Geological hazard assessment based on the models of AHP, catastrophe theory and their combination: A case study in Pingshan County of Hebei Province
-
摘要:
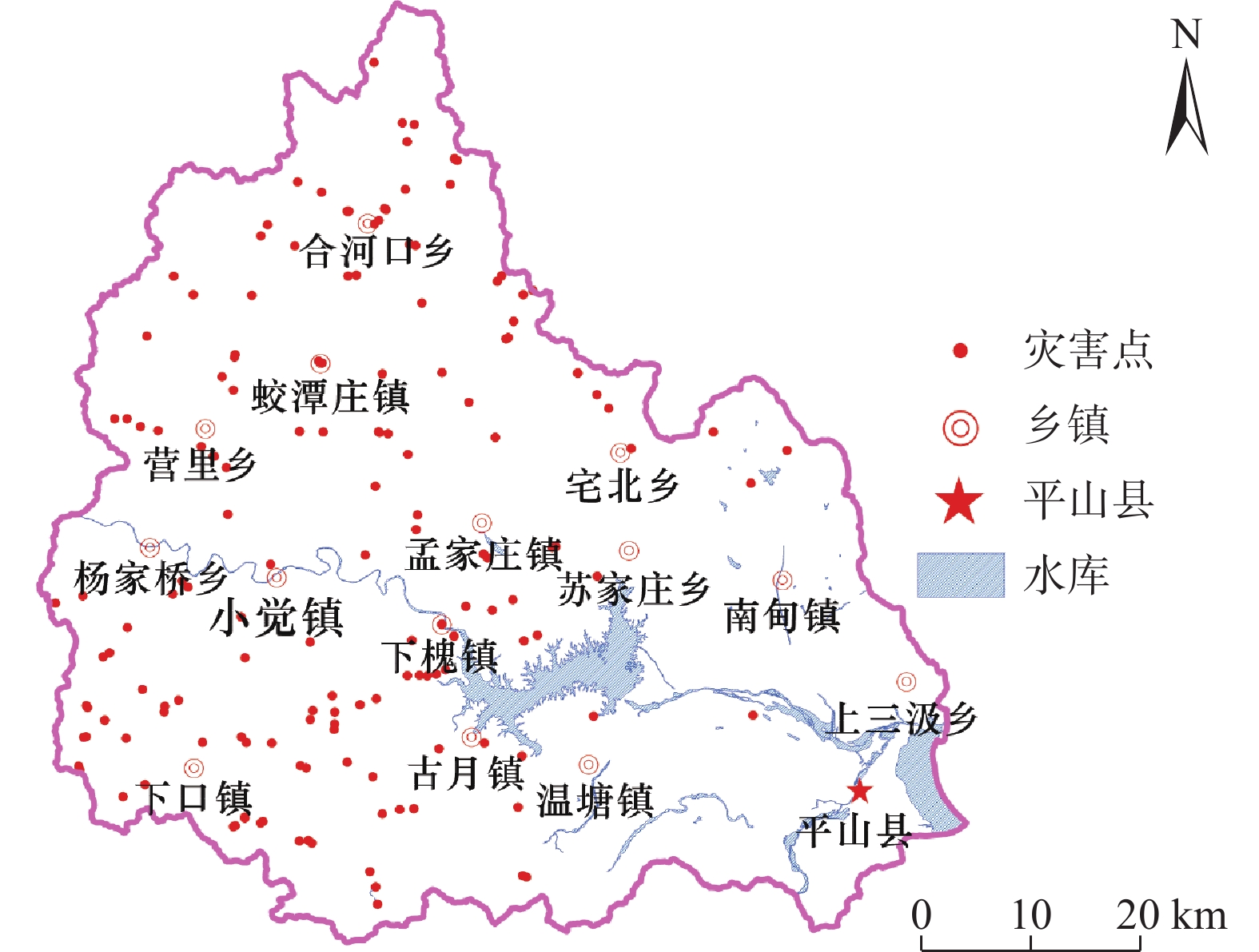
河北平山县受地形地貌、地质构造和生态环境等因素的影响,崩滑流等地质灾害频发。选取地形起伏度、坡度、坡向、河网密度、断裂带密度、地层岩性、NDVI、土地利用类型及地质灾害点密度9个评价因子,用AHP和突变理论分别求各评价因子权重,并按最小信息熵权法结合,建立AHP-突变理论组合模型并应用,对比基于三种方法的平山县地质灾害危险性评价结果。结果表明:组合模型的评价结果精度更高,符合该区地质灾害发育特征;组合模型法将主客观结合,综合考虑因子的影响,评价结果可靠。该研究为平山县及类似地区地质灾害危险性评价提供一种新的尝试和方法。
Abstract:Pingshan County, Hebei was affected by topography, geological structure, ecological environment and other factors, geological disasters such as landslides occurred frequently. Nine evaluation factors including topographic relief, slope, aspect, river network density, fault zone density, stratigraphic lithology, NDVI, land use type and geological disaster point density were selected. The weights of each evaluation factor were calculated by AHP and catastrophe theory, and the combination model of AHP and catastrophe theory was established and applied according to the minimum information entropy weight method. The results of geological disaster risk assessment in Pingshan County based on three methods were compared. The results show that the evaluation results of the combined model have higher accuracy and are in line with the development characteristics of geological disasters in this area. Combined model method combines subjective and objective, considering the influence of factors, the evaluation results are reliable. This study provides a new attempt and method for geological disaster risk assessment in Pingshan County and similar areas.
-

-
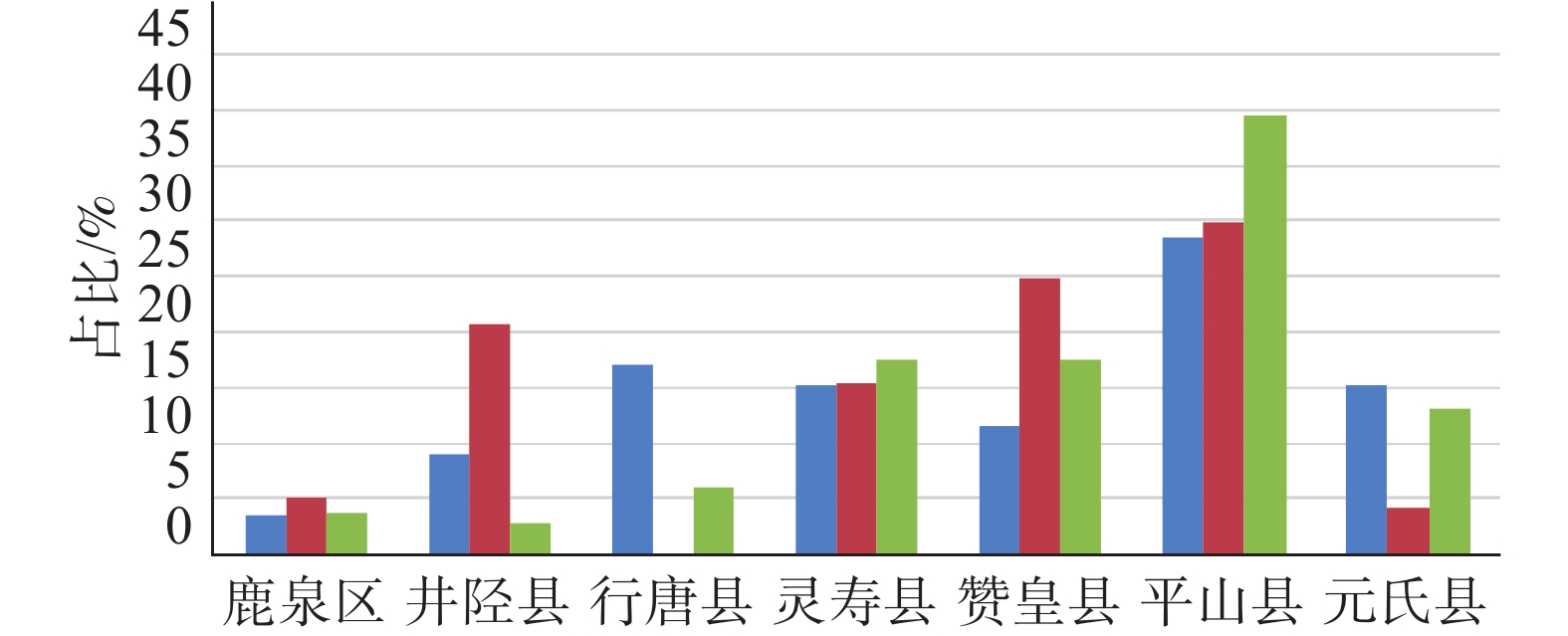
表 1 各评价方法求得权重对比
Table 1. Weight comparison of each evaluation method
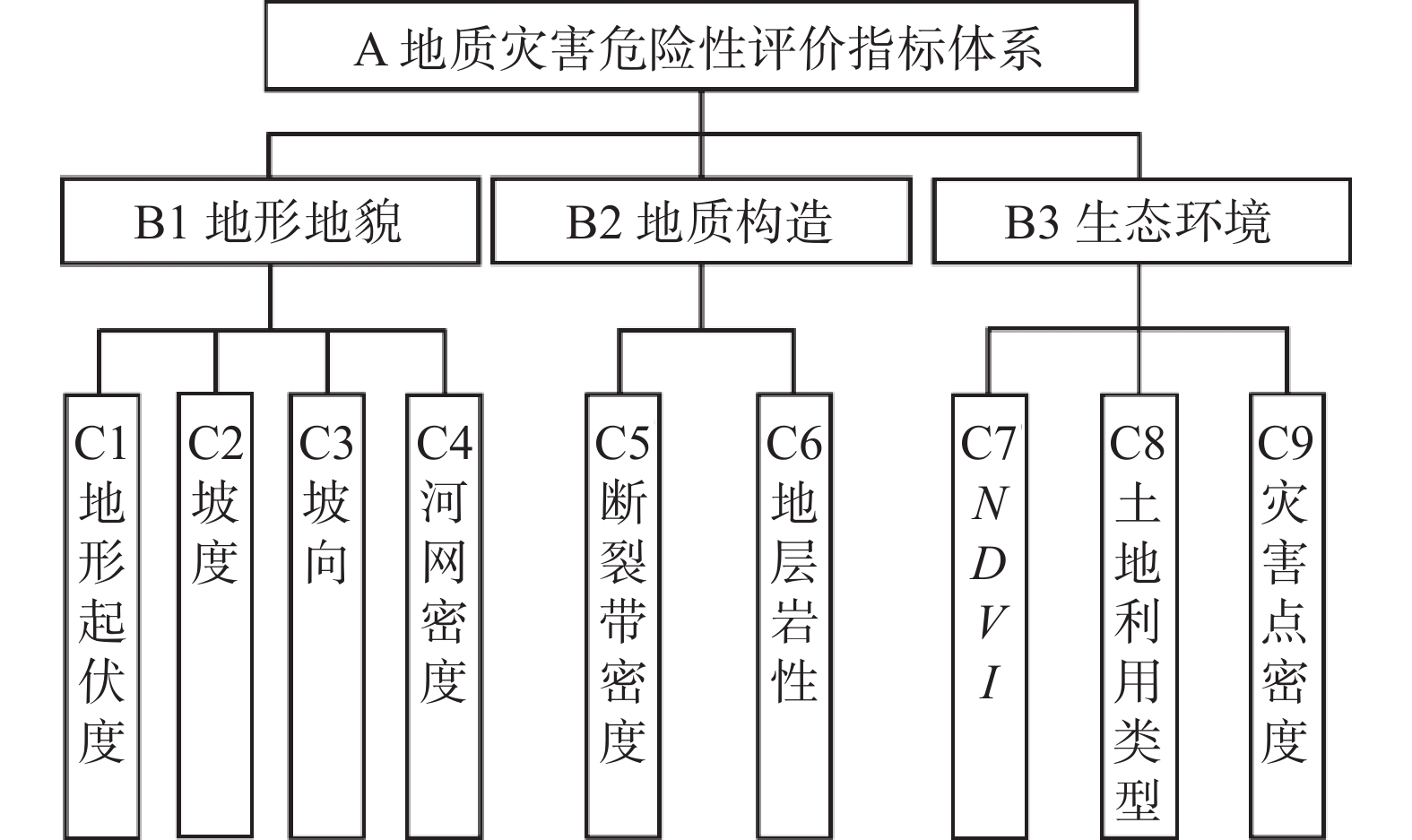
目标层 准则层 评价因子层 AHP权重w1 突变理论权重w2 AHP-突变组合模型权重w3 A平山县地质
灾害危害性评价B1 地形地貌 C1 地形起伏度 0.1761 0.0795 0.1359 C2 坡度 0.3731 0.0717 0.1880 C3 坡向 0.0815 0.0795 0.0925 C4 河网密度 0.0380 0.0818 0.0641 B2 地质构造 C5 断裂带密度 0.0405 0.1065 0.0755 C6 地层岩性 0.2026 0.2486 0.2579 B3 生态环境 C7 NDVI 0.0249 0.1182 0.0624 C8 土地利用类型 0.0567 0.1220 0.0956 C9 灾害点密度 0.0065 0.0921 0.0281 表 2 状态变量的突变模型
Table 2. Catastrophe model of state variable
突变模型 控制变量维数 势函数 归一化公式 折叠突变 1 
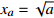
尖点突变 2 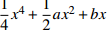
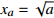 ;
;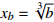
燕尾突变 3 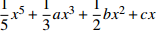
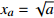 ;
;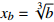 ;
;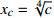
蝴蝶突变 4 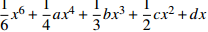
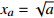 ;
;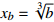 ;
;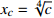 ;
;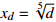
表 3 危险性分区统计与对比
Table 3. Risk zoning statistics and comparison
评价方法 危险性等级 面积占比/% AHP 低 25.14 中 33.37 高 27.16 极高 14.33 突变理论 低 13.96 中 26.36 高 28.16 极高 31.51 AHP-突变理论组合模型 低 18.39 中 32.61 高 27.49 极高 21.51 -
[1] 高泽民,丁明涛,杨国辉,等. 川藏铁路孜热—波密段泥石流灾害危险性评价[J]. 工程地质学报,2021,29(2):478 − 485. [GAO Zemin,DING Mingtao,YANG Guohui,et al. Hazard assessment of debris flow along zire-Bomi section of Sichuan-Xizang railway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021,29(2):478 − 485. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2021-0160
GAO Zemin, DING Mingtao, YANG Guohui, et al. Hazard assessment of debris flow along zire-Bomi section of Sichuan-Xizang railway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2021, 29(2): 478-485. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2021-0160
[2] 洪增林,李永红,张玲玉,等. 一种基于主成分分析法的区域性地质灾害危险性评估方法[J]. 灾害学,2020,35(1):118 − 124. [HONG Zenglin,LI Yonghong,ZHANG Lingyu,et al. A method of regional geological hazard assessment based on principle component analysis[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2020,35(1):118 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2020.01.022
HONG Zenglin, LI Yonghong, ZHANG Lingyu, et al. A method of regional geological hazard assessment based on principle component analysis[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2020, 35(1): 118-124. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2020.01.022
[3] MEJIA-NAVARRO M,WOHL E E. Geological hazard and risk evaluation using GIS:methodology and model applied to Medellin,Colombia[J]. Environmental & Engineering Geoscience,1994(4):459 − 481.
[4] 魏会龙, 施秋华, 周金文, 等. 基于层次分析法的深圳市地面坍塌危险性评价[J]. 中国矿业, 2021, 30(增刊2): 110 − 116
WEI Huilong, SHI Qiuhua, ZHOU Jinwen, et al. Risk assessment of ground collapse in Shenzhen based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2021, 30(Sup 2): 110 − 116. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 王磊,常鸣,邢月龙. 基于信息量法模型与GIS的滑坡地质灾害风险性评价[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,2021,32(2):14 − 20. [WANG Lei,CHANG Ming,XING Yuelong. Risk assessment of landslide geological hazards based on information method model and GIS[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,2021,32(2):14 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2021.02.003
WANG Lei, CHANG Ming, XING Yuelong. Risk assessment of landslide geological hazards based on information method model and GIS[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 2021, 32(2): 14-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2021.02.003
[6] YU Kaining, FAN Cunliang, LI Jian, et al. Formation Characteristic and Comprehensive Classification of Debris Flow in Typical Mountain Area of the North of China[C]. The XVIII Kerulien International Conference on Geology. Geological Engineering and Mining Exploration in Central Asia. Australia: Aussino Academic Publishing House, 2013: 819-826.
[7] 张晓敏,李辉,刘海南,等. 基于灰色系统理论的陕西省地质灾害趋势预测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(5):7 − 12. [ZHANG Xiaomin,LI Hui,LIU Hainan,et al. Trend prediction of geological hazards in Shaanxi Province based on Grey System Theory[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(5):7 − 12. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2018.05.02
ZHANG Xiaomin, LI Hui, LIU Hainan, et al. Trend prediction of geological hazards in Shaanxi Province based on Grey System Theory[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2018, 29(5): 7-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2018.05.02
[8] 郭学飞,王志一,焦润成,等. 基于层次分析法的北京市地质环境质量综合评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(1):70 − 76. [GUO Xuefei,WANG Zhiyi,JIAO Runcheng,et al. Comprehensive evaluation method of geological environment quality in Beijing based on AHP[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(1):70 − 76. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.01.10
GUO Xuefei, WANG Zhiyi, JIAO Runcheng, et al. Comprehensive evaluation method of geological environment quality in Beijing based on AHP[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(1): 70-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.01.10
[9] 李小龙,宋国虎,向灵芝,等. 基于不同评价单元和灾害熵的泥石流危险性分析—以白龙江流域武都段为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(6):107 − 115. [LI Xiaolong,SONG Guohu,XIANG Lingzhi,et al. Hazard analysis of debris flows based on different evaluation units and disaster entropy:A case study in Wudu section of the Bailong River Basin[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(6):107 − 115. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.06-13
LI Xiaolong, SONG Guohu, XIANG Lingzhi, et al. Hazard analysis of debris flows based on different evaluation units and disaster entropy: a case study in Wudu section of the Bailong River Basin[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(6): 107-115. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.06-13
[10] 何珊,李志军,董富权,等. 基于层次分析法的多元信息成矿预测研究—以西藏洛扎地区为例[J]. 地质与勘探,2018,54(1):148 − 157. [HE Shan,LI Zhijun,DONG Fuquan,et al. Multiple information metallogenic prediction based on the analytic hierarchy process:A case study of the lhozhag area in Xizang[J]. Geology and Exploration,2018,54(1):148 − 157. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13712/j.cnki.dzykt.2018.01.016
HE Shan, LI Zhijun, DONG Fuquan, et al. Multiple information metallogenic prediction based on the analytic hierarchy process: a case study of the lhozhag area in Xizang[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2018, 54(1): 148-157. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13712/j.cnki.dzykt.2018.01.016
[11] KAYASTHA P,DHITAL M R,DE SMEDT F. Application of the analytical hierarchy process (AHP) for landslide susceptibility mapping:a case study from the Tinau watershed,west Nepal[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2013,52:398 − 408.
[12] 侯圣山,曹鹏,陈亮,等. 基于数值模拟的耳阳河流域泥石流灾害危险性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(2):143 − 151. [HOU Shengshan,CAO Peng,CHEN Liang,et al. Debris flow hazard assessment of the Eryang River watershed based on numerical simulation[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(2):143 − 151. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202003057
HOU Shengshan, CAO Peng, CHEN Liang, et al. Debris flow hazard assessment of the Eryang River watershed based on numerical simulation[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(2): 143-151. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202003057
[13] WICAKSONO Y S,SIHOMBING F H,INDRA T L. Landslide susceptibility map of Bogor Area using analytical hierarchy process[J]. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science,2020,538(1):012050. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/538/1/012050
[14] 陈绪新,秦哲,付厚利,等. 基于尖点突变模型饱水边坡稳定性分析[J]. 地质与勘探,2018,54(2):376 − 380. [CHEN Xuxin,QIN Zhe,FU Houli,et al. Analysis on stability of water-saturation slopes based on the cusp catastrophic model[J]. Geology and Exploration,2018,54(2):376 − 380. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13712/j.cnki.dzykt.2018.02.016
CHEN Xuxin, QIN Zhe, FU Houli, et al. Analysis on stability of water-saturation slopes based on the cusp catastrophic model[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2018, 54(2): 376-380. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13712/j.cnki.dzykt.2018.02.016
[15] 冯平,李绍飞,李建柱. 基于突变理论的地下水环境风险评价[J]. 自然灾害学报,2008,17(2):13 − 18. [FENG Ping,LI Shaofei,LI Jianzhu. Catastrophe theory-based risk evaluation of groundwater environment[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2008,17(2):13 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2008.02.003
FENG Ping, LI Shaofei, LI Jianzhu. Catastrophe theory-based risk evaluation of groundwater environment[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2008, 17(2): 13-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2008.02.003
[16] 李绍飞,孙书洪,王向余. 突变理论在海河流域地下水环境风险评价中的应用[J]. 水利学报,2007,38(11):1312 − 1317. [LI Shaofei,SUN Shuhong,WANG Xiangyu. Application of catastrophe theory to risk assessment of groundwater environment for river basin[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2007,38(11):1312 − 1317. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2007.11.007
LI Shaofei, SUN Shuhong, WANG Xiangyu. Application of catastrophe theory to risk assessment of groundwater environment for river basin[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2007, 38(11): 1312-1317. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2007.11.007
[17] 袁颖,李佳玉. 岩质边坡稳定性评价的尖点突变理论模型[J]. 地质与勘探,2021,57(1):183 − 189. [YUAN Ying,LI Jiayu. A cusp catastrophe theory model for evaluation of rock slope stability[J]. Geology and Exploration,2021,57(1):183 − 189. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YUAN Ying, LI Jiayu. A cusp catastrophe theory model for evaluation of rock slope stability[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2021, 57(1): 183-189. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 尚志海,蔡文慧,欧先交,等. 基于突变理论的梅州市地质灾害灾度评估[J]. 安全与环境工程,2014,21(3):55 − 59. [SHANG Zhihai,CAI Wenhui,OU Xianjiao,et al. Geological hazard degree assessment of Meizhou City based on catastrophe theory[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2014,21(3):55 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2014.03.011
SHANG Zhihai, CAI Wenhui, OU Xianjiao, et al. Geological hazard degree assessment of Meizhou City based on catastrophe theory[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2014, 21(3): 55-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2014.03.011
[19] 温晓艺,郑秀清,陈军锋,等. 基于突变理论的地质灾害风险性评价[J]. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版),2019,50(4):575 − 581. [WEN Xiaoyi,ZHENG Xiuqing,CHEN Junfeng,et al. Risk assessment of geological disaster based on catastrophe theory[J]. Journal of Shandong Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition),2019,50(4):575 − 581. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2324.2019.04.008
WEN Xiaoyi, ZHENG Xiuqing, CHEN Junfeng, et al. Risk assessment of geological disaster based on catastrophe theory[J]. Journal of Shandong Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 50(4): 575-581. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2324.2019.04.008
[20] 陈菊艳,朱斌,彭三曦,等. 基于AHP和GIS的矿区岩溶塌陷易发性评估—以贵州林歹岩溶矿区为例[J]. 自然灾害学报,2021,30(5):226 − 236. [CHEN Juyan,ZHU Bin,PENG Sanxi,et al. Assessment of susceptibility to Karst collapse in mining area based on AHP and GIS:A case study in Lindai Karst mining area in Guizhou[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2021,30(5):226 − 236. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13577/j.jnd.2021.0522
CHEN Juyan, ZHU Bin, PENG Sanxi, et al. Assessment of susceptibility to Karst collapse in mining area based on AHP and GIS: a case study in Lindai Karst mining area in Guizhou[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2021, 30(5): 226-236. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13577/j.jnd.2021.0522
[21] 杜国梁,杨志华,袁颖,等. 基于逻辑回归-信息量的川藏交通廊道滑坡易发性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):102 − 111. [DU Guoliang,YANG Zhihua,YUAN Ying,et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Xizang traffic corridor using logistic regression-information value method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):102 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DU Guoliang, YANG Zhihua, YUAN Ying, et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Xizang traffic corridor using logistic regression-information value method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(5): 102-111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 李博. GRA—FAHP模型的煤层底板突水危险性评价[J]. 地质论评,2015,61(5):1128 − 1134. [LI Bo. Risk assessment model of coal floor water-irruption based on GRA-FAHP[J]. Geological Review,2015,61(5):1128 − 1134. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2015.05.015
LI Bo. Risk assessment model of coal floor water-irruption based on GRA-FAHP[J]. Geological Review, 2015, 61(5): 1128-1134. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2015.05.015
[23] 刘璐瑶,高惠瑛,李照. 基于CF与Logistic回归模型耦合的永嘉县滑坡易发性评价[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2021,51(10):121 − 129. [LIU Luyao,GAO Huiying,LI Zhao. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on coupling of CF model and logistic regression model in Yongjia County[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China,2021,51(10):121 − 129. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Luyao, GAO Huiying, LI Zhao. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on coupling of CF model and logistic regression model in Yongjia County[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2021, 51(10): 121-129. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] SHAHINUZZAMAN M,HAQUE M N,SHAHID S. Delineation of groundwater potential zones using a parsimonious concept based on catastrophe theory and analytical hierarchy process[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2021,29(3):1091 − 1116. doi: 10.1007/s10040-021-02322-2
[25] 宁娜,马金珠,张鹏,等. 基于GIS和信息量法的甘肃南部白龙江流域泥石流灾害危险性评价[J]. 资源科学,2013,35(4):892 − 899. [NING Na,MA Jinzhu,ZHANG Peng,et al. Debris flow hazard assessment for the Bailongjiang River,southern Gansu[J]. Resources Science,2013,35(4):892 − 899. (in Chinese with English abstract)
NING Na, MA Jinzhu, ZHANG Peng, et al. Debris flow hazard assessment for the Bailongjiang River, southern Gansu[J]. Resources Science, 2013, 35(4): 892-899. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 覃乙根,杨根兰,江兴元,等. 基于确定性系数模型与逻辑回归模型耦合的地质灾害易发性评价—以贵州省开阳县为例[J]. 科学技术与工程,2020,20(1):96 − 103. [QIN Yigen,YANG Genlan,JIANG Xingyuan,et al. Geohazard susceptibility assessment based on integrated certainty factor model and logistic regression model for Kaiyang,China[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2020,20(1):96 − 103. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.01.015
QIN Yigen, YANG Genlan, JIANG Xingyuan, et al. Geohazard susceptibility assessment based on integrated certainty factor model and logistic regression model for Kaiyang, China[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(1): 96-103. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.01.015
[27] 杨宁, 陶志斌, 高松, 等. 基于AHP的DRASTIC模型对莱州地区地下水脆弱性研究[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(增刊 1): 133 − 137
YANG Ning, TAO Zhibin, GAO Song, et al. Study of groundwater vulnerability in Laizhou using AHP-based DRASTIC model[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(Sup 1): 133 − 137. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] YING X,ZENG G M,CHEN G Q,et al. Combining AHP with GIS in synthetic evaluation of eco-environment quality—a case study of Hunan Province,China[J]. Ecological Modelling,2007,209(2/3/4):97 − 109.
[29] 夏兴生,朱秀芳,李月臣,等. 基于AHP-PCA熵组合权重模型的三峡库区(重庆段)农业生态环境脆弱性评价[J]. 南方农业学报,2016,47(4):548 − 556. [XIA Xingsheng,ZHU Xiufang,LI Yuechen,et al. Evaluation for vulnerability of agroecological environment in Three Gorges Reservoir area(Chongqing section)based on AHP-PCA entropy combination weight mode[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture,2016,47(4):548 − 556. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2016.04.548
XIA Xingsheng, ZHU Xiufang, LI Yuechen, et al. Evaluation for vulnerability of agroecological environment in Three Gorges Reservoir area(Chongqing section)based on AHP-PCA entropy combination weight mode[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2016, 47(4): 548-556. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2016.04.548
[30] 杨康,薛喜成,段钊,等. 基于AHP-LR熵组合模型的子长市地质灾害危险性评价[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021,21(27):11551 − 11560. [YANG Kang,XUE Xicheng,DUAN Zhao,et al. Risk assessment of geological hazards in Zichang County based on AHP-LR entropy combined model[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2021,21(27):11551 − 11560. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.27.013
YANG Kang, XUE Xicheng, DUAN Zhao, et al. Risk assessment of geological hazards in Zichang County based on AHP-LR entropy combined model[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(27): 11551-11560. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.27.013
-



 下载:
下载: