Karst collapse characteristics, disaster factors and risk analysis in Xiamao Village, Baiyun District, Guangzhou City
-
摘要:
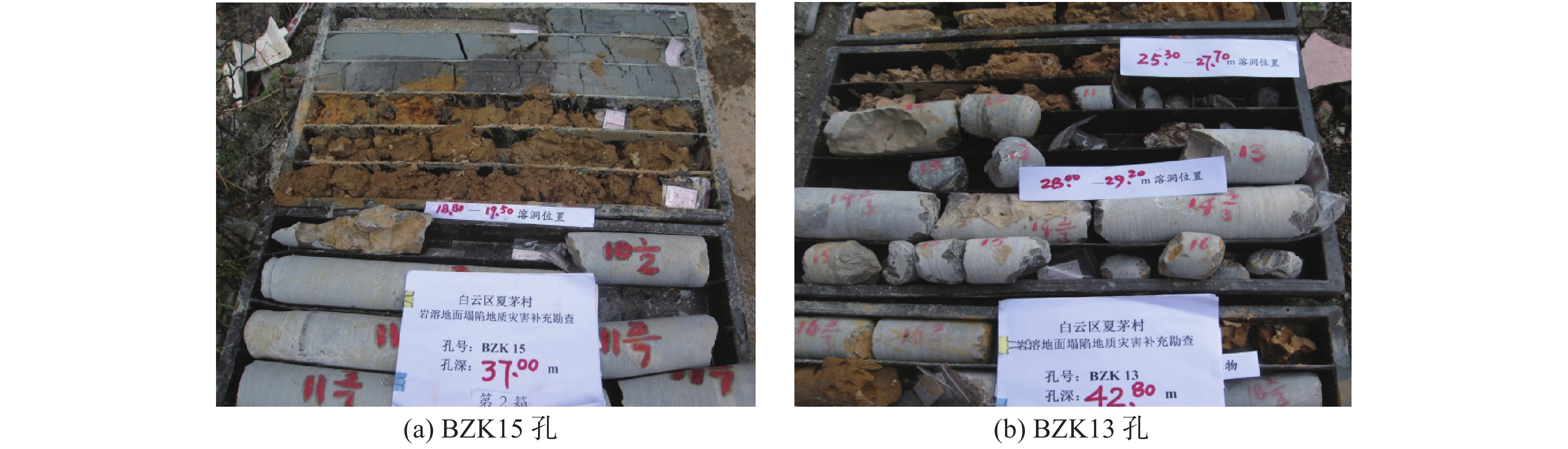
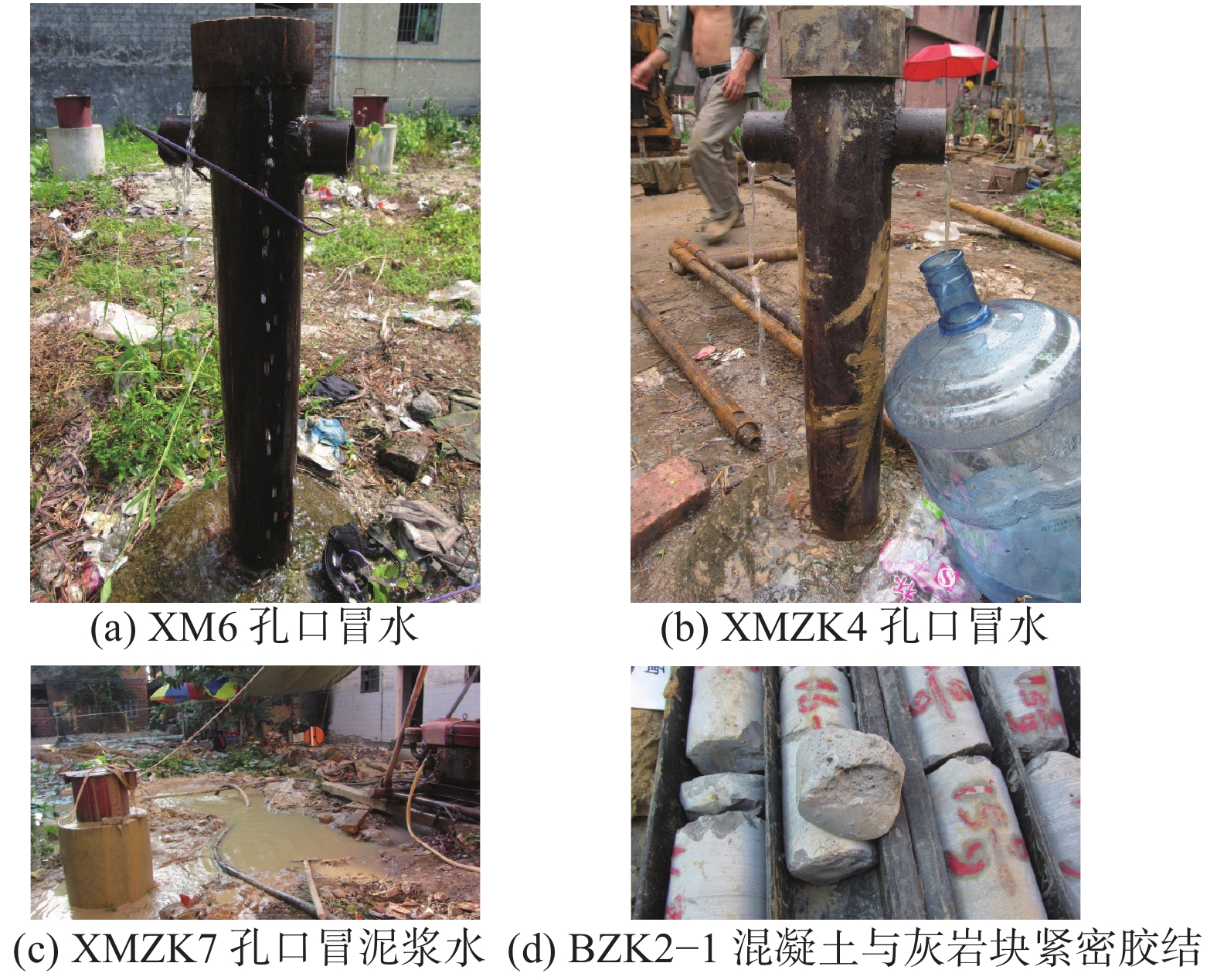
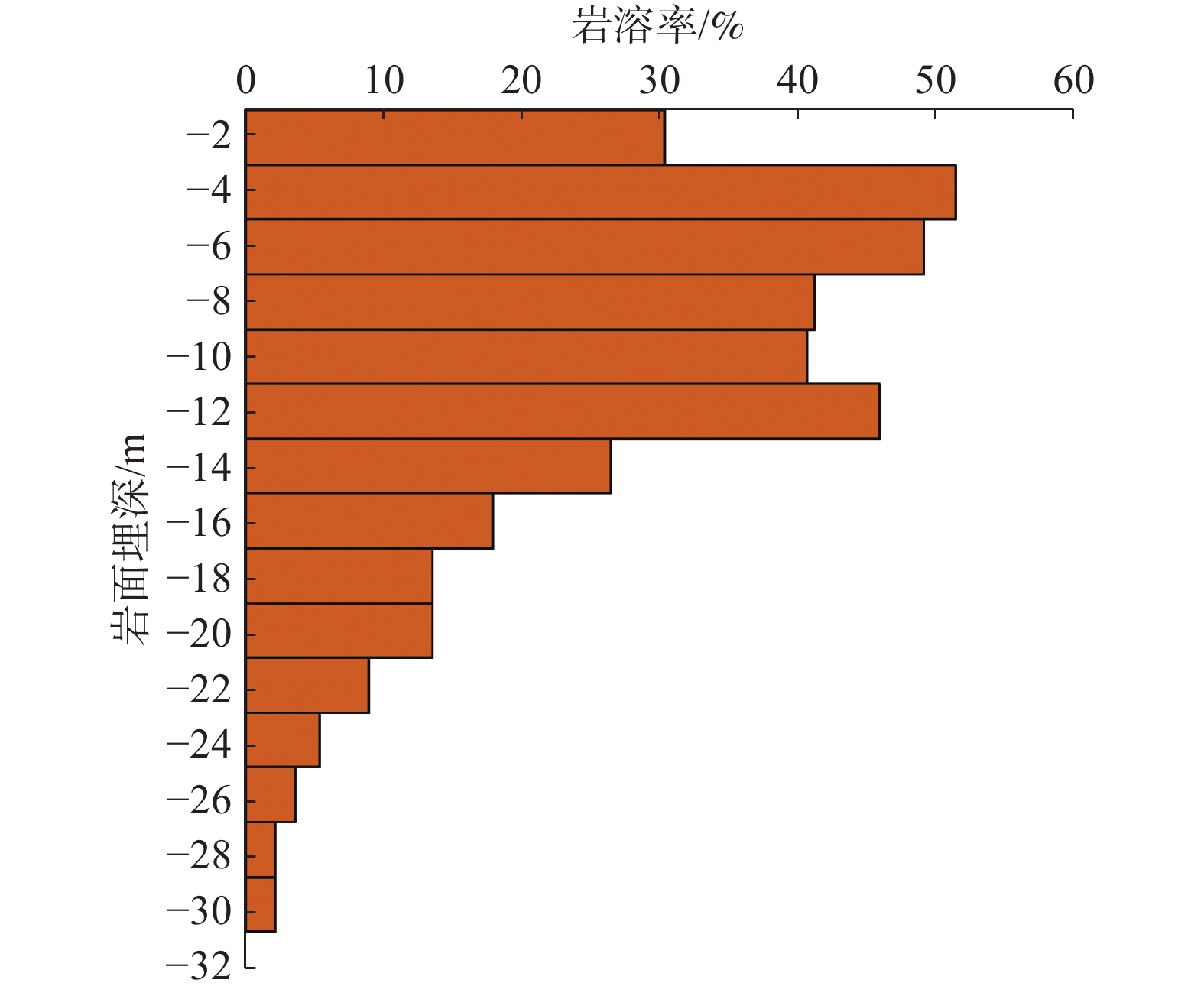
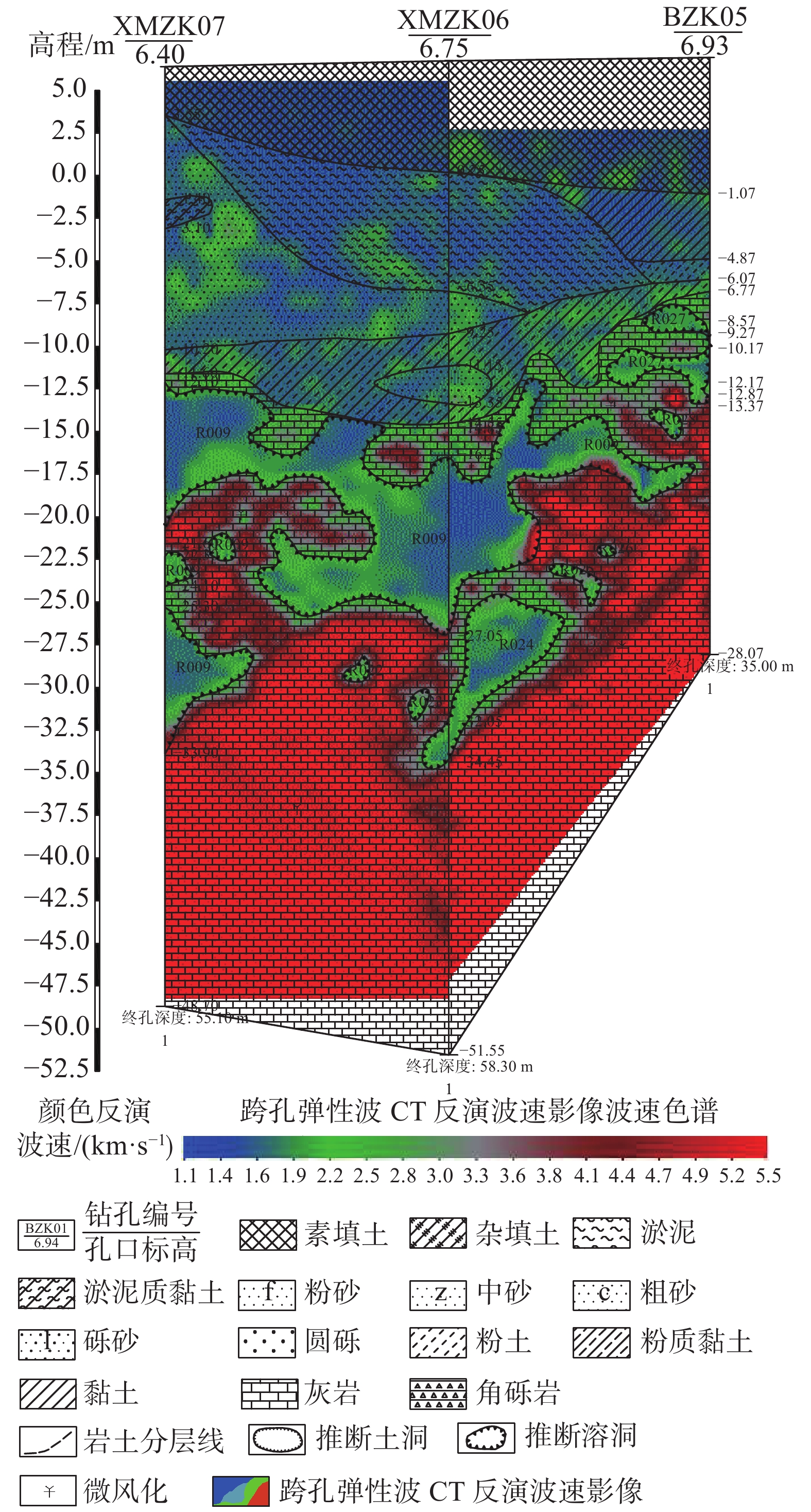
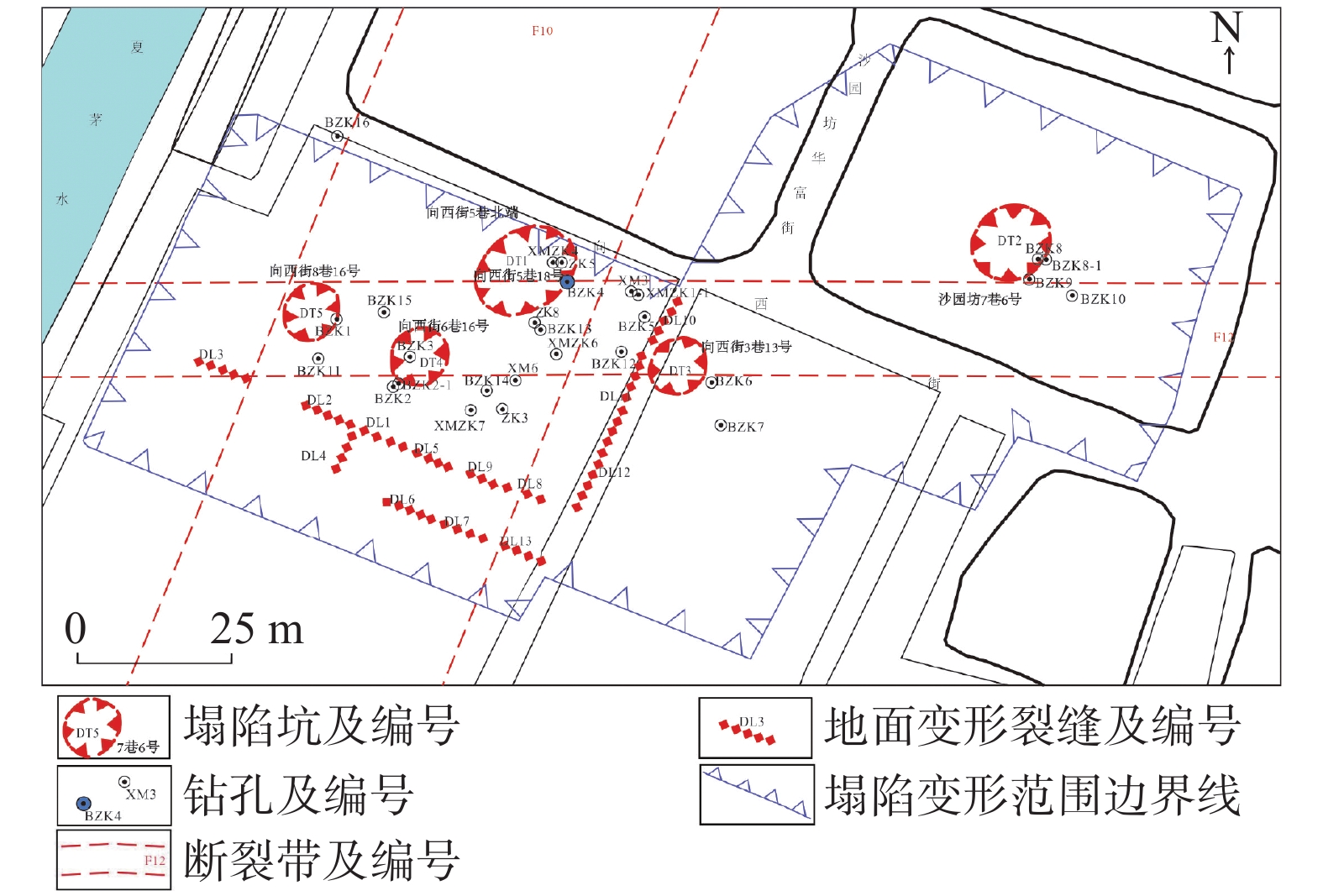
广州市白云区夏茅村岩溶塌陷地质灾害严重,塌陷区内地质环境条件极其复杂,隐伏灰岩岩溶土洞发育强烈,溶洞、土洞规模较大,且发育多层溶洞,溶洞间相互连通,岩溶塌陷区基岩面起伏较大,高程变化剧烈,第四系覆盖层厚度较大,底部粉质黏土层土洞发育,土体中规模巨大的土洞是产生岩溶地面塌陷的基础条件。基岩断裂构造带及其影响带范围内,岩石破碎,形成导水断层,存在地下水迳流通道,沿断裂带地下水循环活跃,溶蚀强烈,形成岩溶强发育带,为岩溶塌陷的发生提供了良好的动力条件。区内楼房基础施工扰动了地下水和土洞间的平衡状态从而成为了地面塌陷发生的诱发因素。运用7项地质环境条件指标和5项经济人口指标分别定性评估岩溶地面塌陷的易发度和易损度,并将二者叠加进行地质灾害风险评估。研究结果表明,夏茅村潜在地质灾害风险大,只有严格控制地下水动力条件,才能避免再次发生岩溶地面塌陷。
Abstract:Xiamao Village has been suffered from serious karst collapse geological disasters. The geological environment conditions in the collapse area are extremely complex. Karst soil caves of hidden limestone have strong development, and karst caves and soil caves are large in scale. Moreover, there are many karst caves with good connectivity among karst caves. The bedrock surface of karst collapse area fluctuates greatly, elevation changes sharply, the Quaternary overburden is thick, and the bottom silty clay layer soil is very large in saze. The cave development, the large-scale cave in the soil is the material foundation of karst ground collapse. In the bedrock fault structural zone and its influence zone, the rock is broken, and the water guide fault is formed. There is groundwater runoff channel. The groundwater circulation along the fault zone is active and the dissolution is strong, forming a strong karst development zone, which provides a good dynamic condition for the occurrence of karst collapse. The construction of the building foundation in the area disturbed the balance between groundwater and soil cave, which became the inducing factor of ground collapse. The risk assessment of karst ground subsidence is carried out by using seven geological environmental conditions and five economic and demographic indexes respectively. The results show that the potential geological disaster risk is large in Xiamao Village. Only by strictly controlling the dynamic conditions of groundwater can avoid karst ground collapse.
-
Key words:
- karst development /
- influencing factors /
- risk assessment /
- Xiamao Village /
- Guangzhou City
-

-
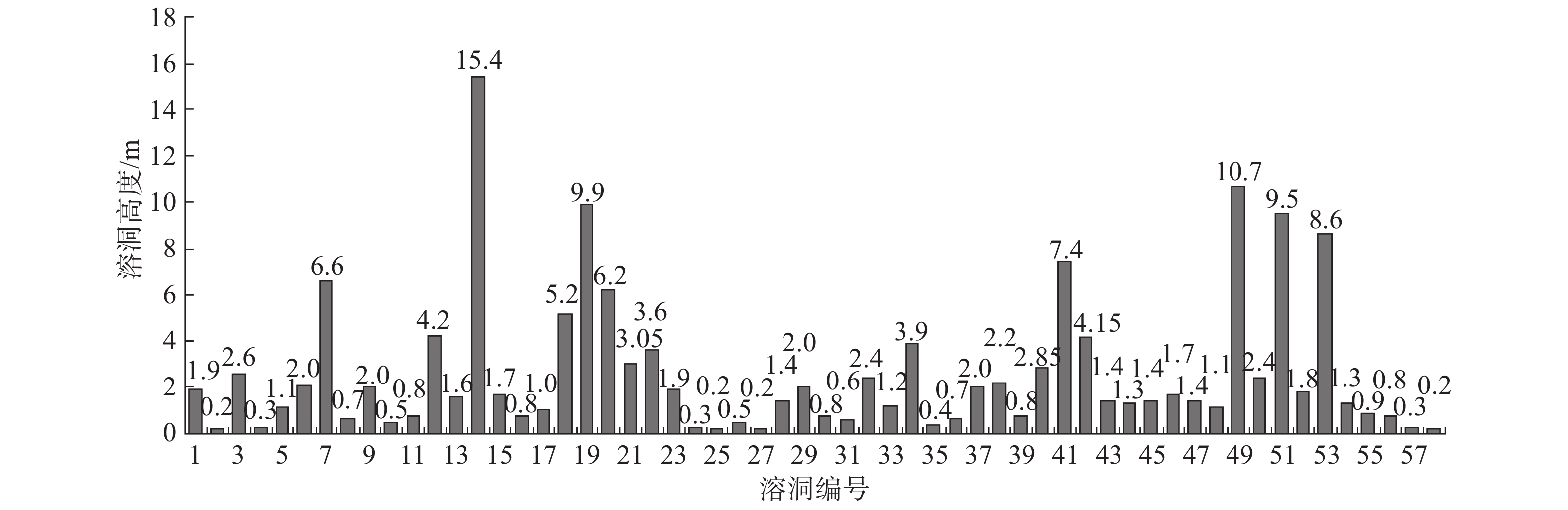
表 1 夏茅村岩溶地面塌陷区钻孔揭露基岩面统计表
Table 1. Statistics of bedrock surface exposed by boreholes in karst ground collapse area of Xiamao Village
序号 钻孔编号 X Y 基岩标高/m 序号 钻孔编号 X Y 基岩标高/m 1 BZK1 40232.48 36294.55 −8.8 15 BZK13 40230.63 36326.76 −17.56 2 BZK2 40221 36303.48 −17.41 16 BZK14 40220.25 36318.33 −12.6 3 BZK2-1 40221 36304.1 −14.41 17 BZK15 40233.53 36302.07 −10.58 4 BZK3 40226.03 36306.16 −12 18 XM3 40237.16 36341.17 −22.83 5 BZK4 40238.71 36331.12 −24.38 19 XMZK1-1 40236.63 36342.35 −11.13 6 BZK5 40232.83 36343.35 −6.8 20 XM6 40222.02 36322.91 −14.03 7 BZK6 40221.68 36353.88 −15.2 21 XMZK4 40242 36328 −16.58 8 BZK7 40214.63 36355.35 −15.3 22 XMZK6 40226.51 36329.41 −14.55 9 BZK8 40242.65 36405.57 −18.9 23 XMZK7 40216.91 36315.78 −11.6 10 BZK8-1 40242.72 36406.85 −26.6 24 ZK3 40274 36316 −23.3 11 BZK9 40239.29 36404.27 −18.9 25 ZK5 40266 36337 −48 12 BZK10 40236.45 36411.06 −41.2 26 ZK8 40256 36357 −38 13 BZK11 40225.66 36291.71 −13.7 27 BZK16 40258 36301 −16.5 14 BZK12 40226.89 36339.67 −7.4 表 2 岩溶地面塌陷易发度指标
Table 2. Karst ground collapse susceptibility index
稳定性
分级
评价要素不稳定
(高易发)较不稳定
(中易发)基本稳定
(低易发)稳定
(不易发)岩溶发育程度 强发育 中等发育 弱发育 不发育 岩溶地下水位及动态变化 水位埋深<5 m,
水位变化大水位埋深5~10 m,
水位变化较大水位埋深10~15 m,
水位变化较小水位埋深≥15 m ,
水位变化小覆盖土层岩性、结构 均一松散砂层或软土 均一稍密-中密砂土;双层或
多层砂土,底为砂砾双层或多层,粘性土
与砂土互层均一可塑-硬塑粘性土 覆盖土层厚度/m <10 10~20 20~30 ≥30 地面地貌特征 低洼地带临近
地表水体平原、谷地、低阶地 山前缓坡、中高阶地 台地、坡地、高阶地 地质构造 两组及以上交叉断裂 两组平行断裂 一组断裂 无断裂 人类工程活动(钻探、抽排水、
基坑开挖、采矿等)100 m以内有活动 200 m以外有活动 300 m以外有活动 无扰动地下水活动 表 3 岩溶地面塌陷易损度指标
Table 3. Vulnerability index of karst ground collaps
损失分级
评价要素损失大
(高易损)损失中等
(中易损)损失小
(低易损)无损失
(不易损)土地利用类型 建成区 耕地(广义) 林草地 空地、裸地 潜在经济损失/万元 >500 100~500 <小于100 无 受威胁人数/人 >30 3~30 <3以下 无 房屋地基基础 天然或浅基础 入土桩基础 入岩桩基础 无 房屋结构 砖混结构 预制板结构 框架结构 无 -
[1] DOĞAN U, YıLMAZ M. Natural and induced sinkholes of the obruk plateau and karapınar-hotamış plain, Turkey[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2011,40(2):496 − 508. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.09.014
[2] BENAC Č, JURAČIĆ M, MATIČEC D, et al. Fluviokarst and classical karst: examples from the dinarics (krk island, northern adriatic, croatia)[J]. Geomorphology,2013,184:64 − 73. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2012.11.016
[3] HEIDARI M, KHANLARI G R, TALEB BEYDOKHTI A R, et al. The formation of cover collapse sinkholes in North of Hamedan, Iran[J]. Geomorphology,2011,132(3/4):76 − 86.
[4] DURINGERA P, BACONB A M, SAYAVONGKHAMDYC T, et al. Karst development, breccias history, and mammalian assemblages in Southeast Asia: A brief review[J]. Comptes Rendus Palevol,2012,11(2−3):133 − 157.
[5] DURINGER P, BACON A M, SAYAVONGKHAMDY T, et al. Karst development, breccias history, and mammalian assemblages in Southeast Asia: A brief review[J]. Comptes Rendus Palevol,2012,11(2/3):133 − 157.
[6] SONG K I, CHO G C, CHANG S B. Identification, remediation, and analysis of karst sinkholes in the longest railroad tunnel in South Korea[J]. Engineering Geology,2012,135/136:92 − 105. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.02.018
[7] EPTING J, HUGGENBERGER P, GLUR L. Integrated investigations of karst phenomena in urban environments[J]. Engineering Geology,2009,109(3/4):273 − 289.
[8] FIDELIBUS M D, GUTIÉRREZ F, SPILOTRO G. Human-induced hydrogeological changes and sinkholes in the coastal gypsum karst of Lesina Marina area (Foggia Province, Italy)[J]. Engineering Geology,2011,118(1/2):1 − 19.
[9] COOPER A H, FARRANT A R, PRICE S J. The use of karst geomorphology for planning, hazard avoidance and development in Great Britain[J]. Geomorphology,2011,134(1/2):118 − 131.
[10] NOVEL J P, DIMADI A, ZERVOPOULOU A, et al. The aggitis karst system, eastern Macedonia, Greece: Hydrologic functioning and development of the karst structure[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2007,334(3/4):477 − 492.
[11] 胡亚波, 刘广润, 肖尚德, 等. 一种复合型岩溶地面塌陷的形成机理: 以武汉市烽火村塌陷为例[J]. 地质科技情报,2007,26(1):96 − 100. [HU Yabo, LIU Guangrun, XIAO Shangde, et al. Mechanism of a compound karst surface collapse: A case study in Fenghuo village of Wuhan city[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2007,26(1):96 − 100. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2007.01.017
[12] 罗小杰. 武汉地区浅层岩溶发育特征与岩溶塌陷灾害防治[J]. 中国岩溶,2013,32(4):419 − 432. [LUO Xiaojie. Features of the shallow karst development and control of karst collapse in Wuhan[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2013,32(4):419 − 432. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 陈学军, 周明芳, 陈富坚, 等. 岩溶地区破坏性抽水致塌试验研究: 以广西桂林西城区为例[J]. 地质科技情报,2002,21(1):79 − 82. [CHEN Xuejun, ZHOU Mingfang, CHEN Fujian, et al. Destructive pumping test to study the characteristics of karst collapses in limestone region: A case study in the western urban area of Guilin City[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2002,21(1):79 − 82. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2002.01.018
[14] 康春景, 张绪教, 吴中海, 等. 滇西怒江河谷潞江段岩溶发育特征及其对工程的影响[J]. 地质通报,2012,31(增刊1):374 − 381. [KANG Chunjing, ZHANG Xujiao, WU Zhonghai, et al. Karst development along Lujiang segment of the Nujiang(Salween) river in western Yunnan Province and its potential influence on the railway project[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2012,31(Sup1):374 − 381. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 郭宇, 周心经, 郑小战, 等. 广州夏茅村岩溶地面塌陷成因机理与塌陷过程分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(5):54 − 59. [GUO Yu, ZHOU Xinjing, ZHENG Xiaozhan, et al. Analysis on formation mechanism and process of karst collapse in Xiamao Village, Guangzhou City of Guangdong Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(5):54 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 黄健民, 吕镁娜, 郭宇, 等. 广州金沙洲岩溶地面塌陷地质灾害成因分析[J]. 中国岩溶,2013,32(2):167 − 174. [HUANG Jianmin, LYV Meina, GUO Yu, et al. Research on the reason for geologic disaster by karst surface collapse at Jinshazhou in Guangzhou[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2013,32(2):167 − 174. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2013.02.007
[17] 黄健民, 郭宇, 胡让全, 等. 广州金沙洲地面沉降成因分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2013,24(2):61 − 67. [HUANG Jianmin, GUO Yu, HU Rangquan, et al. Analysis of land subsidence in Jinshazhou area, Guangzhou City[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2013,24(2):61 − 67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 郑小战, 郭宇, 戴建玲, 等. 广州市典型岩溶塌陷区岩溶发育及影响因素[J]. 热带地理,2014,34(6):794 − 803. [ZHENG Xiaozhan, GUO Yu, DAI Jianling, et al. Karst development and influencing factors in typical karst collapse districts of Guangzhou[J]. Tropical Geography,2014,34(6):794 − 803. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 郑小战, 郭宇, 戴建玲, 等. 岩溶区线性工程影响下的地下水监测及数值模拟研究: 以广州市金沙洲为例[J]. 中国岩溶,2016,35(6):657 − 666. [ZHENG Xiaozhan, GUO Yu, DAI Jianling, et al. Groundwater monitoring and numerical simulation under the influence of linear engineering in karst areas: A case study of the Jinshazhou area, Guangzhou City[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2016,35(6):657 − 666. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 郭宇, 黄健民, 周志远, 等. 广东广州市白云区金沙洲地区地质灾害现状及防治对策[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2013,24(3):100 − 104. [GUO Yu, HUANG Jianmin, ZHOU Zhiyuan, et al. Geological hazard situation and control countermeasures in Jinshazhou area, Baiyun district of Guangzhou City[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2013,24(3):100 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 郭宇, 黄健民, 陈建新, 等. 广州市白云区金沙洲地区地质灾害风险区划[J]. 热带地理,2013,33(6):659 − 665. [GUO Yu, HUANG Jianmin, CHEN Jianxin, et al. Regionalization of geological disaster risk in Jinshazhou area, Baiyun district, Guangzhou[J]. Tropical Geography,2013,33(6):659 − 665. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 苏扣林, 黄永贵, 郑小战. 广州市荔湾区大坦沙岩溶地面塌陷成因及其稳定性评价[J]. 热带地理,2012,32(2):167 − 172. [SU Koulin, HUANG Yonggui, ZHENG Xiaozhan. Karst ground subsidence and stability evaluation for datansha, Guangzhou[J]. Tropical Geography,2012,32(2):167 − 172. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5221.2012.02.009
[23] 骆荣,郑小战,张凡,等. 广花盆地西北部赤坭镇岩溶发育规律[J]. 热带地理,2011,31(6):565 − 569. [LUO Rong, ZHENG Xiaozhan, ZHANG Fan, et al. Study of karst development rule in Chini Town in northwest Guanghua basin[J]. Tropical Geography,2011,31(6):565 − 569. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: