Cloud model for stability evaluation of recently failed soil slopes based on weight inversion of influencing factors
-
摘要:
在强降雨等因素影响下,新近失稳土质边坡易再次发生滑动,并对现场救援人员的安全构成威胁。如何对该类边坡的稳定性进行快速、准确地评价,亟须解决。由于古滑坡的滑动面处土体的抗剪强度随着时间的推移有所提高,故无法直接套用古滑坡复活的评价方法。常用的极限平衡条分法或有限元等数值分析法又需要事先进行现场勘察,耗时较长影响救援进度。因云模型评价方法对评价因子的精度要求较低,可弥补上述方法的不足之处。但目前对云模型评价因子权重的研究,仍存在一些不足之处,故提出采用反分析法来计算各评价因子的权重。选取坡高等9个易于获取且是决定边坡稳定性的主要因素为评价因子,参照《地质灾害调查技术要求》和前人的研究成果对各评价因子的稳定分级区间进行划分,利用MATLAB程序语言平台生成相应的综合云模型。根据滑坡前各评价因子的数值反分析其权重的云模型特征参数,建立可方便快捷地对新近失稳边坡进行稳定性评价的云模型,使用Python 语言和Qt Designer工具进行应用程序的开发。使用该应用程序对福建省永春县冷水村一新近失稳边坡2016年11月3—8日的稳定性进行评价,得到的结果与现场情况基本吻合,初步验证了该方法准确性。该程序的运行过程耗时较短,也验证了该方法的快速性。
Abstract:The stability of newly failed soil slopes, particularly under the influence of heavy rainfall, presents a significant threat to the safety of on-site rescue personnel. It is urgent to find a quick and accurate method for evaluating the stability of such slopes. The evaluation methods used for reactivating ancient landslides cannot be directly applied because the shear strength of the soil at the sliding surface of ancient landslides improves over time. Common numerical analysis methods such as limit equilibrium slice method or finite element method require time-consuming on-site surveys, which may affect the progress of rescue operations. The cloud model evaluation method is suitable for evaluating the stability of these slopes as it has lower accuracy requirements for evaluation factors, thus compensating for the limitations of the aforementioned methods. However, the current research on the weight of evaluation factors in cloud model evaluation still has some deficiencies. Therefore, a weight inversion method is proposed to calculate the weights of each evaluation factor. Nine primary influencing factors, including slope height, which are easily obtainable, were selected as evaluation factors. By referencing the "Technical Requirements for Geological Hazard Investigation" and previous research findings, grading intervals for each evaluation factor were determined. The corresponding comprehensive cloud model was generated using the MATLAB programming platform. According to the value of each evaluation factor before sliding, the cloud model’s characteristic parameters for weight inversion were obtained. And the cloud model for evaluating the stability of the newly failed slope was established. The Python language and the Qt Designer tool were used to develop the application of stability evaluation. The stability of a newly failed slope in Lengshui Village, Yongchun County, Fujian Province, during November 3-8 2016, was assessed using this application. The result align closely with the actual on-site conditions, validating the accuracy of the proposed evaluation method. The efficient runtime of the application further demonstrates its speed.
-
Key words:
- inversion /
- newly failed slope /
- cloud model /
- stability evaluation /
- application
-

-
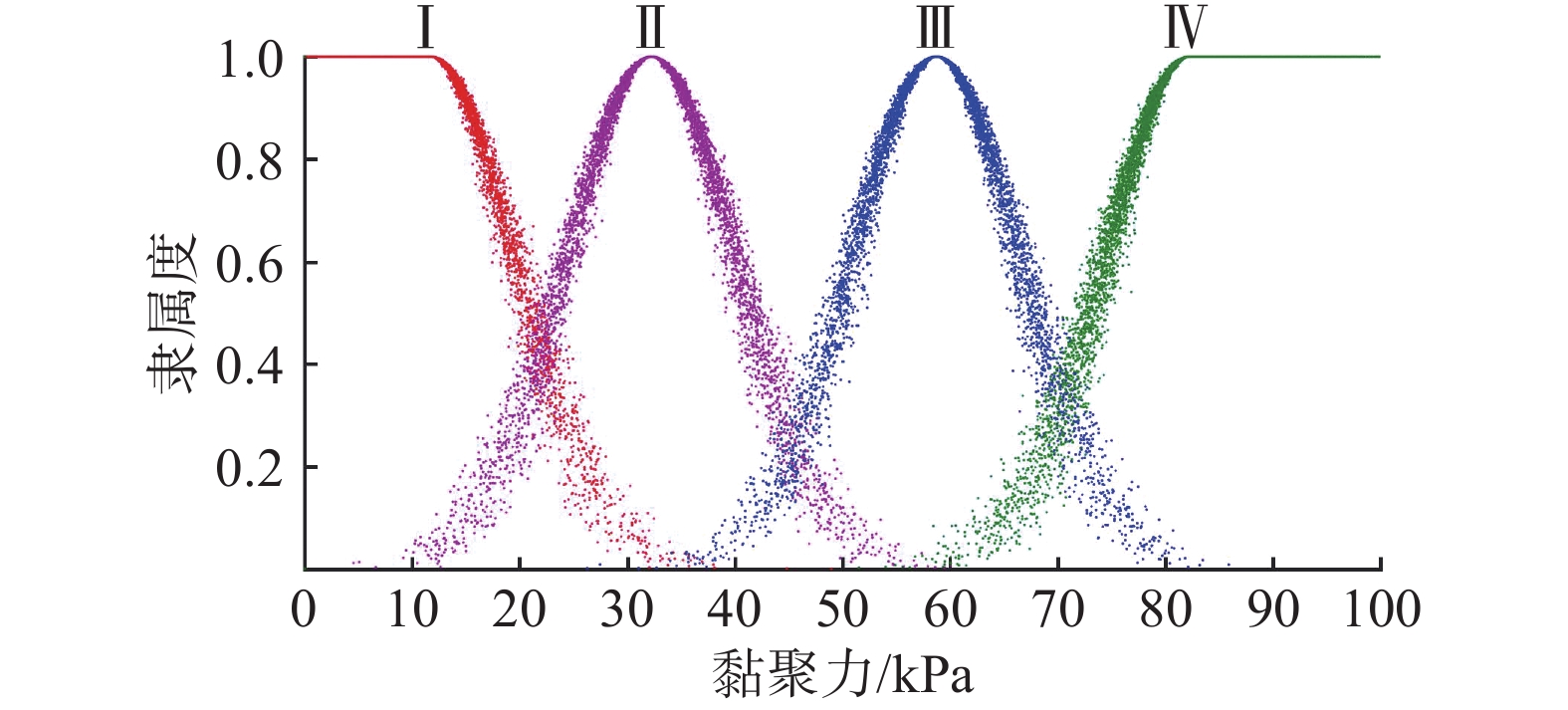
表 1 边坡稳定性评价因子各等级区间
Table 1. Grade intervals of slope stability evaluation factors
评价
因子分级区间 不稳定 欠稳定 基本稳定 稳定 H/m [50, 70) [30, 50) [10, 30) [0, 10) β/(°) [50, 90) [35, 50) [20, 35) [0, 20) c/kPa [0, 23.5) [23.5, 47) [47, 70.5) [70.5, 94) φ/(°) [15, 21.75) [21.75, 28.5) [28.5, 32.25) [32.25, 42) γsat/
(kN·m−3)[23.5, 21.5) [21.5, 19.5) [19.5, 17.5) [17.5, 15.5) P/mm [50, 100) [25, 50) [10, 25) [0, 10) T/h [18, 24) [12, 18) [6, 12) [0, 6) I/
(mm·d−1)[50, 100) [25, 50) [10, 25) [0, 10) η [0, 0.25) [0.25, 0.5) [0.5, 0.75) [0.75, 1] 表 2 各评价因子的权重云模型特征参数
Table 2. Characteristic parameters of weight cloud model for each evaluation factors
评价因子 期望 熵 评价因子 期望 熵 H/m 0.160 0.010 P/mm 0.134 0.027 β/(°) 0.080 0.000 T/h 0.134 0.046 c/kPa 0.103 0.027 I/(mm·d−1) 0.131 0.046 φ/(°) 0.103 0.027 η 0.040 0.000 γsat/(kN·m-3) 0.115 0.027 表 3 2016年11月3—8日的降雨情况
Table 3. Rainfall distribution from November 3 to 8, 2016
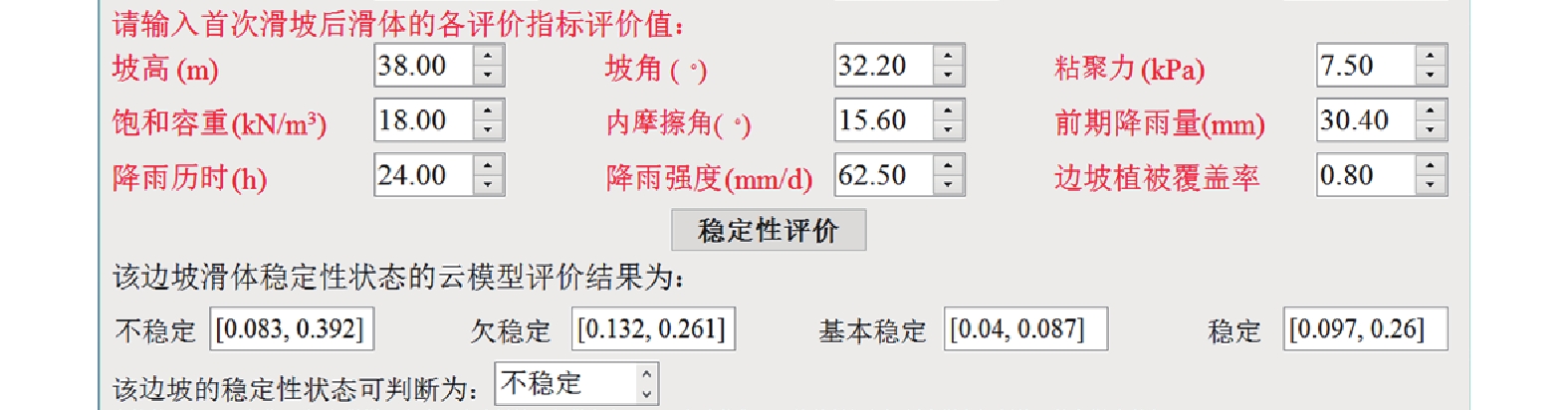
日期 降雨量/mm 降雨历时/h 降雨强度/(mm·d−1) 前期降雨量/mm 11月3日 0 0 0 10.5 11月4日 29.6 12 59.2 8.4 11月5日 62.5 24 62.5 30.4 11月6日 20.8 24 20.8 74.3 11月7日 13.2 12 26.4 76.1 11月8日 0 0 0 71.4 表 4 2016年11月3—8日的边坡稳定性评价结果
Table 4. Stability evaluation results of landslide body from November 3 to 8, 2016
日期 不稳定 欠稳定 基本稳定 稳定 评价结果 隶属度区间 平均
隶属度隶属度区间 平均
隶属度隶属度区间 平均
隶属度隶属度区间 平均
隶属度11月3日 [0.036,0.112] 0.074 [0.113,0.124] 0.119 [0.043,0.103] 0.073 [0.168,0.661] 0.415 稳定 11月4日 [0.049,0208] 0.129 [0.132,0.247] 0.190 [0.049,0.144] 0.097 [0.126,0.401] 0.264 稳定 11月5日 [0.083,0.392] 0.238 [0.132,0.261] 0.197 [0.044,0.087] 0.066 [0.099,0.26] 0.180 不稳定 11月6日 [0.093,0.427] 0.260 [0.11,0.135] 0.123 [0.059,0.19] 0.125 [0.092,0.247] 0.170 不稳定 11月7日 [0.068,0.288] 0.178 [0.13,0.248] 0.189 [0.056,0.2] 0.128 [0.099,0.265] 0.182 欠稳定 11月8日 [0.062,0.263] 0.163 [0.109,0.127] 0.118 [0.035,0.049] 0.042 [0.149,0.562] 0.356 稳定 -
[1] PARK J,VILAYVONG K,SON Y,et al. Slope stability evaluation of an agricultural embankment by statistically derived rainfall patterns[J]. Paddy and Water Environment,2019,17(3):303 − 313. doi: 10.1007/s10333-019-00725-2
[2] 邓夕胜,张元,唐煜. 基于失效概率的边坡降雨阈值曲面探讨[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(3):70 − 75. [DENG Xisheng,ZHANG Yuan,TANG Yu. Investigation on slope rainfall threshold surface based on failure probablolity[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(3):70 − 75. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DENG Xisheng, ZHANG Yuan, TANG Yu. Investigation on slope rainfall threshold surface based on failure probablolity[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(3)70-75(in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 黄明奎,马璐. 极端降雨对边坡土体强度的影响及其稳定性分析[J]. 灾害学,2021,36(3):6 − 9. [HUANG Mingkui,MA Lu. Stability and soil strength analysis of alope under extreme rainfall[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2021,36(3):6 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HUANG Mingkui, MA Lu. Stability and soil strength analysis of alope under extreme rainfall[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2021, 36(3)6-9(in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] SAITO M,MASUDA R. Numerical study on seepage flow in slope at heavy rain considering non-uniformity and pore air flow[J]. Journal of Japan Society of Civil Engineers,Ser B1 (Hydraulic Engineering),2018,74(4):I_7 − I_12. doi: 10.2208/jscejhe.74.I_7
[5] 简文彬,黄聪惠,罗阳华,等. 降雨入渗下非饱和坡残积土湿润锋运移试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(4):1123 − 1133. [JIAN Wenbin,HUANG Conghui,LUO Yanghua,et al. Experimental study on wetting front migration induced by rainfall infiltration in unsaturated eluvial and residual soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2020,41(4):1123 − 1133. (in Chinese with English abstract)
JIAN Wenbin, HUANG Conghui, LUO Yanghua, et al. Experimental study on wetting front migration induced by rainfall infiltration in unsaturated eluvial and residual soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(4): 1123-1133. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 苏永华,李诚诚. 强降雨下基于Green-Ampt模型的边坡稳定性分析[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(2):389 − 398. [SU Yonghua,LI Chengcheng. Stability analysis of slope based on Green-Ampt model under heavy rainfall[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2020,41(2):389 − 398. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SU Yonghua, LI Chengcheng. Stability analysis of slope based on Green-Ampt model under heavy rainfall[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(2): 389-398. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] NOTTI D,WRZESNIAK A,DEMATTEIS N,et al. A multidisciplinary investigation of deep-seated landslide reactivation triggered by an extreme rainfall event:a case study of the Monesi di Mendatica landslide,Ligurian Alps[J]. Landslides,2021,18(7):2341 − 2365. doi: 10.1007/s10346-021-01651-3
[8] 窦晓东,张泽林. 甘肃舟曲垭豁口滑坡复活机理及成因探讨[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(2):51. [DOU Xiaodong,ZHANG Zelin. Mechanism and causal analysis on the Yahuokou landslide reactivation and causes(Zhouqu County,Gansu,China)[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(2):51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOU Xiaodong, ZHANG Zelin. Mechanism and causal analysis on the Yahuokou landslide reactivation and causes(Zhouqu County, Gansu, China)[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(2): 51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 张永双,吴瑞安,任三绍. 降雨优势入渗通道对古滑坡复活的影响[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2021,40(4):777 − 789. [ZHANG Yongshuang,WU Ruian,REN Sanshao. Influence of rainfall preponderance infiltration path on reactivation of ancient landslides[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021,40(4):777 − 789. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang Yongshuang, Wu Ruian, Ren Sanshao. Influence of rainfall preponderance infiltration path on reactivation of ancient landslides[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(4): 777-789. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 李德毅,孟海军,史雪梅. 隶属云和隶属云发生器[J]. 计算机研究与发展,1995,32(6):15 − 20. [LI Deyi,MENG Haijun,SHI Xuemei. Membership clouds and membership cloud generators[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development,1995,32(6):15 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Deyi, MENG Haijun, SHI Xuemei. Membership clouds and membership cloud generators[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 1995, 32(6): 15-20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 李健,汪明武,徐鹏,等. 基于云模型的围岩稳定性分类[J]. 岩土工程学报,2014,36(1):83 − 87. [LI Jian,WANG Mingwu,XU Peng,et al. Classification of stability of surrounding rock using cloud model[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2014,36(1):83 − 87. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li Jian, Wang Mingwu, Xu Peng, et al. Classification of stability of surrounding rock using cloud model[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(1)83-87(in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] WANG Mingwu,WANG Xiao,LIU Qiuyan,et al. A novel multi-dimensional cloud model coupled with connection numbers theory for evaluation of slope stability[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling,2020,77:426 − 438. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2019.07.043
[13] LIU Zaobao,SHAO Jianfu,XU Weiya,et al. Comprehensive stability evaluation of rock slope using the cloud model-based approach[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2014,47(6):2239 − 2252. doi: 10.1007/s00603-013-0507-3
[14] 方前程,商丽. 基于博弈论-云模型的露天矿岩质边坡稳定性分析[J]. 安全与环境学报,2019,19(1):8 − 13. [FANG Qiancheng,SHANG Li. Analysis of the rock slope stability for the open-pit mine based on the game theory and the cloud model[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment,2019,19(1):8 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
FANG Qiancheng, SHANG Li. Analysis of the rock slope stability for the open-pit mine based on the game theory and the cloud model[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2019, 19(1): 8-13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 吴孟龙,叶义成,胡南燕,等. RAGA-PPC云模型在边坡稳定性评价中的应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2019,29(9):57 − 63. [WU Menglong,YE Yicheng,HU Nanyan,et al. Application of RAGA-PPC cloud model in slope stability evaluation[J]. China Safety Science Journal,2019,29(9):57 − 63. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WU Menglong, YE Yicheng, HU Nanyan, et al. Application of RAGA-PPC cloud model in slope stability evaluation[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(9): 57-63. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 陈忠源,戴自航. 水库边坡稳定性评价的改进云模型[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(3):619 − 625. [CHEN Zhongyuan,DAI Zihang. Improved cloud model for stability evaluation of reser-voir slopes[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(3):619 − 625. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHEN Zhongyuan, DAI Zihang. Improved cloud model for stability evaluation of reser-voir slopes[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(3)619-625(in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 陈忠源,戴自航. 基于指标变权重复合云模型的岩质边坡稳定性评价初探[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(6):9 − 17. [CHEN Zhongyuan,DAI Zihang. A preliminary study on evaluation of rock slope stability based on index variable weight compound cloud model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(6):9 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHEN Zhongyuan, DAI Zihang. A preliminary study on evaluation of rock slope stability based on index variable weight compound cloud model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(6)9-17(in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 李江龙,樊燕燕. 基于压力-状态-响应模型框架的城市地震综合易损性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(2):117 − 125. [LI Jianglong,FAN Yanyan. Comprehensive evaluation of urban earthquake vulnerability under the framework of PSR[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(2):117 − 125. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Jianglong, FAN Yanyan. Comprehensive evaluation of urban earthquake vulnerability under the framework of PSR[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(2): 117-125. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 何乐平,罗舒月,胡启军,等. 基于理想点-可拓云模型的隧道围岩稳定性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(2):126 − 134. [HE Leping,LUO Shuyue,HU Qijun,et al. Stability evaluation of tunnel surrounding rock based on ideal point-extension cloud model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(2):126 − 134. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HE Leping, LUO Shuyue, HU Qijun, et al. Stability evaluation of tunnel surrounding rock based on ideal point-extension cloud model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(2)126-134(in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑边坡工程技术规范: GB 50330—2013[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2014
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Technical code for building slope engineering: GB 50330—2013[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2014. (in Chinese)
[21] 自然资源部中国地质调查局. DD 2019-08. 地质灾害调查技术要求[S]. 2019
China Geological Survey Bureau, Ministry of Natural Resources. DD 2019-08. Technical Requirements for Geological Hazard Investigation [S]. 2019. (in Chinese)
[22] BRUCE J P, CLARK R H. Introduction to hydrometeorology [M]. London: Pergamon Press, 1969.
[23] 《工程地质手册》编委会. 工程地质手册[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2018
Editorial Board of Handbook of Engineering Geology. Handbook of engineering geology[M]. Beijing: China Construction Industry Press, 2018. (in Chinese)
[24] 王国胤, 李德毅, 姚一豫, 等. 云模型与粒计算[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012
WANG Guoyin, LI Deyi, YAO Yiyu, et al. Cloud model and granular computing [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012. (in Chinese)
[25] 唐宏阳. 缓倾斜土质斜坡失稳机理及碎石盲沟治理方法研究[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学
TANG Hongyang. Study on instability mechanism of gently inclined soil slope and treatment method of gravel blind ditch[D]. Mianyang: Southwest University of Science and Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 任三绍,张永双,徐能雄,等. 含砾滑带土复活启动强度研究[J]. 岩土力学,2021,42(3):863 − 873. [REN Sanshao,ZHANG Yongshuang,XU Nengxiong,et al. Mobilized strength of sliding zone soils with gravels in reactivated landslides[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2021,42(3):863 − 873. (in Chinese with English abstract)
REN Sanshao, ZHANG Yongshuang, XU Nengxiong, et al. Mobilized strength of sliding zone soils with gravels in reactivated landslides[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(3): 863-873. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: