Analysis on ecological restored effect of Mu Us sandy land in northern Shaanxi
-
摘要:
应用“3S”技术与土壤化学方法,对毛乌素沙地榆林市境内区域的沙质荒漠化土地进行了近45年来变化研究与生态修复效果分析,研究结果表明:研究区土地的沙质荒漠化强度以轻度、中度为主,治理方式以人工修复为主;1975—2019年沙质荒漠化的分布面积与强度呈现先快速发展而后逆转的变化特征。其中,1975—2007年沙质荒漠化的发展与过度放牧、荒地开垦及矿产资源开发等人类活动及强度密切相关。2007—2019年的逆转与生态调控政策及治理工程的实施密切相关。人工修复地区的土壤养分含量优于自然修复地区,在同等背景的自然修复条件下,不同成因的沙质荒漠化土地土壤养分含量有一定区别。采用人工修复与自然修复相结合的方式,以人工修复促进植被自然修复能力,是研究区有效的生态修复方式。
Abstract:The "3S" technology and soil chemical methods were used to study the change and ecological restored effect of sandy desertification land in Yulin City of Mu Us sandy land during the past 45 years. The results show that: the intensity of sandy desertification land in the study area was mainly mild and moderate, and the restored mode was mainly artificial restoration; the distributed area and the intensity of sandy desertification land from 1975 to 2019 showed the desertification developed rapidly and then deteriorated, the development of sandy desertification from 1975 to 2007 was closely related to human activities such as overgrazing, wasteland reclamation and mineral resources development, and the reversal from 2007 to 2019 was closely related to the implementation of ecological control policies and control projects; the soil nutrient content of the artificial restored area was better than the natural restored area, the different causes of sandy desertification land was very different under the same natural restored conditions; combined the artificial restored method and the natural restored method, artificial vegetation construction is proved to be a effective way to promote natural vegetation restoring and ecological restoration in the study area.
-
Key words:
- sandy desertification land /
- remote sensing /
- soil nutrient /
- ecological restored
-

-
表 1 研究区沙质荒漠化分级标准及遥感解译标志
Table 1. Classification standards and remote sensing interpretation marks of sandy desertification in the study area
沙质荒漠化
程度风积、风蚀地表形态
占该地面积/%植被覆盖度/% 地表景观综合特征 遥感解译标志 轻度
沙质荒漠化<10 50~30 风沙活动较明显,原生地表植被已开始被破坏,与沙生植被混杂分布,出现片状、点状沙地,多为固定的灌丛沙堆,农田适耕性下降 呈淡绿色、褐色色彩,具有白色、粉色斑点状影纹;不规则斑块状分布;内部纹理均一,植被覆盖度较高,与周边地物差异明显,边界清晰,解译标志清晰 中度
沙质荒漠化10~30 30~10 风沙活动频繁,原生地表破坏较大,半固定沙丘与滩地相间分布,丘间和滩地一般较开阔,多分布灌草结合的群落;耕地中有明显的风蚀洼地、残丘,地表植被稀少 呈淡绿色、褐色色彩,具有稀疏的白色斑片状影纹;不规则斑块状分布,内部沙丘形态明显;植被覆盖度不高,与周边地物色彩差异较明显,解译标志清晰 重度
沙质荒漠化≥30 ≤10 风沙活动强烈,密集的流动沙丘和风蚀地表,沙生植被稀少或基本没有植被生长 呈白色、粉色色彩,具白色波状或蜂窝状影纹;沙丘形态明显,流动性强,植被覆盖度较低或无植被覆盖;高大沙丘或沙丘链间具有斑点状绿色阴影,边界清晰可辨,解译标志清晰 表 2 研究区沙质荒漠化土地面积四期统计结果
Table 2. The statistical of sandy desertification land area in four periods
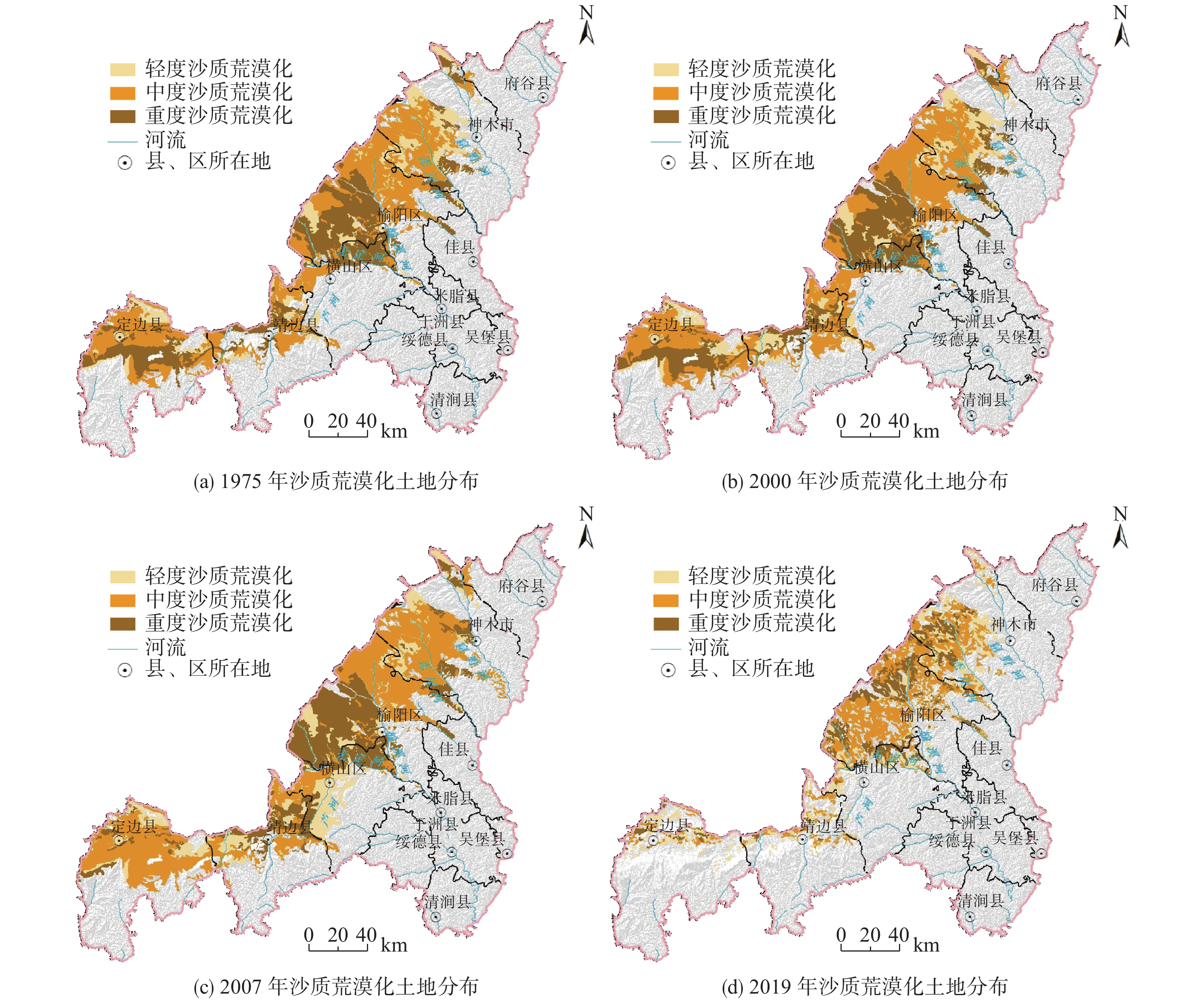
时间/年 轻度沙质
荒漠化/km2中度沙质
荒漠化/km2重度沙质
荒漠化/km2合计/km2 1975 2415.01 6559.23 4649.93 13624.17 2000 2617.75 6756.61 4821.57 14195.93 2007 2930.11 7267.51 4740.71 14938.33 2019 2423.31 3929.08 1855.88 8208.28 表 3 研究区土壤养分测试结果
Table 3. Testing results of soil nutrients in the study area
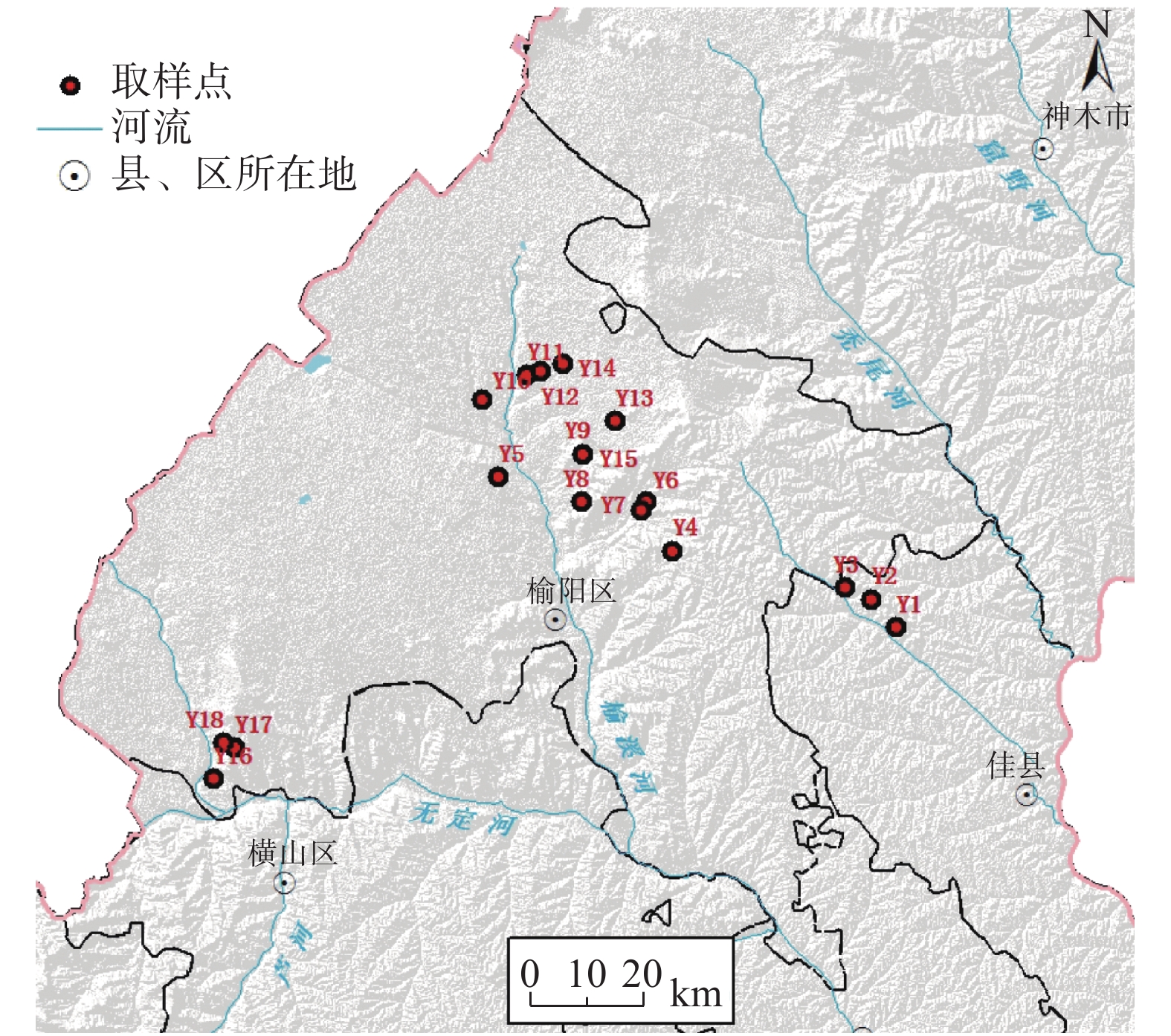
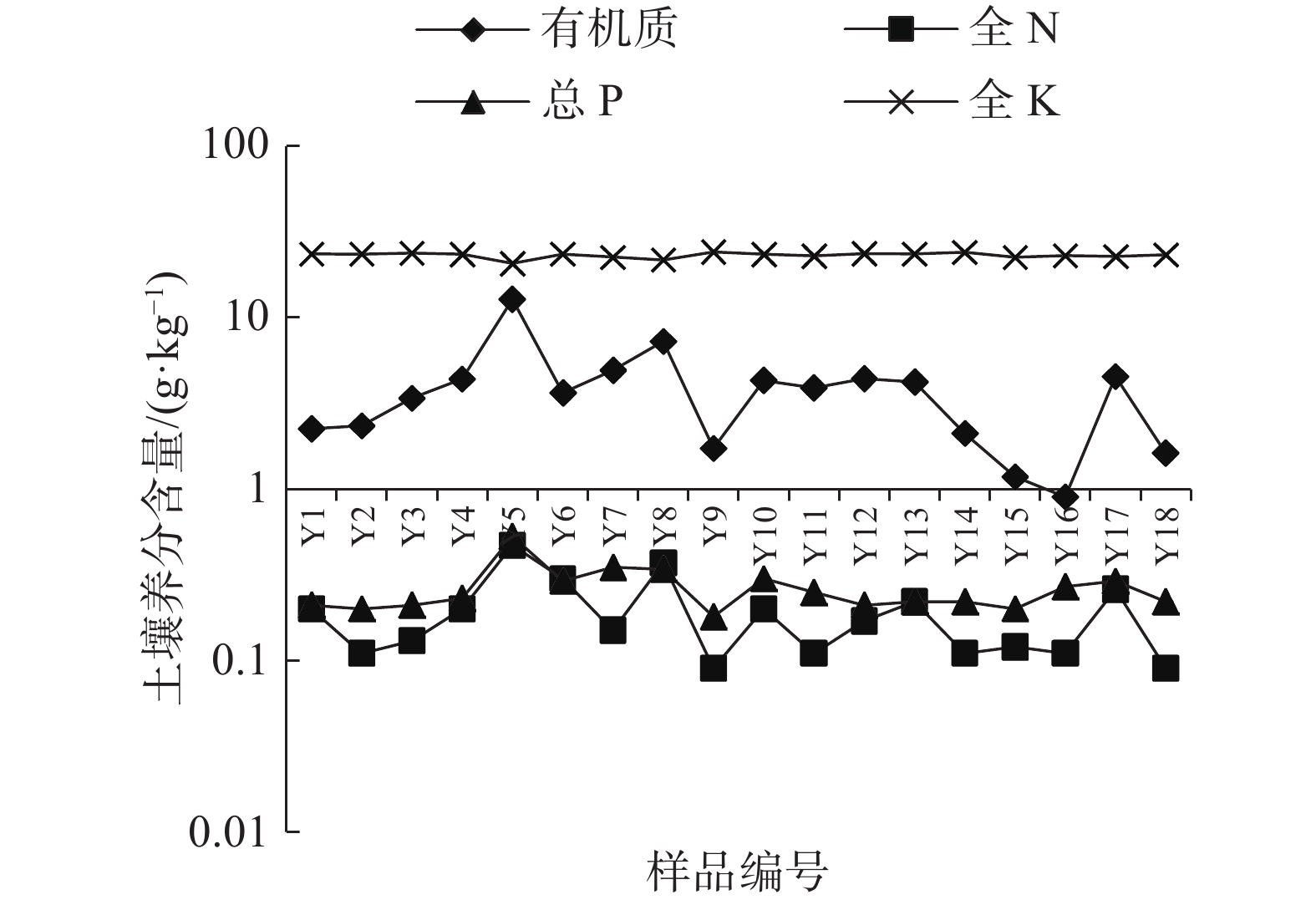
样品编号 有机质含量/
(g·kg−1)全养分 沙化土地类型 采样点地貌、恢复治理方式 全N/
(g·kg−1)总P/
(g·kg−1)全K/
(g·kg−1)Y1 2.25 0.20 0.21 23.59 轻度 覆沙黄土丘陵区,人工修复 Y2 2.34 0.11 0.20 23.48 中度 覆沙黄土丘陵区,自然修复 Y3 3.39 0.13 0.21 23.78 重度 覆沙黄土丘陵区,自然修复 Y4 4.39 0.20 0.23 23.43 重度 覆沙黄土丘陵区,自然修复 Y5 12.8 0.47 0.53 20.72 耕地 黄土梁面,旱地,背景值 Y6 3.64 0.30 0.29 23.48 中度 覆沙黄土丘陵区,自然修复 Y7 4.94 0.15 0.35 22.56 轻度 覆沙黄土丘陵区,自然修复 Y8 7.27 0.37 0.34 21.71 轻度 风沙滩地区,人工修复 Y9 1.73 0.09 0.18 24.20 中度 风沙滩地区,人工修复 Y10 4.30 0.20 0.30 23.45 轻度 风沙滩地区,人工修复 Y11 3.90 0.11 0.25 22.93 重度 风沙滩地区,自然修复 Y12 4.40 0.17 0.21 23.64 中度 风沙滩地区,自然修复 Y13 4.21 0.22 0.22 23.55 耕地 风沙滩地区,背景值 Y14 2.11 0.11 0.22 24.06 轻度 风沙滩地区,自然修复 Y15 1.18 0.12 0.20 22.54 轻度 风沙滩地区,臭柏保护区,背景值 Y16 0.90 0.11 0.27 23.04 重度 风沙滩地区,自然修复 Y17 4.54 0.26 0.29 22.77 轻度 风沙滩地区,自然修复 Y18 1.62 0.09 0.22 23.28 中度 风沙滩地区,自然修复 -
[1] 岳乐平, 杨利荣, 李智佩, 等. 阿拉善高原干涸湖床沉积物与华北地区沙尘暴[J]. 第四纪研究,2004,24(3):311 − 317. [YUE Leping, YANG Lirong, LI Zhipei, et al. Lacustrine deposit in the alxa plateau and the sand-dust stormin northern China[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2004,24(3):311 − 317. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2004.03.010
[2] 王涛, 吴薇, 薛娴, 等. 中国北方沙漠化土地时空演变分析[J]. 中国沙漠,2003,23(3):230 − 235. [WANG Tao, WU Wei, XUE Xian, et al. Time-space evolution of desertification land in northern China[J]. Journal of Desert Research,2003,23(3):230 − 235. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2003.03.004
[3] 高会军, 姜琦刚, 霍晓斌. 中国北方沙质荒漠化土地动态变化遥感分析[J]. 灾害学,2005,20(3):36 − 40. [GAO Huijun, JIANG Qigang, HUO Xiaobin. Remote sensing analysis on dynamic change of sandy desertification land in North China[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2005,20(3):36 − 40. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2005.03.008
[4] 朱震达. 中国土地荒漠化的概念、成因与防治[J]. 第四纪研究,1998,18(2):145 − 155. [ZHU Zhenda. Concept, cause and control of desertification in China[J]. Quaternary Sciences,1998,18(2):145 − 155. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1998.02.006
[5] 董光荣,吴波,慈龙骏. 我国荒漠化现状、成因与防治对策[J]. 中国沙漠,1999,19(4):395 − 398. [DONG Guangrong,WU Bo,CI Longjun. Present situation, cause and control way of desertification in China[J]. Journal of Desert Research,1999,19(4):395 − 398. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 杨晓晖, 张克斌, 慈龙骏. 中国荒漠化评价的现状、问题及其解决途径[J]. 中国水土保持科学,2004,2(1):22 − 28. [YANG Xiaohui, ZHANG Kebin, CI Longjun. Desertification assessment in China: The state-of-art, problems and solution measures[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation,2004,2(1):22 − 28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 高会军, 姜琦刚. 基于遥感技术的中国北方沙漠及沙质荒漠化土地区划研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2006,17(4):68 − 72. [GAO Huijun, JIANG Qigang. Zonation of desert and sandy desertification land in North China based on remote sensing technology[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2006,17(4):68 − 72. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2006.04.016
[8] 李鑫. 黄土高原北部风沙区土地沙漠化问题及防治对策[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2006,17(1):133 − 137. [LI Xin. Land desertification of the northern loess plateau in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2006,17(1):133 − 137. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2006.01.032
[9] 王涛, 薛娴, 吴薇, 等. 中国北方沙漠化土地防治区划(纲要)[J]. 中国沙漠,2005,25(6):816 − 822. [WANG Tao, XUE Xian, WU Wei, et al. Regionalization of desertification lands in north of China:A program[J]. Journal of Desert Research,2005,25(6):816 − 822. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2005.06.002
[10] 杨洪晓, 卢琦, 吴波, 等. 青海共和盆地沙化土地生态修复效果的研究[J]. 中国水土保持科学,2006,4(2):7 − 12. [YANG Hongxiao, LU Qi, WU Bo, et al. Ecological restoration in alpine sandy lands of Gonghe basin, Qinghai Province[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation,2006,4(2):7 − 12. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3007.2006.02.002
[11] 李娜, 颜长珍. 毛乌素沙地现代人为活动的生态环境效应研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠,2015,35(2):487 − 492. [LI Na, YAN Changzhen. Research progress on eco-environmental effects of modern human activities in the Mu Us sandy land, China[J]. Journal of Desert Research,2015,35(2):487 − 492. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2014.00022
[12] 张雷, 洪光宇, 李卓凡, 等. 基于层次分析法的毛乌素沙地3种造林模式恢复成效评价[J]. 林业资源管理,2017(6):108 − 112. [ZHANG Lei, HONG Guangyu, LI Zhuofan, et al. Assessment of three kinds of reforestation models recovery effect in Mu Us sandy land based on analytical hierarchy process[J]. Forest Resources Management,2017(6):108 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 杨梅焕, 曹明明, 朱志梅. 毛乌素沙地东南缘沙漠化过程中植被的退化和稳定性[J]. 水土保持通报,2017,37(5):10 − 15. [YANG Meihuan, CAO Mingming, ZHU Zhimei. Vegetation degradation and its stability in desertification at southeastern edge of Mu Us sandy land[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2017,37(5):10 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 吴晓旭, 邹学勇. 基于3S的毛乌素沙地腹地景观格局演变及其驱动力分析: 以内蒙古乌审旗为例[J]. 中国沙漠,2010,30(4):763 − 769. [WU Xiaoxu, ZOU Xueyong. Analysis of landscape pattern change and its driving factors based on 3S technology: A case study in uxin banner of Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Desert Research,2010,30(4):763 − 769. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 中华人民共和国林业部防治荒漠化办公室. 联合国关于发生严重干旱和荒漠化的国家特别是在非洲防治荒漠化的公约[S]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 1994.
Desertification control office of the Ministry of forestry of the people’s Republic of China. United Nations convention to combat desertification in those countries experiencing serious drought and/or desertification particularly in Africa[S]. Beijing: China Forestry Press,1994. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 中华人民共和国林业局.沙化土地监测技术规程: GB/T 24255-2009 [S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009.
Forestry Administration of the people’s Republic of China. Technical specification for desertification land monitoring: GB/T 24255-2009 [S]. Beijing: China Standards Press,2009. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 申元村, 王秀红, 丛日春, 等. 中国沙漠、戈壁生态地理区划研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2013,27(1):1 − 13. [SHEN Yuancun, WANG Xiuhong, CONG Richun, et al. Eco-geographical zoning of deserts and Gobi in China[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment,2013,27(1):1 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 刘淑珍, 柴宗新, 范建容. 中国土地荒漠化分类系统探讨[J]. 中国沙漠,2000,20(1):35 − 39. [LIU Shuzhen, CHAI Zongxin, FAN Jianrong. Discussion on classification system of land desertification in China[J]. Journal of Desert Research,2000,20(1):35 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2000.01.007
[19] 中华人民共和国环境保护部.土壤质量-全氮的测定-凯氏法: HJ 717-2014 [S].北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2014.
Ministry of environmental protection of the people’s Republic of China. Soil quality –Determination of total nitrogen –Modified Kjeldahl method: HJ 717-2014 [S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 中华人民共和国林业局.森林土壤磷的测定: LY/T 1232-2015 [S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015.
Forestry Administration of the people’s Republic of China. Phosphorous determination methods of forest soils: LY/T 1232-2015 [S]. Beijing: China Standards Press,2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 中华人民共和国林业局.森林土壤钾的测定: LY/T 1234-2015 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015.
Forestry Administration of the people’s Republic of China. Potassium determination methods of forest soils: LY/T 1234-2015 [S]. Beijing: China Standards Press,2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 中华人民共和国农业部.土壤有机质的测定: NY/T11121.6-2006 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006.
Ministry of Agriculture of the people’s Republic of China. Method for determination of soil organic matter: NY/T11121.6-2006 [S]. Beijing: China Standards Press,2006. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 任朝霞, 杨达源. 近50a西北干旱区气候变化趋势及对荒漠化的影响[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2008,22(4):91 − 95. [REN Zhaoxia, YANG Dayuan. Climate change and surface runoff change impact on desertification in the arid area of northwest China in resent 50 years[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment,2008,22(4):91 − 95. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7578.2008.04.017
[24] 王文科,尹红美,黄金廷,等. 基于蒸渗仪和解析法估算毛乌素沙地潜水蒸发量[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(4):1 − 6. [WANG Wenke, YIN Hongmei, HUANG Jinting, et al. Estimation of groundwater evaporation based on lysimeter experiment and analytical solution in the Mu Us sandy land[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(4):1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 郝启勇. 山东黄河北矿区土壤盐渍化特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(1):65 − 69. [HAO Qiyong. Soil salinization characteristics in Huanghebei mining area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(1):65 − 69. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: