Distributive characteristics of physical and mechaniscal parameters of the loess soils in Lüliang mountainous area
-
摘要:
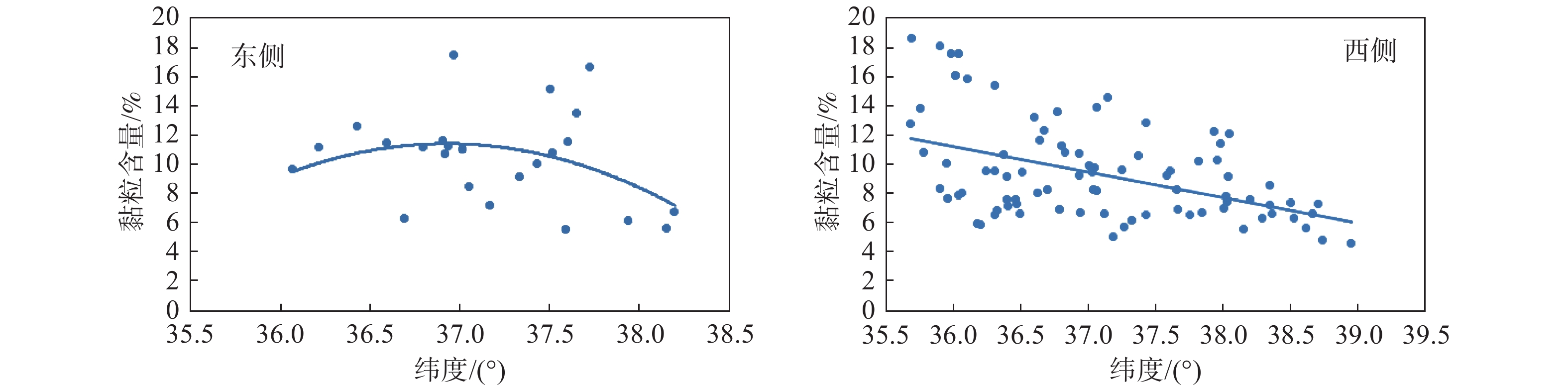
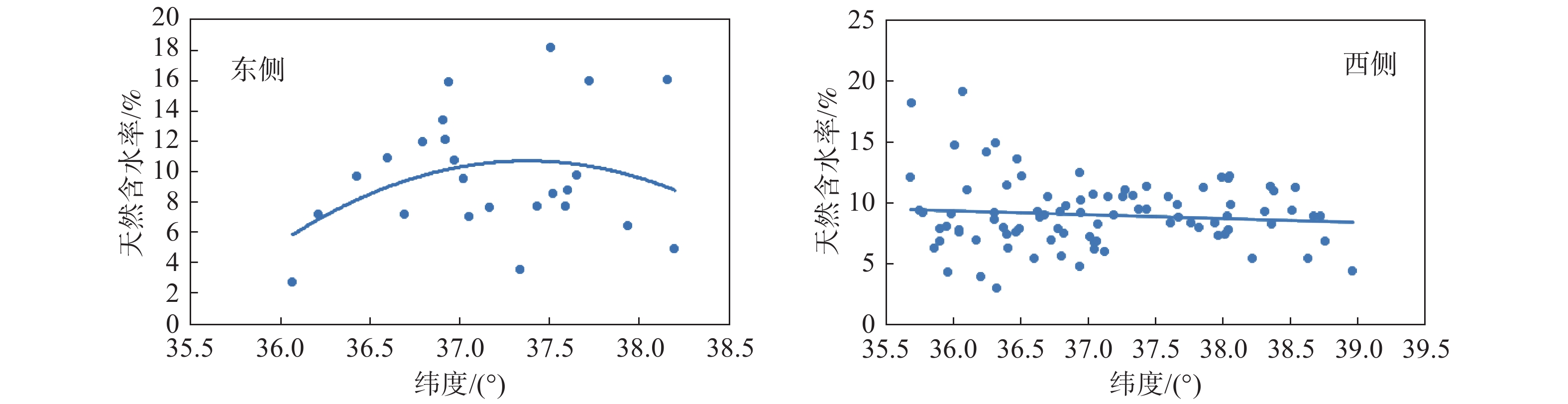
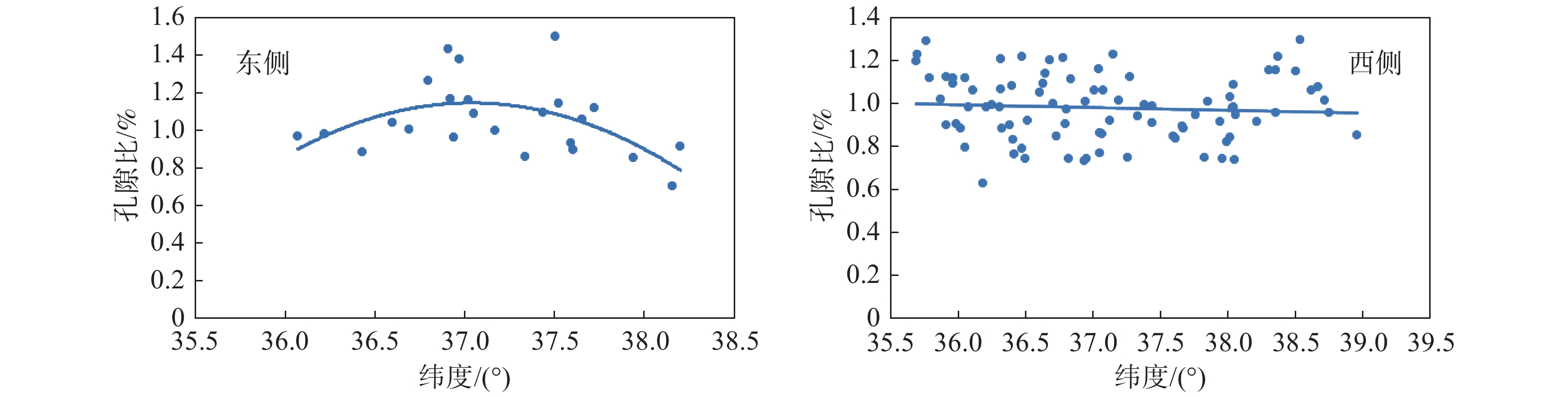
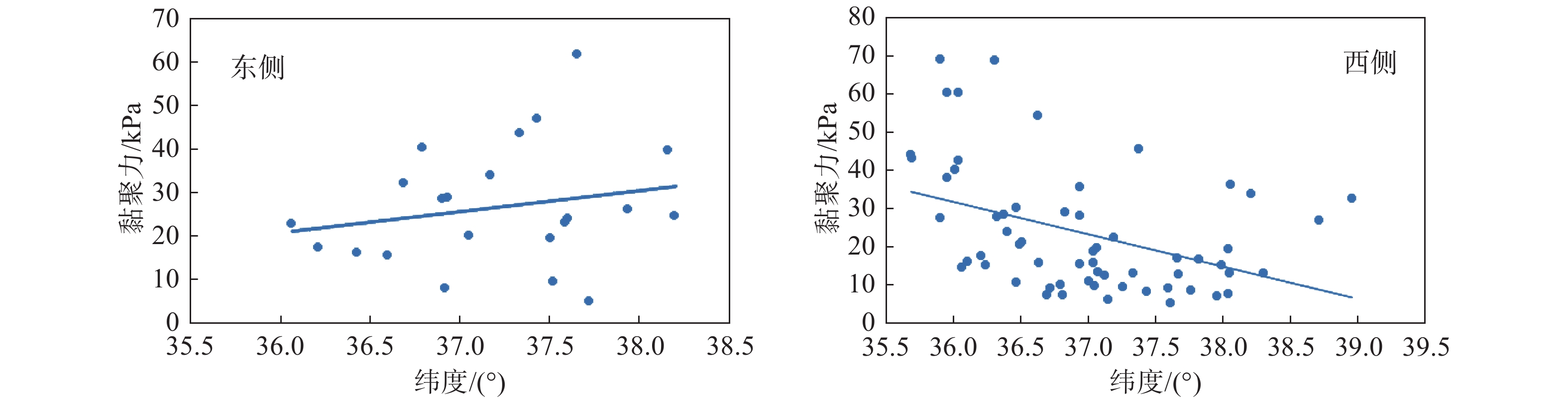
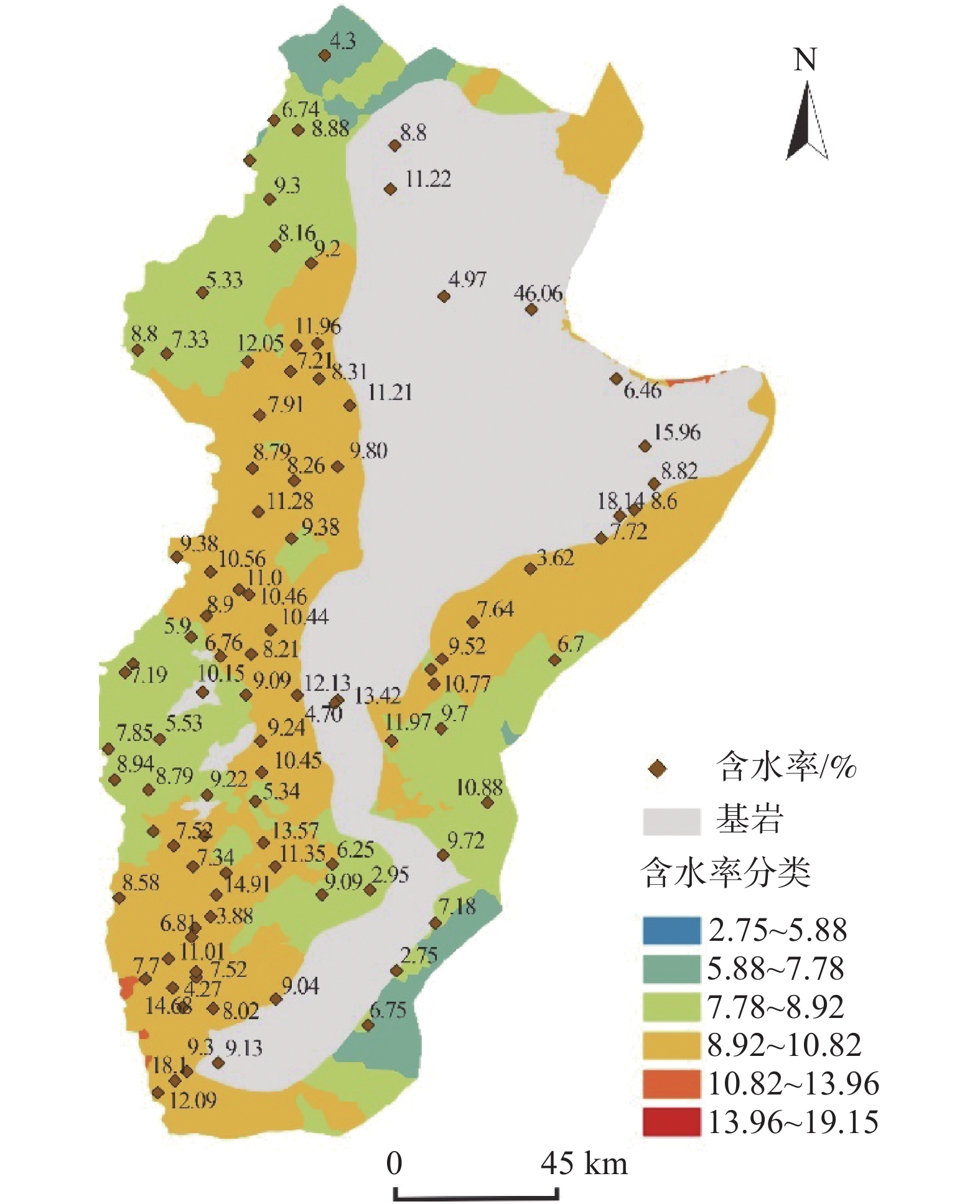
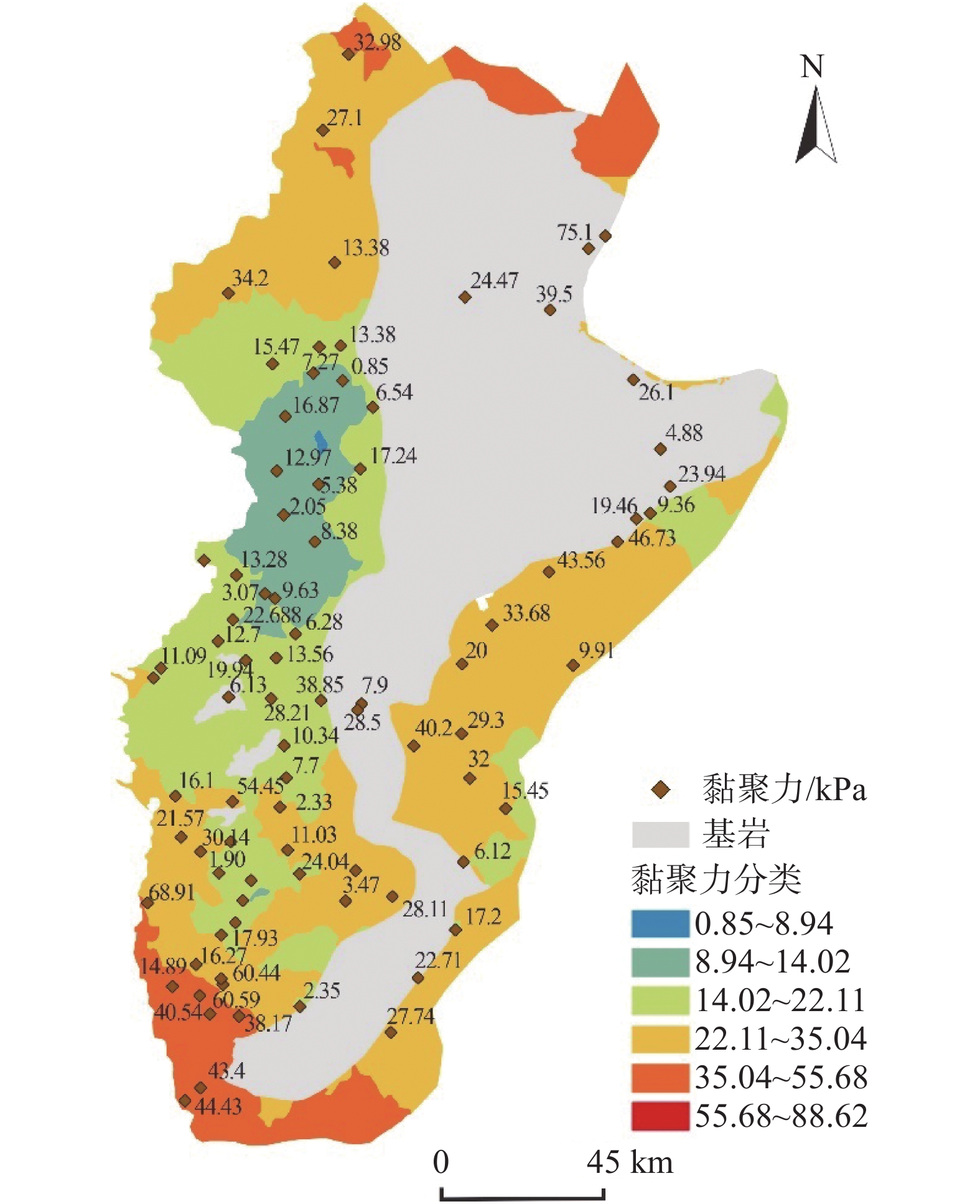
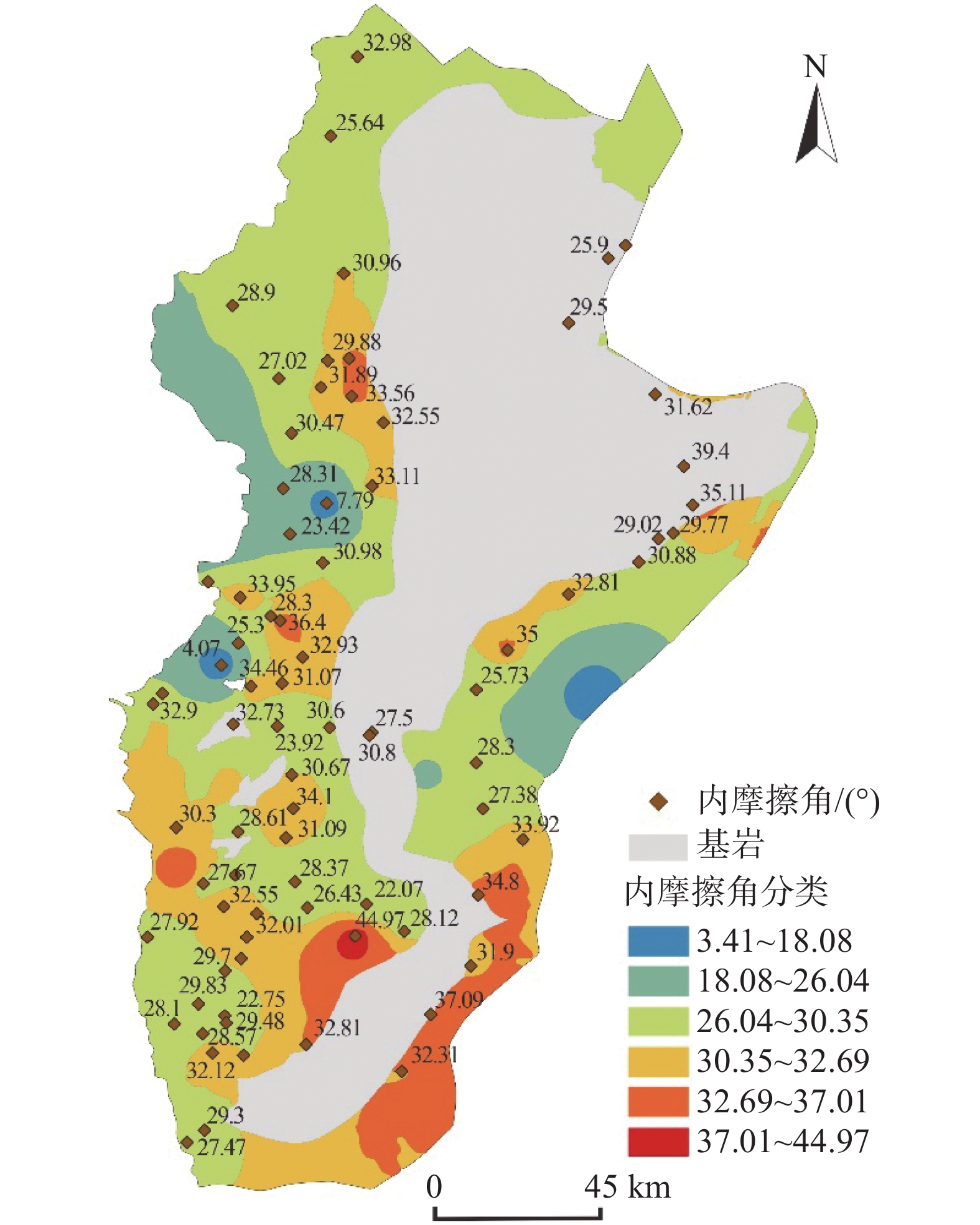
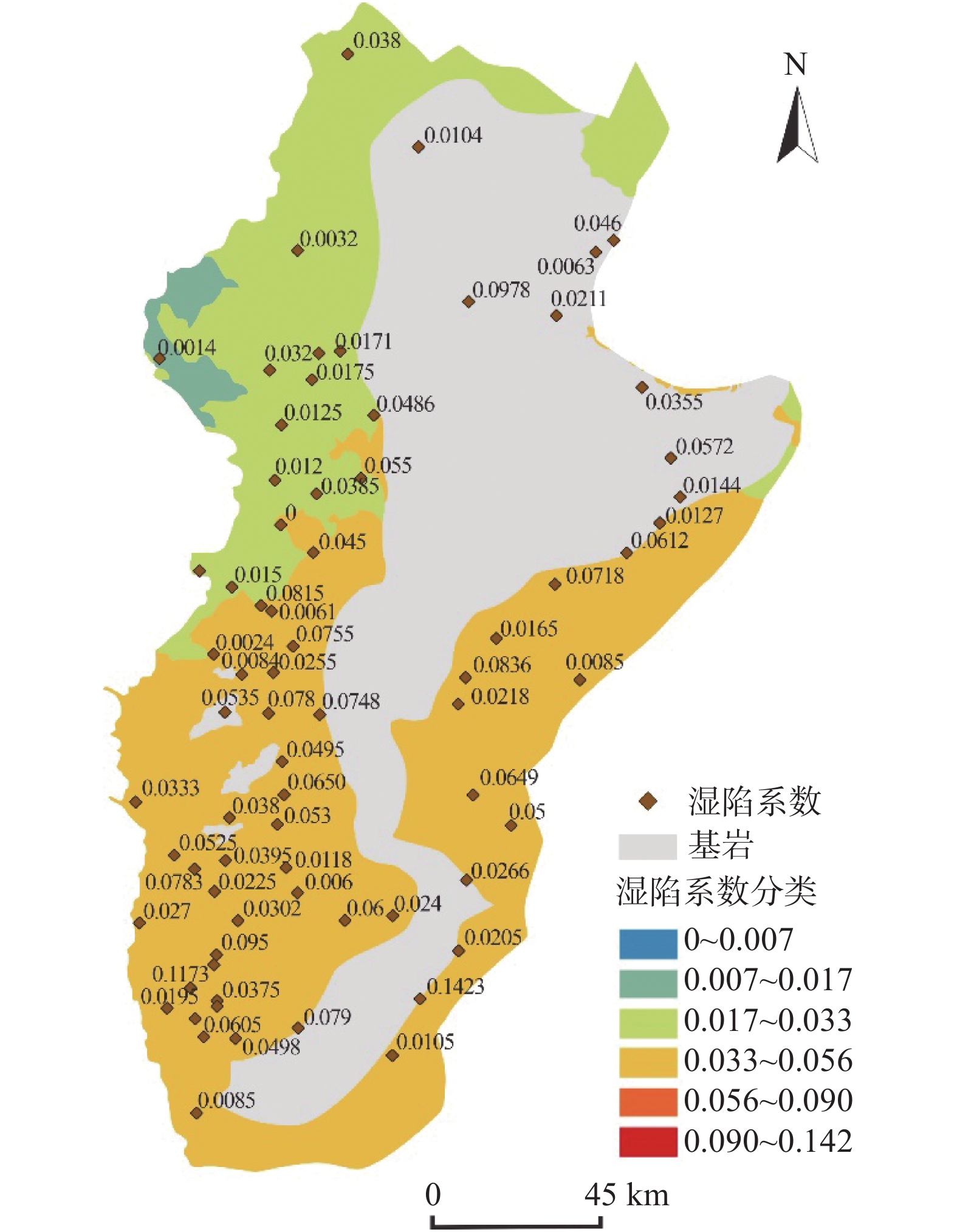
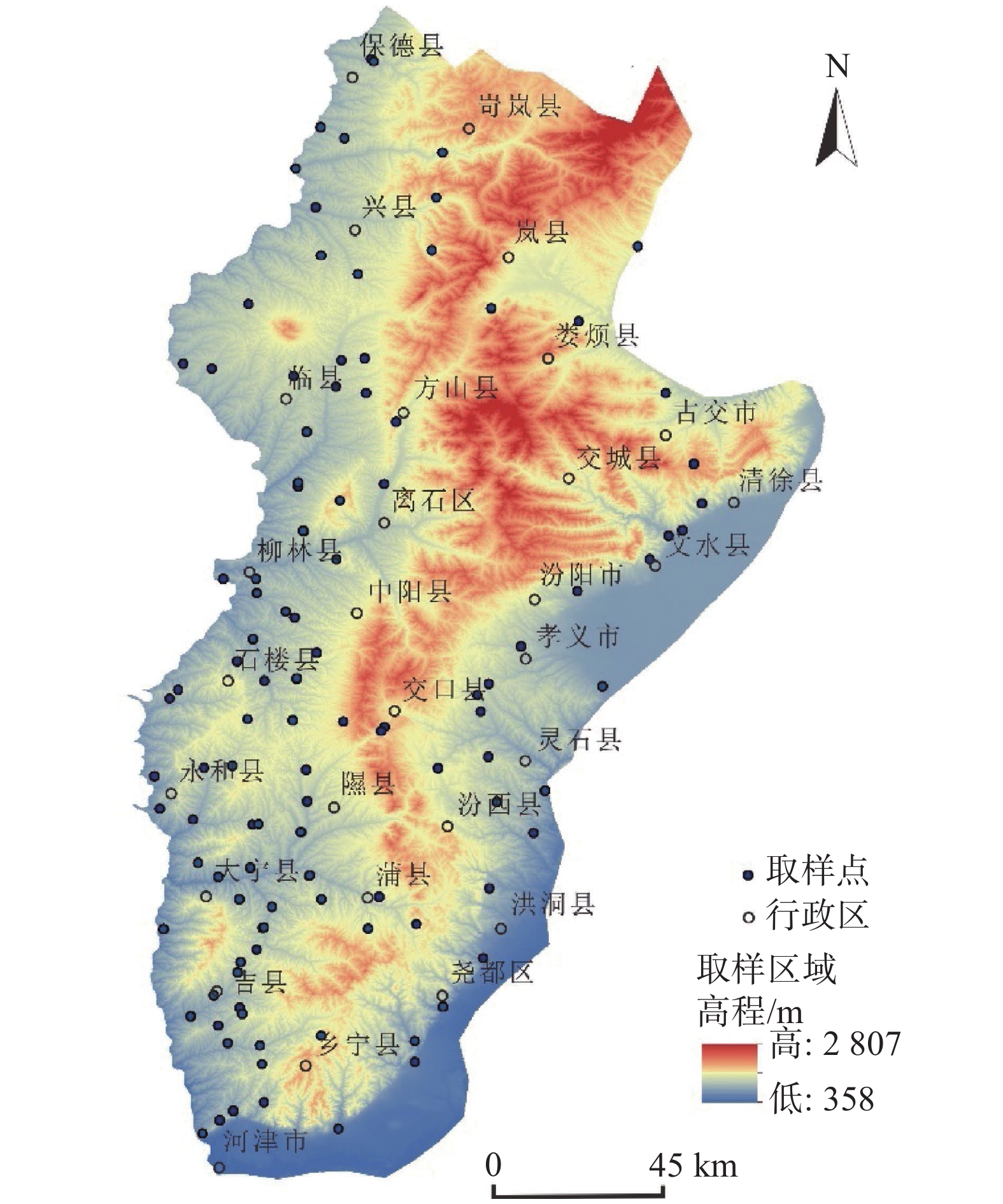
黄土因其特殊的物理力学性质及工程特性,在外界环境影响下易引发诸如黄土崩塌、滑坡、泥流等地质灾害。因此,研究黄土土性参数区域性分布特征对地质灾害防灾减灾具有重要意义。以吕梁山区L1黄土地层为研究对象,在野外调查、代表性点位取样的基础上,对研究区内133个取样点340组黄土试样进行黄土土性参数室内试验,获得其土性参数;基于所得数据,通过统计分析及ArcGIS软件平台,分析研究区内L1黄土地层土性参数分布特征。结果表明:黏粒含量、天然含水率、孔隙比、黏聚力、内摩擦角的分布在南北方向上具有较好的规律性,山脉东西两侧规律略有不同。另外,黏粒含量、天然含水率、黏聚力、湿陷系数的区域分布规律较为明显,内摩擦角区域分布上较为离散。研究结果为从土性特征方面对地质灾害易发性评价提供基础数据支撑。
Abstract:Loess is prone to geological hazards such as landslide, spalling and mud flow due to its special physical and mechanical properties and engineering characteristics. Therefore, it is of great significance to study regional distributive characteristics of loess parameters for geological hazard prevention and mitigation. The L1 loess stratum in Lüliang Mountains is taken as the research object. Based on field investigation and sampling at representative points, the soil properties of 340 groups of loess samples from 133 sites in the study area were tested in laboratory. Based on the obtained data, the distributive characteristics rules of soil properties of L1 loess strata in the study area were analyzed by statistical analysis and ArcGIS software platform. The results show that the distribution of clay content, natural water content, pore ratio, cohesion and internal friction angle have good regularity in north-south direction, but the regularities are slightly different between the eastern and western of the mountains. In addition, the regional distributive characteristics law of clay content, natural water content, cohesion and collapsibility coefficient is obvious. However, the internal friction angle is relatively discrete in regional distribution. The research results provide basic data for the evaluation of geological hazard susceptibility from the perspective of soil characteristics.
-
Key words:
- loess /
- Lüliang mountains /
- soil parameters /
- regionality /
- distributive characteristics
-

-
表 1 黄土土性参数室内试验类型一览表
Table 1. List of laboratory test types of loess parameters
试验类型 数量/个 试验类型 数量/个 颗分试验 286 密度试验 289 含水率试验 289 液塑限试验 272 比重试验 270 固结试验 220 直剪试验 241 常规三轴试验 185 渗透试验 209 湿陷性试验 212 动三轴试验 57 环剪试验 36 崩解试验 20 流变试验 50 表 2 吕梁山脉东侧L1黄土地层常规物理性质指标数据
Table 2. Data of physical properties of L1 loess strata in eastern Lüliang mountains
编号 市县名 取样点数 黏粒含量/% 含水率/% 密度/(g·cm−3) 比重 孔隙比/% 饱和度/% 塑限/% 液限/% 塑性指数 液性指数 1 临汾市(尧都区) 1 9.590 2.752 1.384 2.654 0.971 7.524 18.000 29.695 11.695 −1.304 2 洪洞县 2 11.850 8.453 1.483 2.640 0.932 24.197 18.225 28.773 10.548 −1.010 3 汾西县 2 8.830 9.060 1.436 2.663 1.021 23.535 19.750 33.575 13.825 −0.770 4 灵石县 1 11.240 15.890 1.564 2.650 0.964 43.699 18.650 32.280 13.630 −0.202 5 交口县 5 12.366 11.562 1.332 2.718 1.280 24.589 15.880 33.200 17.360 −0.273 6 孝义市 2 7.800 7.336 1.387 2.642 1.046 18.595 18.450 32.133 13.683 −0.827 7 汾阳县 1 9.070 3.615 1.497 2.688 0.860 11.296 14.700 30.425 15.725 −0.705 8 文水县 3 12.555 12.930 1.313 2.663 1.297 25.611 16.720 32.330 15.630 −0.271 9 清徐县 1 5.490 7.770 1.469 2.631 0.930 21.977 15.700 30.590 14.890 −0.533 10 交城县 2 11.930 9.061 1.436 2.672 1.036 23.624 17.210 30.770 13.570 −0.601 11 古交市 1 16.620 15.961 1.432 2.619 1.121 37.296 18.550 46.390 27.840 −0.093 12 娄烦县 2 5.795 11.257 1.673 2.663 0.779 40.650 17.425 30.493 13.068 −0.413 13 岚县 1 6.720 4.970 1.458 2.658 0.913 14.465 15.700 25.720 10.020 −1.071 表 3 吕梁山脉西侧L1黄土地层常规物理性质指标数据
Table 3. Data of physical properties of L1 loess strata in western Lüliang mountains
编号 市县名 取样点数 黏粒含量/% 含水率/% 密度/(g·cm−3) 比重 孔隙比/% 饱和度/% 塑限/% 液限/% 塑性指数 液性指数 1 河津市 2 15.735 15.140 1.400 2.695 1.216 33.445 18.610 34.535 15.900 −0.235 2 乡宁县 7 13.162 8.040 1.402 2.681 1.072 20.264 17.403 32.763 15.358 −0.816 3 吉县 11 10.862 10.239 1.490 2.659 0.977 28.154 21.607 32.434 10.826 −1.104 4 蒲县 5 7.394 8.642 1.452 2.669 1.006 22.208 18.978 32.938 13.960 −0.758 5 大宁县 5 8.386 8.543 1.556 2.629 0.837 26.782 20.908 31.666 10.758 −1.201 6 隰县 4 9.118 8.562 1.429 2.646 1.015 22.593 20.728 31.410 10.683 −1.155 7 永和县 7 12.560 7.618 1.403 2.615 1.013 19.919 17.800 31.067 13.300 −0.701 8 石楼县 13 8.923 8.089 1.505 2.626 0.901 24.998 15.357 31.457 16.100 −0.543 9 中阳县 1 14.590 10.440 1.370 2.768 1.231 23.467 25.750 32.620 6.870 −2.229 10 柳林县 6 8.568 10.345 1.518 2.679 0.952 29.520 19.863 30.704 10.841 −0.941 11 离石区 2 8.915 9.031 1.543 2.643 0.867 27.490 17.885 29.835 11.950 −0.764 12 方山县 2 6.700 13.178 1.577 2.678 0.927 38.870 16.700 28.890 12.090 −0.451 13 临县 12 9.059 9.183 1.534 2.665 0.902 27.647 16.924 29.945 13.023 −0.690 14 兴县 8 6.943 8.845 1.394 2.704 1.117 21.150 14.013 31.013 17.005 −0.405 15 岢岚县 1 6.590 8.800 1.430 2.736 1.082 22.259 17.160 29.120 12.000 −0.699 16 保德县 3 5.560 6.640 1.467 2.672 0.943 18.593 14.350 28.712 14.382 −0.578 表 4 吕梁山脉东侧L1黄土地层其他土性参数试验数据
Table 4. Data of other parameters of L1 loess strata in eastern Lüliang mountains
编号 市县名 取样点数 压缩系数/MPa−1 压缩模量/MPa 内摩擦角/(°) 黏聚力/kPa 湿陷系数 渗透系数/(cm·s−1) 1 临汾市(尧都区) 1 0.157 13.076 37.085 22.711 1.42E-01 3.31E-04 2 洪洞县 2 0.766 2.789 33.350 16.659 2.35E-02 7.60E-05 3 汾西县 2 0.129 16.776 30.648 23.727 5.75E-02 1.90E-04 4 灵石县 1 0.143 13.793 30.192 28.775 1.30E-02 9.97E-05 5 交口县 5 0.167 12.060 27.467 25.533 2.18E-02 9.31E-06 6 孝义市 2 0.618 7.600 30.365 26.840 5.01E-02 3.30E-04 7 汾阳县 1 0.140 13.333 32.810 43.556 7.18E-02 6.80E-04 8 文水县 3 0.607 5.861 29.955 33.096 6.12E-02 1.38E-04 9 清徐县 1 0.224 8.621 27.570 22.962 4.60E-02 − 10 交城县 2 0.129 21.843 31.377 31.607 1.35E-02 9.43E-05 11 古交市 1 1.357 1.580 39.400 4.880 5.72E-02 1.91E-04 12 娄烦县 2 0.152 11.827 30.560 32.800 2.83E-02 8.26E-05 13 岚县 1 0.243 7.874 21.710 24.465 9.78E-02 2.61E-04 表 5 吕梁山脉西侧L1黄土地层其他土性参数试验数据
Table 5. Data of other parameters of L1 loess strata in western Lüliang mountains
编号 市县名 取样点数 压缩系数/MPa−1 压缩模量/MPa 内摩擦角/(°) 黏聚力/kPa 湿陷系数 渗透系数/(cm·s−1) 1 河津市 2 0.476 4.112 28.385 43.915 8.50E-03 5.64E-05 2 乡宁县 7 0.642 7.888 32.585 34.392 5.50E-02 1.14E-04 3 吉县 11 0.262 14.306 29.437 26.666 5.97E-02 7.32E-05 4 蒲县 5 0.168 15.110 29.992 31.055 2.54E-02 1.20E-04 5 大宁县 5 0.224 7.410 31.788 20.716 4.82E-02 1.22E-04 6 隰县 4 0.462 7.377 31.118 18.705 5.14E-02 7.15E-05 7 永和县 7 0.230 17.317 17.405 15.615 3.37E-02 9.96E-05 8 石楼县 13 0.231 14.834 20.020 16.945 2.93E-02 1.32E-04 9 中阳县 1 0.982 1.018 32.930 6.280 7.55E-02 1.07E-04 10 柳林县 6 0.436 8.421 31.032 13.724 3.81E-02 8.63E-05 11 离石区 2 0.398 4.809 20.452 11.310 4.68E-02 1.11E-04 12 方山县 2 0.407 4.938 32.550 6.540 4.86E-02 7.72E-05 13 临县 12 0.240 17.675 30.802 14.543 1.34E-02 8.03E-05 14 兴县 8 0.219 8.938 28.587 40.893 4.70E-03 − 15 岢岚县 1 0.146 13.407 − − 1.04E-02 − 16 保德县 3 0.125 21.887 27.890 30.040 3.80E-02 − 表 6 黄土湿陷性分类
Table 6. Loess collapsibility classification
分类名称 分类标准 黄土湿陷程度 非湿陷性黄土 δs < 0.015 无湿陷性 湿陷性黄土 0.015 ≤ δs ≤0.03 湿陷性轻微 0.03 < δs ≤ 0.07 湿陷性中等 δs > 0.07 湿陷性强烈 -
[1] 刘东生. 黄土与环境[J]. 西安交通大学学报(社会科学版),2002,22(4):7 − 12. [LIU Dongsheng. Loess and environment[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University (Social Sciences Edition),2002,22(4):7 − 12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 高国瑞. 兰州黄土显微结构和湿陷机理的探讨[J]. 兰州大学学报,1979,15(2):123 − 134. [GAO Guorui. Study of the microstructures and the collapse mechanism in loess soil from Lanzhou[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University,1979,15(2):123 − 134. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 高国瑞. 黄土显微结构分类与湿陷性[J]. 中国科学,1980,10(12):1203 − 1208. [GAO Guorui. Classification and collapsibility of loess[J]. Scientia Sinica,1980,10(12):1203 − 1208. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 雷祥义. 黄土的显微结构与古气候的关系[J]. 地质论评,1989,35(4):333 − 341. [LEI Xiangyi. The relations between microfabrics of loess and paleoclimate in China[J]. Geological Review,1989,35(4):333 − 341. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1989.04.006
[5] 丁仲礼, 孙继敏, 刘东生. 联系沙漠-黄土演变过程中耦合关系的沉积学指标[J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学),1999,29(1):82 − 87. [DING Zhongli, SUN Jimin, LIU Dongsheng. A sedimentological proxy indicator linking changes in loess and desert in the quaternary[J]. Science in China (Series in D),1999,29(1):82 − 87. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 李同录, 张辉, 李萍, 等. 不同沉积环境下马兰黄土孔隙分布与土水特征的模式分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):107 − 114. [LI Tonglu, ZHANG Hui, LI Ping, et al. Mode analysis of pore distribution and soil-water characteristic curve of Malan loess under different depositional environments[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):107 − 114. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 李萍, 李同录. 黄土物理性质与湿陷性的关系及其工程意义[J]. 工程地质学报,2007,15(4):506 − 512. [LI Ping, LI Tonglu. Relation between loess collapsibility and physical properties and its engineering significance[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2007,15(4):506 − 512. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2007.04.013
[8] WEN B P, YAN Y J. Influence of structure on shear characteristics of the unsaturated loess in Lanzhou, China[J]. Engineering Geology,2014,168:46 − 58. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.10.023
[9] 慕焕东, 邓亚虹, 李荣建, 等. 砂粒含量对砂质黄土力学性质影响试验研究[J]. 水利与建筑工程学报,2018,16(6):36 − 39. [MU Huandong, DENG Yahong, LI Rongjian, et al. Experimental study on effects of sand content on sandy loess mechanical properties[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering,2018,16(6):36 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1144.2018.06.007
[10] 袁中夏, 赵未超, 叶帅华, 等. 含水量对黄土边坡稳定性的影响[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(3):37 − 43. [YUAN Zhongxia, ZHAO Weichao, YE Shuaihua, et al. Influence of water content on loess slope stability[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(3):37 − 43. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 刘钊钊, 钟秀梅, 张洪伟, 等. 典型地貌区原状黄土孔隙细观特征研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(2):148 − 155. [LIU Zhaozhao, ZHONG Xiumei, ZHANG Hongwei, et al. Research on pore microscopic characteristics of undisturbed loess in typical geomorphologies[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(2):148 − 155. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 鲁拓, 唐亚明, 李喜安, 等. 马兰黄土孔隙分形特征与渗透性关系[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021,21(19):8138 − 8144. [LU Tuo, TANG Yaming, LI Xi’an, et al. Relationship between pore fractal characteristics and permeability of Malan loess[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2021,21(19):8138 − 8144. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.19.038
[13] 杨泽, 蔺晓燕, 李同录, 等. 陇东黄土的物理力学性质指标统计分析[J]. 重庆科技学院学报(自然科学版),2021,23(1):111 − 114. [YANG Ze, LIN Xiaoyan, LI Tonglu, et al. Statistical analysis of physical and mechanical properties of longdong loess[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Science and Technology (Natural Sciences Edition),2021,23(1):111 − 114. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 张卜平, 朱兴华, 成玉祥, 等. 黄土潜蚀机理及其致灾效应研究综述[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(6):41 − 52. [ZHANG Buping, ZHU Xinghua, CHENG Yuxiang, et al. A review on loess subsurface-erosion mechanism and it's hazard effects[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(6):41 − 52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 张玲玲, 龙建辉, 邢鲜丽, 等. 冻融循环作用下吕梁地区马兰黄土性质研究[J]. 太原理工大学学报,2021,52(4):557 − 563. [ZHANG Lingling, LONG Jianhui, XING Xianli, et al. Study on the properties of Malan loess in Lüliang area under freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology,2021,52(4):557 − 563. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] TANG Y M, BI Y Q, GUO Z Z, et al. A novel method for obtaining the loess structural index from computed tomography images: A case study from the Lüliang mountains of the loess plateau (China)[J]. Land,2021,10(3):291. doi: 10.3390/land10030291
[17] 宋拴萍. 吕梁市离石区地质灾害概况及防治建议[J]. 山西建筑,2014,40(35):78 − 79. [SONG Shuanping. The geological disaster situation and prevention suggestion of Lishi District in Lüliang[J]. Shanxi Architecture,2014,40(35):78 − 79. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2014.35.043
[18] 薛强, 唐亚明, 白轩. 吕梁山区大宁县城地质灾害破坏模式及风险管控[J]. 山地学报,2021,39(1):151 − 162. [XUE Qiang, TANG Yaming, BAI Xuan. Failure modes and risk control of geohazards in the county town of Daning in the Lüliang mountains, China[J]. Mountain Research,2021,39(1):151 − 162. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 黄虎城. 山西主要地质灾害分布规律和影响因素研究[J]. 能源与环保,2020,42(1):87 − 90. [HUANG Hucheng. Study on distribution law and influence factors of main geological disasters in Shanxi Province[J]. China Energy and Environmental Protection,2020,42(1):87 − 90. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 王鹏, 闫治利. 山西省地质灾害总体特征与分布规律研究[J]. 山西煤炭,2018,38(1):20 − 22. [WANG Peng, YAN Zhili. General features and distribution of geological disasters in Shanxi Province[J]. Shanxi Coal,2018,38(1):20 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: