Influence of trees and shrubs on the stability of landslides induced by typhoon rainstorm
-
摘要:
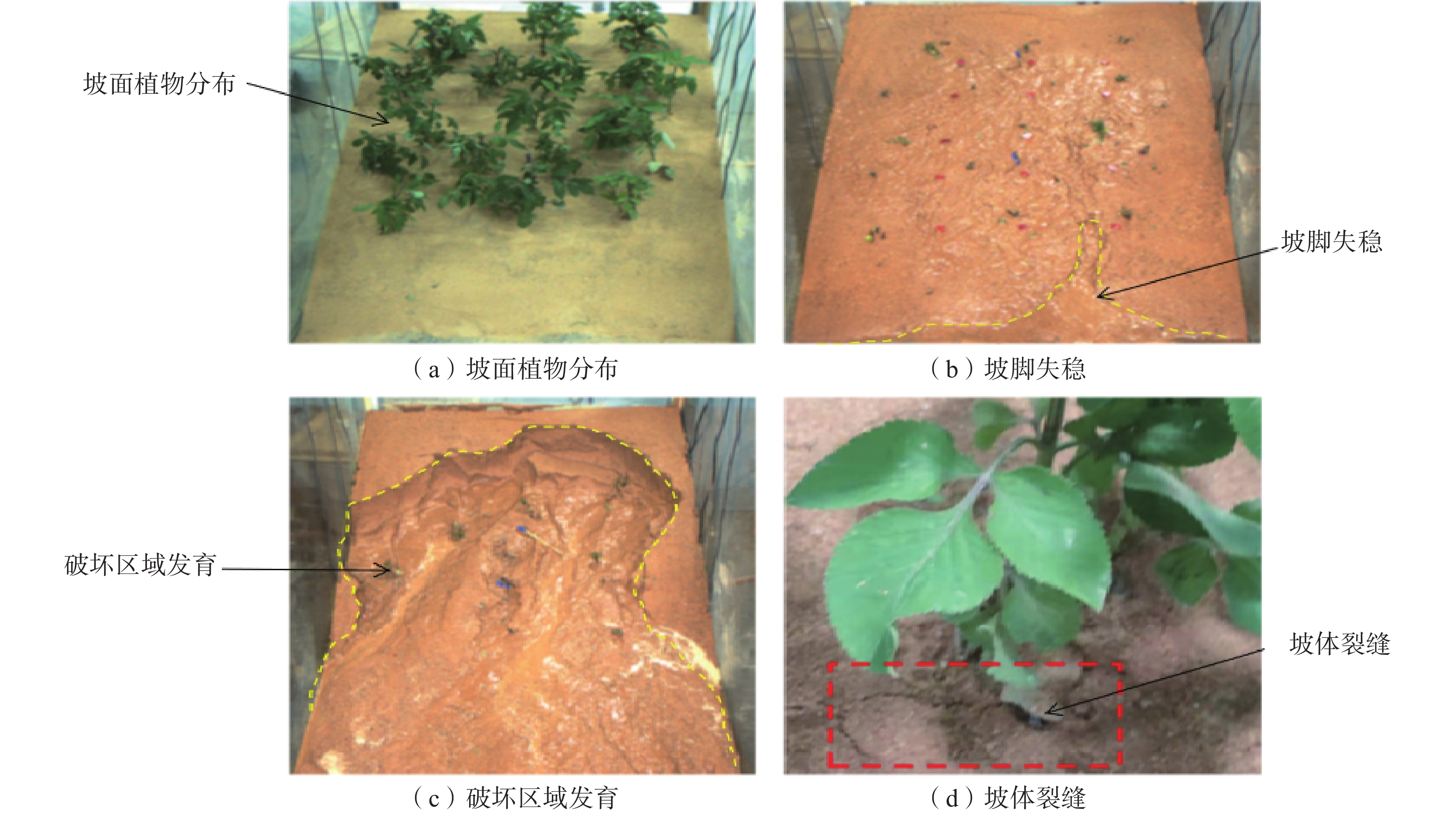
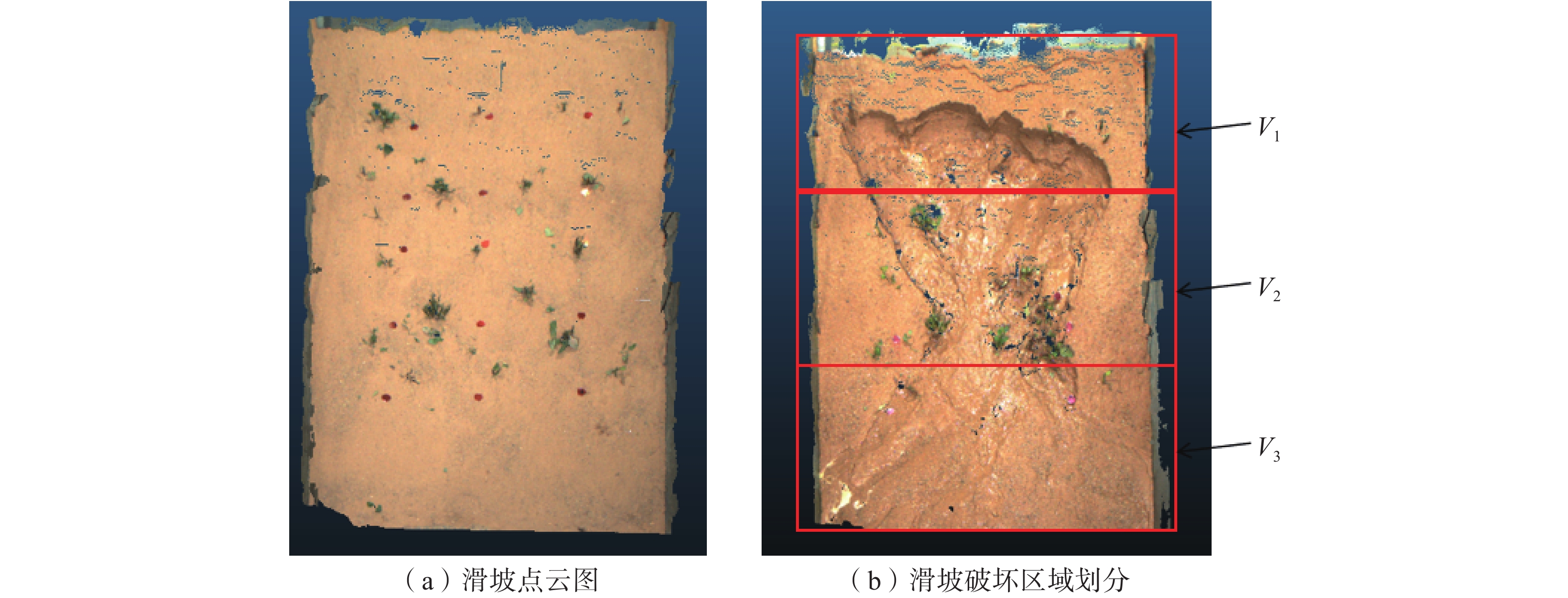
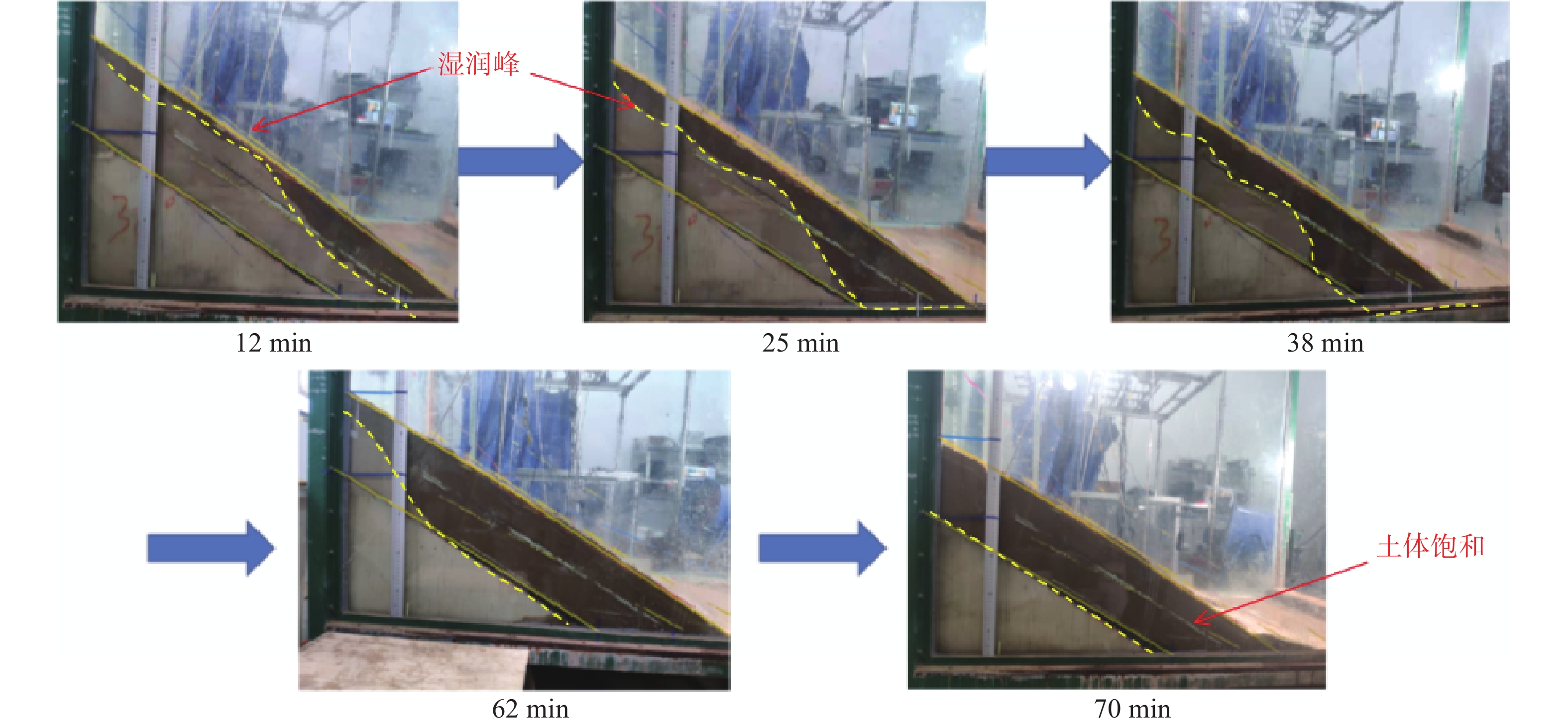
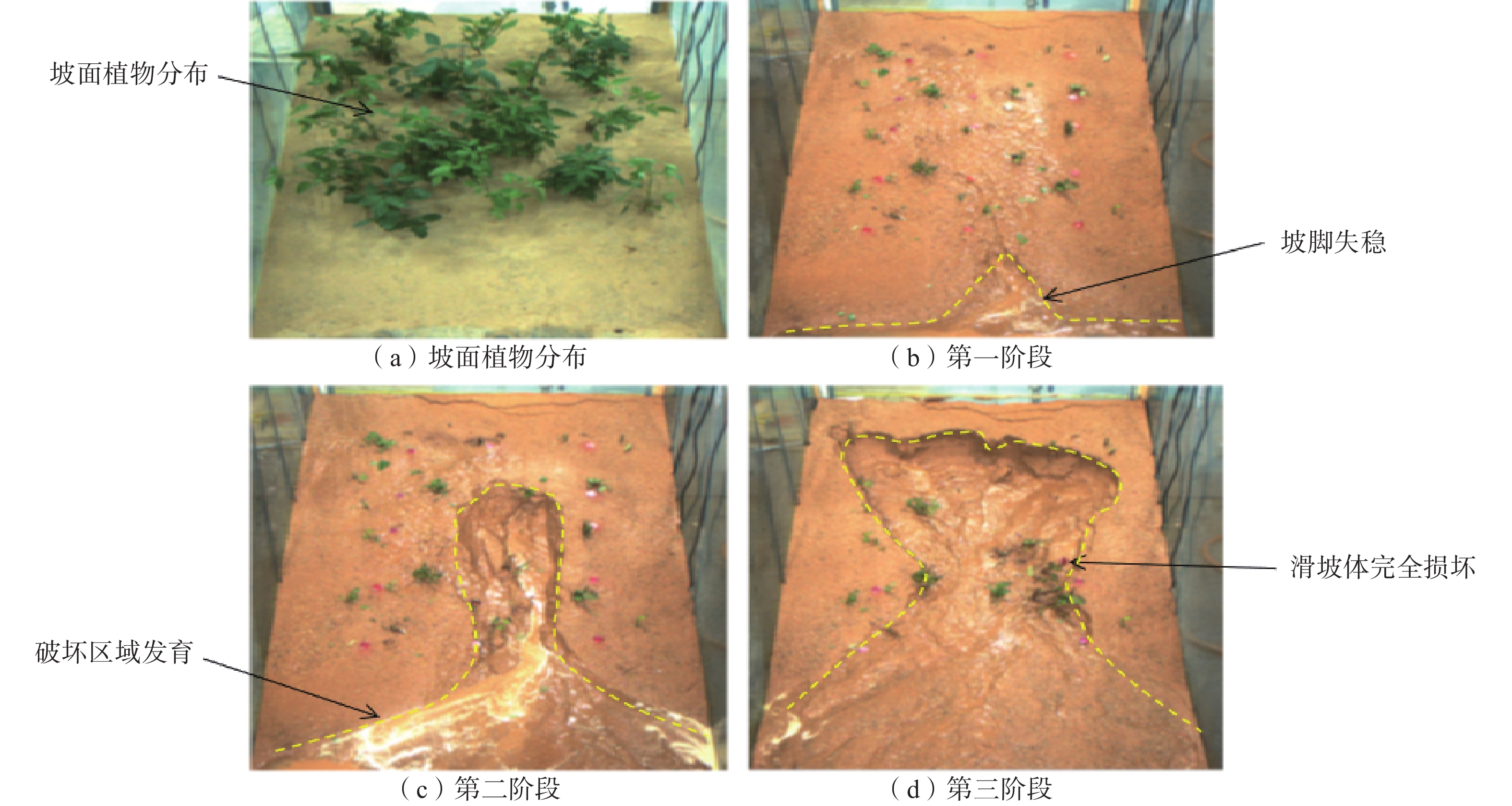
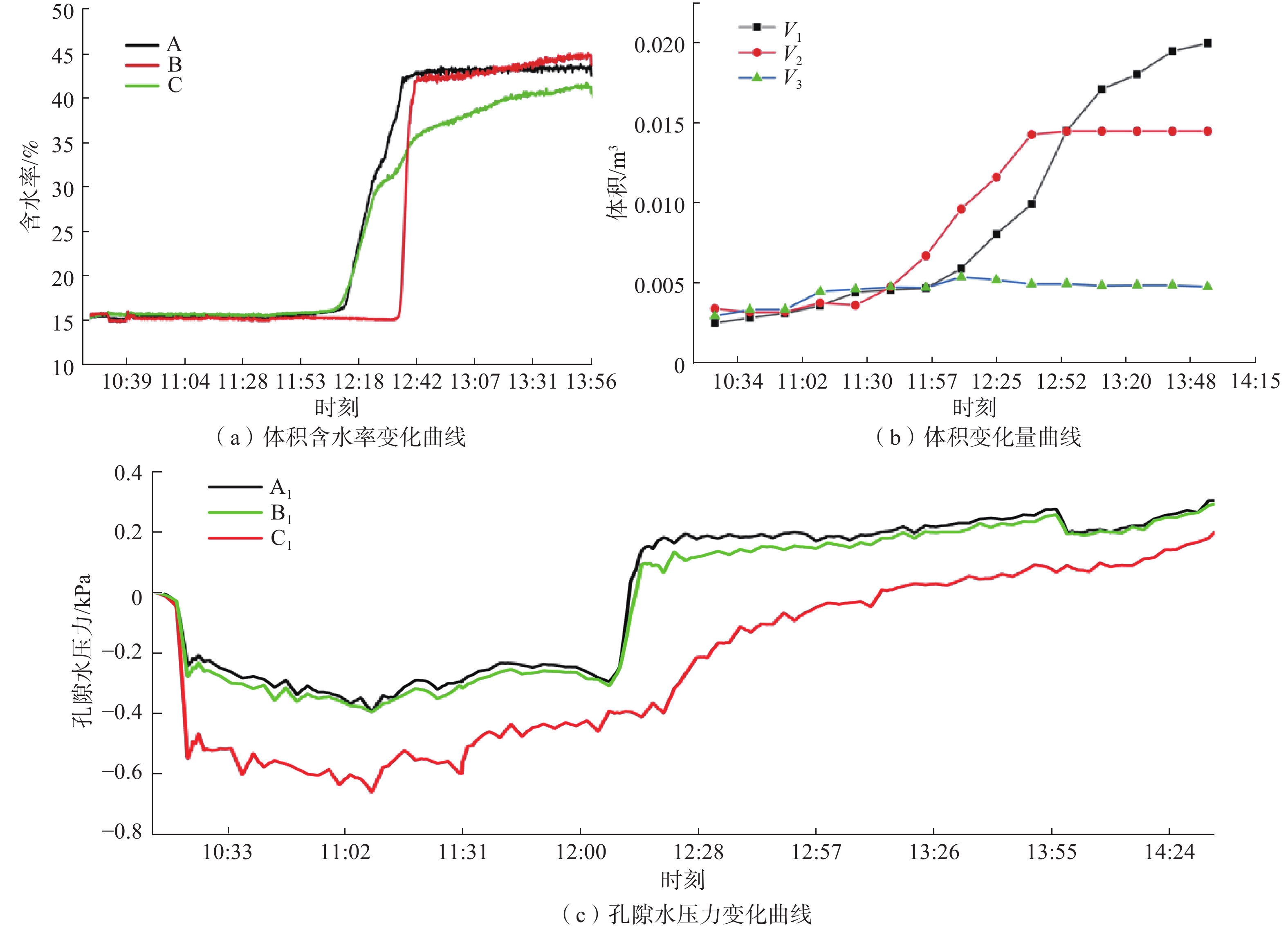
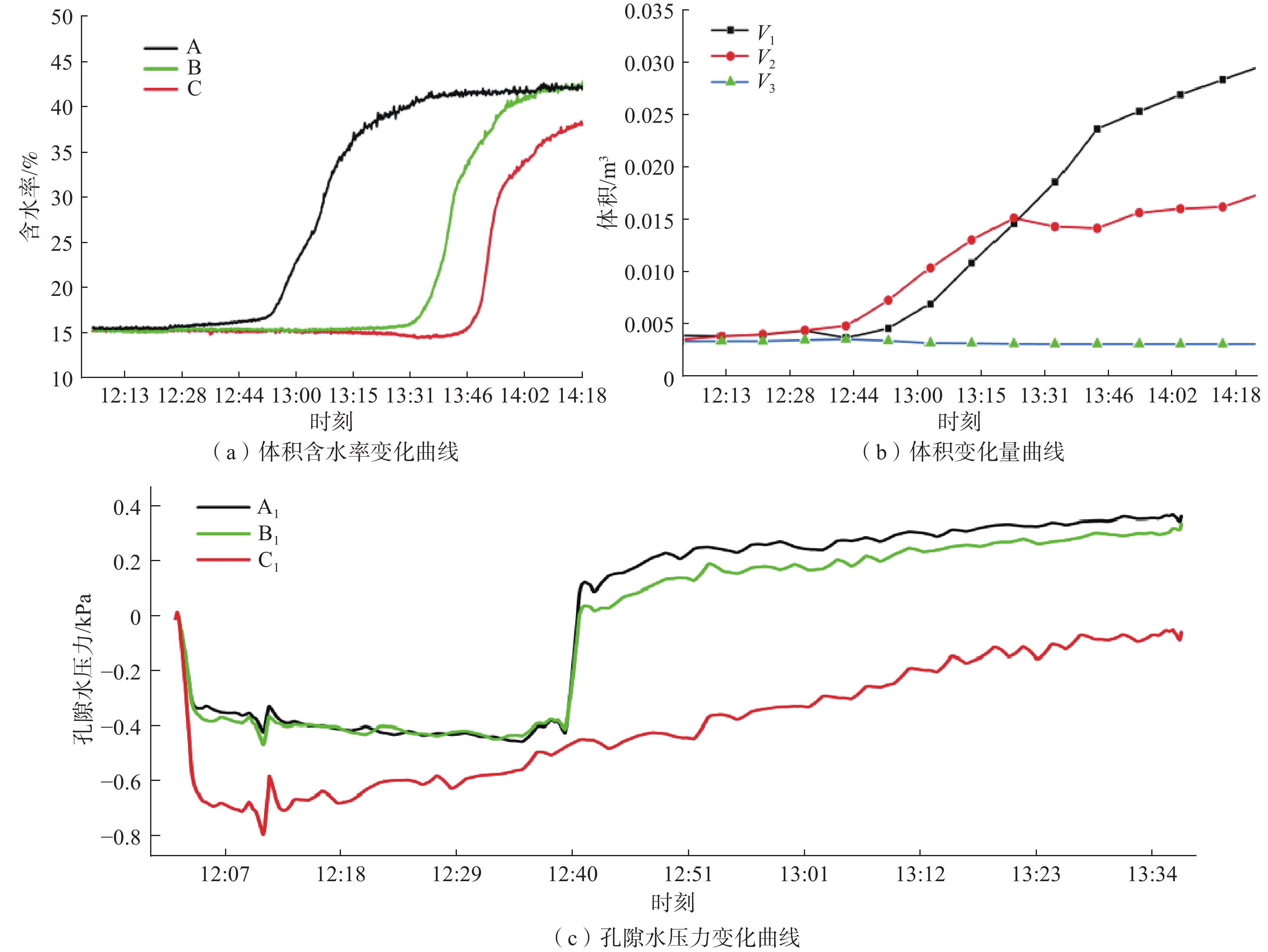
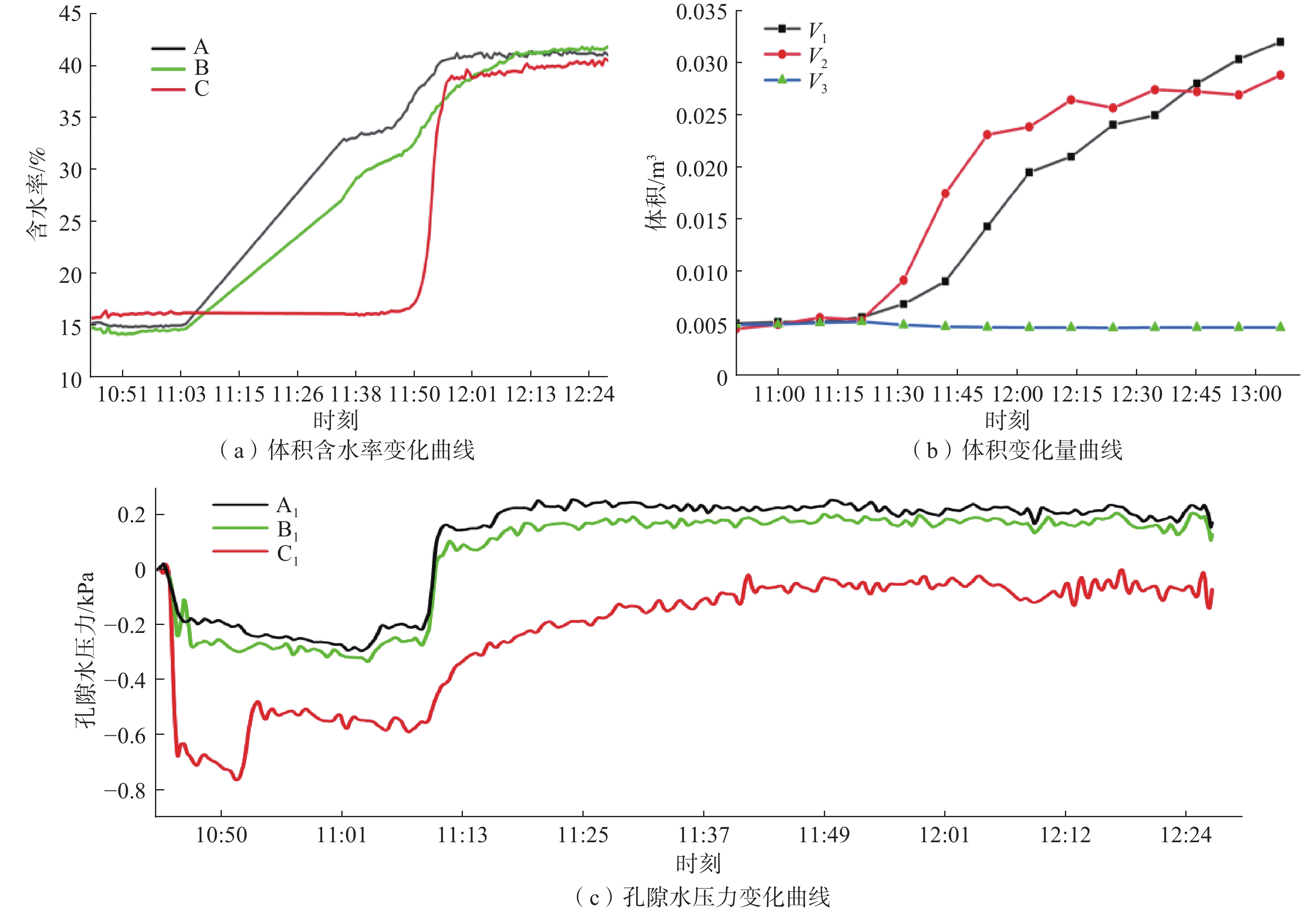
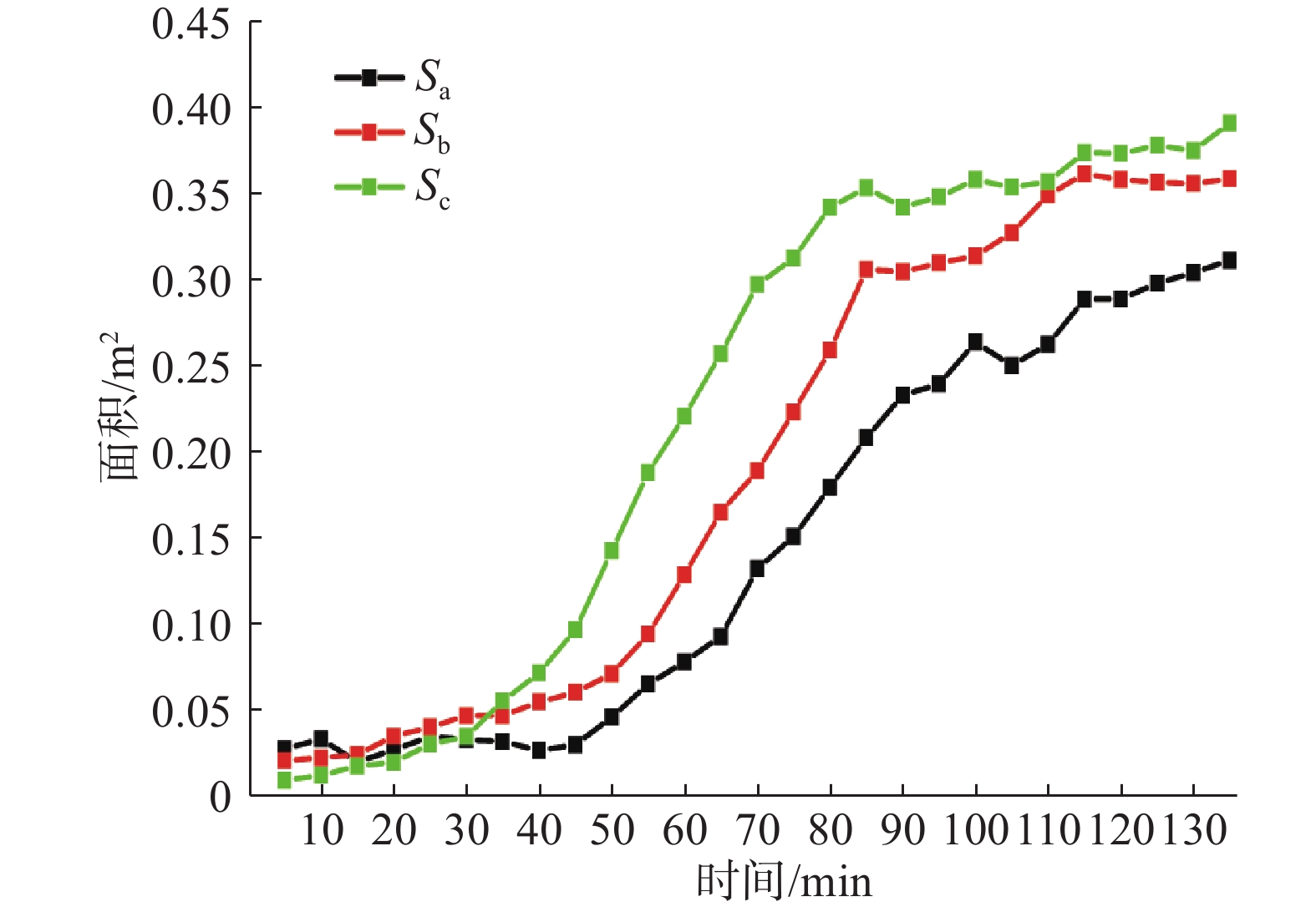
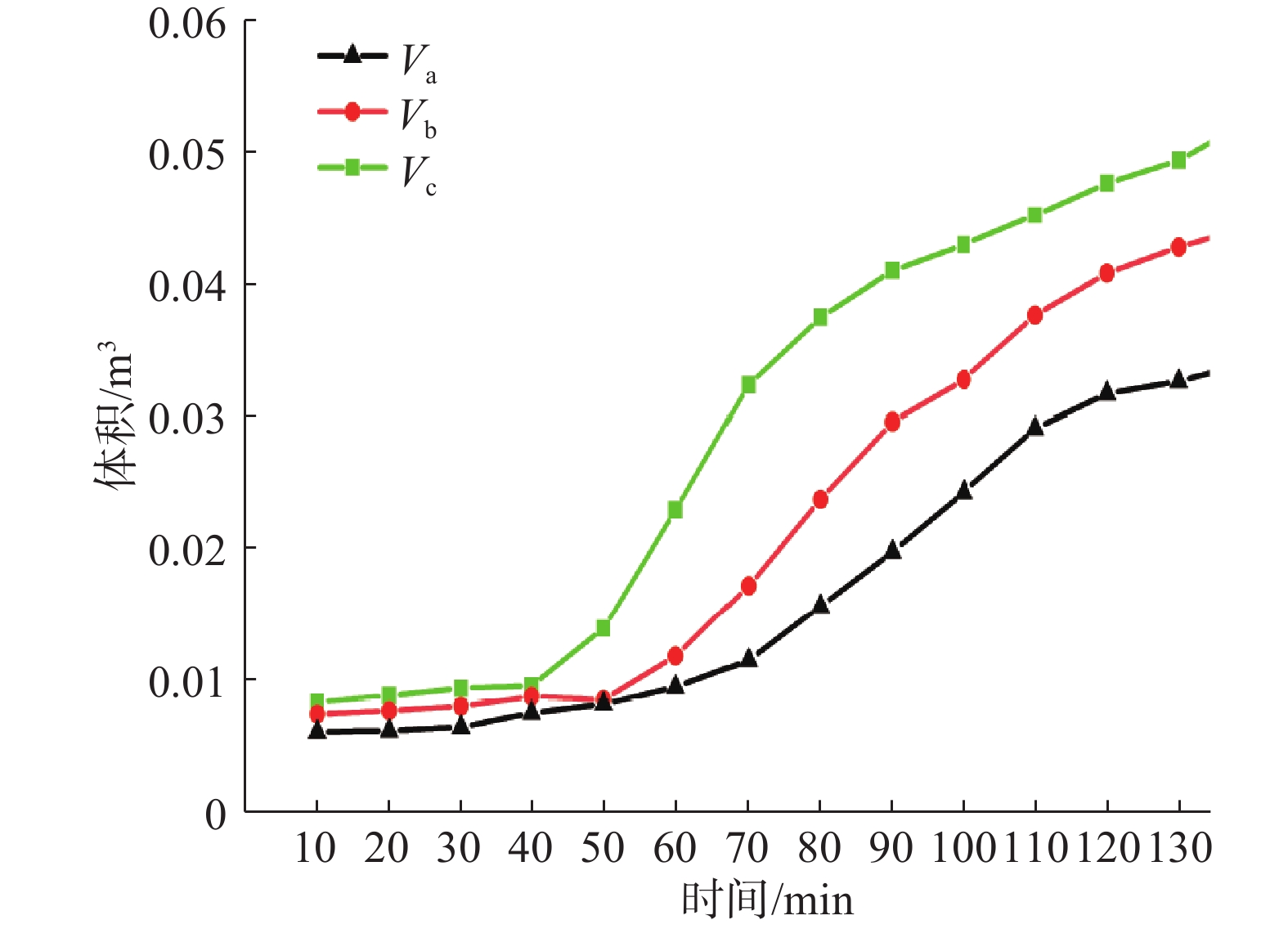
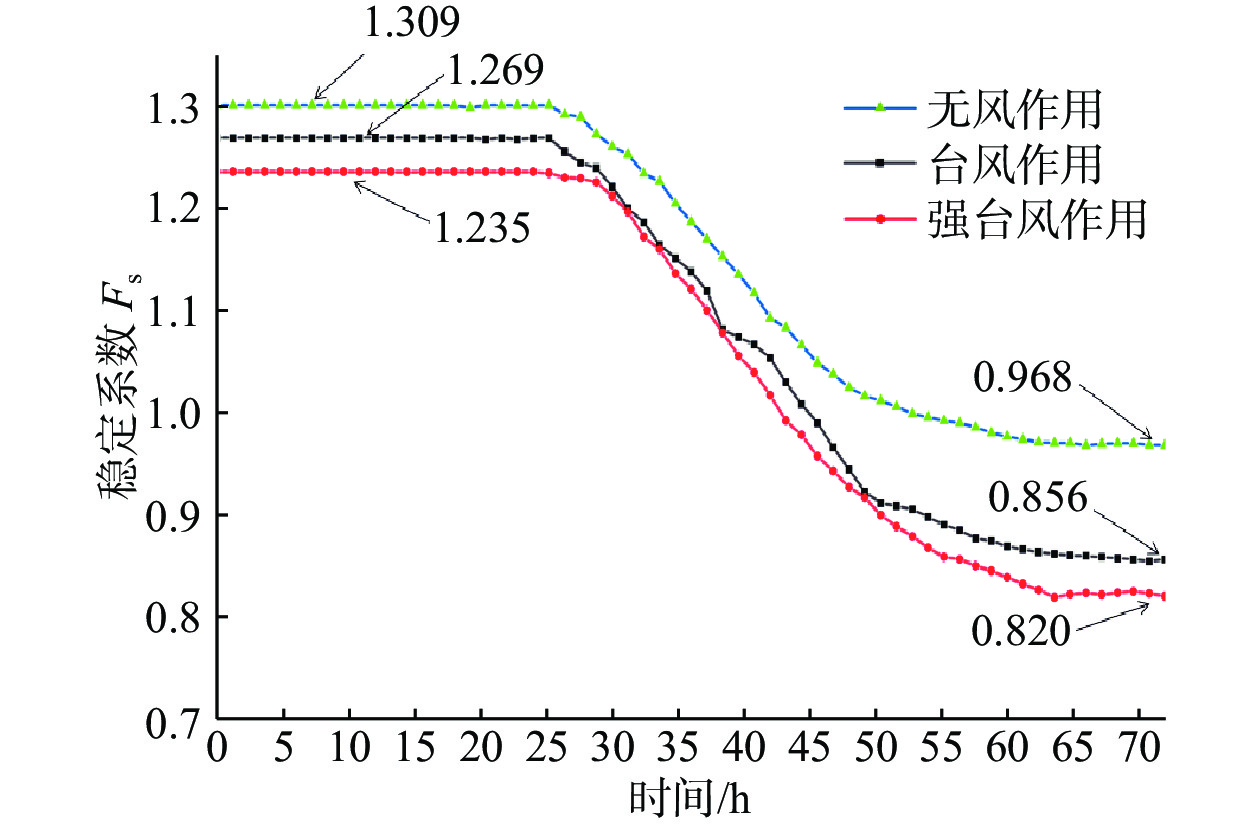
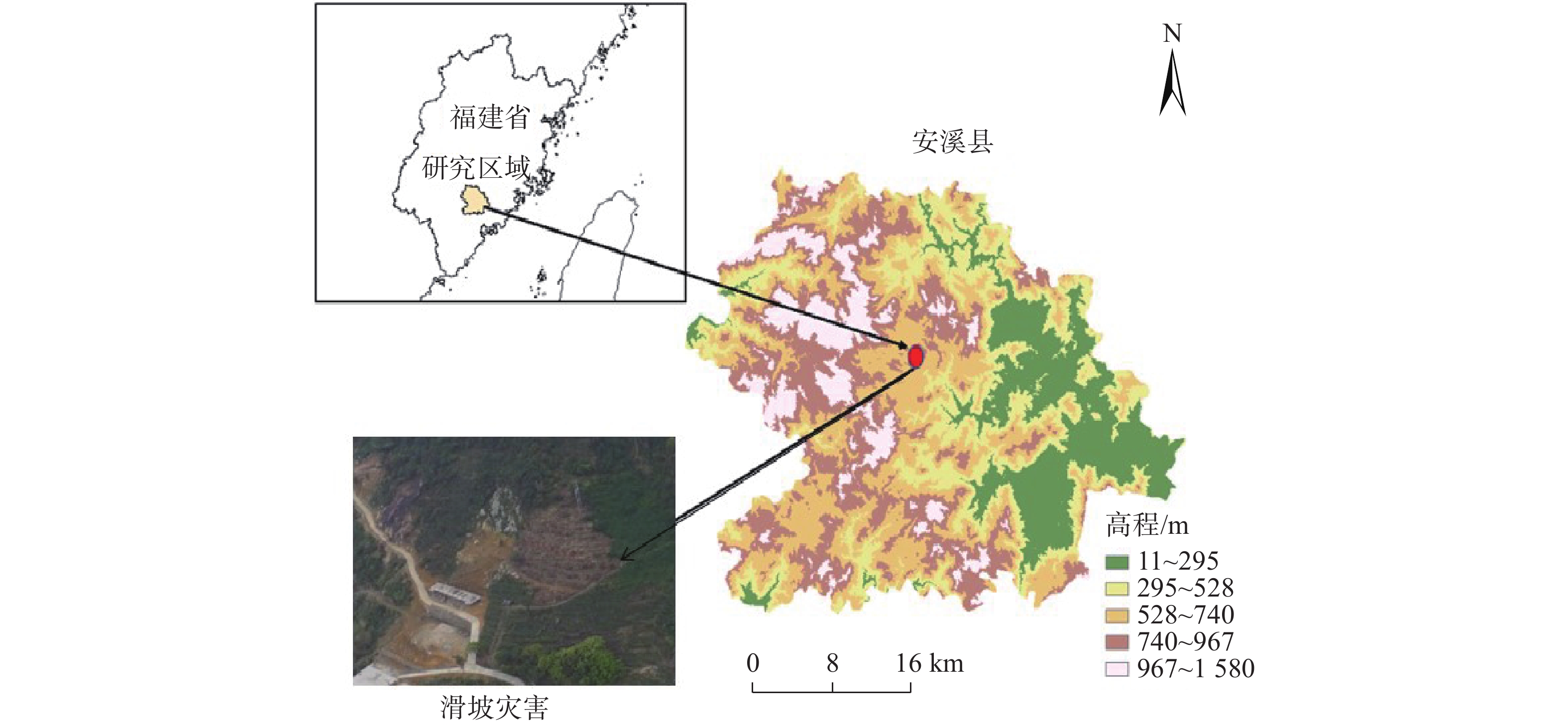
在降雨工况下,乔灌木通过其根系对边坡体的加筋锚固和茎叶减少坡体被雨水冲刷,对边坡稳定性产生了积极作用。然而台风暴雨季节,台风又通过植被的摇曳使地表开裂,强化了降雨入渗效果,进一步使土体的基质吸力、黏聚力下降,使边坡的稳定性降低。为了探索台风暴雨季节乔灌木对边坡起到正向作用还是反向作用,文章通过室内模型试验和数值模拟进行量化分析,比较有无台风作用和不同强度台风作用对边坡稳定性的影响。结果表明:随着台风从无到有、由弱变强的过程中,边坡体内孔隙水压力和含水率发生突变的时间不断提前;同时施加台风暴雨耦合作用的滑坡相对于单纯降雨作用的滑坡,其滑坡破坏的面积与体积更大,且台风等级越强,坡体的破坏的面积体积区域越大。通过Geo-studio数值模拟软件进行验证,比较模拟边坡的稳定性发现:在无台风作用下初始稳定性系数最大且下降速度最慢,台风作用次之,强台风作用下最差。
Abstract:Under the condition of rainfall, trees and shrubs’ leaves can reduce the slope being washed and anchoring the slope by their roots, which had a positive effect on the slope stability. However, in typhoon rainstorm season, typhoon cracks the ground through swaying vegetation, strengthens the effect of rainfall infiltration, and further reduces the matrix suction and cohesion of soil, to reduce the stability of slope. In order to explore whether trees and shrubs have a positive or negative effect on slope during typhoon rainstorm season, this paper conducted quantitative analysis through indoor model experiment and numerical simulation, comparing the influence of no typhoon, typhoon and typhoon with different intensity on slope stability. It was found that the abrupt change time of pore water pressure curve and water content curve was advanced with the typhoon developing from nothing and becoming stronger from weak. At the same time, the effect of landslide with typhoon coupled rainstorm compared the simple rainfall, the area and volume of landslide damage were larger, and the stronger the typhoon grade was, the larger the area and volume of landslide damage were.Compared the stability coefficient of simulated slope by Geo-Studio numerical simulation software verifying, the initial stability coefficient was the largest and the decline speed was the slowest under the effect of no typhoon, the typhoon was bad and under the strong typhoon condition was the worst.
-
Key words:
- typhoon rainstorm /
- Anxi County /
- landslide /
- trees /
- landslide identification /
- safety margin
-

-
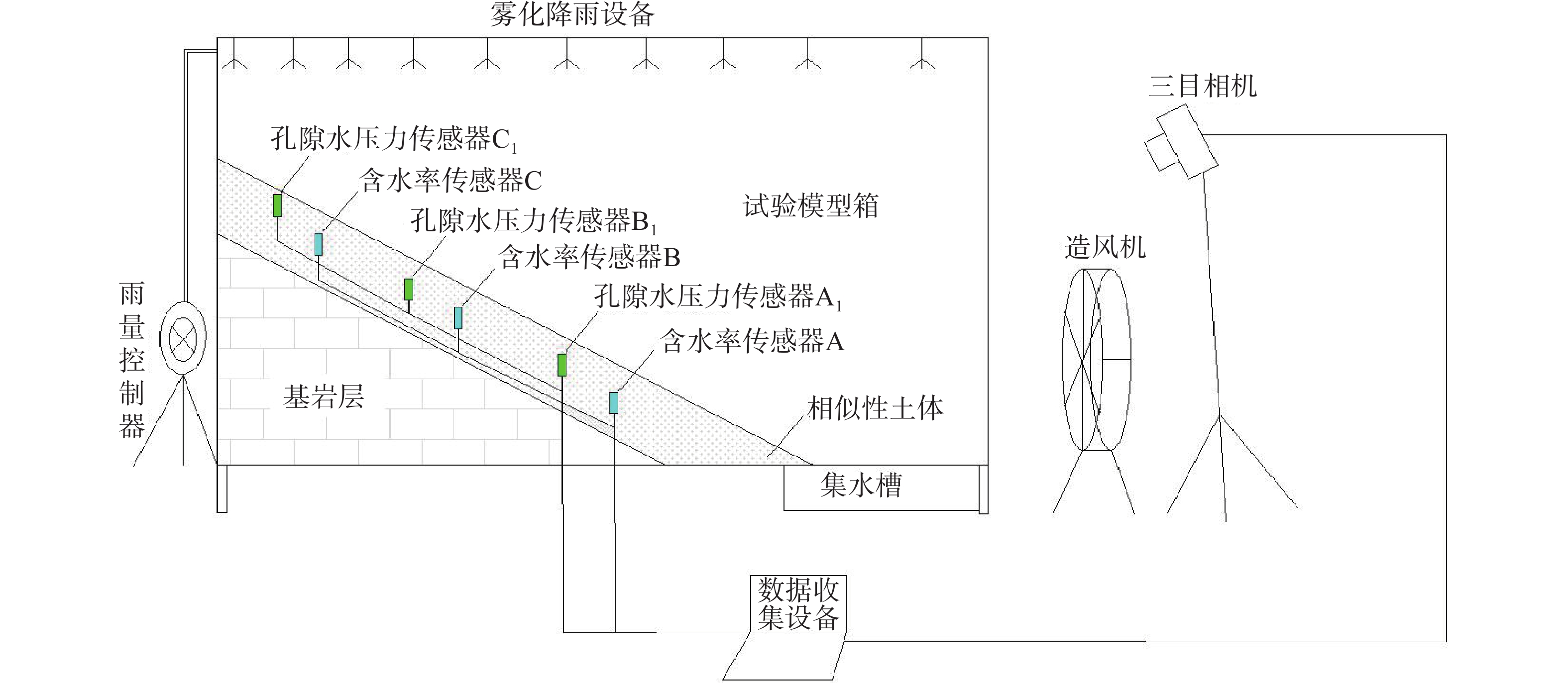
表 1 岩土力学参数
Table 1. The geotechnical mechanical parameters
岩石性质 重度
/(kN·m−1)抗剪强度 渗透系数
/(cm·s−1)泊松比 杨氏模量
/kPa黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 坡积土 18.5 14.5 27.8 1.5×10−4 0.32 5.1×103 残积土 17.7 17.0 26.2 1.01×10−5 0.41 3.2×103 强风化凝灰岩 21.0 35.0 32.0 7.52×10−5 0.28 4.2×104 中风化凝灰岩 23.0 70.0 35.0 − 0.25 1.5×106 表 2 材料参数对比
Table 2. Comparison of material parameters
物理力学参数 原型材料 相似材料 重度/(g·cm−3) 1.77~1.85 1.84 渗透系数/(cm·s−1) 1.01×10−5 ~1.5×10−4 8.5×10−4 黏聚力/kPa 14.5~17.0 4.5 内摩擦角/(°) 26.2~27.8 30.2 表 3 试验工况参数
Table 3. Parameters of experimental conditions
工况 降雨强度
/(mm·h−1)风速
/(m·s−1)降雨持续时间
/h风力持续时间
/min植被情况 Ⅰ 60 0 3 45 接骨木 Ⅱ 60 5.6~5.8 3 45 接骨木 Ⅲ 60 7.3~7.6 3 45 接骨木 -
[1] 2020全国地质灾害灾情2021年趋势预测[R]. 自然资源部. 2021
Trend prediction of national geological disasters in 2020 and 2021[R]. Ministry of Natural Resources. 2021. (in Chinese)
[2] 陈香,陈静. 福建台风灾害风险分布的初步估计[J]. 自然灾害学报,2007,16(3):18 − 23. [CHEN Xiang,CHEN Jing. Preliminary estimation of risk distribution of typhoon disaster in Fujian[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2007,16(3):18 − 23. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2007.03.004
[3] 庄希澄. 福建省台风暴雨特性分析[J]. 水资源研究, 2005, (1): 31 − 32
ZHUANG Xicheng. Characteristic analysis of typhoon and rainstorm in Fujian Province [J]. Study on Water Resources, 2005, (1): 31 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 黄俊宝. 闽东南台风暴雨型滑坡成灾临界降雨量研究. “资源保障环境安全—地质工作使命”华东六省一市地学科技论坛[C]. 2011
HUANG Junbao. Study on critical rainfall of typhoon-rainstorm landslide in southeast Fujian. "Resources Guarantee and Environmental Safety-Geological Work Mission", Geoscience Science and Technology Forum of Six Provinces and One City in East China[C]. 2011. (in Chinese)
[5] 李凯,孙悦迪,江宝骅,等. 基于像元二分法的白龙江流域植被覆盖度与滑坡时空格局分析[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2014,50(3):376 − 382. [LI Kai,SUN Yuedi,JIANG Baohua,et al. Analysis on spatial-temporal patterns of the vegetation coverage and landslides in Bailongjiang River Basin based on the Dimidiate Pixel Model[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),2014,50(3):376 − 382. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 李国旗,安树青,张纪林,吕跃凯,陈兴龙,程晓莉,季永华,沈邦勤. 海岸带防护林4种树木的风压应力分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报,1999,23(4):76 − 80. [LI Guoqi,AN Shuqing,ZHANG Jilin,et al. The bending stress analysis of 4 species of woods caused by wind pressure in coastal shelter forest[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University,1999,23(4):76 − 80. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 闫金凯,黄俊宝,李海龙,等. 台风暴雨型浅层滑坡失稳机理研究[J]. 地质力学学报,2020,26(4):481 − 491. [YAN Jinkai,HUANG Junbao,LI Hailong,et al. Study on instability mechanism of shallow landslide caused by typhoon and heavy rain[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2020,26(4):481 − 491. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.04.041
[8] 王照财,赵其华,韩俊,等. 台风作用下植被对斜坡稳定性影响的物理模拟[J]. 自然灾害学报,2013,22(4):145 − 152. [WANG Zhaocai,ZHAO Qihua,HAN Jun,et al. Physical modeling of the effect of vegetation on slope stability under typhoon[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2013,22(4):145 − 152. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13577/j.jnd.2013.0418
[9] 蔡泽宏. 基于监测数据的台风暴雨型土质滑坡预警判据研究[D]. 福州: 福州大学, 2015
CAI Zehong. Research on early warning criterion of soil landslides using monitoring data[D]. Fuzhou: Fuzhou University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 沈佳,董岩松,简文彬,等. 台风暴雨型土质滑坡演化过程研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(6):1290 − 1299. [SHEN Jia,DONG Yansong,JIAN Wenbin,et al. Study on evolution process of landslides triggered by typhoon rainstorm[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(6):1290 − 1299. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-540
[11] 王照财. 风荷载作用下植被对边坡稳定性影响研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2014
WANG Zhaocai. Study on the effect of vegetation on slope stability under the wind load[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 文海家,张岩岩,付红梅,等. 降雨型滑坡失稳机理及稳定性评价方法研究进展[J]. 中国公路学报,2018,31(2):15 − 29. [WEN Haijia,ZHANG Yanyan,FU Hongmei,et al. Research status of instability mechanism of rainfall-induced landslide and stability evaluation methods[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport,2018,31(2):15 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2018.02.002
[13] 苏燕,邱俊炳,兰斯梅,等. 基于室内试验的降雨型滑坡机理研究[J]. 福州大学学报(自然科学版),2015,43(1):118 − 122. [SU Yan,QIU Junbing,LAN Simei,et al. Research on mechanism in rainfall landslides based on laboratory test[J]. Journal of Fuzhou University (Natural Science Edition),2015,43(1):118 − 122. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7631/issn.1000-2243.2015.01.0118
[14] 张泰丽. 浙江省东部台风暴雨诱发滑坡变形特征和成因机制研究[D]. 中国地质大学. 2016
ZHANG Taili. Research on deformation characteristics and genetic mechanism of landslide induced by typhoon rainstorm in eastern Zhejiang Province[D]China University of Geosciences. 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 韩俊. 温州地区台风滑坡形成机理物理模拟研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2012
HAN Jun. Physical simulation study on the formation mechanism of typhoon landslide in Wenzhou region[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 刘胡玫,顾延生,葛继稳,等. 福建省安溪县崩岗区植物资源分析[J]. 湖北林业科技,2016,45(3):15 − 18. [LIU Humei,GU Yansheng,GE Jiwen,et al. Analysis on plant resources around collapsing gullies in Anxi County of Fujian Province[J]. Hubei Forestry Science and Technology,2016,45(3):15 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3020.2016.03.007
[17] 张丹,李传荣,许景伟,等. 沙质海岸黑松分枝格局特征及其抗风折能力分析[J]. 植物生态学报,2011,35(9):926 − 936. [ZHANG Dan,LI Chuanrong,XU Jingwei,et al. Branching pattern characteristics and anti-windbreakage ability of Pinus thunbergii in sandy coast[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2011,35(9):926 − 936. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1258.2011.00926
[18] 张国丽,魏传喜. 三维激光扫描技术在小区域滑坡体变形监测中的应用[J]. 海河水利,2018(4):62 − 64. [ZHANG Guoli,WEI Chuanxi. Application of 3D laser scanning technology in landslide deformation monitoring in small area[J]. Haihe Water Resources,2018(4):62 − 64. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7328.2018.04.019
[19] 宋书亮. 基于三目视觉技术的人工降雨型滑坡监测分析[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2019
SONG Shuliang. Monitoring and analysis of artificial rainfall landslide based on binocular vision technology[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 任帅. 基于三维激光扫描技术的滑坡表面形变特征分析[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2017
REN Shuai. Analysis of characteristics of landslide deformation using 3D laser scanning technique[D]. Mianyang: Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 叶春阳,许传华,孙国权,等. 机器视觉技术估算边坡连续形变体积[J]. 金属矿山,2021(9):60 − 64. [YE Chunyang,XU Chuanhua,SUN Guoquan,et al. Estimation of continuous deformation volume of slope using machine vision technique[J]. Metal Mine,2021(9):60 − 64. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19614/j.cnki.jsks.202109008
[22] 丁少林. 福建省台风降雨型滑坡渗流场规律及流—固耦合分析[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2016
DING Shaolin. Seepage characteristics and fluid-solid couple analysis of typhoon precipitation-induced land slide in Fujian Province[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 彭书生. 植被护坡对土质边坡浅层稳定性影响研究[D]. 武汉: 中国科学院研究生院(武汉岩土力学研究所), 2007
PENG Shusheng. Research on the effect of the biotechnical slope protection on the shallow stability[D]. Wuhan: Institute of Rock and Soil Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 罗建林,田鑫,钟文,等. 基于Geo-Slope的凝灰岩岩质边坡稳定性分析[J]. 化工矿物与加工,2020,49(12):9 − 13. [LUO Jianlin,TIAN Xin,ZHONG Wen,et al. Slope stability analysis of tuff rock based on Geo-Slope[J]. Industrial Minerals & Processing,2020,49(12):9 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16283/j.cnki.hgkwyjg.2020.12.003
[25] 伍宇明,兰恒星,高星,等. 台风暴雨型滑坡降雨阈值曲线研究—以福建地区为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2014,22(2):255 − 262. [WU Yuming,LAN Hengxing,GAO Xing,et al. Rainfall threshold of storm-induced landslides in typhoon areas:a case study of Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2014,22(2):255 − 262. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2014.02.015
[26] XU J W,UEDA K,UZUOKA R. Evaluation of failure of slopes with shaking-induced cracks in response to rainfall[J]. Landslides,2022,19(1):119 − 136. doi: 10.1007/s10346-021-01734-1
[27] 李晨,徐卫卫. 关于土体裂缝对边坡稳定性影响的讨论[J]. 中国港湾建设,2018,38(5):28 − 31. [LI Chen,XU Weiwei. Influence of cracks in soil on slope stability[J]. China Harbour Engineering,2018,38(5):28 − 31. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7640/zggwjs201805007
[28] 刘华磊,徐则民,张勇,等. 降雨条件下边坡裂缝的演化机制及对边坡稳定性影响—以云南省双柏县丁家坟滑坡为例[J]. 灾害学,2011,26(1):26 − 29. [LIU Hualei,XU Zemin,ZHANG Yong,et al. Evolutionary mechanism of slope fissures during rainfall and their effect on slope stability:A case study of Dingjiafen landslide in Shuangbo Country,Yunnan[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2011,26(1):26 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2011.01.006
[29] 杨阳. 黄土滑坡裂缝发育特征及其对滑坡孕灾模式的影响——以泾阳南塬黄土滑坡为例[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2016
YANG Yang. Crack characteristics of loess landslides and its influence on landslides geo-hazard model: Illustrated by the south Jingyang Plateau landslides[D]. Xi’an: Changan University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 李永益, 黄大庭. 后缘开裂对斜坡稳定性影响的有限元分析[J]. 四川科学技术出版社, 1989
Li Yongyi, Huang Dating. Finite element analysis of the influence of trailing edge cracking on slope stability [J]. Sichuan Science and Technology Press, 1989. (in Chinese)
[31] 樊建利. 裂缝充水对土质滑坡稳定性影响的试验研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2008
FAN Jianli. The test research on soil landslide's stability influenced by crack water[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2008. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 李洪建,洪五华,史文兵,等. 贵州惠水鑫朋滑坡变形破坏机制[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(5):19 − 26. [LI Hongjian,HONG Wuhua,SHI Wenbing,et al. Deformation and failure mechanism of Xinpeng Landslide in Huishui County,Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(5):19 − 26. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2019.05.03
[33] 郭斌,贾燕,梁彧,等. 四川宝轮服务区降雨型滑坡活动过程分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(4):45 − 51. [GUO Bin,JIA Yan,LIANG Yu,et al. Analysis on process of rainfall-induced landslide in Baolun service area,Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(4):45 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.04.06
-



 下载:
下载: