Influence of hydraulic-mechanical coupling and dry-wet cycle effect on surficial layer stability of residual soil slopes
-
摘要:
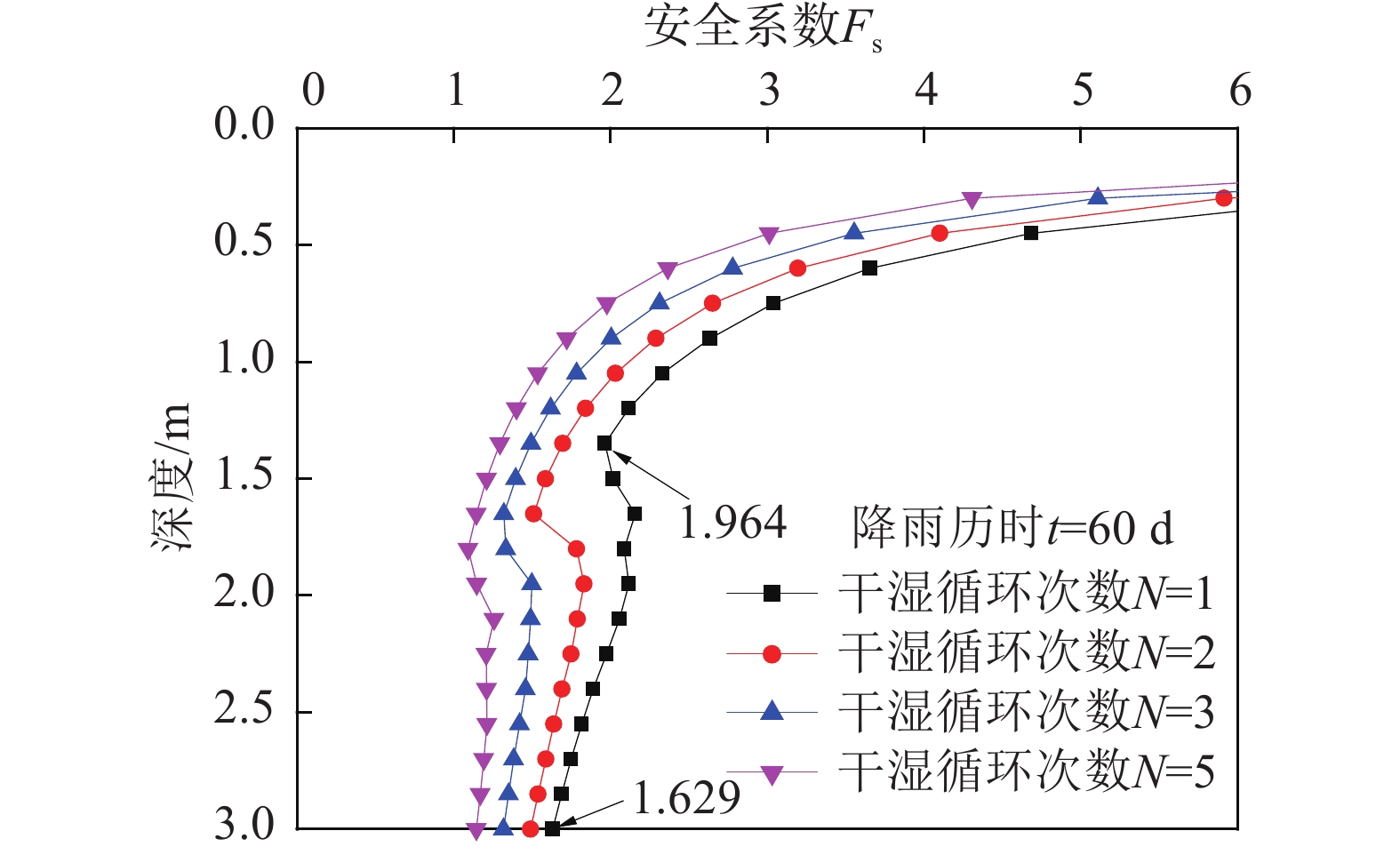
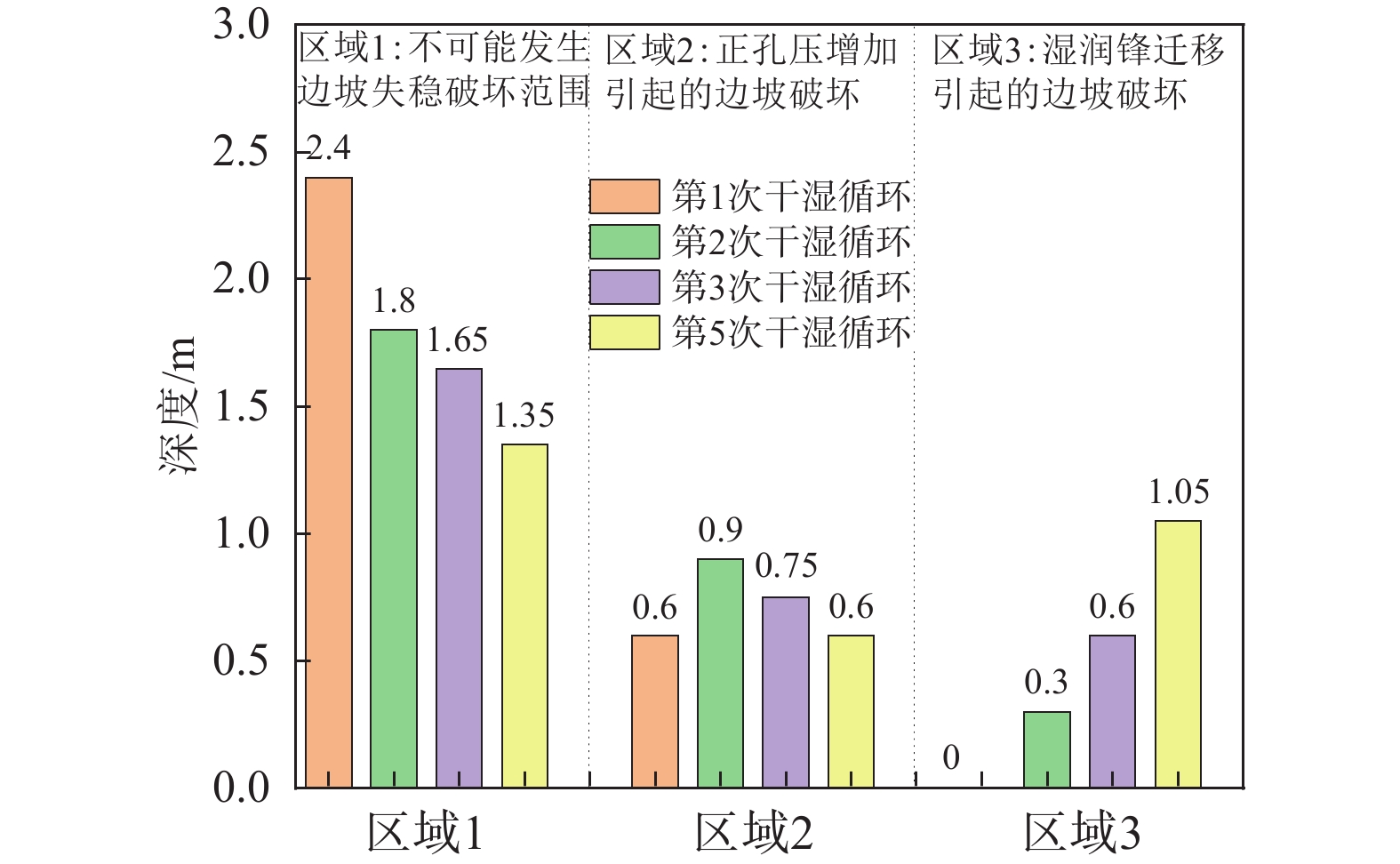
降雨入渗过程中,土体吸力降低,体积明显改变。天然浅层土体长期受到季节性气候变化的影响,因此,开展水-力耦合及干湿交替对浅层残积土坡稳定性影响的数值分析,分析浅层土坡孔隙水压力、湿润锋及安全系数的时空演变规律,并对水-力耦合及干湿交替条件下的浅层土坡失稳破坏机制进行探讨显得尤为必要。研究结果表明:随着干湿循环次数的增加,水-力耦合分析下孔隙水压力以及湿润锋的迁移速度增加更快,边坡也更易失稳破坏;干湿交替初期,雨水入渗易引起地下水位上升,边坡可因正孔隙水压力的增加而失稳;干湿交替后期,湿润锋的快速推进加剧基质吸力迅速丧失及土体强度下降,边坡安全系数显著降低,发生失稳破坏的时间缩短。因此,可将湿润锋处的安全系数(局部最小值)作为控制边坡长期稳定性的临界值。
Abstract:During rainfall infiltration, soil suction decreased and volume changed significantly. Since the natural shallow soil was under the influence of seasonal climate changes for a long time, numerical analysis of the influence of hydraulic-mechanical coupling and dry-wet alternation on the stability of shallow residual soil slopes was carried out. The temporal and spatial evolution law of pore water pressure, wetting front and safety factor of shallow soil slopes were analyzed deeply, then, the failure mechanisms of soil slopes under hydraulic-mechanical coupling and alternating dry-wet conditions were further discussed. Results show that with the increase of dry-wet cycles, the migration velocity of wetting front and pore water pressure increased more quickly, and the slope was more unstable under hydro-mechanical coupling analysis. At the early stage of the dry-wet cycle, the infiltration of rainwater would easily cause the groundwater level to rise, and the slope might lose its stability due to the increase of positive pore water pressure. In the later stage of dry-wet cycle, the rapid advance of wetting front accelerated the rapid loss of matrix suction and the decrease of soil strength, the safety factor of slope was significantly reduced and the time of failure was shorter. Therefore, the safety factor (local minimum) at the wetting front could be used as the critical value to control the long-term stability of the slope.
-
Key words:
- hydro-mechanical coupling /
- dry-wet cycle /
- residual soil slope /
- wetting front /
- safety factor /
- long-term stability
-
随着社会经济的发展和人口的增长,我国城市建设用地的短缺和交通拥堵严重制约了许多新兴城市的可持续发展[1]。在土地资源有限的情况下,城市地下空间的开发利用已成为城市发展的必然选择[2-3]。深圳市是粤港澳大湾区的核心城市之一,也是我国最早的经济特区[4]。改革开放以来,深圳市在产业经济、城市建设和人居环境等方面都取得了巨大的成就。随着城市建设的迅速发展和人口的急剧增长,深圳市土地资源逐渐紧缺,合理开发城市地下空间资源,对提升城市综合承载能力有重要作用[5]。
城市地下空间的开发与周围地质环境密切相关。因此,科学的地质适宜性评价是规划和利用城市地下空间的必要前提[6,7]。前人研究显示[8],地质适宜性评价可通过地质适宜性分区和多个地质指标权重的叠加计算实现。其中,通常利用层次分析法(AHP)、熵权法和梯形模糊数定权法确定评价体系及指标权重[9-11]。地质适宜性评价模型主要包括经验分值法、模糊综合评价法、优劣解距离法(TOPSIS)和神经网络法等[12-14]。
科学合理的评价体系是地质适宜性评价的重要条件。在地质适宜性评价过程中,通常会根据研究区实际情况选取相应的评价体系与指标[15-16]。除地形地貌、地质构造、水文地质、工程地质等常规地质因素,部分约束性地质因素仍在很大程度上制约着城市地下空间的开发利用,且表现出明显的地区差异性。例如北京、郑州地区主要敏感地质因素为地面沉降和断裂带[7,17];武汉地区主要为砂土液化和河流冲蚀[11];昆明地区主要为岩溶和地面塌陷[18];咸阳地区主要为黄土湿陷、地裂缝等[19]。然而,以往研究通常将各个约束性地质因素作为一级评价指标不良地质作用下的二级指标[11,20],一定程度上削弱了各个约束性地质因素对评价结果的制约,使得最终的地质适宜性评价结果不符合实际地质条件的限制。
深圳市地下空间资源开发涉及的约束性地质因素包括地表水体、断裂带、地质灾害易发性等[21]。地质适宜性评价中,着重考虑约束性地质条件可使评价结果更加符合当地实际情况[22]。深圳市现有地下空间资源利用规划侧重考虑已有设施等社会经济因素,仍需深入开展地质适宜性评价以指导地下空间的开发利用。为此,本文以深圳市南山区为研究区,结合研究区地质条件,选取恰当的评价指标,将地表水体、断裂带、砂土液化和地质灾害易发性等约束条件作为一级评价指标,建立约束评价体系;采用经验分值法和模糊综合评价法,评价常规体系和约束体系的地下空间地质适宜性;对比分析评价结果,阐明研究区不同区域地下空间开发的地质适宜性,厘清规划中重点开发区地下空间开发时应该注意的地质环境问题,为深圳市南山区地下空间资源开发利用规划提供有力支撑。
1. 研究区概况
1.1 地理位置
研究区为深圳市南山区的主要陆域范围,位于广东省深圳市西南部,陆地面积187.5 km2。地处亚热带,年平均气温22.3 ℃,年平均相对湿度79%,年平均降水量1924.7 mm。此外,南山区是深圳的科研、教育、体育中心。截至2020年11月,南山区常住人口约180万,人口密度约9700人/ km2。
1.2 地质条件
研究区位于深圳市西南部,北部高、南部低。地貌类型主要有丘陵、残丘、台地、平原和人工地貌(图1)。丘陵面积约34.57 km2,坡度40°~70°。研究区残丘零散分布,面积较小,约6.33 km2,坡度10°~30°。台地是一种由平原向丘陵和低山过渡的地形,主要分布在研究区中北部平原和丘陵之间,海拔10~50 m,总面积39.33 km2,该区地形相对平坦,坡度0°~10°。平原分布较为广泛,总面积约44.54 km2。该地区地貌为以河流冲积、海相冲积和江海相互作用沉积为主的三角洲地貌,坡度0°~5°。人工地貌以人工挖填区和填海区为主,分布在研究区南部沿海地区,总面积35.89 km2。
研究区地下水按储存条件可分为松散岩孔隙水和基岩裂隙水。第四系松散岩孔隙水主要分布在中南部平原和人工地貌区,单井涌水量10.7~452.74 m³/d,整体水质较差,地下水化学类型为HCO3·Cl—Na型。白垩、奥陶系基岩裂隙水为层状基岩裂隙水和块状基岩裂隙水,主要分布在丘陵、台地地区,水质一般较好。该区地下水类型为Cl·HCO3—Na·Ca型和Cl·HCO3—Na·Ca型。
南山区工程地质条件主要分为 2 个大区,分别为丘陵、台地隆起岩土工程地质区和丘陵、台地平原沉降岩土工程地质区。其中,丘陵、台地隆起岩土工程地质区又分为侵入岩岩土亚区和变质岩岩土亚区。侵入岩岩土亚区在南山区分布较广,为浅肉红色中细粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩、灰白色片麻状细粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩。变质岩岩土亚区主要为变粒岩、混合花岗岩。丘陵、台地平原沉降岩土工程地质区又分为丘间谷地冲洪积土亚区和平原海-河冲积土亚区。其中,丘间谷地冲洪积土亚区多为单一结构黏性土。平原海-河冲积土亚区包括软土地段、液化砂土地段和一般沉积土地段。
此外,研究区还存在若干不利于地下空间开发利用的约束性地质因素。例如,该地区潜在的地质灾害广泛分布,现有地质灾害点和地质灾害隐患点共60处,包括崩塌、滑坡、不稳定斜坡等;断裂带有21个,主要分布在山区和丘陵地区,大部分为活动断裂,宽度以2~10 m为主;砂土液化区面积约为27.19 km2,主要分布在南部平原第四系地区。
2. 评价方法
2.1 评价体系
深圳市地下空间资源利用规划提出深层地下空间是资源能源储备与运输、大型物流通道和安全设施等功能空间的预留空间,需要谨慎利用[21]。因此,本次研究只针对浅层地层(0~15 m)和次浅层地层(>15~30 m)地下空间开展地质适宜性评价。基于研究区地质概况与深圳市地下空间资源利用规划,科学合理的确定评价指标,然后将选取的评价指标因子按照不同属性加权,建立评价体系。本研究分别建立常规评价体系和约束评价体系。
2.1.1 常规体系
结合研究区地质条件,浅层地质适宜性评价是以城市地下空间浅层地质适宜性评价为目标层;以地形地貌、水文地质、工程地质和敏感地质因素为准则层;以地貌类型、地形坡度、水位埋深、地表水体、腐蚀性、水质、工程分区、第四系厚度、软土厚度、土体结构、断裂带、砂土液化、地质灾害易发性为指标层,建立层次评价体系。
次浅层地质适宜性评价是以城市地下空间次浅层地质适宜性评价为目标层;以水文地质、工程地质和敏感地质因素为准则层;以地表水体、腐蚀性、水质、工程分区、第四系厚度、断裂带、砂土液化、地质灾害易发性为指标层,建立层次评价体系。
2.1.2 约束体系
深圳市地下空间资源利用规划中的禁止开采区涉及的主要地质因素为地表水体、断裂带、砂土液化和地质灾害易发性。其中地表水体主要考虑水库等水源地区域。断裂带考虑距断裂带水平距离300 m 以内,大于300 m无影响。砂土液化根据液化程度划分为重度、中度、轻度和无液化区。地质灾害易发性根据易发程度分为高发区、中发区、低发区和不发区。本研究将以上4个指标作为约束条件划分到准则层,构建约束评价体系(表1、表2)。
表 1. 研究区浅层地质适宜性的约束评价体系Table 1. Constraint system of shallow geological suitability evaluation in the study area目标层 准则层 指标层 城市地下空间
浅层地质适宜性
评价地形地貌 地貌类型 地形坡度 水文地质 水位埋深 腐蚀性 水质 工程地质 工程分区 第四系厚度 软土厚度 土质结构 地表水体 地表水体 断裂带 断裂带 砂土液化 砂土液化 地质灾害易发性 地质灾害易发性 表 2. 研究区次浅层地质适宜性评价的约束体系Table 2. Constraint system of sub-shallow geological suitability evaluation in the study area目标层 准则层 指标层 城市地下空间
次浅层地质适宜性
评价水文地质 腐蚀性 水质 工程地质 工程分区 第四系厚度 地表水体 地表水体 断裂带 断裂带 砂土液化 砂土液化 地质灾害易发性 地质灾害易发性 2.1.3 指标权重的确定
各个层次的评价因子对目标层的影响程度不同,表现为权重不同。对于评价因子权重的确定,需要依据同一层次中所有评价因子对上一层因素的重要程度两两进行比较,按照数字1~9标度进行衡量,构造判断矩阵[20]。采用经验分值法确定比较标度,经过不断调整,最终分层次确定判断矩阵。确定判断矩阵后,计算出矩阵最大特征值对应的特征向量,将特征向量归一化处理后作为相应的权重值[20]。
通过构建判断矩阵,得到了研究区常规体系和约束体系下不同层次指标的权重值(表3、表4)。结果显示,常规体系中浅层的地表水体、断裂带、砂土液化和地质灾害易发性的权重排名分别为4、1、7和3,而约束体系中其排名分别为1、3、4和2。相对于常规体系,约束体系中砂土液化和地质灾害易发性的权重均有所提升,使得地表水体、断裂带、砂土液化和地质灾害易发性成为权重最大的4个指标。权重计算结果显示,约束评价体系一定程度上提高了常规评价体系中地表水体、断裂带、砂土液化和地质灾害易发性4个指标的权重,增强了其对地下空间开发利用影响的程度。
表 3. 常规体系下浅层指标权重Table 3. Index weights of the conventional evaluation system for shallow layers准则层因素 准则层权重 指标层因素 指标层权重 总权重 权重排序 地形地貌 0.1070 地貌类型 0.3333 0.0357 10 地形坡度 0.6667 0.0713 6 水文地质 0.1849 水位埋深 0.2968 0.0549 8 地表水体 0.4852 0.0897 4 腐蚀性 0.1090 0.0202 12 水质 0.1090 0.0202 13 工程地质 0.2926 工程分区 0.1564 0.0458 9 第四系厚度 0.2938 0.0860 5 软土厚度 0.4621 0.1352 2 土体结构 0.0877 0.0257 11 敏感地质因素 0.4155 断裂带 0.6301 0.2618 1 砂土液化 0.1515 0.0629 7 地质灾害易发性 0.2184 0.0907 3 注:总权重=准则层权重×指标层权重。 表 4. 约束体系下浅层指标权重Table 4. Index weights of the constraint system for shallow layers准则层因素 准则层权重 指标层因素 指标层权重 总权重 权重排序 地形地貌 0.0381 地貌类型 0.3333 0.0127 12 地形坡度 0.6667 0.0254 8 水文地质 0.0676 水位埋深 0.6000 0.0406 6 腐蚀性 0.2000 0.0135 10 水质 0.2000 0.0135 11 工程地质 0.0942 工程分区 0.1564 0.0147 9 第四系厚度 0.2938 0.0277 7 软土厚度 0.4621 0.0435 5 土质结构 0.0877 0.0083 13 地表水体 0.2268 地表水体 1 0.2268 1 断裂带 0.2136 断裂带 1 0.2136 3 砂土液化 0.1329 砂土液化 1 0.1329 4 地质灾害易发性 0.2268 地质灾害易发性 1 0.2268 2 2.2 赋值方法
2.2.1 经验分值法
基于相关地质条件,每个评价指标划分成若干区域。根据各个指标不同分区对地下空间开发的影响程度,利用经验分值法对评价指标的不同分区进行评分,评分范围为1~10分(表5)。分数越高,表明该区域越不利于地下空间的开发利用;反之,该区域越适宜地下空间的开发利用。
表 5. 各个指标不同分区的评分Table 5. Scores of each index in different zones一级指标 二级
指标评 分 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 地形地貌 地貌类型 填海 人工挖填 丘陵 残丘 台地 平原 地形坡度 >80° >70°~80° >60°~70° >50°~60° >40°~50° >30°~40° >20°~30° >10°~20° 5°~10° <5° 水文地质 水位埋深 <2 m 2~<3 m 3~<4 m 4~<5 m 5~<6 m 6~<7 m 7~<8 m 8~<9 m 9~11 m 地表水体 有 无 腐蚀性 强腐蚀性 中腐蚀性 弱腐蚀性 无腐蚀性 水质 较差 较好 良好 工程地质 工程分区 人工填土地段 丘间谷地 侵入岩岩土亚区 一般沉积地段 变质岩岩土亚区 第四系厚度 >15 m >10~15 m 5~10 m <5 m 软土厚度 >16 m >14~16 m >12~14 m >10~12 m >8~10 m >6~8 m >4~6 m >2~4 m 0~2 m 土体结构 多层 单层 敏感地质
因素断裂带 ≤300 m >300m 砂土液化 严重 中等 轻微 其他 地质灾害
易发性高发 中发 低发 不发 根据评分规则对所有指标的不同区域进行了赋分。然后将各个指标图层剖分成250 m×250 m的栅格图,利用栅格叠加功能将各个指标图层按照权重进行叠加计算,每个栅格将会得到一个最终得分。最后,将各个栅格分数值进行聚类分析,重新划分为4类,根据分值从小到大,将4类区域的地下空间开发地质适宜性依次评定为适宜、较适宜、适宜性差和不适宜。
2.2.2 模糊综合评价法
模糊综合评价是根据模糊数学的隶属度原理论,把定性评价转化为定量评价的一种方法,是用模糊数学对受到多种因素制约的对象做出总结评价[15]。城市地下空间地质适宜性评价中,通常采用梯形隶属函数确定各个区域在不同等级的隶属度,再根据最大隶属度原则综合评价各区域的地质适宜性等级。上述评价指标有定量指标和定性指标2种。其中,地形坡度、水位埋深、第四系厚度和软土厚度为定量指标,其梯形隶属函数如式(1)所示,按照赋值标准给出评定值,并采用梯形隶属函数计算隶属度。
u(x)={0x⩽a1x−a1a2−a1a1<x⩽a21a2<x⩽a3a4−xa4−a3a3<x⩽a40x>a4 (1) 式中:a1、a2、a3、a4——不同指标隶属度分区临界值;
x——各网格的分值;
u——隶属度。
其他指标为定性指标,需要按照分级法进行量化处理。按照以下标准将指标不同区域分为4个等级并附分值:适宜Ⅰ(0.2分)、较适宜Ⅱ(0.4分)、适宜性差Ⅲ(0.7分)和不适宜Ⅳ(0.9分)。并采用梯形隶属函数计算隶属度,具体见式(2)—(5)。
按照250 m×250 m的网格精度,本次将研究区剖分为2899个网格。将每个网格对应的所有二级指标量化值代入对应的隶属函数,均得到相应的隶属度评价矩阵。其中,浅层13个指标得到的隶属度评价矩阵为B13×4,权向量矩阵为A1×13;次浅层8个指标得到的隶属度评价矩阵为B8×4,权向量矩阵为A1×8,则综合评价结果为C1×4=AB。根据最大隶属度原则,在C1×4矩阵中取最大值对应的评价等级i为相应网格的适宜性等级,即Ci=max(CI, CII,CIII, CIV)。
uⅠ(x)={1x⩽0.23−10x0.2<x⩽0.30x>0.3 (2) uⅡ(x)={0x⩽0.210x−20.2<x⩽0.310.3<x⩽0.56−10x0.5<x⩽0.60x>0.6 (3) uⅢ(x)={0x≤0.510x−50.5<x⩽0.610.6<x⩽0.89−10x0.8<x⩽0.90x>0.9 (4) uⅣ(x)={0x⩽0.810x−80.8<x⩽0.91x>0.9 (5) 式中:uⅠ——隶属于适宜区的程度;
uⅡ——隶属于较适宜区的程度;
uⅢ——隶属于适宜性差区的程度;
uⅣ——隶属于不适宜区的程度。
3. 评价结果
3.1 经验分值法评价结果
常规评价体系的经验分值法评价结果见图2(a)(b),研究区以适宜区和较适宜区为主。其中,浅层适宜区域主要为研究区北部麻凹南、大密山、石光山、桃源街道以及中部的直升机场—南山街道,面积约为78.31 km2,约占研究区总面积的46%。较适宜区域主要为研究区中南部沙河桥至招商街道、西站天桥和兴海街道,面积约为35.00 km2,约占总面积的21%。研究区适宜性差和不适宜区域主要受砂土液化和断裂带影响。其中,适宜性差的区域主要分布在直升机场北部、西站天桥西南和沙河街道,面积约为39.13 km2,约占总面积的23%。不适宜区域面积较小,主要位于桃园路口、蛇口街道和南山至狮山区域,面积约为16.31 km2,约占总面积的10%。
次浅层地质适宜性评价结果同样以适宜区和较适宜区为主。其中,适宜区域主要分布在研究区北部台地、丘陵地区,包括麻凹南、石光山、麒麟山、下围岭和中山桥区域,面积为77.81 km2,约占研究区总面积的46%。较适宜区域主要分布在研究区北部的西丽水库、桃源街道和南部的科技园、西站桥和兴海街区域,面积约为25.06 km2,约占总面积的15%。研究区适宜性差和不适宜区域同样主要受砂土液化和断裂带影响。其中,适宜性差的区域主要分布在沙河街道、沙河南至招商街道和西站桥西南区域,面积约为42.38 km2,约占总面积的25%。不适宜地区主要分布在桃园路口、蛇口街道和南山至狮山区域,面积约为23.50 km2,约占总面积的14%。
而约束评价体系的经验分值法得到的浅层和次浅层地质适宜性评价结果相似,见图2(c)(d)。其中,适宜区域主要为研究区北部麒麟山、桃源街道、西丽中学和中部的中山桥和深圳大学区域,面积约占研究区总面积的36%。较适宜区域主要为西站天桥至兴海街、沙河街道至粤海街道以及麻凹南至石光山区域,约占总面积的32%。适宜性差和不适宜的区域主要分布在西丽水库、长岭皮水库、留仙小学南部、桃园路口和南山至狮山区域,面积分别占总面积的20%和12%,该区主要有水库、断裂带分布,且为地质灾害高发区。
3.2 模糊综合法评价结果
常规评价体系的浅层模糊综合评价结果见图3(a),可知研究区地质适宜性以适宜和较适宜为主。其中地下空间开发适宜区域面积约为71.81 km2,占研究区总面积的43%,主要分布在桃源街道、西丽中学、南头街道、沙河街道和粤海街道区域;较适宜区域面积为73.94 km2,占总面积的44%,分布在大密山、西丽水库、下围岭和西站天桥至兴海街区域,并在研究区中部有零星分布。适宜性差和不适宜区域面积约为23.00 km2,占总面积的13%,主要分布在桃源路口、南山、狮山和蛇口街道的断裂带分布区。
如图3(b)所示,次浅层地下空间开发适宜区域面积较小,约为30.63 km2,占研究区总面积的18%,主要分布在大密山西部、桃源街道、西丽中学和沙河街道,呈带状分布。较适宜区域面积较大,约为99.81 km2,占总面积的59%,主要分布在麻凹南、西丽水库、下围岭、中山桥至兴海街和科技园区域。适宜性差和不适宜区域主要分布在粤海街道东部砂土液化区域、桃园路口和南山至狮山的断裂带分布区,面积约为38.31 km2,占总面积的23%。
如图3(c)(d)所示,约束体系下的模糊综合评价结果中,浅层和次浅层地下空间开发适宜性较为一致。其中适宜性差和不适宜区域面积约为21.50 km2,占总面积的13%,主要分布在桃园路口、南山、狮山和蛇口街道,为断裂带和地质灾害高发区域。较适宜区域面积约为32.31 km2,占总面积的19%,主要分布在大密山、西丽水库和下围岭。其他区域均为适宜区,分布面积较大,约为114.94 km2,占研究区总面积的68%。
4. 讨论
4.1 约束评价体系的构建
地下空间地质适宜性评价通常是自然因素对地下空间开发的影响,进一步考虑社会经济因素的影响[23],即可得到地下空间综合质量评价结果[24],指导城市地下空间资源开发利用。前人研究表明,针对不同研究区,选取合适的评价指标和体系是地质适宜性评价的关键[15,25]。结合研究区地质特点,本次将地表水体、断裂带、砂土液化和地质灾害易发性作为一级评价指标,得到约束评价体系。约束体系中砂土液化和地质灾害易发性的权重相对于常规体系均有所提升,该体系下地表水体、断裂带、砂土液化和地质灾害易发性为权重最大的四个指标,增强了约束性地质因素对地下空间开发利用的制约性。
4.2 地质适宜性评价结果对比
本次研究结合常规评价体系和约束评价体系,利用经验分值法和模糊综合法分别评价了研究区浅层和次浅层地下空间开发的地质适宜性,如图4所示。其中,经验分值法常规体系和约束体系评价结果有所不同。常规评价体系适宜性差和不适宜区域受地表水体影响较弱,在禁止开发的西丽水库和长岭皮水库区域评价结果为适宜和较适宜区,该结果不符合地下空间开发的地质条件要求。而约束体系下评价结果中适宜性差和不适宜区域主要分布在断裂带、地质灾害高发区以及水库分布区,例如西丽水库,长岭皮水库和南山。各个程度的地质适宜性较为符合地表水体等约束性地质因素对地下空间开发的制约性。因此,约束体系下经验分值法的评价结果更加符合实际地质条件,更能有效指导研究区地下空间开发利用规划。
此外,模糊综合法地质适宜性评价结果中,常规体系和约束体系下均以适宜和较适宜区为主,占研究区总面的70%以上。但各类区域在空间分布上也具有一定差异。其中,常规体系浅层评价结果显示,适宜区和较适宜区域分布凌乱,适宜性差和不适宜区主要受断裂带的影响。常规体系次浅层适宜性差和不适宜区域面积有所增加,主要分布在断裂带和砂土液化区域。而在考虑约束条件时,适宜区和较适宜区分布较为集中。研究区以适宜区为主,较适宜区主要分布在西丽水库、长岭皮水库和下围岭区域。适宜性差和不适宜区主要分布在桃园路口、南山和蛇口街道的断裂带分布区。总体上讲,模糊综合评价法 2 个体系的适宜性差和不适宜区均受约束条件影响,而约束体系评价结果能够更集中的圈定不同评价级别的范围,相比常规体系评价结果更具有指导意义。综上所述,约束评价体系较常规评价体系更加适用于研究区地质适宜性评价,可为深圳市地质适宜性规划提供有力支撑。
4.3 地下空间开发利用建议
城市地质适宜性评价阐明了地下空间开发利用过程中地质环境因素的影响,能够合理指导城市地下空间资源的开发利用[26]。结合约束体系评价结果,本次研究阐明了深圳市地下空间资源利用规划中的地下空间重点开发区的地质环境问题。
经验分值法评价结果显示规划中的重点开发区主要位于适宜区和较适宜区,部分重点开发区包含适宜性差和不适宜区,见图4(a)(b)。位于西站天桥、南山街道和科技园南部的重点开发区包含较适宜区,该区域需注意砂土液化引起的地层失稳、地面塌陷等地质问题。星海街道、蛇口街道、白石洲和西丽中学附近的重点开发区的部分区域为适宜性差和不适宜区,地下空间开发时应该注意活动断裂带区域岩体破碎和地下水富集等不利于施工的因素。此外,重点开发区的水位埋深均小于5 m,需建造必要的防水工程。位于西站桥和粤海街道以南的重点开发区还需注意防护地下水的强腐蚀作用。
模糊综合评价结果显示规划中的重点开发区域均位于适宜开发区,见图4(c)(d),仅有兴海街道西部和蛇口街道的重点开发区包含部分不适宜区,该区域需注意活动断裂带区域岩体破碎和地下水富集等不利于施工的因素。但是进一步结合模糊综合评价在大密山、长岭皮水库和西丽水库等禁止开发区的评价结果为较适宜区,模糊综合评价结果趋于乐观,在地下空间开发过程中还需根据实际地质条件采取相应防护措施。另外,地质适宜性评价显示,除了规划中的禁止开发区,桃源路口、蛇口街道、小南山和狮山区域均为不适宜开发区,主要受活动断裂带影响。如无特别需要,该区域地下空间需禁止开发利用。
5. 结论
(1)相对于常规体系,约束体系提高了地表水体、断裂带、砂土液化和地质灾害易发性的评价权重。
(2)约束体系下适宜性差和不适宜区域主要分布在断裂带、地质灾害高发区以及水源地区域,比常规体系评价结果更加符合实际约束性地质条件。
(3)深圳市地下空间资源利用规划中地下空间重点开发区在开发利用过程中应该注意不适宜地区约束性砂土液化引起的地层失稳、地面塌陷等地质问题,合理规避约束性活动断裂带区域岩体破碎、地下水富集等地质问题。
-
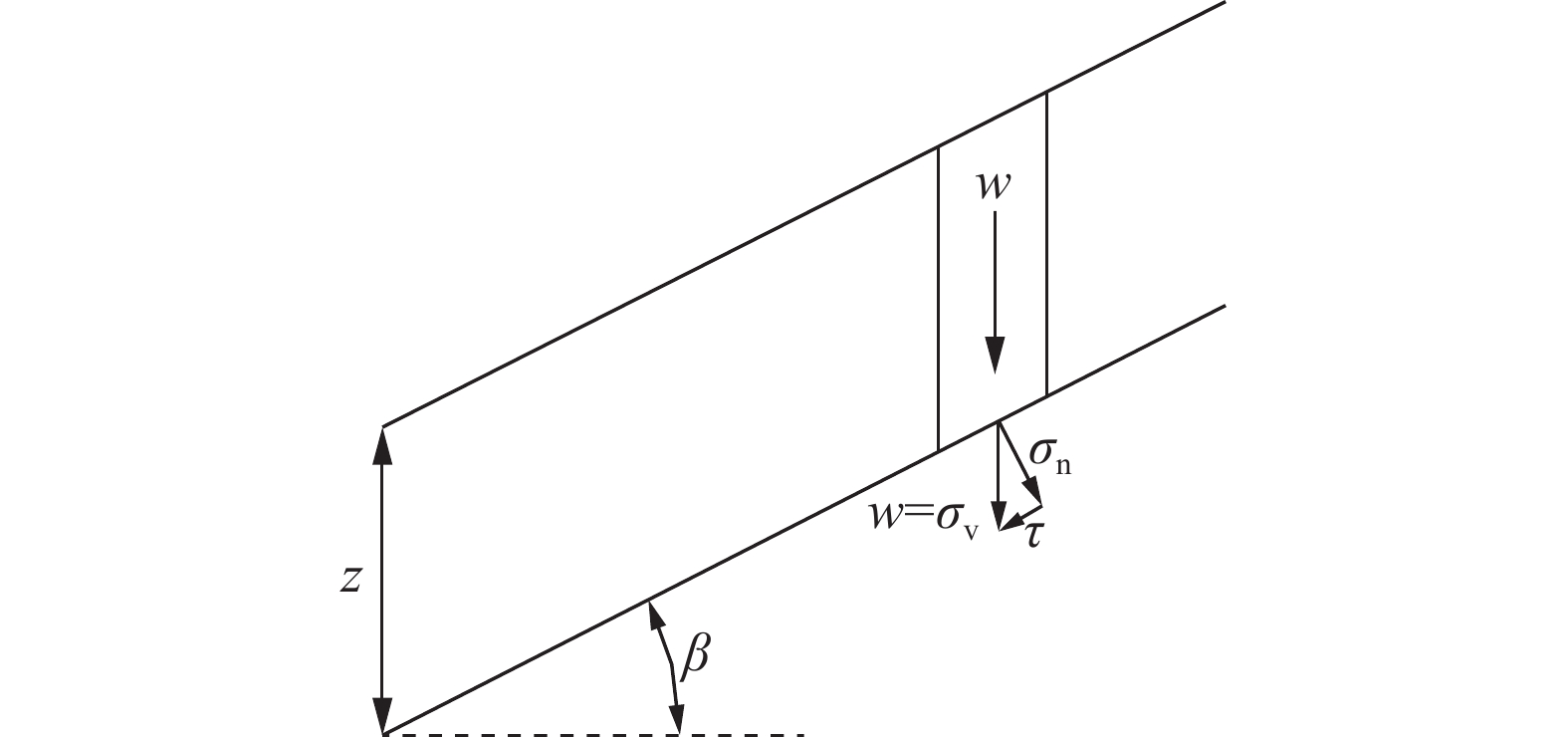
图 1 无限边坡计算简图[15]
Figure 1.
表 1 数值计算所需参数取值
Table 1. Parameter value required for numerical calculation
性质 单位 数值 重度γ kN·m−3 18.5 杨氏模量 Esat kPa 2300 泊松比 μ − 0.4 有效强度指标 c' kPa 16 φ' ° 15 饱和渗透系数 ksat m·d−1 1.8×10−3 饱和体积含水率 θs − 0.51 残余体积含水率 θr − 0.15 表 2 考虑水-力耦合及干湿循环的数值计算方案
Table 2. Numerical calculation scheme considering hydraulic-coupling and dry-wet cycle
干湿循环次数 分析类型 SWCC
(图4)ksat
/(m·d−1)c'
/kPaφ'
/kPa1 耦合 曲线1 1.8×10−3 16 15 2 耦合 曲线2 2.2×10−3 14 3 耦合 曲线3 2.4×10−3 12 5 耦合 曲线4 2.8×10−3 10 -
[1] 蔡沛辰,阙云,李显. 非饱和花岗岩残积土水-气两相驱替过程数值模拟[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):54 − 63. [CAI Peichen,QUE Yun,LI Xian. Numerical simulation of water-gas two-phase displacement process in unsaturated granite residual soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):54 − 63. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202010017
[2] ZENG H,TANG C S,CHENG Q,et al. Coupling effects of interfacial friction and layer thickness on soil desiccation cracking behavior[J]. Engineering Geology,2019,260:105220. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105220
[3] 蔡荣坤,戴自航,徐根连,等. 降雨对花岗岩风化层路堑边坡滑动模式影响—以福建云平高速云霄段为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(2):27 − 35. [CAI Rongkun,DAI Zihang,XU Genlian,et al. Influence of rainfall on sliding modes of cutting slope of weathered granite stratum:taking Yunxiao section in the Yunping freeway in Fujian for example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(2):27 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] TANG G P,HUANG J S,SHENG D C,et al. Stability analysis of unsaturated soil slopes under random rainfall patterns[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,245:322 − 332. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.09.013
[5] WANG Y X,CHAI J R,CAO J,et al. Effects of seepage on a three-layered slope and its stability analysis under rainfall conditions[J]. Natural Hazards,2020,102(3):1269 − 1278. doi: 10.1007/s11069-020-03966-1
[6] 饶鸿,王金淑,赵志明,等. 基于有限元软件自定义本构模型的膨胀土边坡降雨入渗分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):154 − 162. [RAO Hong,WANG Jinshu,ZHAO Zhiming,et al. An analysis of rainfall infiltration of expansive soil slope based on the finite element software custom constitutive model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):154 − 162. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] ZENG L,BIAN H B,SHI Z N,et al. Forming condition of transient saturated zone and its distribution in residual slope under rainfall conditions[J]. Journal of Central South University,2017,24(8):1866 − 1880. doi: 10.1007/s11771-017-3594-6
[8] 郑开欢,罗周全,江宏. 天气因素对排土场生态边坡稳定性的影响[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(6):97 − 102. [ZHENG Kaihuan,LUO Zhouquan,JIANG Hong. Weather factors' influence on the stability of ecological slopes of waste dump[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(6):97 − 102. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] SONG S,BROCCA L,WANG W,et al. Testing the potential of soil moisture observations to estimate rainfall in a soil tank experiment[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2020,581:124368. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124368
[10] 曾铃,史振宁,付宏渊,等. 降雨入渗对边坡暂态饱和区分布特征的影响[J]. 中国公路学报,2017,30(1):25 − 34. [ZENG Ling,SHI Zhenning,FU Hongyuan,et al. Influence of rainfall infiltration on distribution characteristics of slope transient saturated zone[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport,2017,30(1):25 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2017.01.004
[11] 邱祥,蒋煌斌,欧健,等. 降雨条件下边坡暂态饱和区形成条件与演化特征数值分析[J]. 水利学报,2020,51(12):1525 − 1535. [QIU Xiang,JIANG Huangbin,OU Jian,et al. Numerical analysis of formation conditions and evolution characteristics of transient saturation zone of a slope under rainfall conditions[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2020,51(12):1525 − 1535. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13243/j.cnki.slxb.20200254
[12] 张良以,陈铁林,张顶立. 降雨诱发膨胀土边坡渐进破坏研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2019,41(1):70 − 77. [ZHANG Liangyi,CHEN Tielin,ZHANG Dingli. Progressive failure of expansive soil slopes under rainfall[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2019,41(1):70 − 77. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 熊勇林,朱合华,叶冠林,等. 降雨入渗引起非饱和土边坡破坏的水-土-气三相渗流-变形耦合有限元分析[J]. 岩土力学,2017,38(1):284 − 290. [XIONG Yonglin,ZHU Hehua,YE Guanlin,et al. Analysis of failure of unsaturated soil slope due to rainfall based on soil-water-air seepage-deformation coupling FEM[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2017,38(1):284 − 290. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2017.01.036
[14] ZHAI Q,RAHARDJO H,SATYANAGA A,et al. Estimation of unsaturated shear strength from soil-water characteristic curve[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2019,14(6):1977 − 1990. doi: 10.1007/s11440-019-00785-y
[15] 叶万军,张宇鹏. 长期降雨作用下黄土边坡失稳模型试验[J]. 中国科技论文,2021,16(6):603 − 609. [YE Wanjun,ZHANG Yupeng. Model test study on instability of loess slopes under long-term rainfall[J]. China Sciencepaper,2021,16(6):603 − 609. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2021.06.006
[16] INTERNATIONAL G S. SEEP/W for finite element seepage analysis, version 3 and 4[M/OL]. GEO-SLOPE International Ltd;. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/37407388_seepw_for_finite_element_seepage_analysis_version_3_and_4
[17] GEOSLOPE international Ltd. Sigma/W user’s guide for stress-deformation analysis. Calgary, Alta: GEO-SLOPE International Ltd; 2007.
[18] 许旭堂,简文彬,吴能森,等. 降雨诱发残积土坡失稳的模型试验[J]. 中国公路学报,2018,31(2):270 − 279. [XU Xutang,JIAN Wenbin,WU Nengsen,et al. Model test of rainfall-induced residual soil slope failure[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport,2018,31(2):270 − 279. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2018.02.029
[19] 许旭堂, 简文彬. 土坡对降雨入渗的响应及其失稳演变[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2020
XU Xutang, JIAN Wenbin. Research on the response and failing process of unsaturated soil slope under rainfall infiltration[M]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2020. (in Chinese)
[20] YANG K H,UZUOKA R,THUO J N,et al. Coupled hydro-mechanical analysis of two unstable unsaturated slopes subject to rainfall infiltration[J]. Engineering Geology,2017,216:13 − 30. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.11.006
[21] HAN Z,VANAPALLI S,ZOU W L. Integrated approaches for predicting soil-water characteristic curve and resilient modulus of compacted fine-grained subgrade soils[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2016,54(5):646 − 663. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2016-0349
[22] XU X T,SHAO L J,HUANG J B,et al. Effect of wet-dry cycles on shear strength of residual soil[J]. Soils and Foundations,2021,61(3):782 − 797. doi: 10.1016/j.sandf.2021.03.001
[23] XU X T,JIAN W B,WU N S,et al. Void ratio-dependent water retention model for a deformable residual clay[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics,2020,20(8):04020131. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0001773
[24] 安然,孔令伟,黎澄生,等. 炎热多雨气候下花岗岩残积土的强度衰减与微结构损伤规律[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(9):1902 − 1911. [AN Ran,KONG Lingwei,LI Chengsheng,et al. Strength attenuation and microstructure damage of granite residual soils under hot and rainy weather[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(9):1902 − 1911. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2020.0073
[25] 简文彬,胡海瑞,罗阳华,等. 干湿循环下花岗岩残积土强度衰减试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(3):592 − 597. [JIAN Wenbin,HU Hairui,LUO Yanghua,et al. Experimental study on deterioration of granitic residual soil strength in wetting-drying cycles[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017,25(3):592 − 597. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 刘越,陈东霞,王晖,等. 干湿循环下考虑裂隙发育的残积土边坡响应分析[J]. 岩土力学,2021,42(7):1933 − 1943. [LIU Yue,CHEN Dongxia,WANG Hui,et al. Response analysis of residual soil slope considering crack development under drying-wetting cycles[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2021,42(7):1933 − 1943. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] OH W T,VANAPALLI S K,PUPPALA A J. Semi-empirical model for the prediction of modulus of elasticity for unsaturated soils[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2009,46(8):903 − 914. doi: 10.1139/t09-030
[28] ADEM H H, VANAPALLI S K. A simple method for prediction of the modulus of elasticity of unsaturated expansive soils. In: Khalili N, Russell A, Khoshghalb A, editors. Proceedings of the 6th international conference on unsaturated soils, Sydney, Australia. Unsaturated soils: research & applications. CRC Press; 2014.
[29] 唐栋,李典庆,周创兵,等. 考虑前期降雨过程的边坡稳定性分析[J]. 岩土力学,2013,34(11):3239 − 3248. [TANG Dong,LI Dianqing,ZHOU Chuangbing,et al. Slope stability analysis considering antecedent rainfall process[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2013,34(11):3239 − 3248. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] LI J L,ZHANG L. Soil-water characteristic curve and permeability function for unsaturated cracked soil[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2011,48(7):1010 − 1031. doi: 10.1139/t11-027
-






 下载:
下载: