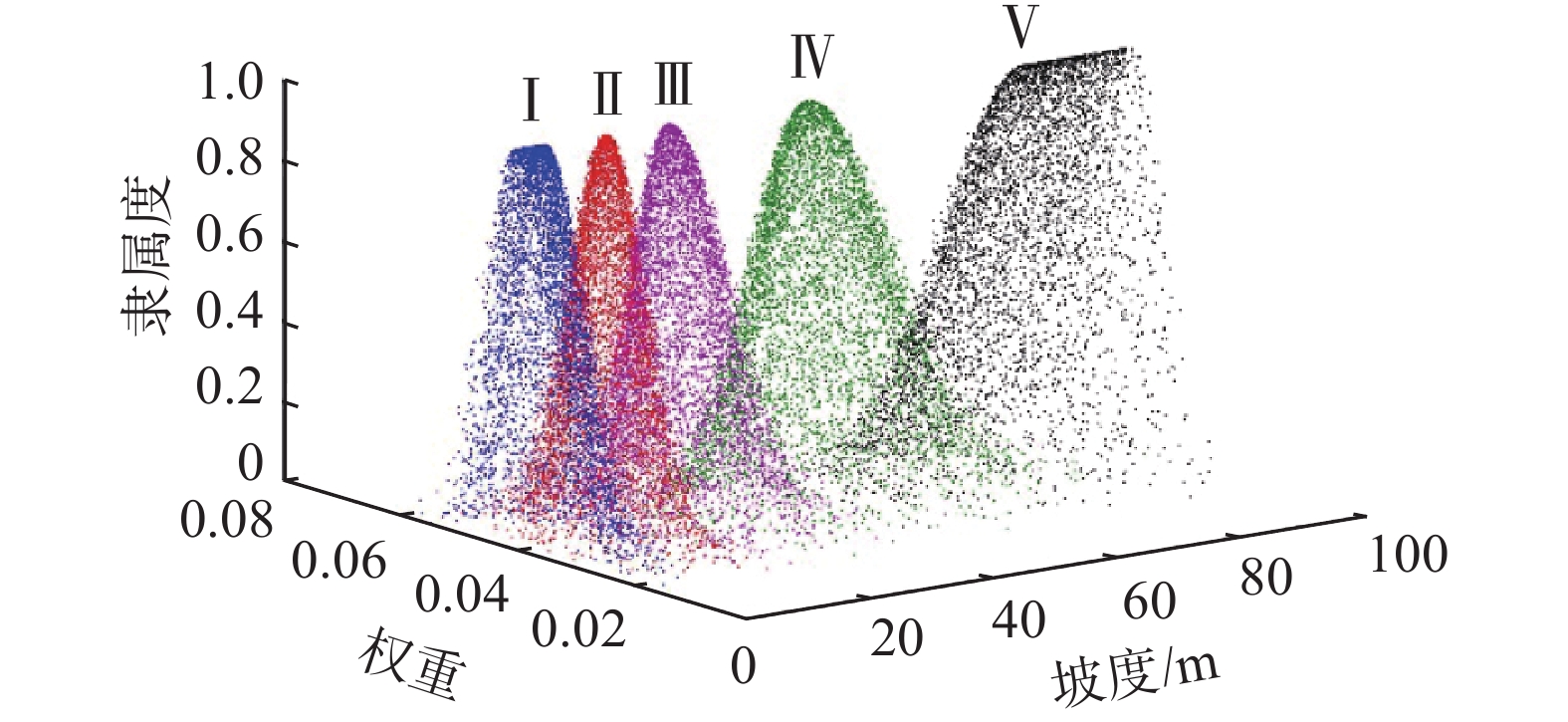
评价指标 稳定性等级 很稳定 稳定 基本稳定 不稳定 很不稳定 坡高 /m(I1) [0,10) [10,20) [20,30) [30,65) [65,100) 坡角 /(°)(I2) [0,10) [10,30) [30,45) [45,65) [65,90) 岩石强度评分值(I3) [12,15) [9,12) [6,9) [3,6) [0,3) 岩石质量指标评分值(I4) [16,20) [12,16) [8,12) [4,8) [0,4) 结构面间距评分值(I5) [16,20) [12,16) [8,12) [4,8) [0,4) 结构面条件评分值(I6) [24,30) [18,24) [12,18) [6,12) [0,6) 地下水条件评分值(I7) [12,15) [9,12) [6,9) [3,6) [0,3) 结构面方向修正值(I8) [0,12) [12,24) [24,36) [36,48) [48,60) 边坡开挖方法修正值(I9) [6,10) [3,6) [0,3) [−4,0) [−8,−4) 年平均降雨量(I10) [1070,1580.6) [1580.6,1650.4) [1650.4,1720.2) [1720.2,1790) [1790,1859.8) 表 4 各专家对评价指标的初始权重
Table 4. Initial weight of each expert on the evaluation index
/10−3 指标 专家
1专家
2专家
3专家
4专家
5专家
6专家
7专家
8专家
9专家
10专家
11专家
12I1 19 21 20 15 22 18 17 19 25 24 21 22 I2 76 72 60 66 76 83 79 72 78 75 78 71 I3 32 37 38 40 39 34 37 38 33 40 40 48 I4 106 103 99 93 89 87 84 105 99 97 101 93 I5 24 26 31 33 43 29 37 31 38 39 43 48 I6 158 159 158 156 158 164 164 160 166 169 182 188 I7 18 22 29 25 23 29 27 24 39 32 30 26 I8 277 283 288 280 276 275 261 271 279 261 246 220 I9 14 18 22 20 20 23 20 17 30 28 23 20 I10 276 259 255 272 253 258 273 263 213 236 237 264 表 5 各指标的基于信心指数云模型特征值
Table 5. Characteristic values of various indicators based on confidence index cloud model
/10−3 指标 Ex En He I1 40 5.1 1.0 I2 66 5.4 1.9 I3 55 4.9 1.2 I4 86 7.6 1.7 I5 53 9.8 2.2 I6 148 7.3 2.3 I7 45 6.4 1.5 I8 240 20.9 8.5 I9 41 6.4 1.1 I10 227 21.2 8.6 表 6 黄岐镇边坡场地内岩土层特性参数
Table 6. Property parameters of strata in slope of Huangqi town
序号 地层名称 天然
重度
γ/(kN·m−3)饱和
重度
γsat/(kN·m−3)天然快剪 饱和快剪 厚度/m ck/kPa φk/(°) ck/kPa φk/(°) ① 素填土 17.5 18.0 10.0 15.0 8.5 11.5 0.50~1.40 ② 坡积粉质黏土 18.64 18.78 22.0 20.0 19.19 17.45 0.5~1.3 ③ 残积砂质黏土 18.5 19.0 23.0 22.0 20.0 18.0 1.5~2.8 ④ 全风化花岗岩 19.0 19.5 25.0 27.0 22.0 23.0 0~3.0 ⑤-1 砂土状强风化花岗岩 21.0 21.5 30.0 32.0 26.0 28.0 2.3~7.3 ⑤-2 碎块状强风化花岗岩 22.0 22.5 35.0 35.0 28.0 30.0 1.1~2.4 ⑥ 中风化花岗岩 24.0 - 40.0 50.0 - - 7.4~15.4 表 7 指标评价在各评价等级中的隶属度范围
Table 7. The range of the membership degree of the index evaluation in each evaluation grade
评价指标 稳定性等级 很稳定 稳定 基本稳定 不稳定 很不稳定 I1 [0,0] [0,0] [0.74,0.82] [0.04,0.11] [0,0] I2 [0,0] [0.15,0.28] [0.39,0.53] [0,0] [0,0] I3 [0,0] [0.01,0.05] [0.96,0.97] [0,0] [0,0] I4 [0,0] [0,0] [0.25,0.39] [0.25,0.39] [0,0] I5 [0,0] [0,0.02] [1,1] [0,0] [0,0] I6 [0,0.02] [0,1] [0,0] [0,0] [0,0] I7 [0,0] [0.95,0.97] [0.01,0.04] [0,0] [0,0] I8 [1,1] [0,0] [0,0] [0,0] [0,0] I9 [0,0] [0,0] [0,0] [0,0] [1,1] I10 [0,0] [0.98,0.99] [0.01,0.04] [0,0] [0,0] 表 8 评价指标的指标权重及其隶属度范围
Table 8. Weight of evaluation index and its range of membership degree
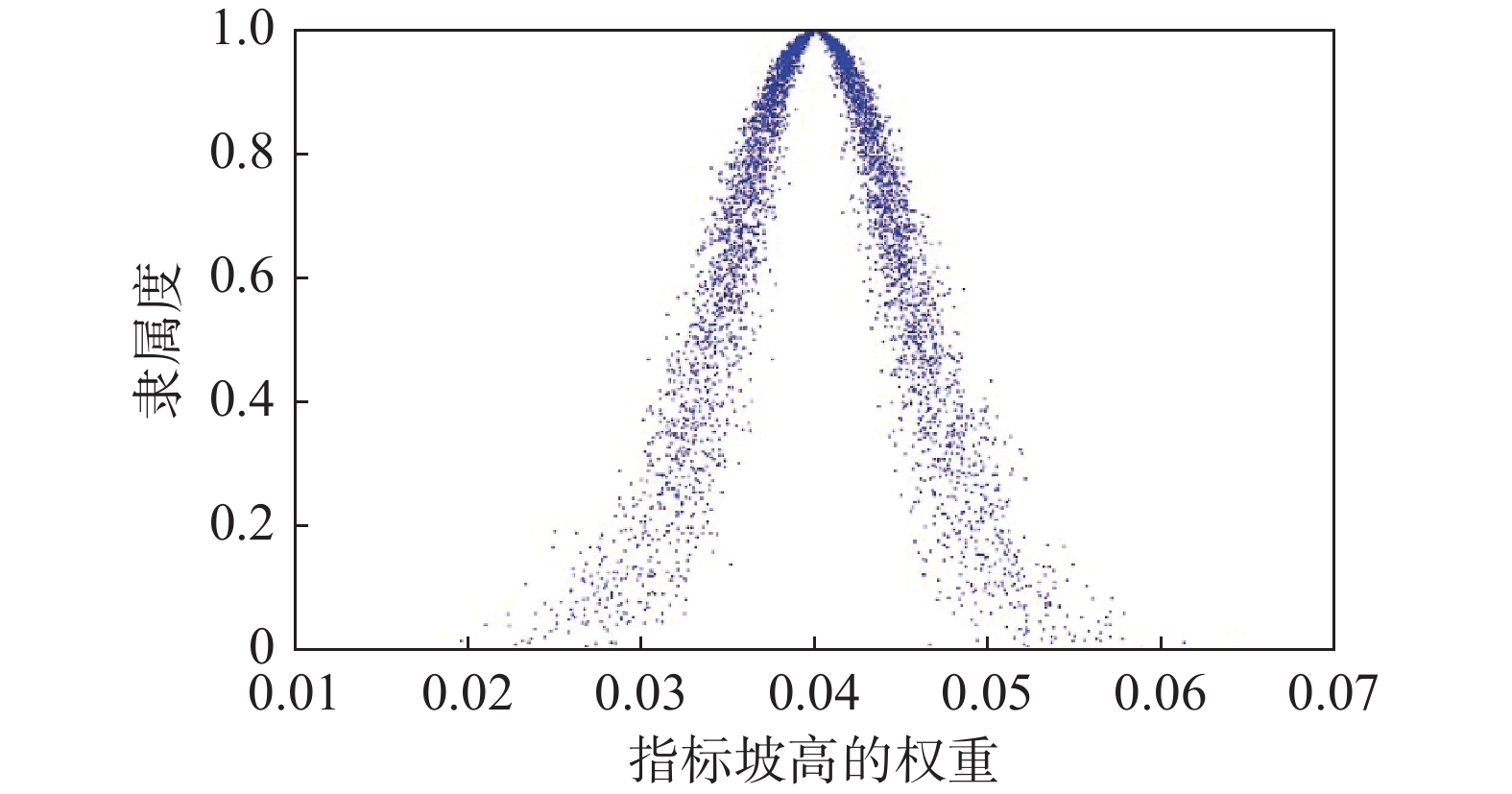
评价指标 Ex 权重取值 隶属度 I1 0.040 0.037 [0.763,0.944] I2 0.066 0.067 [0.641,0.985] I3 0.055 0.054 [0.549,0.991] I4 0.086 0.085 [0.975,0.989] I5 0.053 0.050 [0.214,0.682] I6 0.148 0.147 [0.904,0.998] I7 0.045 0.045 [0.992,0.999] I8 0.240 0.223 [0.009,0.870] I9 0.041 0.043 [0.799,0.960] I10 0.227 0.230 [0,0.997] -
[1] 李德毅, 孟海军, 史雪梅. 隶属云和隶属云发生器[J]. 计算机研究与发展,1995,32(6):15 − 20. [LI Deyi, MENG Haijun, SHI Xuemei. Membership clouds and membership cloud generators[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development,1995,32(6):15 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] SHI Y Z, ZHOU H C. Research on monthly flow uncertain reasoning model based on cloud theory[J]. Science China (Technological Sciences),2010,53(9):2408 − 2413. doi: 10.1007/s11431-010-4048-7
[3] SPIRIDONOV V, CURIC M. A storm modeling system as an advanced tool in prediction of well organized slowly moving convective cloud system and early warning of severe weather risk[J]. Asia-Pacific Journal of Atmospheric Sciences,2015,51(1):61 − 75. doi: 10.1007/s13143-014-0060-3
[4] SHI H, LIU H C, LI P, et al. An integrated decision making approach for assessing healthcare waste treatment technologies from a multiple stakeholder[J]. Waste Management,2017,59:508 − 517. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2016.11.016
[5] 梁伟章, 赵国彦. 矿山泥石流险情的变权云模型综合预测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2017,28(1):82 − 88. [LIANG Weizhang, ZHAO Guoyan. Comprehensive prediction of mine debris flow' risk based on weight-varying cloud model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2017,28(1):82 − 88. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 黄仁东, 吴寒, 张惕, 等. 基于云模型的岩溶隧道涌水灾害危险性评价及其在青岩头隧道的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(5):44 − 51. [HUANG Rendong, WU Han, ZHANG Ti, et al. Evaluation of water burst hazard in Karst tunnel based on cloud model and its application in Qingyantou Tunnel[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(5):44 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 张军, 陈征宙, 刘登峰. 基于云模型的岩质边坡稳定性评估研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2014,41(6):44 − 50. [ZHANG Jun, CHEN Zhengzhou, LIU Dengfeng. Stability evaluation of a rock slope based on the cloud model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2014,41(6):44 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] LIU Z B, SHAO J F, XU W Y, et al. Comprehensive stability evaluation of rock slope using the cloud model-based approach[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2014,47(6):2239 − 2252. doi: 10.1007/s00603-013-0507-3
[9] 于伟, 张浩, 杨鹏, 等. 基于云模型的黄土区公路边坡灾害风险评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2015,26(4):111 − 115. [YU Wei, ZHANG Hao, YANG Peng, et al. Risk assessment of highway slope disasters in loess areas based on cloud model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2015,26(4):111 − 115. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 袁爱平. 基于层次分析法-正态云模型的岩质边坡稳定性预测[J]. 水电能源科学,2016,34(9):153 − 156. [YUAN Aiping. Stability evaluation of rocky slope based on AHP-normal cloud model[J]. Water Resources and Power,2016,34(9):153 − 156. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 方成杰, 钱德玲, 徐士彬, 等. 基于云模型的泥石流易发性评价[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版),2017,40(12):1659 − 1665. [FANG Chengjie, QIAN Deling, XU Shibin, et al. An evaluation model of debris flow susceptibility based on cloud model[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science),2017,40(12):1659 − 1665. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 徐镇凯, 温勇兵, 魏博文, 等. 基于组合赋权模糊云理论的高边坡稳定性评价[J]. 水利水运工程学报,2017(1):10 − 17. [XU Zhenkai, WEN Yongbing, WEI Bowen, et al. Stability evaluation method for high slope based on fuzzy cloud theory combined with weights[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering,2017(1):10 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 杨文东, 杨栋, 谢全敏. 基于云模型的边坡风险评估方法及其应用[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2018,46(4):30 − 34. [YANG Wendong, YANG Dong, XIE Quanmin. Study on slope risk assessment method based on cloud model and its application[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition),2018,46(4):30 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 崔涛, 郑淑芬. 基于组合赋权-改进云模型的边坡稳定性评价方法[J]. 中外公路,2019,39(5):33 − 38. [CUI Tao, ZHENG Shufen. Slope stability evaluation method based on combination weighting approach and improved cloud model[J]. Journal of China & Foreign Highway,2019,39(5):33 − 38. (in Chinese)
[15] WANG M W, WANG X, LIU Q Y, et al. A novel multi-dimensional cloud model coupled with connection numbers theory for evaluation of slope stability[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling,2020,77:426 − 438. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2019.07.043
[16] 陈忠源, 戴自航. 水库边坡稳定性评价的改进云模型[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(3):619 − 625. [CHEN Zhongyuan, DAI Zihang. Improved cloud model for stability evaluation of reservoir slopes[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(3):619 − 625. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 陈忠源, 戴自航. 降雨条件下建筑边坡稳定性的云模型评价方法[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(2):50 − 56. [CHEN Zhongyuan, DAI Zihang. Cloud model evaluation method for building slope stability under rainfall[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(2):50 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 中华人民共和国国家发展和改革委员会. 水电水利工程边坡工程地质勘察技术规程: DLT5337-2006. [M]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2006.
National Development and Reform Commission, People's Republic of China. Technical specification for slope engineering geological survey of hydropower and water conservancy projects: DLT5337-2006[M]. Beijing: China Electric Power Press, 2006. (in Chinese)
[19] 自然资源部中国地质调查局. 地质灾害调查技术要求: DD 2019-08[S]. 2019.
China Geological Survey, MNR. Technical requirements for geological disaster investigation: DD 2019-08.[S]. 2019. (in Chinese)
[20] 谢晓平, 刘光生. 近60年来福建省降雨时空分布特征[J]. 水电能源科学,2020,38(8):5 − 8. [XIE Xiaoping, LIU Guangsheng. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of rainfall in Fujian Province in recent 60 years[J]. Water Resources and Power,2020,38(8):5 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: