Distribution characteristics and causes of land subsidence in Nansha District, Guangzhou
-
摘要:
广州南沙区地面沉降已经影响到城市发展和人民生命财产安全,为了制定科学有效的措施防止地面沉降进一步发展,文中基于InSAR监测数据和水准监测数据,总结分析了地面沉降分布特征,地表形变多为小范围的、局部地区的剧烈沉降。在此基础上,针对6个沉降严重区域,采用机理模型定量估算了各因素引起的地面沉降量及所占比重,得可压缩土层引起的沉降量为34.43~96.97 mm/a,所占比重在37.07%~75.67%,地下水水位和地面荷载的最大影响比重分别为26.28%和52.40%。并且通过研究分析地面沉降主要因素及影响程度,为科学防治该地区地面沉降提供科学依据。
Abstract:Land subsidence in Nansha District has affected urban development and the safety of people’s lives and properties. In order to formulate scientific and effective measures to prevent the further development of land subsidence, this paper summarizes and analyzes the distribution characteristics of land subsidence based on InSAR monitoring data and level monitoring data, the surface deformation is mostly severe settlement in a small and local area. On this basis, for 6 areas with subsidence. The mechanism model is used to quantitatively estimate the amount of land subsidence caused by each factor and its proportion. The subsidence caused by the compressible soil layer was 34.43−96.97 mm/a, the proportion is between 37.07% and 75.67%, and the largest influence proportions of groundwater level and ground load are 26.28% and 52.40%. And through research and analysis of the main factors and impact of land subsidence, this paper provide a scientific basis for scientific prevention and control of land subsidence in this area.
-
Key words:
- Nansha District /
- land subsidence /
- PS-InSAR /
- groundwater exploitation /
- building load
-

-
表 1 土体工程地质单元分类
Table 1. Classification of soil engineering geological units
土体类型 岩性类型 黏性土 黏性土、粉质黏土 粉土 粉土 砂土 粉砂、细砂、中砂、粗砂、砾砂 碎石土 圆砾、角砾、卵石、碎石 特殊类土 残坡积土 黏性土、砂质黏性土、
砾质黏性土粉土 人工填土 素填土、杂填土、冲填土 淤泥类土 淤泥质砂土、淤泥质土、淤泥 表 2 岩体工程地质岩性组分类
Table 2. Classification of engineering geological lithologic group of rock mass
岩性组 岩性综合体 岩性类型 侵入岩
岩性组花岗岩,
闪长岩综合体似斑状黑云母二长花岗岩,细粒花岗岩,
细粒细斑状黑云母二长花岗岩,花岗
闪长岩,片麻状花岗岩,伟晶岩混合岩、
片麻岩岩性组混合岩综合体 花岗混合岩,混合岩 片麻岩综合体 花岗片麻岩,片麻岩 含膏盐红层
碎屑岩岩性组− 砾岩,砂砾岩,粉—细砂岩,细砂岩,
含砾中—粗砂岩,泥岩,泥质粉砂岩,
灰岩,泥灰岩,灰质泥岩,凝灰岩表 3 收集到的珠江三角洲地区Sentinel-1数据
Table 3. The collection of sentinel-1 data of pearl river delta
模式 入射角/(°) 分辨率 幅宽/km 条带成像 20~45 5 m×5 m 80 干涉成像 29~46 5 m×20 m 250 超幅宽 19~47 5 m×40 m 400 波浪 22~35,35~38 5 m×5 m 20×20 表 4 InSAR监测成果及其原因分析
Table 4. InSAR monitoring results and cause analysis
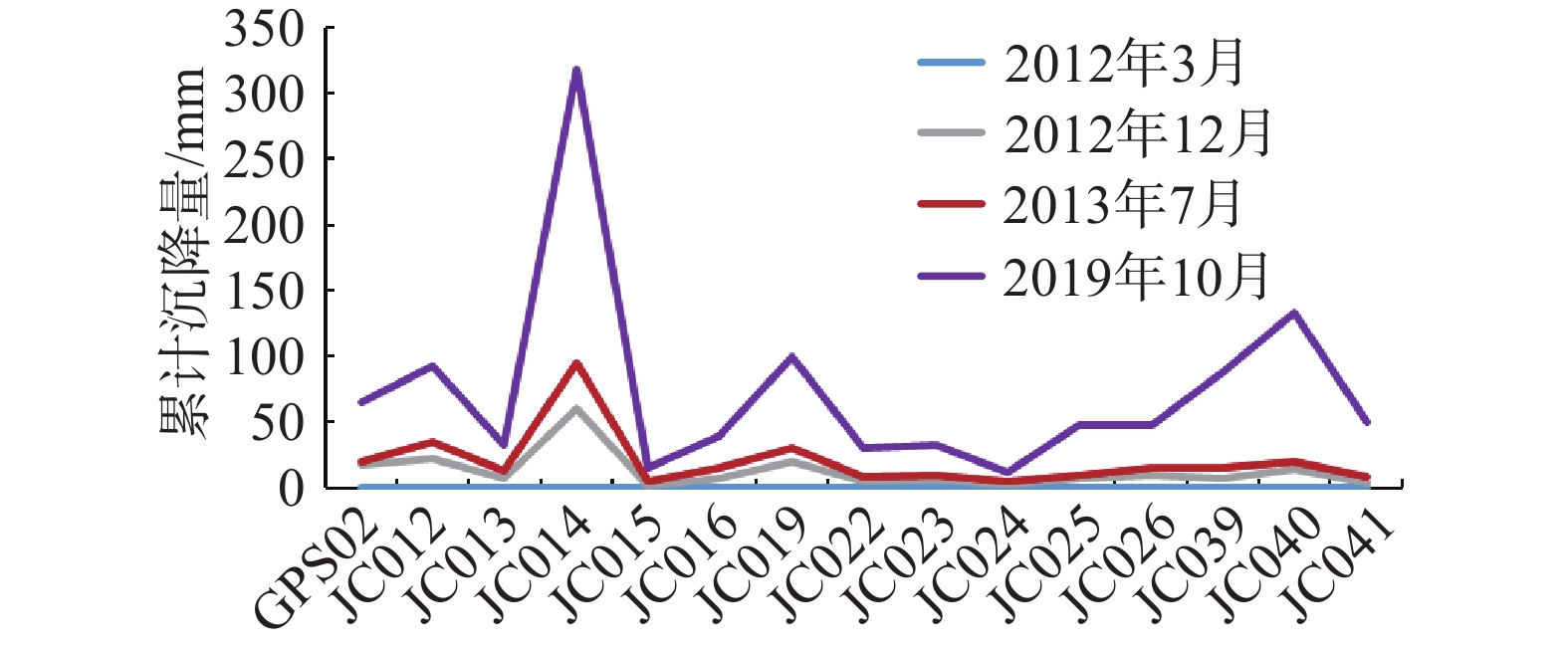
年份 具体原因分析 综合分析 2015 万顷沙镇红港村围垦区域主要受软土固结作用,南沙街道摊位村、地铁4号线锦州站附近受荷载影响较为严重 监测时期内均存在沉降的新垦镇、珠江出海口前沿的养殖场区域主要受软土固结等地质条件影响,拟开发建设用地的工程施工及城镇内的建筑设施都会造成地表形变,并且分布在江河沿岸的大部分形变较大沉降点及其外围区域,在一个水文年内受地下水水位变动较为明显 2016 仅在该年发生的东涌镇、鱼窝头镇、万洲村一带受施工建筑影响,沉降的形变区域较大 2017 沿西南江边分部的养殖场附近受地下水影响发生沉降,大岗镇施工区域受建筑荷载较为严重 2018 南沙街道环市中大道中、金沙路和市南大道三路环绕区域受地面荷载和地下水水位的共同影响 2018—
2019大岗镇庙青村围和珠江街道智隆村的围垦区域、及南沙区中东部城镇建筑区域主要受地面荷载及可压缩土层的影响,少部分区域受地下水水位影响,珠江街道均和围村工地、黄阁村沙仔村施工区域的则主要受可压缩土层影响 表 5 沉降点计算统计信息表
Table 5. Statistical information of settlement point calculation
区域编号 土地利用类型 地处位置 1 出海口养殖场 新垦镇、珠江出海口前沿的养殖场区域 2 城区建筑区域 龙穴街道龙穴村鸡抱沙北路北东方向 3 城区建筑区域 万顷沙镇十三涌和十四涌之间的主镇区 4 施工区域 珠江街道八涌和十涌之间的义和围村 5 城区建筑区域 珠江街五涌周边区域 6 施工区域 南沙明珠湾 表 6 可压缩土层土工试验参数表
Table 6. Geotechnical test parameters of compressible soil
岩性名称 取样埋深/m 初始孔隙比 压缩系数/(MPa−1) 压缩模量/MPa 液限/% 塑限/% 塑性指数 液性指数 人工填土(粉土) 0~9.4 0.890~0.910 0.41~0.51 4.34~4.63 30.00~36.65 21.80~23.25 8.20~13.63 0.71~1.01 淤泥质土 0~25.0 1.038~1.550 0.64~1.03 2.70~3.35 32.40~45.83 17.50~28.48 14.90~18.61 1.27~1.57 黏土(粉质黏土、砂质黏土) 2.8~32.5 0.910~1.210 0.34~0.43 4.83~6.02 41.23~41.31 23.92~24.94 16.33~17.99 0.33~0.41 注:执行标准为GB/T50123−2019、DT−92(固结实验快速法)。 表 7 沉降点主导因素影响程度的沉降量分析表
Table 7. Settlement analysis table of influence degree of dominant factors of settlement point
区域编号 地面沉降总量/(mm·a−1) 可压缩土层/(mm·a−1) 主导因素
面积占比/%地下水水位/(mm·a−1) 主导因素
面积占比/%地面荷载/(mm·a−1) 主导因素
面积占比/%1 112.56~127.03 84.51~95.97 75.43 17.60~19.20 15.24 10.45~11.86 9.32 2 92.9~101.36 34.43~38.26 37.55 13.20~14.64 14.66 43.83~48.70 47.79 3 111.27~121.92 51.17~56.40 46.24 1.28~2.40 1.62 57.70~63.60 52.14 4 91.96~100.02 45.91~51.74 49.74 22.80~24.80 24.85 22.61~25.48 25.40 5 118.96~129.46 55.62~61.50 47.40 9.60~12.00 8.86 51.34~56.76 43.75 6 107.66~117.02 69.76~75.63 64.43 9.40~11.30 9.26 28.50~30.89 26.31 -
[1] 许烨霜, 沈水龙, 唐翠萍, 等. 基于地下水渗流方程的三维地面沉降模型[J]. 岩土力学, 2005, 26(增刊1): 109 − 112
XU Yeshuang, SHEN Shuilong, TANG Cuiping, et al. Three-dimensional analysis of land subsidence based on groundwater flow model[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2005, 26(Sup 1): 109 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 刘桂卫,黄海军,杜廷芹,等. 黄河三角洲地区地面沉降驱动因素研究[J]. 海洋科学,2011,35(8):43 − 50. [LIU Guiwei,HUANG Haijun,DU Tingqin,et al. Effective factors of land subsidence in the Yellow River delta[J]. Marine Sciences,2011,35(8):43 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 彭青华. 沧州市地面沉降模型研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2007
PENG Qinghua. Study on the model of land subsidence in Cangzhou City[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 薛禹群,张云,叶淑君,等. 我国地面沉降若干问题研究[J]. 高校地质学报,2006,12(2):153 − 160. [XUE Yuqun,ZHANG Yun,YE Shujun,et al. Research on the problems of land subsidence in China[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2006,12(2):153 − 160. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2006.02.001
[5] 王伟,党亚民,章传银,等. CORS网和GNSS技术在地面变形监测中的应用—以浙江东南部为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(2):73 − 77. [WANG Wei,DANG Yamin,ZHANG Chuanyin,et al. Application of CORS network and GNSS technology in ground deformation monitoring:Taking southeast Zhejiang Province as an example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(2):73 − 77. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 陈立国,吴昊天,陈晓斌,等. 超载预压处理软土的次固结特征及沉降计算[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):138 − 145. [CHEN Liguo,WU Haotian,CHEN Xiaobin,et al. Secondary consolidation characteristics and settlement calculation of soft soil treated by overload preloading[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):138 − 145. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 胡长明,林成. 黄土深基坑潜水区降水诱发地面沉降的简化算法[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(3):76 − 83. [HU Changming,LIN Cheng. Simplified calculation of settlement due to dewatering of phreatic aquifer in loess area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(3):76 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 张建全,张克利,程贵方. 北京不同区域明挖基坑地表沉降变形特征研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):131 − 139. [ZHANG Jianquan,ZHANG Keli,CHENG Guifang. Characteristics of surface settlement and deformation of open cut foundation pit in different areas of Beijing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):131 − 139. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 许强,董秀军,李为乐. 基于天-空-地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):957 − 966. [XU Qiang,DONG Xiujun,LI Weile. Integrated space-air-ground early detection,monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):957 − 966. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 吴龙飞,陈凌伟,彭卫平. PSInSAR技术在广州市南沙区地面沉降监测中的应用研究[J]. 城市勘测,2019(3):127 − 130. [WU Longfei,CHEN Lingwei,PENG Weiping. Research of PSInSAR technology in land subsidence monitoring in Nansha of Guangzhou[J]. Urban Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2019(3):127 − 130. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8262.2019.03.029
[11] 陈玉林,匡翠林,戴吾蛟,等. 广州南沙区GPS地面沉降监测数据处理[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,2015,35(5):849 − 852. [CHEN Yulin,KUANG Cuilin,DAI Wujiao,et al. Land subsidence monitoring using GPS network in Nansha,Guangzhou[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,2015,35(5):849 − 852. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 高磊, 陈运坤, 屈尚侠, 等. 广州南沙区软土地面沉降特征及监测预警分析[J]. 人民长江, 2020, 51(增刊2): 94 − 97
GAO Lei, CHEN Yunkun, QU Shangxia, et al. Analysis on land subsidence characteristics, monitoring and early warning of soft soil in Nansha District of Guangzhou[J]. Yangtze River, 2020, 51(Sup 2): 94 − 97. (in Chinese)
[13] 张德波. 广州市南沙区地面沉降易发性评价[J]. 中外建筑,2018(8):252 − 255. [ZHANG Debo. Susceptibility evaluation of ground subsidence in Nansha District in Guangzhou[J]. Chinese & Overseas Architecture,2018(8):252 − 255. (in Chinese)
[14] 陈小月. 广州市南沙区软土地面沉降特征及城市防灾减灾的建议[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,2018,29(2):17 − 22. [CHEN Xiaoyue. Ground subsidence characteristics of soft soil in Nansha District of Guangzhou City and the suggestions for disaster prevention and reduction in urban development[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,2018,29(2):17 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 陈运坤,高磊,屈尚侠. 广州南沙区软土分布和地面沉降特征分析[J]. 资源信息与工程,2021,36(2):19 − 21. [CHEN Yunkun,GAO Lei,QU Shangxia. Study on soft soil distribution and land subsidence features in Nansha District,Guangzhou[J]. Resource Information and Engineering,2021,36(2):19 − 21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 介玉新,高燕,李广信. 城市建设对地面沉降影响的原因分析[J]. 岩土工程技术,2007,21(2):78 − 82. [JIE Yuxin,GAO Yan,LI Guangxin. Analysis on the land subsidence induced by city construction[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique,2007,21(2):78 − 82. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 孟世豪,崔亚莉,田芳,等. 基于MODFLOW-SUB建立变渗透系数的地下水流-地面沉降模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2022,52(2):550 − 559. [MENG Shihao,CUI Yali,TIAN Fang,et al. Modeling of groundwater flow-land subsidence with variable hydraulic conductivity based on MODFLOW-SUB[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2022,52(2):550 − 559. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: