Intelligent prediction and analysis of influencing factors of Quaternary accumulation layer thickness in landslide-prone areas: A case study in the Tiefeng area of Wanzhou District, Chongqing City
-
摘要:
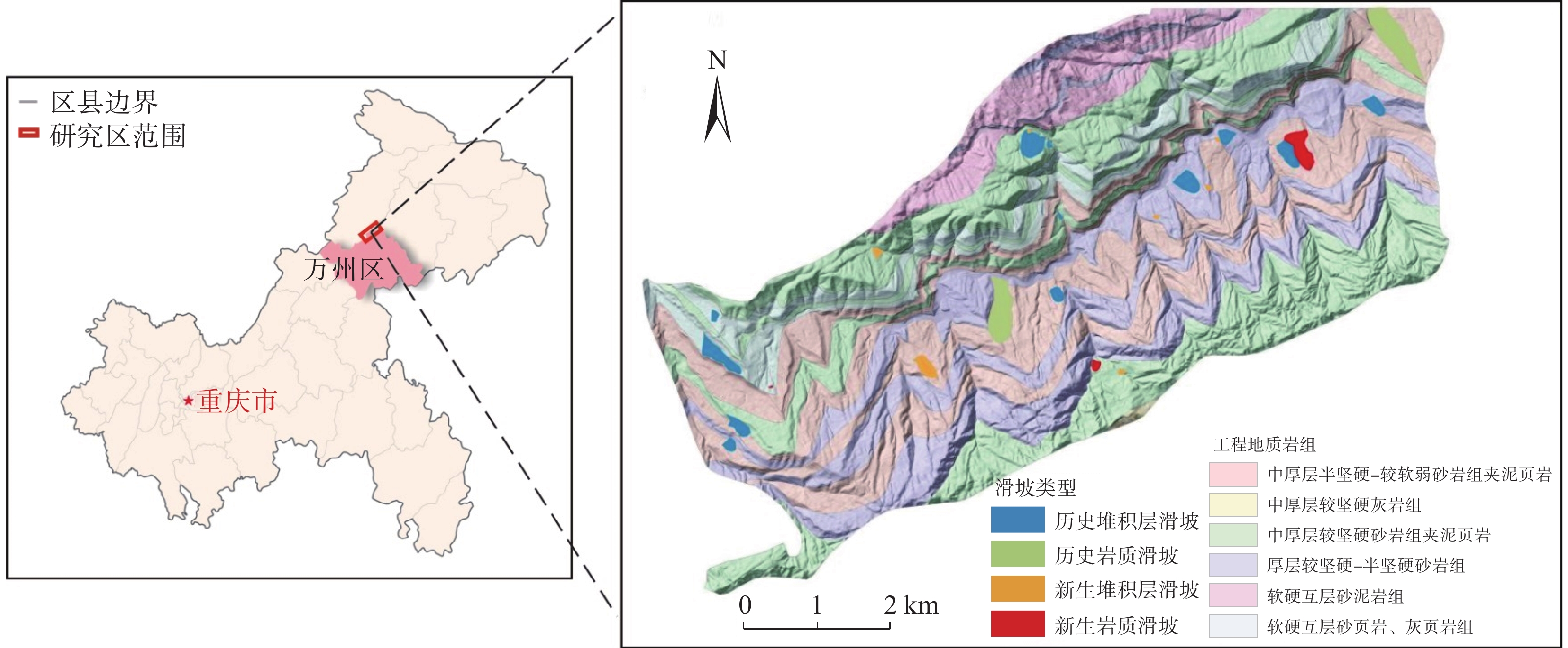
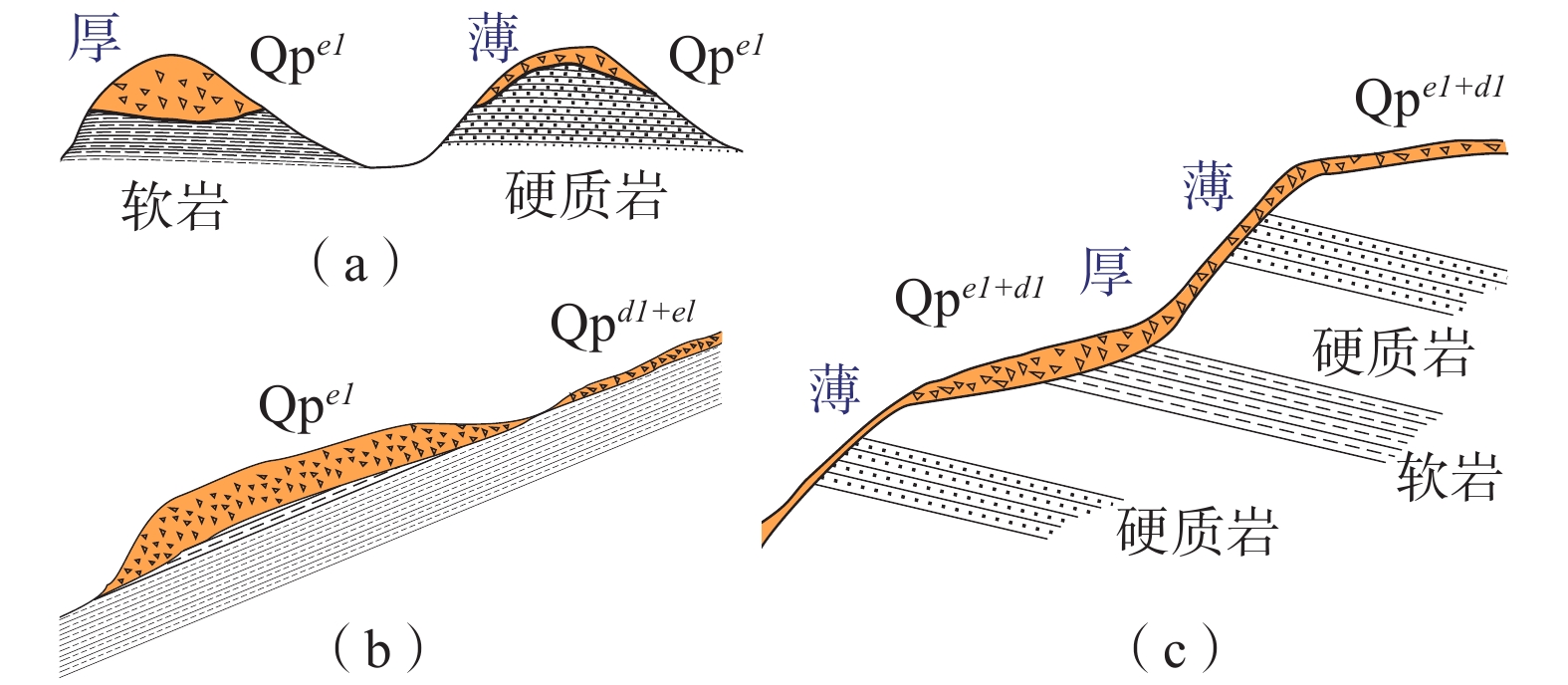
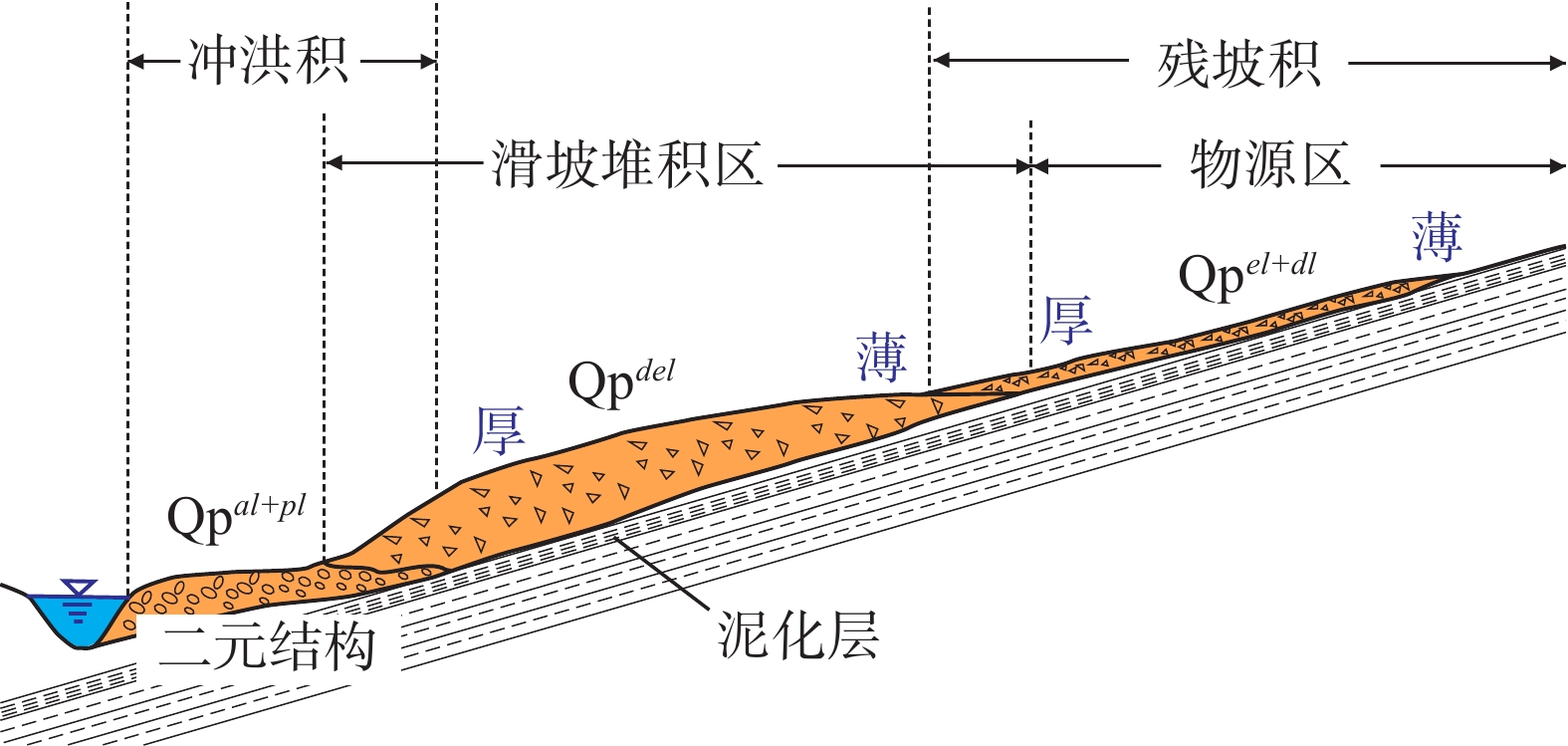
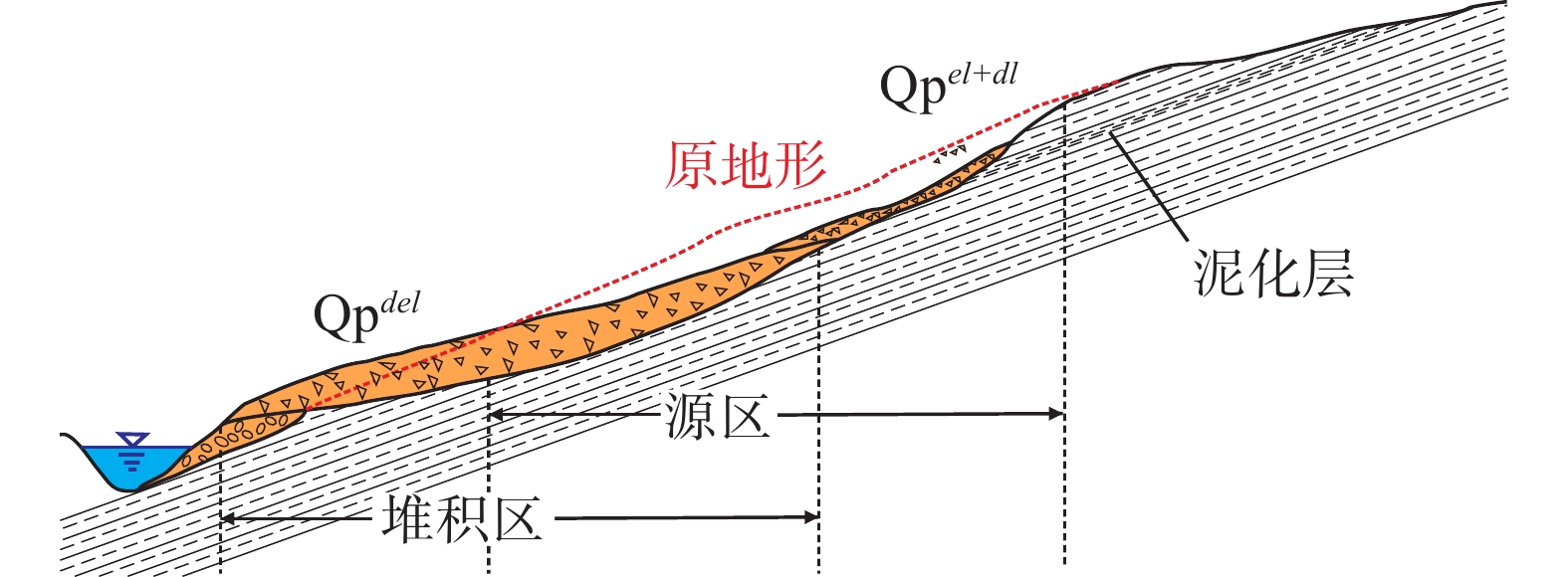
堆积层厚度是区域工程地质调查的基础数据,对识别滑坡具有重要意义,在滑坡的稳定性评价和风险评估中发挥着重要的作用。传统的空间插值方法对外界因素考虑不足,难以满足精度要求。文章以三峡库区万州区铁峰乡为研究对象,在实地调查的基础上,总结提出了堆积层的成因模式,并据此添加区域堆积层厚度控制点;基于Apriori算法挖掘影响因子与堆积层厚度分布之间的关联准则,利用已知样本点采用三种机器学习方法建立模型,最后将模型应用于整个区域得到堆积层厚度分布图,并对结果进行对比分析。结果表明:选取的13种影响因子中6种因子与堆积层厚度表现出较强的相关性;数据挖掘显示坡度和地形起伏是影响堆积层厚度空间分布差异的主要因素。3种机器学习模型中GWO-SVM模型的预测结果与实际最为吻合。研究结果揭示了区域第四系堆积层的成因机制,为机器学习技术在堆积层厚度预测领域奠定了基础。
Abstract:Accumulation layer thickness is the basic data of regional engineering geological investigation, which is of great significance to identifying landslides and plays an important role in landslide stability evaluation and risk assessment. The traditional interpolation method does not take into account external factors, and it is difficult to meet the accuracy requirements. This study takes the Tiefeng Township of Wanzhou District in the Three Gorges Reservoir as the research object, summarizing the formation model of the accumulation layer and regional accumulation layer thickness control points are added accordingly. The Apriori algorithm is used to mine the association rules between the influence factors and the thickness distribution of accumulation layers. Three machine learning methods are used to build the model by using the known sample points, which are applied to the entire area to obtain the thickness distribution map of the accumulation layer, then compare the results. Results show that 6 of the 13 selected influence factors have a strong correlation with the accumulation layer thickness, and slope and topographic undulation are the main factors that cause the difference in the spatial distribution of accumulation layer thickness. Among the three machine learning methods, the prediction result of the GWO-SVM model is the most consistent with the actual situation. The results reveal the formation mechanism of regional quaternary accumulation layer and lay a foundation for machine learning in the field of accumulation layer thickness prediction.
-
Key words:
- accumulation layer thickness /
- spatial prediction /
- formation model /
- data mining /
- machine learning
-

-
表 1 各因子与堆积层厚度相关性指标
Table 1. Correlation index between each factor and accumulation layer thickness
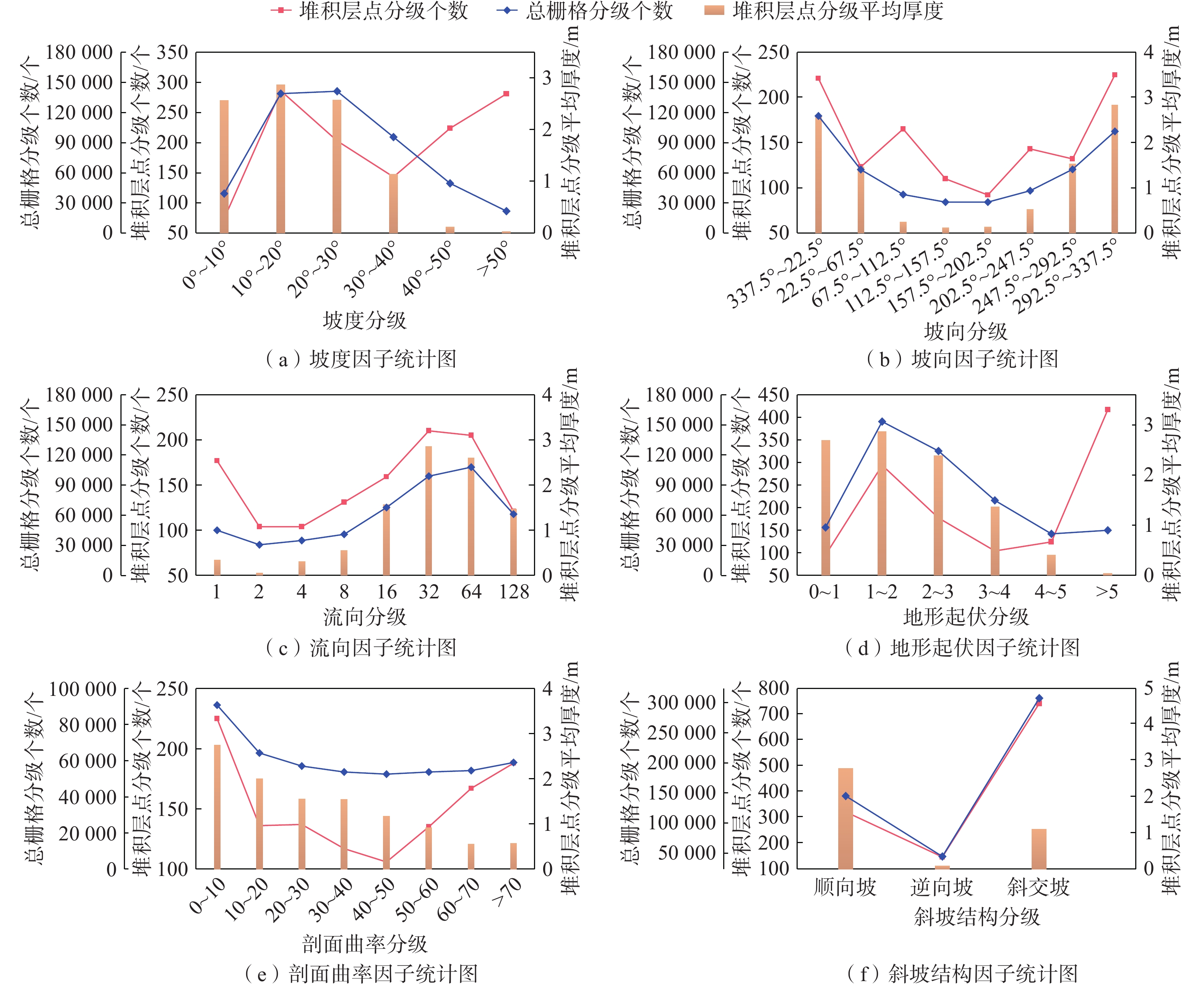
因子 GRA MIC 因子1 坡度 0.6923 0.6977 因子2 坡向 0.6878 0.5285 因子3 流向 0.8673 0.4696 因子4 高程 0.7050 0.0752 因子5 汇水条件 0.6349 0.0417 因子6 地形起伏 0.6856 0.6933 因子7 地层 0.7546 0.0486 因子8 距水系距离 0.6366 0.0525 因子9 距陡崖距离 0.6063 0.0637 因子10 剖面曲率 0.6953 0.2141 因子11 平面曲率 0.6783 0.0784 因子12 斜坡结构 0.6364 0.3271 因子13 植被覆盖 0.6440 0.0943 表 2 各因子属性指标
Table 2. Attribute indicators of each factor
因子 属性 类别 因子1 坡度 0~20° F11 20°~40° F12 >40° F13 因子2 坡向 337.5°~67.5° F21 67.5°~157.5° F22 157.5°~247.5° F23 247.5°~337.5° F24 因子3 流向 1&2 F31 4&8 F32 16&32 F33 64&128 F34 因子6 地形起伏 0~2 F61 2~4 F62 >4 F63 因子10 剖面曲率 0~20 F101 20~40 F102 40~60 F103 >60 F104 因子12 斜坡结构 顺向坡 F121 逆向坡 F122 斜交坡 F123 表 3 堆积层厚度关联准则
Table 3. Association criterion of accumulation layer thickness
规则 ID 规则 支持度/% 置信度/% 1 YZ3=F31 & YZ6=F62 & YZ2=F21  HD5
HD50.08 100.00 2 YZ3=F31 & YZ2=F21 & YZ1=F12  HD5
HD50.08 100.00 3 YZ2=F22 & YZ3=F34 & YZ1=F11  HD3
HD30.08 100.00 4 YZ2=F22 & YZ3=F34 & YZ6=F61  HD3
HD30.08 100.00 5 YZ3=F34 & YZ1=F12 & YZ2=F24  HD2
HD20.17 100.00 6 YZ2=F23 & YZ10=F102 & YZ1=F11  HD2
HD20.08 100.00 7 YZ10=F102 & YZ2=F22 & YZ1=F11  HD2
HD20.08 100.00 8 YZ3=F31 & YZ6=F63  HD1
HD118.58 100.00 9 YZ3=F31 & YZ1=F13 & YZ6=F63  HD1
HD117.18 100.00 10 YZ2=F22 & YZ1=F13 & YZ6=F63  HD1
HD117.01 100.00 表 4 各模型预测精度对比
Table 4. Comparison of prediction accuracy of each model
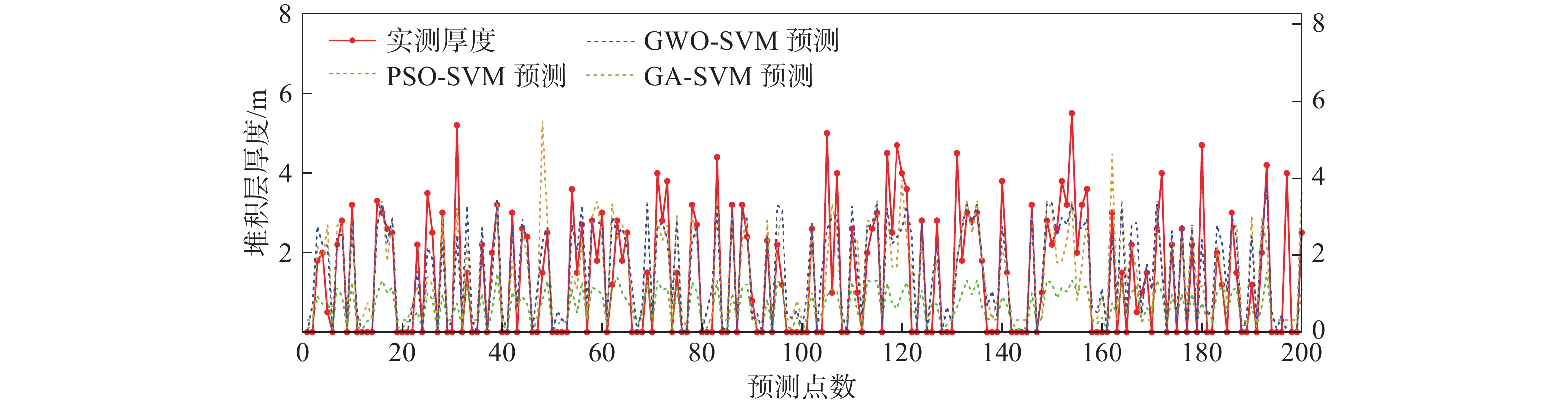
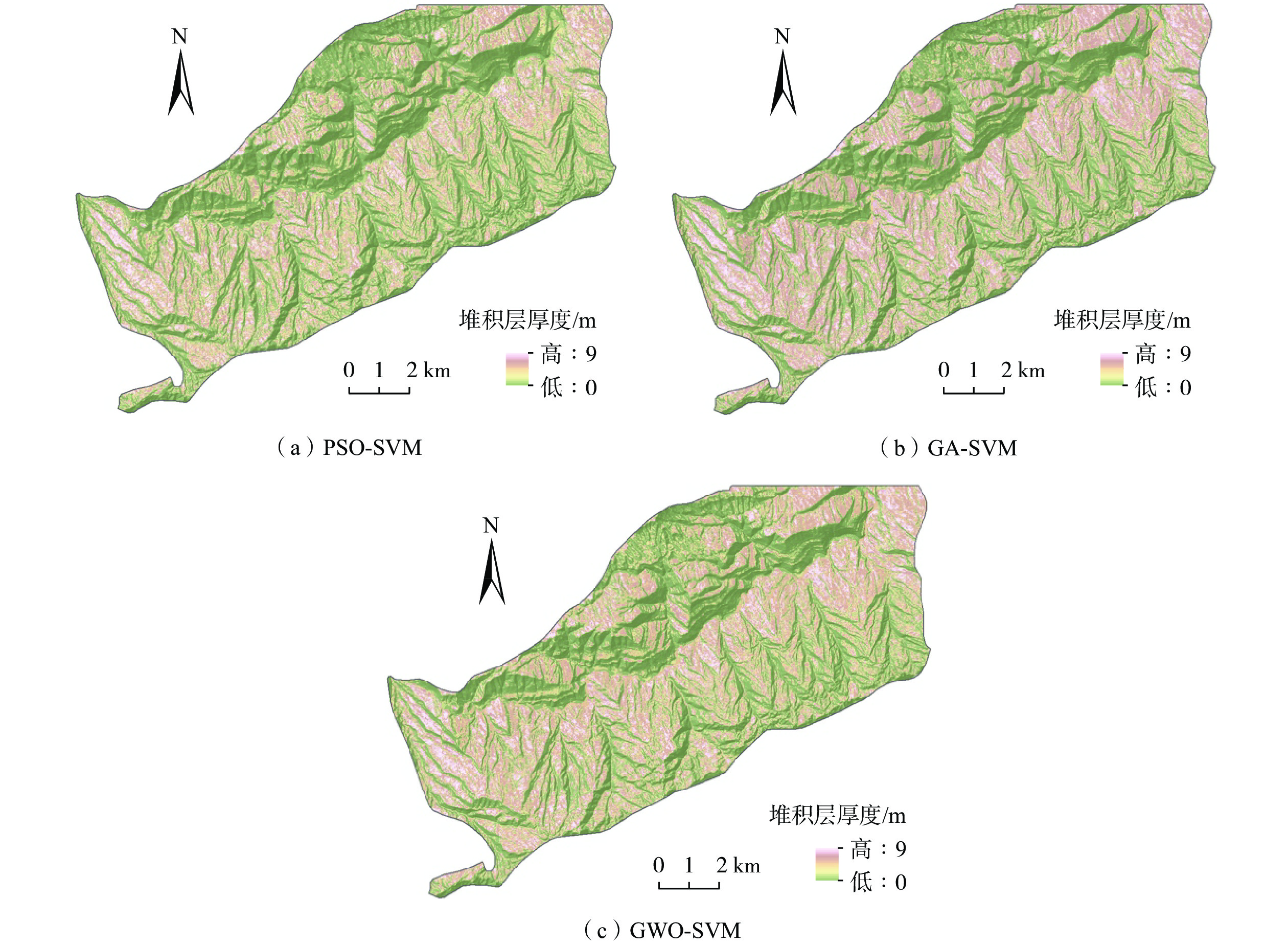
预测模型 MSE RMSE Q C 平均厚度/m PSO-SVM 401.22 1.42 0.47 0.79 1.49 GA-SVM 198.57 1.00 0.23 0.76 1.76 GWO-SVM 152.24 0.87 0.19 0.83 1.83 -
[1] 王强,吴炳方,朱亮. 土壤厚度研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学,2012,40(9):5273 − 5277. [WANG Qiang,WU Bingfang,ZHU Liang. Review of soil depth[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2012,40(9):5273 − 5277. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2012.09.071
[2] 李岩,尚士友,阿拉塔其其格,等. 典型草原栗钙土层厚度空间插值方法研究[J]. 中国农机化学报,2015,36(1):344 − 348. [LI Yan,SHANG Shiyou,A Lataqiqige,et al. Research of spatial interpolation methods of typical grassland chestnut soil thickness[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization,2015,36(1):344 − 348. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13733/j.jcam.issn.2095-5553.2015.01.090
[3] 王桂林,向林川,孙帆. 粒子群优化协同克里金法在确定山地斜坡土层厚度中的应用[J]. 土木建筑与环境工程,2018,40(6):60 − 66. [WANG Guilin,XIANG Linchuan,SUN Fan. Application of cooperative Kriging method based on particle swarm optimization in estimation slope soil thickness[J]. Journal of Civil,Architectural & Environmental Engineering,2018,40(6):60 − 66. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] SCARPONE C,SCHMIDT M G,BULMER C E,et al. Modelling soil thickness in the critical zone for Southern British Columbia[J]. Geoderma,2016,282:59 − 69. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.07.012
[5] PRADHAN A M S,KIM Y T. Development and evaluation of relative relief based soil thickness model:A comparative study in hilly terrain,south Korea[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering,2021,25(6):2186 − 2198. doi: 10.1007/s12205-021-1379-9
[6] LI X C,LUO J H,JIN X L,et al. Improving soil thickness estimations based on multiple environmental variables with stacking ensemble methods[J]. Remote Sensing,2020,12(21):3609. doi: 10.3390/rs12213609
[7] 刘磊,殷坤龙,张俊. 三峡库区万州主城区第四系堆积层厚度的估算方法及应用[J]. 地质科技情报,2016,35(1):177 − 183. [LIU Lei,YIN Kunlong,ZHANG Jun. Estimation method of the quaternary deposits thickness and its application in Wanzhou central district,Three Gorges Reservoir region[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2016,35(1):177 − 183. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 段贵娟,李飒,孙立强,等. 基于水平相关距离的土层厚度区域评价方法研究[J]. 水力发电学报,2021,40(2):177 − 186. [DUAN Guijuan,LI Sa,SUN Liqiang,et al. Study of soil thickness regional evaluation using horizontal scales of fluctuation[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering,2021,40(2):177 − 186. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11660/slfdxb.20210218
[9] 邵晨灿,向喜琼. 基于成因分类的土层厚度空间分布研究[J]. 中国水运(下半月),2021,21(3):115 − 117. [SHAO Chencan,XIANG Xiqiong. Study on spatial distribution of soil thickness based on genetic classification[J]. China Water Transport,2021,21(3):115 − 117. (in Chinese)
[10] WANG Q,WU B F,STEIN A,et al. Soil depth spatial prediction by fuzzy soil-landscape model[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments,2018,18(3):1041 − 1051. doi: 10.1007/s11368-017-1779-0
[11] AKUMU C E,WOODS M,JOHNSON J A,et al. GIS-fuzzy logic technique in modeling soil depth classes:Using parts of the Clay Belt and Hornepayne region in Ontario,Canada as a case study[J]. Geoderma,2016,283:78 − 87. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.07.028
[12] CHENG W,ZHU A X,QIN C Z,et al. Updating conventional soil maps by mining soil-environment relationships from individual soil polygons[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture,2019,18(2):265 − 278. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(18)61938-0
[13] AGRAWAL R, IMIELIŃSKI T, SWAMI A. Mining association rules between sets of items in large databases[C]//Proceedings of the 1993 ACM SIGMOD international conference on Management of data. Washington, D. C. , USA. New York: ACM, 1993: 207-216.
[14] VAPNIK V N. The nature of statistical learning theory[M]. New York: Springer , 2000.
-



 下载:
下载: