Application of the ground-penetrating radar technology in detection of soil properties of the high cutting and filling slopes in collapsible loess area
-
摘要:
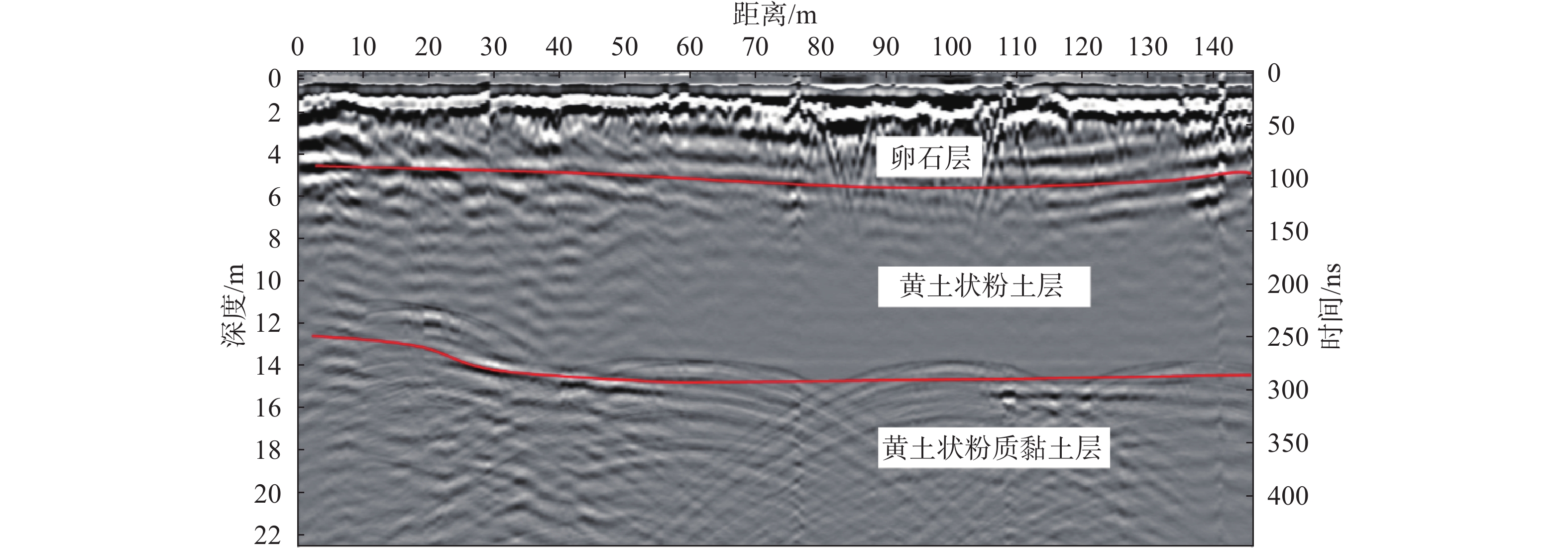
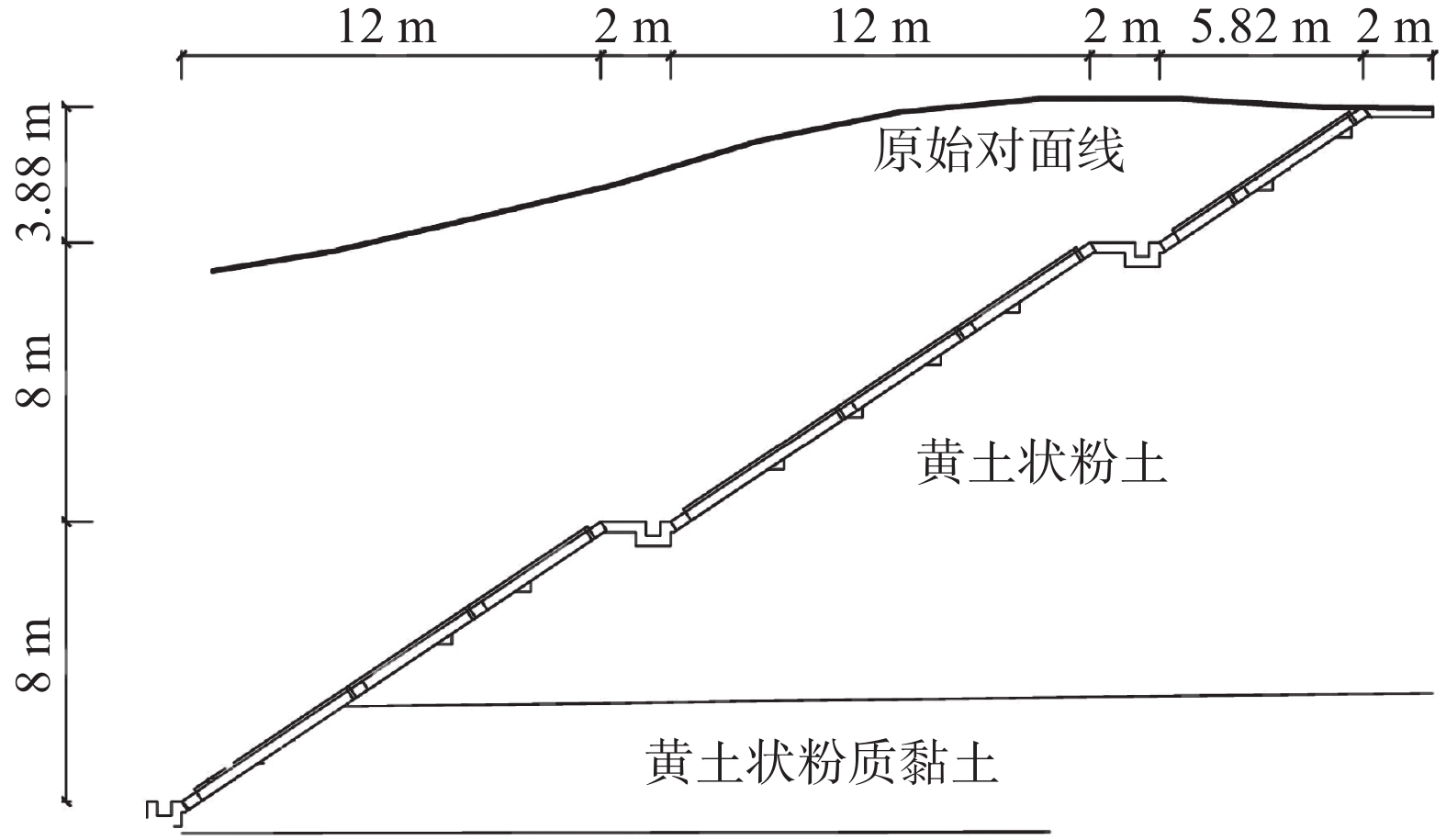
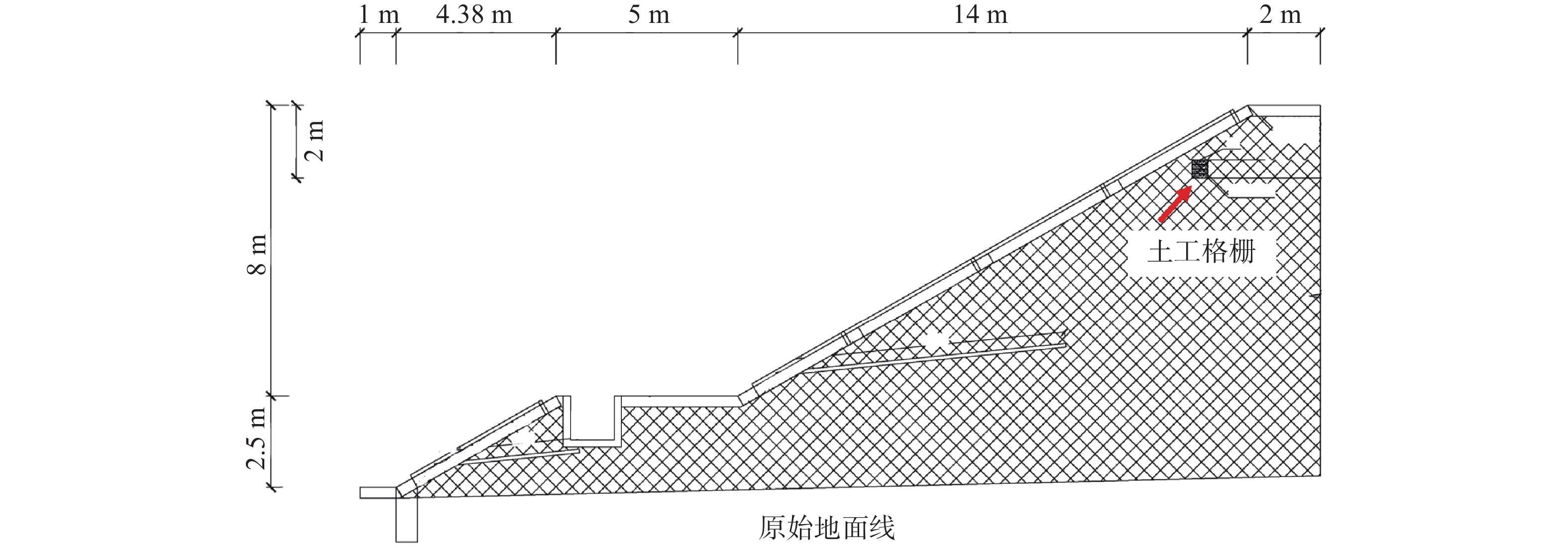
在湿陷性黄土丘陵山区通过平山造地开辟建筑场地,施工后高挖填方边坡变形特征及其交界线在坡面出露位置土体内部性状是边坡稳定性评价的关键环节。为掌握西电东送重要枢纽——同心妙岭变电站湿陷性黄土高边坡稳定性,在该场地挖、填方区域边坡顶端布设了长度为416 m和372 m的测线,同时在挖填交界线两侧分别布设了长度为15 m和20 m的测线,利用pulseEKKO PRO专业型探地雷达,在所选测线上以0.5 m间隔为测点实施相关探测工作。结果表明:高挖方边坡波谱特征图像和地勘报告相同位置处土层分布一致,反射波较杂乱,边坡内部存在卸荷裂缝、零星破碎带等现象;高填方边坡无裂缝、局部沉陷等异常反射波面,填土均匀,填土下伏自重湿陷性黄土,土体存在潜在危险;挖填交界区域有较明显的挖填方交界线,该交界线坡度较缓,过渡均匀;交界线左侧(挖方区)探测波形复杂,岩性种类多,土体密实度高,右侧(填方区)波形规则,土性单一,土体密实度低,挖填方土性的差异性易导致不均匀沉降。研究结果可为平山造地建筑场地的高边坡支护设计与施工提供基础资料。
Abstract:Building sites are created by leveling hills and creating land in the hilly mountainous areas of collapsible loess. The deformation characteristics of the high slopes of excavation and filling and the internal properties of the soil at the exposed position of the boundary line are the key aspect of slope stability evaluation. To investigate the stability of the collapsible loess high slope for the Tongxin Miaoling transformer station from the important hub of the West-East power transmission project, this study conducted field detection tests using professional ground-penetrating radar (GPR) of model pulseEKKO PRO, Survey lines with lengths of 416 m and 372 m were laid at the top of the slope in the excavation area and the fill area. Meanwhile, survey lines of 15 m and 20 m in length were laid on both sides of the excavation and filling boundary. GPR is used to carry out detection work on all survey lines at 0.5 m intervals. The results show that the wave spectrum characteristics image of the high excavation slope is consistent with the soil distribution at the same location in the geological survey results. Meanwhile, its reflected wave is messier, which indicates that there are unloading cracks and sporadic fracture zones inside the slope. There is no abnormal reflective wave surface such as cracks and local subsidence on the high fill slope, and its filling soil is uniform. The original soil in the high fill slope area is self-weight collapsing loess, thus the soil of the high fill slope has potential risks. The boundary area of excavation and filling has a more obvious boundary line of excavation and filling, which has a slow slope and uniform transition. The detection waveform on the side of the boundary line is complex, with many types of lithology, and high soil compactness, while the right side has regular waveforms, single soil properties, low soil compactness, and differences in soil properties between excavation and filling.easily lead to unenen settlement. These results could provide a reference for the design and construction of the high side slope of the cutting hills to the backfill ditch project.
-

-
[1] 张茂省,谭新平,董英,等. 黄土高原平山造地工程环境效应浅析—以延安新区为例[J]. 地质论评,2019,65(6):1409 − 1421. [ZHANG Maosheng,TAN Xinping,DONG Ying,et al. Initial analysis on environmental effect of cutting hills to backfill ditch project on Loess Plateau:Take Yan’an New District as an example[J]. Geological Review,2019,65(6):1409 − 1421. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2019.06.008
[2] 刘琨,卢育霞,徐舜华. 黄土丘陵沟壑区挖填场地动力响应特征研究[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2021,41(5):1096 − 1104. [LIU Kun,LU Yuxia,XU Shunhua. Study on characteristics of dynamic response at digging-filling sites in the loess hilly and gully region[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering,2021,41(5):1096 − 1104. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13409/j.cnki.jdpme.201908017
[3] 黄伟杰, 蔡军君, 熊翠红. 净值分析在电力工程进度控制中的应用—以某1000 kV变电站为例[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 2018, 51(增刊1): 387 − 392
HUANG Weijie, CAI Junjun, XIONG Cuihong. Application of earned value analysis to electric power construction schedule control: Take a 1 000 kV substation as an example[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2018, 51(Sup 1): 387 − 392. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 蔺晓燕, 杨泽, 李萍, 等. 地层划分对黄土高边坡稳定性分析的影响研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2021, 43(增刊1): 76 − 80
LIN Xiaoyan, YANG Ze, LI Ping, et al. Effects of stratigraphic division on stability analysis of high loess slopes[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2021, 43(Sup 1): 76 − 80. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 孔令伟,陈正汉. 特殊土与边坡技术发展综述[J]. 土木工程学报,2012,45(5):141 − 161. [KONG Lingwei,CHEN Zhenghan. Advancement in the techniques for special soils and slopes[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal,2012,45(5):141 − 161. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 龚伟翔, 张晓超, 裴向军, 等. 基于高陡交填界面软弱带影响下黄土填方边坡失稳模式研究[J/OL]. 工程地质学报: 1 − 11(2021-5-13)[2021-10-23]
GONG Weixiang, ZHANG Xiaochao, PEI Xiangjun, et al. Study on the instability model of loess filled slope based on the influence of weak zone of high and steep filling interface[J/OL]. Journal of Engineering Geology: 1 − 11(2021-5-13)[2021-10-23]. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 毛洪运,朱江鸿,喻小,等. 强夯法消除风积粉细砂湿陷性研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(4):745 − 752. [MAO Hongyun,ZHU Jianghong,YU Xiao,et al. Dynamic compaction study of eliminating the collapsibility of eolian deposit fine sand[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(4):745 − 752. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2018-113
[8] 毛正君,张瑾鸽,仲佳鑫,等. 梯田型黄土滑坡隐患发育特征与成因分析—以宁夏南部黄土丘陵区为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(6):142 − 152. [MAO Zhengjun,ZHANG Jinge,ZHONG Jiaxin,et al. Analysis of basic characteristics and deformation mechanism of loess potential landslide of terrace: Taking loess hilly region in southern Ningxia as an example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(6):142 − 152. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 马闫,王家鼎,彭淑君,等. 黄土贴坡高填方变形破坏机制研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2016,38(3):518 − 528. [MA Yan,WANG Jiading,PENG Shujun,et al. Deformation and failure mechanism of high sticking loess slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2016,38(3):518 − 528. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201603016
[10] 蒲小武,王兰民,吴志坚,等. 兰州丘陵沟壑区挖方黄土高边坡面临的工程地质问题及稳定性分析[J]. 地震工程学报,2016,38(5):787 − 794. [PU Xiaowu,WANG Lanmin,WU Zhijian,et al. Engineering geological problems of loess high excavation slope in loess hilly and gully region of Lanzhou and its stability analysis[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2016,38(5):787 − 794. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2016.05.0787
[11] 吕远强,董转运. 公路黄土路堑、路堤的湿陷性评价分析[J]. 工程勘察,2010,38(9):28 − 31. [LYU Yuanqiang,DONG Zhuanyun. Analysis of appraisement collapsibility on loess embankment and cutting of road[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2010,38(9):28 − 31. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 梁小龙,王建业,白泽朝,等. 基于PS-InSAR技术的黄土大厚度挖方区回弹变形规律分析[J]. 测绘通报,2020(3):163 − 166. [LIANG Xiaolong,WANG Jianye,BAI Zechao,et al. Research on rebound deformation using PS-InSAR technology in loess plateau area[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping,2020(3):163 − 166. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] WANG J D,XU Y J,MA Y,et al. Study on the deformation and failure modes of filling slope in loess filling engineering:A case study at a loess mountain airport[J]. Landslides,2018,15(12):2423 − 2435. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-1046-5
[14] 江丽,吴栋,李春林,等. 地质雷达在边坡稳定性检测和预警中的应用[J]. 人民长江,2012,43(5):51 − 53. [JIANG Li,WU Dong,LI Chunlin,et al. Application of GPR in slope stability monitoring and pre-warning[J]. Yangtze River,2012,43(5):51 − 53. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2012.05.012
[15] STEELMAN C M,KENNEDY C S,PARKER B L. Geophysical conceptualization of a fractured sedimentary bedrock riverbed using ground-penetrating radar and induced electrical conductivity[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2015,521:433 − 446. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.12.001
[16] ZAJC M,POGAČNIK Ž,GOSAR A. Ground penetrating radar and structural geological mapping investigation of Karst and tectonic features in flyschoid rocks as geological hazard for exploitation[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2014,67:78 − 87. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.01.011
[17] ZHANG J,LIN H,DOOLITTLE J. Soil layering and preferential flow impacts on seasonal changes of GPR signals in two contrasting soils[J]. Geoderma,2014,213:560 − 569. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2013.08.035
[18] 蒲虹宇,张立峰,何毅,等. 甘肃通渭黄土滑坡二维形变时序监测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(6):114 − 124. [PU Hongyu,ZHANG Lifeng,HE Yi,et al. Time-series monitoring of two-dimensional deformation of Tongwei loess landslide in Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(6):114 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 王永强,曹竹,谭钦文,等. 露天矿滑坡体的探地雷达检测技术[J]. 煤炭学报,2011,36(7):1093 − 1097. [WANG Yongqiang,CAO Zhu,TAN Qinwen,et al. GPR detection of open-pit landslide[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2011,36(7):1093 − 1097. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2011.07.028
[20] XIE P,WEN H J,XIAO P,et al. Evaluation of ground-penetrating radar (GPR) and geology survey for slope stability study in mantled Karst region[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2018,77(4):122. doi: 10.1007/s12665-018-7306-9
[21] HAN X L,LIU J T,ZHANG J,et al. Identifying soil structure along headwater hillslopes using ground penetrating radar based technique[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2016,13(3):405 − 415. doi: 10.1007/s11629-014-3279-7
[22] 程久龙,潘冬明,李伟,等. 强电磁干扰区灾害性采空区探地雷达精细探测研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2010,35(2):227 − 231. [CHENG Jiulong,PAN Dongming,LI Wei,et al. Study on the detecting of hazard abandoned workings by ground penetrating radar on strong electromagnetic interference area[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2010,35(2):227 − 231. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 王韵,王红雨,常留成,等. 基于探地雷达的水库坝前淤积土沉积规律研究[J]. 水土保持学报,2021,35(4):152 − 158. [WANG Yun,WANG Hongyu,CHANG Liucheng,et al. Study on sedimentation regulation of silted soil in the front of reservoir dam based on GPR[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2021,35(4):152 − 158. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 蔡少峰. 探地雷达在河流水下地形及基岩探测中的试验研究[J]. 工程地球物理学报,2019,16(5):680 − 685. [CAI Shaofeng. The experimental study on ground penetrating radar in underwater topography and bedrock detection[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics,2019,16(5):680 − 685. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2019.05.021
[25] 李勉,杨二,李平,等. 黄土丘陵区小流域淤地坝泥沙沉积特征[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(3):161 − 167. [LI Mian,YANG Er,LI Ping,et al. Characteristics of sediment deposition in check dam in small watershed in Loess Hilly Area[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2017,33(3):161 − 167. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.03.022
[26] JOL H M,BRISTOW C S. GPR in sediments:Advice on data collection,basic processing and interpretation,a good practice Guide[J]. Geological Society,London,Special Publications,2003,211(1):9 − 27. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2001.211.01.02
[27] 蒲川豪,许强,赵宽耀,等. 基于遥感分析的延安新区平山造城工程地面沉降及植被恢复特征研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(3):597 − 609. [PU Chuanhao,XU Qiang,ZHAO Kuanyao,et al. Remote sensing analysis of land subsidence and vegetation restoration characteristics in excavation and filling areas of mountain region for urban extension in Yan'an[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(3):597 − 609. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 骆祖江, 成磊, 张兴旺, 等. 悬挂式止水帷幕深基坑降水方案模拟优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2022,52(6):1946 − 1956. [LUO Zujiang, CHENG Lei, ZHANG Xingwang, et al. Simulation and optimization of dewatering scheme for suspended impervious curtain in deep foundation pit[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2022,52(6):1946 − 1956. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 秦胜伍,张延庆,张领帅,等. 基于Stacking模型融合的深基坑地面沉降预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2021,51(5):1316 − 1323. [QIN Shengwu,ZHANG Yanqing,ZHANG Lingshuai,et al. Prediction of ground settlement around deep foundation pit based on stacking model fusion[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2021,51(5):1316 − 1323. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: