Preliminary analysis on basic characteristics and mechanism of rockfalls in layered red rocks with gentle dip angle: A case study of the Tiejiangwan rockfall in Hongya County, Sichuan Province
-
摘要:
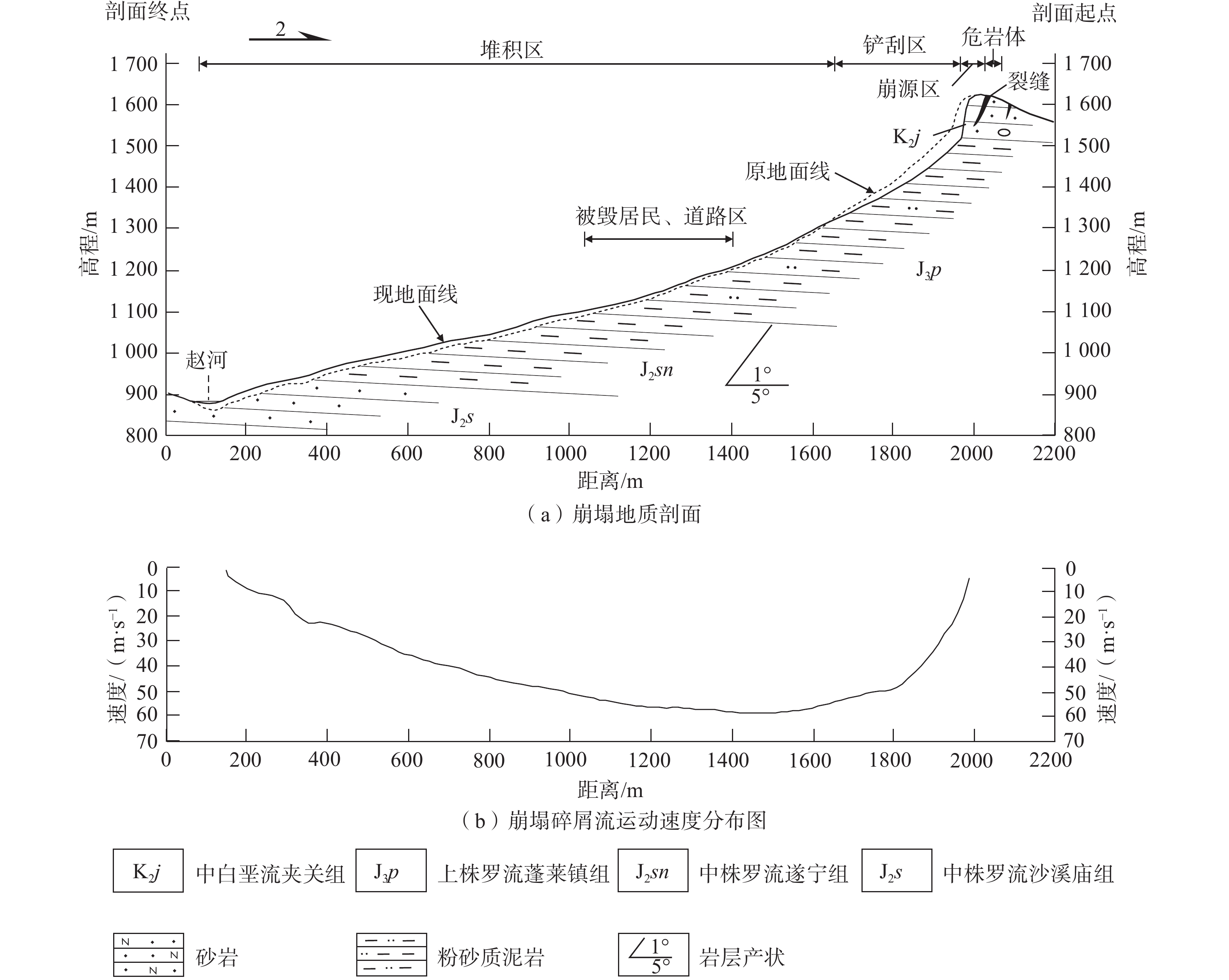
红层区常发育缓倾角岩质边坡,因其软硬相间的岩性组合,地质灾害频发,灾害严重。基于光学卫星遥感、无人机航空摄影测量、现场调查等天空地一体化的技术手段,以2021年4月5日发生的四川洪雅铁匠湾缓倾角红层岩质崩塌为研究对象,探讨了崩塌的基本特征和成因机理,分析了铁匠湾陡崖区崩塌灾害发展趋势,以期为红层区类似灾害的研究提供资料支撑。结果表明:铁匠湾崩塌可分为主崩塌区和崩塌影响区两个区域,其中主崩塌区包括崩源区1处、铲刮区1处、堆积区1处、流水二次搬运堆积区1处,崩塌影响区包括潜在崩源区1处、扰动变形区5处。崩塌源区具有“上硬下软”的岩石组合,岩体发育两组近于垂直的优势结构面,2013年已表现出变形迹象,在降雨、温差的持续作用下导致源区危岩体的最终失稳垮塌,巨大的冲击力作用于危岩体下方的老崩塌堆积体和基岩,引起崩塌-碎屑流灾害链。在光学遥感影像解译和野外调查的基础上,认为铁匠湾崩塌存在二次崩塌的风险,在崩塌邻区识别出类似崩塌隐患点6处,建议采用无人机、机载LiDAR等技术手段开展铁匠湾陡崖区崩塌隐患的早期识别与持续监测。
Abstract:Gentle dip angle rock slopes are often developed in layered red rocks, which are prone to geological disasters due to the combination of soft and hard lithology. This paper discusses the Tiejiangwan rockfall that occurred on April 5, 2021, in Hongya County of Sichuan province, China, on a layered red rocks slope with a gentle dip angle. Using an air-space-ground integrated earth observation network, including optical remote sensing, UAV aerial photogrammetry, and on-site investigation, the study analyzes the basic characteristics and mechanism of rockfall and predicts the development trend of similar disasters in the steep cliff area of layered red rocks. The results show that the Tiejiangwan rockfall can be divided into two areas, namely the main rockfall area and the rockfall influence area. The main rockfall area comprises one rockfall source area, one shoveling area, one accumulation area, and one water secondary transportation accumulation area. The rockfall influence area includes one potential rockfall source area and five disturbance deformation areas. The rockfall source area has a combination of hard rocks at the top and soft rocks at the bottom, and the rock mass develops two groups of nearly vertical dominant structural planes. In 2013, the source area showed signs of deformation, which eventually lead to the instability of the dangerous rock mass due to the continuous effect of rainfall and temperature differences. The huge impact force caused the rockfall debris flow disaster chain, affecting the old rockfall accumulation body and bedrock under the dangerous rock mass. Optical remote sensing images and field investigation indicate the risk of secondary collapse in Tiejiangwan rockfall. Additionally, six similar potential rockfalls were identified in the adjacent area. To prevent similar disasters, it is recommended to use UAV aerial photogrammetry and airborne LiDAR for early identification and continuous monitoring of potential rockfalls in the steep cliff area of the Tiejianwan. The findings of this study provide valuable data support for the study of similar disasters in layered red rocks.
-
Key words:
- rockfall /
- zoning characteristics /
- genetic mechanism /
- gentle dip angle /
- layered red rocks
-

-
表 1 铁匠湾崩塌光学遥感精细解译统计表
Table 1. Statistical table of optical remote sensing interpretation in Tiejiangwan rockfall
名称 编号 面积/m2 厚度/m 估算体积/(104 m3) 潜在崩源区 Ⅰ 2311 110 25.42 崩源区 Ⅱ 9578 110 105.36 铲刮区 Ⅲ 30573 15 45.86 堆积区 Ⅳ 146296 10 146.30 流水二次搬运堆积区 Ⅴ 8852 3 2.66 扰动变形区 A 4836 15 7.25 B 2874 10 2.87 C 9190 5 4.60 D 3104 5 1.55 E 2004 5 1.00 -
[1] 徐瑞春, 周建军. 红层与大坝[M]. 2版. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2010
XU Ruichun, ZHOU Jianjun. Red beds and dams[M]. 2nd ed. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 黄绍槟,程强,胡厚田. 四川红层分布及工程环境特征研究[J]. 公路,2005,50(5):81 − 85. [HUANG Shaobin,CHENG Qiang,HU Houtian. A study on distribution of Sichuan red beds and engineering environment characteristics[J]. Highway,2005,50(5):81 − 85. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0451-0712.2005.05.019
HUANG Shaobin, CHENG Qiang, HU Houtian. A study on distribution of Sichuan red beds and engineering environment characteristics[J]. Highway, 2005, 50(5): 81-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0451-0712.2005.05.019
[3] 彭华,吴志才. 关于红层特点及分布规律的初步探讨[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版),2003,42(5):109 − 113. [PENG Hua,WU Zhicai. A preliminary study on the characteristics and the distribution of red beds[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni,2003,42(5):109 − 113. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Peng Hua, Wu Zhicai. A preliminary study on the characteristics and the distribution of red beds[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2003, 42(5)109-113(in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 曹先康,温智,陈海兰. 四川巴中市红层地区滑坡发育特征与防范措施[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(6):20 − 24. [CAO Xiankang,WEN Zhi,CHEN Hailan. Landslide development characteristics and preventive measures in the area with red beds in Bazhong City,Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(6):20 − 24. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2019.06.03
CAO Xiankang, WEN Zhi, CHEN Hailan. Landslide development characteristics and preventive measures in the area with red beds in Bazhong City, Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2019, 30(6)20-24(in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2019.06.03
[5] 马贤杰,张玉芳,侯李杰,等. 红层地区滑坡的分类及形成机制[J]. 铁道建筑,2021,51(2):75 − 78. [MA Xianjie,ZHANG Yufang,HOU Lijie,et al. Study on classification and formation mechanism of landslide in red bed area[J]. Railway Engineering,2021,51(2):75 − 78. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2021.02.18
MA Xianjie, ZHANG Yufang, HOU Lijie, et al. Study on classification and formation mechanism of landslide in red bed area[J]. Railway Engineering, 2021, 51(2): 75-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2021.02.18
[6] 张涛,谢忠胜,石胜伟,等. 川东红层缓倾岩质滑坡的演化过程及其识别标志探讨[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(2):496 − 503. [ZHANG Tao,XIE Zhongsheng,SHI Shengwei,et al. Discussion on evolution process of flat rock landslide and its identification in red strata at eastern Sichuan[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017,25(2):496 − 503. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017.02.029
ZHANG Tao, XIE Zhongsheng, SHI Shengwei, et al. Discussion on evolution process of flat rock landslide and its identification in red strata at eastern Sichuan[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2017, 25(2): 496-503. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017.02.029
[7] 王家柱,葛华,高延超,等. 川南红层区黄子树滑坡形成过程与运动特征[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(2):9 − 17. [WANG Jiazhu,GE Hua,GAO Yanchao,et al. Mechanism and kinematic characteristics of Huangzishu Landslide in the red mudstone of southern Sichuan[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(2):9 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.02.02
WANG Jiazhu, GE Hua, GAO Yanchao, et al. Mechanism and kinematic characteristics of Huangzishu Landslide in the red mudstone of southern Sichuan[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(2): 9-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.02.02
[8] 徐伟,冉涛,田凯. 西南红层地区地质灾害发育规律与成灾模式—以云南彝良县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(6):127 − 133. [XU Wei, RAN Tao,TIAN Kai. Developing law and disaster modes of geohazards in red bed region of southwestern China:A case study of Yiliang County of Yunnan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(6):127 − 133. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WEI Xu, TAO Ran, KAI Tian. Developing law and disaster modes of geohazards in red bed region of southwestern China: a case study of Yiliang County of Yunnan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(6): 127-133. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 王军朝,孙金辉. 川东红层缓倾角岩质崩塌特征与稳定性分析[J]. 地质力学学报,2019,25(6):1091 − 1098. [WANG Junchao,SUN Jinhui. Characteristics and stability analysis of rock collapse of low-angled red-bed slope in east Sichuan[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2019,25(6):1091 − 1098. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.06.092
WANG Junchao, SUN Jinhui. Characteristics and stability analysis of rock collapse of low-angled red-bed slope in east Sichuan[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 25(6): 1091-1098. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.06.092
[10] 胡斌,黄润秋. 软硬岩互层边坡崩塌机理及治理对策研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2009,17(2):200 − 205. [HU Bin,HUANG Runqiu. Collapse mechanism and treatment measures of slopes with interbeddings of soft and hard rocks[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2009,17(2):200 − 205. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.02.008
HU Bin, HUANG Runqiu. Collapse mechanism and treatment measures of slopes with interbeddings of soft and hard rocks[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2009, 17(2): 200-205. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.02.008
[11] 郭永春,谢强,文江泉. 我国红层分布特征及主要工程地质问题[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2007,34(6):67 − 71. [GUO Yongchun,XIE Qiang,WEN Jiangquan. Red beds distribution and engineering geological problem in China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2007,34(6):67 − 71. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2007.06.016
GUO Yongchun, XIE Qiang, WEN Jiangquan. Red beds distribution and engineering geological problem in China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2007, 34(6): 67-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2007.06.016
[12] 李江,许强,胡泽铭,等. 红层缓倾角土质滑坡发育环境、分布规律及影响因素研究[J]. 科学技术与工程,2014,14(12):88 − 93. [LI Jiang,XU Qiang,HU Zeming,et al. Study on development environment,distribution characteristics and factors of soil landslides on low-angled rock formation of red bed[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2014,14(12):88 − 93. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.12.017
LI Jiang, XU Qiang, HU Zeming, et al. Study on development environment, distribution characteristics and factors of soil landslides on low-angled rock formation of red bed[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2014, 14(12)88-93(in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.12.017
[13] 张群,许强,易靖松,等. 南江红层地区缓倾角浅层土质滑坡降雨入渗深度与成因机理研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2016,38(8):1447 − 1455. [ZHANG Qun,XU Qiang,YI Jingsong,et al. Rainfall infiltration depthand formation mechanism ofslow-inclination soillandslides in Nanjiang[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2016,38(8):1447 − 1455. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201608012
ZHANG Qun, XU Qiang, YI Jingsong, et al. Rainfall infiltration depthand formation mechanism ofslow-inclination soillandslides in Nanjiang[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2016, 38(8): 1447-1455. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201608012
[14] 廖勇,乐建,胡力,等. 基于Fredlund & Xing模型的渗流分析在川东红层梯田滑坡中的应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(3):104 − 114. [LIAO Yong, LE Jian, HU Li, et al. Application of seepage analyses based on Fredlund & Xing model in red beds terrace landslides in eastern Sichuan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(3):104 − 114. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[LIAO Yong, LE Jian, HU Li, et al. Application of seepage analyses based on Fredlund & Xing model in red beds terrace landslides in eastern Sichuan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(3): 104-114.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 郭永春,赵峰先,闫圣龙,等. 红层泥岩三轴膨胀力的试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(3):87 − 93. [GUO Yongchun, ZHAO Fengxian, YAN Shenglong, et al. An experimental study of the triaxial expansion force of red-bed mudstone[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(3):87 − 93. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GUO Yongchun, ZHAO Fengxian, YAN Shenglong, et al. An experimental study of the triaxial expansion force of red-bed mudstone[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(3): 87-93.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 杨成忠,杨鹏,王威,等.红层泥质砂岩隧道进口段注浆加固及效果评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(3):98 − 105. [YANG Chengzhong, YANG Peng, WANG Wei, et al. Grouting reinforcement and effect evaluation of the inlet section of a red-layer shaly sandstone tunnel[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(3):98 − 105. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[YANG Chengzhong, YANG Peng, WANG Wei, et al. Grouting reinforcement and effect evaluation of the inlet section of a red-layer shaly sandstone tunnel[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2018, 45(3): 98-105.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 四川省地质局第二区域地质测量队. 峨眉幅1∶20万区域地质测量报[R]. 1971
The second regional geological survey team of Sichuan Geological Bureau. Emei 1 ∶ 200000 regional geological survey report[R]. 1971. (in Chinese)
[18] SCHEIDEGGER A E. On the prediction of the reach and velocity of catastrophic landslides[J]. Rock Mechanics,1973,5(4):231 − 236. doi: 10.1007/BF01301796
-




 下载:
下载: