Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on landslide failure mode analysis: A case study of the left bank of Xietan River in the first section of Three Gorges Reservoir
-
摘要:
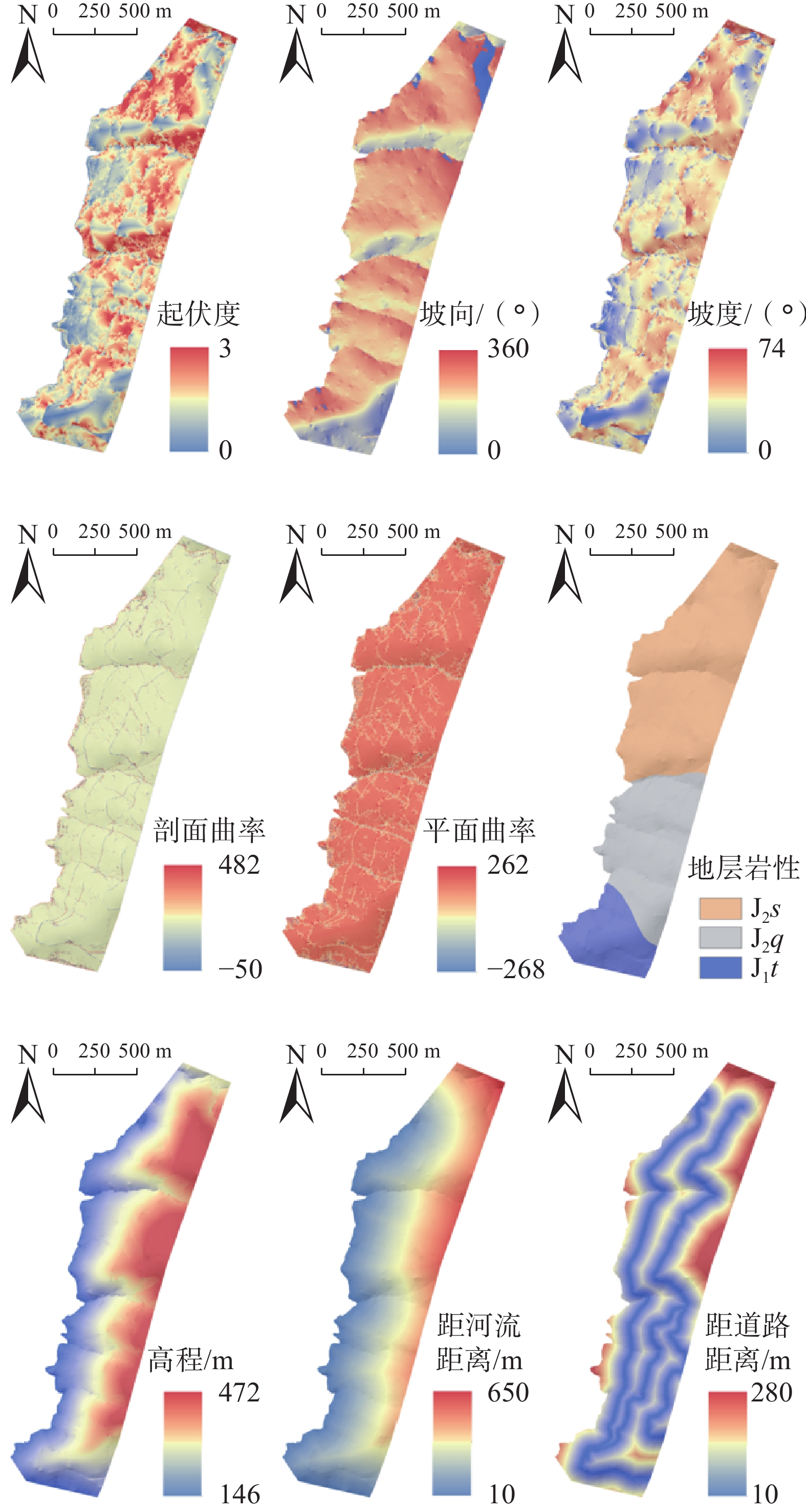
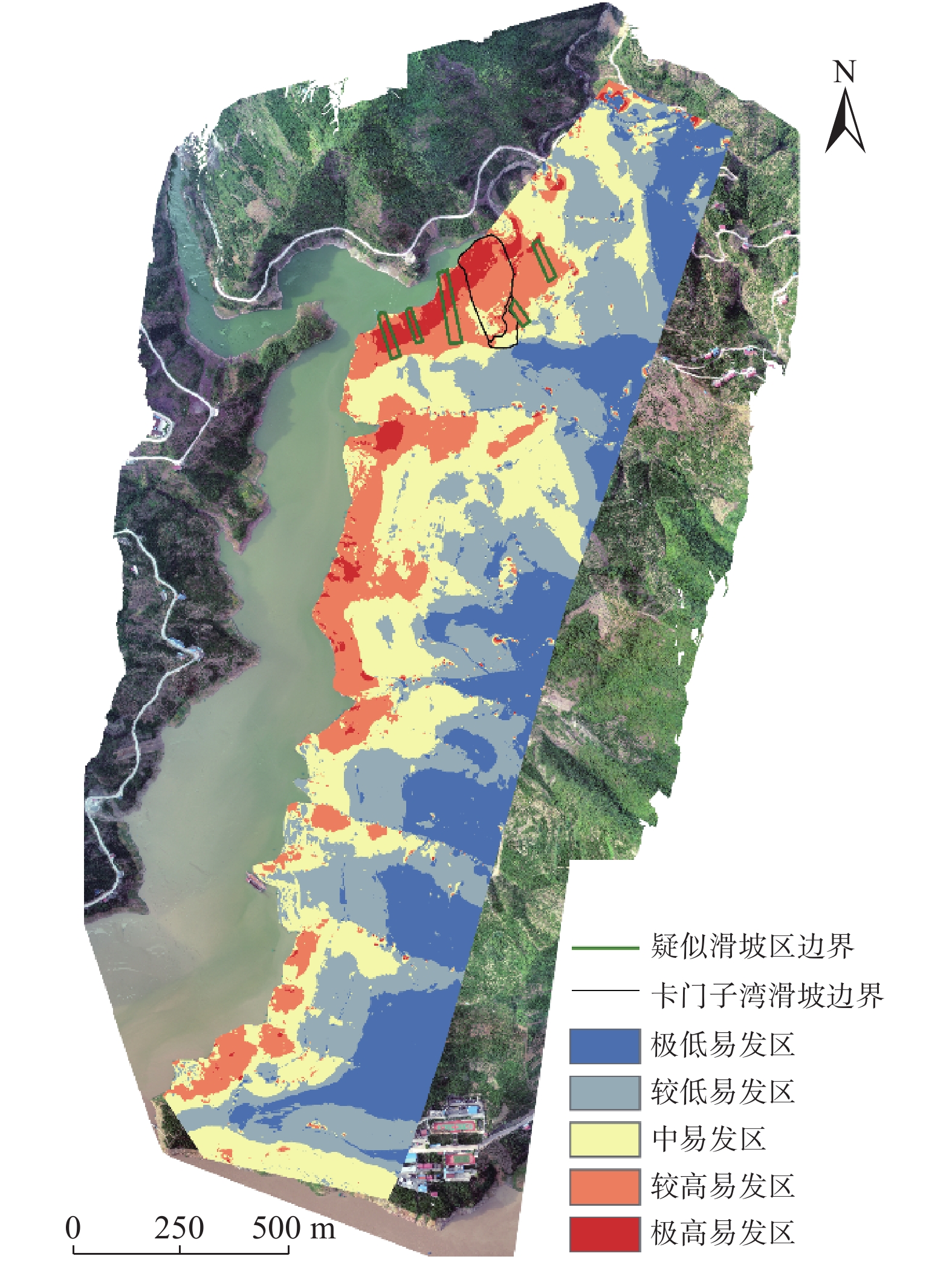
三峡库区首段发育有大量岩质滑坡,其中很多灾害点极具隐蔽性且目前并未被查明。文中以三峡库区首段泄滩河左岸为研究区,以区内唯一破坏的卡门子湾顺层岩质滑坡为例,在分析其成因机制的基础上归纳总结了该地区顺层岩质滑坡的破坏模式,并以此确定了高程、坡度、坡向、起伏度、平面曲率、剖面曲率、地层岩性、距河流距离及距道路距离共9个评价指标因子及疑似滑坡隐患点,将这些灾害隐患点作为滑坡样本,运用ALSA模型开展研究区的滑坡易发性分区,最后采用ROC曲线及现场复查等方法验证评价结果的可靠性。预测结果表明:研究区内顺层岩质滑坡的极高易发区和较高易发区大致呈面状分布,主要集中在岩性为侏罗系中统上沙溪庙组紫红色泥岩夹砂岩和西北坡向的近库岸地区。现场验证发现易发分区结果与滑坡破坏模式分布规律较吻合,表明基于滑坡破坏模式选择滑坡样本得到的滑坡易发性结果在整体上也能反映研究区滑坡概率空间分布规律,在缺乏准确滑坡样本时可作为一种替补方案。上述研究结果为基于滑坡破坏模式选取滑坡样本开展易发性评价工作提供了理论支持和科学依据。
Abstract:There are a large number of rock landslide disasters developed in the first section of the Three Gorges Reservoir area, many of which are very hidden and have not been identified. In this paper, taking the left bank of Xietan River in the first section of the Three Gorges Reservoir as the study area, taking the only bedding rock landslide in Kamenziwan as an example, the failure mode of bedding rock landslide in this area is summarized on the basis of analyzing its genesis mechanism. Nine evaluation index factors, including elevation, slope aspect, slope, relief, plane curvature, profile curvature, formation lithology, distance from river and distance from road, as well as suspected hidden danger points of landslide disaster are determined. These hidden danger points are taken as landslide samples. Automatic Landside Susceptibility Assessment Model (ALSA) was used to carry out landslide Susceptibility zoning in the study area. Finally, ROC curve and field review were used to verify the reliability of the evaluation results. The prediction results show that the extremely high and highly prone areas of bedding rock landslides in the study area are distributed in a plane shape, mainly concentrated in the middle Jurassic Upper Shaximiao Formation purplish red mudstone intercalated sandstone, and the northwest slope direction near the reservoir bank area. Field verification shows that the results of prone zoning are consistent with the distribution law of landslide failure mode, indicating that the landslide susceptibility results obtained by selecting landslide samples based on landslide failure mode can also reflect the spatial distribution law of landslide probability in the study area on the whole, and can be used as a substitute scheme in the absence of accurate landslide samples. The above research results provide theoretical support and scientific basis for selecting landslide samples to carry out vulnerability assessment based on landslide failure mode.
-

-
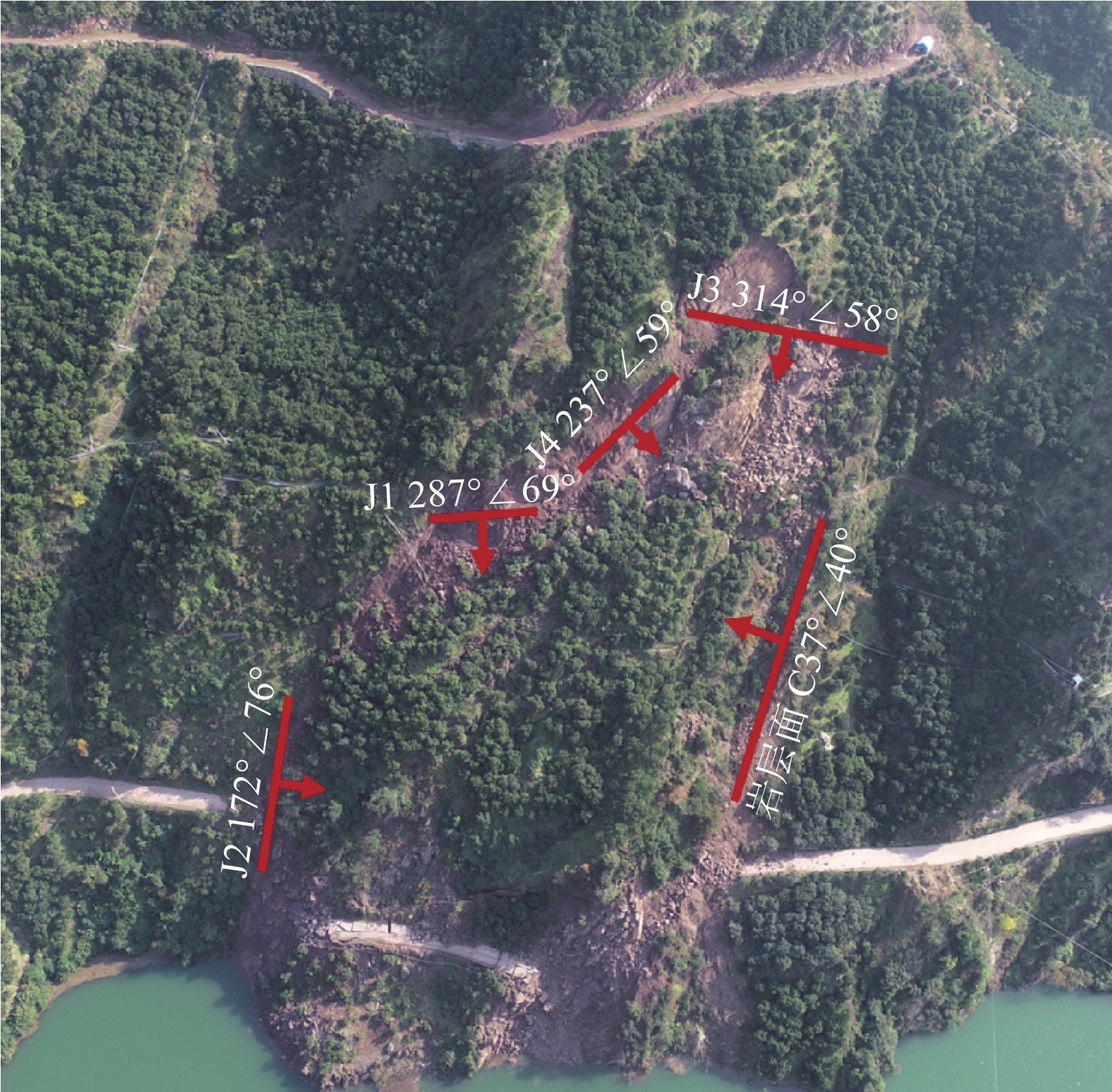
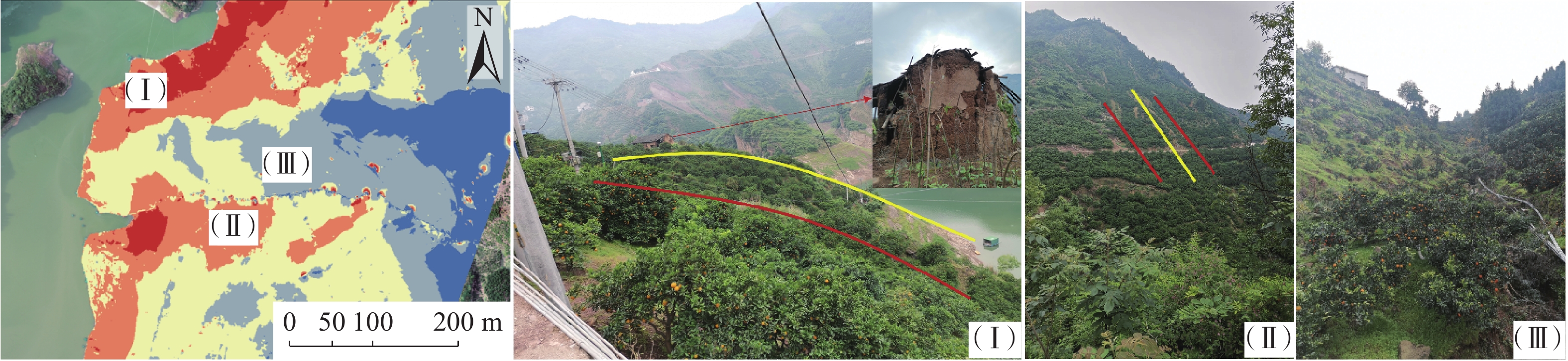
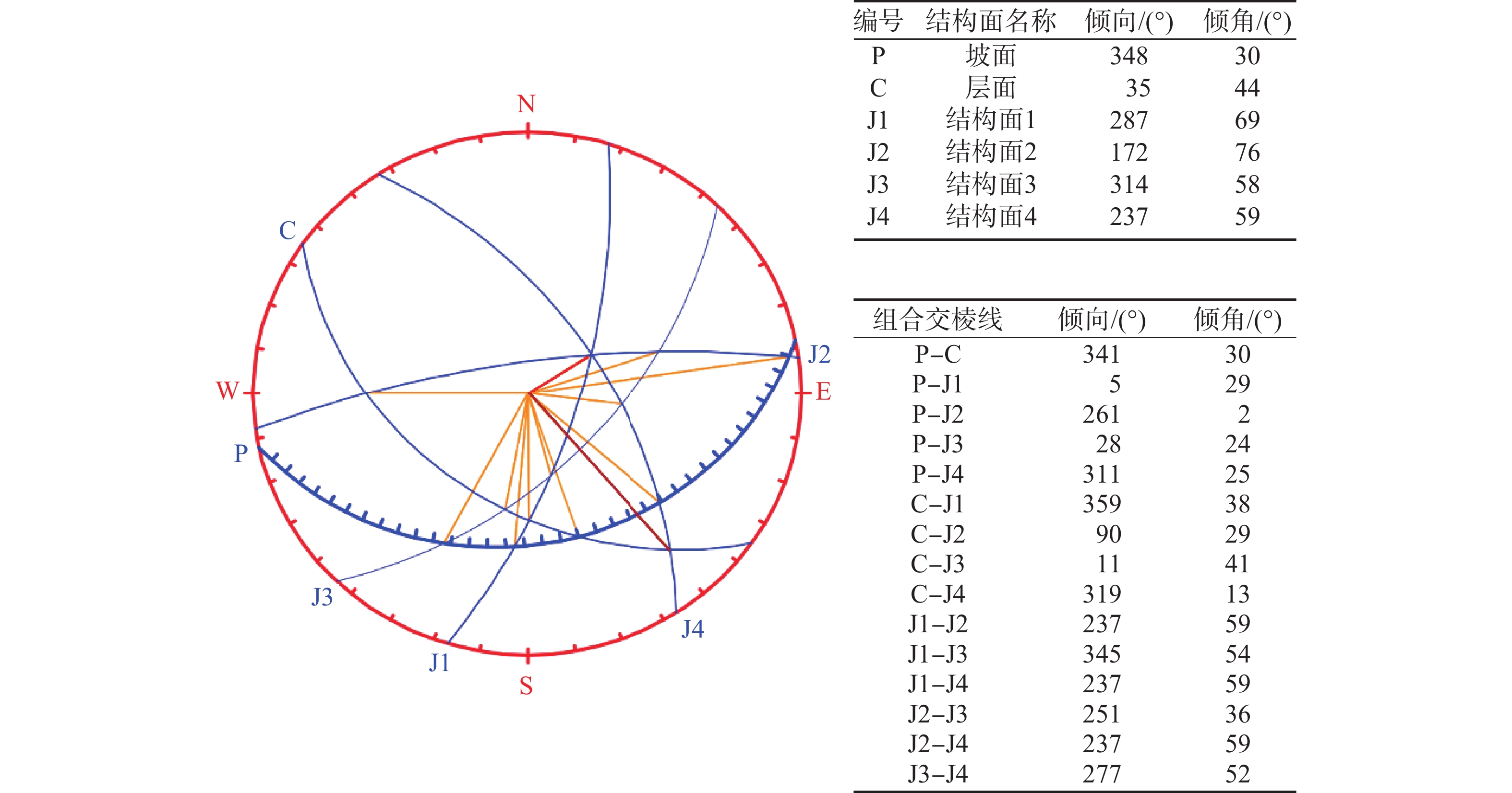
表 1 卡门子湾滑坡破坏模式总结表
Table 1. Summary table of failure mode of Kamenziwan landslide
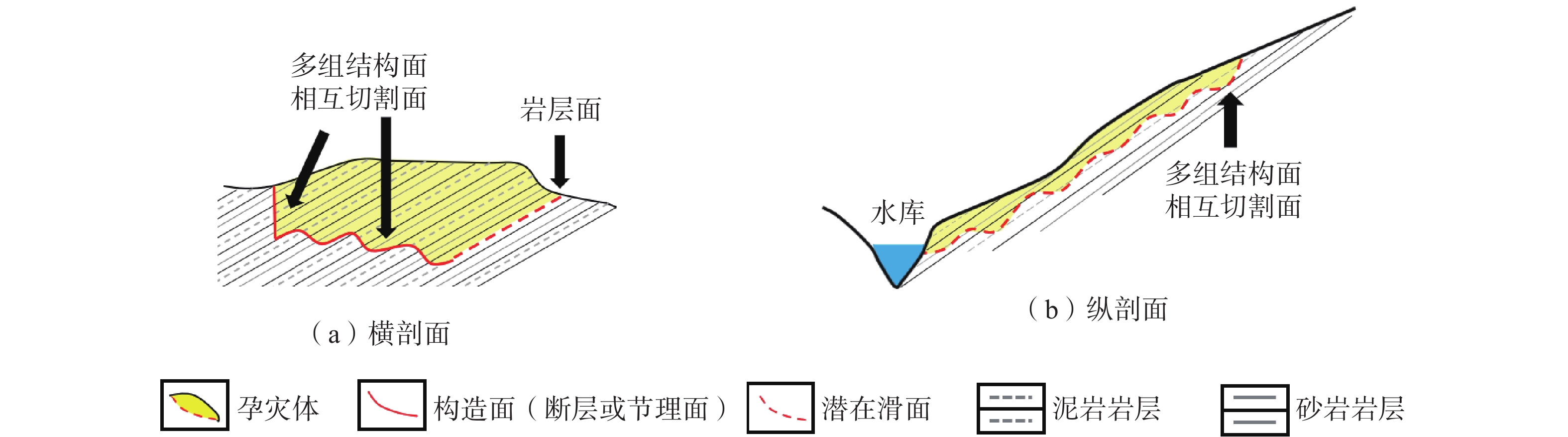
岸坡类型 缓倾切向坡 破坏模式 视倾向顺层牵引式滑坡 孕灾(六面体)
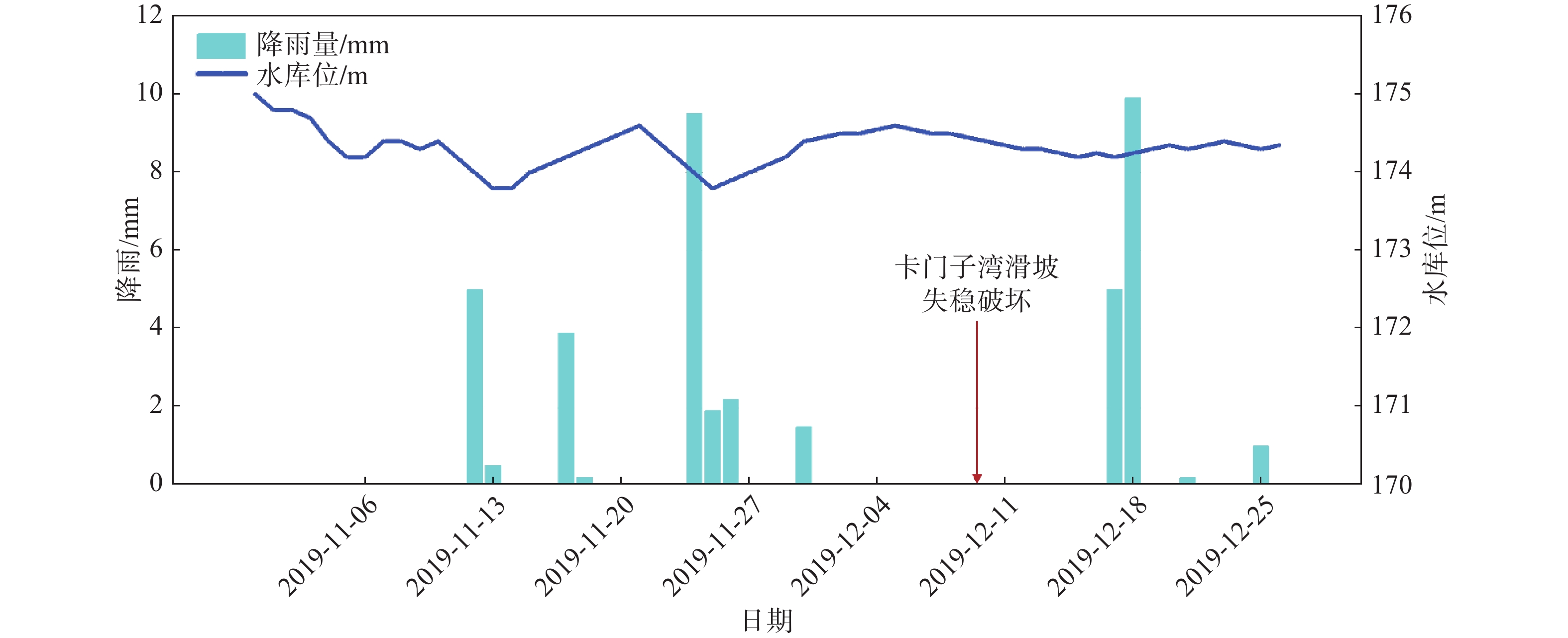
结构面斜坡表面 “上陡下缓前临空”的台阶状折线地形 底部滑带 左侧顺层,右侧切层 前缘剪出口 河流冲刷侵蚀形成临空面,
剪出口高程在145~175 m后缘边界 一组陡倾结构面切割,出露岩层切面 左侧边界 多组结构面相互切割形成阶梯状边界 右侧边界 岩层面 边界特征 两个约束边界(右、后)+两个自由边界(左、前) 物质组成
条件滑体 块裂岩体 滑带 中后部由三组结构面及岩层面形成阶梯状
滑带,前部岩层溃曲形成缓倾结构面滑床 侏罗系中统沙溪庙组(J2s)上部灰绿色砂岩
夹泥岩,下部紫红色泥岩夹砂岩表 2 卡门子湾滑坡区易发性结果分析表
Table 2. Summey table of landslide susceptibility results at Kamenziwan landslide area
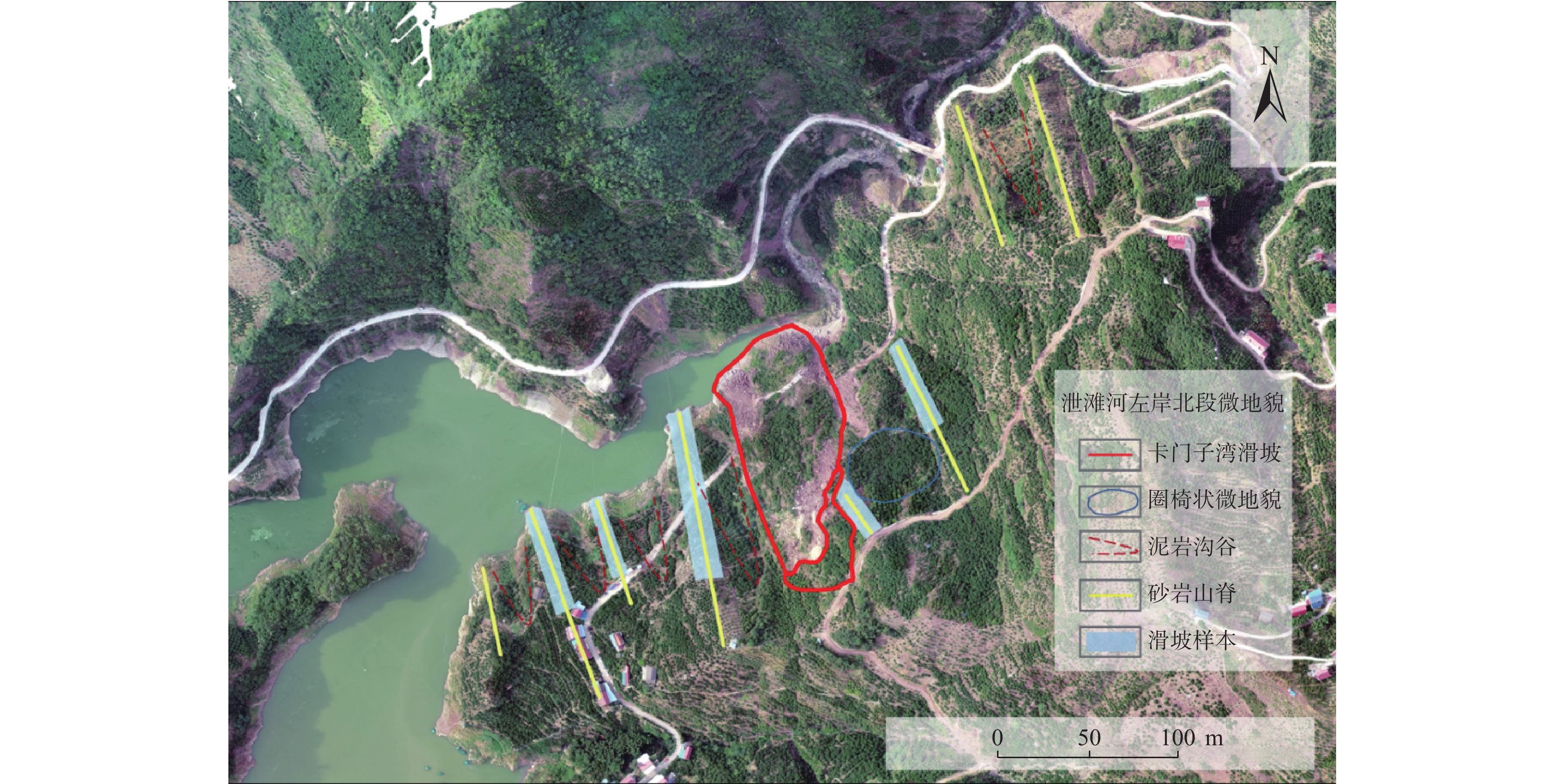
以疑似滑坡区为样本的滑坡易发性评价结果 卡门子湾滑坡区 栅格数 各分区占比/% 极高及较高易发区占比/% 极高易发 5986 26.6 82.8 高易发 12640 56.2 中易发 3750 16.7 低易发 113 0.5 极低易发 0 0.0 总计 22489 100 -
[1] 殷坤龙,朱良峰. 滑坡灾害空间区划及GIS应用研究[J]. 地学前缘,2001,8(2):279 − 284. [YIN Kunlong,ZHU Liangfeng. Landslide hazard zonation and application of GIS[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2001,8(2):279 − 284. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2001.02.010
[2] 黄波林,殷跃平,李滨,等. 三峡工程库区岩溶岸坡岩体劣化及其灾变效应[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):51 − 61. [HUANG Bolin,YIN Yueping,LI Bin,et al. Rock mass deterioration and its catastrophic effect of karst bank slope in the Three Gorges Project Reservoir area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):51 − 61. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202003055
[3] 卫童瑶,殷跃平,高杨,等. 三峡库区巫山县塔坪H1滑坡变形机制[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):73 − 81. [WEI Tongyao,YIN Yueping,GAO Yang,et al. Deformation mechanism of the taping H1 landslide in Wushan County in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):73 − 81. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202003043
[4] 郭子正,殷坤龙,付圣,等. 基于GIS与WOE-BP模型的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地球科学,2019,44(12):4299 − 4312. [GUO Zizheng,YIN Kunlong,FU Sheng,et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on GIS and WOE-BP model[J]. Earth Science,2019,44(12):4299 − 4312. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 张钟远,邓明国,徐世光,等. 镇康县滑坡易发性评价模型对比研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2022,41(1):157 − 171. [ZHANG Zhongyuan,DENG Mingguo,XU Shiguang,et al. Comparison of landslide susceptibility assessment models in Zhenkang County,Yunnan Province,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2022,41(1):157 − 171. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] MOHAMMADY M,POURGHASEMI H R,PRADHAN B. Landslide susceptibility mapping at Golestan Province,Iran:a comparison between frequency ratio,Dempster-Shafer,and weights-of-evidence models[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2012,61:221 − 236. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.10.005
[7] 王世宝,庄建琦,樊宏宇,等. 基于频率比与集成学习的滑坡易发性评价:以金沙江上游巴塘—德格河段为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(3):817 − 828. [WANG Shibao,ZHUANG Jianqi,FAN Hongyu,et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on frequency ratio and ensemble learning:Taking the Batang-Dege section in the upstream of Jinsha River as an example[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(3):817 − 828. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] DU Juan,GLADE T,WOLDAI T,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on an incomplete landslide inventory in the Jilong Valley,Xizang,Chinese Himalayas[J]. Engineering Geology,2020,270:105572. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105572
[9] STEGER S,BRENNING A,BELL R,et al. Exploring discrepancies between quantitative validation results and the geomorphic plausibility of statistical landslide susceptibility maps[J]. Geomorphology,2016,262:8 − 23. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.03.015
[10] MEINHARDT M,FINK M,TÜNSCHEL H. Landslide susceptibility analysis in central Vietnam based on an incomplete landslide inventory:Comparison of a new method to calculate weighting factors by means of bivariate statistics[J]. Geomorphology,2015,234:80 − 97. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2014.12.042
[11] ABEDINI M,TULABI S. Assessing LNRF,FR,and AHP models in landslide susceptibility mapping index:A comparative study of Nojian watershed in Lorestan Province,Iran[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2018,77(11):405. doi: 10.1007/s12665-018-7524-1
[12] 夏辉,殷坤龙,梁鑫,等. 基于SVM-ANN模型的滑坡易发性评价—以三峡库区巫山县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(5):13 − 19. [XIA Hui,YIN Kunlong,LIANG Xin,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on SVM-ANN Models:A case stualy for Wushan County in the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(5):13 − 19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 殷坤龙,柳源. 滑坡灾害区划系统研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2000,11(4):28 − 32. [YIN Kunlong,LIU Yuan. Systematic studies on landslide hazard zonation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2000,11(4):28 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2000.04.007
[14] 周天伦,曾超,范晨,等. 基于快速聚类-信息量模型的汶川及周边两县滑坡易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(5):137 − 150. [ZHOU Tianlun,ZENG Chao,FAN Chen,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on K-means cluster information model in Wenchuan and two neighboring counties,China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(5):137 − 150. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.05-17
[15] 石菊松,张永双,董诚,等. 基于GIS技术的巴东新城区滑坡灾害危险性区划[J]. 地球学报,2005,26(3):275 − 282. [SHI Jusong,ZHANG Yongshuang,DONG Cheng,et al. GIS-based landslide hazard zonation of the new Badong County site[J]. Acta Geosicientia Sinica,2005,26(3):275 − 282. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2005.03.014
[16] 郭子正,殷坤龙,黄发明,等. 基于滑坡分类和加权频率比模型的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2019,38(2):287 − 300. [GUO Zizheng,YIN Kunlong,HUANG Faming,et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on landslide classification and weighted frequency ratio model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2019,38(2):287 − 300. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2018.0838
[17] MA Shuyue,QIU Haijun,HU Sheng,et al. Quantitative assessment of landslide susceptibility on the Loess Plateau in China[J]. Physical Geography,2020,41(6):489 − 516. doi: 10.1080/02723646.2019.1674559
[18] 罗路广,裴向军,黄润秋,等. GIS支持下CF与Logistic回归模型耦合的九寨沟景区滑坡易发性评价[J]. 工程地质学报,2021,29(2):526 − 535. [LUO Luguang,PEI Xiangjun,HUANG Runqiu,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment in Jiuzhaigou scenic area with GIS based on certainty factor and Logistic regression model[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021,29(2):526 − 535. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-202
[19] 罗路广,裴向军,崔圣华,等. 九寨沟地震滑坡易发性评价因子组合选取研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2021,40(11):2306 − 2319. [LUO Luguang,PEI Xiangjun,CUI Shenghua,et al. Combined selection of susceptibility assessment factors for Jiuzhaigou earthquake-induced landslides[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021,40(11):2306 − 2319. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2021.0198
[20] HONG Haoyuan,CHEN Wei,XU Chong,et al. Rainfall-induced landslide susceptibility assessment at the Chongren area (China) using frequency ratio,certainty factor,and index of entropy[J]. Geocarto International,2017,32(2):139 − 154.
[21] 刘璐瑶,高惠瑛. 基于证据权与Logistic回归模型耦合的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 工程地质学报,2021:1 − 11 [2021-05-13]. [LIU Luyao,GAO Huiying. landslide susceptibility assessment based on coupling of woe model and Logistic regression model[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021:1 − 11 [2021-05-13]. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2020-482
[22] 李郎平,兰恒星,郭长宝,等. 基于改进频率比法的川藏铁路沿线及邻区地质灾害易发性分区评价[J]. 现代地质,2017,31(5):911 − 929. [LI Langping,LAN Hengxing,GUO Changbao,et al. Geohazard susceptibility assessment along the Sichuan-Xizang railway and its adjacent area using an improved frequency ratio method[J]. Geoscience,2017,31(5):911 − 929. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2017.05.004
[23] LI Langping,LAN Hengxing,GUO Changbao,et al. A modified frequency ratio method for landslide susceptibility assessment[J]. Landslides,2017,14(2):727 − 741. doi: 10.1007/s10346-016-0771-x
[24] ZHANG Yixing,LAN Hengxing,LI Langping,et al. Optimizing the frequency ratio method for landslide susceptibility assessment:A case study of the Caiyuan Basin in the southeast mountainous area of China[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2020,17(2):340 − 357. doi: 10.1007/s11629-019-5702-6
[25] HE Keqiang,WANG Shangqing,DU Wen,et al. Dynamic features and effects of rainfall on landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir region,China:Using the Xintan landslide and the large Huangya landslide as the examples[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2010,59(6):1267. doi: 10.1007/s12665-009-0114-5
[26] TANG Huiming,WASOWSKI J,JUANG C H. Geohazards in the three Gorges Reservoir Area,China - Lessons learned from decades of research[J]. Engineering Geology,2019,261:105267. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105267
[27] YIN Yueping,HUANG Bolin,ZHANG Quan,et al. Research on recently occurred reservoir-induced Kamenziwan rockslide in Three Gorges Reservoir,China[J]. Landslides,2020,17(8):1935 − 1949. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01394-7
[28] Regional level landslide inventory maps of the Shyok River watershed, Northern Pakistan[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2016, 75(2): 563 − 574.
[29] 吴润泽,胡旭东,梅红波,等. 基于随机森林的滑坡空间易发性评价—以三峡库区湖北段为例[J]. 地球科学,2021,46(1):321 − 330. [WU Runze,HU Xudong,MEI Hongbo,et al. Spatial susceptibility assessment of landslides based on random forest:A case study from Hubei section in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Earth Science,2021,46(1):321 − 330. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 周超,殷坤龙,曹颖,等. 基于集成学习与径向基神经网络耦合模型的三峡库区滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地球科学,2020,45(6):1865 − 1876. [ZHOU Chao,YIN Kunlong,CAO Ying,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment by applying the coupling method of radial basis neural network and adaboost:A case study from the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Earth Science,2020,45(6):1865 − 1876. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 闫举生,谭建民. 基于不同因子分级法的滑坡易发性评价—以湖北远安县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(1):52 − 60. [YAN Jusheng,TAN Jianmin. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on different factor classification methods:A case study in Yuanan County of Hubei Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(1):52 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] LIU Zhongqiang,GILBERT G,CEPEDA J M,et al. Modelling of shallow landslides with machine learning algorithms[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2021,12(1):385 − 393. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2020.04.014
[33] LAN H X,ZHOU C H,WANG L J,et al. Landslide hazard spatial analysis and prediction using GIS in the Xiaojiang watershed,Yunnan,China[J]. Engineering Geology,2004,76(1/2):109 − 128.
[34] 周越,曾昭发,唐海燕,等. 公路勘察中滑坡体的地球物理特征与分析—以张榆线公路勘察为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2021,51(2):638 − 644. [ZHOU Yue,ZENG Zhaofa,TANG Haiyan,et al. Geophysical characteristics of landslide body in highway reconnaissance: A case study in highway prospecting of Zhangyu line[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2021,51(2):638 − 644. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: