Application of SBAS-InSAR and PS-InSAR technologies in analysis of landslide subsidence along a linear infrastructure in Southwestern Shandong
-
摘要:
地面沉降问题严重影响着鲁西南经济发展区交通工程建设。文中选择某线性工程两侧5 km范围作为研究区,文章收集RadarSAT-2(2017—2020年)、Sentinel-1A(2019—2020年)存档数据和沿线区域地质、水文地质、矿产开发资料,采用时序InSAR分析的方法,对研究区沿线地面沉降分布特征及规律进行综合分析。研究结果表明:研究区主要地面沉降诱因是煤矿采空区塌陷和地下水超量开采,前者以矿区工作面为中心形成沉降漏斗,沉降速率变化和沉降中心移动与煤矿作业工作面挖掘进度和转移密切相关;后者沉降分布规律与地下水开采使用点相关,形成与地下水开采使用范围相近的沉降带。研究区在2017—2020年内持续发生沉降,最大年均沉降速率为136.5 mm/a,单年累计最大沉降量为220 mm。经同期CPI水准点观测结果校核,InSAR数据处理成果平均误差小于1 cm/a,相关系数到达70%以上。本文采用的分析方法能及时准确反映出线路方案穿行研究区内各处地面沉降变化,为线路方案规划和地质灾害整治提供有效合理参考。
Abstract:Land subsidence is a serious problem that affects the construction of traffic engineering in the economic development zone in southwestern Shandong Province. This paper selects the range of 5 km on both sides of a linear project as the research area. The article collects RadarSAT-2(2017-2020), Sentinel-1A(2019-2020) archived data , geological data, hydrogeological data, and mineral development data, and uses time-series InSAR measurement to analyze the distribution characteristics and laws of land subsidence in the study area. The research indicates: the main causes of ground subsidence in the study area are coal mine goaf collapse and excessive groundwater mining; the former forms a settlement funnel with the mining area as the center, the change of settlement rate and the movement of the settlement center are closely related to the mining progress and transfer of the coal mining area; The latter’s settlement distribution law is related to the distribution of groundwater use areas, forming a subsidence zone that similar to the range of groundwater mining. The study area continued to experience subsidence during 2017 to 2020, with the maximum annual subsidence rate at 136.5 mm/a, and the cumulative maximum subsidence in a single year at 220 mm. After checking the observation results of CPI benchmarking points during the same period, the average error of InSAR data processing results is less than 1cm/a, and the correlation coefficient is more than 70%. The analysis method adopted in this paper can timely and accurately reflect the changes in land subsidence throughout the study area, provide effective and reasonable reference for route planning and geological disaster remediation.
-
0. 引言
鲁西南某线性工程连接着山东省西南部经济隆起带的临、枣、济、菏发展轴,是鲁西南经济发展的重要支撑。鲁西南尤其是曲阜至菏泽区域采煤历史悠久,随着该地区以煤矿开采为主的矿产资源开发规模逐年增大,采空区上方岩层在重力作用下发生弯曲、离层乃至冒落,从而引发一系列规模不等、形状各异的采煤地面沉陷问题[1];并且由于受到不同的矿层条件、顶板岩性特征、地质构造和采高、开采条件的影响,地表变形程度和发展过程在空间上呈现不规则分布[2]。
永久散射体干涉测量技术(persistent scatterer interferometric synthetic aperture radar, PS-InSAR)和短基线集干涉测量技术(Small baseline subsets interferometric synthetic aperture radar, SBAS-InSAR)是近年来基于合成孔径雷达干涉测量技术(interferometric synthetic aperture radar, InSAR)开展都市圈和矿区地面沉降监测分析的热门研究方向[3-6]:在都市圈应用方向,李海君等[7]采用PS-InSAR技术对覆盖河北廊坊北部地区的33景Envisat ASAR影像进行处理,并将处理得到的廊坊北部地区地表时序形变速率场,通过耦合分析时序形变速率场与沉降影像数据,分析得到该地区的地面时序沉降情况和影响因素;雷坤超等[8]采用PS-InSAR技术获取天津地面沉降时间序列演变特征,从而实现对不同含水层系统地下水开采、活动断裂等地面沉降诱发因素的分析研究;徐小波等[9]收集11期Envisat/Alos数据,采用PS-InSAR技术得到安阳市区水冶镇两年间大面积地表形变动态演化信息,分析得到超采地下水与地面沉降之间的动态变化关系;张红峰等[10]提出了一种基于经验模态分解的改进PS-InSAR技术,并成功应用于非城区形变监测研究;而冉培廉、潘超、高二涛等分别对比分析了PS-InSAR与SBAS-InSAR技术处理西安地区31幅Sentinel-1A SAR影像、成都地区30景Sentinel-1A影像和南京地区23幅Sentinel-1A影像的结果,实验结果表明两种方法得到的时序性沉降变化趋势相关性极高,与实际变化情况相符,能有效应用于都市圈地面沉降监测[11-13]。在矿区沉降监测分析应用方向,陈国浒等[14]通过总结北京地区采空塌陷变形特征,针对PS-InSAR技术的特点和局限性进行可行性分析,详细比对传统形变监测手段和PS-InSAR技术的优劣,肯定了该项技术在矿区时序地表形变监测中的应用前景;卢欣奇等[15]基于PS-InSAR技术对广西平南锡基坑老采空区进行沉降监测分析,并将处理结果与数值模拟计算结论对比,证明PS-InSAR技术在采空区沉降监测分析研究中的有效性和准确性;潘光永等[16]则利用SBAS-InSAR技术对济阳井田矿区40景Sentienl-1A数据进行处理,矿区持续开采会直接影响矿区及周边地区地表形变情况,地面沉降量随开采时间的推移持续增大;李达等[17]对比了SBAS-InSAR技术和传统差分干涉技术在处理陕西某矿区13景TerraSAR-X数据的结果,实验结果表明两种方法差值在5 mm以内,SBAS-InSAR技术在矿区地表沉降监测与分析方面具有良好应用前景。
文中针对鲁西南线性工程走廊带沿线地区地面沉降开展研究,收集覆盖该地区2016年7月至2020年7月28景RadarSAT-2影像和2019年2月至2020年7月32景Sentinel-1A影像,分别采用SBAS-InSAR技术和PS-InSAR技术进行处理,最终得到沉降时间序列与沉降速率信息。然后借助GIS空间数据分析技术,结合地质、气象和矿产资料详细分析该地区地面沉降原因,并与同期地面GPS监测结果进行了可靠性验证。
1. 研究区域及数据源
研究区主要包括鲁西南曲阜市、济宁市兖州区、任城区、汶上县和嘉祥县、菏泽市巨野县、郓城县、定陶区和牡丹区。研究区以京杭大运河为界,主要划分为汶泗河冲洪积平原和黄河冲积平原两大地貌单元(图1)。
研究区位于华北地层大区(Ⅴ)、晋察冀豫地层区(Ⅴ4)、鲁西地层分区(Ⅴ410)的济宁地层小区,区内地层发育较为齐全,由老至新依次发育古生代寒武系、奥陶系、石炭系、二叠系;中生代侏罗系;新生代古近系以及第四系。上覆第四系地层广泛发育于平原区和东部山间洼地及河谷地带,厚度分布不均一,由东向西依次加深,厚度范围在50~400 m。沿线性工程附近5 km范围内,主要有古城煤矿、星村煤矿等多处煤矿采空区(图2)。
研究区位于华北板块(I)鲁西地块(II)、鲁中隆起区和鲁西南潜隆起区(Ⅲ级)、泗水—平邑坳陷和尼山隆起及菏泽-兖州隆起(Ⅳ级)构造单元内,主要区域断裂包括菏泽断裂、曹县断裂、巨野断裂等。其中,菏泽断裂、曹县断裂、巨野断裂属于第四纪活动断层,嘉祥断裂为早中更新世活动断层,孙氏店断裂和峄山断裂属于第四纪不活动断层,研究区整体位于菏泽——济宁断块缓慢倾斜沉降平原区。
根据覆盖研究区的星载雷达影像的存档情况,本文分别选用RadarSAT-2和Sentinel-1A数据进行研究区地面沉降监测,具体数据的基本参数信息见表1。
表 1. 研究区星载SAR数据源基本参数Table 1. Basic parameters of satellite SAR data sources in the study area参数 SAR传感器 RadarSAT-2 Sentinel-1A 幅宽/km 125 250 雷达波长/cm 5.6 5.6 空间分辨率/m2 5×5 5×20 重访周期/d 24 12 影像数量 26 32 时间覆盖范围 2017-01-14—2020-07-27 2019-02-03—2020-07-15 2. InSAR数据处理
综合考虑研究时间跨度和研究区面积,为了维持干涉图的相干性,本文实验基于GAMMA软件综合使用PS-InSAR技术和SBAS-InSAR技术实现对雷达影像的处理。SBAS-InSAR和PS-InSAR技术处理流程如图3和图4所示。
传统D-InSAR数据处理主要包括原始信号成像聚焦、成像质量检查、数据预处理、差分干涉计算、形变量计算等几个主要步骤。PS-InSAR数据处理则是在D-InSAR数据处理基础上再进行时间/空间域形变估算处理——PS-InSAR数据处理的核心在于PS点目标选取,以及对于PS点目标的时间/空间域形变估算。和前两种方法不同,SBAS-InSAR数据处理方法需要通过差分干涉相位和相邻点间参数相减得到残余相位,并通过对残余相位进行低通滤波、奇异值分解等处理最终得到PS点目标的时间序列形变相位。
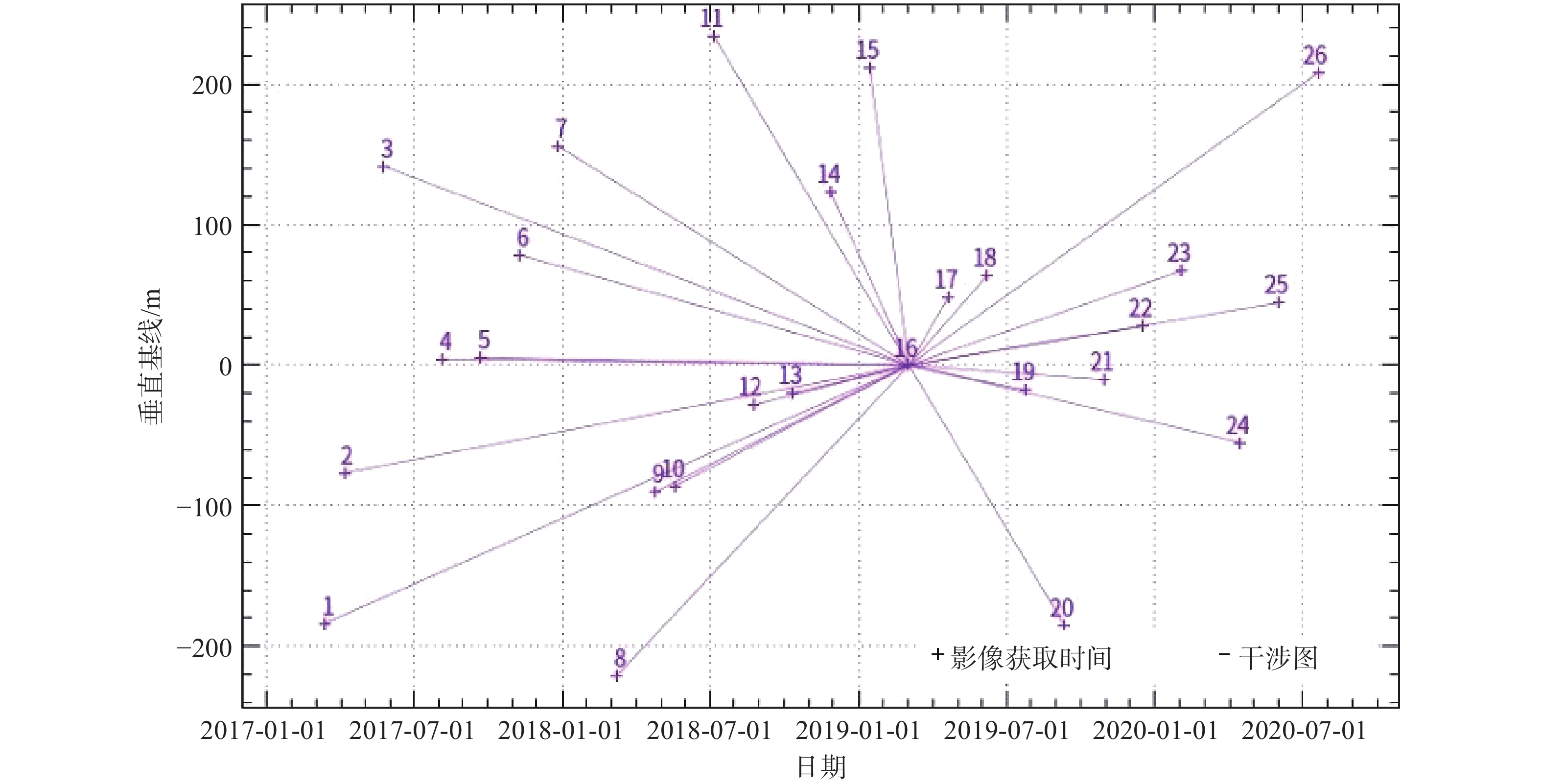
根据数据获取时间和数据获取途径不同,本文采用SBAS-InSAR数据处理技术对Radarsat-2影像,采用PS-InSAR数据处理技术对Sentinel-1A影像进行处理。以Radarsat-2影像为例,综合考虑数据时相上的分布密度,选择2019年3月4日获取的雷达影像作为配准主影像,采用30 m SRTM DEM(Shuttle Radar Topography Mission Digital Elevation Model)数据与主影像进行地理配准,并将所有其他SAR影像配准到主影像上。为进行基线估计以确定差分像对,实验设置时间基线为1250 d,空间基线为480 m(图5)。
3. 研究结果与分析
3.1 区域时序形变分析
应用InSAR数据处理方法提取研究区2017年到2020年地面年平均沉降速率,结果见图6。数据处理结果表明研究区在2017—2020年间出现3处主要形变区域,分别是线路280 km附近古城—星村—红楼煤矿重点沉降区域P1、线路370~380 km附近郭屯—赵楼煤矿重点沉降区域P2和线路400~420 km附近菏泽市城郊工业园重点沉降区域P3。
监测结果中P1区域位于曲阜市西北部古城—星村—红楼煤矿采矿区域内,2017—2020年最大年平均沉降速率为−136.5 mm/a,P2区域位于郓城县以南郭屯—赵楼煤矿采矿区域内,2017—2020年最大年平均沉降速率为−130 mm/a,P3区域位于菏泽市东北城郊工业园区,2017—2020年最大年平均沉降速率为−45 mm/a。如图7所示,P1和P2区域沉降中心位于线路附近的煤矿采空区范围内,沉降速率向外逐渐减小,形成沉降漏斗,中心最大沉降量达到480 mm和622 mm;而P3区域则呈现出整体沉降形变的状态,无明显沉降中心。
如图8所示,研究区主要沉降区域P1沉降中心在2017—2020年间逐渐向西移动,该区域单年累计最大沉降量保持在220 mm左右,同时该区域整体年沉降量在该时间段内呈现出先加剧后减缓的趋势,沉降区域范围缓慢扩大;主要沉降区域P2的沉降中心在2017—2020年间基本保持不变,该区域单年累计最大沉降量保持在210 mm左右,而该区域整体单年沉降量和沉降区域范围在该时间段逐步扩大;主要沉降区域P3在2017—2020年间整体单年沉降量和沉降范围基本保持不变。
3.2 诱发因素分析
研究区位于鲁西南济宁至菏泽区域,由于工农业生产、民政生活、矿业开采等因素的影响,该研究区存在长期地面沉降历史。该地区地面沉降诱发因素可分为人为因素和自然因素两大类:人为因素主要包括矿业生产活动、地下水开采等,自然因素主要包括区域构造运动影响。
3.2.1 煤矿采空区塌陷
地下煤层开采后,采空区围岩应力会进行重新分布,导致围岩向临空方向出现变形;当采空区的直接顶板变形过大形成崩落后,会继续诱发上部岩层产生新的应力重分布过程;这个过程的重复发生导致掩体变形不断扩展,直至发展到地表形成地表塌陷、地裂缝或地表连续变形。因此,煤矿采空区诱发区域地面沉降的移动、变形、扩展等过程会随着采煤工作面的扩大、开采深度和范围推进而逐渐发生,并最终形成稳定的沉降漏斗;随着开采区域的转移和采空区回填措施,沉降中心会随之转移,原沉降区域沉降速率则逐渐减缓[18-20]。
①古城—星村—红楼煤矿重点沉降区域P1
根据山东省鲁南地质工程勘察院收集矿区资料显示,古城—星村—红楼煤矿重点沉降区域P1主要开采面集中在古城煤矿矿区,红楼煤矿暂属于探矿阶段,星村煤矿开采面不在研究区范围内。古城煤矿开采深度为1000~1200 m,煤层厚度约8 m,采用综合采放顶煤工艺条带式开采。
2017年古城煤矿3107和3209等工作面开始作业,导致以3107和3209工作面为中心的沉降漏斗初步形成,中心沉降量达到180~200 mm,边缘沉降量为50 mm左右;随着开采作业的持续,该沉降漏斗加速发展,截至2018年12月,沉降中心沉降量达到410 mm,边缘沉降量达到150 mm左右,同时影响范围逐渐扩大;为避免采空区地面沉降对线路方案施工造成影响,该两处工作面开采工作于2018年年底逐步停止并向矿区西北转移,沉降漏斗的发展也随之发生改变。截至2020年7月,沉降中心沉降量为480 mm,沉降速率自2019年3月起沉降速率大幅减缓;沉降漏斗向西发展,原沉降中心东侧沉降量保持在150 mm左右,沉降范围未扩大,原沉降中心西北侧沉降量由250 mm递增到350 mm,沉降范围也逐渐扩大(图9)。
②郭屯—赵楼煤矿重点沉降区域P2
根据山东省鲁南地质工程勘察院收集矿区资料显示,郭屯—赵楼煤矿重点沉降区域P2主要开采面集中在郭屯煤矿矿区,赵楼煤矿开采面不在研究区范围内。郭屯煤矿以开采山西组含煤地层为主,其中3上煤层赋存于唐官屯村东,煤层厚度1.61m,处于研究区边缘位置;3下煤层赋存于西付庄北,煤层厚度约4.77m。
截至2017年底该区域尚无明显沉降中心,唐官屯庄开采面累计沉降最大值仅150 mm,平均沉降量为100 mm;而西付庄煤矿赋存处最大沉降量为50 mm,表明2017年内该区域沉降受煤矿开采导致的采空区塌陷影响较小。截至2018年底,唐官屯庄开采面累计最大沉降值达到400 mm,该区域整体沉降速率处于加速状态,并逐渐形成以唐官屯庄为中心的沉降漏斗;同时,西付庄煤矿赋存处最大沉降量达到200 mm,整体沉降速率较2017年也有所提高,表明2018年内该区域开始受到煤矿开采导致的采空区塌陷影响。从2018年底至2020年7月,通过采集郭屯—赵楼煤矿重点沉降区域P2每隔4个月的累计沉降数据发现,唐官屯庄沉降中心沉降量以每期50 mm沉降量增长,整体沉降深度持续加深,同时沉降范围向郭屯矿区东南角不断扩大,最终形成中心沉降量达到622 mm的沉降漏斗;此外,西付庄煤矿赋存处和郭屯煤矿东南角区域中心沉降量也由200 mm增长到300 mm,形成另一处小型沉降漏斗,表明2019—2020年间,该区域受到煤矿开采导致的采空区塌陷影响日趋明显。2017—2020年间,唐官屯庄沉降漏斗边缘距线路方案最近仍有1km,而西付庄煤矿赋存处漏斗边缘最近距线路方案仅200 m,有侵入线路方案范围的迹象(图10)。
3.2.2 地下水开采
太沙基(Terazghi)固结理论认为:饱和多孔介质可以看作等效的连续介质,其总应力与孔隙压力的差被视为有效应力。土颗粒本身的压缩量是很微小的,在研究中可以忽略,骨架的压缩只有通过颗粒的排列变化(拓扑变化)来实现,即只有通过颗粒接触点传递的有效应力,才能引起土的变形和影响土的强度,抽水造成的饱和土孔隙水压力消散引起粒间有效应力的增加,是土层发生压缩变形的基本机理[21]。
①古城—星村—红楼煤矿重点沉降区域P1
古城—星村—红楼煤矿重点沉降区域P1范围内无集中供水水源地,部分村庄开采中深层孔隙水和浅层孔隙水作为生活饮用和农业灌溉。资料收集得到沉降中心东北约3 km的孔村中深层孔隙水水位长期观测资料,地下水位标高保持在49~50 m,在2017~2018年P1区域下沉量变化较大时,水位未出现剧烈下降的趋势,水位整体属于自然波动状态,因此该区域地面沉降基本不受地下水开采影响。
②郭屯—赵楼煤矿重点沉降区域P2
通过实地调查,郭屯—赵楼煤矿重点沉降区域P2范围内无集中供水水源地,也无深层地下水开采井,生活用水取自黄河水,农田灌溉取用浅层地下水,人类生产生活过量开采地下水引起地面沉降可能性小。
③菏泽市城郊工业园重点沉降区P3
早在20世纪80年代,菏泽城区部分水准点高程出现下降;之后经过1979、1986、2002、2014四次水准测量发现菏泽市整体出现不同程度的沉降。该区域沉降趋势呈现出东大西小,城区东侧沉降较困、城区南北两侧沉降相对较慢,沉降速率相对较快的区域主要集中城东郊区。
菏泽市城郊工业园重点沉降区P3呈现整体缓慢沉降趋势,2017—2020年间年平均沉降基本保持在30 mm/a左右,年最大沉降速率为30.82 mm/a,主要沉降区域集中在菏泽市牡丹化工园区和唐庙镇—皇镇区域(图11)。
菏泽地区属于黄河冲积平原前部,区内地层主要为第四系全新统冲积层,以粉土、粉质黏土、粉砂为主,第四系地层厚度为300~500 m,局部发育有湖沼积淤泥质土,埋深35~50 m。如表2所示,该地区地下水以深层承压水为主,深层含水层与浅层孔隙水无水力联系;加之中间有中层咸水层的阻隔,补给来源较少,限制措施无法快速恢复地下水位,黏性土所失去的有效应力也难以恢复。根据菏泽市水文观测数据显示,2013—2018年间,菏泽城区地下水呈现逐年下降的趋势,深层地下水水位下降超过20 m;同时随着开采量持续增大,第四系深层孔隙水水位也逐渐下降,从而导致菏泽市城郊工业园重点沉降区P3出现整体沉降。
表 2. 菏泽地区第四系含水岩组水文地质特征[22]Table 2. Hydrogeological characteristics of the Quaternary water-bearing rock group in Heze[22]岩组划分 浅层潜水孔隙水 中-深层承压孔隙水 深层承压孔隙水 埋深/m 20~80 200~300 300~450 岩性 粉砂、粉细砂为主,多层分布,被黏土和淤泥质土隔开,砂层分布不均,累计厚度为10~30 m 粉砂、粉细砂为主,因上部有黏土隔水层,该层水具有承压性。砂层连续性差,分布有4~6层,累计厚度为8~20 m 粉细砂、细砂为主,砂层连续性差,
累计厚度为20~50 m水文地质特征 接受大气降水、地表水及农业灌溉回渗补给、富水性较强,单井涌水量为500~3000 m3/d,该层地下水位菏泽市农业灌溉主要用水 接受上层潜水的越流补给及侧向径流补给,富水性相对较弱,单井涌水量为500 m3/d,该层地下水主要为矿化度大
于2 g/L的咸水,基本没有开发利用补给单一,接受侧向径流补给,水流滞缓,
补给量较小。单井涌水量小于500~
1000 m3/d,为菏泽地区城区工业及
生活主要用水3.3 外部检校与分析
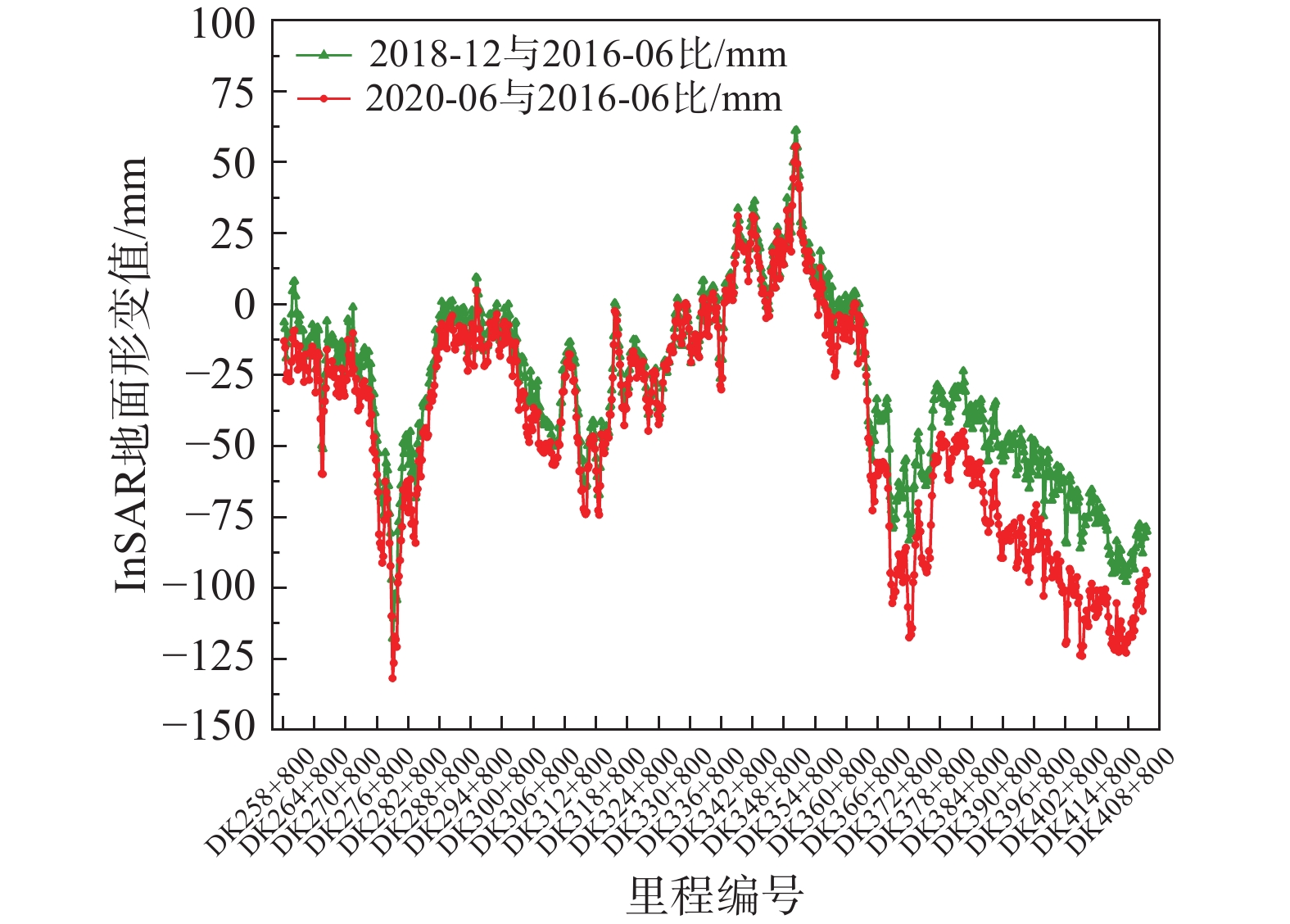
为了验证InSAR数据处理得到的研究区地面沉降数据精度,将同期InSAR数据处理结果和CPI水准点测量值进行对比。文中研究选择了线路方案两侧InSAR数据处理结果覆盖范围内共59个CPI水准点与水准点所在位置的InSAR数据采样值,采用中误差、平均误差和相关系数进行验证,最终结果如表3所示。
表 3. CPI测量值与InSAR数据采样值精度评估Table 3. Accuracy evaluation of CPI measurement value and InSAR data sampling value2018年12月较2016年6月 2020年6月较2016年6月 中误差 23.45 mm/a 23.682 mm/a 平均误差 7.23 mm/a 6.98 mm/a 相关系数 0.72 0.75 取同期线路方案中线InSAR数据处理成果和高铁水准CPI点测量结果进行对比(图12、图13),同期曲线变化趋势基本一致。CPI点测量为剔除了部分采空区影响的测量结果,InSAR结果为处理成果,部分地区出现差异较大的情况主要为煤矿采空区范围内,差异主要为采矿造成地面变形引起,例如DK275+700处由于现场地形及施工等因素影响,未设置足够的CPI水准测量点,因此导致该段数据量较少。
4. 结论
文中采用时间序列InSAR技术对鲁西南线性工程穿越区域内的RadarSAT-2及Sentinel-1A数据进行处理,得到了研究区的2017—2020年年平均形变速率图和时间序列形变。研究结果表明,研究区存在3个主要沉降区域,在该时间段沉降范围及沉降量级均发生了巨大的变化。其中,沉降区域P1和P2位于煤矿矿区开采范围内,最大沉降速率分别达到136.5 mm/a和130 mm/a,累计最大沉降量为482 mm和634 mm;沉降区域P3位于城郊工业园区范围,最大沉降速率为45 mm/a,累计最大沉降量为158 mm左右。
经过论证分析得到以下结论:
(1)研究区地面沉降主要诱发因素是矿产资源开采引起的采空区塌陷和地下水超量开采,区域构造运动对该地区地表形变影响较小。
(2)沉降区域P1和P2地面沉降形变主要由矿产资源的开采引起,地下水开采对地面沉降的影响不明显;随着开采工作面的推进和转移,沉降中心会随之发生改变或移动,沉降范围逐步扩大,形成明显的沉降漏斗。
(3)沉降区域P3受深层地下水过度开采影响,由于地下水开采使用点平均分散,因此该区域未形成沉降漏斗,而是出现和地下水开采使用范围相近的沉降带。
(4)比较与InSAR数据处理成果同时期线路方案附近CPI水准点观测数据发现,两者平均误差小于1cm,相关系数达到70%以上,表明InSAR数据处理结果有效可靠,能够及时准确反映出线路方案穿行研究区内各处地面沉降变化,为线路方案规划和地质灾害整治提供有效合理参考。
-
表 1 研究区星载SAR数据源基本参数
Table 1. Basic parameters of satellite SAR data sources in the study area
参数 SAR传感器 RadarSAT-2 Sentinel-1A 幅宽/km 125 250 雷达波长/cm 5.6 5.6 空间分辨率/m2 5×5 5×20 重访周期/d 24 12 影像数量 26 32 时间覆盖范围 2017-01-14—2020-07-27 2019-02-03—2020-07-15 表 2 菏泽地区第四系含水岩组水文地质特征[22]
Table 2. Hydrogeological characteristics of the Quaternary water-bearing rock group in Heze[22]
岩组划分 浅层潜水孔隙水 中-深层承压孔隙水 深层承压孔隙水 埋深/m 20~80 200~300 300~450 岩性 粉砂、粉细砂为主,多层分布,被黏土和淤泥质土隔开,砂层分布不均,累计厚度为10~30 m 粉砂、粉细砂为主,因上部有黏土隔水层,该层水具有承压性。砂层连续性差,分布有4~6层,累计厚度为8~20 m 粉细砂、细砂为主,砂层连续性差,
累计厚度为20~50 m水文地质特征 接受大气降水、地表水及农业灌溉回渗补给、富水性较强,单井涌水量为500~3000 m3/d,该层地下水位菏泽市农业灌溉主要用水 接受上层潜水的越流补给及侧向径流补给,富水性相对较弱,单井涌水量为500 m3/d,该层地下水主要为矿化度大
于2 g/L的咸水,基本没有开发利用补给单一,接受侧向径流补给,水流滞缓,
补给量较小。单井涌水量小于500~
1000 m3/d,为菏泽地区城区工业及
生活主要用水表 3 CPI测量值与InSAR数据采样值精度评估
Table 3. Accuracy evaluation of CPI measurement value and InSAR data sampling value
2018年12月较2016年6月 2020年6月较2016年6月 中误差 23.45 mm/a 23.682 mm/a 平均误差 7.23 mm/a 6.98 mm/a 相关系数 0.72 0.75 -
[1] 向铮. 山东煤城转型能力及提升分析研究[J]. 山东师范大学学报(自然科学版),2019,34(4):468 − 477. [XIANG Zheng. Analysis of transformative ability of Shandong coal-based cities and improvement[J]. Journal of Shandong Normal University (Natural Science),2019,34(4):468 − 477. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 黄庆享, 杜君武, 侯恩科, 等. 浅埋煤层群覆岩与地表裂隙发育规律和形成机理研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2019,36(1):7 − 15. [HUANG Qingxiang, DU Junwu, HOU Enke, et al. Research on overburden and ground surface cracks distribution and formation mechanism in shallow coal seams group mining[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2019,36(1):7 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 姚佳明, 姚鑫, 陈剑, 等. 基于InSAR技术的缓倾煤层开采诱发顺层岩体地表变形模式研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):135 − 146. [YAO Jiaming, YAO Xin, CHEN Jian, et al. A study of deformation mode and formation mechanism of a bedding landslide induced by mining of gently inclined coal seam based on InSAR technology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):135 − 146. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 周定义, 左小清, 喜文飞, 等. 基于SBAS-InSAR技术的深切割高山峡谷区滑坡灾害早期识别[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):16 − 24. [ZHOU Dingyi, ZUO Xiaoqing, XI Wenfei, et al. Early identification of landslide hazards in deep cut alpine canyon using SBAS-InSAR technology[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):16 − 24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 王之栋, 文学虎, 唐伟, 等. 联合多种InSAR技术的龙门山-大渡河区域地灾隐患早期探测[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版,2020,45(3):451 − 459. [WANG Zhidong, WEN Xuehu, TANG Wei, et al. Early detection of geological hazards in Longmenshan-Dadu River area using various InSAR techniques[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2020,45(3):451 − 459. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 张佳佳, 高波, 刘建康, 等. 基于SBAS-InSAR技术的川藏铁路澜沧江段滑坡隐患早期识别[J]. 现代地质,2021,35(1):64 − 73. [ZHANG Jiajia, GAO Bo, LIU Jiankang, et al. Early landslide detection in the Lancangjiang region along the Sichuan-Tibet railway based on SBAS-InSAR technology[J]. Geoscience,2021,35(1):64 − 73. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 李海君, 张耀文, 谷洪彪, 等. 基于PS-InSAR技术的廊坊北部地区地面沉降监测研究[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,2018,38(11):1122 − 1127. [LI Haijun, ZHANG Yaowen, GU Hongbiao, et al. Land subsidence detection based on PS-InSAR technology in northern area of Langfang City[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,2018,38(11):1122 − 1127. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 雷坤超, 陈蓓蓓, 宫辉力, 等. 基于PS-InSAR技术的天津地面沉降研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2013,40(6):106 − 111. [LEI Kunchao, CHEN Beibei, GONG Huili, et al. Detection of land subsidence in Tianjin based on PS-InSAR technology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2013,40(6):106 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 徐小波, 马超, 屈春燕, 等. 豫北安阳市区及水冶镇城市地面沉降的时间序列分析[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,40(1):74 − 82. [XU Xiaobo, MA Chao, QU Chunyan, et al. Time series analysis of urban ground subsidence in Anyang City and Shuiye town, northern Henan Province[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Natural Science),2021,40(1):74 − 82. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 张红峰, 刘瀛. 基于改进PSInSAR技术的非城区地表形变监测[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,2021,41(6):568 − 571. [ZHANG Hongfeng, LIU Ying. Non-urban surface deformation monitoring based on improved PSInSAR[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,2021,41(6):568 − 571. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 冉培廉, 李少达, 杨晓霞, 等. 基于SBAS-InSAR技术的西安市地面沉降监测[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,40(3):66 − 74. [RAN Peilian, LI Shaoda, YANG Xiaoxia, et al. Monitoring of Xi’an City land subsidence based on SBAS-InSAR[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Natural Science),2021,40(3):66 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 高二涛, 范冬林, 付波霖, 等. 基于PS-InSAR和SBAS技术监测南京市地面沉降[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,2019,39(2):158 − 163. [GAO Ertao, FAN Donglin, FU Bolin, et al. Land subsidence monitoring of Nanjing area based on PS-InSAR and SBAS technology[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,2019,39(2):158 − 163. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 潘超, 江利明, 孙奇石, 等. 基于Sentinel-1雷达影像的成都市地面沉降InSAR监测分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,2020,40(2):198 − 203. [PAN Chao, JIANG Liming, SUN Qishi, et al. Monitoring and analyzing Chengdu ground subsidence based on InSAR technology by using sentinel-1 radar image[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,2020,40(2):198 − 203. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 陈国浒, 刘云华, 单新建. PS-InSAR技术在北京采空塌陷区地表形变测量中的应用探析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2010,21(2):59 − 63. [CHEN Guohu, LIU Yunhua, SHAN Xinjian. Application of PS-InSAR technique in the deformation monitoring in mining collapse areas in Beijing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2010,21(2):59 − 63. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2010.02.012
[15] 卢欣奇, 李学峰, 张勤斌, 等. 基于PS-InSAR技术的老采空区地表沉陷监测与分析[J]. 中国矿业,2019,28(4):104 − 110. [LU Xinqi, LI Xuefeng, ZHANG Qinbin, et al. Surface subsidence monitoring of old goaf based on the PS-InSAR technology[J]. China Mining Magazine,2019,28(4):104 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 潘光永, 陶秋香, 陈洋, 等. 基于SBAS-InSAR的山东济阳矿区沉降监测与分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(4):100 − 106. [PAN Guangyong, TAO Qiuxiang, CHEN Yang, et al. Monitoring and analysis of sedimentation in Jiyang mining area of Shandong Province based on SBAS-InSAR[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(4):100 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 李达, 邓喀中, 高晓雄, 等. 基于SBAS-InSAR的矿区地表沉降监测与分析[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版,2018,43(10):1531 − 1537. [LI Da, DENG Kazhong, GAO Xiaoxiong, et al. Monitoring and analysis of surface subsidence in mining area based on SBAS-InSAR[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2018,43(10):1531 − 1537. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 李玉飞, 叶义成, 胡南燕, 等. 机械施工动荷载-采空区顶板失稳判据[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(3):87 − 93. [LI Yufei, YE Yicheng, HU Nanyan, et al. Instability criterion of the goaf roof under dynamic loading of construction[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(3):87 − 93. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 谢猛. 综合勘察方法在蒙华铁路石膏矿采空区选线勘察中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(1):58 − 64. [XIE Meng. Application of comprehensive survey methods in the gypsum mine goaf for Mengxi-Huazhong railway route selection[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(1):58 − 64. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 杨逾, 于洁瑜, 王宇. 条带开采采空区覆岩移动规律数值模拟分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2017,28(1):96 − 101. [YANG Yu, YU Jieyu, WANG Yu. Numerical simulation study on movement law of overlying strata of goaf in strip mining[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2017,28(1):96 − 101. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 高江平, 胡海波, 孙世界, 等. 太沙基地基极限承载力的三剪应力统一强度理论解[J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报(自然科学版),2019,51(2):186 − 191. [GAO Jiangping, HU Haibo, SUN Shijie, et al. Three-shear stress unified strength theoretical solution of Terzaghi ultimate bearing capacity of foundation[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Architecture & Technology (Natural Science Edition),2019,51(2):186 − 191. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 岳建刚. 鲁南高铁沿线地面沉降现状及原因分析[J]. 铁道勘察,2020,46(2):60 − 65. [YUE Jiangang. Analysis on the current situation and causes of land subsidence along the lunan high speed railway[J]. Railway Investigation and Surveying,2020,46(2):60 − 65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
期刊类型引用(20)
1. 张熠斌,宋金红,徐誉维,徐思瑜. 基于时序InSAR的吉林省煤炭采空区地表形变监测及时空演化态势分析. 水文地质工程地质. 2025(01): 202-213 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 赵志远,葛超英,徐雯佳. 时序InSAR技术对淮扬区域地面沉降监测. 四川地质学报. 2025(01): 162-169 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 徐林荣,何元幸子,邓志兴,肖源杰,李永威,陈昀灏. 基于时序InSAR与机器学习的岩溶地区铁路沿线形变监测及预测方法. 中南大学学报(自然科学版). 2025(03): 998-1014 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘艺梁,樊西丰,申高伟,左清军,唐玄,李永奕,朱前. 基于时序InSAR技术的木鱼包滑坡时空变形特征分析. 地质科技通报. 2025(02): 78-93 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘春雷,张媛静,陆晨明,李亚松,李剑锋. 基于时序InSAR的九龙江河口地区地面沉降时空演变规律及成因分析. 应用海洋学学报. 2024(01): 116-125 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张通德,冯晓,党升,万灿. 基于时序InSAR的成都地铁沿线形变时空特征分析. 测绘工程. 2024(02): 28-32+55 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 俞江,文亦举,鹿鸣,姚武韬,刘一霖,翁永椿. 基于PS-InSAR技术的矿山区域时序沉降特征研究. 工业安全与环保. 2024(04): 24-29 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 马驷骏,王静,王鹏. 联合传统测量与InSAR技术的锰矿地表形变预测研究. 中国锰业. 2024(02): 62-66+71 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 管静. 基于改进SBAS-InSAR方法的地下水动态监测的沉降分析. 地下水. 2024(03): 65-68 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 高启凤,张磊,赵萌阳,李峰,李海君,谌华,李小华,周萌. SBAS-InSAR技术在河北三河市地面沉降演化特征及成因分析中的应用. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(03): 97-107 .  本站查看
本站查看
11. 何虎振,刘国林,王凤云,陶秋香. 基于SBAS-InSAR和PSO-BP模型的鲁南高铁沿线地表沉降监测与预测. 大地测量与地球动力学. 2024(08): 820-826 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 张凯翔,蒋道君,吕小宁,张曦. 机器学习模型在地质灾害遥感调查数据分析中的应用现状. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(04): 126-134 .  本站查看
本站查看
13. 寇保德,周乐勋,杨兴业. 基于SBAS-InSAR技术的水工环地质调查在某矿山地质构造沉降检测中的应用. 中国锰业. 2024(04): 70-75 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 陈择慧. 静态和动态荷载双重作用下的路面沉降分层监测分析. 路基工程. 2024(05): 163-168 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 刘传正. 论线状工程地质灾害预防应对问题. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(05): 1-4 .  本站查看
本站查看
16. 李佳琦,徐佳,刘杰,易长荣,顾立军. 天津地面沉降严重区分布特征及变化规律. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2023(02): 53-60 .  本站查看
本站查看
17. 张兰军,王世杰,金鑫田,姜鑫. 矿区地表形变监测及预测方法研究. 科技和产业. 2023(07): 248-253 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 林聪. SBAS-InSAR与PS-InSAR技术在陈旗两矿区地表沉降分析中的应用. 科技创新与应用. 2023(26): 184-187 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 何清,魏路,肖永红. 基于SBAS-InSAR技术的安徽亳州市地面沉降时空分布特征与影响因素分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2023(05): 81-90 .  本站查看
本站查看
20. 柴龙飞,魏路,张震. 基于SBAS-InSAR的安徽省宿州市埇桥区2019—2022年地面沉降监测及影响因素分析研究. 安徽地质. 2023(04): 348-352 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)
-






 下载:
下载: