Early identification of landslide hazards in deep cut alpine canyon using SBAS-InSAR technology
-
摘要:
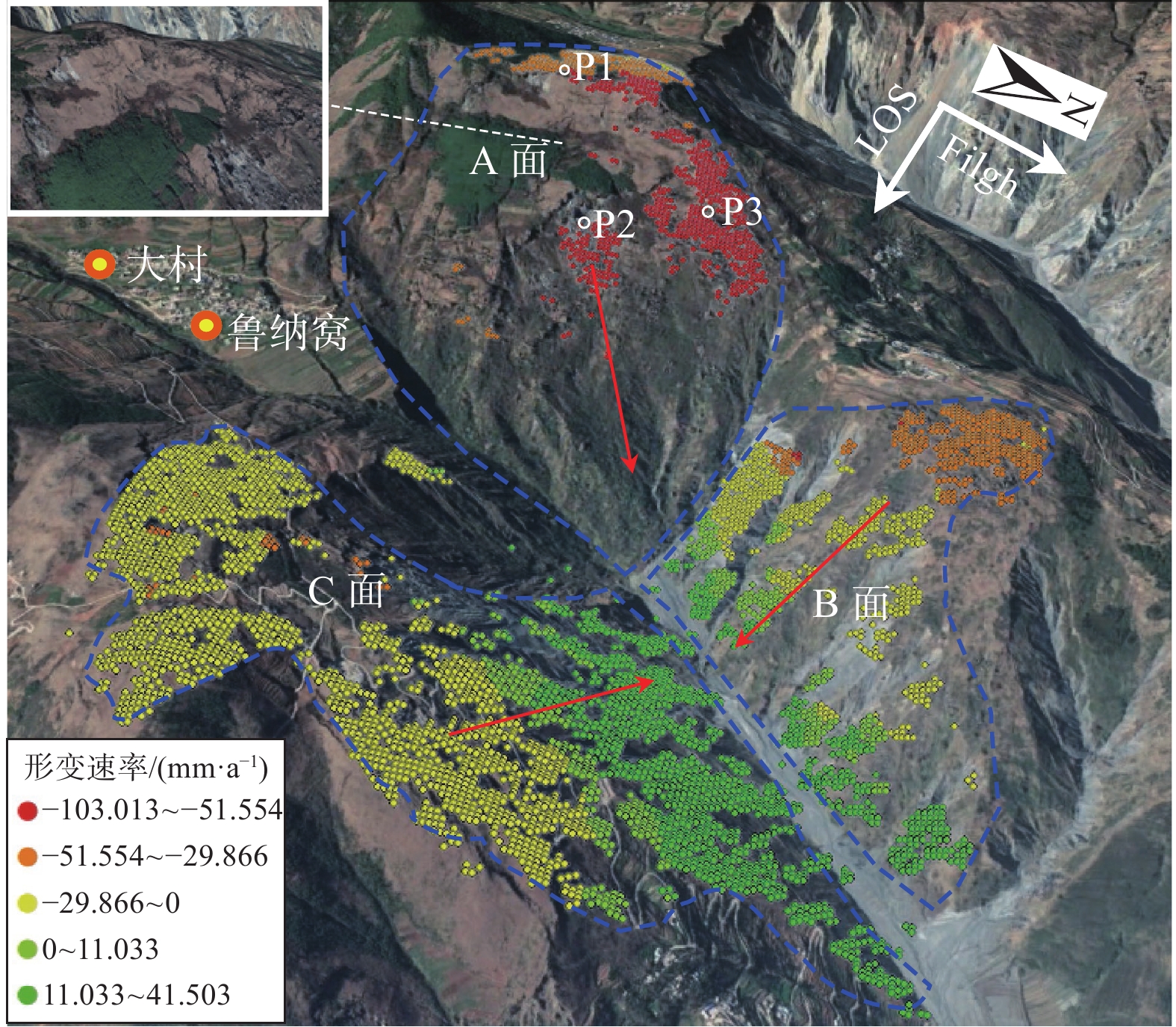
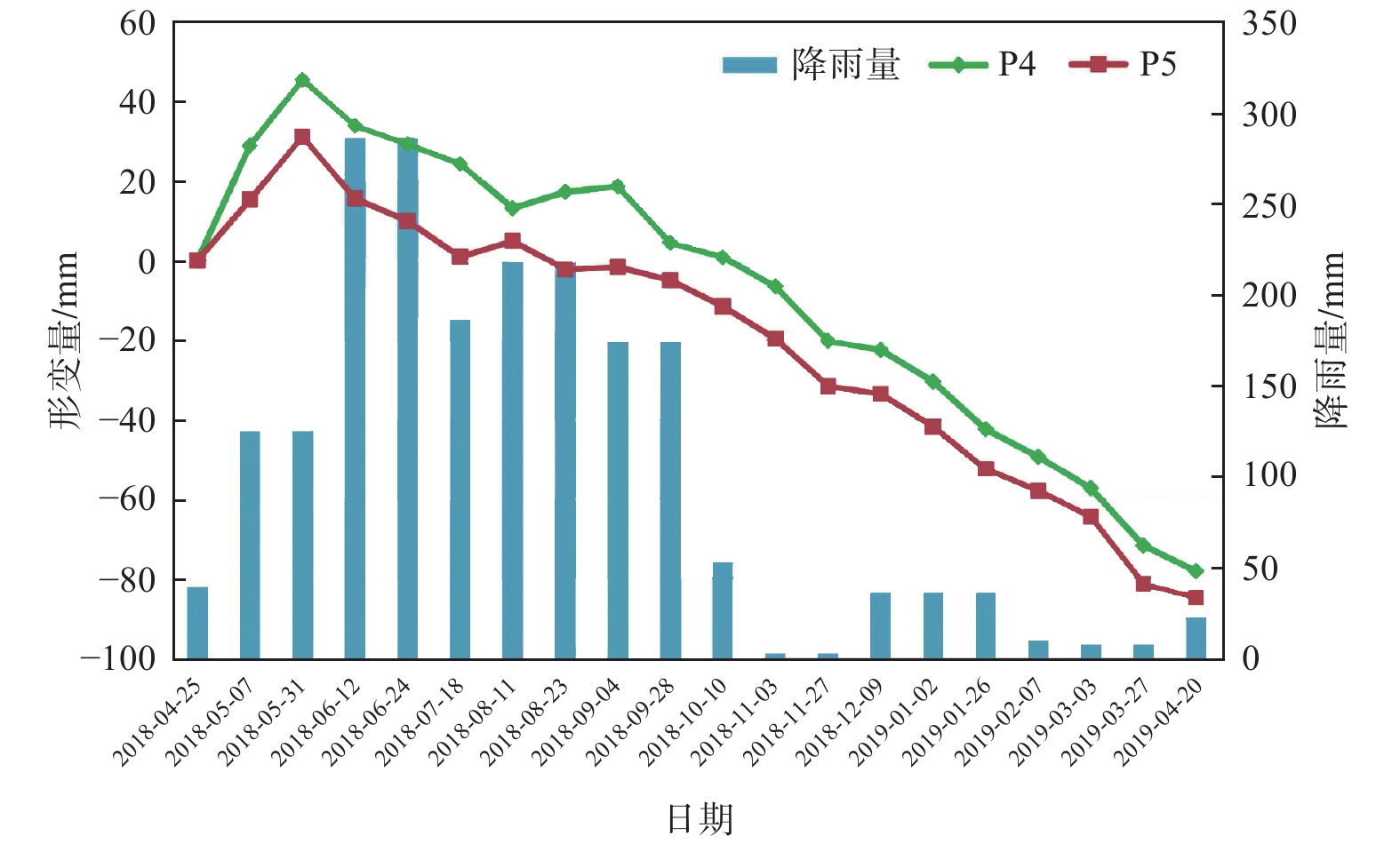
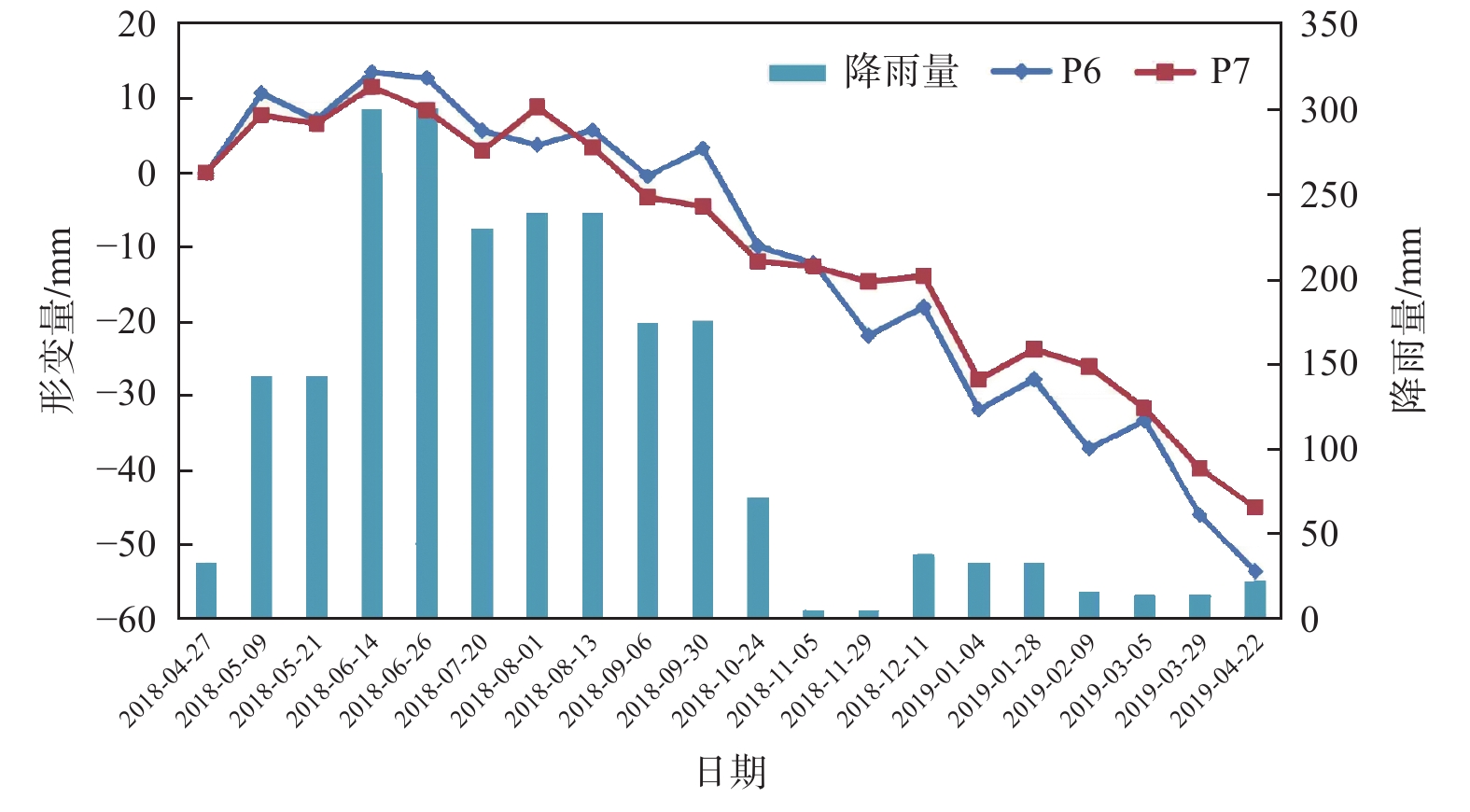
近年来,高山峡谷区滑坡灾害频频发生,给人民生命和财产安全带来严重威胁。针对多数学者利用SAR单轨道数据对高山峡谷区滑坡进行早期识别,存在SAR成像几何畸变造成部分滑坡不能识别、识别结果不全面等问题。为全面准确的对高山峡谷区滑坡隐患进行早期识别,文章采用SBAS-InSAR技术,以东川小江沿线两侧深切割高山峡谷区为研究区,通过升降轨SAR数据结合互补的方式进行滑坡灾害隐患识别,引入高分辨率光学影像等作为辅助识别,最终共识别出18处滑坡灾害体,其中5处为高风险潜在滑坡,并对三类典型潜在滑坡进行分析。分析结果表明:利用升降轨SAR数据结合互补的方式,能有效避免SAR单轨道数据在高山峡谷地区产生的几何畸变问题,同时,该方法能更为准确全面地对高山峡谷区滑坡隐患进行早期识别,为防灾减灾事业及政府部门决策提供一种有效的手段。
-
关键词:
- 高山峡谷区 /
- SBAS-InSAR /
- 滑坡灾害 /
- 早期识别 /
- 东川小江
Abstract:In recent years, landslides occurred frequently in mountain and gorge areas, which brought serious threats to people's life and property safety. Most scholars use SAR single-track data for early identification of landslides in alpine and canyon areas, but some landslides cannot be identified due to geometric distortion of SAR imaging, and the identification results are not comprehensive. In order to carry out comprehensive and accurate early identification of landslide hazards in alpine valley area, this paper adopts bas-INSAR technology, takes the deep cut alpine valley area along the Xiaojiang River in Dongchuan as the research area, and adopts the combination of SAR data of lifting and lowering orbit to identify landslide hazards, and introduces high-resolution optical images as auxiliary identification. Finally, 18 landslide disaster bodies were identified, among which 5 were high-risk potential landslides, and three types of typical potential landslides were analyzed. The analysis results show that the use of elevator rail SAR data combined with complementary way, can effectively avoid the SAR single orbital data geometric distortion problem in mountain valley area, at the same time, this method can more accurately comprehensively to early identification of alpine valley area of landslide hazard, the cause of disaster prevention and mitigation and government decision-making provides a effective means.
-
Key words:
- alpine canyon area /
- SBAS - InSAR /
- landslide disaster /
- early recognition /
- Dongchuan Xiaojiang
-

-
表 1 Sentinenl-1A数据参数
Table 1. Sentinenl-1A data parameters
轨道
方向成像
模式波段 波长 入射角
/(°)极化
方式距离
分辨率/m方位
分辨率/m重访
周期/d升轨 IW C 5.63 34.17 VV 5 20 12 降轨 IW C 5.63 39.35 VV 5 20 12 -
[1] 王之栋, 文学虎, 唐伟, 等. 联合多种InSAR技术的龙门山-大渡河区域地灾隐患早期探测[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2020,45(3):451 − 459. [WANG Zhidong, WEN Xuehu, TANG Wei, et al. Early detection of geological hazards in Longmenshan-Dadu river area using various InSAR techniques[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2020,45(3):451 − 459. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 张路, 廖明生, 董杰, 等. 基于时间序列InSAR分析的西部山区滑坡灾害隐患早期识别—以四川丹巴为例[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2018,43(12):2039 − 2049. [ZHANG Lu, LIAO Mingsheng, DONG Jie, et al. Early detection of landslide hazards in mountainous areas of West China using time series SAR interferometry:A case study of Danba, Sichuan[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2018,43(12):2039 − 2049. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 石固林, 徐浪, 张璇钰, 等. 西山村滑坡时序形变的SBAS-InSAR监测[J]. 测绘科学,2021,46(2):93 − 98. [SHI Gulin,XU Lang,ZHANG Xuanyu,et al. Monitoring time series deformation of Xishanchun landslide with SBAS-InSAR[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping,2021,46(2):93 − 98. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2021.02.014
[4] 黄润秋. 中国西部地区典型岩质滑坡机理研究[J]. 地球科学进展,2004,19(3):443 − 450. [HUANG Runqiu. Mechanism of large scale landslides in Western China[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences,2004,19(3):443 − 450. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.03.016
[5] 张拴宏, 纪占胜. 合成孔径雷达干涉测量(InSAR)在地面形变监测中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2004,115(1):112 − 117. [ZHANG Shuanhong, JI Zhansheng. A review on the application of Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar on surface deformation monitoring[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2004,115(1):112 − 117. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 王志勇, 张金芝. 基于InSAR技术的滑坡灾害监测[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,2013,33(3):87 − 91. [WANG Zhiyong, ZHANG Jinzhi. Landslides monitoring based on insar technique[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,2013,33(3):87 − 91. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] GUO J M, HU J Y, LI B, et al. Land subsidence in Tianjin for 2015 to 2016 revealed by the analysis of Sentinel-1A with SBAS-InSAR[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing,2017,11(2):026024 − 026024. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.11.026024
[8] 代聪, 李为乐, 陆会燕, 等. 甘肃省舟曲县城周边活动滑坡InSAR探测[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2021,46(7):994 − 1002. [DAI Cong, LI Weile, LU Huiyan, et al. Active landslides detection in Zhouqu County, Gansu Province using InSAR technology[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2021,46(7):994 − 1002. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] INTRIERI E, RASPINI F, FUMAGALLI A, et al. The Maoxian landslide as seen from space: detecting precursors of failure with Sentinel-1 data[J]. Landslides,2018,15(1):123 − 133. doi: 10.1007/s10346-017-0915-7
[10] DAI K, CHEN G, XU Q, et al. Potential landslide early detection near Wenchuan by a qualitatively multi-baseline dinsar method[J]. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences,2018,XLII-3:253 − 256.
[11] 韩守富, 赵宝强, 殷宗敏, 等. 基于PS InSAR技术的黄土高原地质灾害隐患识别[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2020,56(1):1 − 7. [HAN Shoufu, ZHAO Baoqiang, YIN Zongmin, et al. The identification of potential geological hazards on the Loess Plateau based on PS InSAR technology[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),2020,56(1):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 冯文凯, 顿佳伟, 易小宇, 等. 基于SBAS-InSAR技术的金沙江流域沃达村巨型老滑坡形变分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(2):384 − 393. [FENG Wenkai, DUN Jiawei, YI Xiaoyu, et al. Deformation analysis of woda village old landslide in Jinsha river basin using sbas-insar technology[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(2):384 − 393. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-411
[13] 戴可人, 铁永波, 许强, 等. 高山峡谷区滑坡灾害隐患InSAR早期识别—以雅砻江中段为例[J]. 雷达学报,2020,9(3):554 − 568. [DAI Keren, TIE Yongbo, XU Qiang, et al. Early identification of potential landslide geohazards in alpine-canyon terrain based on SAR interferometry:A case study of the middle section of Yalong river[J]. Journal of Radars,2020,9(3):554 − 568. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 杨成生, 张勤, 赵超英, 等. 短基线集InSAR技术用于大同盆地地面沉降、地裂缝及断裂活动监测[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2014,39(8):945 − 950. [YANG Chengsheng, ZHANG Qin, ZHAO Chaoying, et al. Small baseline bubset InSAR technology used in Datong basin ground subsidence, fissure and fault zone monitoring[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2014,39(8):945 − 950. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 徐富强. 滑坡转化成泥石流的流态化机理研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2003
XU Fuqiang. The mechanism research on the fluidization of the landslide translating into debris flow[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2003. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 李德仁, 廖明生, 王艳. 永久散射体雷达干涉测量技术[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2004,29(8):664 − 668. [LI Deren, LIAO Mingsheng, WANG Yan. Progress of permanent scatterer interferometry[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2004,29(8):664 − 668. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 周华云, 赵林, 田黎明, 等. 基于Sentinel-1数据对青藏高原五道梁多年冻土区地面形变的监测与分析[J]. 冰川冻土,2019,41(3):525 − 536. [ZHOU Huayun, ZHAO Lin, TIAN Liming, et al. Monitoring and analysis of surface deformation in the permafrost area of Wudaoliang on the Xizang Plateau based on Sentinel-1 data[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2019,41(3):525 − 536. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 张勇, 洪敏, 崔兴平, 等. 小江断裂带近场活动特征分析[J]. 地震研究,2018,41(3):375 − 380. [ZHANG Yong, HONG Min, CUI Xingping, et al. Evaluation of near field activity in Xiaojiang fault zone[J]. Journal of Seismological Research,2018,41(3):375 − 380. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2018.03.005
[19] 冯金良, 崔之久, 张威, 等. 云南东川地区层状地貌面的成因[J]. 山地学报,2004,22(2):165 − 174. [FENG Jinliang, CUI Zhijiu, ZHANG Wei, et al. Genesis of the layered landform surfaces in Dongchuan, Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of Mountain Research,2004,22(2):165 − 174. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2004.02.006
-




 下载:
下载: