Early identification of hidden dangers of lanslides based on the combination of ascending and descending orbits InSAR and high spatial resolution optical remote sensing: A case study of landslides in Longde County, southern Ningxia
-
摘要:
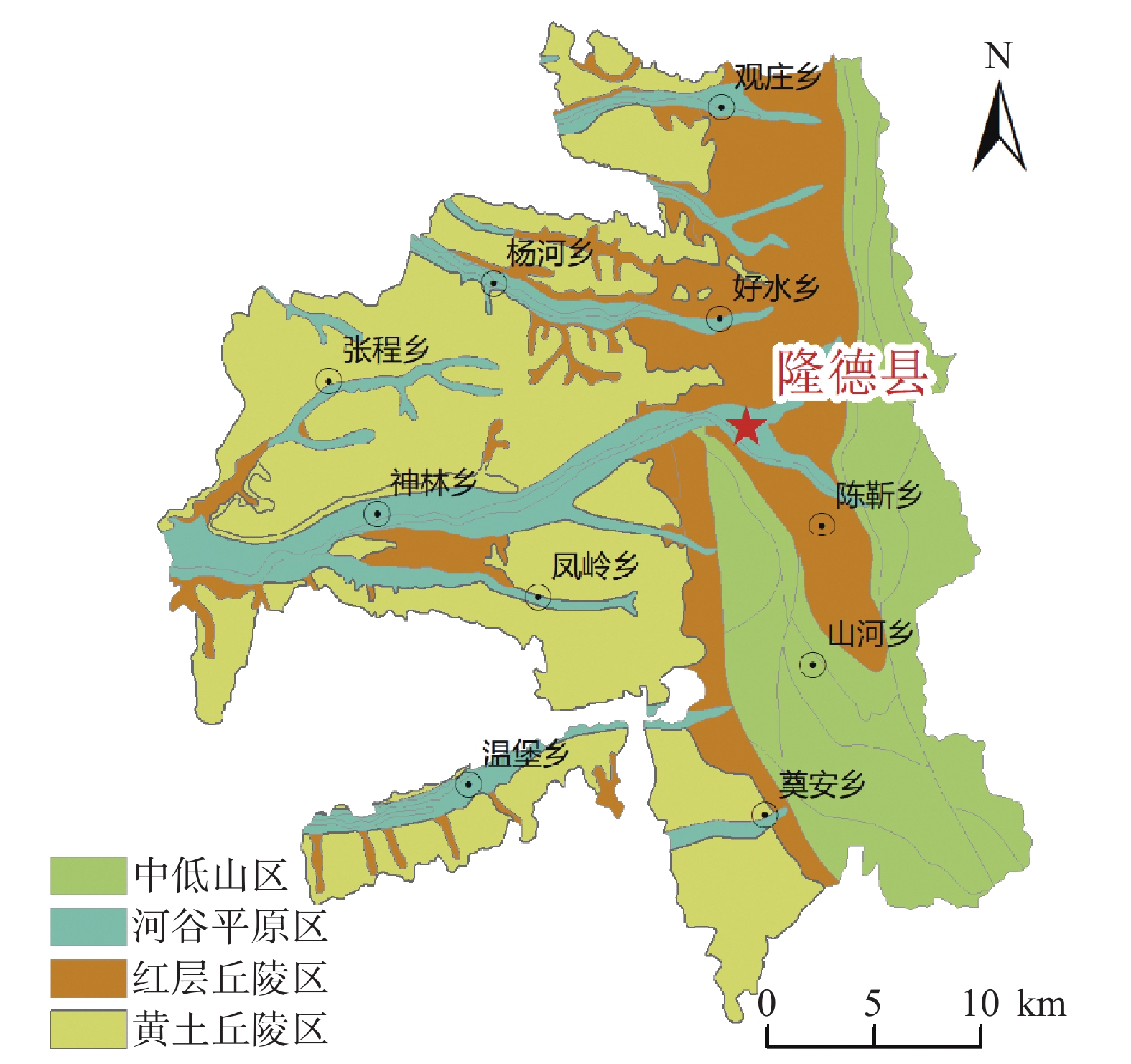
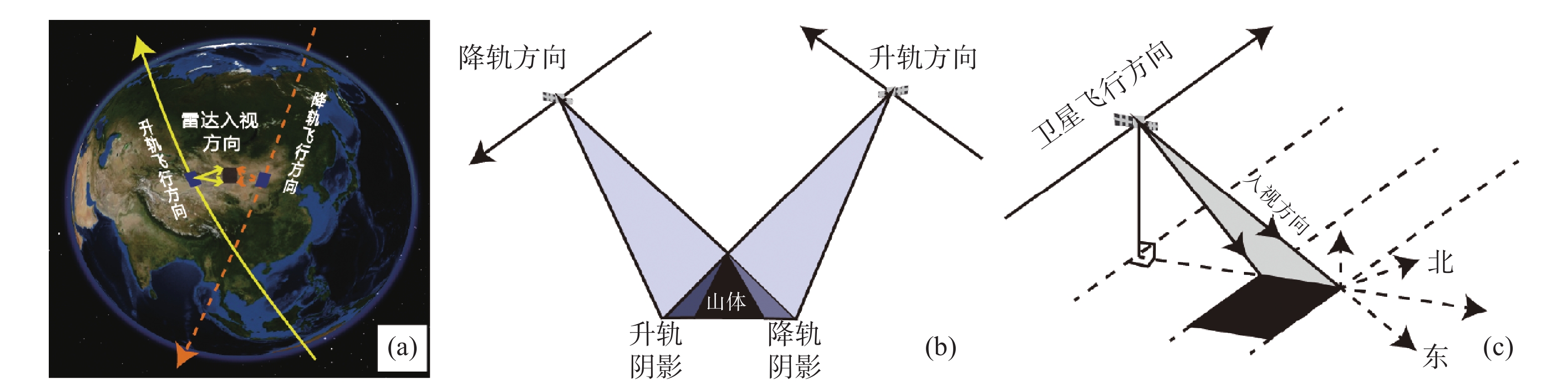
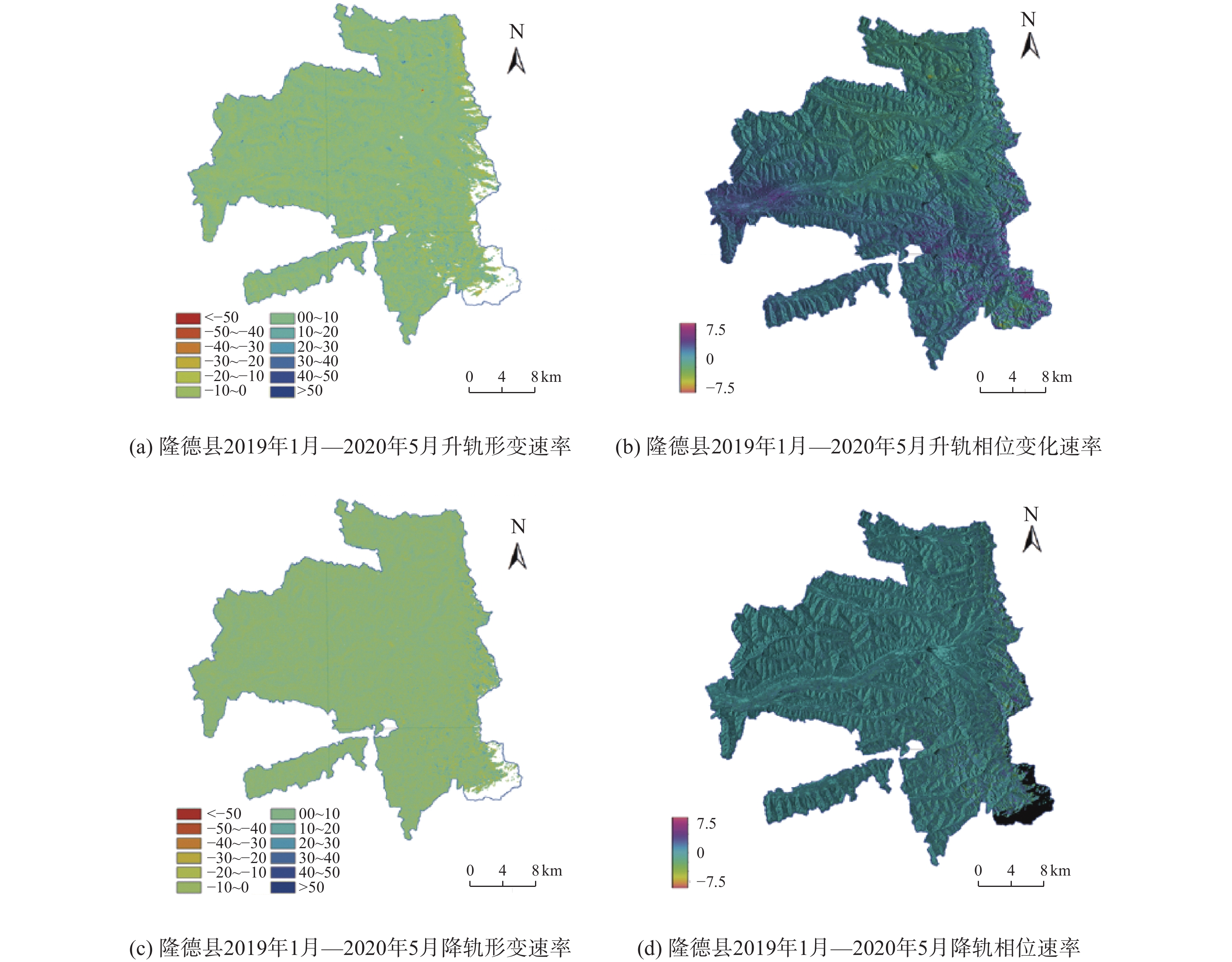
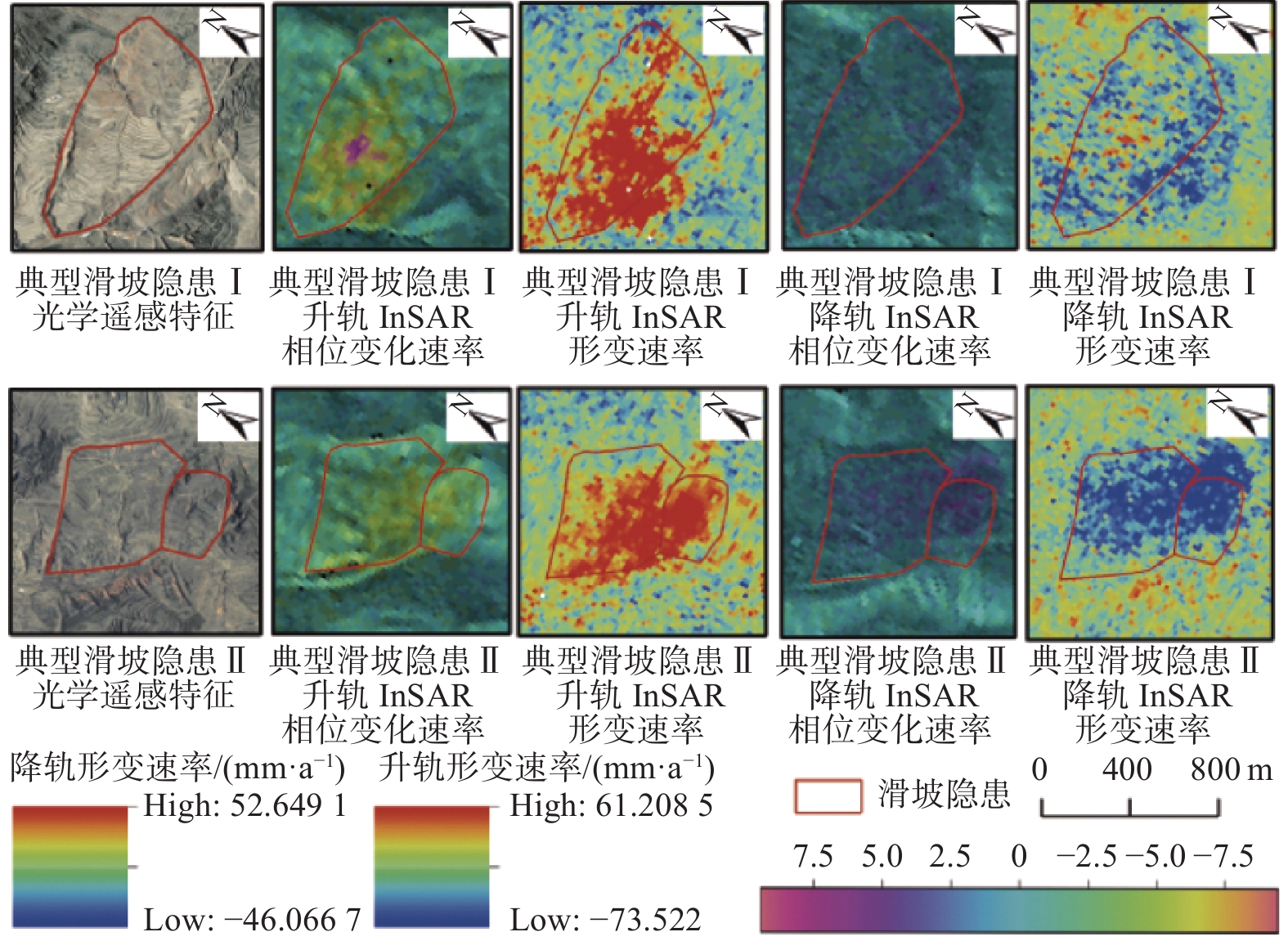
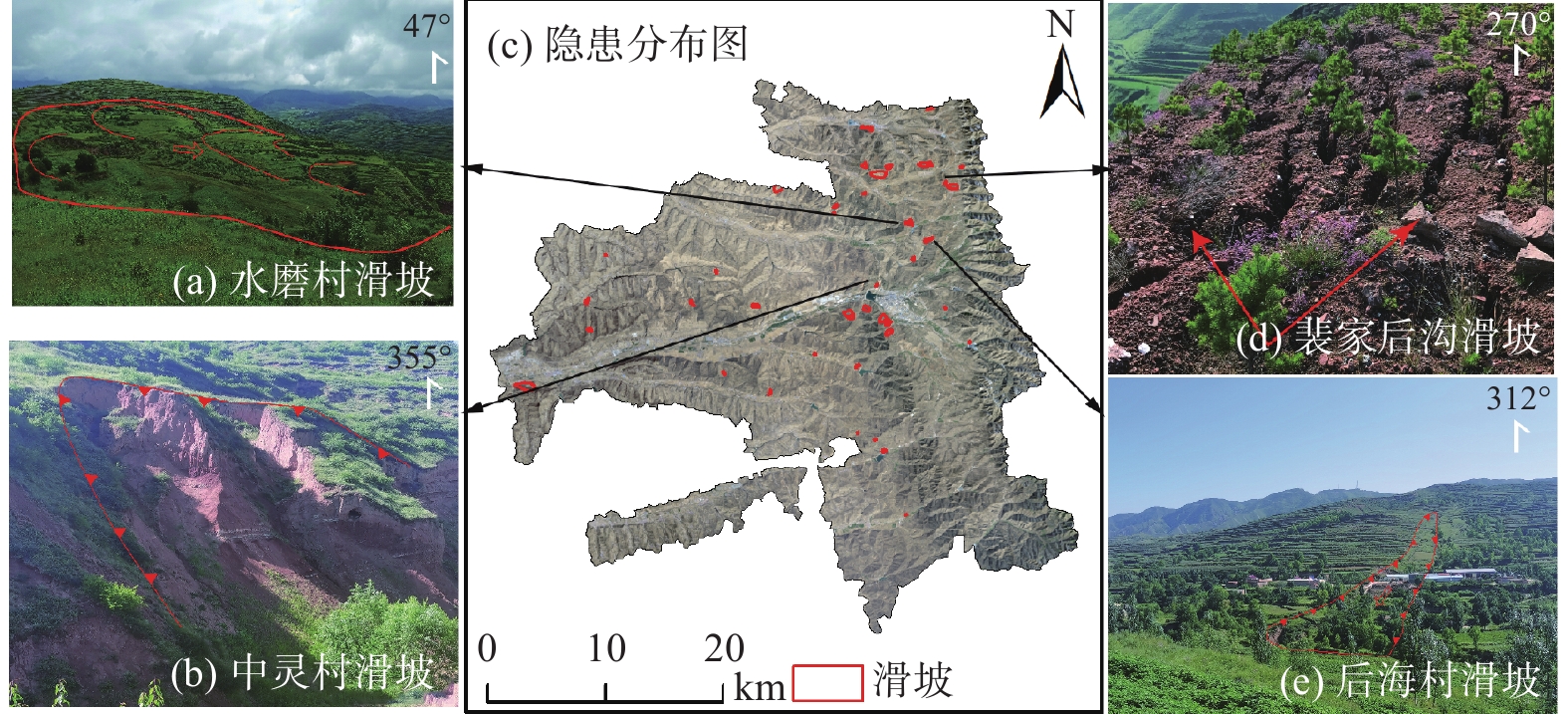
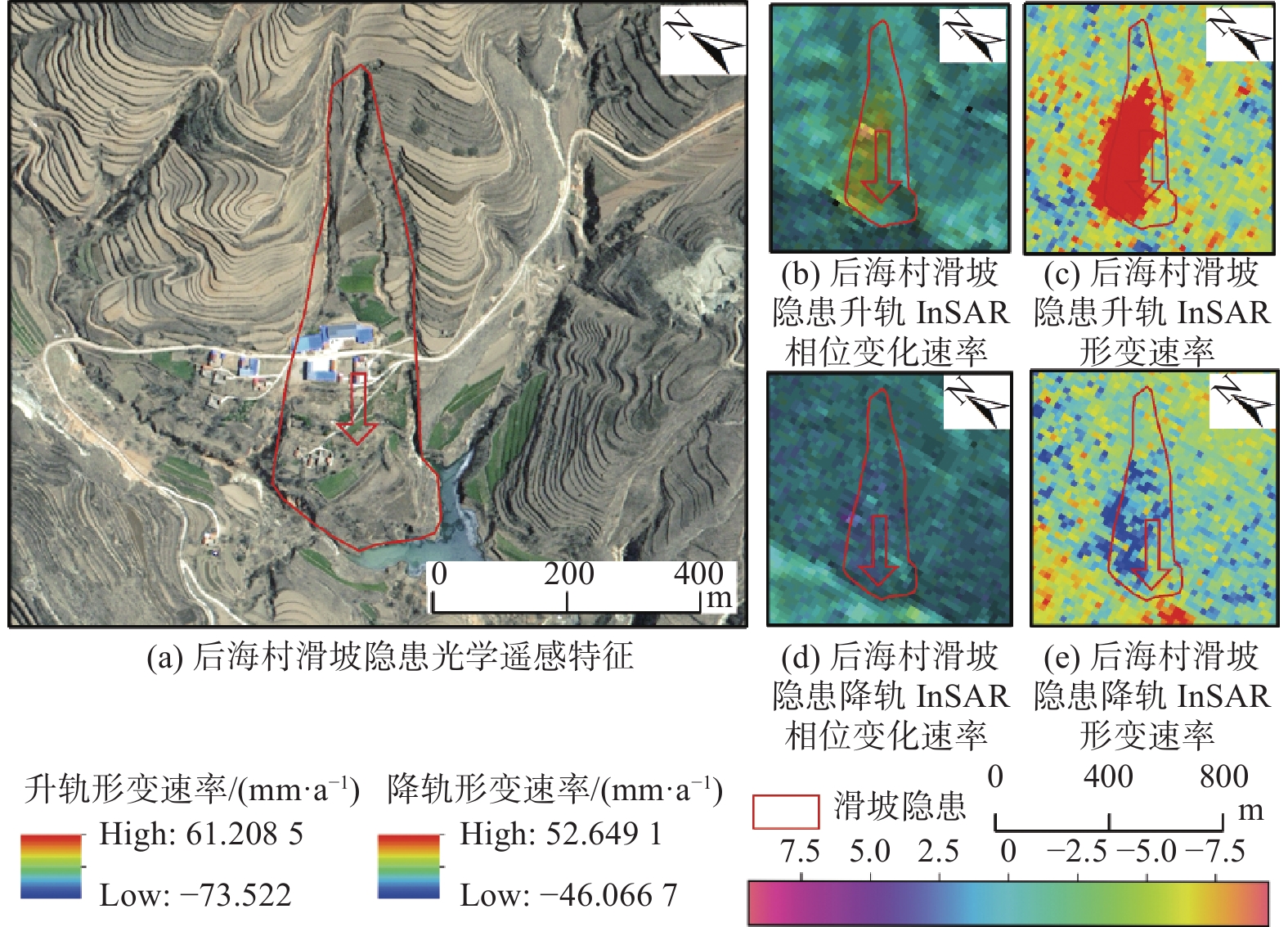
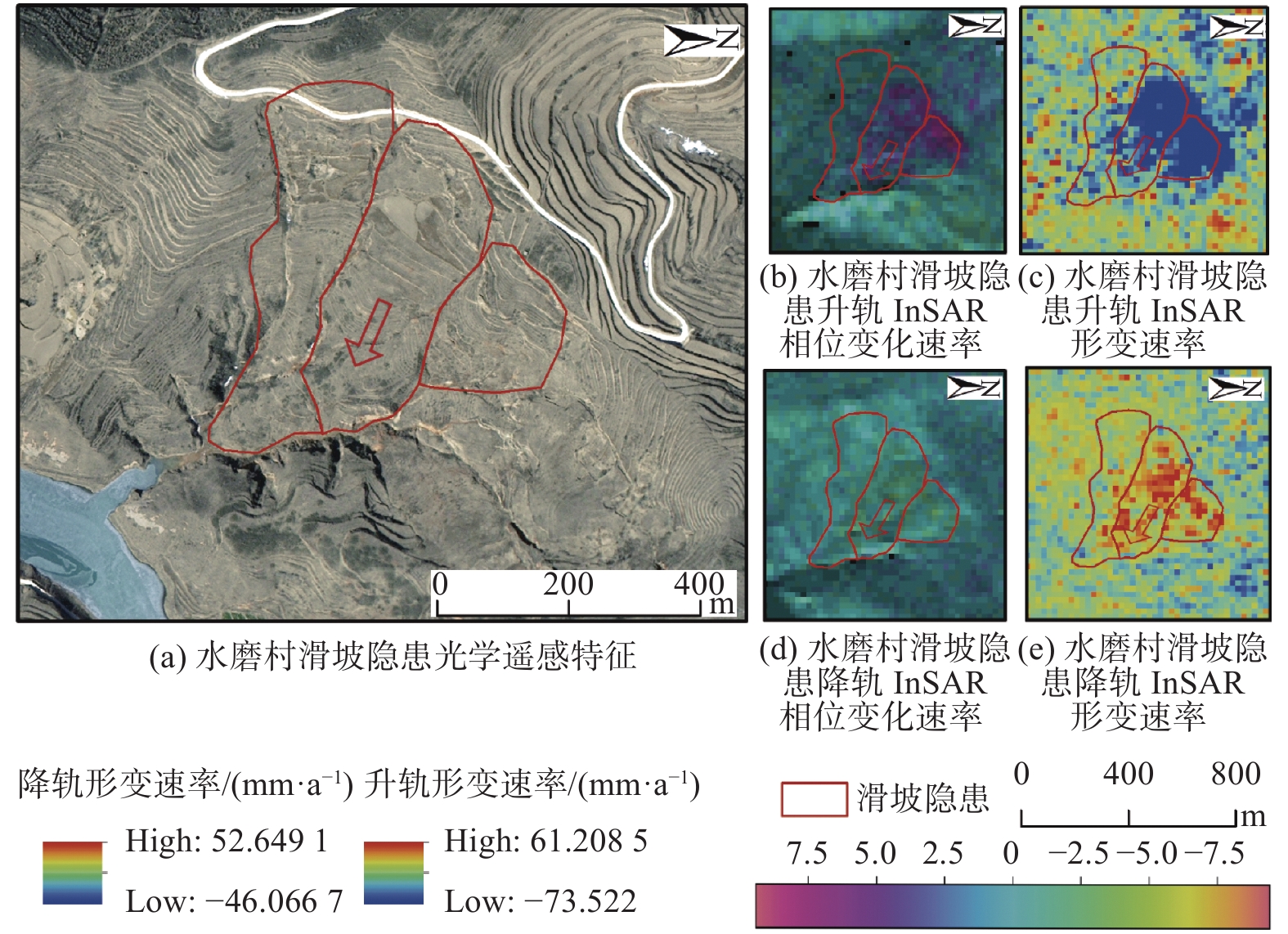
宁夏隆德县地处六盘山西麓,地质条件复杂,受季节性强降雨影响,滑坡地质灾害频发,给当地人民生命财产安全造成了严重威胁。针对宁夏东部和南部植被覆盖率高的特点,文章利用合成孔径雷达升降轨差分干涉测量(Synthetic Aperture Radar Difference Interferometry, D-InSAR)技术与高分辨率光学遥感相结合,对隆德县展开滑坡隐患早期识别与探测研究。首先通过干涉叠加技术(Stacking)分别获得2019年1月—2020年5月隆德县升轨和降轨方向的雷达视向形变速率,然后结合高分辨率光学遥感影像产品和数字高程模型(DEM),基于专家判识经验建立适用于该研究区的滑坡隐患形态和变形解译标志,完成全县范围的滑坡隐患综合遥感识别和地面调查工作。本次遥感调查工作共识别滑坡隐患47处,野外调查验证21处,其中核实16处,准确率为71.4%。实地调查结果验证了综合遥感识别与探测技术在宁夏南部地质灾害隐患遥感调查的适用性和可行性,同时也验证了识别结果的准确性,为宁夏南部地区滑坡防治和突发地质灾害应急提供了重要的科学依据。
Abstract:Longde County in southern Ningxia is located at the western foot of Liupan mountain. Geological conditions is complicated. Affected by seasonal heavy rainfall, landslides and geological disasters occur frequently in the area, which poses a serious threat to local people's lives and property. In consideration of the high fractional vegetation in study area, integrated remote sensing technologies combined of Synthetic Aperture Radar Difference Interferometry technology and high spatial resolution optical remote sensing have been used in early detection of Landslides in the Longde county. Stacking technology has been used to calculate the rate of deformation from 2019.01 to 2021.05, in the direction of ascending and descending orbit. Combining high spatial resolution optical remote sensing images and digital elevation model (DEM), the interpretation key of landslide in the area deformation has been established. Then the early detection of landslides and ground survey in Longde county have been done. Through the integrated remote sensing technologies, 47 landslides were detected. 21 landslides were surveyed by field, of which 16 were verified, with an accuracy rate of 71.4%. The results of field survey demonstrated the applicability and feasibility of integrated remote sensing technology in the detection of landslides in southern Ningxia. Meanwhile, and the accuracy of the results in Longde county has been testified. The results of the early detection through integrated remote sensing technology provided significant scientific bases for the landslide protection and emergency response to sudden geological disasters in southern Ningxia.
-

-
表 1 Sentinel-1A卫星属性
Table 1. Sentinel-1A satellite parameters
卫星名称 幅宽/km 入射角/(°) 极化方式 影像时间 影像数量 Sentinel-1A 250 29.1~46.0 双极化:HH+HV、VV+HH单极化:HH、VV 2019年1月—2020年5月 升轨42期降轨43期 直接解译标志 表现为圈椅、双沟同源、椭圆、长条、簸箕形、舌形、弧形、不规则多边形等。斜坡上部分坡体较周围地形平缓,但能与侵蚀平台、阶地等区分。 间接
解译标志颜色 滑坡体显浅色色调,后缘弧形线性清晰,与外围深色调基岩反差明显。 地形地貌 常分布在沟谷、河流等陡峭边坡的局部凹陷地段或河道偏移异常部位。滑坡体后缘发育有弧形异常影像,包括陡坎、地形变异线和色调异常线等。滑坡体前缘边坡向谷地凸出,常有地形微突起及小型崩滑流堆积影像。 水系特征 常形成相对独立封闭的汇水区和特殊的水网系统或发育有与邻近区域不协调的网纹结构,往往导致现代水系变迁等地形变异现象。 -
[1] 高丽琰, 余江宽, 张幼莹, 等. 基于GIS的层次分析法在宁夏地质灾害易发性评价的应用[J]. 防灾科技学院学报,2017,19(4):8 − 15. [GAO Liyan, YU Jiangkuan, ZHANG Youying, et al. Application of GIS-based analytic hierarchy process in geological hazards assessment in Ningxia region[J]. Journal of Institute of Disaster Prevention,2017,19(4):8 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8047.2017.04.002
[2] 王成, 孟方, 李天斌. 宁夏回族自治区区域地质志 [R]. 银川: 宁夏回族自治区地质调查院, 2013: 23−30.
WANG Cheng, MENG Fang, LI Tianbin. Regional geology of the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region [R]. Yinchuan: Geology Survey Institute of Ningxia, 2013: 23−30. (in Chinese)
[3] 吕世民, 吴凯, 杜光波, 等. 宁夏隆德县地质灾害发育特征及形成条件分析[J]. 水利与建筑工程学报,2015,13(6):42 − 47. [LYU Shimin, WU Kai, DU Guangbo, et al. Development characteristics and formation conditions of geological hazards in Longde County of Ningxia[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering,2015,13(6):42 − 47. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1144.2015.06.008
[4] 许强, 董秀军, 李为乐. 基于天-空-地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):957 − 966. [XU Qiang, DONG Xiujun, LI Weile. Integrated space-air-ground early detection, monitoring and warning system for portential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):957 − 966. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 许强. 对地质灾害隐患早期识别相关问题的认识与思考[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2020,45(11):1651 − 1659. [XU Qiang. Understanding and consideration of related issues in early identification of potential geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2020,45(11):1651 − 1659. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 葛大庆. 地质灾害早期识别与监测预警中的综合遥感应用[J]. 城市与减灾,2018(6):53 − 60. [GE Daqing. Comprehensive application of remote sensing in early identification, monitoring and early warning in geological disasters[J]. City and Disaster Reduction,2018(6):53 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0495.2018.06.011
[7] 葛大庆, 戴可人, 郭兆成, 等. 重大地质灾害隐患早期识别中综合遥感应用的思考与建议[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版,2019,44(7):949 − 956. [GE Daqing, DAI Keren, GUO Zhaocheng, et al. Integrated space-air-ground early detection, monitoringand warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):949 − 956. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 葛大庆, 郭兆成. 重大地质灾害隐患早期识别中综合遥感应用的思考[J]. 中国应急救援,2019(1):10 − 14. [GE Daqing, GUO Zhaocheng. Thoughts of early identification of serious geological hazards with integrated remote sensing technologies[J]. China Emergency Rescue,2019(1):10 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5579.2019.01.002
[9] ZEBKER H A, ROSEN P A. Atmospheric artifacts in interferometric SAR surface deformation and topographic maps [J]. Department of Electrical Engineering and Geophysics, University of Stanford, Stanford, CA. 1996.
[10] FERRETTI A, PRATI C, ROCCA F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2001,39(1):8 − 20. doi: 10.1109/36.898661
[11] COLESANTI C, FERRETTI A, NOVALI F, et al. SAR monitoring of progressive and seasonal ground deformation using the permanent scatterers technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2003,41(7):1685 − 1701. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.813278
[12] FERRETTI A, PRATI C, ROCCA F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2000,38(5):2202 − 2212. doi: 10.1109/36.868878
[13] LANARI R, MORA O, MANUNTA M, et al. A small-baseline approach for investigating deformations on full-resolution differential SAR interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2004,42(7):1377 − 1386. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.828196
[14] WERNER C, WEGMULLER U, STROZZI T, et al. Interferometric point target analysis for deformation mapping[C]//IGARSS 2003.2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Proceedings (IEEE Cat. No. 03CH37477). July 21−25, 2003, Toulouse, France. IEEE, 2003: 4362−4364.
[15] FERRETTI A, FUMAGALLI A, NOVALI F, et al. A new algorithm for processing interferometric data-stacks: SqueeSAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2011,49(9):3460 − 3470. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2124465
[16] 李振洪, 宋闯, 余琛, 等. 卫星雷达遥感在滑坡灾害探测和监测中的应用: 挑战与对策[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):967 − 979. [LI Zhenhong, SONG Chuang, YU Chen, et al. Application of satellite remote sensing to landslide detection and mornitoring: Challenges and solutions[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):967 − 979. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] FRUNEAU B, ACHACHE J, DELACOURT C. Observation and modelling of the Saint-Étienne-de-Tinée landslide using SAR interferometry[J]. Tectonophysics,1996,265(3/4):181 − 190.
[18] RAUCOULES D, MAISONS C, CARNEC C, et al. Monitoring of slow ground deformation by ERS radar interferometry on the Vauvert salt mine (France)[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2003,88(4):468 − 478. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2003.09.005
[19] 王绚, 范宣梅, 杨帆, 等. 植被茂密山区地质灾害遥感解译方法研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2020,45(11):1771 − 1781. [WANG Xuan, FAN Xuanmei, YANG Fan, et al. Remote sensing interpretation method of geological hazards in lush mountainous area[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2020,45(11):1771 − 1781. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 张幼莹, 余江宽, 步凡, 等. “高分二号”卫星在黄土地质灾害解译中的应用研究[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息,2017,40(11):31 − 34. [ZHANG Youying, YU Jiangkuan, BU Fan, et al. Application of GF-2Satellite to geological hazard interpretation in loess plateau[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology,2017,40(11):31 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2017.11.009
[21] 彭令, 徐素宁, 梅军军, 等. 地震滑坡高分辨率遥感影像识别[J]. 遥感学报,2017,21(4):509 − 518. [PENG Ling, XU Suning, MEI Junjun, et al. Earthquake-induced landslide recognition using high-resolution remote sensing images[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing,2017,21(4):509 − 518. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 陆会燕, 李为乐, 许强, 等. 光学遥感与InSAR结合的金沙江白格滑坡上下游滑坡隐患早期识别[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(9):1342 − 1354. [LU Huiyan, LI Weile, XU Qiang, et al. Early detection of landslides in the upstream and downstream areas of the Baige landslide, the Jinsha River based on optical remote sensing and InSAR technologies[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(9):1342 − 1354. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] CARLÀ T, INTRIERI E, RASPINI F, et al. Perspectives on the prediction of catastrophic slope failures from satellite InSAR[J]. Scientific Reports,2019,9:14137. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50792-y
[24] DIAO X P, WU K, HU D H, et al. Combining differential SAR interferometry and the probability integral method for three-dimensional deformation monitoring of mining areas[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing,2016,37(21):5196 − 5212. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2016.1230284
[25] 刘星洪, 姚鑫, 周振凯, 等. 滑坡灾害InSAR应急排查技术方法研究[J]. 地质力学学报,2018,24(2):229 − 237. [LIU Xinghong, YAO Xin, ZHOU Zhenkai, et al. Study of the technique for landslide rapid recognition by InSAR[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2018,24(2):229 − 237. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2018.24.02.024
[26] HU J, LI Z W, DING X L, et al. Resolving three-dimensional surface displacements from InSAR measurements: a review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2014,133:1 − 17. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.02.005
[27] HU X, WANG T, PIERSON T C, et al. Detecting seasonal landslide movement within the Cascade landslide complex (Washington) using time-series SAR imagery[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2016,187:49 − 61. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2016.10.006
[28] ERIKSEN H Ø, LAUKNES T R, LARSEN Y, et al. Visualizing and interpreting surface displacement patterns on unstable slopes using multi-geometry satellite SAR interferometry (2D InSAR)[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2017,191:297 − 312. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2016.12.024
[29] PRICE E J, SANDWELL D T. Small-scale deformations associated with the 1992 Landers, California, earthquake mapped by synthetic aperture radar interferometry phase gradients[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,1998,103(B11):27001 − 27016. doi: 10.1029/98JB01821
[30] STROZZI T, WEGMULLER U, WERNER C, et al. Measurement of slow uniform surface displacement with mm/year accuracy[C]//IGARSS 2000. IEEE 2000 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Taking the Pulse of the Planet: The Role of Remote Sensing in Managing the Environment. Proceedings (Cat. No. 00CH37120). July 24-28, 2000, Honolulu, HI, USA. IEEE, 2000: 2239-2241.
[31] 彭令, 徐素宁, 梅军军, 等. 资源三号卫星在汶川震区滑坡快速识别中的应用方法研究[J]. 遥感技术与应用,2018,33(1):185 − 192. [PENG Ling, XU Suning, MEI Junjun, et al. Research on Wenchuan earthquake-induced landslides rapid recognition from ZY-3 imagery[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application,2018,33(1):185 − 192. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] CASCINI L, FORNARO G, PEDUTO D. Advanced low- and full-resolution DInSAR map generation for slow-moving landslide analysis at different scales[J]. Engineering Geology,2010,112(1/2/3/4):29 − 42.
[33] 董文, 潘建平, 阳振宇, 等. 高分二号卫星数据在地质灾害调查中的应用: 以重庆万州区为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(1):106 − 111. [DONG Wen, PAN Jianping, YANG Zhenyu, et al. Application of GF-2 satellite data in geological hazard survey: A case study in Wanzhou district of Chongqing City[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(1):106 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 潘腾. 高分二号卫星的技术特点[J]. 中国航天,2015(1):3 − 9. [PAN Teng. The technology characteristics of Gaofen-2 satellite[J]. Aerospace China,2015(1):3 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] 王智勇, 文强, 李晶晶, 等. 从开拓到引领: 赋能国内商业遥感卫星运行服务[J]. 中国测绘,2019(10):28 − 30. [WANG Zhiyong, WEN Qiang, LI Jingjing, et al. From pioneering to leading: Enabling domestic commercial remote sensing satellite operation services[J]. China Surveying and Mapping,2019(10):28 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6831.2019.10.008
[36] ZHANG Y, MENG X M, JORDAN C, et al. Investigating slow-moving landslides in the Zhouqu region of China using InSAR time series[J]. Landslides,2018,15(7):1299 − 1315. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-0954-8
-




 下载:
下载: