Evaluation of landslide susceptibility in Ya’an City based on depth neural network model
-
摘要:
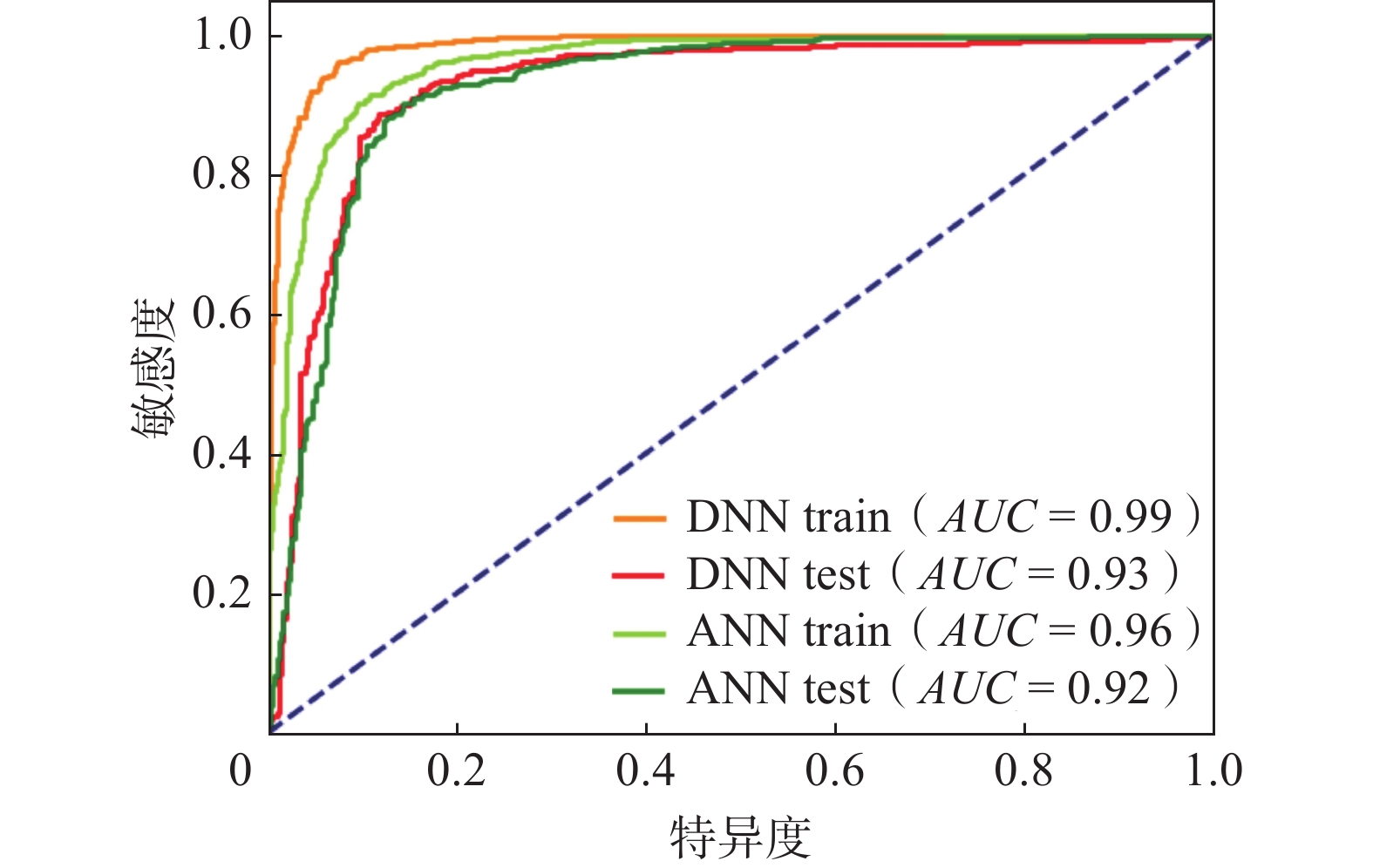
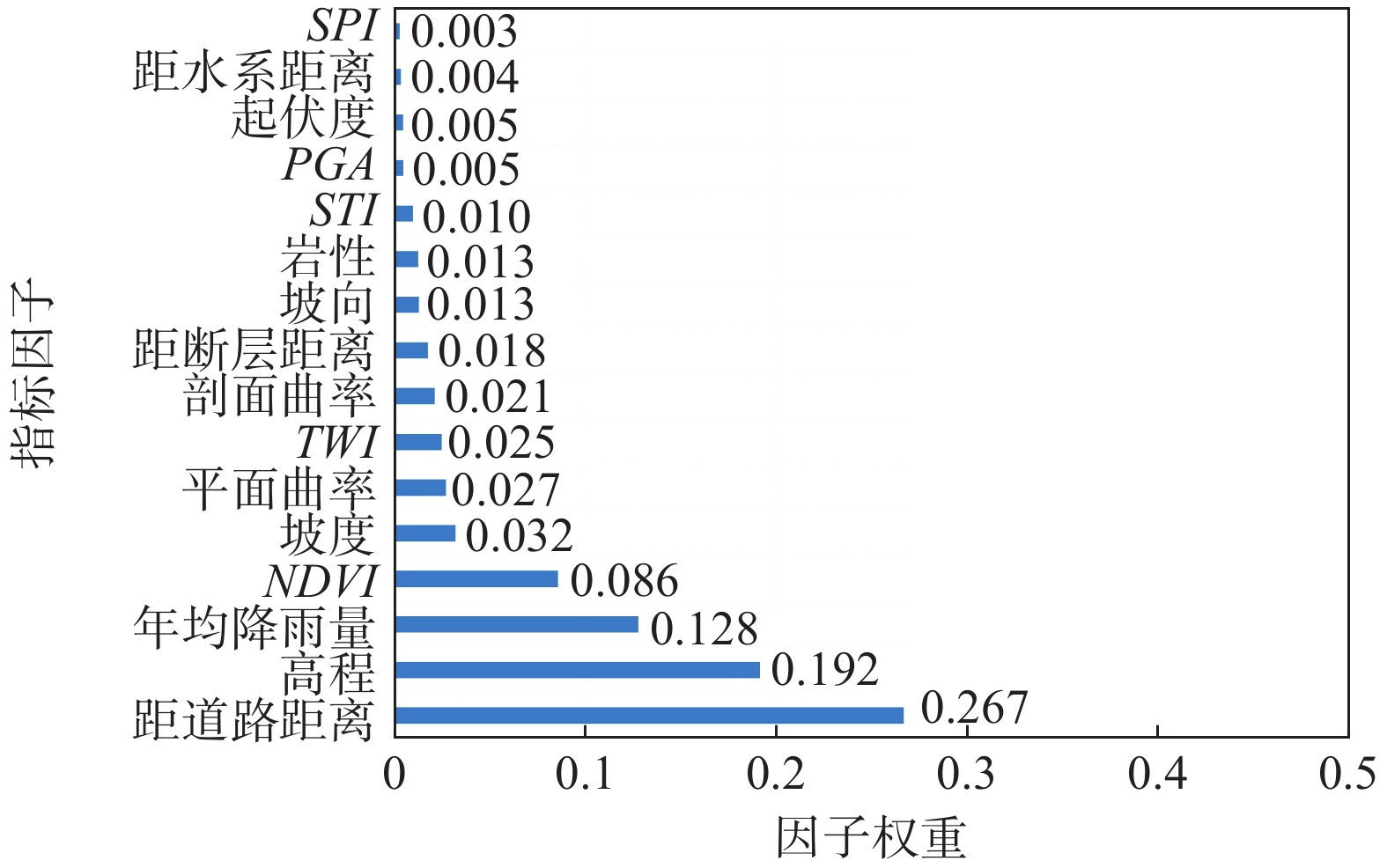
准确的滑坡易发性评价结果是滑坡风险评估的基础,对防灾减灾工作有着重要的意义。文章以雅安市为研究区,在野外地质调查的基础上,选取高程、坡度、坡向、平面曲率、剖面曲率、地形湿度指数、泥沙输运指数、径流强度指数、归一化植被指数、年均降雨量、地震动峰值加速度、地形起伏度、距断层距离、地层岩性、距河流距离、距道路距离等16个因子,构建研究区滑坡易发性评价指标体系,采用度神经网深络(DNN)模型进行滑坡易发性评价,根据易发性指数将研究区划分为极高易发区(12.2%)、高易发区(7.0%)、中易发区(9.8%)、低易发区(17.0%)、极低易发区(54.1%)五个等级,并与人工神经网络(ANN)模型进行对比,用ROC曲线的AUC值进行精度检验。结果表明,DNN模型的评价精度AUC(0.99)大于ANN(0.96)模型。因此,相比ANN模型,DNN模型在该研究区有着更好的拟合能力和预测能力,滑坡极高和高易发区主要分布于雅安市人类工程活动强烈的低海拔地区,沿着道路和水系分布,距道路距离、高程、年均降雨量是影响雅安滑坡发育的主要影响因子。
Abstract:Accurate evaluation of landslide susceptibility results are the basis of landslide risk assessment and are of great significance to disaster prevention and reduction. This paper focuses on Ya’an City as the study area and selects various factors, including elevation, slope, aspect, plane curvature, profile curvature, topographic wetness index, sediment transport index, runoff intensity index, normalized difference vegetation index, annual rainfall, peak ground acceleration, topographic relief, distance from fault, stratum lithology, distance from river, and distance from road, to construct a landslide susceptibility evaluation index system. Based on field geological survey data, a deep neural network model is used to evaluate the landslide susceptibility. The study area is classified into five categories based on susceptibility index, including landslide extremely high-prone area (12.2%), landslide high-prone area (7.0%), landslide moderate-prone area (9.8%), landslide low-prone area (17.0%) and landslide extremely low-prone area (54.1%). The accuracy of the DNN model was tested with an AUC value and compared to the artificial neural network (ANN) model. The results show that the DNN model has a higher evaluation accuracy AUC (0.99) compared to ANN (0.96). Thus, the DNN model has a better fitting degree and prediction ability in the study area than the ANN model. The extremely high-prone area and high-prone area of landslides are primarily distributed in the low altitude areas with significant human engineering activities in Ya’an City, along the roads and water systems. The main control factors affecting the development of Ya’an landslide are distance from the road, elevation and annual average rainfall.
-
Key words:
- landslide /
- susceptibility /
- deep neural network /
- Ya’an City
-

-
表 1 滑坡易发性评价因子分级
Table 1. Classification of landslide susceptibility evaluation factors
评价因子 因子分级 栅格数 分级面积
占比/%滑坡数/个 滑坡占比/% 频率比 高程/m <1 500 5 204 401 0.31 1 233 0.82 2.69 [1 500,2 500) 6 332 165 0.37 244 0.16 0.44 [2 500,3 500) 3 923 903 0.23 21 0.01 0.06 [3 500,4 500] 1 422 562 0.08 0 0.00 0.00 >4 500 137 525 0.01 0 0.00 0.00 坡度/(°) <10 1 838 336 0.11 298 0.20 1.85 [10,20) 3 394 994 0.20 579 0.39 1.95 [20,30) 4 388 262 0.26 367 0.25 0.96 [30,40) 4 265 068 0.25 181 0.12 0.49 [40,50) 2 411 994 0.14 51 0.03 0.24 [50,60] 642 955 0.04 11 0.01 0.20 >60 78 947 0.00 1 0.00 0.14 坡向 平地 1 347 0.00 0 0.00 0.00 北向 1 967 849 0.12 122 0.08 0.71 东北 2 188 728 0.13 168 0.11 0.88 东向 2 267 964 0.13 226 0.15 1.14 东南 2 482 029 0.15 224 0.15 1.03 南向 1 998 089 0.12 172 0.12 0.98 西南 1 974 369 0.12 206 0.14 1.19 西向 1 942 033 0.11 168 0.11 0.99 西北 2 198 148 0.13 202 0.14 1.05 平面曲率 <-1.5 1 670 196 0.10 67 0.05 0.46 [−1.5,−0.5) 3 515 500 0.21 256 0.17 0.83 [−0.5,0.5) 6 569 423 0.39 828 0.56 1.44 [0.5,1.5] 3 535 554 0.21 258 0.17 0.83 >1.5 1 729 882 0.10 79 0.05 0.52 剖面曲率 <−1.5 2 178 456 0.13 75 0.05 0.39 [−1.5,−0.5) 3 463 053 0.20 271 0.18 0.90 [−0.5,0.5) 6 083 729 0.36 703 0.47 1.32 [0.5,1.5] 3 582 013 0.21 344 0.23 1.10 >1.5 2 207 544 0.13 95 0.06 0.49 TWI <4 2 338 941 0.14 55 0.04 0.27 [4,6) 9 159 642 0.54 775 0.52 0.97 [6,8) 3 579 077 0.21 378 0.25 1.21 [8,10) 1 206 481 0.07 170 0.11 1.61 [10,12] 435 025 0.03 66 0.04 1.74 >12 301 390 0.02 44 0.03 1.67 SPI <30 6 586 113 0.39 647 0.43 1.12 [30,70) 3 369 824 0.20 273 0.18 0.93 [70,110) 1 583 666 0.09 127 0.09 0.92 [110,150] 938 662 0.06 70 0.05 0.85 >150 4 542 291 0.27 371 0.25 0.93 STI <10 4 335 955 0.25 567 0.38 1.50 [10,20) 4 286 230 0.25 340 0.23 0.91 [20,30) 2 423 036 0.14 185 0.12 0.87 [30,40) 1 498 141 0.09 103 0.07 0.79 [40,50] 965 895 0.06 56 0.04 0.66 >50 3 511 299 0.21 237 0.16 0.77 NDVI <0 572 046 0.03 12 0.01 0.24 [0,0.1) 4 391 796 0.26 243 0.16 0.63 [0.1,0.2) 7 452 084 0.44 755 0.51 1.16 [0.2,0.3] 4 210 818 0.25 445 0.30 1.21 >0.3 393 811 0.02 33 0.02 0.96 降雨/mm <1 100 347 828 0.02 51 0.03 1.68 [1 100,1 200) 5 875 063 0.35 1 123 0.75 2.19 [1 200,1 300) 6 988 356 0.41 306 0.21 0.50 [1 300,1 400] 3 161 041 0.19 8 0.01 0.03 >1 400 648 268 0.04 0 0.00 0.00 PGA 0.10 5 547 189 0.33 642 0.43 1.32 0.15 6 626 792 0.39 687 0.46 1.19 0.20 4 846 575 0.28 159 0.11 0.38 地形起伏度/m <200 3 046 522 0.18 718 0.48 2.70 [200,400) 8 659 562 0.51 660 0.44 0.87 [400,600) 4 893 981 0.29 106 0.07 0.25 [600,800] 400 489 0.02 4 0.01 0.11 >800 20 002 0.00 0 0.00 0.00 岩性 A 6 690 039 0.39 469 0.32 0.80 B 1 930 133 0.11 412 0.28 2.44 C 2 589 329 0.15 86 0.06 0.38 D 2 805 880 0.16 86 0.06 0.35 E 1 280 290 0.08 54 0.04 0.48 F 607 260 0.04 142 0.10 2.67 G 1 117 652 0.07 239 0.16 2.45 距河流距离/m <200 359 325 0.02 96 0.06 3.06 [200,400) 356 325 0.02 75 0.05 2.41 [400,600) 353 757 0.02 80 0.05 2.59 [600,800) 350 074 0.02 81 0.05 2.65 [800,1 000] 348 031 0.02 70 0.05 2.30 >1 000 15 253 044 0.90 1 086 0.73 0.81 距断层距离/m <1 000 3 769 155 0.22 239 0.16 0.73 [1 000,2 000) 2 849 793 0.17 166 0.11 0.67 [2 000,3 000) 2 175 357 0.13 143 0.10 0.75 [3 000,4 000) 1 662 881 0.10 116 0.08 0.80 [4 000,5 000] 1 315 010 0.08 156 0.10 1.36 >5 000 5 248 360 0.31 668 0.45 1.46 距道路距离/m <500 1 770 408 0.10 606 0.41 3.92 [500,1 000) 1 391 697 0.08 233 0.16 1.92 [1 000,1 500) 1 222 996 0.07 222 0.15 2.08 [1 500,2 000) 1 081 568 0.06 127 0.09 1.34 [2 000,2 500] 968 316 0.06 69 0.05 0.82 >2 500 10 585 571 0.62 231 0.16 0.25 注:A为较坚硬的砂岩页岩板岩;B为较软的泥岩千枚岩页岩;C为软硬相间的碳酸盐岩及碎屑岩;D为较坚硬的石灰岩白云岩;E为坚硬的玄武岩苦橄岩角质岩;F为松散的堆积物冲积物;G为较坚硬的长石石英砂岩。 表 2 影响因子的相关性分析
Table 2. Correlation analysis of impact factors
因子 高程 坡度 坡向 平面曲率 剖面曲率 TWI STI SPI NDVI 降雨 PGA 起伏度 断层 岩性 河流 道路 高程 1.00 坡度 0.41 1.00 坡向 −0.03 −0.01 1.00 平面曲率 0.01 0.00 0.01 1.00 剖面曲率 0.01 0.05 0.03 0.18 1.00 TWI −0.19 −0.39 0.02 −0.28 0.17 1.00 STI 0.17 0.45 0.02 −0.35 0.17 0.51 1.00 SPI 0.08 0.25 0.03 −0.39 0.18 0.64 0.92 1.00 NDVI −0.23 −0.10 −0.68 −0.01 0.07 0.04 −0.04 −0.01 1.00 降雨 0.67 0.28 −0.04 0.01 0.02 −0.16 0.10 0.03 −0.23 1.00 PGA 0.28 0.21 −0.01 −0.02 0.09 −0.05 0.15 0.10 0.01 0.31 1.00 起伏度 0.31 0.18 0.01 0.01 0.08 −0.06 0.05 0.16 −0.36 0.23 0.12 1.00 断层 −0.14 −0.20 0.02 0.00 −0.03 0.05 −0.13 −0.09 −0.07 0.00 −0.15 0.01 1.00 岩性 −0.08 −0.08 −0.01 0.01 0.03 0.03 −0.06 −0.03 0.02 −0.01 0.10 −0.04 −0.01 1.00 河流 0.24 0.06 0.03 −0.02 −0.01 −0.16 −0.04 −0.09 0.04 0.29 0.08 −0.06 −0.07 −0.07 1.00 道路 0.61 0.30 −0.02 −0.03 −0.01 −0.17 0.12 0.03 −0.06 0.56 0.27 0.10 −0.16 −0.08 0.39 1.00 表 3 滑坡易发性评价频率比
Table 3. Frequency ratio of landslide susceptibility assessment
模型 易发性等级 分级栅格数 分级比例 滑坡数量 滑坡比例 频率比 ANN 极低 10 574 871 0.62 28 0.02 0.03 低 1 397 388 0.21 33 0.02 0.27 中 1 264 627 0.43 64 0.04 0.58 高 1 698 651 0.01 341 0.23 2.30 极高 2 085 018 0.12 1 022 0.69 5.61 DNN 极低 9 211 525 0.54 12 0.01 0.01 低 2 876 474 0.17 17 0.01 0.07 中 1 673 121 0.10 76 0.05 0.52 高 1 189 737 0.07 170 0.11 1.63 极高 2 069 700 0.12 1 213 0.82 6.70 -
[1] 彭建兵,崔鹏,庄建琦. 川藏铁路对工程地质提出的挑战[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(12):2377 − 2389. [PENG Jianbing,CUI Peng,ZHUANG Jianqi. Challenges to engineering geology of Sichuan—Xizang railway[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(12):2377 − 2389. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2020.0446
Peng Jianbing, Cui Peng, Zhuang Jianqi. Challenges to engineering geology of Sichuan—Xizang railway[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(12): 2377-2389. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2020.0446
[2] ZHUANG Jianqi, PENG Jianbing , WANG Gonghui, et al. Distribution and characteristics of landslide in loess plateau:A case study in Shaanxi Province[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,236:89 − 96. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.03.001
[3] GUO Changbao, WU Ruian, JIANG Liangwen,et al. Typical geohazards and engineering geological problems along the Ya’an-Linzhi section of the Sichuan-Xizang railway,China[J]. Geoscience,2021,35(1):1 − 17.
[4] 王涛,王嘉昆,潘冬. 四川汉源康家坡滑坡形成机理与滑坡—堰塞坝—泥石流灾害链分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(1):1 − 7. [WANG Tao,WANG Jiakun,PAN Dong. Analysis on mechanism of Kangjiapo landslide and consequent debris flow in Hanyuan County of Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(1):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.01.01
WANG Tao, WANG Jiakun, PAN Dong. Analysis on mechanism of Kangjiapo Landslide and consequent debris flow in Hanyuan County of Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(1)1-7(in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.01.01
[5] 黄发明,殷坤龙,蒋水华,等. 基于聚类分析和支持向量机的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(1):156 − 167. [HUANG Faming,YIN Kunlong,JIANG Shuihua,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on clustering analysis and support vector machine[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018,37(1):156 − 167. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2017.0824
Huang Faming, Yin Kunlong, Jiang Shuihua, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on clustering analysis and support vector machine[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(1): 156-167. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2017.0824
[6] OMAR F,Althuwaynee. A novel ensemble bivariate statistical evidential belief function with knowledge-based analytical hierarchy process and multivariate statistical logistic regression for landslide susceptibility mapping[J]. CATENA,2014,114:21 − 36. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2013.10.011
[7] 许冲,戴福初,姚鑫,等. GIS支持下基于层次分析法的汶川地震区滑坡易发性评价[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2009,28(增刊 2):3978 − 3985. [XU Chong,DAI Fuchu,YAO Xin,et al. GIS-based landslide susceptibility assessment using analytical hierarchy process in Wenchuan earthquake region[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2009,28(Sup 2):3978 − 3985. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XU Chong, DAI Fuchu, YAO Xin, et al. Gis-based landslide susceptibility assessment using analytical hierarchy process in Wenchuan earthquake region[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(S2): 3978-3985. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 刘磊,殷坤龙,王佳佳,等. 降雨影响下的区域滑坡危险性动态评价研究—以三峡库区万州主城区为例[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(3):558 − 569. [LIU Lei,YIN Kunlong,WANG Jiajia,et al. Study on dynamic evaluation of regional landslide risk under the influence of rainfall:A case study of Wanzhou main city in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(3):558 − 569. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2015.0495
Liu Lei, Yin Kunlong, Wang Jiajia, et al. Study on dynamic evaluation of regional landslide risk under the influence of rainfall—a case study of Wanzhou main city in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(3): 558-569. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2015.0495
[9] 张俊,殷坤龙,王佳佳,等. 三峡库区万州区滑坡灾害易发性评价研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(2):284 − 296. [ZHANG Jun,YIN Kunlong,WANG Jiajia,et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility for Wanzhou District of Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(2):284 − 296. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang Jun, Yin Kunlong, Wang Jiajia, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility for Wanzhou district of Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(2): 284-296. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] CHEN Wei,POURGHASEMI H,KORNEJADY A,et al. Landslide spatial modeling:Introducing new ensembles of ANN,MaxEnt,and SVM machine learning techniques[J]. Geoderma,2017,305:314 − 327. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.06.020
[11] 张纫兰,王少军,李江风. 基于Mamdani FIS模型的滑坡易发性评价研究[J]. 岩土力学,2014,35(增刊 2):437 − 444. [ZHANG Renlan,WANG Shaojun,LI Jiangfeng. Research on landslide susceptibility based on Mamdani-FIS model[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2014,35(Sup 2):437 − 444. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Renlan, WANG Shaojun, LI Jiangfeng. Research on landslide susceptibility based on Mamdani-FIS model[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(S2): 437-444. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 方然可,刘艳辉,黄志全. 基于机器学习的区域滑坡危险性评价方法综述[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(4):1 − 8. [FANG Ranke,LIU Yanhui,HUANG Zhiquan. A review of the methods of regional landslide hazard assessment based on machine learning[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(4):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.04-01
FANG Ranke, LIU Yanhui, HUANG Zhiquan. A review of the methods of regional landslide hazard assessment based on machine learning[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(4)1-8(in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.04-01
[13] 刘福臻,王灵,肖东升. 机器学习模型在滑坡易发性评价中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(6):98 − 106. [LIU Fuzhen,WANG Ling,XIAO Dongsheng. Application of machine learning model in landslide susceptibility evaluation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(6):98 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.06-12
LIU Fuzhen, WANG Ling, XIAO Dongsheng. Application of machine learning model in landslide susceptibility evaluation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(6)98-106(in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.06-12
[14] 庄育龙,田原,程楚云. 基于深度神经网络的滑坡危险性评价—以深圳市为例[J]. 地理与地理信息科学,2019,35(2):104 − 110. [ZHUANG Yulong,TIAN Yuan,CHENG Chuyun. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on deep neural network:A case study of Shenzhen[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science,2019,35(2):104 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2019.02.016
ZHUANG Yulong, TIAN Yuan, CHENG Chuyun. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on deep neural network: a case study of Shenzhen[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2019, 35(2)104-110(in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2019.02.016
[15] 桂蕾. 三峡库区万州区滑坡发育规律及风险研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学
GUI Lei. Study on the development law and risk of landslide in Wanzhou District of Three Gorges Reservoir area[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 牛瑞卿,彭令,叶润青,等. 基于粗糙集的支持向量机滑坡易发性评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2012,42(2):430 − 439. [NIU Ruiqing,PENG Ling,YE Runqing,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on rough sets and support vector machine[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2012,42(2):430 − 439. (in Chinese with English abstract)
NIU Ruiqing, PENG Ling, YE Runqing, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on rough sets and support vector machine[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2012, 42(2)430-439(in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 胡鹏,文章,胡新丽,等. 基于遗传算法-支持向量机的滑坡渗透系数反演[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(4):160 − 168. [HU Peng,WEN Zhang,HU Xinli,et al. Estimation of hydraulic conductivity of landslides based on support vector machine method optimized with genetic algorithm[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(4):160 − 168. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[HU Peng, WEN Zhang, HU Xinli, et al. Estimation of hydraulic conductivity of landslides based on support vector machine method optimized with genetic algorithm[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(4): 160-168.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] PARK Lee. Spatial prediction of landslide susceptibility using a decision tree approach:A case study of the Pyeongchang area,Korea[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing,2014,35(16):6089 − 6112. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2014.943326
[19] 田乃满,兰恒星,伍宇明,等. 人工神经网络和决策树模型在滑坡易发性分析中的性能对比[J]. 地球信息科学学报,2020,22(12):2304 − 2316. [TIAN Naiman,LAN Hengxing,WU Yuming,et al. Performance comparison of BP artificial neural network and CART decision tree model in landslide susceptibility prediction[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science,2020,22(12):2304 − 2316. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2020.190766
TIAN Naiman, LAN Hengxing, WU Yuming, et al. Performance comparison of BP artificial neural network and CART decision tree model in landslide susceptibility prediction[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2020, 22(12): 2304-2316. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2020.190766
[20] 王世宝, 庄建琦, 樊宏宇, 等. 基于频率比与集成学习的滑坡易发性评价——以金沙江上游巴塘—德格河段为例[J/OL]. 工程地质学报, 2021: 1 − 13. (2021-05-14). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3249.P.20210514.1018.004.html.
WANG Shibao, ZHUANG Jianqi, FAN Hongyu, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on frequency ratio and ensemble learning: Taking the Batang-Dege section in the upstream of Jinsha River as an example[J/OL]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2021: 1 − 13. (2021-05-14). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3249.P.20210514.1018.004.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] WANG Shibao, ZHUANG J, ZHENG Jia, et al. Application of Bayesian hyperparameter optimized random forest and XGBoost model for landslide susceptibility mapping[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2021.
[22] 陈涛,钟子颖,牛瑞卿,等. 利用深度信念网络进行滑坡易发性评价[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2020,45(11):1809 − 1817. [CHEN Tao,ZHONG Ziying,NIU Ruiqing,et al. Mapping landslide susceptibility based on deep belief network[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2020,45(11):1809 − 1817. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHEN Tao, ZHONG Ziying, NIU Ruiqing, et al. Mapping landslide susceptibility based on deep belief network[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2020, 45(11): 1809-1817. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 王世宝,庄建琦,郑佳,等. 基于深度学习的CZ铁路康定—理塘段滑坡易发性评价[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(3):908 − 919. [WANG Shibao,ZHUANG Jianqi,ZHENG Jia,et al. Landslide susceptibility evaluation based on deep learning along Kangding-Litang section of CZ railway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(3):908 − 919. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2021-0115
WANG Shibao, ZHUANG Jianqi, ZHENG Jia, et al. Landslide susceptibility evaluation based on deep learning along Kangding-Litang section of cz railway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2022, 30(3): 908-919. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2021-0115
[24] 王志祥,李建阁. 基于DNN改性沥青中SBS含量的预测模型[J]. 建筑材料学报,2021,24(3):630 − 636. [WANG Zhixiang,LI Jiange. Determination model of SBS content in modified asphalt based on DNN[J]. Journal of Building Materials,2021,24(3):630 − 636. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2021.03.025
WANG Zhixiang, LI Jiange. Determination model of SBS content in modified asphalt based on DNN[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2021, 24(3): 630-636. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2021.03.025
[25] 李仪,林建君,朱习军. 基于改进DNN的糖尿病预测模型设计[J]. 计算机工程与设计,2021,42(5):1418 − 1424. [LI Yi,LIN Jianjun,ZHU Xijun. Diabetes prediction model design based on improved DNN[J]. Computer Engineering and Design,2021,42(5):1418 − 1424. (in Chinese)
LI Yi, LIN Jianjun, ZHU Xijun. Diabetes prediction model design based on improved DNN[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2021, 42(5)1418-1424(in Chinese)
[26] HINTON G E,SALAKHUTDINOV R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks[J]. Science,2006,313(5786):504 − 507. doi: 10.1126/science.1127647
[27] 王山海. 基于深度学习神经网络的语音识别研究[D]. 桂林: 桂林电子科技大学, 2015
WANG Shanhai. Research on speech recognition based on deep learning neural network[D]. Guilin: Guilin University of Electronic Technology, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] TIAN Yingying,XU Chong,HONG Haoyuan,et al. Mapping earthquake-triggered landslide susceptibility by use of artificial neural network (ANN) models:An example of the 2013 Minxian (China) Mw 5.9 event[J]. Geomatics,Natural Hazards and Risk,2019,10(1):1 − 25. doi: 10.1080/19475705.2018.1487471
[29] KALANTAR B,PRADHAN B,NAGHIBI S A,et al. Assessment of the effects of training data selection on the landslide susceptibility mapping:A comparison between support vector machine (SVM),logistic regression (LR) and artificial neural networks (ANN)[J]. Geomatics,Natural Hazards and Risk,2018,9(1):49 − 69. doi: 10.1080/19475705.2017.1407368
[30] 彭建兵, 张骏, 苏生瑞, 等. 渭河盆地活动断裂与地质灾害[M]. 西安: 西北大学出版社, 1992
PENG Jianbing, ZHANG Jun, SUN Shengrui. Active faults and geological hazards in Weihe Basin[M]. Xi’an: Northwest University Press, 1992. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] GUO Changbao. Quantitative assessment of landslide susceptibility along the Xianshuihe fault zone,Xizang Plateau,China[J]. Geomorphology,2015,248:93 − 110. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.07.012
[32] 戴福初,邓建辉. 青藏高原东南三江流域滑坡灾害发育特征[J]. 工程科学与技术,2020,52(5):3 − 15. [DAI Fuchu,DENG Jianhui. Development characteristics of landslide hazards in three-rivers basin of southeast Xizang Plateau[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences,2020,52(5):3 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DAI Fuchu, DENG Jianhui. Development characteristics of landslide hazards in three-rivers basin of southeast Xizang Plateau[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2020, 52(5)3-15(in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 张钟远,邓明国,徐世光,等. 镇康县滑坡易发性评价模型对比研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2022,41(1):157 − 171. [ZHANG Zhongyuan,DENG Mingguo,XU Shiguang,et al. Comparison of landslide susceptibility assessment models in Zhenkang County,Yunnan Province,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2022,41(1):157 − 171. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2021.0360
Zhang Zhongyuan, Deng Mingguo, Xu Shiguang, et al. Comparison of landslide susceptibility assessment models in Zhenkang County, Yunnan Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(1): 157-171. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2021.0360
[34] 刘艳芳,方佳琳,陈晓慧,等. 基于确定性系数分析方法的秭归县滑坡易发性评价[J]. 自然灾害学报,2014,23(6):209 − 217. [LIU Yanfang,FANG Jialin,CHEN Xiaohui,et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility in Zigui County based on deterministic coefficient analysis method[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2014,23(6):209 − 217. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu Yanfang, Fang Jialin, Chen Xiaohui, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility in Zigui County based on deterministic coefficient analysis method[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2014, 23(6): 209-217. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] 张玘恺,凌斯祥,李晓宁,等. 九寨沟县滑坡灾害易发性快速评估模型对比研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(8):1595 − 1610. [ZHANG Qikai,LING Sixiang,LI Xiaoning,et al. Comparison of landslide susceptibility mapping rapid assessment models in Jiuzhaigou County,Sichuan Province,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(8):1595 − 1610. (in Chinese)
Zhang Qikai, Ling Sixiang, Li Xiaoning, et al. Comparison of landslide susceptibility mapping rapid assessment models in Jiuzhaigou County, Sichuan Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(8): 1595-1610. (in Chinese)
[36] HONG Haoyuan, et al . Modeling landslide susceptibility using LogitBoost alternating decision trees and forest by penalizing attributes with the bagging ensemble[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,718:137231. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137231
[37] 屠水云,张钟远,付弘流,等. 基于CF模型与CF-LR模型的地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):96 − 104. [TU Shuiyun,ZHANG Zhongyuan,FU Hongliu,et al. Evaluation of geological hazard susceptibility based on CF model and CF-LR model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):96 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
TU Shuiyun, ZHANG Zhongyuan, FU Hongliu, et al. Evaluation of geological hazard susceptibility based on CF model and CF-LR model [J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(2): 96-104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[38] HOSMER D W, LEMESHOW S, STURDIVANT R X. Applied logistic regression[M]. 3rd ed.New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell, 2013
-




 下载:
下载: