Spatial-temporal evolution characteristics of land subsidence in Dongguan City based on improved InSAR technology
-
摘要:
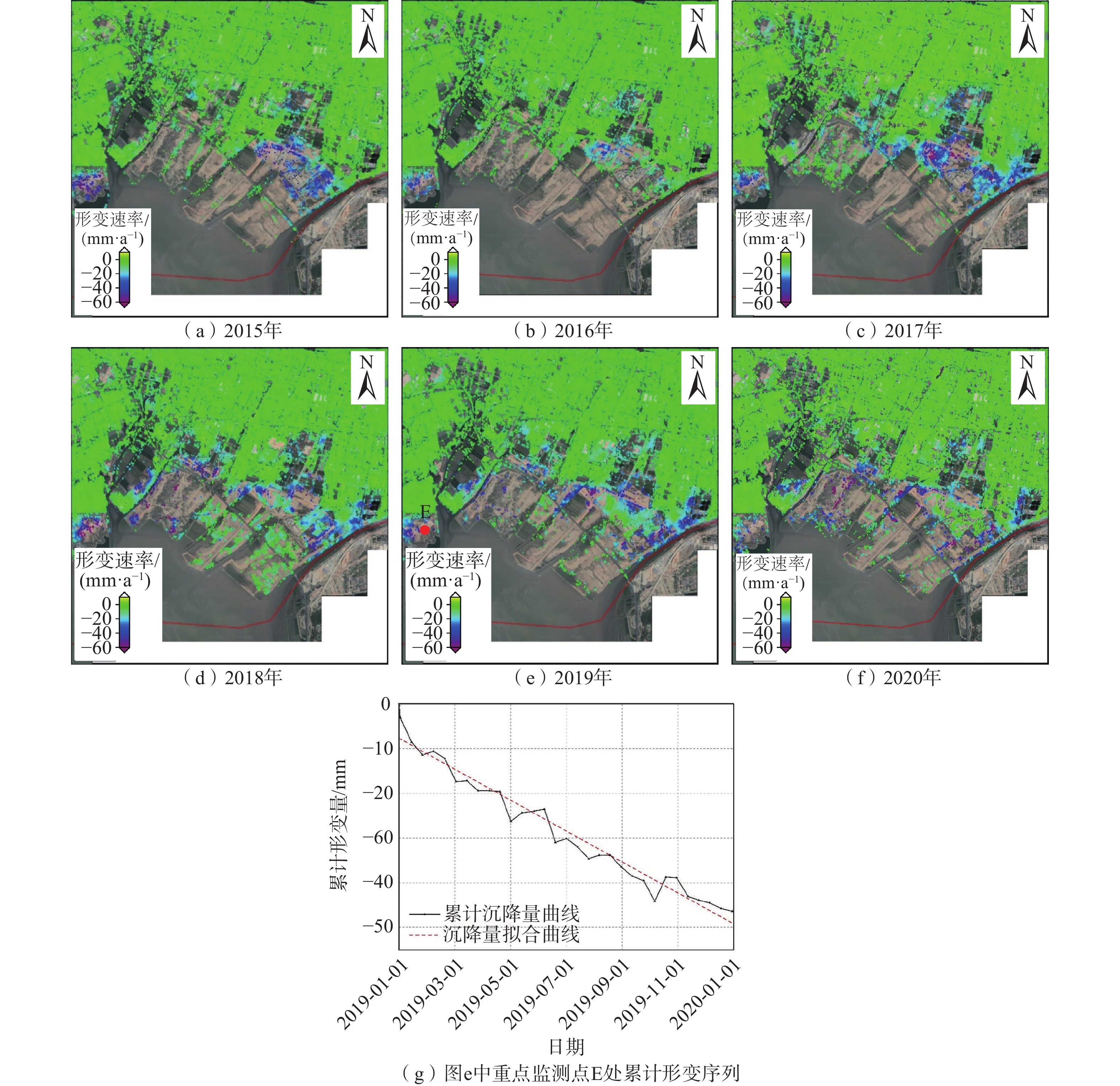
东莞市是珠三角城市群和粤港澳大湾区的重要节点城市,深厚欠固结软弱土及其诱发的地面沉降已成为湾区内代表性的区域地质灾害问题,影响城市地质环境安全。为研究东莞市地面沉降发育规律及时空演变特征,采用改进时序InSAR技术对覆盖东莞地区的137景Sentinel-1 SLC SAR影像数据进行处理,分析了2015年6月至2020年6月地表形变动态演化规律。结果表明:(1)全域内地表沉降变形整体较稳定,沉降发育区占市域面积的34.6%,变形严重发育区主要集中在麻涌镇、道滘镇、洪梅镇、中堂镇、沙田镇及滨海湾新区;(2)大部分沉降变形点处于缓慢发展变形阶段,年平均沉降速率在20 mm/a以内,累计沉降量在1000 mm以内;(3)结合形变监测和现场调查,认为地面沉降与深厚软土发育和人类工程活动的耦合作用有很强的相关性。证明该方法能较好地识别和反映城市复杂形态区地面沉降发育的时空演化特征,为灾害预警、减避及治理提供技术支持。
-
关键词:
- 粤港澳大湾区 /
- 地面沉降 /
- PS-InSAR /
- SBAS-InSAR /
- 时序形变
Abstract:Dongguan City is an important city of Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration and Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Deep unconsolidated soft soil and its land subsidence have become a representative regional geological disaster in the Bay area, affecting the safety of urban geological environment. In order to study the development features and spatial-temporal evolution characteristics of land subsidence in Dongguan City, 137 sentinel-1 SLC SAR images covering whole Dongguan City were processed by improved InSAR technology, and the dynamic evolution characteristics of land deformation from June 2015 to June 2020 was analyzed. The results show that: (1) The land surface subsidence and deformation are stable in the whole region, and the subsidence developing areas account for 34.6% of the total urban area. The serious subsidence areas are mainly concentrated in Mayong Town, Daojiao Town, Hongmei Town, Zhongtang Town, Shatian Town and Binhai Bay New Area. (2) Most of the subsidence points are in the slow developing stage, the annual average subsidence rate is within 20 mm/yr, and the accumulated settlement is less than 1000 mm. (3) Combined with deformation monitor results and field investigation, land subsidence hazard has a great correlation with the coupling effect of deep soft soil development and human engineering activities. This method can better identify and reflect the temporal and spatial evolution characteristics of soft land subsidence development in urban area, and provide technical support for disaster early warning, mitigation and management.
-

-
表 1 Sentinel-1卫星数据参数表
Table 1. Parameters of Sentinel-1 satellite
Sentinel-1 参数值 轨道高度/km 700 重返周期/d 12 入射角/(°) 29~46 分辨率 5 m×20 m 幅宽/km 250 极化方式 HH+HV、VH+VV、HH、VV 影像时间 2015年6月15日—2020年6月12日 影像数量/景 137 表 2 东莞市沉降速率统计表
Table 2. Statistics data of annual average subsiding rate
发育程度 年均形变速率/(mm·a−1) 分布面积/km2 2015年 2016年 2017年 2018年 2019年 2020年 平均值 弱发育 0~−10 2444.27 2453.04 2444.70 2409.44 2413.01 2429.43 2432.31 中等发育 −20~−10 13.70 6.41 11.76 45.35 42.83 26.59 24.44 −30~−20 1.46 0.53 2.47 4.17 3.08 2.66 2.40 强发育 −40~−30 0.51 0.11 0.80 0.80 0.79 0.82 0.64 −40及以上 0.16 0.01 0.37 0.34 0.39 0.60 0.31 -
[1] 葛伟丽,李元杰,张春明,等. 基于InSAR技术的内蒙古巴彦淖尔市地面沉降演化特征及成因分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(4):198 − 206. [GE Weili,LI Yuanjie,ZHANG Chunming,et al. An attribution analysis of land subsidence features in the city of Bayannur in InnerMongolia based on InSAR[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(4):198 − 206. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 王双,严学新,揭江,等. 珠三角平原区软土分布与地面沉降相关性分析[J]. 上海国土资源,2019,40(2):75 − 79. [WANG Shuang,YAN Xuexin,JIE Jiang,et al. Correlation analysis between soft soil distribution and land subsidence in the Pearl River Delta Plain[J]. Shanghai Land & Resources,2019,40(2):75 − 79. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2019.02.015
[3] 姚佳明,姚鑫,陈剑,等. 基于InSAR技术的缓倾煤层开采诱发顺层岩体地表变形模式研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):135 − 146. [YAO Jiaming,YAO Xin,CHEN Jian,et al. A study of deformation mode and formation mechanism of a bedding landslide induced by mining of gently inclined coal seam based on InSAR technology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):135 − 146. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 张凯翔. 基于“3S”技术的地质灾害监测预警系统在我国应用现状[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(6):1 − 11. [ZHANG Kaixiang. Review on geological disaster monitoring and early warning system based on “3S” technology in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(6):1 − 11. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.06.01
[5] 潘光永,陶秋香,陈洋,等. 基于SBAS-InSAR的山东济阳矿区沉降监测与分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(4):100 − 106. [PAN Guangyong,TAO Qiuxiang,CHEN Yang,et al. Monitoring and analysis of sedimentation in Jiyang mining area of Shandong Province based on SBAS-InSAR[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(4):100 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] FERRETTI A,PRATI C,ROCCA F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2000,38(5):2202 − 2212. doi: 10.1109/36.868878
[7] FERRETTI A, PRATI C, ROCCA F L. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry[C]//Remote Sensing. Proc SPIE 3869, SAR Image Analysis, Modeling, and Techniques II, Florence, Italy. 1999, 3869: 139 − 145.
[8] BERARDINO P,FORNARO G,LANARI R,et al. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2002,40(11):2375 − 2383. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.803792
[9] 姜兆英,于胜文,陶秋香. StaMPS-MTI技术在地面沉降监测中的应用[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2017,52(2):295 − 302. [JIANG Zhaoying,YU Shengwen,TAO Qiuxiang. Application of StaMPS-MTI technology in monitoring ground subsidence[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University,2017,52(2):295 − 302. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.02.012
[10] 孔祥如,罗勇,刘贺,等. PS-InSAR技术在北京通州区地面沉降监测中的应用[J]. 城市地质,2021,16(1):25 − 31. [KONG Xiangru,LUO Yong,LIU He,et al. Application of PS-InSAR technology in the land subsidence survey in Tongzhou District,Beijing[J]. Urban Geology,2021,16(1):25 − 31. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2021.01.004
[11] 晏霞,刘媛媛,赵振宇. 利用时序InSAR技术监测南水进京后北京平原地区的地面沉降[J]. 地球物理学进展,2021,36(6):2351 − 2361. [YAN Xia,LIU Yuanyuan,ZHAO Zhenyu. Land subsidence monitoring after the start of the South to North Water Transfer in the Beijing plain based on multi-temporal InSAR[J]. Progress in Geophysics,2021,36(6):2351 − 2361. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 狄桂栓. 基于InSAR技术的黄河三角洲区域地表形变浅析[J]. 地理空间信息,2020,18(9):106 − 109. [DI Guishuan. Primary investigation of surface deformation in the Yellow River Delta based on InSAR technology[J]. Geospatial Information,2020,18(9):106 − 109. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4623.2020.09.027
[13] 张宏雪,曾润强,孙萍萍,等. 基于SBAS-InSAR的延安新区地表沉降监测与分析[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2021,57(2):185 − 193. [ZHANG Hongxue,ZENG Runqiang,SUN Pingping,et al. Surface subsidence monitoring and analysis in Yan'an New District based on SBAS-InSAR[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),2021,57(2):185 − 193. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 蒲川豪,许强,蒋亚楠,等. 延安新区地面沉降分布及影响因素的时序InSAR监测分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2020,45(11):1728 − 1738. [PU Chuanhao,XU Qiang,JIANG Yanan,et al. Analysis of land subsidence distribution and influencing factors in Yan'an new district based on time series InSAR[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2020,45(11):1728 − 1738. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20190372
[15] 冉培廉,李少达,杨晓霞,等. 基于SBAS-InSAR技术的西安市地面沉降监测[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,40(3):66 − 74. [RAN Peilian,LI Shaoda,YANG Xiaoxia,et al. Monitoring of Xi'an City land subsidence based on SBAS-InSAR[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Natural Science),2021,40(3):66 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 范军,左小清,李涛,等. PS-InSAR和SBAS-InSAR技术对昆明主城区地面沉降监测的对比分析[J]. 测绘工程,2018,27(6):50 − 58. [FAN Jun,ZUO Xiaoqing,LI Tao,et al. Analysis and comparison of PS-InSAR and SBAS-InSAR for ground subsidence monitoring in the main city of Kunming[J]. Engineering of Surveying and Mapping,2018,27(6):50 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19349/j.cnki.issn1006-7949.2018.06.010
[17] 周书东, 张益. 东莞市工程地质特征及常见工程问题[J]. 现代隧道技术, 2020, 57(增刊1): 78 − 88
ZHOU Shudong, ZHANG Yi. Engineering geological characteristics and common engineering issues in Dongguan City[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2020, 57(Sup 1): 78 − 88. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 黄建龙,刘亦农,曾伟国. 粤港澳大湾区地质特点与地质环境保护策略分析[J]. 人民珠江,2019,40(9):103 − 109. [HUANG Janlong,LIU Yinong,ZENG Weiguo. Analysis of geological characteristics and geological environment protection in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area[J]. Pearl River,2019,40(9):103 − 109. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9235.2019.09.015
[19] 杨魁,杨建兵,江冰茹. Sentinel-1卫星综述[J]. 城市勘测,2015(2):24 − 27. [YANG Kui,YANG Jianbing,JIANG Bingru. Sentinel-1 satellite overview[J]. Urban Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2015(2):24 − 27. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8262.2015.02.006
[20] 刘琦,岳国森,丁孝兵,等. 佛山地铁沿线时序InSAR形变时空特征分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):1099 − 1106. [LIU Qi,YUE Guosen,DING Xiaobing,et al. Temporal and spatial characteristics analysis of deformation along Foshan subway using time series InSAR[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):1099 − 1106. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20190025
[21] 伍素贞,谢荣安,谢文珠,等. 时序InSAR 2018—2019年广州市南沙区形变监测与分析[J]. 工程勘察,2020,48(8):48 − 52. [WU Suzhen,XIE Rongan,XIE Wenzhu,et al. Ground subsidence monitoring in Nansha District by using Sentinel 1A/B SAR images[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2020,48(8):48 − 52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 梁景才. 雷州半岛地区InSAR时序形变监测与分析[J]. 地矿测绘,2020,36(4):21 − 26. [LIANG Jingcai. InSAR time series deformation monitoring and analysis in Leizhou peninsula[J]. Surveying and Mapping of Geology and Mineral Resources,2020,36(4):21 − 26. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9394.2020.04.006
[23] 谢思梅,吴曼乔,钟惠润. 短基线集技术(SBAS)在南沙自贸区地面沉降监测中的应用研究[J]. 信息技术与信息化,2020(8):136 − 138. [XIE Simei,WU Manqiao,ZHONG Huirun. Application of short baseline set technique (SBAS) in land subsidence monitoring in Nansha free trade zone[J]. Information Technology and Informatization,2020(8):136 − 138. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9528.2020.08.044
[24] 贾会会,张海清,李克达,等. 融合分布式散射体时序InSAR技术在矿区形变调查中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2022,52(1):202 − 213. [JIA Huihui, ZHANG Haiqing, LI Keda, et al. Application of fusion distributed scatterer time-series InSAR technique in deformation survey of mining area[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2022,52(1):202 − 213. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: