Landslide susceptibility assessment by the coupling method of RBF neural network and information value: A case study in Min Xian,Gansu Province
-
摘要:
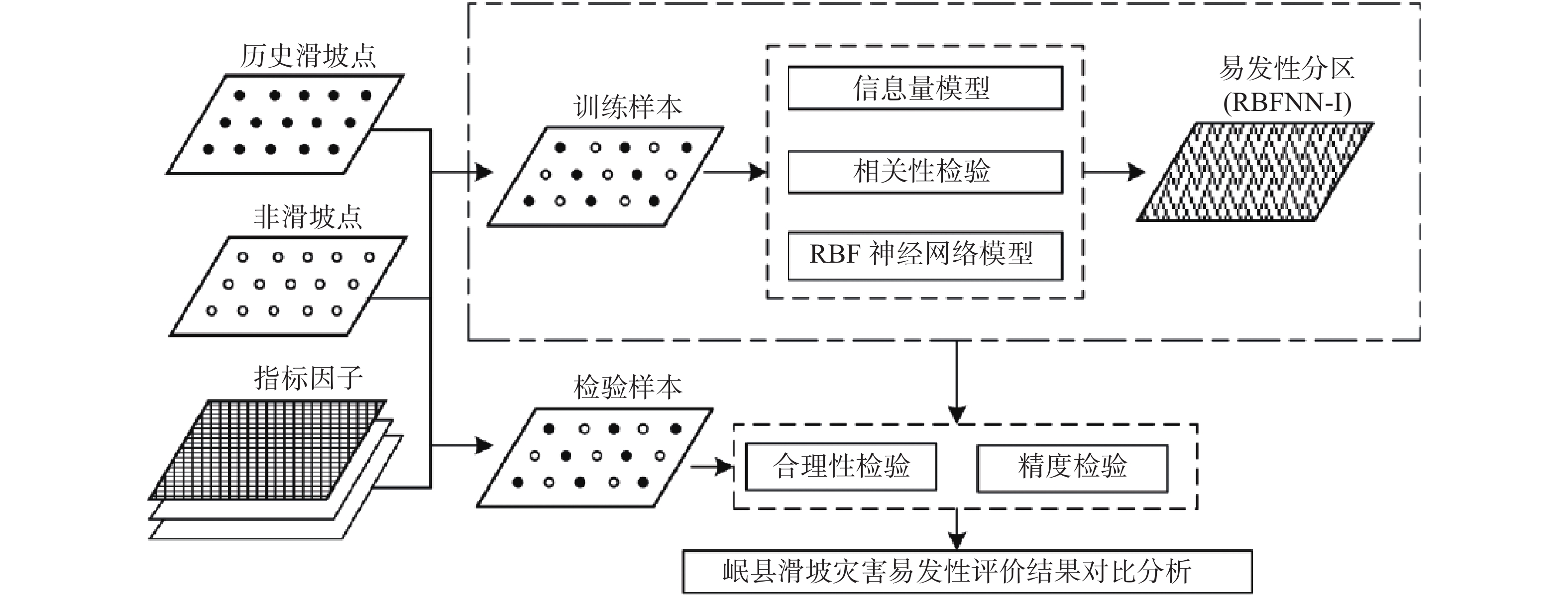
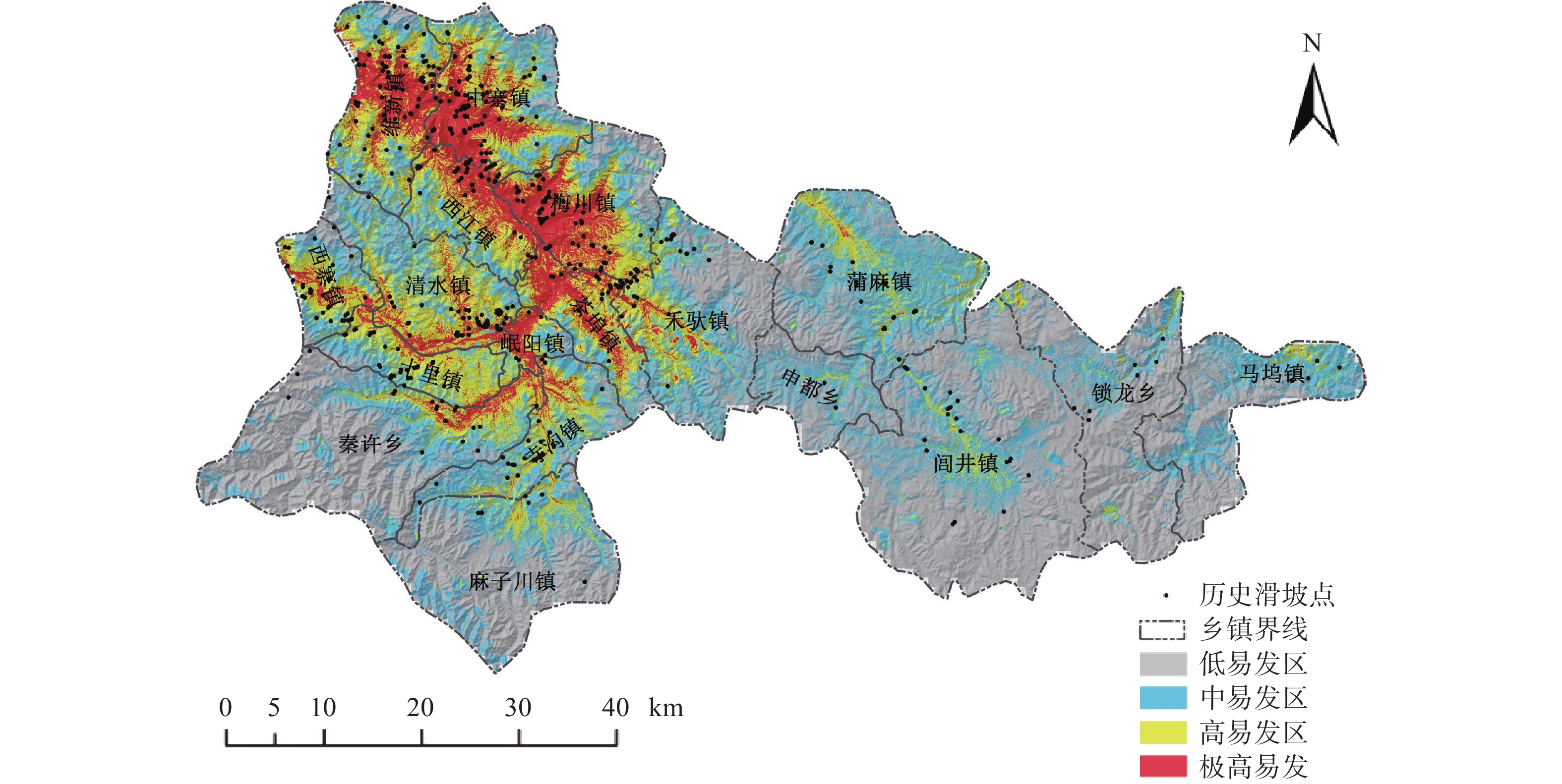
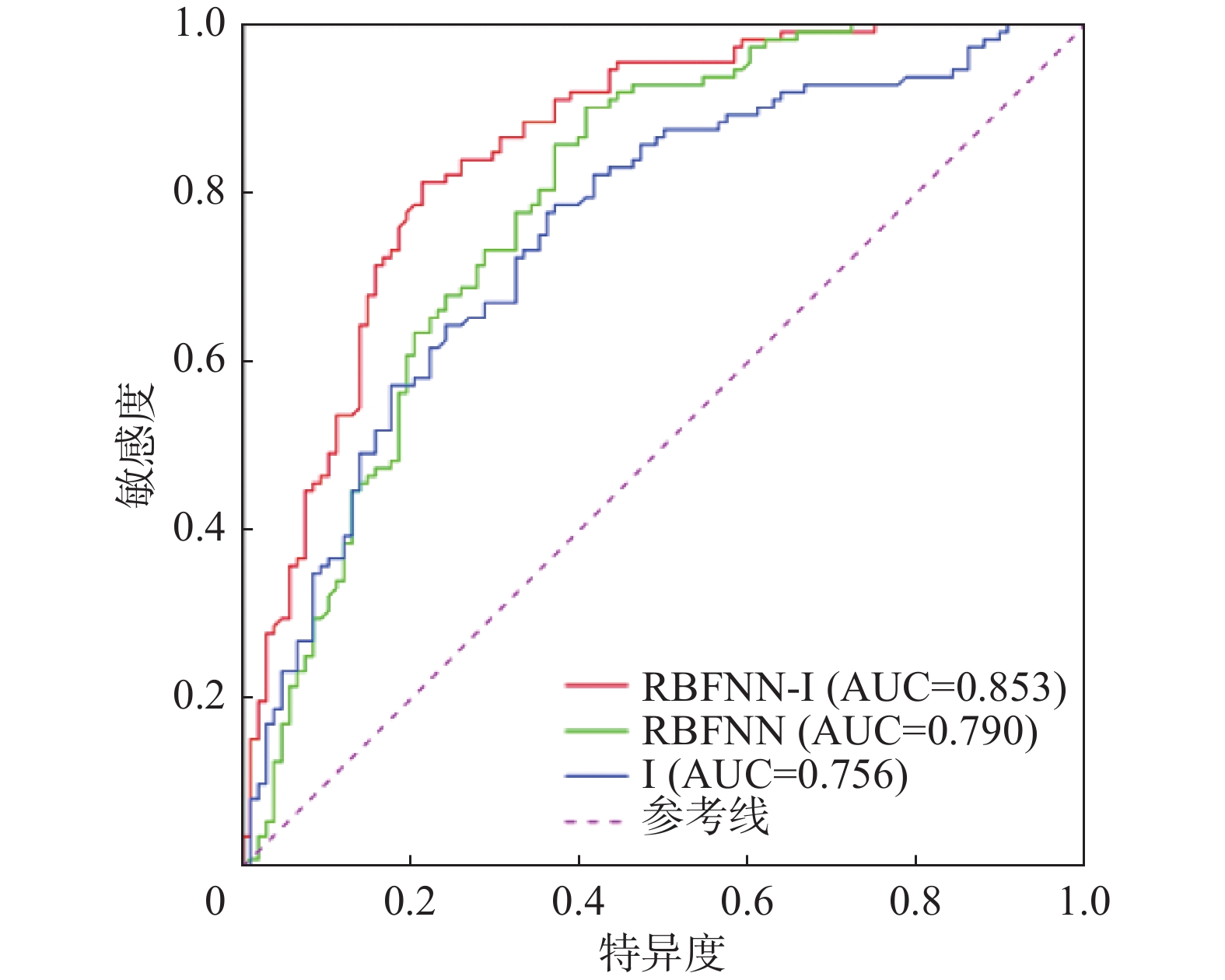
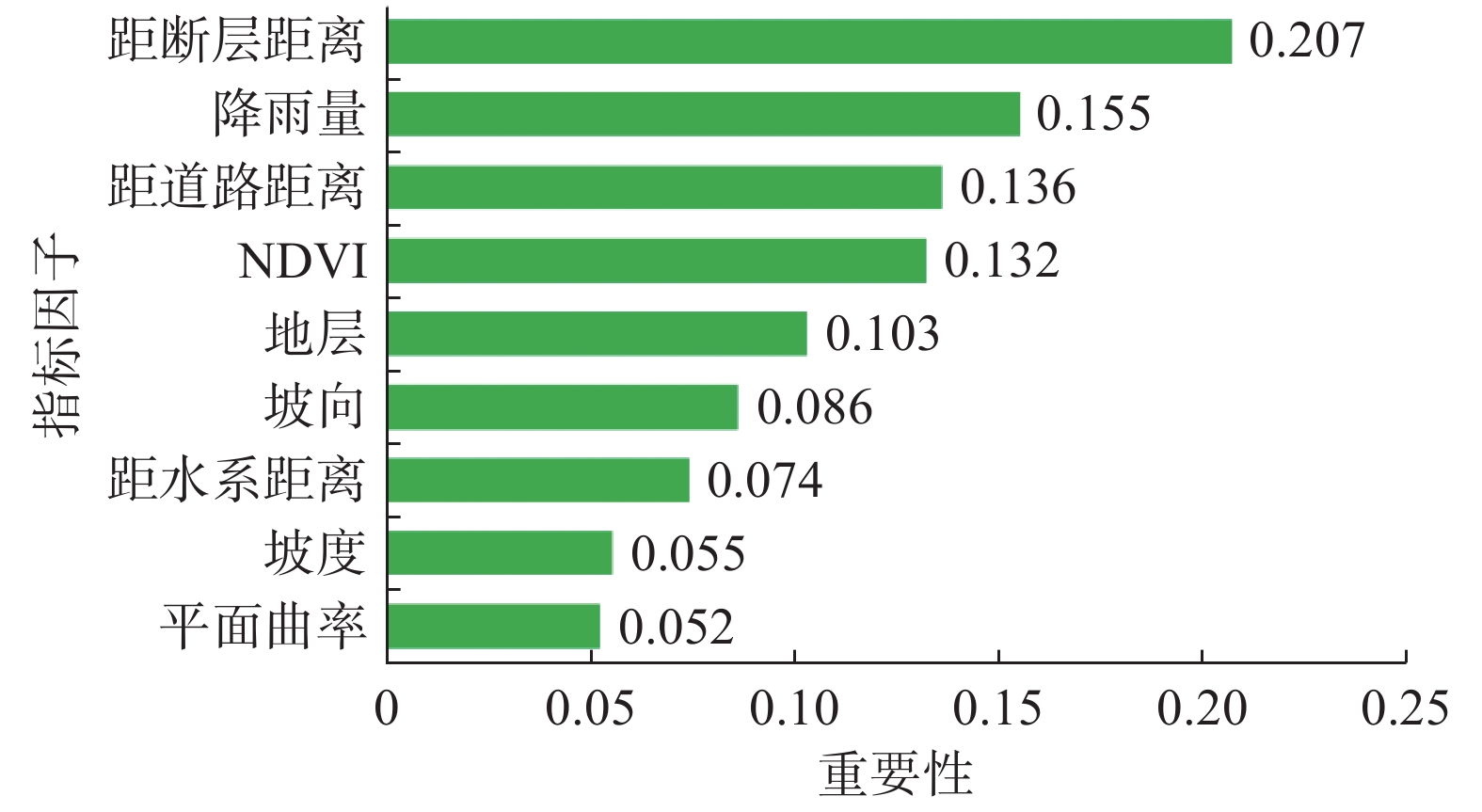
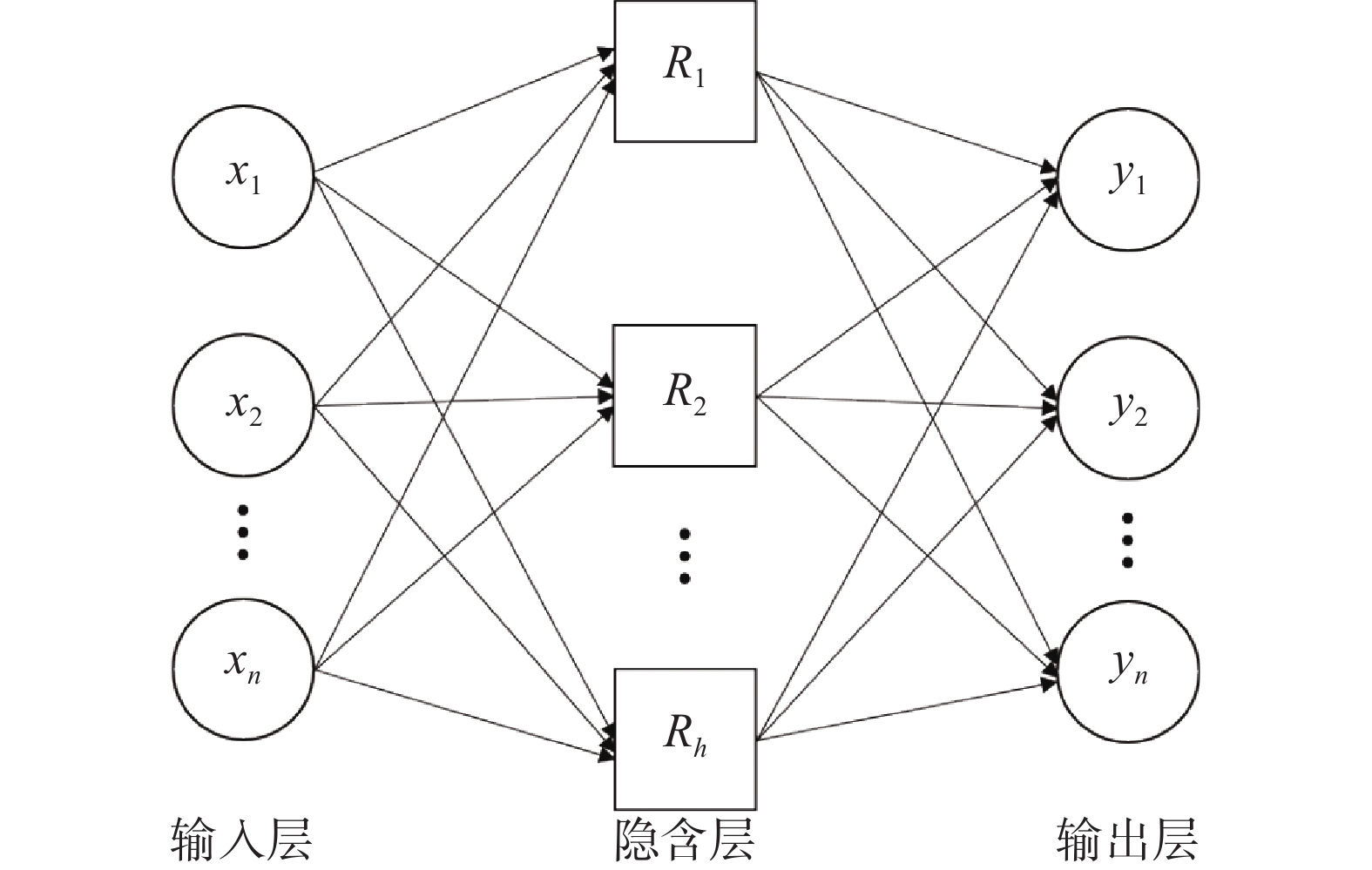
滑坡易发性评价是滑坡灾害管理的基础工作,也是制定各项防灾减灾措施的重要依据。针对传统的信息量模型在评价过程中确定权重值存在准确性不高的缺点,文章提出RBF神经网络和信息量耦合模型。以甘肃省岷县为研究区,筛选坡度等9个指标因子构建了滑坡灾害易发性评价指标体系,应用RBF神经网络-信息量耦合模型(RBFNN-I)进行滑坡灾害易发性评价,利用合理性检验和ROC曲线对模型的评价结果进行精度检验。结果表明:(1)RBFNN-I模型的AUC值为0.853,相比单一的RBFNN和I模型分别提高了6.3%和9.7%,说明RBFNN-I模型具有更好的评价精度;(2)岷县滑坡灾害的极高易发区和高易发区主要分布在临潭—宕昌断裂带、洮河及其支流、闾井河和蒲麻河两侧河谷地带,距断层距离、降雨量、距道路距离和NDVI是影响岷县滑坡灾害分布的主控因子。
Abstract:The landslide susceptibility evaluation is the basic work of landslide management, and it is also an important basis for formulating various disaster prevention and mitigation measures. In view of the low accuracy of the traditional information model in determining the weight value in the evaluation process, this paper proposes a coupling model of RBF neural network and Information value model. 9 index factors such as slope are selected to build the evaluation index system of landslide susceptibility in Min Xian of Gansu Province. The RBF neural network information value coupling model (RBFNN-I) is used to carry out the landslide hazard susceptibility evaluation. Rationality test and ROC curve are used to test the accuracy of the evaluation results of the model. The results show that: (1) the AUC value of RBFNN-I model is 0.853, which is 6.3% and 9.7% higher than that of single RBFNN and I model, respectively, indicating that RBFNN-I model has better evaluation accuracy; (2) the extremely high and high susceptible areas of landslide disasters in Min Xian are mainly distributed along Lintan-Dangchang fault zone, Tao He and its tributaries, and the valleys on both sides of Lyuning River and Puma River.
-
Key words:
- landslide /
- susceptibility assessment /
- RBF neural network /
- information value /
- Min Xian
-

-
表 1 指标因子相关性检验表
Table 1. Correlation of controlling index factors
高程 坡度 坡向 平面曲率 距断层距离 地层 降雨量 距水系距离 NDVI 距道路距离 高程 1 坡度 −0.06 1 坡向 −0.01 0.03 1 平面曲率 0.05 0.05 0.04 1 距断层距离 0.37 −0.20 0.00 0.10 1 地层 −0.32 −0.14 −0.06 0.04 −0.01 1 降雨量 0.75 −0.11 −0.01 0.09 0.19 −0.33 1 距水系距离 0.48 −0.09 0.01 −0.02 0.20 −0.13 0.25 1 NDVI 0.32 −0.08 0.00 0.04 0.35 −0.13 0.38 0.14 1 距道路距离 0.52 −0.14 −0.03 −0.01 0.17 −0.24 0.47 0.26 0.25 1 表 2 指标因子分类等级信息量值计算表
Table 2. The classification information for index factors of landslide
指标因子 分类等级 滑坡面积/km2 滑坡面积比例A/% 分级面积/km2 分级面积比例B/% 频率比(A/B) 信息量值I
坡度/(°)0~5 0.05 2.55 299.99 8.40 0.30 −1.20 5~10 0.10 4.96 546.03 15.28 0.32 −1.14 10~15 0.22 11.06 687.10 19.23 0.58 −0.54 15~20 0.36 18.21 713.50 19.97 0.91 −0.09 20~25 0.48 24.03 617.77 17.29 1.39 0.33 25~30 0.40 20.25 410.29 11.48 1.76 0.57 30~35 0.23 11.83 202.24 5.66 2.09 0.74 35~40 0.08 4.01 72.21 2.02 1.98 0.68 40~45 0.05 2.33 18.55 0.53 4.47 1.50 >45 0.02 0.77 5.13 0.14 5.39 1.68 坡向 平地 0.00 0.00 1.37 0.04 0.00 0.00 北向 0.05 2.69 452.59 12.67 0.21 −1.56 东北 0.09 4.51 510.81 14.30 0.32 −1.14 东向 0.28 13.97 503.66 14.10 0.99 −0.01 东南 0.46 23.03 416.25 11.65 1.98 0.68 南向 0.46 23.17 354.90 9.93 2.33 0.85 西南 0.39 19.89 400.81 11.22 1.77 0.57 西向 0.19 9.46 471.18 13.18 0.72 −0.33 西北 0.06 3.28 461.22 12.91 0.25 −1.39 平面曲率 <−0.8 0.01 0.64 20.21 0.57 1.13 0.12 −0.8~−0.6 0.05 2.28 43.79 1.23 1.86 0.62 −0.6~−0.4 0.13 6.60 142.80 4.00 1.65 0.50 −0.4~−0.2 0.31 15.84 458.93 12.85 1.23 0.21 −0.2~0 0.58 29.18 1144.97 32.05 0.91 −0.09 0~0.2 0.55 27.58 1010.38 28.28 0.98 −0.02 0.2~0.4 0.24 11.93 501.62 14.04 0.85 −0.16 0.4~0.6 0.08 4.05 171.91 4.81 0.84 −0.17 0.6~0.8 0.03 1.32 53.27 1.49 0.89 −0.12 >0.8 0.01 0.59 24.92 0.70 0.85 −0.16 距断层距离/km <1 0.42 21.35 282.66 7.91 2.70 0.99 1~2 0.36 18.02 282.74 7.91 2.28 0.82 2~3 0.23 11.83 253.39 7.09 1.67 0.51 3~4 0.13 6.74 198.62 5.56 1.21 0.19 4~5 0.16 8.33 186.26 5.21 1.60 0.47 5~6 0.19 9.60 176.83 4.95 1.94 0.66 6~7 0.14 6.83 166.75 4.67 1.46 0.38 7~8 0.03 1.55 124.82 3.49 0.44 −0.82 8~9 0.02 1.23 136.00 3.81 0.32 −1.14 9~10 0.02 1.23 95.39 2.67 0.46 −0.78 >10 0.27 13.29 1701.76 46.73 0.29 −1.24 地层 第四系 0.47 23.67 694.20 19.43 1.22 0.20 侏罗系 0.00 0.00 5.79 0.16 0.00 0.00 三叠系 0.53 26.85 1195.33 33.46 0.80 −0.22 二叠系 0.68 34.41 973.57 27.25 1.26 0.23 石炭系 0.01 0.32 31.15 0.87 0.37 −0.99 泥盆系 0.29 14.75 672.76 18.83 0.78 −0.25 降雨量/mm 554~571 0.32 16.02 156.72 4.39 3.65 1.29 571~582 0.66 33.36 445.17 12.46 2.68 0.99 582~590 0.51 25.58 595.83 16.68 1.53 0.43 590~598 0.27 13.65 746.20 20.89 0.65 −0.43 598~606 0.16 8.24 607.02 16.99 0.48 −0.73 606~615 0.04 1.96 438.82 12.28 0.16 −1.83 615~626 0.01 1.19 333.59 9.33 0.13 −2.04 626~639 0.00 0.00 169.48 4.74 0.00 0.00 639~659 0.00 0.00 79.96 2.24 0.00 0.00 距水系距离/km <0.2 0.52 26.08 412.24 11.54 2.26 0.82 0.2~0.4 0.25 12.74 395.79 11.08 1.15 0.14 0.4~0.6 0.19 9.47 378.06 10.58 0.89 −0.12 0.6~0.8 0.18 9.33 355.84 9.96 0.94 −0.06 0.8~1.0 0.19 9.65 328.86 9.20 1.05 0.05 1.0~1.2 0.18 8.88 295.52 8.27 1.07 0.07 1.2~1.4 0.16 8.19 260.91 7.30 1.12 0.11 1.4~1.6 0.12 6.05 225.50 6.31 0.96 −0.04 1.6~1.8 0.03 1.41 188.56 5.28 0.27 −1.31 1.8~2.0 0.07 3.38 153.32 4.30 0.78 −0.25 >2.0 0.10 4.82 578.20 16.18 0.30 −1.20 NDVI −0.75~−0.15 0.00 0.00 5.20 0.15 0.00 0.00 −0.15~0.08 0.00 0.09 3.70 0.10 0.88 −0.13 0.08~0.27 0.26 13.2 99.87 2.80 4.72 1.55 0.27~0.40 0.49 24.85 158.74 4.44 5.59 1.72 0.40~0.50 0.47 23.85 299.27 8.38 2.85 1.05 0.50~0.60 0.39 19.66 419.73 11.75 1.67 0.51 0.60~0.70 0.25 12.74 595.47 16.67 0.76 −0.27 0.70~0.80 0.11 5.43 1030.79 28.84 0.19 −1.66 0.80~1.00 0.00 0.18 960.04 26.87 0.01 −4.61 距道路距离/km <0.2 0.46 23.40 285.40 7.99 2.93 1.08 0.2~0.4 0.20 10.29 268.18 7.51 1.37 0.31 0.4~0.6 0.13 6.6 252.80 7.08 0.93 −0.07 0.6~0.8 0.16 8.28 235.52 6.59 1.26 0.23 0.8~1.0 0.18 9.19 216.71 6.07 1.52 0.42 1.0~1.2 0.12 6.28 202.54 5.67 1.11 0.10 1.2~1.4 0.12 6.19 190.95 5.34 1.16 0.15 1.4~1.6 0.12 6.14 176.72 4.95 1.24 0.22 1.6~1.8 0.09 4.60 161.19 4.51 1.02 0.02 1.8~2.0 0.11 5.51 146.41 4.09 1.34 0.29 >2.0 0.27 13.52 1436.39 40.20 0.34 −1.08 表 3 岷县滑坡灾害易发性分区合理性检验表
Table 3. Rationality test table of landslide susceptibility zone in Min Xian
模型类型 易发区等级 P/个 Cp /% S/km2 Sp/% R RBFNN-I 极高易发区 308 56.10 373.70 10.41 5.39 高易发区 175 31.88 717.96 20.00 1.59 中易发区 51 9.29 975.40 27.17 0.34 低易发区 15 2.73 1522.80 42.42 0.06 注:P代表各等级易发区内滑坡点的数量;Cp代表各等级易发区内的滑坡点数量的比例;S代表各等级易发区的面积;
Sp代表各等级易发区面积占整个研究区总面积的比例;R代表Cp和Sp的比值。 -
[1] 赵忠国, 张峰, 郑江华. 多元自适应回归样条法的滑坡敏感性评价[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2021,46(3):442 − 450. [ZHAO Zhongguo, ZHANG Feng, ZHENG Jianghua. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility by multiple adaptive regression spline method[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2021,46(3):442 − 450. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] SEVGEN, KOCAMAN, NEFESLIOGLU, et al. A novel performance assessment approach using photogrammetric techniques for landslide susceptibility mapping with logistic regression, ANN and random forest[J]. Sensors,2019,19(18):3940. doi: 10.3390/s19183940
[3] 连志鹏, 徐勇, 付圣, 等. 采用多模型融合方法评价滑坡灾害易发性: 以湖北省五峰县为例[J]. 地质科技通报,2020,39(3):178 − 186. [LIAN Zhipeng, XU Yong, FU Sheng, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on multi-model fusion method: A case study in Wufeng County, Hubei Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2020,39(3):178 − 186. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 李文彦, 王喜乐. 频率比与信息量模型在黄土沟壑区滑坡易发性评价中的应用与比较[J]. 自然灾害学报,2020,29(4):213 − 220. [LI Wenyan, WANG Xile. Application and comparison of frequency ratio and information value model for evaluating landslide susceptibility of loess gully region[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2020,29(4):213 − 220. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 王雷, 吴君平, 赵冰雪, 等. 基于GIS和信息量模型的安徽池州地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(3):96 − 103. [WANG Lei, WU Junping, ZHAO Bingxue, et al. Susceptibility assessment of geohazards in Chizhou City of Anhui Province based on GIS and informative model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(3):96 − 103. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 张玘恺, 凌斯祥, 李晓宁, 等. 九寨沟县滑坡灾害易发性快速评估模型对比研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(8):1595 − 1610. [ZHANG Qikai, LING Sixiang, LI Xiaoning, et al. Comparison of landslide susceptibility mapping rapid assessment models in Jiuzhaigou County, Sichuan Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(8):1595 − 1610. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 夏辉, 殷坤龙, 梁鑫, 等. 基于SVM-ANN模型的滑坡易发性评价: 以三峡库区巫山县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(5):13 − 19. [XIA Hui, YIN Kunlong, LIANG Xin, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on SVM-ANN Models: A case stualy for Wushan County in the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(5):13 − 19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] SAHA S, SAHA A, HEMBRAM T K, et al. Evaluating the performance of individual and novel ensemble of machine learning and statistical models for landslide susceptibility assessment at rudraprayag district of Garhwal Himalaya[J]. Applied Sciences,2020,10(11):3772. doi: 10.3390/app10113772
[9] 陈飞, 蔡超, 李小双, 等. 基于信息量与神经网络模型的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(增刊1): 2859 − 2870
CHEN Fei, CAI Chao, LI Xiaoshuang, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on information volume and neural network model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(Sup 1): 2859 − 2870. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 闫举生, 谭建民. 基于不同因子分级法的滑坡易发性评价: 以湖北远安县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(1):52 − 60. [YAN Jusheng, TAN Jianmin. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on different factor classification methods:A case study in Yuan'an County of Hubei Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(1):52 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] LUO X G, LIN F K, CHEN Y H, et al. Coupling logistic model tree and random subspace to predict the landslide susceptibility areas with considering the uncertainty of environmental features[J]. Scientific Reports,2019,9:15369. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51941-z
[12] CHEN W, SHIRZADI A, SHAHABI H, et al. A novel hybrid artificial intelligence approach based on the rotation forest ensemble and naïve Bayes tree classifiers for a landslide susceptibility assessment in Langao County, China[J]. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk,2017,8(2):1955 − 1977. doi: 10.1080/19475705.2017.1401560
[13] 何永波, 李青, 张宁, 等. RBF神经网络可靠度分析方法在边坡稳定性研究中的应用[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术,2019,15(7):130 − 136. [HE Yongbo, LI Qing, ZHANG Ning, et al. Application of RBF neural network reliability analysis method in slope stability research[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology,2019,15(7):130 − 136. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 薛萍, 郝鹏, 王宏民. 基于径向基神经网络的新型齿轮故障诊断方法研究[J/OL]. 控制与决策. https://doi.org/10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.0836.
XUE Ping, HAO Peng, WANG Hongmin. Research on a novel gear fault diagnosis method based on RBF neural network [J/OL]. Control and Decision. https://doi.org/10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.0836. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 刘希林, 庙成, 田春山. 区域滑坡和泥石流灾害两种危险性评价方法的比较分析[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2017,37(1):71 − 78. [LIU Xilin, MIAO Cheng, TIAN Chunshan. Comparative analysis of two methods for assessing hazard of landslide and debris-flow on a regional scale[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering,2017,37(1):71 − 78. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 许冲, 徐锡伟, 郑文俊. 2013年7月22日岷县漳县MS6.6级地震滑坡编录与空间分布规律分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2013,21(5):736 − 749. [XU Chong, XU Xiwei, ZHENG Wenjun. Compiling inventory of landslides triggered by Minxian-Zhangxian earthquake of July 22, 2013 and their spatial distribution analysis[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2013,21(5):736 − 749. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2013.05.010
[17] 田颖颖. 2013年甘肃省岷县地震滑坡空间分布规律及几何特征分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016.
TIAN Yingying. Spatial distribution and geometrical characteristic of landslides related to the 2013 Minxian earthquake of Gansu Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 海兰, BOBROWSKY P, 等. 滑坡灾害防治手册-认识滑坡: 防治滑坡[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009: 3 − 5.
HIGHLAND L H, BOBROWSKY P, et al. Handbook of landslide disaster prevention: Understanding landslide prevention and landslide [M]. Beijing: Geological Press, 2009: 3 − 5. (in Chinese)
[19] 杨先全, 周苏华, 邢静康, 等. 肯尼亚滑坡灾害分布特征及敏感性区划[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(5):65 − 74. [YANG Xianquan, ZHOU Suhua, XING Jingkang, et al. Distribution patterns and susceptibility mapping of landslides in Kenya[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(5):65 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 解明礼, 巨能攀, 赵建军, 等. 区域地质灾害易发性分级方法对比分析研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2021,46(7):1003 − 1014. [XIE Mingli, JU Nengpan, ZHAO Jianjun. et al. Comparative analysis on classification methods of geological disaster susceptibility assessment[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2021,46(7):1003 − 1014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 孙长明, 马润勇, 尚合欣, 等. 基于滑坡分类的西宁市滑坡易发性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):173 − 181. [SUN Changming, MA Runyong, SHANG Hexin, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment in Xining based on landslide classification[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):173 − 181. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 张勇, 温智, 程英建. 四川巴中市滑坡灾害与降雨雨型关系探讨[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(2):178 − 182. [ZHANG Yong, WEN Zhi, CHENG Yingjian. A discussion of the relationship between landslide disaster and rainfall types in Bazhong of Sichuan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(2):178 − 182. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 郑迎凯, 陈建国, 王成彬, 等. 确定性系数与随机森林模型在云南芒市滑坡易发性评价中的应用[J]. 地质科技通报,2020,39(6):131 − 144. [ZHENG Yingkai, CHEN Jianguo, WANG Chengbin, et al. Application of certainty factor and random forests model in landslide susceptibility evaluation in Mangshi City, Yunnan Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2020,39(6):131 − 144. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 王念秦, 郭有金, 刘铁铭, 等. 基于支持向量机模型的滑坡危险性评价[J]. 科学技术与工程,2019,19(35):70 − 78. [WANG Nianqin, GUO Youjin, LIU Tieming, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on support vector machine model[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2019,19(35):70 − 78. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 地质灾害调查技术要求(1: 50000): DD2019-08[S]. 北京: 中国地质调查局, 2019.
Technical requirement for geo-hazard survey(1: 50000): DD2019-08[S]. Beijing:China Geological Survey, 2019. (in Chinese)
[26] DAI F C, LEE C F, LI J, et al. Assessment of landslide susceptibility on the natural terrain of Lantau Island, Hong Kong[J]. Environmental Geology,2001,40(3):381 − 391. doi: 10.1007/s002540000163
-



 下载:
下载: