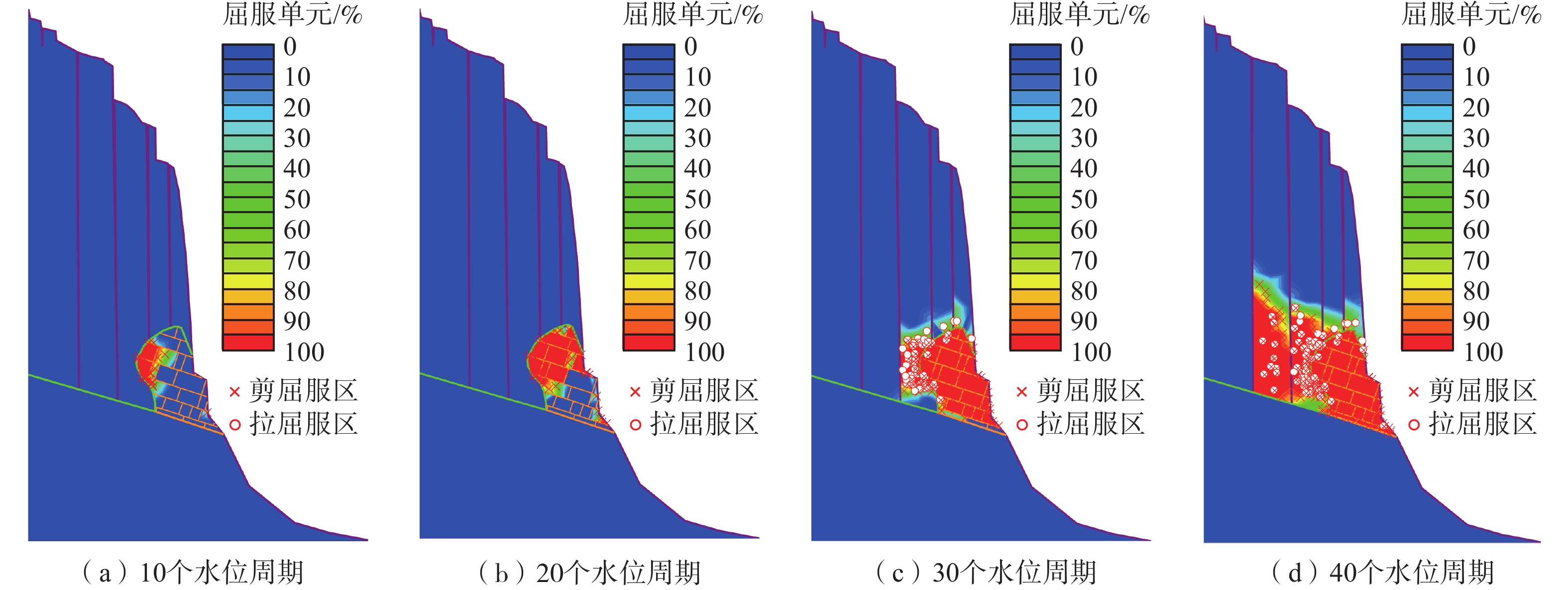
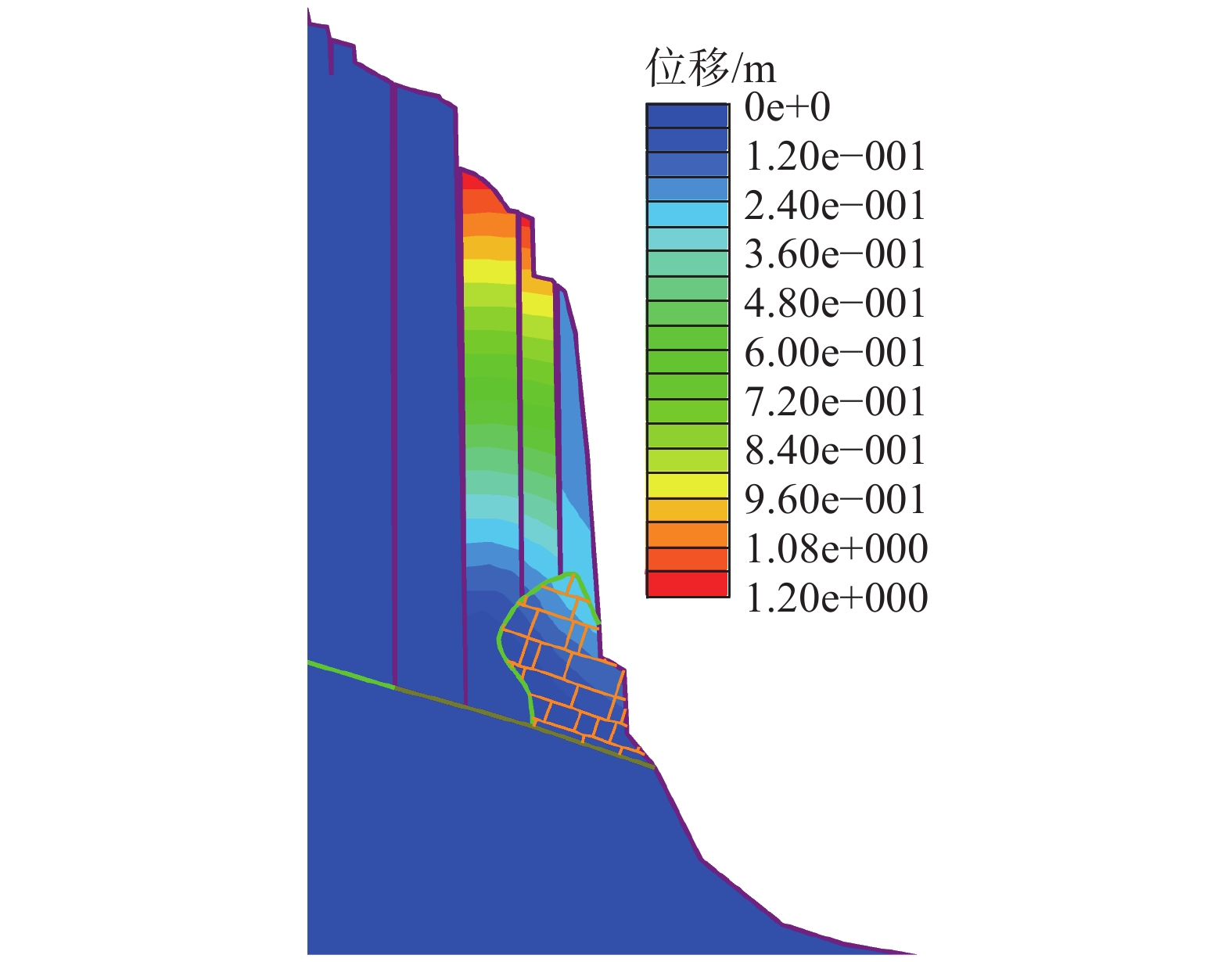
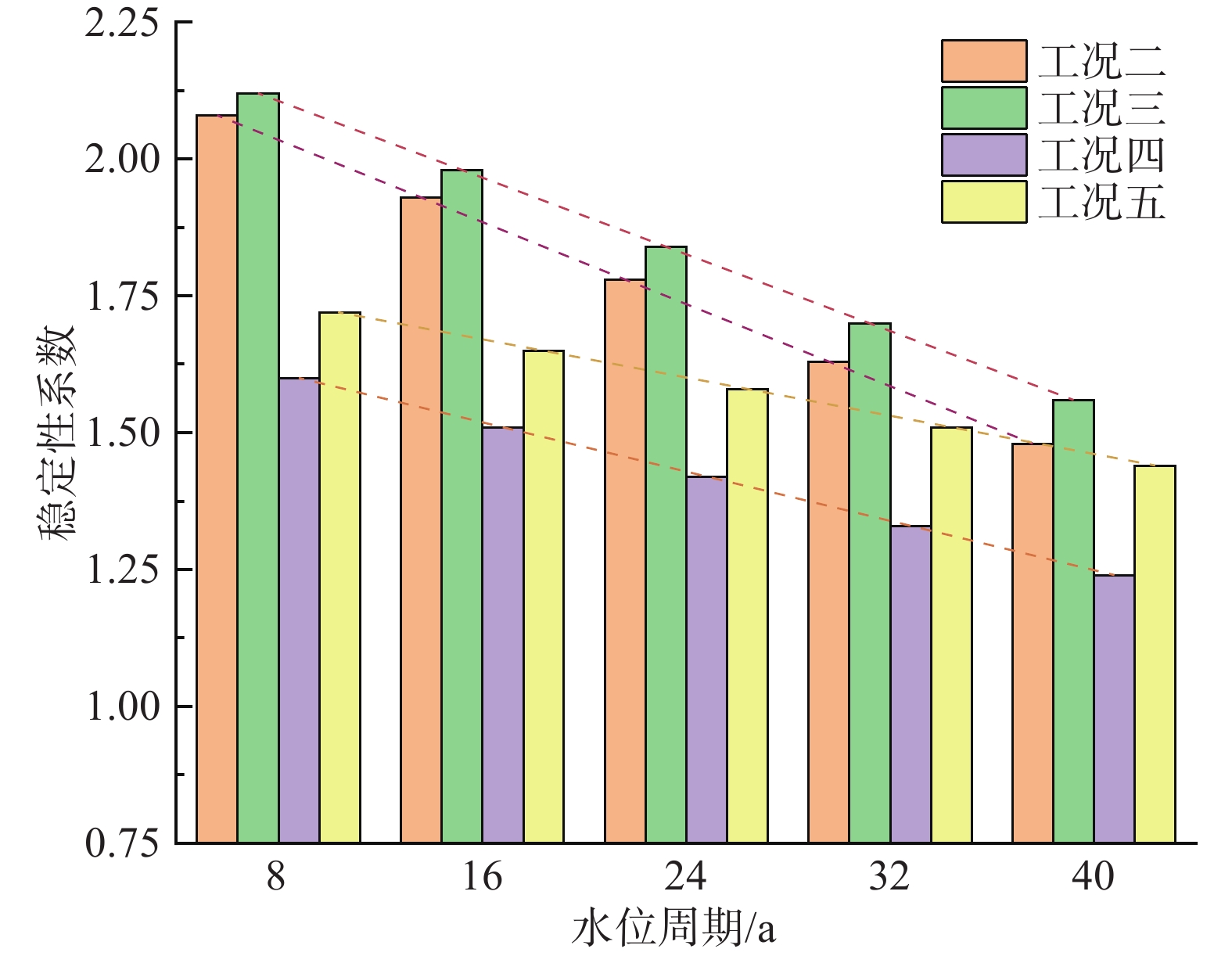
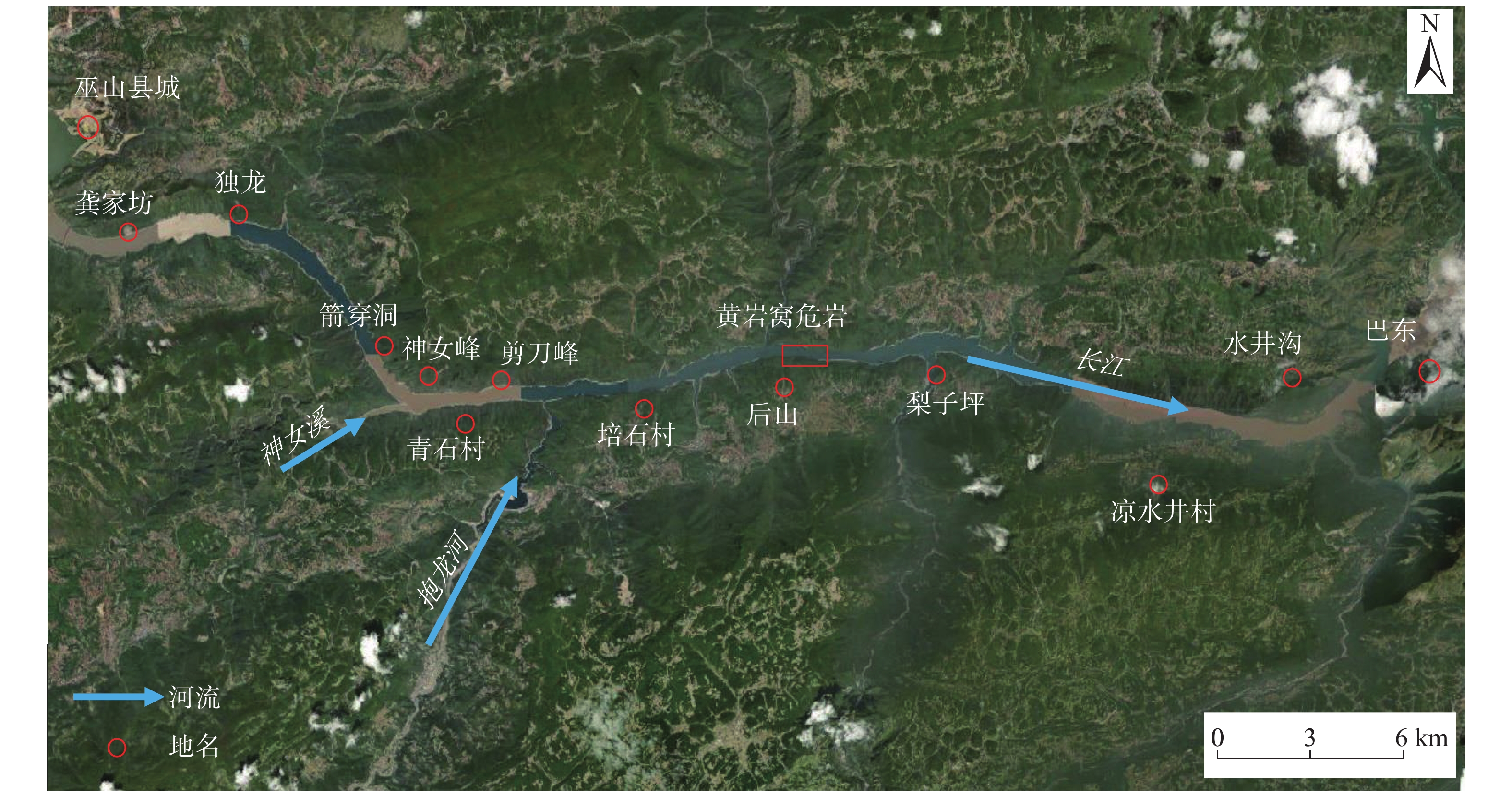
Analysis of failure modes and long-term stability of dangerous rock mass on typical karst bank slope in the Three Gorges Reservoir area
-
摘要:
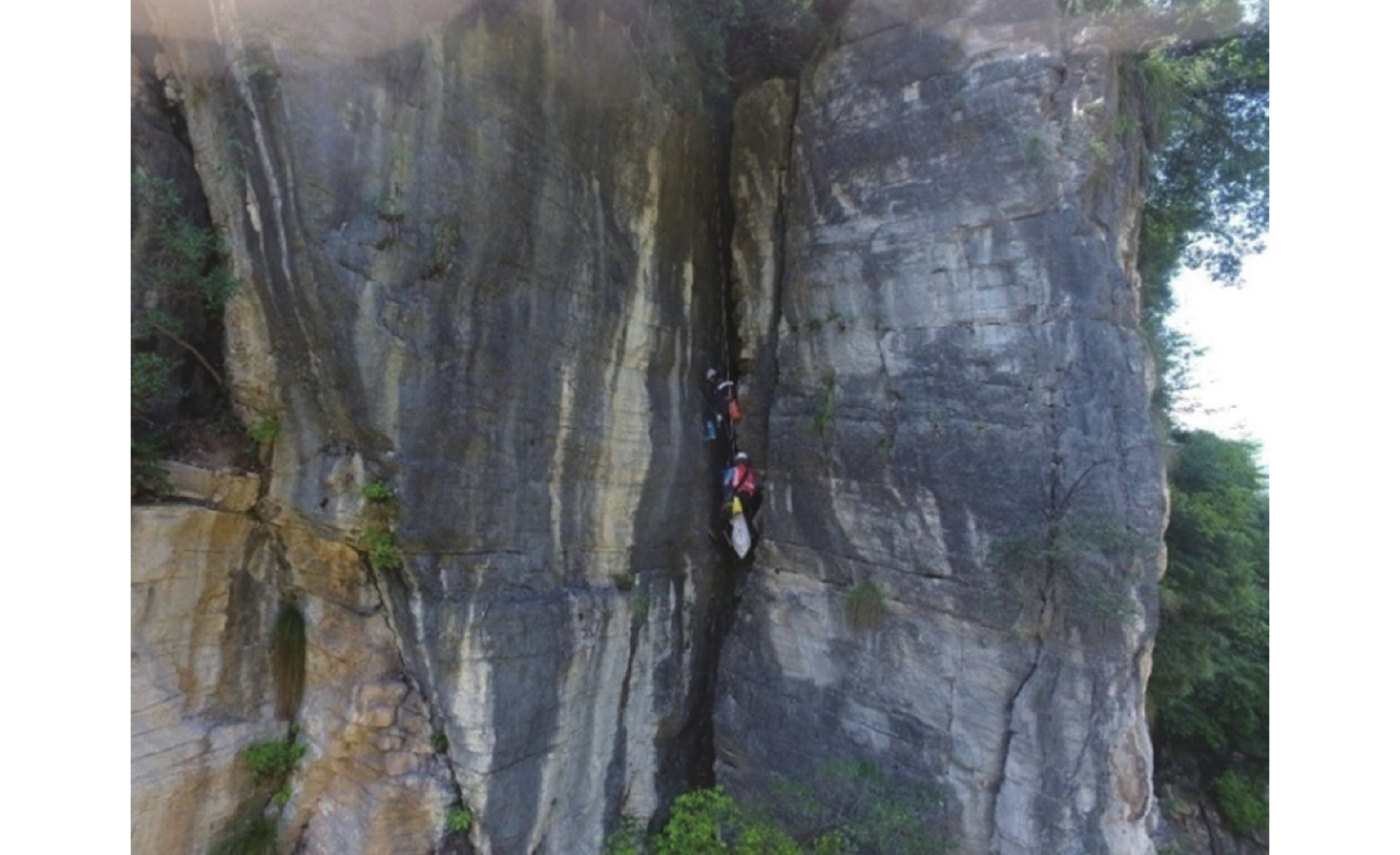
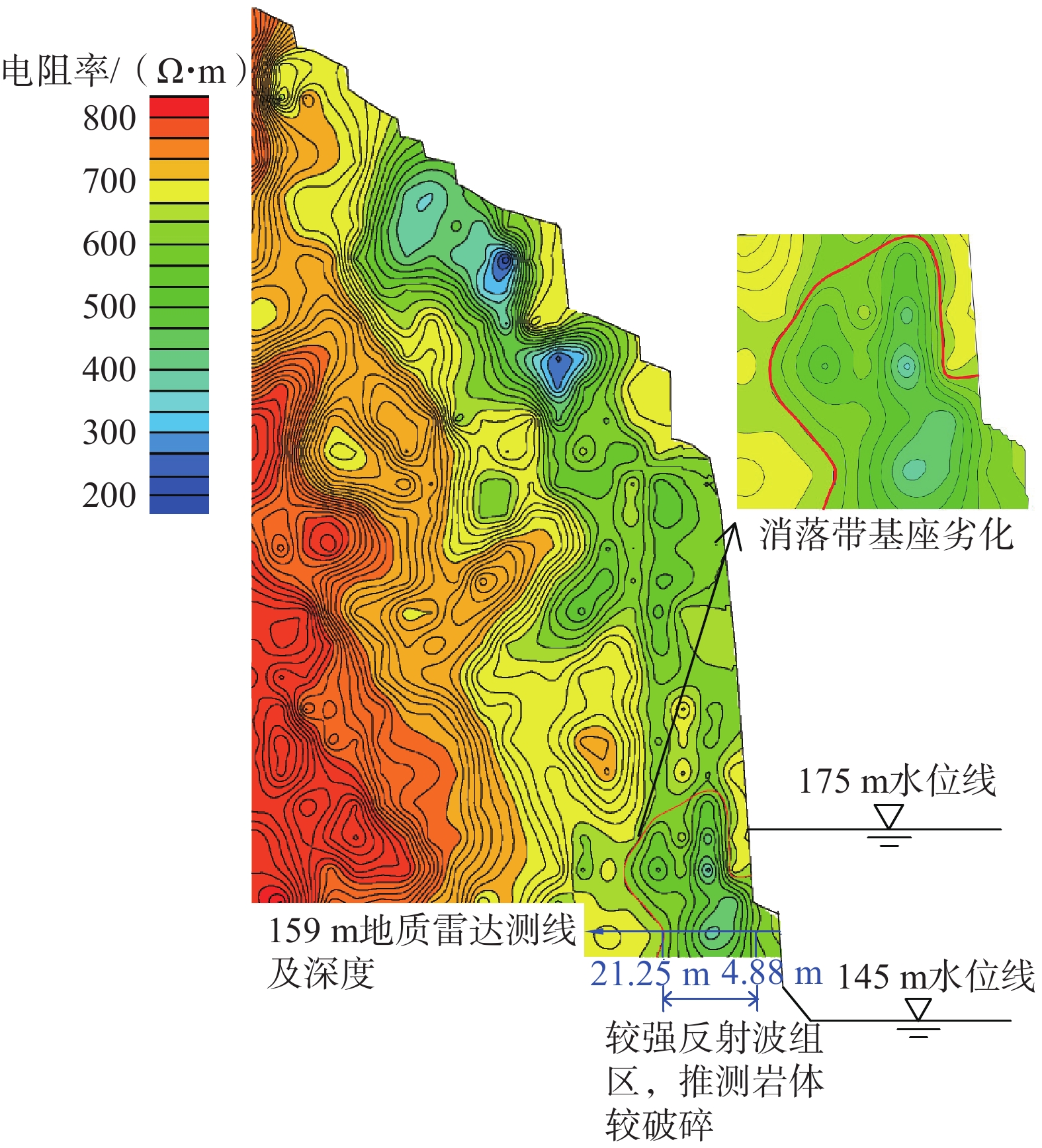
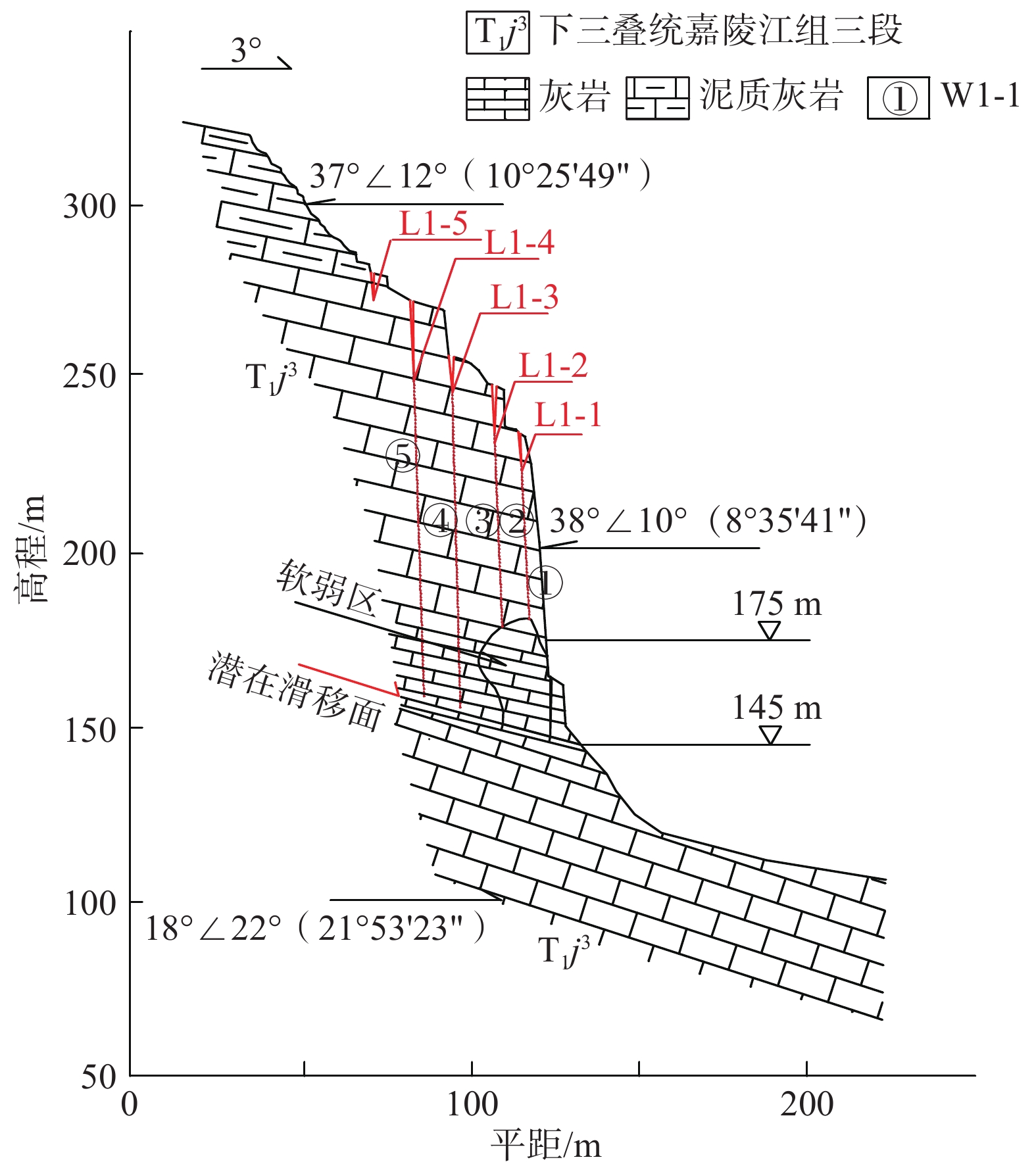
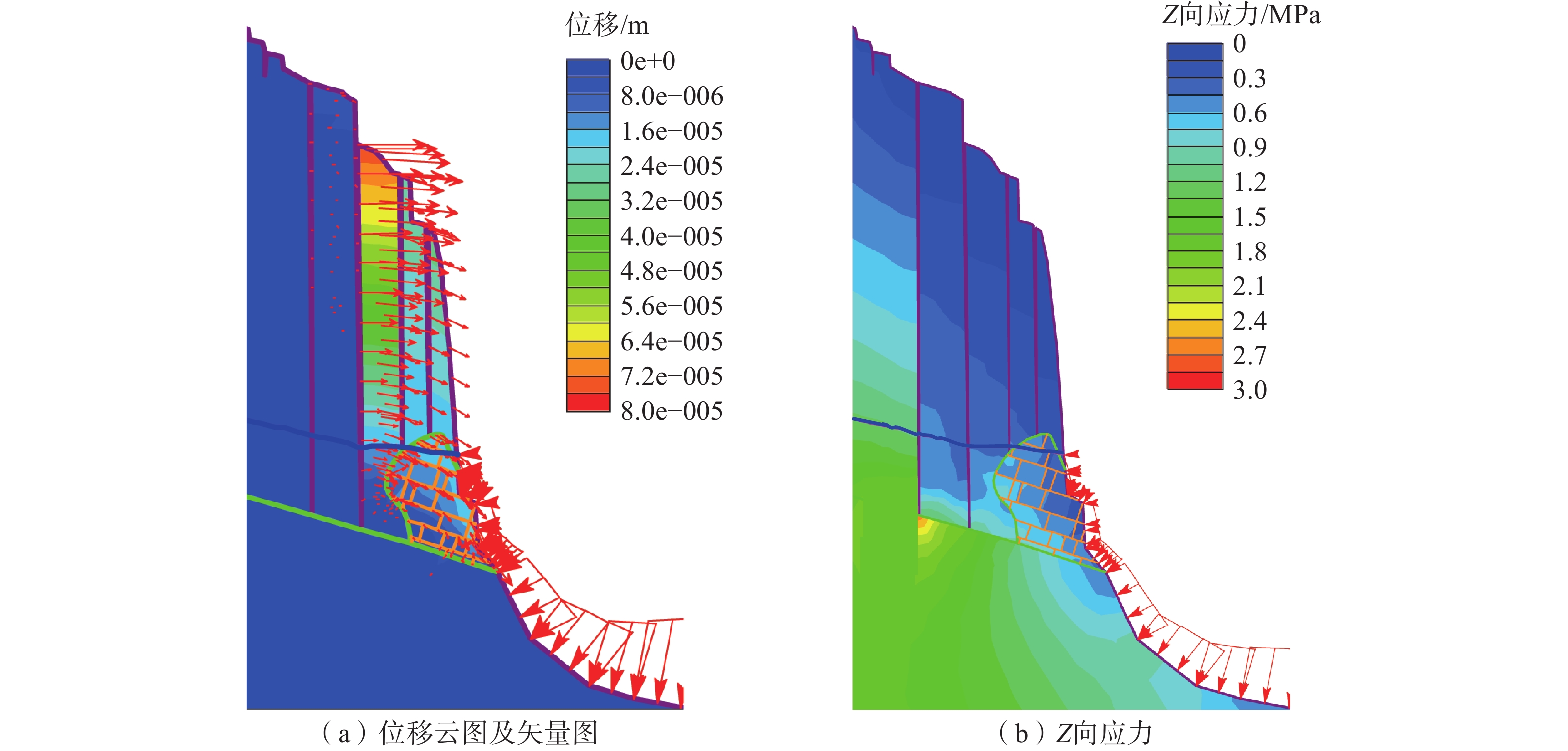
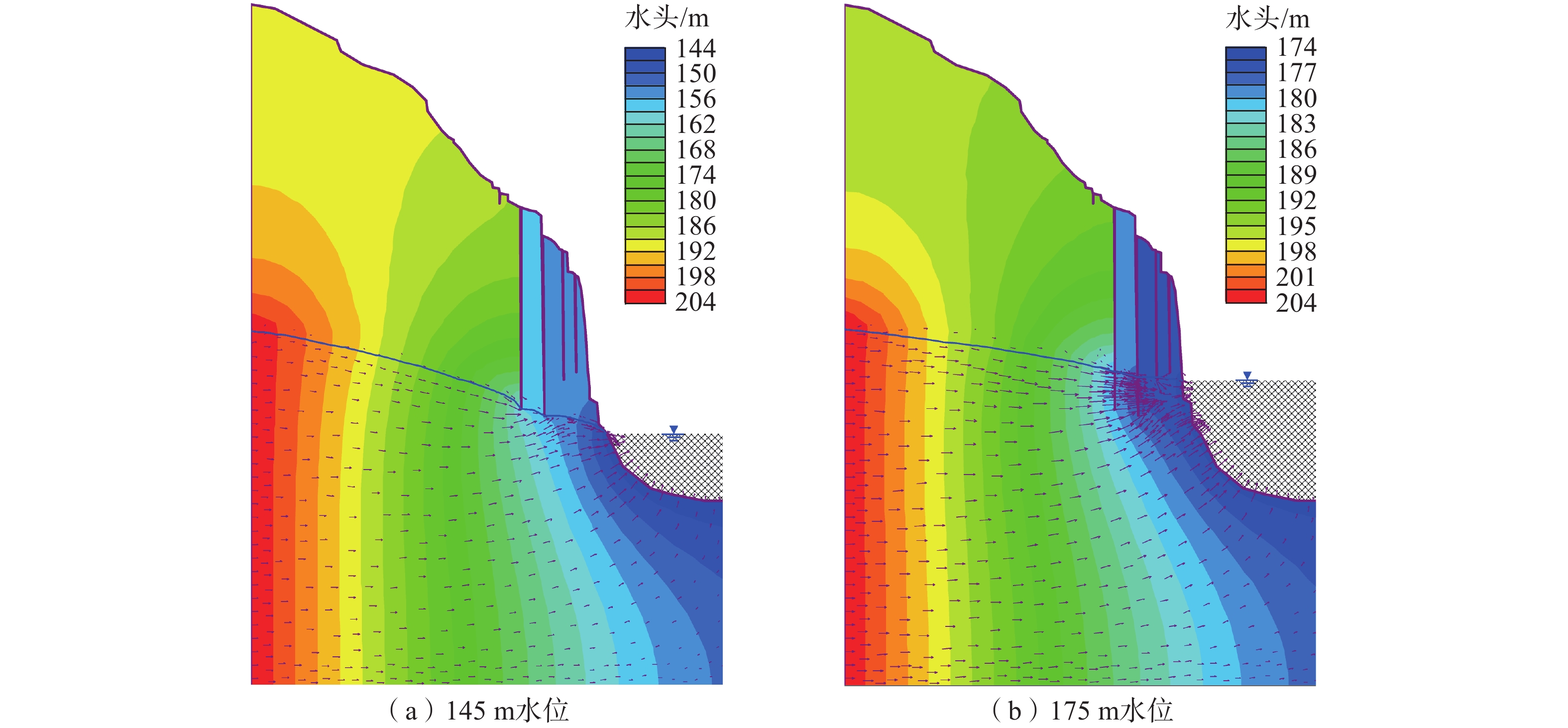
三峡库区地质环境复杂,受库水位升降作用影响岩溶岸坡消落区岩体劣化,加快了岸坡不稳定性发展。文章以三峡库区黄岩窝危岩体为研究对象,现场详查了消落带岩体劣化现象,计算了危岩体的长期稳定性数值。研究表明:黄岩窝危岩体存在垂直岩溶带和底部渗流带;底部渗流带处于消落带部位,存在软弱区和岩体劣化现象。考虑库水位和暴雨时岩溶水压岸坡稳定性系数为1.69,危岩体处于稳定状态。随着岩体劣化导致底部软弱区岩体参数不断下降,稳定性系数年均下降约0.01。预测在约57个周期性水位变动之后黄岩窝危岩体变为欠稳定状态,62个周期后发生失稳破坏。危岩体的破坏模式是顶部出现岩块倾倒崩落和底部软弱区贯通之后发生滑移的复合式破坏,与野外调查定性认识基本一致。研究结果对库区类似的地质灾害预警和防治有着重要的指导意义。
Abstract:The Three Gorges Reservoir area presents a complex geological environment, where the deterioration of rock masses in the riparian zone of karst bank slopes is expedited by the fluctuating reservoir water levels of the reservoir, thereby hastening the evolution of the bank slopes towards instability. This study focuses on the Huangyanwo dangerous rock mass in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. A comprehensive filed investigation was conducted to scrutinize the deterioration phenomenon of rock masses within the water–level fluctuation zone, and a numerical analysis was performed to assess the long–term stability of the dangerous rock mass. The findings reveal the presence of a vertical karst zone and a bottom seepage zone in the Huangyanwo dangerous rock mass. The bottom seepage zone is situated within the water–level–fluctuation zone, characterized by areas of weakness and rock mass deterioration. Considering the influence of reservoir water levels and rainfall events, the stability coefficient of karst water pressure on the bank slope is calculated to be 1.69, indicating that the dangerous rock mass remains stable. Nevertheless, due to the progressive deterioration of rock mass parameters within the weak area at the bottom, the stability coefficient experiences an annual decline of approximately 0.01. It is predicted that the Huangyanwo dangerous rock mass will transition to an unstable state after approximately 57 cycles of periodic water level variations, and the instability failure will occur after 62 cycles. The failure mode of the dangerous rock mass involves a compound failure mechanism of toppling and sliding subsequent to the connection of the weak zone at the bottom, aligning closely with the qualitative understanding grained from field investigations. The research results hold significant instructive implications for the early warning and prevention strategies concerning analogous geological disasters in reservoir areas.
-
Key words:
- rock mass deterioration /
- stability /
- Three Gorges Reservoir /
- buckling mode
-

-
表 1 危岩单体形态特征
Table 1. Morphological characteristics of the dangerous rock mass monomer
危岩
编号危岩形态 体积
/m3主崩方向
/(°)宽/m 高/m 厚/m W1 280~300 100~120 20~41.30 540000 3 W2 100~120 100~110 25~32 360000 2 W3 20~50 70 9 22050 352 W4 50 30~45 5 9000 4 W5 28~35 90~100 7 18480 1 W6 20 65 4 5200 2 合计 — — — 954730 — 表 2 黄岩窝危岩体物理力学参数表
Table 2. Physical and mechanical parameters of Huangyanwo dangerous rock mass
岩性 重度/(kN·m−3) 弹性模量/MPa 泊松比 黏聚力/MPa 内摩擦角/(°) 抗拉强度
/MPa灰岩(基岩) 26.82 50 400 0.20 5.48 44.4 2.71 灰岩(危岩体) 26.91 27 200 0.33 1.79 37.6 2.71 灰岩(破碎带) 26.82 27 200 0.33 1.79 37.6 2.71 结构面 黏聚力/MPa 内摩擦角/(°) 抗拉强度
/MPa法向刚度
/(MPa·m−1)切向刚度
/(MPa·m−1)1.534 34.34 0.542 40 000 10 000 表 3 传统公式法计算的稳定性系数
Table 3. Stability coefficients calculated by traditional formula method
库水位/m 175 145 稳定系数 抗滑移 2.60 2.61 抗倾覆 2.49 2.51 表 4 数值计算工况表
Table 4. Numerical computational conditions table
工况一 1-1:自重+145 m水位 1-2:自重+175 m水位 1-3:自重+145 m库水位+暴雨 工况二 2-1/10自重+145 m水位+岩体强度劣化 工况三 3-1/10自重+175 m水位+岩体强度劣化 工况四 4-1/10自重+145 m水位+暴雨+岩体强度劣化 工况五 5-1/10自重+175 m水位+暴雨+岩体强度劣化 -
[1] 殷跃平,黄波林,李滨,等. 三峡库区消落带溶蚀岩体劣化指标研究[J]. 地质学报,2021,96(8):2590 − 2600. [YIN Yueping,HUANG Bolin,LI Bin,et al. Research on the deterioration index of karst rock mass in the fluctuating water level zone of Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2021,96(8):2590 − 2600. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.08.021
YIN Yueping, HUANG Bolin, ZHANG Zhihua, Yan Guoqiang, Zheng Jiahao. Research on the deterioration index of karst rock mass in the fluctuating water level zone of Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 96(8): 2590~2600.(in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.08.021
[2] 杨何,汤明高,许强,等. 三峡库区消落带岸坡岩体劣化特性测试及质量评价[J]. 水利学报,2020,51(11):1360 − 1371. [YANG He,TANG Minggao,XU Qiang,et al. Deterioration characteristic test and quality evaluation of bank slope rock mass in hydro–fluctuation belt of Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2020,51(11):1360 − 1371. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YANG He, TANG Minggao, XU Qiang, et al. Deterioration characteristic test and quality evaluation of bank slope rock mass in hydro–fluctuation belt of Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2020, 51(11): 1360–1371.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 刘新荣,景瑞,缪露莉,等. 巫山段消落带岸坡库岸再造模式及典型案例分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(7):1321 − 1332. [LIU Xinrong,JING Rui,MIU Luli,et al. Reconstruction models and typical case analysis of the fluctuation belt of reservoir bank slopes in Wushan[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(7):1321 − 1332. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Xinrong, JING Rui, MIU Luli, et al. Reconstruction models and typical case analysis of the fluctuation belt of reservoir bank slopes in Wushan. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(7): 1321 – 1332(in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] XU Q, YANG H, TANG M G, et al. Variability of permeability and seepage characteristics in soil landslides: A tests case in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China[J]. Water Science & Technology Water Supply, 2019.
[5] 王世昌,陈小婷,黄波林,等. 三峡库区青石滑坡的变形特征及形成机理研究[J]. 人民长江,2013,44(增刊2):66 − 70. [WANG Shichang,CHEN Xiaoting,HUANG Bolin,et al. Study on deformation characteristics and formation mechanism of Qingshi landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Yangtze River,2013,44(Sup2):66 − 70. (in Chinese)
WANG Shichang, CHEN Xiaoting, HUANG Bolin, LIU Guangning. Study on deformation characteristics and formation mechanism of Qingshi landslide in three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Yangtze River, 2013, 44(S2): 66–70. (in Chinese
[6] 黄波林. 水库滑坡涌浪灾害水波动力学分析方法研究[D]. 中国地质大学, 2014.
HUANG Bolin. Study on hydrodynamic analysis method of reservoir landslide surge disaster[D]. China University of Geosciences, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 王文沛,李滨,黄波林,等. 三峡库区近水平厚层斜坡滑动稳定性研究—以重庆巫山箭穿洞危岩为例[J]. 地质力学学报,2016,22(3):725 − 732. [WANG Wenpei,LI Bin,HUANG Bolin,et al. Stability analysis of sub–horizontal thick–bedded slope in three gorges reservior area:A case study of jianchuandong dangerous rockmass in Wushan,Chongqing[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2016,22(3):725 − 732. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Wenpei, LI Bin, HUANG Bolin, et al. Stability analysis of sub–horizontal thick–bedded slope in three gorges reservior area: a case study of jianchuandong dangerous rockmass in wushan, chongqing[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2016, 22(3): 725–732.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 黄波林,殷跃平. 水库区滑坡涌浪风险评估技术研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(3):621 − 629. [HUANG Bolin,YIN Yueping. Risk assessment research on impulse wave generated by landslide in reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018,37(3):621 − 629. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HUANG Bolin, YIN Yueping. Risk assessment research on impulse wave generated by landslide in reservoir[J]. Yanshilixue Yu Gongcheng Xuebao/Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(3): 621–629. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 陈小婷,王健,黄波林,等. 库水位变动条件下柱状危岩体变形破坏机理[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(2):9 − 18. [CHEN Xiaoting,WANG Jian,HUANG Bolin,et al. Deformation and failure mechanism of columnar dangerous rock mass under changing reservoir water level[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(2):9 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHEN Xiaoting, WANG Jian, HUANG Bolin, et al. Deformation and failure mechanism of columnar dangerous rock mass under changing reservoir water level[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2019, 30(02): 9–18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] HALE P A,SHAKOOR A. A laboratory investigation of the effects of cyclic heating and cooling,wetting and drying,and freezing and thawing on the compressive strength of selected sandstones[J]. Environmental & Engineering Geoscience,2003,9(2):117 − 130.
[11] 刘新荣,袁文,傅晏,等. 干湿循环作用下砂岩溶蚀的孔隙度演化规律[J]. 岩土工程学报,2018,40(3):527 − 532. [LIU Xinrong,YUAN Wen,FU Yan,et al. Porosity evolution of sandstone dissolution under wetting and drying cycles[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2018,40(3):527 − 532. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Xinrong, YUAN Wen, FU Yan, et al. Porosity evolution of sandstone dissolution under wetting and drying cycles[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 40(03): 527–532.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 胡玉,邓华锋,李建林,等. 水–岩作用下砂岩微细观结构变化特性及机理研究[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2018,38(2):265 − 273. [HU Yu,DENG Huafeng,LI Jianlin,et al. Research on characteristics and mechanism of micro–structure variation in sandstone under water–rock interaction[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering,2018,38(2):265 − 273. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HU Yu, DENG Huafeng, LI Jianlin, et al. Research on Characteristics and Mechanism of Micro–structure Variation in Sandstone under Water–rock Interaction[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2018, 38(02): 265–273(in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 邓华锋,原先凡,李建林,等. 浸泡作用下砂岩断裂力学特性及劣化机理[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报),2014,39(1):108 − 114. [DENG Huafeng,YUAN Xianfan,LI Jianlin,et al. Fracture mechanics characteristics and deterioration mechanism of sandstone under reservoir immersion interaction[J]. Earth Science(Journal of China University of Geosciences),2014,39(1):108 − 114. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2014.011
DENG Huafeng, YUAN Xianfan, LI Jianlin, et al. Fracture mechanics characteristics and deterioration mechanism of sandstone under reservoir immersion interaction[J]. Earth Science(Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2014, 39(1): 108–114.(in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2014.011
[14] 张景昱,宛良朋,潘洪月,等. 考虑水–岩作用特点的典型岸坡长期稳定性分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2017,39(10):1851 − 1858. [ZHANG Jingyu,WAN Liangpeng,PAN Hongyue,et al. Long–term stability of bank slope considering characteristics of water–rock interaction[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2017,39(10):1851 − 1858. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201710013
ZHANG Jingyu, WAN Liangpeng, PAN Hongyue, et al. Long–term stability of bank slope considering characteristics of water–rock interaction[J]. Yantu Gongcheng Xuebao/Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 39(10): 1851–1858.(in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201710013
[15] 张夏冉,殷坤龙,夏辉,等. 渗透系数与库水位升降对下坪滑坡稳定性的影响研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(2):488 − 495. [ZHANG Xiaran,YIN Kunlong,XIA Hui,et al. Influence of permeability coefficient and reservoir water level fluctuation on Xiaping landslide stability[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017,25(2):488 − 495. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Xiaran, YIN Kunlong, XIA Hui, et al. Influence of permeability coefficient and reservoir water level fluctuation on xiaping landslide stability[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2017, 25(02): 488–495.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 工程岩体试验方法标准: GB/T50266—1999[S]. 1999.
Standard for tests method of engineering rock massas: GB/T50266—1999[S]. 1999. (in Chinese)
[17] 土工试验方法标准: GB/T50123—1999[S]. 1999.
Standard for geotechnical tests method: GB/T50123–1999[S]. 1999. (in Chinese)
[18] 地质灾害防治工程勘察规范: DB50/143—2003[S]. 2003.
Code for investigation of geological disaster prevention works: DB50/143—2003[S]. 2003. (in Chinese)
[19] 杨光华,钟志辉,张玉成,等. 用局部强度折减法进行边坡稳定性分析[J]. 岩土力学,2010,31(增刊2):53 − 58. [YANG Guanghua,ZHONG Zhihui,ZHANG Yucheng,et al. Slope stability analysis by local strength reduction method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2010,31(Sup2):53 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YANG Guanghua, ZHONG Zhihui, ZHANG Yucheng , et al. Slope stability analysis by local strength reduction method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010, 31(S2): 53–58.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 殷跃平, 闫国强, 黄波林, 等. 三峡水库消落带斜坡岩体劣化过程地质强度指标研究[J]. 水利学报, 2020, 51(8): 883 – 896.
YIN Yueping, YAN Guoqiang, HUANG Bolin, et al. Geological strength index of the slope rock mass deterioration process of the hydro–fluctuation belt in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2020, 51(8): 883 – 896. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: