Distribution and susceptibility assessment of geological hazards in Zemuhe fault zone (Puge section)
-
摘要:
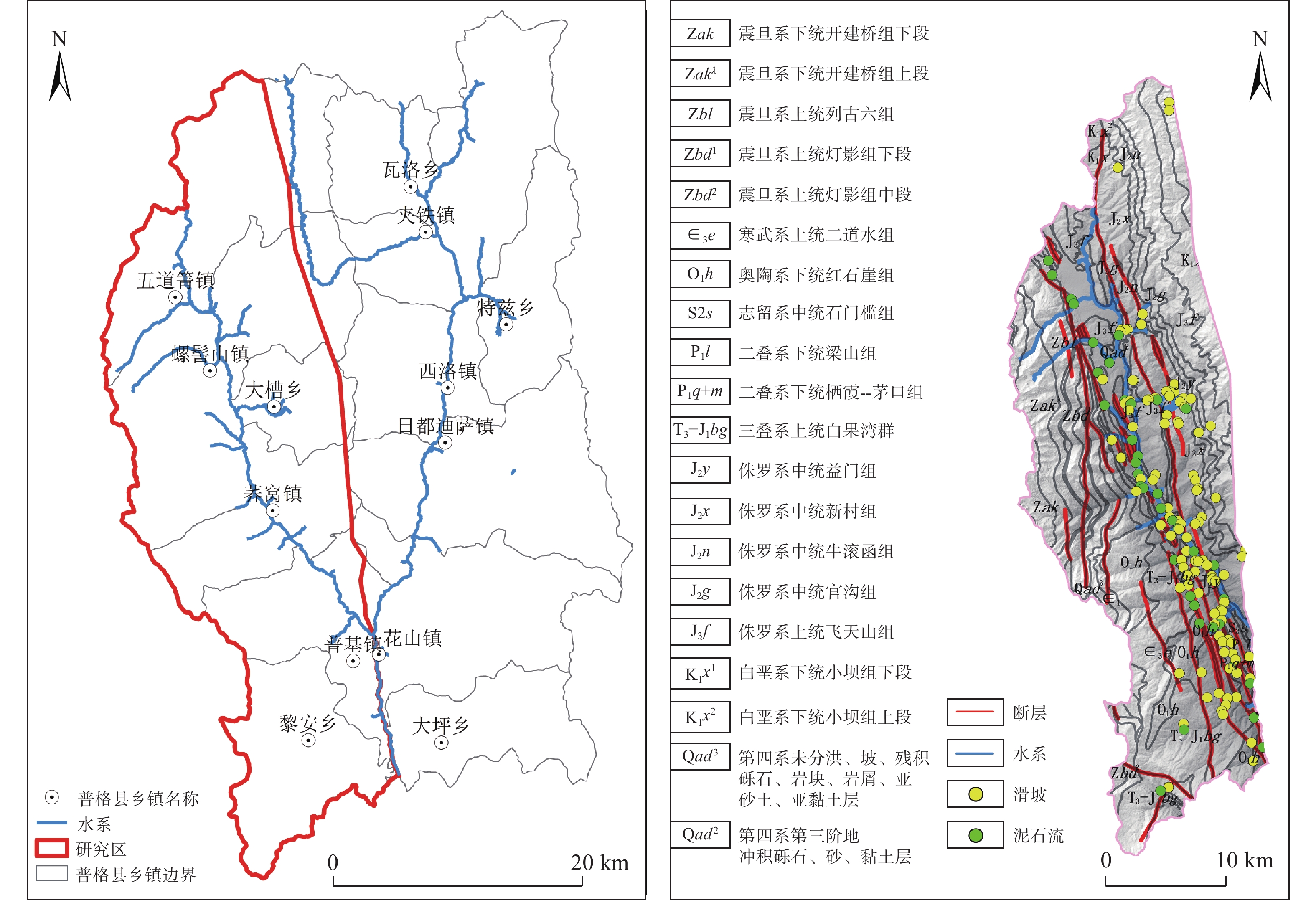
以则木河断裂带(普格段)为研究区,分析研究区的地质灾害控制效应以及发育规律;选取海拔高程、坡向、坡度等7个评价因子构建评价指标体系,运用确定性系数模型与信息量模型耦合的加权信息量模型,通过ArcGIS进行地质灾害易发性评价。结果显示,研究区地质灾害发育具有断层距离效应、地层效应以及高程和坡度微地貌效应;极高易发区、高易发区、中易发区和低易发区的面积分别为46.75 km2、123.78 km2、215.73 km2、285.34 km2,面积占比分别为6.96%、18.43%、32.12%、42.49%。研究结果对指导则木河断裂带地区以及同类区域的国土空间规划与地灾防治等方面具有重要现实意义。
Abstract:Taking Zemuhe fault zone (Puge section) as the study area, the control effect and development law of geological disasters in the study area are analyzed; Seven evaluation factors such as elevation, aspect and slope from fault are selected to construct the evaluation index system. The weighted information model coupled with deterministic coefficient model and information model is used to evaluate the susceptibility of geological disasters through ArcGIS. The results show that the development of geological hazards in the study area has fault distance effect, elevation and slope micro geomorphic effect and stratigraphic effect;The areas of extremely high, high, medium and low prone areas are 46.75 km2, 123.78 km2, 215.73 km2 and 285.34 km2 respectively, accounting for 6.96%, 18.43%, 32.12% and 42.49% respectively. The research results have important practical significance for guiding the land spatial planning and geological disaster prevention in Zemuhe fault zone and similar regions.
-

-
表 1 则木河断裂带(普格段)地质灾害规模统计表
Table 1. Statistical table of geological disaster scale of Zemuhe fault zone (Puge section)
规模 特大型/处 大型/处 中型/处 小型/处 合计/处 滑坡 0 6 19 80 105 泥石流 0 0 20 18 38 合计 0 6 39 98 143 表 2 灾害点分布与距断层距离的关系
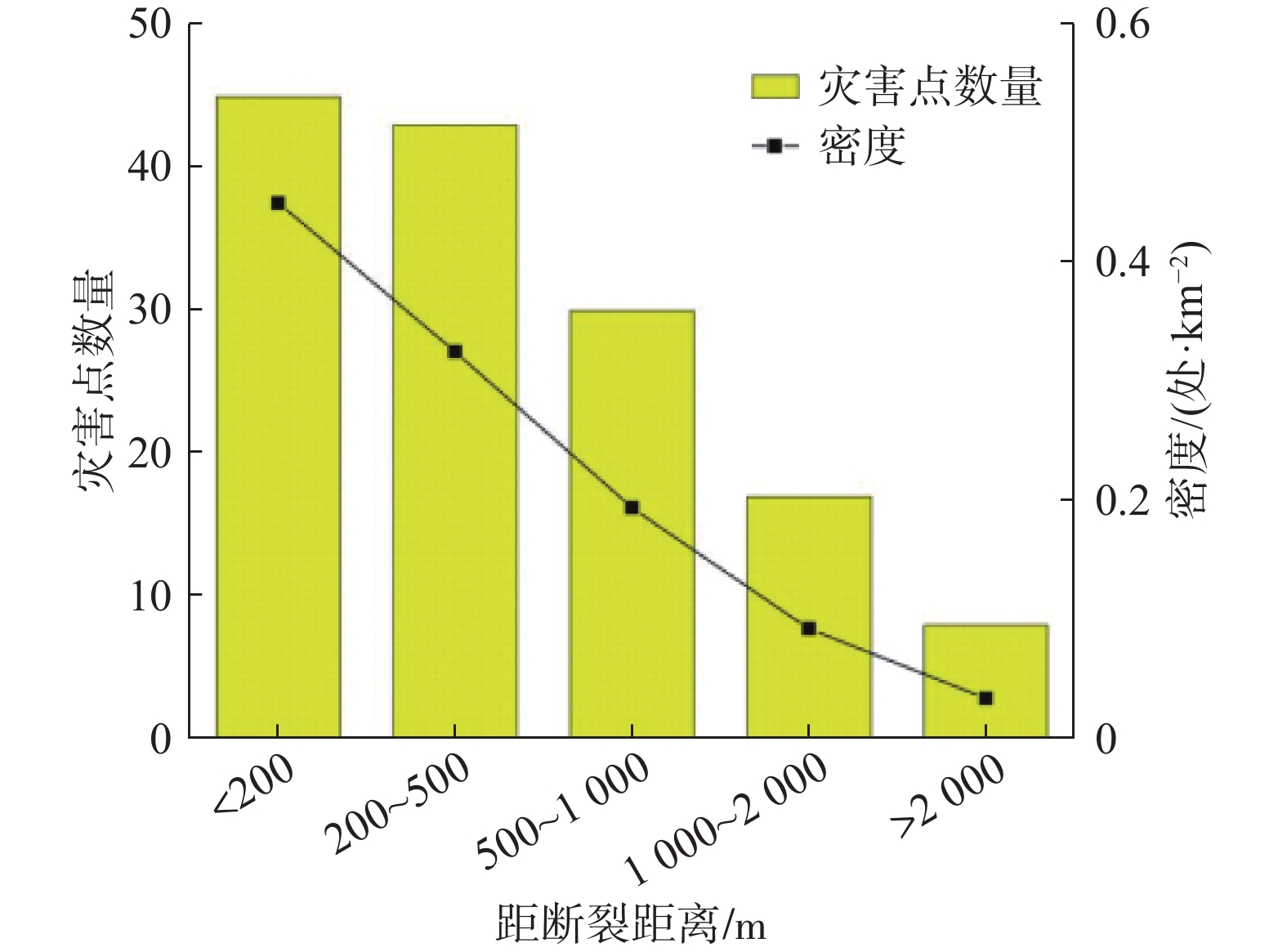
Table 2. Relationship between distribution of disaster points and fault distance
距断裂距离/m 灾害点数量/处 面积/km2 密度/(处·km−2) <200 45 83.71788828 0.53751953 200~500 43 110.7142871 0.388387092 500~1000 30 129.3603065 0.231910397 1000~2 000 17 153.1572232 0.11099705 >2 000 8 194.6502949 0.041099347 表 3 灾害点分布与岩类的关系
Table 3. Relationship between distribution of disaster points and rocks
岩类 灾害点数量/处 面积/km2 密度/(处·km−2) 松散岩土类 37 57.25807612 0.646197052 碎屑岩类 101 561.6624813 0.179823298 碳酸盐岩 4 51.48866247 0.077687005 岩浆岩类 1 1.190780142 0.839785587 表 4 灾害点分布与高程的关系
Table 4. Relationship between disaster point distribution and elevation
高程/m 灾害点数量/处 面积/km2 密度/(处·km−2) ≤1500 58 47.29627874 1.226312123 1500~1800 34 61.81273055 0.550048505 1800~2100 33 95.51799726 0.345484631 2100~2400 14 123.1613209 0.113672051 2400~2700 2 106.0693742 0.018855584 2700~3000 1 102.444593 0.009761374 >3000 1 135.2977053 0.007391108 表 5 灾害点分布与坡度的关系
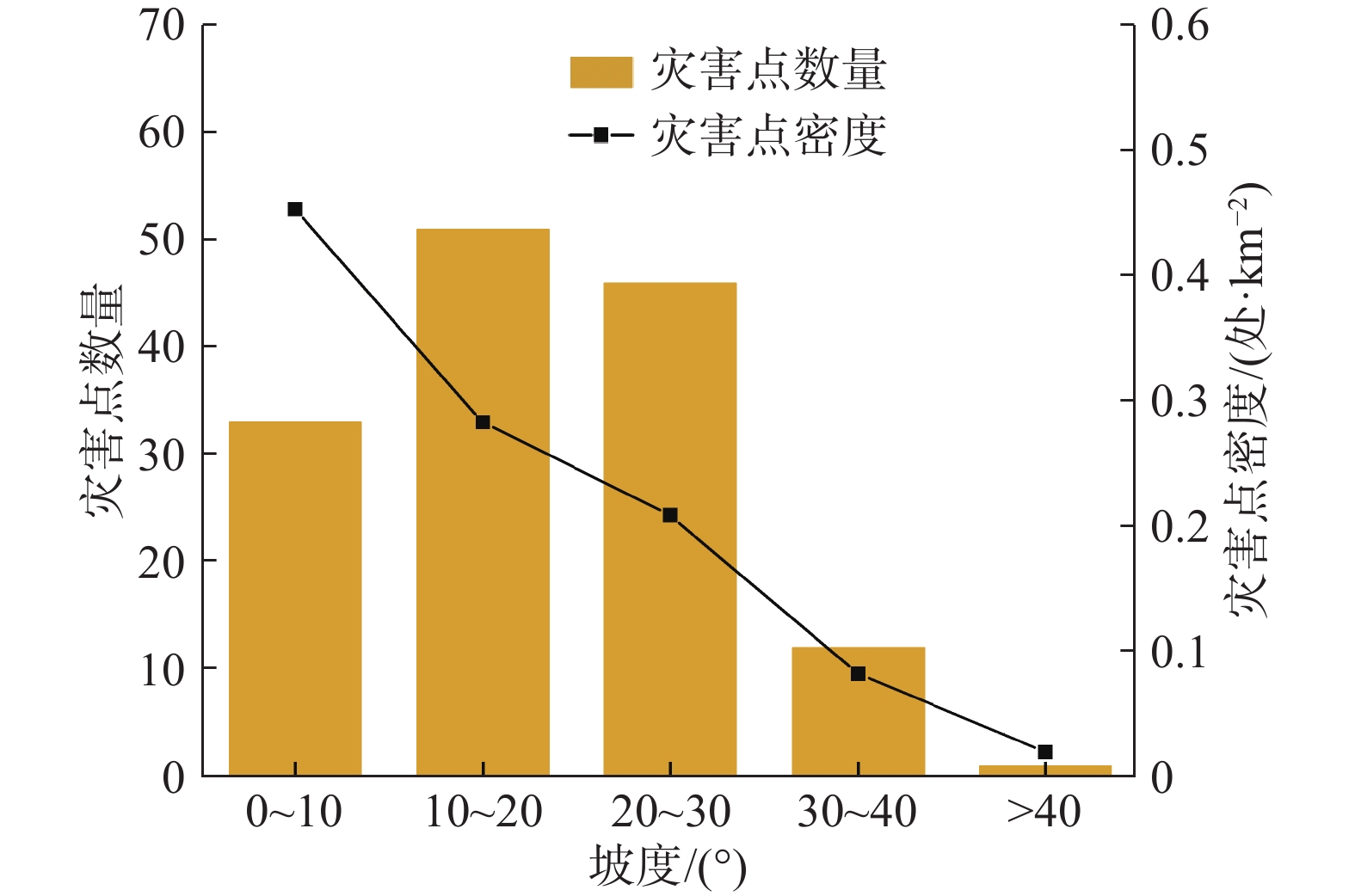
Table 5. Relationship between disaster point distribution and slope
坡度/(°) 灾害点数量/处 面积/km2 密度/(处·km−2) 0~10 33 72.82142422 0.453163342 10~20 51 180.4059596 0.282695761 20~30 46 220.8611978 0.208275607 30~40 12 146.3258923 0.082008726 >40 1 51.18552612 0.019536773 表 6 评价因子分级信息量值
Table 6. Evaluation factor classification information value
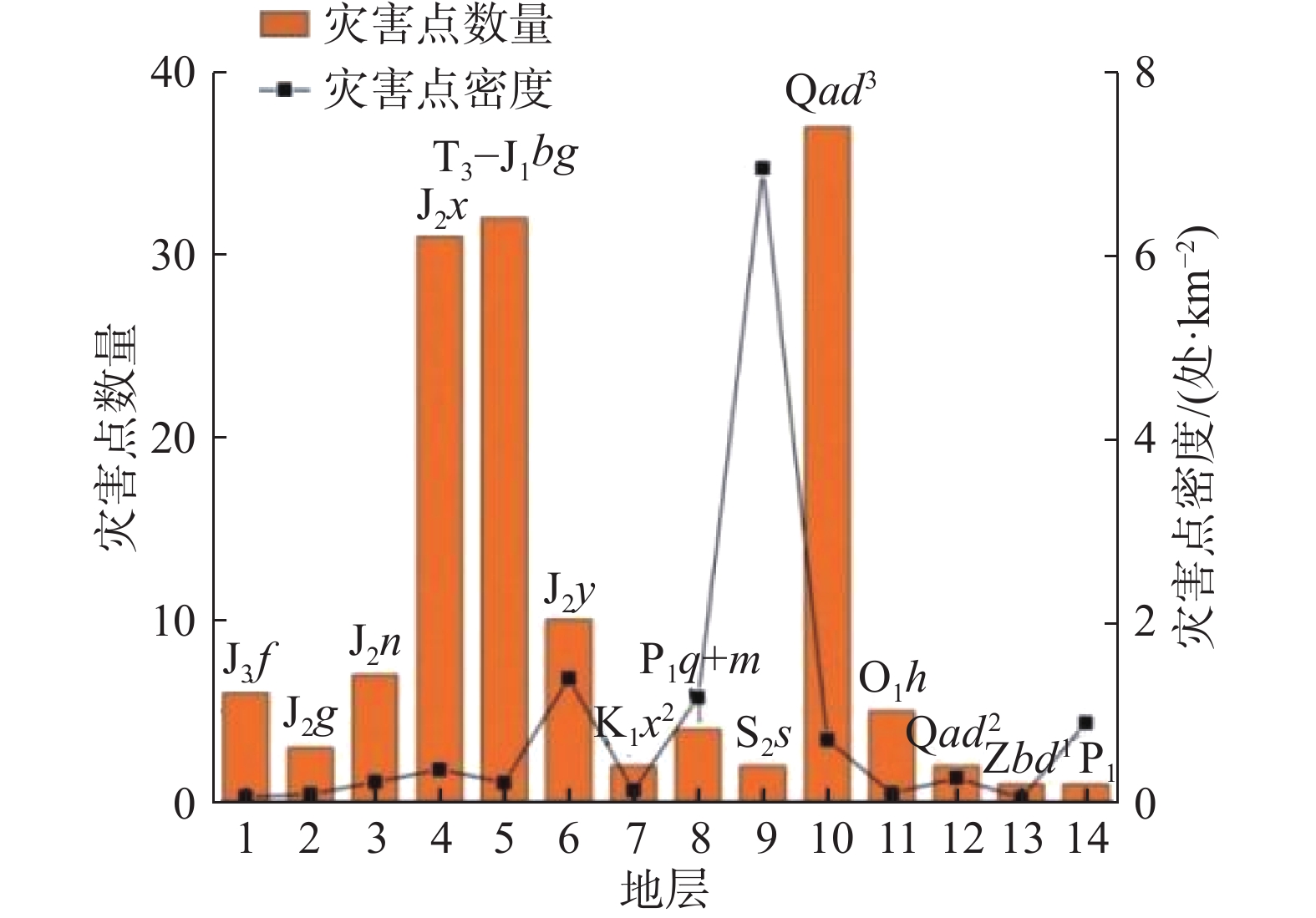
评价因子 分级 Ni Si 信息量 高程/m ≤1500 58 166506 1.750829687 1500~1800 34 217611 0.94906948 1800~2100 33 336270 0.484011174 2100~2400 14 433588 −0.627619424 2400~2700 2 373416 −2.424127878 2700~3000 1 360655 −3.082503802 >3000 1 476314 −3.36065928 坡度/(°) 0~10 33 255445 0.755315656 10~20 51 632833 0.283434285 20~30 46 774743 −0.022074748 30~40 12 513286 −0.954111328 >40 1 179550 −2.388638504 坡向 平地 1 1517 2.385080516 北 8 271199 −0.72159611 东北 24 351885 0.116564629 东 26 463075 −0.077977273 东南 25 360163 0.134134335 南 18 259672 0.132767678 西南 18 214302 0.324800739 西 14 200257 0.141271005 西北 9 233787 −0.455370651 工程地质岩组 松散岩类 37 210750 1.108369157 碎屑岩类 101 2067259 −0.170734496 碳酸盐岩类 4 189510 −1.010023591 岩浆岩类 1 4393 1.368111476 距断层距离/m 0~200 45 294975 1.86212416 200~400 31 272326 1.569339604 400~600 24 236142 1.455972789 600~800 11 202457 0.829720032 800~1000 7 176491 0.514992543 1000~1200 8 161212 0.73907355 1200~1400 1 154822 −1.299923793 1400~1600 3 139739 −0.098811831 1600~1800 4 129360 0.266047423 1800~2000 1 121499 −1.057553755 >2000 8 4145167 −2.507904537 距水系距离/m 0~300 54 190197 2.660820212 300~600 25 179240 1.950046678 600~900 6 168052 0.587382557 900~1200 11 156140 1.267038775 >1200 47 6512889 −1.011494271 距道路距离/m 0~300 74 594601 2.421824195 300~600 20 475861 1.336256172 600~900 14 427658 1.086383213 900~1200 6 401098 0.303203376 >1200 29 11046163 −1.436892883 表 7 评价因子权重
Table 7. Evaluation factor weight
评价因子 CFmax CFmin 权重 高程 0.826 −0.965 1.792 坡度 0.530 −0.908 1.438 工程地质岩组 0.745 −0.636 1.381 距断层距离 0.845 −0.919 1.763 距水系距离 0.930 −0.636 1.566 距道路距离 0.911 −0.762 1.674 坡向 0.908 −0.514 1.422 表 8 研究区地质灾害易发分区统计表
Table 8. Statistical table of geological hazard prone zones in the study area
易发性分区 面积/km2 面积占比/% 灾害点/处 灾害占比/% 每百平方公里灾害点密度/处 灾害占比与面积占比比值 低易发区 285.34 42.49 3 2.10 1.05 0.05 中易发区 215.73 32.12 22 15.38 10.20 0.48 高易发区 123.78 18.43 51 35.66 41.20 1.94 极高易发区 46.75 6.96 67 46.85 143.31 6.73 合计 671.60 100.00 143 100.00 − − -
[1] 则木河活断裂填图组. 则木河活动断裂带1∶5万地质填图及综合研究[J]. 四川地震,2000(增刊 1):1 − 4. [Working group for geologic mapping on Zemuhe fault. Geologic mapping and comprehensive analysis on the active faults of Zemuhe[J]. Earthquake Research in Sichuan,2000(Sup 1):1 − 4. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Working group for geologic mapping on Zemuhe fault. Geologic mapping and comprehensive analysis on the active faults of zemuhe[J]. Earthquake Research in Sichuan, 2000(Sup 1): 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] REN J W, PING L. Earthquake-caused landforms and paleoseismic study on the northern segment of the Zemuhe fault[J]. Seismology & Geology, 1989.
[3] REN Z K, LIN A M. Deformation characteristics of co-seismic surface ruptures produced by the 1850 M 7.5 Xichang earthquake on the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2010,38(1/2):1 − 13.
[4] 任治坤, 田勤俭, 张军龙. 后差分GPS测量则木河断裂地震微地貌特征[J]. 地震,2007,27(3):97 − 104. [REN Zhikun, TIAN Qinjian, ZHANG Junlong. Micro geomorphology of Zemuhe Fault surveyed by virtue deferential GPS[J]. Earthquake,2007,27(3):97 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2007.03.013
REN Zhikun, TIAN Qinjian, ZHANG Junlong. Micro geomorphology of Zemuhe Fault surveyed by virtue deferential GPS[J]. Earthquake, 2007, 27(3): 97-104. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2007.03.013
[5] 杜平山. 则木河断裂带的演化历史及变形机制[J]. 四川地震,2000(增刊 1):65 − 79. [DU Pingshan. Evolution histories and deformation mechanism about active fault of Zemuhe[J]. Earthquake Research in Sichuan,2000(Sup 1):65 − 79. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DU Pingshan. Evolution histories and deformation mechanism about active fault of zemuhe[J]. Earthquake Research in Sichuan, 2000(Sup 1): 65 − 79. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 闻学泽. 则木河断裂的第四纪构造活动模式[J]. 地震研究,1983,6(1):41 − 50. [WEN Xueze. Model of active tectonic of the quaternary period of Zemu river fault[J]. Journal of Seismological Research,1983,6(1):41 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WEN Xueze. Model of active tectonic of the quaternary period of zemu river fault[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 1983, 6(1): 41-50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 唐荣昌, 黄祖智, 伍先国, 等. 则木河断裂全新世以来的新活动与地震[J]. 中国地震,1986,2(4):84 − 90. [TANG Rongchang, HUANG Zuzhi, WU Xianguo, et al. The new activities and earthquakes of the Zemuhe fault since the Holocene[J]. Earthquake Research in China,1986,2(4):84 − 90. (in Chinese with English abstract)
TANG Rongchang, HUANG Zuzhi, WU Xianguo, et al. The new activities and earthquakes of the zemuhe fault since the Holocene[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 1986, 2(4): 84-90. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 冯元保, 杜平山. 1850年西昌地震孕育和发生的地质构造条件[J]. 四川地震,2000(增刊 1):97 − 101. [FENG Yuanbao, DU Pingshan. Geologic tectonic and earthquake preparation conditions about 1850 Xuchuan earthquake[J]. Earthquake Research in Sichuan,2000(Sup 1):97 − 101. (in Chinese with English abstract)
FENG Yuanbao, DU Pingshan. Geologic tectonic and earthquake preparation conditions about 1850 xuchuan earthquake[J]. Earthquake Research in Sichuan, 2000(Sup 1): 97-101. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 王虎, 冉勇康, 李彦宝, 等. 则木河断裂上古地震破裂与小型三角状拉分盆地演化[J]. 中国科学(地球科学),2013,43(7):1106 − 1114. [WANG Hu, RAN Yongkang, LI Yanbao, et al. Upper paleoseismic rupture of Zemuhe fault and evolution of small triangular pull apart basin[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae),2013,43(7):1106 − 1114. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1360/zd-2013-43-7-1106
WANG Hu, RAN Yongkang, LI Yanbao, et al. Upper paleoseismic rupture of Zemuhe fault and evolution of small triangular pull apart basin [J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2013, 43(7): 1106-1114. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1360/zd-2013-43-7-1106
[10] 郭乾. 则木河断裂带中段典型古地震滑坡动力学特征研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2014
GUO Qian. Research on dynamical characteristics of historical seismic landslide in the middle of Zemuhe fault zone[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 曹文正. 则木河断裂带西昌—普格段重大古滑坡发育特征及成因机理研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2015
CAO Wenzheng. Research on development characteristics and genetic mechanism of the seismic landslides from Xichang to Puge along Zemuhe fault zone[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 黄润秋, 向喜琼, 巨能攀. 我国区域地质灾害评价的现状及问题[J]. 地质通报,2004,23(11):1078 − 1082. [HUANG Runqiu, XIANG Xiqiong, JU Nengpan. Assessment of China's regional geohazards: Present situation and problems[J]. Regional Geology of China,2004,23(11):1078 − 1082. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.11.005
HUANG Runqiu, XIANG Xiqiong, JU Nengpan. Assessment of China's regional geohazards: present situation and problems[J]. Regional Geology of China, 2004, 23(11): 1078-1082. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.11.005
[13] GUZZETTI F, REICHENBACH P, CARDINALI M, et al. Probabilistic landslide hazard assessment at the basin scale[J]. Geomorphology,2005,72(1/2/3/4):272 − 299.
[14] 倪化勇, 王德伟, 陈绪钰, 等. 四川雅江县城地质灾害发育特征与稳定性评价[J]. 现代地质,2015,29(2):474 − 480. [NI Huayong, WANG Dewei, CHEN Xuyu, et al. Formation characteristics and stability assessment of geological hazards in Yajiang City, Sichuan Province[J]. Geoscience,2015,29(2):474 − 480. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2015.02.036
NI Huayong, WANG Dewei, CHEN Xuyu, et al. Formation characteristics and stability assessment of geological hazards in Yajiang City, Sichuan Province[J]. Geoscience, 2015, 29(2): 474-480. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2015.02.036
[15] 阮沈勇, 黄润秋. 基于GIS的信息量法模型在地质灾害危险性区划中的应用[J]. 成都理工学院学报,2001,28(1):89 − 92. [RUAN Shenyong, HUANG Runqiu. Application of gis-based information model on assessment of geological hazards risk[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology,2001,28(1):89 − 92. (in Chinese with English abstract)
RUAN Shenyong, HUANG Runqiu. Application of gis-based information model on assessment of geological hazards risk[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 2001, 28(1): 89-92. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 薛强, 张茂省, 李林. 基于斜坡单元与信息量法结合的宝塔区黄土滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地质通报,2015,34(11):2108 − 2115. [XUE Qiang, ZHANG Maosheng, LI Lin. Loess landslide susceptibility evaluation based on slope unit and information value method in Baota District, Yanan[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2015,34(11):2108 − 2115. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.11.017
XUE Qiang, ZHANG Maosheng, LI Lin. Loess landslide susceptibility evaluation based on slope unit and information value method in Baota District, Yan'an[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2015, 34(11): 2108-2115. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.11.017
[17] 陈朝亮, 张文君, 钱静, 等. 基于改进Logistic回归模型在地质灾害评价中的应用[J]. 环境科学与技术,2019,42(4):188 − 193. [CHEN Chaoliang, ZHANG Wenjun, QIAN Jing, et al. Application of improved logistic regression model in geological hazard evaluation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2019,42(4):188 − 193. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHEN Chaoliang, ZHANG Wenjun, QIAN Jing, et al. Application of improved logistic regression model in geological hazard evaluation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 42(4): 188-193. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 赵成, 张永军, 赵玉红. 层次分析法在甘肃省地质灾害易发性评价中的应用[J]. 冰川冻土,2009,31(1):182 − 188. [ZHAO Cheng, ZHANG Yongjun, ZHAO Yuhong. Application of the hierarchical analytical methods to evaluating geological hazard tendency in Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2009,31(1):182 − 188. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHAO Cheng, ZHANG Yongjun, ZHAO Yuhong. Application of the hierarchical analytical methods to evaluating geological hazard tendency in Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2009, 31(1): 182-188. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 许冲, 戴福初, 姚鑫, 等. 基于GIS与确定性系数分析方法的汶川地震滑坡易发性评价[J]. 工程地质学报,2010,18(1):15 − 26. [XU Chong, DAI Fuchu, YAO Xin, et al. GIS platform and certainty factor analysis method based Wenchuan earthquake-induced landslide susceptibility evaluation[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2010,18(1):15 − 26. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.01.003
XU Chong, DAI Fuchu, YAO Xin, et al. GIS platform and certainty factor analysis method based Wenchuan earthquake-induced landslide susceptibility evaluation[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2010, 18(1): 15-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.01.003
[20] 李益敏, 李驭豪, 赵志芳. 基于确定性系数模型的泸水市泥石流易发性评价[J]. 水土保持研究,2019,26(4):336 − 342. [LI Yimin, LI Yuhao, ZHAO Zhifang. Assessment on susceptibility of debris flow in Lushui based on the certain factor model[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2019,26(4):336 − 342. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Yimin, LI Yuhao, ZHAO Zhifang. Assessment on susceptibility of debris flow in Lushui based on the certain factor model[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 26(4): 336-342. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] SANDRIC I, IONITA C, CHITU Z, et al. Using CUDA to accelerate uncertainty propagation modelling for landslide susceptibility assessment[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software,2019,115:176 − 186.
[22] ADITIAN A, KUBOTA T, SHINOHARA Y. Comparison of GIS-based landslide susceptibility models using frequency ratio, logistic regression, and artificial neural network in a tertiary region of Ambon, Indonesia[J]. Geomorphology,2018,318:101 − 111. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.06.006
[23] 张书豪, 吴光. 随机森林与GIS的泥石流易发性及可靠性[J]. 地球科学,2019,44(9):3115 − 3134. [ZHANG Shuhao, WU Guang. Debris flow susceptibility and its reliability based on random forest and GIS[J]. Earth Science,2019,44(9):3115 − 3134. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Shuhao, WU Guang. Debris flow susceptibility and its reliability based on random forest and GIS[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(9): 3115-3134. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 黄立鑫, 郝君明, 李旺平, 等. 基于RBF神经网络-信息量耦合模型的滑坡易发性评价: 以甘肃岷县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(6):116 − 126. [HUANG Lixin, HAO Junming, LI Wangping, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment by the coupling method of RBF neural network and information value: A case study in Min Xian, Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(6):116 − 126. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HUANG Lixin, HAO Junming, LI Wangping, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment by the coupling method of RBF neural network and information value: a case study in Min Xian, Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(6): 116-126. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 刘福臻, 王灵, 肖东升. 机器学习模型在滑坡易发性评价中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(6):98 − 106. [LIU Fuzhen, WANG Ling, XIAO Dongsheng. Application of machine learning model in landslide susceptibility evaluation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(6):98 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Fuzhen, WANG Ling, XIAO Dongsheng. Application of machine learning model in landslide susceptibility evaluation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(6): 98-106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 周天伦, 曾超, 范晨, 等. 基于快速聚类-信息量模型的汶川及周边两县滑坡易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(5):137 − 150. [ZHOU Tianlun, ZENG Chao, FAN Chen, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on K-means cluster information model in Wenchuan and two neighboring counties, China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(5):137 − 150. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Tianlun ZHOU, Chao ZENG, Chen FAN, Hongji BI, Enhui GONG, Xiao LIU. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on K-means cluster information model in Wenchuan and two neighboring counties, China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(5): 137-150. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 方然可, 刘艳辉, 黄志全. 基于机器学习的区域滑坡危险性评价方法综述[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(4):1 − 8. [FANG Ranke, LIU Yanhui, HUANG Zhiquan. A review of the methods of regional landslide hazard assessment based on machine learning[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(4):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ranke FANG, Yanhui LIU, Zhiquan HUANG. A review of the methods of regional landslide hazard assessment based on machine learning[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(4): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 郭学飞, 王志一, 焦润成, 等. 基于层次分析法的北京市地质环境质量综合评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(1):70 − 76. [GUO Xuefei, WANG Zhiyi, JIAO Runcheng, et al. Comprehensive evaluation method of geological environment quality in Beijing based on AHP[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(1):70 − 76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GUO Xuefei, WANG Zhiyi, JIAO Runcheng, et al. Comprehensive evaluation method of geological environment quality in Beijing based on AHP[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(1): 70-76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 张晓东, 刘湘南, 赵志鹏, 等. 信息量模型、确定性系数模型与逻辑回归模型组合评价地质灾害敏感性的对比研究[J]. 现代地质,2018,32(3):602 − 610. [ZHANG Xiaodong, LIU Xiangnan, ZHAO Zhipeng, et al. Comparative study of geological hazards susceptibility assessment: Constraints from the information value + logistic regression model and the CF + logistic regression model[J]. Geoscience,2018,32(3):602 − 610. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Xiaodong, LIU Xiangnan, ZHAO Zhipeng, et al. Comparative study of geological hazards susceptibility assessment: constraints from the information value + logistic regression model and the CF + logistic regression model[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(3): 602-610. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 田春山, 刘希林, 汪佳. 基于CF和Logistic回归模型的广东省地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(6):154 − 161. [TIAN Chunshan, LIU Xilin, WANG Jia. Geohazard susceptibility assessment based on CF model and Logistic Regression models in Guangdong[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(6):154 − 161. (in Chinese with English abstract)
TIAN Chunshan, LIU Xilin, WANG Jia. Geohazard susceptibility assessment based on CF model and Logistic Regression models in Guangdong[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(6): 154-161. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 李远远, 梅红波, 任晓杰, 等. 基于确定性系数和支持向量机的地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 地球信息科学学报,2018,20(12):1699 − 1709. [LI Yuanyuan, MEI Hongbo, REN Xiaojie, et al. Geological disaster susceptibility evaluation based on certainty factor and support vector machine[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science,2018,20(12):1699 − 1709. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2018.180349
LI Yuanyuan, MEI Hongbo, REN Xiaojie, et al. Geological disaster susceptibility evaluation based on certainty factor and support vector machine[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2018, 20(12): 1699-1709. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2018.180349
[32] 樊芷吟, 苟晓峰, 秦明月, 等. 基于信息量模型与Logistic回归模型耦合的地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(2):340 − 347. [FAN Zhiyin, GOU Xiaofeng, QIN Mingyue, et al. Information and logistic regression models based coupling analysis for susceptibility of geological hazards[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(2):340 − 347. (in Chinese with English abstract)
FAN Zhiyin, GOU Xiaofeng, QIN Mingyue, et al. Information and logistic regression models based coupling analysis for susceptibility of geological hazards[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(2): 340-347. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 何原荣, 傅文杰. 模糊支持向量机在滑坡危险性评价中的应用[J]. 自然灾害学报,2009,18(5):107 − 112. [HE Yuanrong, FU Wenjie. Application of fuzzy support vector machine to landslide risk assessment[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2009,18(5):107 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2009.05.016
HE Yuanrong, FU Wenjie. Application of fuzzy support vector machine to landslide risk assessment[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2009, 18(5): 107-112. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2009.05.016
[34] 冯文凯, 黄润秋, 许强. 斜坡震裂变形发育分布规律及危险性分析[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2010,37(6):679 − 684. [FENG Wenkai, HUANG Runqiu, XU Qiang. Analysis of the development, distribution rules and risk of slope shattering deformation[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition),2010,37(6):679 − 684. (in Chinese with English abstract)
FENG Wenkai, HUANG Runqiu, XU Qiang. Analysis of the development, distribution rules and risk of slope shattering deformation[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2010, 37(6): 679-684. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] 殷坤龙, 晏同珍. 汉江河谷旬阳段区域滑坡规律及斜坡不稳定性预测[J]. 地球科学,1987,12(6):631 − 638. [YIN Kunlong, YAN Tongzhen. Distribution regularity of landslides and prediction of slope instability nearby Xunyang, Han River valley[J]. Earth Science,1987,12(6):631 − 638. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YIN Kunlong, YAN Tongzhen. Distribution regularity of landslides and prediction of slope instability nearby Xunyang, Han River valley[J]. Earth Science, 1987, 12(6): 631-638. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[36] SHORTLIFFE E H, BUCHANAN B G. A model of inexact reasoning in medicine[J]. Mathematical Biosciences,1975,23(3/4):351 − 379.
[37] HECKERMAN D. Probabilistic interpretations for MYCIN's certainty factors[J]. CoRR,2013,abs/1304.3419:167 − 196.
[38] 刘艳辉, 刘传正, 唐灿, 等. 基于确定性系数模型的地质灾害多因子权重计算方法[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2015,26(1):92 − 97. [LIU Yanhui, LIU Chuanzheng, TANG Can, et al. CF-based multi-factor overlay method to determine weights of the factors for geo-hazards[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2015,26(1):92 − 97. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Yanhui, LIU Chuanzheng, TANG Can, et al. CF-based multi-factor overlay method to determine weights of the factors for geo-hazards[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2015, 26(1): 92-97. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: