Landslide hazard identification based on slope unit: A case study of shallow soil slope in Wanshan, Guizhou Province
-
摘要:
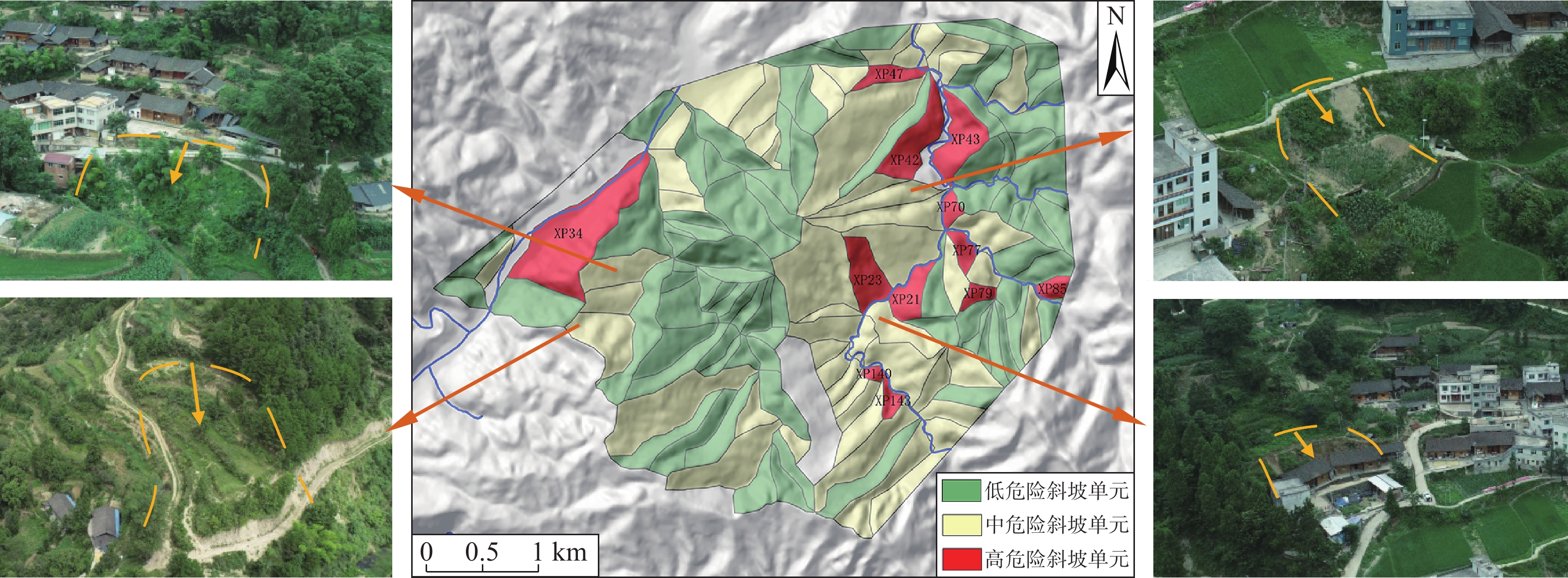
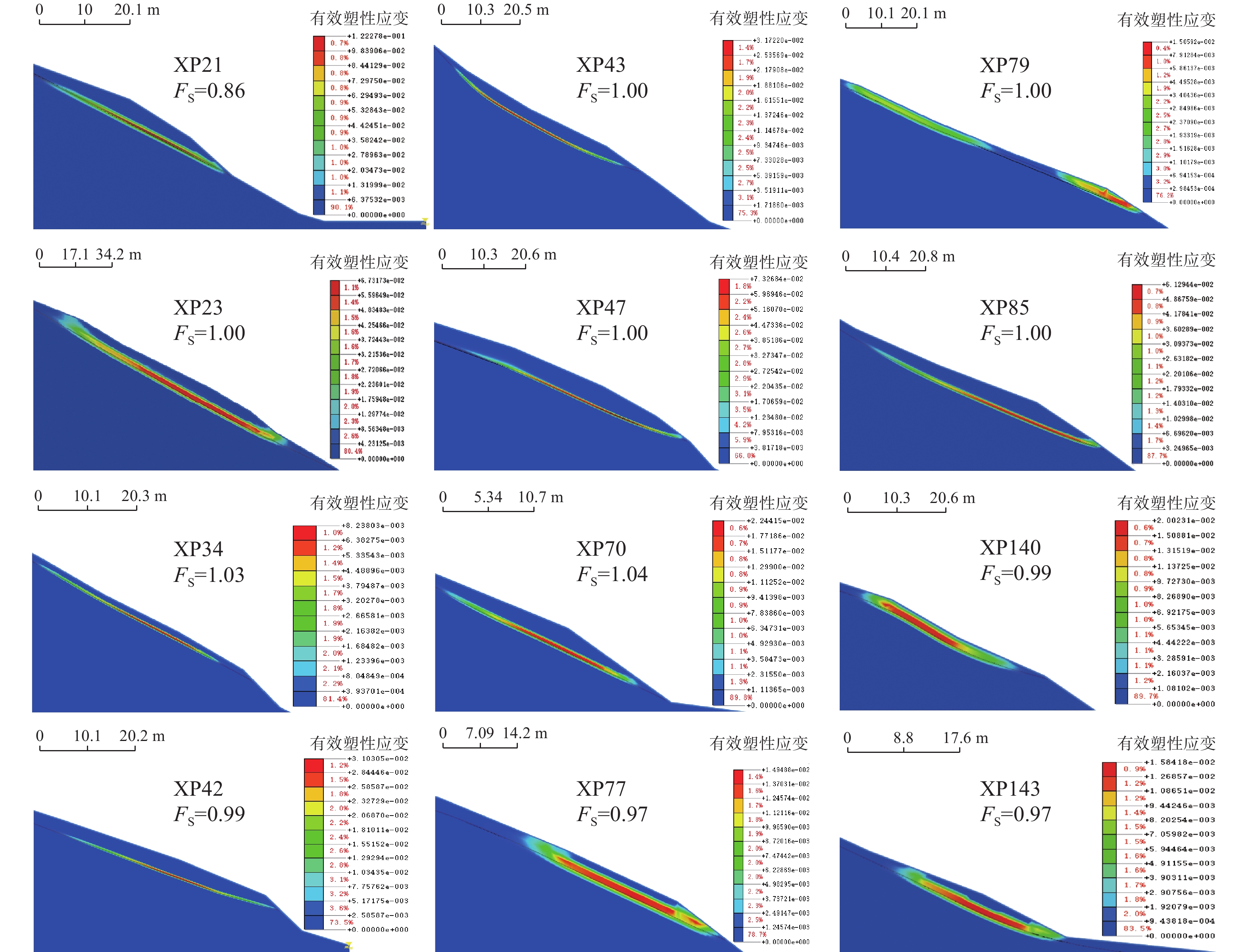
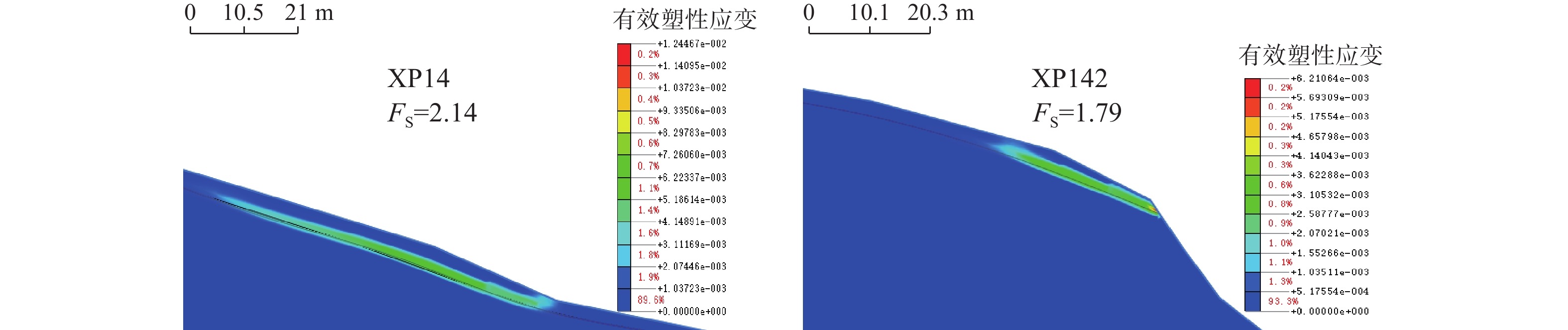
识别斜坡地质灾害风险已成为西南山区地质灾害防治的重要基础工作,通过GIS软件划分出孕灾斜坡单元,选取坡度、坡高、覆盖层厚度、滑体土类型、人类工程活动、日最大降雨量等6项指标作为评价因子,利用层次分析法开展山区大比例尺地质灾害危险性评价,初步评价出研究区危险性斜坡。以万山区1:1万地质灾害风险调查获取的斜坡剖面模型为基础,通过取样、试验,综合选取岩土体物理力学参数,利用有限元软件对暴雨状态下的高危险斜坡进行数值模拟,通过强度折减计算出安全系数均小于1.05,并存在不同程度的塑性贯通区。其分析结果与层次分析法评价结果一致,可作为西南山区浅层土质滑坡隐患识别的定量化评价方法。
Abstract:The identification of slope geological disaster risk has become an important basic work for geological disaster prevention and control in southwest mountainous areas. The potential unstable slope units are divided by GIS program, and six factors including dip angle, elevation, thickness of covering, slope soil type、human engineering activities and maximum rainfall were selected as evaluation factors. Analytic hierarchy process (AHP) is carried out to assess risk of large-scale geological hazards in mountainous areas and preliminarily evaluate the unstable slopes in the study area. While taking slope models in study area of Wanshan as examples, the safety factors under heavy rain condition are analyzed with FEM approaches. In this method, we only reduce the strength parameters of elements whose shear strain is beyond the limit value.The reduction process will continue until the global slope failure associated with the formation of whole sliding surface whose limit shear strains beyond the limit value.It is found that all of the safety factors in 12 slopes are below 1.05 which accorded with the results of AHP. It is proved that proposed method can be seen as a quantitative evaluation method for geological hazard identification of the soil unstable slope in southwest mountainous area.
-
Key words:
- slope unit /
- analytic hierarchy process /
- strength reduction method /
- risk of landslide /
- identification
-

-
表 1 重要性标度值
Table 1. Importance scale values
标度 含义 1 两个因素相比,具有相同重要性 3 两个因素相比,前者比后者稍重要 5 两个因素相比,前者比后者明显重要 7 两个因素相比,前者比后者强烈重要 9 两个因素相比,前者比后者极端重要 2、4、6、8 上述相邻判断的中间值 倒数 若因素后者比前者重要 表 2 近20年日最大降雨量统计表
Table 2. Maximum daily rainfall statistics in 20 years
日期 日最大降雨量/mm 日期 日最大降雨量/mm 2001-08-10 104.4 2011-06-05 69.9 2002-05-13 84.4 2012-07-17 128.8 2003-06-26 71.9 2013-09-24 129.5 2004-07-18 100.0 2014-08-18 123.1 2005-06-01 98.8 2015-06-08 85.1 2006-05-05 157.7 2016-07-04 221.4 2007-07-26 144.0 2017-08-13 53.4 2008-06-08 94.0 2018-07-06 88.7 2009-05-06 60.9 2019-05-19 100.9 2010-09-22 80.0 2020-07-02 111.1 表 3 斜坡危险性评分表
Table 3. Scoring table of slope instability hazard
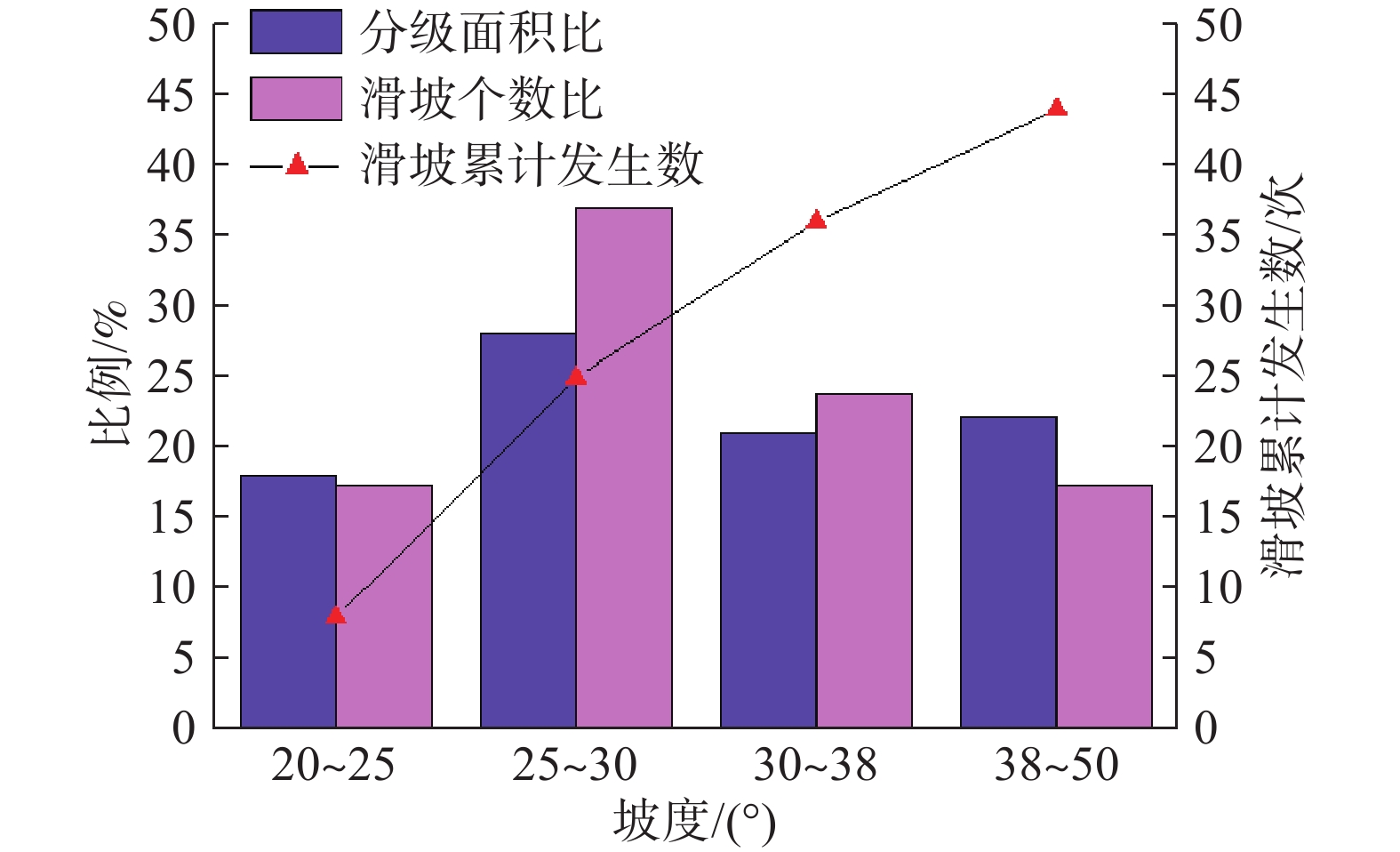
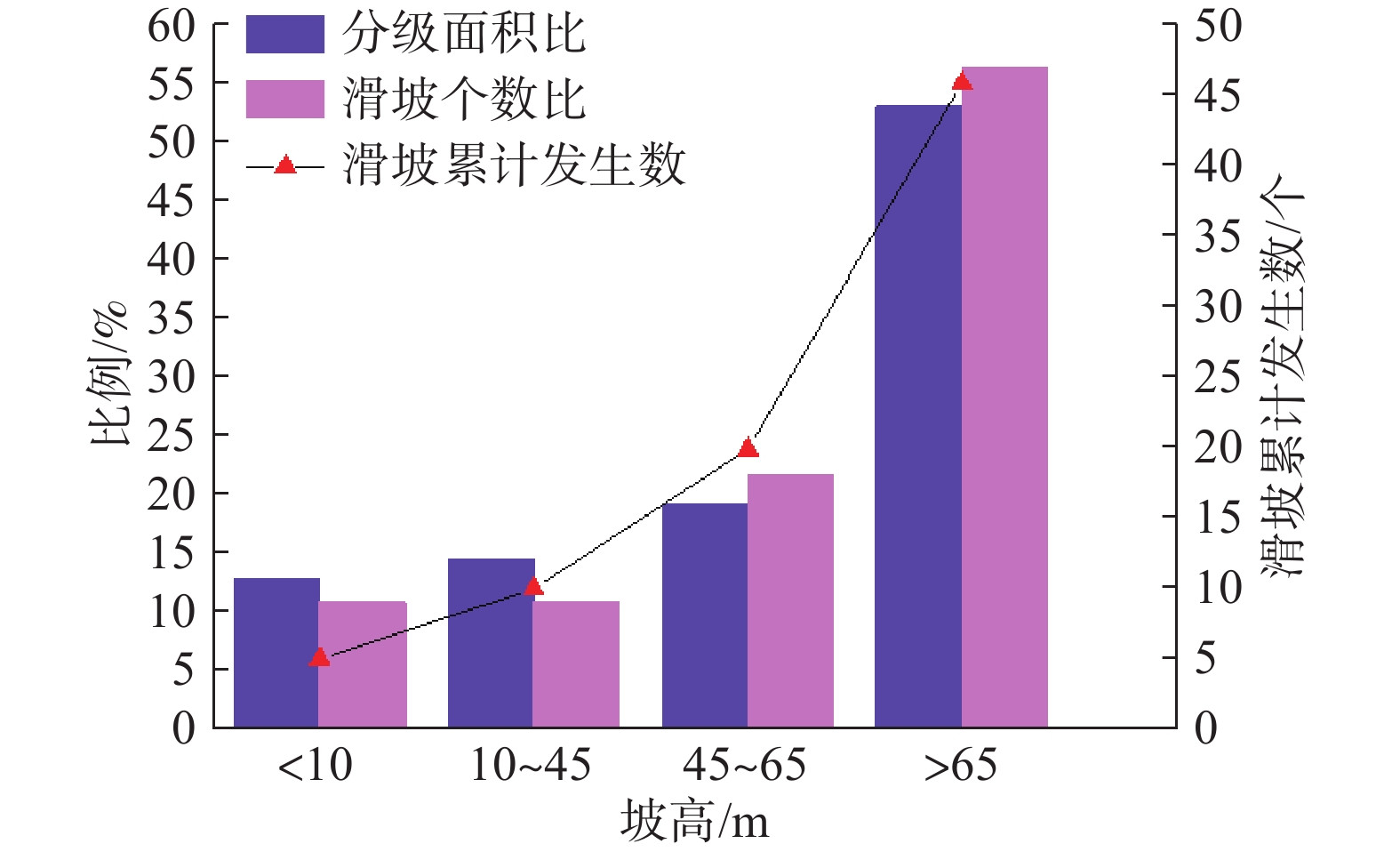
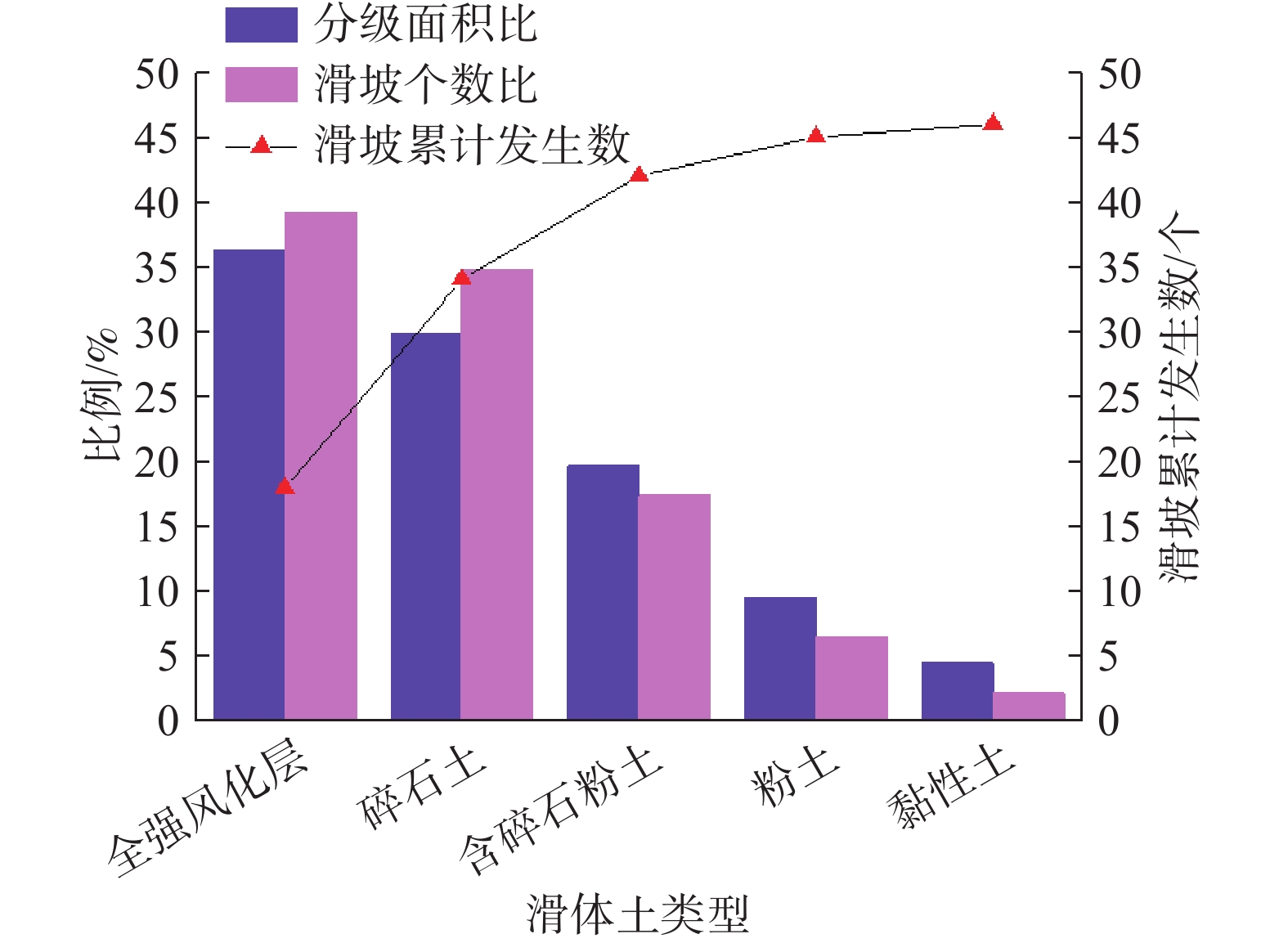
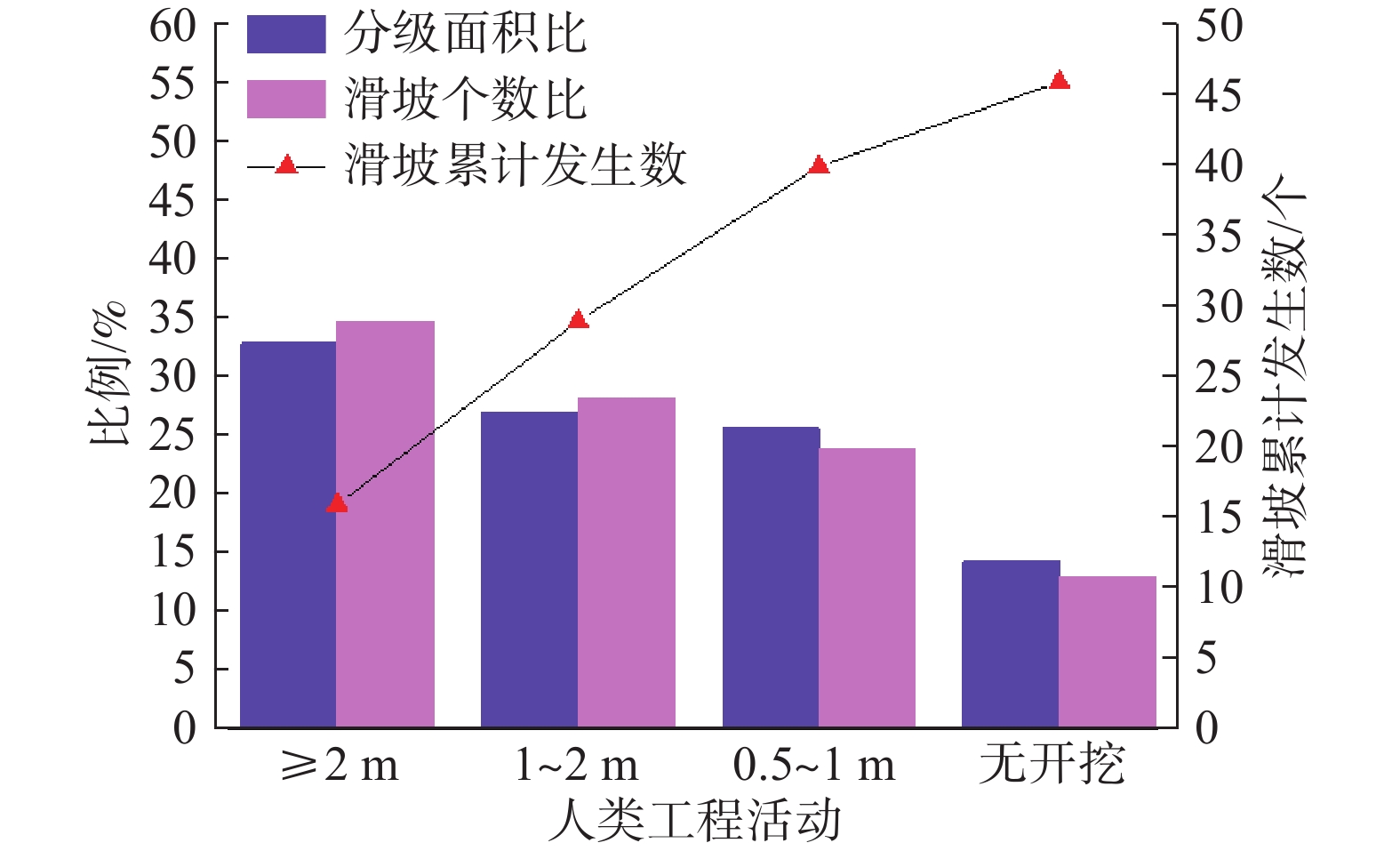
序号 影响因素 危险等级与分值 权重 I级(100分) Ⅱ级(80分) Ⅲ级(60分) Ⅳ级(30分) 1 坡度/(°) 0.149 25~30 30~38 >38、<25 − 2 坡高/m 0.031 >65 − 45~65 <45 3 覆盖层厚度/m 0.092 3.2~4 4~5.5、1~2 2~3.2 >5.5 4 滑体土类型 0.254 全、强风化层; 碎石土 含碎石粉土(20%≤碎石含量<50%) 粉土(碎石含量<20%) 5 人类工程活动 0.051 斜坡开挖高度≥2 m;
无坡面排水和
边坡支护措施斜坡开挖高度1~2 m;
坡面排水和边坡
支护措施部分满足斜坡开挖高度0.5~1 m;
坡面排水和边坡
支护措施较好无开挖 6 日最大降雨量/mm 0.423 >105 85~105 53~85 <53 表 4 风险斜坡区土体物理力学参数
Table 4. Physical and mechanical parameters of soil in unstable slope area
土样编号 泊松比 弹性模量/GPa 天然状态 暴雨状态 重度/(kN·m−3) 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 重度/(kN·m−3) 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) XP21 0.3 5 17.3 33.9 10.3 17.5 31.1 9 XP23 0.3 5 17.1 35.8 9.6 17.3 32 6.9 XP34 0.3 5 17.1 32.2 9.3 17.3 29.9 7.6 XP42 0.3 5 17.1 33.7 10.4 17.2 30.6 7.6 XP43 0.3 5 16.9 33.4 9.3 17.2 31.7 6.9 XP47 0.3 5 16.8 30.8 9.1 17.3 29.8 8.1 XP70 0.3 5 17.2 34.5 7.9 17.5 29.1 6.9 XP77 0.3 5 17.3 35 8.7 17.6 29.9 8 XP79 0.3 5 17.4 32.8 9.3 17.4 29.7 7.1 XP85 0.3 5 16.8 33.5 7.9 17.1 28.5 7.6 XP140 0.3 5 17.1 33.9 8.8 17.4 30.5 6.8 XP143 0.3 5 17.2 33.8 8.4 17.3 28 6.8 -
[1] 薛强, 张茂省, 李林. 基于斜坡单元与信息量法结合的宝塔区黄土滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地质通报,2015,34(11):2108 − 2115. [XUE Qiang, ZHANG Maosheng, LI Lin. Loess landslide susceptibility evaluation based on slope unit and information valuemethod in Baota District, Yan’an[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2015,34(11):2108 − 2115. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xue Qiang, Zhang Maosheng, Li Lin. Loess landslide susceptibility evaluation based on slope unit and information valuemethod in Baota District, Yan'an. Geological Bulletin of China, 2015, 34(11): 2108-2115. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 孟田, 许晓露, 刘汉湖. 基于斜坡单元优化的高海拔地区滑坡危险性评价—以金沙江白格滑坡为例[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,40(1):65 − 72. [MENG Tian, XU Xiaolu, LIU Hanhu. Landslide risk assessment in high altitude areas based on slope unit optimization: Taking the Baige landslide in Jinsha River as an example[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Natural Science),2021,40(1):65 − 72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
MENG Tian, XU Xiaolu, LIU Hanhu. Landslide risk assessment in high altitude areas based on slope unit optimization: Taking the Baige landslide in Jinsha River as an example[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University( Natural Science), 2021, 40(1): 65-72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 颜阁, 梁收运, 赵红亮. 基于GIS的斜坡单元划分方法改进与实现[J]. 地理科学,2017,37(11):1764 − 1770. [YAN Ge, LIANG Shouyun, ZHAO Hongliang. An Approach to Improving Slope Unit Division Using GIS Technique[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica,2017,37(11):1764 − 1770. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yan Ge, Liang Shouyun, Zhao Hongliang. An Approach to Improving Slope Unit Division Using GIS Technique. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2017, 37(11): 1764-1770. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 冯卫, 唐亚明, 马红利, 等. 一种基于斜坡单元的山区城镇地质灾害高危险坡段识别方法[J]. 灾害学,2021,36(1):64 − 68. [FENG Wei, TANG Yaming, MA Hongli, et al. Identification Method of High-Risk Slopes of Geological Disaster in Mountain Towns Based on Slope Unit[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2021,36(1):64 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2021.01.013
FENG Wei, TANG Yaming, MA Hongli, et al. Identification Method of High-Risk Slopes of Geological Disaster in Mountain Towns Based on Slope Unit[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2021, 36(1): 64-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2021.01.013
[5] 薛强, 张茂省, 高波. 斜坡单元支持下基于土体含水率的陕西省清涧县城区黄土滑坡危险性评价[J]. 中国地质,2020,47(6):1904 − 1914. [XUE Qiang, ZHANG Maosheng, GAO Bo. Hazard assessment of loess landslide based on soil moisture content and supported by slope unit in Qingjian City, Shaanxi Province[J]. Geology in China,2020,47(6):1904 − 1914. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12029/gc20200624
Xue Qiang, Zhang Maosheng, Gao Bo. Hazard assessment of loess landslide based on soil moisture content and supported by slope unit in Qingjian City, Shaanxi Province[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6): 1904-1914. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12029/gc20200624
[6] 贵州省地质环境监测院. 贵州省万山区地质灾害详细调查及风险评价报告[R]. 贵阳: 贵州省地质环境监测院, 2021
Guizhou Geological Environment Monitoring Institute. Report on the results of geological disaster investigation and risk assessment in Wanshan of Guizhou[R]. Guiyang: Guizhou Geological Environment Monitoring Institute, 2021. (in Chinese)
[7] 杜国梁, 杨志华, 袁颖, 等. 基于逻辑回归-信息量的川藏交通廊道滑坡易发性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):102 − 111. [DU Guoliang, YANG Zhihua, YUAN Ying, et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Xizang traffic corridor using logistic regression- information value method[J]. Hydrogeology& Engineering,2021,48(5):102 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Du Guoliang, YangZhihua, YuanYing, et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Xizang traffic corridor using logistic regression- information value method[J]. Hydrogeology& Engineering, 2021, 48(5): 102-111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 常金源, 包含, 伍法权, 等. 降雨条件下浅层滑坡稳定性探讨[J]. 岩土力学,2015,4(36):995 − 1000. [CHANG Jinyuan, BAO Han, WU Faquan, et al. Discussion on stability of shallow landslide under rainfall[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2015,4(36):995 − 1000. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chang Jinyuan, BaoHan, Wu Faquan, et al. Discussion on stability of shallow landslide under rainfall[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 4(36): 995-1000. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 许晓露, 刘汉湖, 蒋川东. 基于斜坡单元的滑坡易发性评价—以易贡地区为例[J]. 河南科学,2019,37(11):1825 − 1831. [XU Xiaolu, LIU Hanhu, JIANG Chuandong. Key Laboratory of Geoscience Spatial Information Technology of Ministry of Land and Resources, Chengdu University of Technology[J]. Henan Science,2019,37(11):1825 − 1831. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XU Xiaolu, LIU Hanhu, JIANG Chuandong. Key Laboratory of Geoscience Spatial Information Technology of Ministry of Land and Resources, Chengdu University of Technology[J]Henan Science, 2019, 37(11): 1825-1831. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 邓雪, 李家铭, 曾浩健, 等. 层次分析法权重计算方法分析及其应用研究[J]. 数学的实践与认识,2012,42(7):93 − 100. [DENG Xu, LI Jiaming, ZENG Haojian, et al. Research on computation methods of AHP weight vector and its applications[J]. Mathematics in Practice and Theory,2012,42(7):93 − 100. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0984.2012.07.012
Deng Xu, Li Jiaming, Zeng Haojian, et al. Research on computation methods of AHP weight vector and its applications[J]. Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 2012, 42(7): 93-100. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0984.2012.07.012
[11] 高晨曦, 刘艺梁, 薛欣, 等. 三峡库区典型堆积层滑坡变形滞后时间效应研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2021,29(5):1427 − 1436. [GAO Chenxi, LIU Yiliang, XUE Xin, et al. Study on deformation lag time effect of typical colluvial landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021,29(5):1427 − 1436. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Gao Chenxi, Liu Yiliang, Xue Xin, et al. Study on deformation lag time effect of typical colluvial landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2021, 29(5): 1427-1436. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] KUMARD, THAKUR M, DUBEYCS, et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping & prediction using support vector machine for mandakini river basin, Garhwal Himalaya, India[J]. Geomorphology,2017:S0169555 − X16309485.
[13] TIEN BUI D, TUAN T A, HOANG N D, et al. Spatial prediction of rainfall-induced landslides for the Lao Cai area( Vietnam) using a hybrid intelligent approach of least squares support vector machines inference model and artificial bee colony optimization[J]. Landslides,2017,14(2):447 − 458. doi: 10.1007/s10346-016-0711-9
[14] ADITIANA, KUBOTAT, SHINOHARAY. Comparison of GIS-based landslide susceptibility models using frequency ratio, logistic regression, and artificial neural network in a tertiary region of Ambon, Indonesia[J]. Geomorphology,2018,318:101 − 111. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.06.006
[15] TAALAB K, CHENG T, ZHANG Y. Apping landslide susceptibility and types using Random Forest[J]. Big Earth Data,2018,2(2):159 − 178. doi: 10.1080/20964471.2018.1472392
[16] 陈国庆, 黄润秋, 石豫川, 等. 基于动态和整体强度折减法的边坡稳定性分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2014,33(2):243 − 256. [CHEN Guoqing, HUANG Runqiu, SHI Yuchuan, et al. Stability analysis of slope based on dynamic and whole strength reduction methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2014,33(2):243 − 256. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHEN Guoqing, HUANG Runqiu, SHI Yuchuan, et al. Stability analysis of slope based on dynamic and whole strength reduction methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(2): 243–256. ( in Chinese with English abstract
[17] 刘康琦, 刘红岩, 祁小博. 基于强度折减法的土石混合体边坡长期稳定性研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(2):327 − 334. [LIU Kangqi, LIU Hongyan, QI Xiaobo. Numerical study on long-term stability of soil-rock mixture slope using strength reduction technique[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(2):327 − 334. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu Kangqi, Liu Hongyan, Qi Xiaobo. Numerical study on long-term stability of soil-rock mixture slope using strength reduction technique[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28( 2): 327-334. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 林姗, 郭昱葵, 孙冠华, 等. 边坡稳定性分析的虚单元强度折减法[J]. 工程地质学报, 2019, 38(增刊2): 3429 − 3436
LIN Shan, GAO Yukui, SUN Guanhua, et al. Slope stability analysis using the virtual element method and shear strength reduction technique[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2019, 38(Sup 2): 3429 − 3436. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: