Ground pulsation tests and analysis on seismic response of typical ground fissure sites in Xi’an
-
摘要:
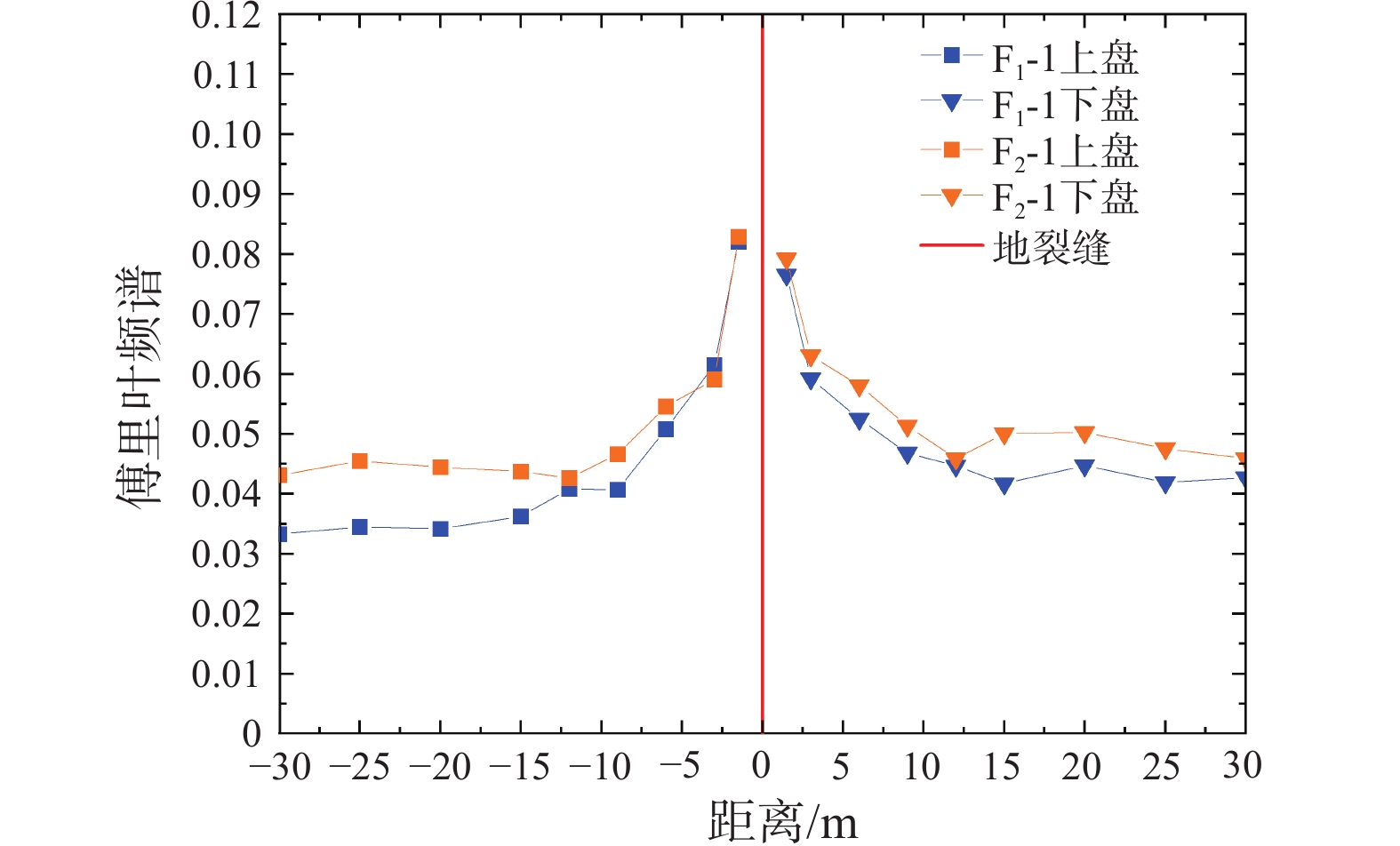
西安地裂缝广泛发育,严重的制约了城市的建设和规划。地裂缝的存在使得建筑场地在地震作用下表现出不同的地震响应特征,因此,研究西安地裂缝场地地震响应特征对地裂缝场地的建筑抗震设防具有重要意义。以西安地区典型地裂缝为研究对象,通过野外调查获得了西安地裂缝场地特征;在此基础上选取典型地裂缝场地,通过地脉动现场测试方法,获取了地裂缝场地卓越频率这一反映地层动力特性的重要参数,通过不同测点傅里叶谱分析得出了场地动力响应规律抗震设防距离。研究表明:西安地裂缝场地的卓越频率在2.79~3.16 Hz,平均卓越频率为2.96 Hz;地裂缝处场地地震响应明显,随着距地裂缝距离的增加场地地震响应逐渐减小,影响范围为15 m左右;地裂缝场地地震响应放大倍数上盘大于下盘,表现出“上盘效应”,放大倍数在1.64~2.38。研究结果对西安地裂缝场地工程抗震设防具有重要意义。
Abstract:The extensive development of ground fissures in Xi’an severely restricts the construction and planning of the city. The existence of ground fissures makes the building sites show different seismic response characteristics under earthquakes. Therefore, it is of great significance to study the seismic response characteristics of ground fissure sites in Xi’an for the seismic fortification of ground fissure sites. Taking typical ground fissures in Xi’an as the research object, the characteristics of ground fissures in Xi’an were obtained on the basis of field investigation; the predominant frequency of the ground fissure sites, which is an important parameter reflecting the dynamic characteristics of the formation, is obtained. The seismic fortification distance of the dynamic response law of the site is obtained through the Fourier spectrum analysis of different measuring points. The research shows that the predominant frequency of the ground fissure site in Xi’an is in the range of 2.79−3.16 Hz, and the average predominant frequency is 2.96 Hz; the influence range is about 15 m; the seismic response magnification of the hanging wall is greater than that of the footwall, showing the "hanging wall effect", and the magnification is between 1.64 and 2.38. The research results are of great significance to the seismic fortification of Xi'an ground fissure site engineering.
-
Key words:
- loess /
- ground fissure site /
- ground pulsation /
- seismic response /
- spectrum analysis
-

-
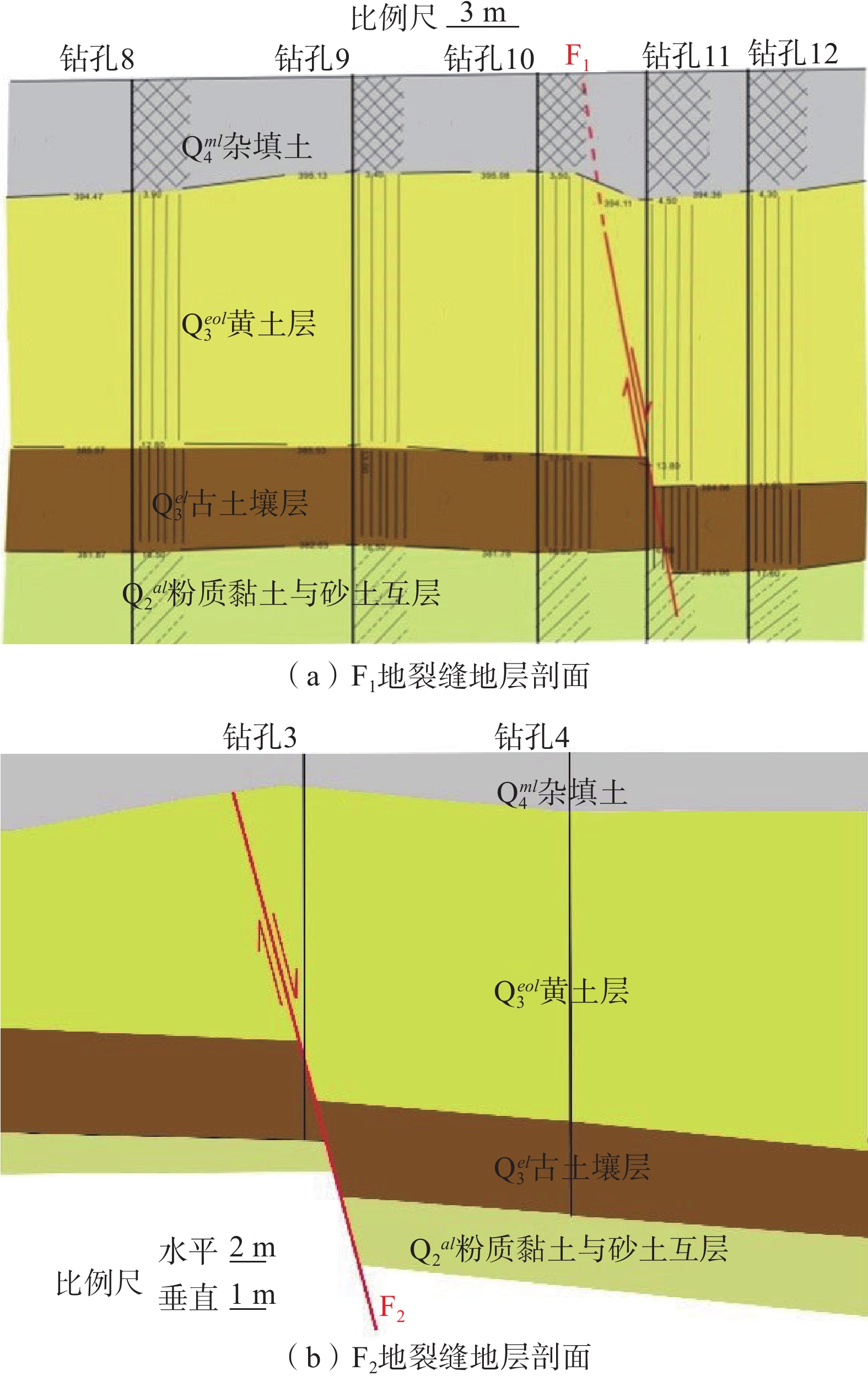
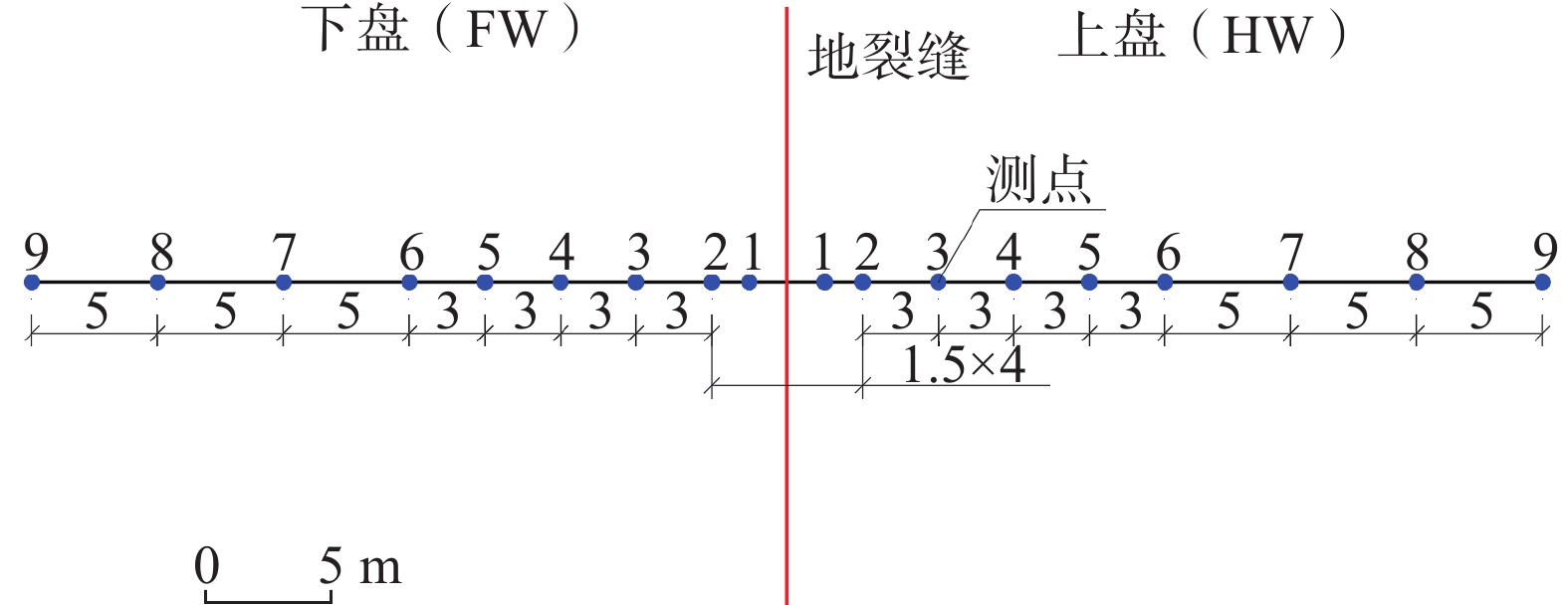
表 1 地脉动测试统计表
Table 1. Statistical table of micro-tremor test
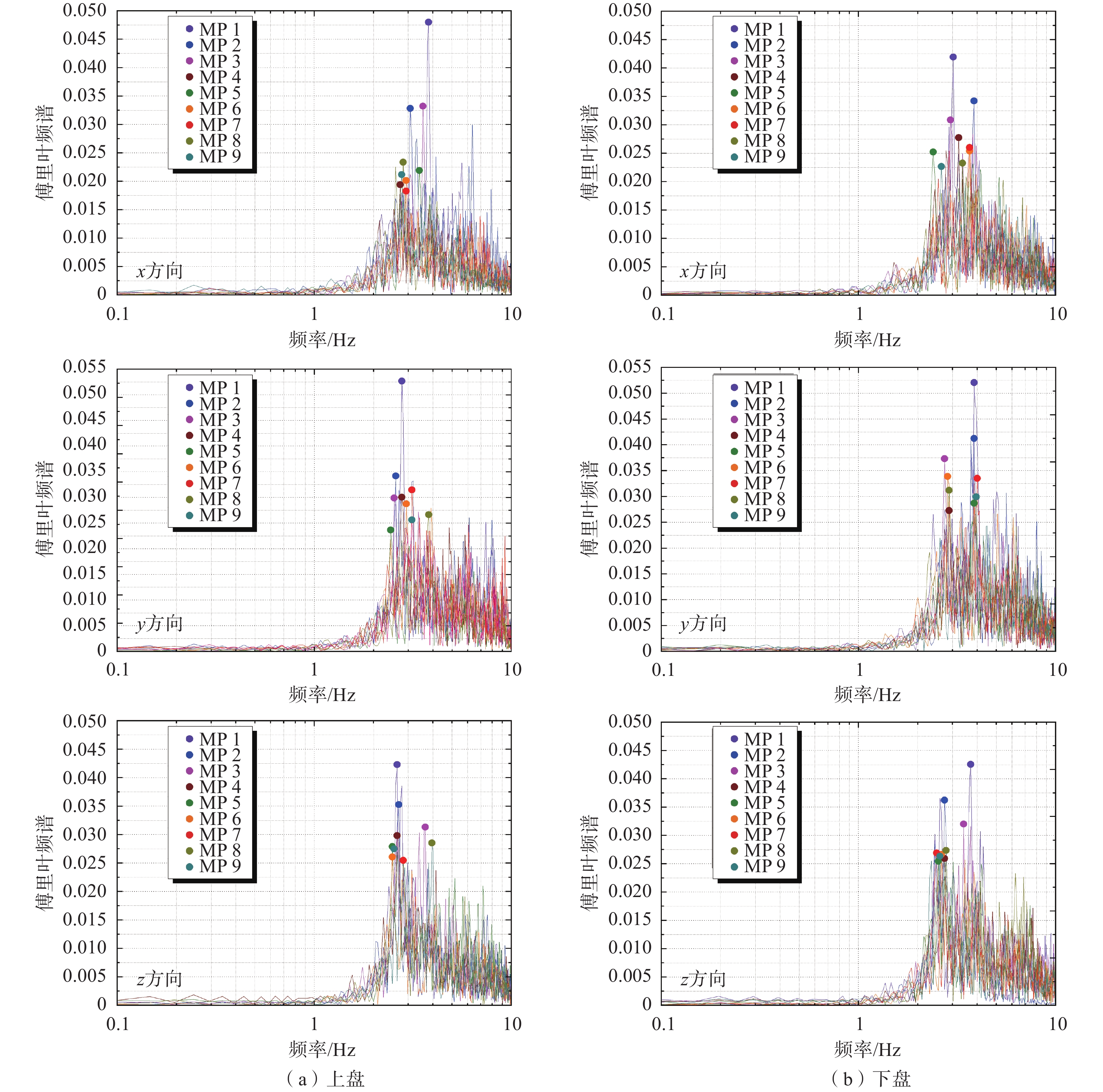
测线编号 工程地质分区 测线地点 走向 F1-1 II2-1 新房村 WE F2-1 II2-1 老人仓村 NE80° 表 2 F1-1测线上盘卓越频率及峰值统计表
Table 2. Superior frequency and peak statistical table of F1-1 hanging wall
测点
编号卓越频率/Hz 合成振幅 距离/m 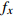
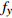
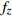
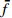
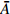
HW1 2.98 3.17 2.98 3.04 0.0820 1.5 HW2 2.44 2.34 2.49 2.42 0.0615 3 HW3 2.98 2.78 2.69 2.82 0.0508 6 HW4 3.13 2.73 3.08 2.98 0.0407 9 HW5 3.13 2.69 3.13 2.98 0.0408 12 HW6 2.69 2.49 2.69 2.62 0.0362 15 HW7 2.54 2.44 2.73 2.57 0.0341 20 HW8 2.78 2.88 3.32 2.99 0.0345 25 HW9 3.13 2.44 2.39 2.65 0.0333 30 平均卓越频率 2.70 放大因子 2.38 注: 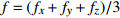 ,
,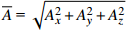 ,下文同。
,下文同。表 3 F1-1测线下盘卓越频率及峰值统计表
Table 3. Superior frequency and peak statistical table of F1-1 footwall
测点
编号卓越频率/Hz 合成振幅 距离/m 
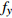
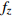
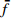
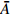
FW1 2.64 2.69 2.64 2.66 0.0766 1.5 FW2 2.39 2.25 2.25 2.30 0.0592 3 FW3 2.98 2.98 3.02 2.99 0.0525 6 FW4 3.61 2.98 2.93 3.17 0.0468 9 FW5 3.08 2.88 2.65 2.87 0.0447 12 FW6 2.78 2.93 3.08 2.93 0.0417 15 FW7 2.88 2.78 2.98 2.88 0.0447 20 FW8 3.17 2.78 3.08 3.01 0.0419 25 FW9 2.64 3.76 2.88 3.09 0.0427 30 平均卓越频率 2.88 放大因子 1.79 表 4 F2-1测线上盘卓越频率及峰值统计表
Table 4. Superior frequency and peak statistical table of F2-1 hanging wall
测点
编号卓越频率/Hz 合成振幅 距离/m 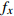
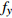
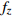
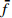
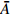
HW1 3.81 2.78 2.64 3.08 0.0829 1.5 HW2 3.08 2.59 2.69 2.79 0.0591 3 HW3 2.93 3.13 2.83 2.96 0.0546 6 HW4 2.73 2.78 2.64 2.72 0.0466 9 HW5 3.42 2.44 2.49 2.78 0.0427 12 HW6 2.93 2.93 2.49 2.78 0.0438 15 HW7 2.93 3.13 2.83 2.96 0.0445 20 HW8 2.83 3.81 3.96 3.53 0.0456 25 HW9 2.78 3.13 2.54 2.82 0.0431 30 平均卓越频率 2.94 放大因子 1.87 表 5 F2-1测线下盘卓越频率及峰值统计表
Table 5. Superior frequency and peak statistical table of F2-1 footwall
测点
编号卓越频率/Hz 合成振幅 距离/m 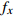
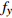
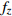
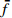
FW1 3.03 3.86 3.71 3.53 0.0793 1.5 FW2 3.86 3.86 2.73 3.48 0.0646 3 FW3 2.93 2.73 3.42 3.03 0.0581 6 FW4 3.22 2.88 2.73 2.94 0.0468 9 FW5 2.39 3.86 2.54 2.93 0.0459 12 FW6 3.66 2.83 2.64 3.04 0.0501 15 FW7 3.66 4.00 2.49 3.38 0.0502 20 FW8 3.37 2.88 2.78 3.01 0.0476 25 FW9 2.64 3.96 2.59 3.06 0.0458 30 平均卓越频率 3.16 放大因子 1.64 表 6 F1-1和F2-1测线地脉动响应特征
Table 6. Response to micro-tremor of F1-1 and F2-1
测线 位置 平均卓越频率/Hz 平稳段
峰值放大
因子影响范围/m F1-1 上盘 2.79 0.0345 2.38 15 下盘 2.88 0.0423 1.79 15 F2-1 上盘 2.94 0.0443 1.87 15 下盘 3.16 0.0484 1.64 15 -
[1] LEONARD R J. An earth fissure in southern Arizona[J]. The Journal of Geology,1929,37:765 − 774. doi: 10.1086/623676
[2] 谭鹏,刘阳,蒋富强,等. 肯尼亚裂谷区地裂缝特征及成因分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(6):53 − 62. [TAN Peng,LIU Yang,JIANG Fuqiang,et al. Analysis of the characteristics and causes of ground fissures in Kenya rift region[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(6):53 − 62. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 万佳威,李滨,谭成轩,等. 中国地裂缝的发育特征及成因机制研究—以汾渭盆地、河北平原、苏锡常平原为例[J]. 地质论评,2019,65(6):1383 − 1396. [WAN Jiawei,LI Bin,TAN Chengxuan,et al. Characteristics and mechanism of earth fissures in China:A case study of Fenhe river—Weihe river basin,Hebei plain and Suzhou—Wuxi—Changzhou plain[J]. Geological Review,2019,65(6):1383 − 1396. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 乔建伟, 彭建兵, 郑建国, 等. 中国地裂缝发育规律与运动特征研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(5): 1016 − 1027
QIAO Jianping, PENG Jianbing, ZHENG Jianguo, et al. Development rules and movement characteristics of earth fissures in china[R]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(5): 1016 − 1027. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 吴玉涛,杨为民,周俊杰,等. 河北隆尧地裂缝灾害及其安全避让距离分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(2):67 − 73. [WU Yutao,YANG Weimin,ZHOU Junjie,et al. Study on Longyao ground fissure disaster and safety avoidance distance[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(2):67 − 73. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 贺鸣,翟栋梁,乔建伟,等. 山西运城盆地大吕-白张地裂缝的基本特征与成因分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(6):74 − 83. [HE Ming,ZHAI Dongliang,QIAO Jianwei,et al. Basic features and mechanism of Dalyu-Baizhang ground fissure in Yuncheng Basin,Shanxi Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(6):74 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 孟令超,彭建兵,卢全中,等. 山西太原盆地地裂缝群发机制与深部构造关系[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(1):76 − 85. [MENG Lingchao,PENG Jianbing,LU Quanzhong,et al. Relationship between mechanism of ground fissure group and deep tectonic structures in Taiyuan basin,Shanxi Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(1):76 − 85. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 龚绪龙,杨蕴,朱锦旗,等. 苏南平原区地裂缝现状及其需要解决的几个问题[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2015,26(2):103 − 109. [GONG Xulong,YANG Yun,ZHU Jinqi,et al. Ground fissures in south plain of Jiangsu Province and related issues[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2015,26(2):103 − 109. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 李永善. 西安地裂缝[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1986.
LI Yongshan. Ground fissures in Xi’an[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 1986. (in Chinese)
[10] 王景明. 地裂缝及其灾害的理论与应用[M]. 西安: 陕西科学技术出版社, 2000.
WANG Jingming. Theory of ground fissures hazards and its application[M]. Xi’an: Shaanxi Science & Technology Press, 2000. (in Chinese)
[11] 彭建兵. 西安地裂缝灾害[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012
PENG Jianbing. Ground fissure disaster in Xi’an [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012. (in Chinese)
[12] 张家明,佟永贺,徐光黎,等. 西安地裂缝与地貌成生关系研究[J]. 地质灾害与防治,1991,2(2):67 − 73. [ZHANG Jiaming,TONG Yonghe,XU Guangli,et al. Genetic relationship between Xi’an ground fractures and landform[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,1991,2(2):67 − 73. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 刘玉海, 陈志新, 倪万魁. 西安地裂缝与地面沉降致灾机理及防治对策研讨[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 1994, 5(增刊1): 67 − 74
LIU Yuhai, CHEN Zhixin, NI Wankui. A study on hazard-forming mechanisms of geofracture and land subsidence and control countermeasure in Xi’an[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 1994, 5(Sup 1): 67 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 宋彦辉,李忠生,李新生,等. 临潼—长安断裂带内地裂缝特征[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2012,23(2):50 − 54. [SONG Yanhui,LI Zhongsheng,LI Xinsheng,et al. Characteristics of ground fissures located at Lintong-Chang’an fault zone[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2012,23(2):50 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2012.02.011
[15] PENG J B,QU W,REN J,et al. Geological factors for the formation of Xi’an ground fractures[J]. Journal of Earth Science,2018,29(2):468 − 478. doi: 10.1007/s12583-018-0841-1
[16] 彭建兵,范文,李喜安,等. 汾渭盆地地裂缝成因研究中的若干关键问题[J]. 工程地质学报,2007,15(4):433 − 440. [PENG Jianbing,FAN Wen,LI Xi’an,et al. Some key questions in the formation of ground fissures in the Fen-Wei Basin[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2007,15(4):433 − 440. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2007.04.001
[17] 邓亚虹,彭建兵,慕焕东,等. 渭河盆地深部构造活动的地裂缝孕育机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2013,43(2):521 − 527. [DENG Yahong,PENG Jianbing,MU Huandong,et al. Ground fissures germination mechanism of deep structure activities in Weihe basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2013,43(2):521 − 527. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 于文才,杨亚磊,卢全中,等. 不同活动速率下隐伏地裂缝的模型试验研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(2):98 − 105. [YU Wencai,YANG Yalei,LU Quanzhong,et al. Comparative study on physical model test of concealed ground fissure rupture propagation under different activity rates[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(2):98 − 105. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 李勇. 西安地裂缝常规监测方法及近期活动规律[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2014,25(1):33 − 37. [LI Yong. The monitoring methods and recent activities orderliness of Xi’an fissure ground[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2014,25(1):33 − 37. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 石玉玲,门玉明,彭建兵,等. 西安市地裂缝对长安路立交桥致灾机理调查研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2009,20(2):65 − 69. [SHI Yuling,MEN Yuming,PENG Jianbing,et al. Analysis on Xi’an ground-fissure destruction to Chang’an Road overpass[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2009,20(2):65 − 69. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2009.02.014
[21] 张茂省,董英,张新社,等. 地面沉降预测及其风险防控对策—以大西安西咸新区为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2013,24(4):115 − 118. [ZHANG Maosheng,DONG Ying,ZHANG Xinshe,et al. Prediction of land subsidence and Its mitigation methods:A case study in the new urban district of Xi’an-Xianyang[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2013,24(4):115 − 118. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 熊仲明,韦俊,陈轩,等. 跨越地裂缝框架结构振动台试验及数值模拟研究[J]. 工程力学,2018,35(5):214 − 222. [XIONG Zhongming,WEI Jun,CHEN Xuan,et al. Research on shaking table test and numerical modelling of frame structure crossing ground fissure[J]. Engineering Mechanics,2018,35(5):214 − 222. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 胡志平,王启耀,罗丽娟,等. “y”形地裂缝场地主次裂缝地震响应差异的振动台试验[J]. 土木工程学报,2014,47(11):98 − 107. [HU Zhiping,WANG Qiyao,LUO Lijuan,et al. Shaking table test on seismic response difference between primary and secondary ground fissures on sites with y-shape ground fissure[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal,2014,47(11):98 − 107. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 王启耀,胡志平,王瑞,等. 地震作用下地裂缝场地地表加速度响应的振动台试验研究[J]. 铁道学报,2015,37(12):121 − 128. [WANG Qiyao,HU Zhiping,WANG Rui,et al. Shaking table test study on seismic acceleration response of ground fissure sites under horizontal seismic action[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society,2015,37(12):121 − 128. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2015.12.018
[25] LIU N,FENG X Y,HUANG Q B,et al. Dynamic characteristics of a ground fissure site[J]. Engineering Geology,2019,248:220 − 229. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.12.003
[26] 慕焕东, 邓亚虹, 常江, 等. 西安地裂缝场地动力响应规律振动台模型试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(增刊1): 3139 − 3149
MU Huandong, DENG Yahong, CHANG Jiang, et al. Shaking table model test study on dynamic response of Xi’an ground fissure site [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(Sup 1): 3139 − 3149. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] KIYOSHI K,TEIJI T. Measurements of the micro-tremor[J]. Bulletin of the earthquake research Institute,1954,34(4):302 − 306.
[28] KIYOSHI K,TEIJI T. On Micro-tremors[J]. Bulletin of the earthquake research Institute,1961,39:97 − 114.
[29] KABAYASHI H K. Report on seismic microzoning studies of the Mexico earthquake of Septempe 19, 1985. Part I measurement of micro-tremors in and around Mexico D. F, Tokyo inst. Tech, 1986: 1 − 98.
[30] FIELD E,HOUGH S,JACOB K. Using microtremors to assess potential earthquake site response:A case study in Flushing Meadows,New York City[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America,1990,80:1456 − 1480. doi: 10.1016/0148-9062%2892%2991061-9
[31] FINN L. Geotechnical engineering aspects of microzonation[C]. Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Seismic zonation, 1991(1): 199 − 259.
[32] 陶夏新,师黎静,董连成. 中日地脉动台阵联合观测[J]. 世界地震工程,2002,18(2):24 − 31. [TAO Xiaxin,SHI Lijing,DONG Liancheng. Sino-Japan joint microtremor array observation[J]. World Information on Earthquake Engineering,2002,18(2):24 − 31. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6069.2002.02.004
[33] 师黎静,陶夏新,赵纪生. 地脉动台阵方法的有效性分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2006,25(8):1683 − 1690. [SHI Lijing,TAO Xiaxin,ZHAO Jisheng. Validation of microtremors array method[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2006,25(8):1683 − 1690. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.08.025
-




 下载:
下载: