Risk assessment of geological hazards in Song County, Henan Province
-
摘要:
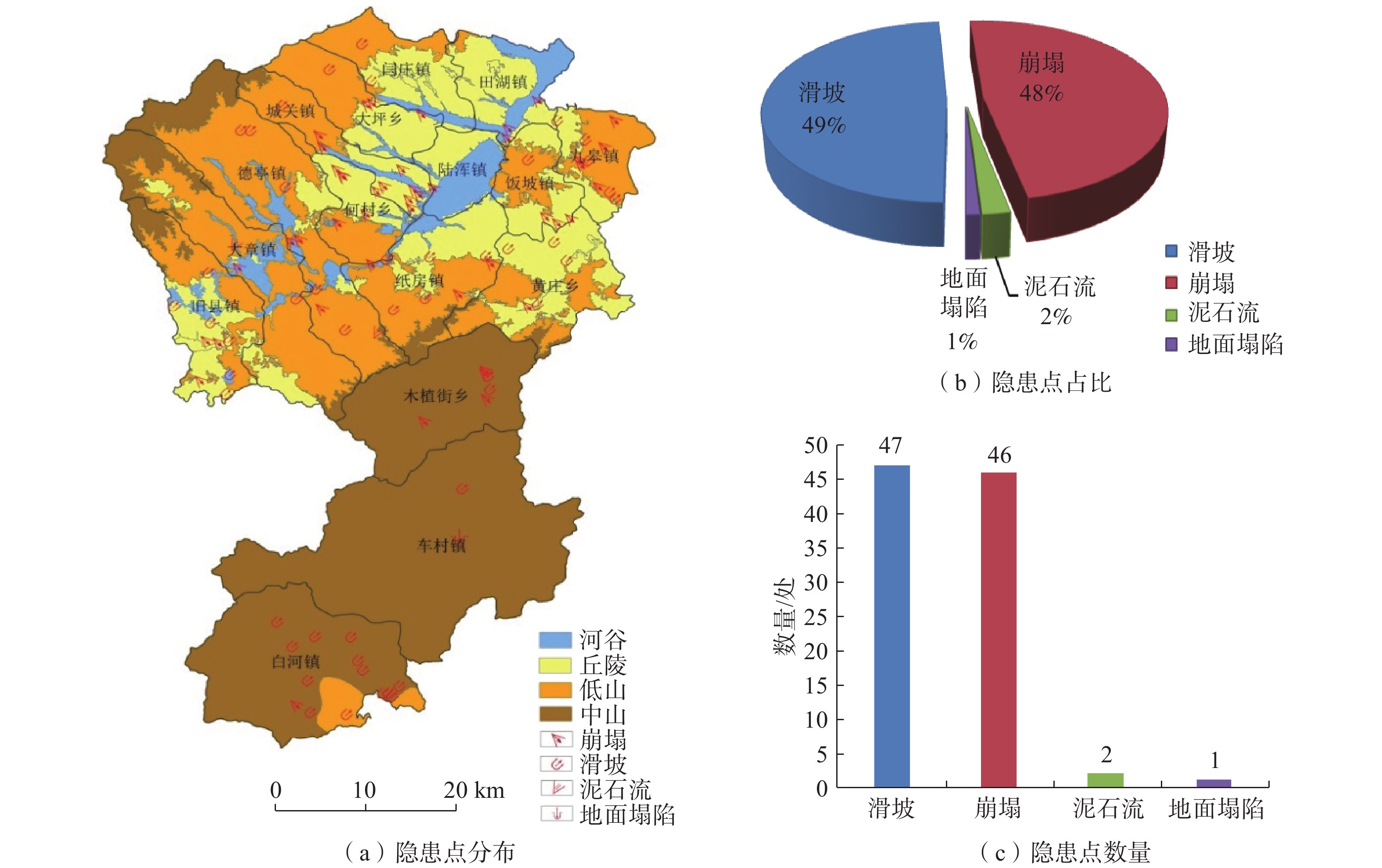
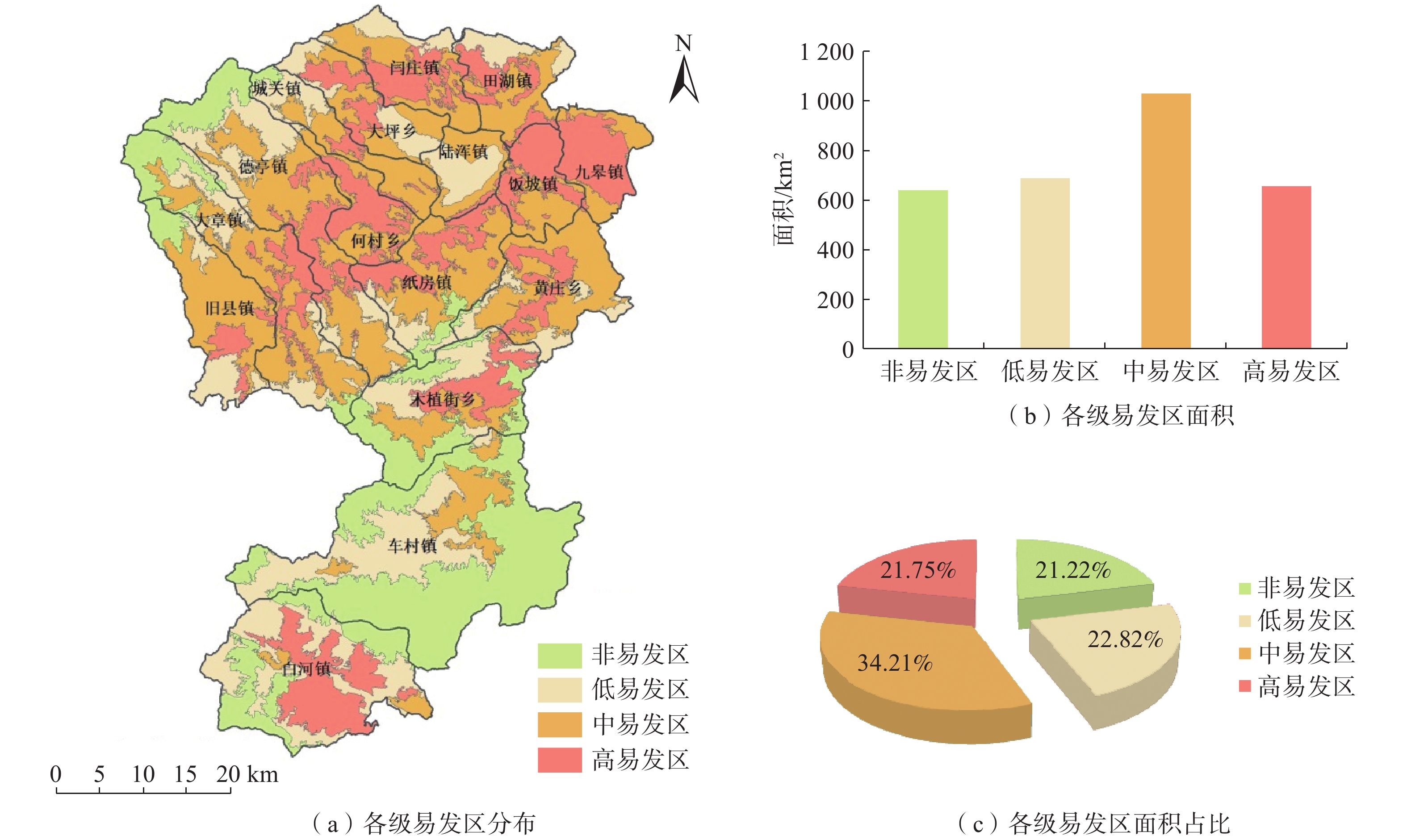
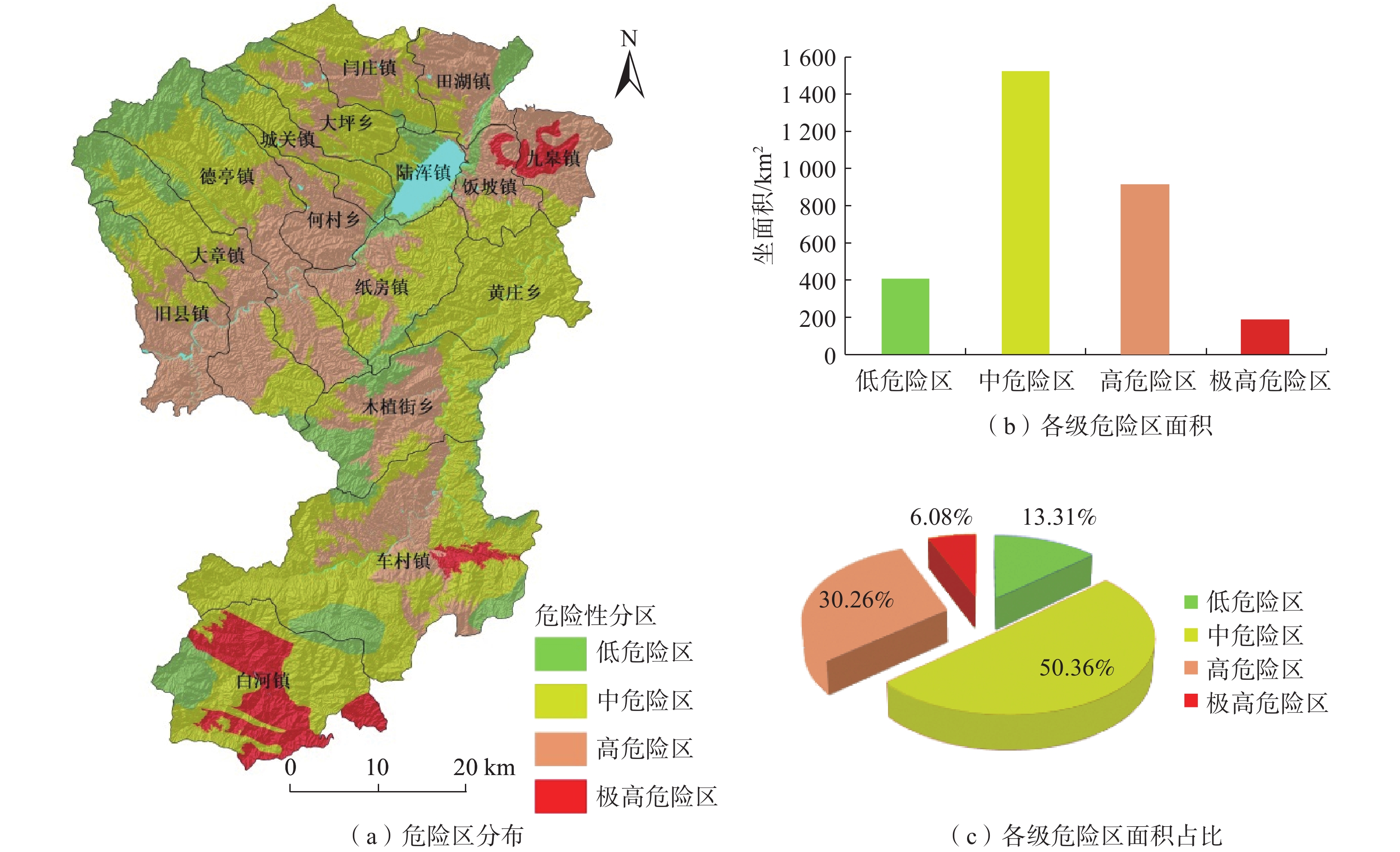
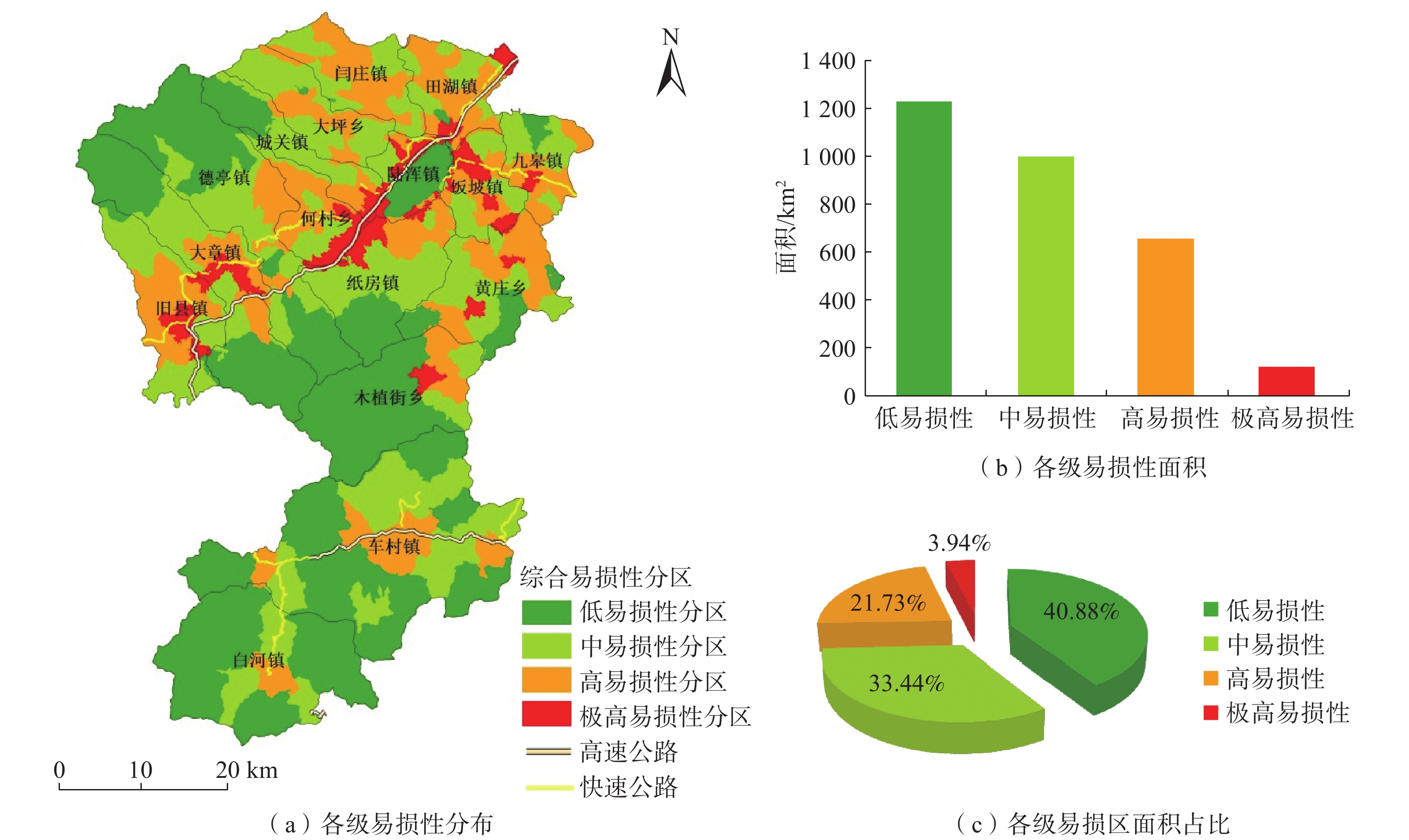
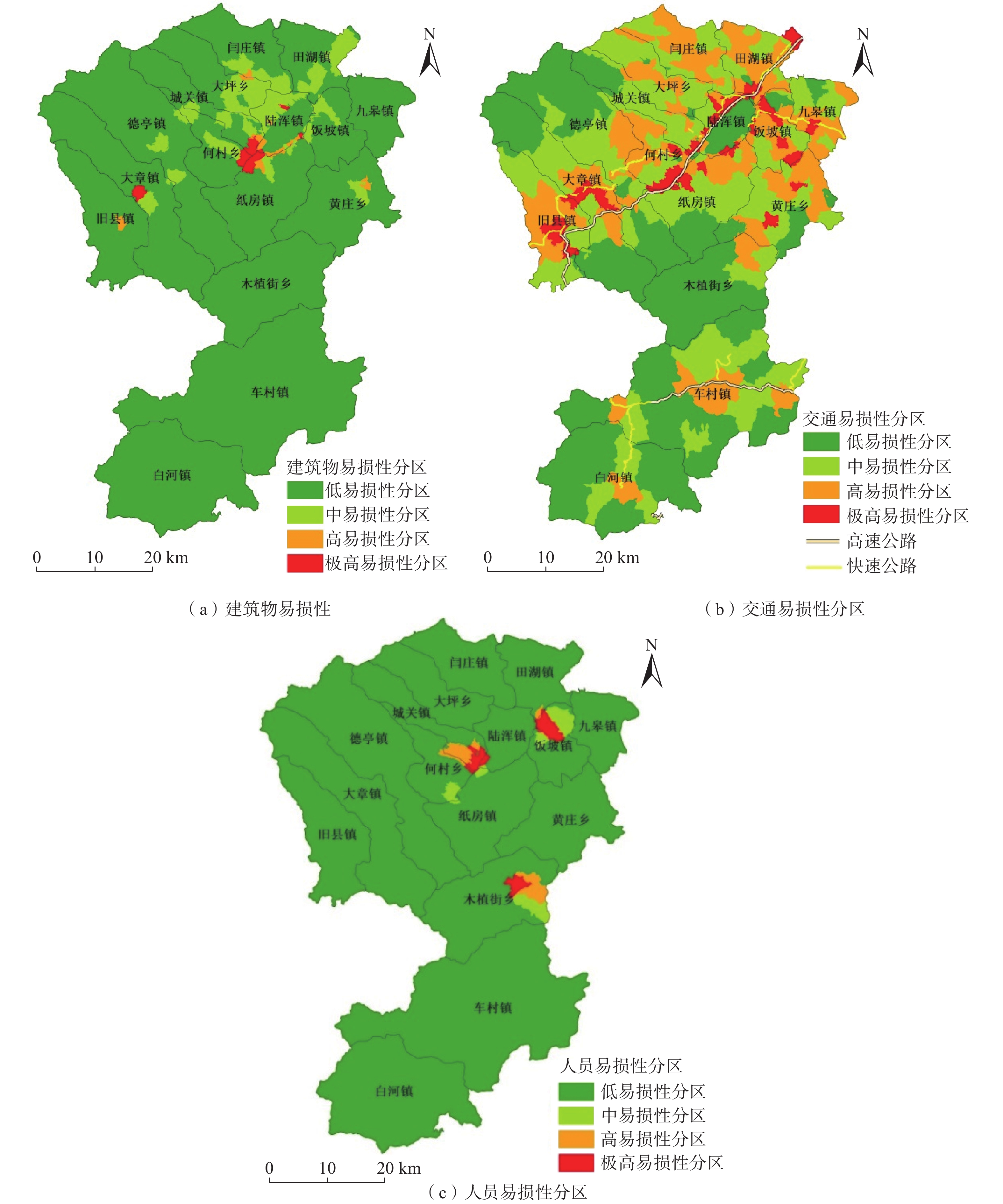
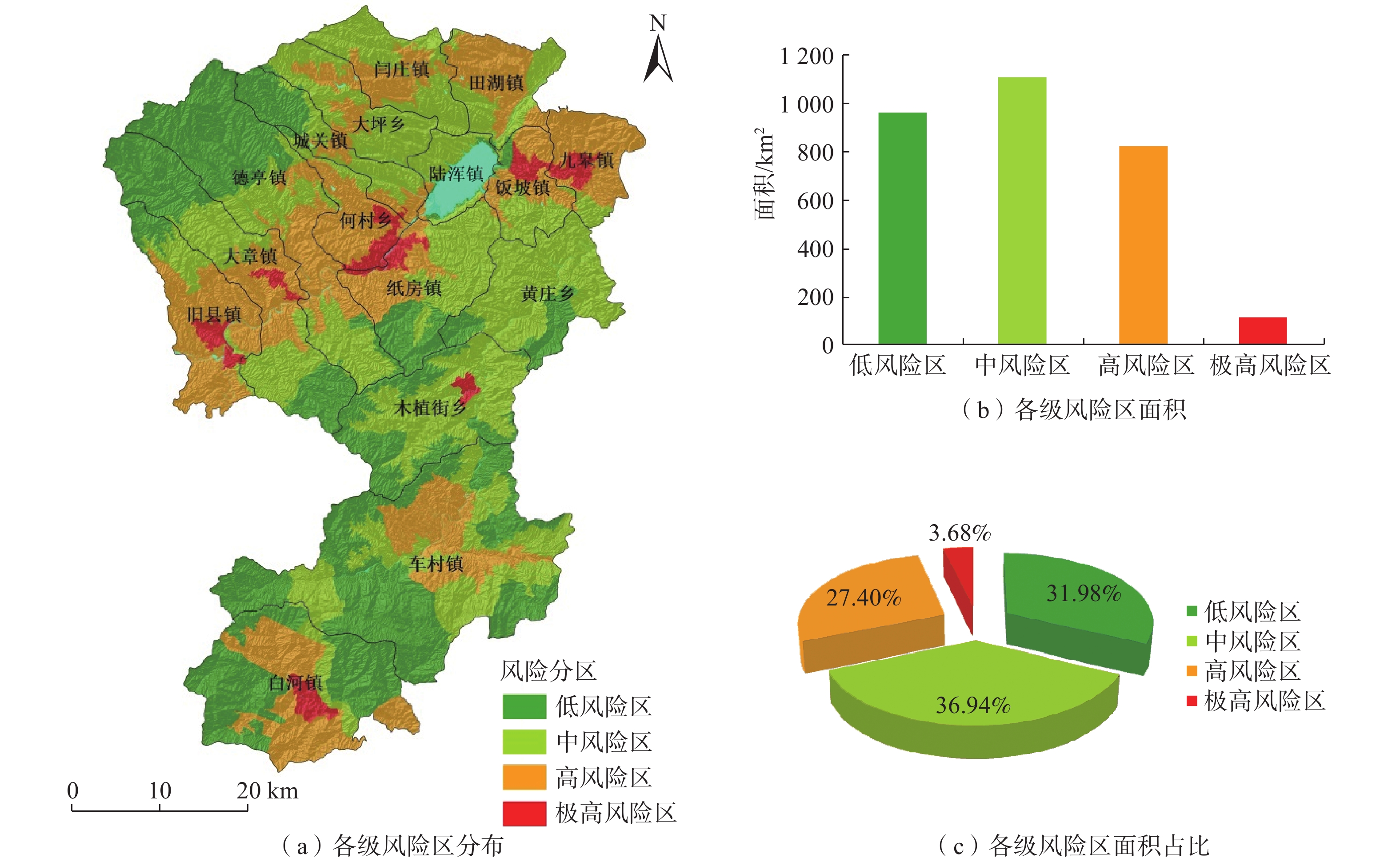
基于ArcGIS环境下,通过选取河南省嵩县区域高程、地貌、工程岩组、植被覆盖度、距构造距离、距水系距离、坡度、坡向等 8个因子建立危险性评价模型,易损性选取建筑物、人员和交通等 3 个承灾因子,分别采用信息量模型和层次分析法对河南省嵩县区域进行地质灾害易发性、危险性和易损性评价。研究结果表明,嵩县区域划分为低风险区面积为965.34 km2,占嵩县区域面积32%;中风险区面积为1114.65 km2,占嵩县区域面积的37%;高风险区面积为826.23 km2,占嵩县区域面积的27%;极高风险区面积为102.68 km2,占嵩县区域面积的3%。研究成果可应用于嵩县防灾减灾及地质灾害风险管控等方面。
Abstract:Using the ArcGIS environment, a risk assessment model is established by selecting eight indicator factors, including regional elevation, landform, engineering rock group, vegetation coverage, distance from structures, distance from water systems, slope, and slope direction in Song county, Henan Province, China. The vulnerability is evaluated under three disaster-bearing factors: buildings, personnel and traffic. The information volume model and analytic hierarchy process are used to assess the susceptibility, risk and vulnerability of geological disasters in Song county. The results show that the area of Song county is divided into low-risk areas, covering 965.34 km2, accounting for 32% of the total area; medium risk area, covering 1114.65 km2, accounting for 37% of the total area; high-risk area, covering 826.23 km2, accounting for 27% of the total area; and extremely high risk area, covering 102.68 km2, accounting for 3% of the area. These research findings can be widely applied to disaster prevention, mitigation, and geological disaster risk control in Song county.
-
Key words:
- ArcGIS /
- Song County, Henan Province /
- geologic hazard /
- risk assessment
-

-
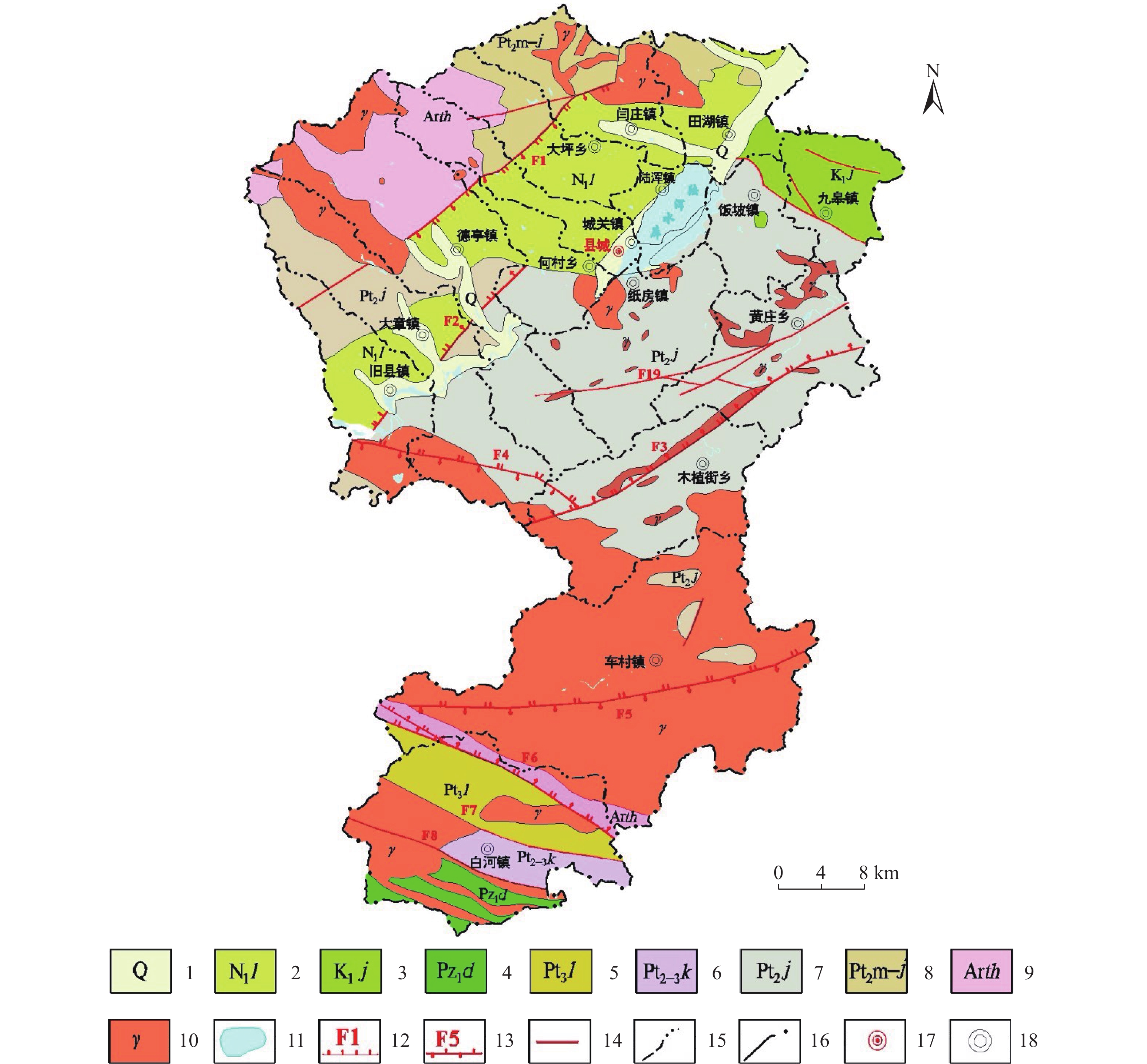
表 1 易发性评价因子分级及信息量值
Table 1. Classification and information value of susceptibility assessment factors
评价因子 指标分级 Ni/N Si/S 信息量值 高程/m [0, 500] 0.3800 0.2146 0.5715 [500, 1000) 0.5800 0.5620 0.0316 [1000, 1500) 0.0400 0.1952 −1.5854 ≥1500 0.0000 0.0282 0.0000 地貌 河谷 0.0558 0.0609 −0.0883 中山 0.2988 0.3985 −0.2879 低山 0.3183 0.3176 0.0037 丘陵 0.3267 0.2230 0.3817 工程岩组 坚硬花岗岩岩组 0.1520 0.3001 −0.6803 坚硬片麻岩岩组 0.0280 0.0563 −0.6992 软弱黏性土岩组 0.1000 0.0881 0.1268 较软弱砾岩岩组 0.0360 0.0164 0.7832 较坚硬砂岩页岩互层岩组 0.0160 0.0113 0.3452 较软弱砂质砾岩岩组 0.1880 0.1178 0.4674 坚硬安山岩类岩组 0.3080 0.3421 −0.1049 较软弱石英云母片岩岩组 0.1520 0.0455 1.2065 较坚硬硅质板岩岩组 0.0120 0.0145 −0.1910 较软弱页岩岩组 0.0040 0.0021 0.6393 较坚硬灰岩岩组 0.0040 0.0057 −0.3503 植被覆盖度 [0, 0.5) 0.1004 0.0553 0.5967 [0.5, 0.65) 0.5100 0.2945 0.5493 [0.65, 0.75) 0.3133 0.3799 −0.1928 [0.75, 1] 0.0763 0.2704 −1.2651 距构造距离/m [0, 500) 0.5000 0.3065 0.4892 [500, 1000) 0.1960 0.1905 0.0286 [1000, 1500) 0.1320 0.1241 0.0616 [1500, 2000) 0.0480 0.0903 −0.6318 ≥2000 0.1240 0.2886 −0.8446 距水系距离/m [0, 500) 0.7800 0.5490 0.3512 [500, 1000) 0.1200 0.2563 −0.7588 [1000, 1500) 0.0600 0.1101 −0.6069 [1500, 2000) 0.0240 0.0415 −0.5476 ≥2000 0.0160 0.0431 −0.9919 坡度/(°) [0, 10) 0.0680 0.1321 −0.6637 [10, 25) 0.3200 0.2117 0.4133 [25, 40) 0.2960 0.2936 0.0082 ≥40 0.3160 0.3627 −0.1378 坡向/(°) FLAT(−1) 0.0000 0.0106 0.0000 N[337.5, 22.5) 0.0680 0.1427 −0.7415 NE[22.5, 67.5) 0.1480 0.1352 0.0903 E[67.5, 112.5) 0.1360 0.1130 0.1856 SE[112.5, 157.5) 0.1720 0.1164 0.3901 S[157.5, 202.5) 0.2160 0.1630 0.2814 SW[202.5, 247.5) 0.1240 0.1236 0.0032 W[247.5, 292.5) 0.0840 0.0922 −0.0928 NW[292.5, 337.5) 0.0520 0.1033 −0.6862 表 2 嵩县1992—2021年降雨量统计表
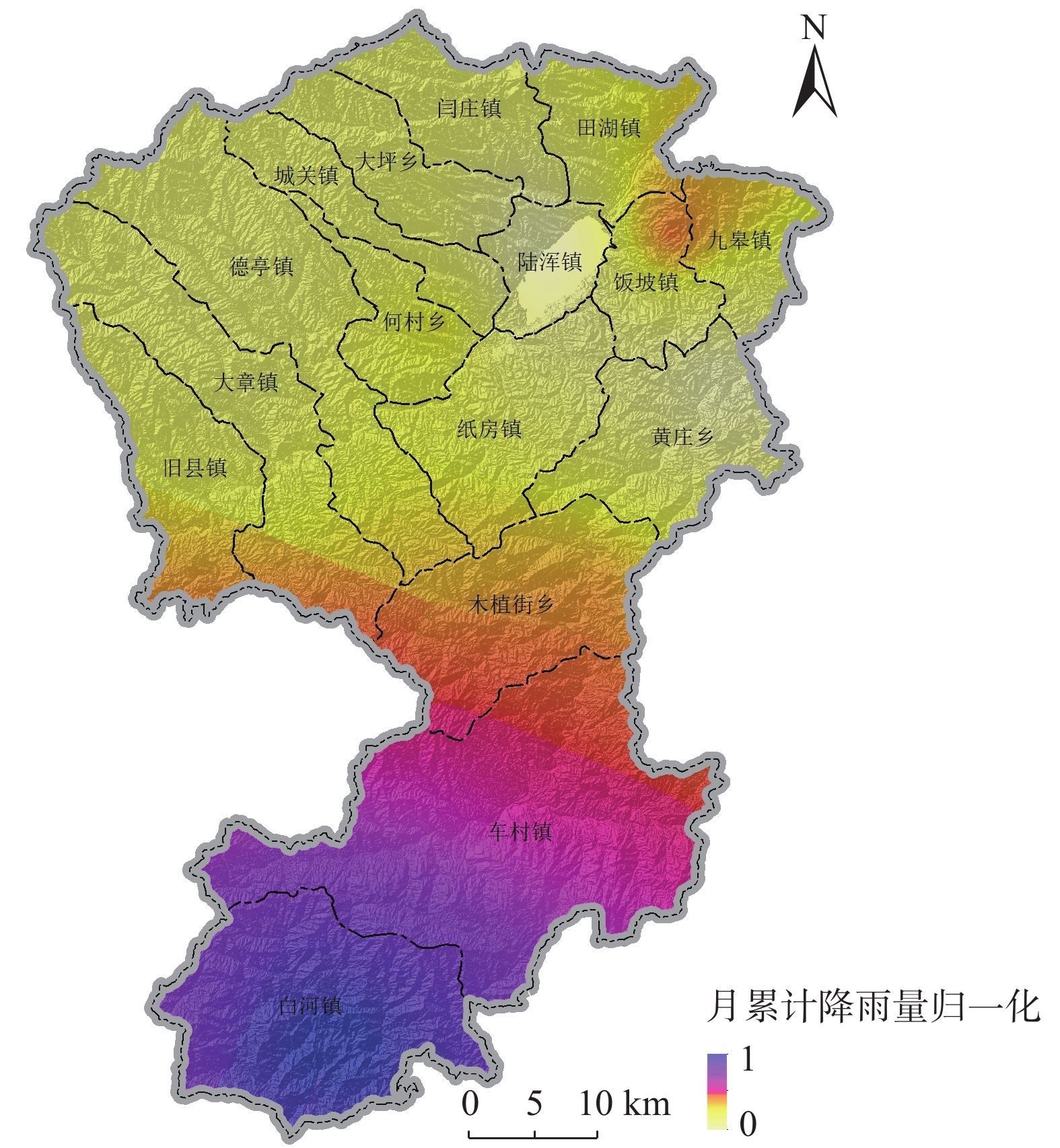
Table 2. Statistical table of Rainfall level in Song county from 1992—2021
年份 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 年降雨量/mm 576.90 675.20 529.60 470.70 959.10 418.10 773.10 589.90 760.30 433.10 月平均降雨量/mm 48.08 56.27 44.13 39.23 79.93 34.84 64.43 49.16 231.50 36.09 年份 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 年降雨量/mm 657.60 1067.40 690.90 718.40 636.70 565.10 558.80 764.30 924.00 931.50 月平均降雨量/mm 54.80 88.95 57.58 59.87 53.06 47.09 46.57 63.69 77.00 77.63 年份 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 年降雨量/mm 649.50 518.60 674.10 594.80 562.70 745.30 690.10 690.10 642.50 944.40 月平均降雨量/mm 54.13 43.22 56.18 49.57 46.89 62.11 57.51 53.26 53.54 145.29 表 3 承灾体易损性赋值表
Table 3. Vulnerability evaluation table for disaster-bearing bodies
承灾体类型 分级 赋值 受地质灾害直接威胁人口数量 10~100 人 0.40 <10 人 0.20 交通设施 高速公路 0.80 国家级公路 0.70 省级公路 0.40 其他道路 0.25 -
[1] 齐信,唐川,陈州丰,等. 地质灾害风险评价研究[J]. 自然灾害学报,2012,21(5):33 − 40. [QI Xin,TANG Chuan,CHEN Zhoufeng,et al. Research of geohazards risk assessment[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2012,21(5):33 − 40. (in Chinese with English abstract)
QI Xin, TANG Chuan, CHEN Zhoufeng, et al. Research of geohazards risk assessment[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2012, 21(5): 33-40. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] MANTOVANI F,SOETERS R,VAN WESTEN C J. Remote sensing techniques for landslide studies and hazard zonation in Europe[J]. Geomorphology,1996,15(3/4):213 − 225.
[3] MICHAEL-LEIBA M,BAYNES F,SCOTT G,et al. Regional landslide risk to the Cairns community[J]. Natural Hazards,2003,30(2):233 − 249. doi: 10.1023/A:1026122518661
[4] UROMEIHY A,MAHDAVIFAR M R. Landslide hazard zonation of the khorshrostam area,Iran[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2000,58(3):207 − 213. doi: 10.1007/s100640050076
[5] ALEOTTI P,CHOWDHURY R. Landslide hazard assessment:summary review and new perspectives[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,1999,58(1):21 − 44. doi: 10.1007/s100640050066
[6] Einstein H H. Landslide risk-systenatic approaches to assessment and management[C]//In: Cruden D. and Fell R. ( eds. ) , Landslide Risk Assessment. Rotterdam: Balkema, 1997: 25 − 50.
[7] VAN WESTEN C. Geo-Information tools for landslide risk assessment: An overview of recent developments[M]//Landslides: Evaluation and Stabilization/Glissement de Terrain: Evaluation et Stabilisation, Set of 2 Volumes. CRC Press, 2004: 39 − 56.
[8] 罗路广,裴向军,谷虎,等. 基于GIS的“8·8”九寨沟地震景区地质灾害风险评价[J]. 自然灾害学报,2020,29(3):193 − 202. [LUO Luguang,PEI Xiangjun,GU Hu,et al. Risk assessment of geohazards induced by “8·8” earthquake based on GIS in Jiuzhaigou scenic area[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2020,29(3):193 − 202. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LUO Luguang, PEI Xiangjun, GU Hu, et al. Risk assessment of geohazards induced by “8.8” earthquake based on GIS in Jiuzhaigou scenic area[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2020, 29(3): 193-202. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 高克昌,崔鹏,赵纯勇,等. 基于地理信息系统和信息量模型的滑坡危险性评价—以重庆万州为例[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2006,25(5):991 − 996. [GAO Kechang,CUI Peng,ZHAO Chunyong,et al. Landslide hazard evaluation of Wanzhou based on GIS information value method in the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2006,25(5):991 − 996. (in Chinese)
GAO Kechang, CUI Peng, ZHAO Chunyong, et al. Landslide hazard evaluation of Wanzhou based on GIS information value method in the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(5): </span>991-996<spanstyle=color: rgb(51. (in Chinese)
[10] 阮沈勇,黄润秋. 基于GIS的信息量法模型在地质灾害危险性区划中的应用[J]. 成都理工学院学报,2001,28(1):89 − 92. [RUAN Shenyong,HUANG Runqiu. Application of GIS-based information model on assessment of geological hazards risk[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology,2001,28(1):89 − 92. (in Chinese with English abstract)
RUAN Shenyong, HUANG Runqiu. Application of gis-based information model on assessment of g eological hazards risk[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 2001, 28(1): 89-92. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 刘福臻,王灵,肖东升. 机器学习模型在滑坡易发性评价中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(6):98 − 106. [LIU Fuzhen,WANG Ling,XIAO Dongsheng. Application of machine learning model in landslide susceptibility evaluation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(6):98 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Fuzhen, WANG Ling, XIAO Dongsheng. Application of machine learning model in landslide susceptibility evaluation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(6): 98-106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 倪晓娇,南颖. 基于GIS的长白山地区地质灾害风险综合评估[J]. 自然灾害学报,2014,23(1):112 − 120. [NI Xiaojiao,NAN Ying. Comprehensive assessment of geological disasters risk in Changbai Mountain region based on GIS[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2014,23(1):112 − 120. (in Chinese with English abstract)
NI Xiaojiao, NAN Ying. Comprehensive assessment of geological disasters risk in Changbai Mountain region based on GIS[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2014, 23(1): 112-120. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 冯凡,唐亚明,潘学树,等. 不同尺度下地质灾害风险评价方法探讨—以陕西吴堡县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):115 − 124. [FENG Fan,TANG Yaming,PAN Xueshu,et al. An attempt of risk assessment of geological hazards in different scales:A case study in Wubao County of Shaanxi Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):115 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract)
FENG Fan, TANG Yaming, PAN Xueshu, et al. An attempt of risk assessment of geological hazards in different scales: a case study in Wubao County of Shaanxi Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(2): 115-124. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 李阳春,刘黔云,李潇,等. 基于机器学习的滑坡崩塌地质灾害气象风险预警研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(3):118 − 123. [LI Yangchun,LIU Qianyun,LI Xiao,et al. Exploring early warning and forecasting of meteorological risk of landslide and rockfall induced by meteorological factors by the approach of machine learning[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(3):118 − 123. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Yangchun, LIU Qianyun, LI Xiao, et al. Exploring early warning and forecasting of meteorological risk of landslide and rockfall induced by meteorological factors by the approach of machine learning[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(3): 118-123. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 乔建平,王萌,石莉莉. 区域滑坡风险评估中的风险区划与概率分析[J]. 自然灾害学报,2012,21(2):51 − 56. [QIAO Jianping,WANG Meng,SHI Lili. Risk zoning and probability analysis of regional landslide risk assessment[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2012,21(2):51 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
QIAO Jianping, WANG Meng, SHI Lili. Risk zoning and probability analysis of regional landslide risk assessment[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2012, 21(2): 51-56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 刘希林. 泥石流风险评价中若干问题的探讨[J]. 山地学报,2000,18(4):341 − 345. [LIU Xilin. Approaches to risk assessment of debris flow[J]. Journal of Mountain Research,2000,18(4):341 − 345. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Xilin. Approaches to risk assessment of debris flow[J]. Journal of Mountain Research, 2000, 18(4): 341-345. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 王嘉君,何亚伯,杨琳,等. 基于GIS的山区村镇多灾种耦合风险评估[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(1):102 − 112. [WANG Jiajun,HE Yabo,YANG Lin,et al. Comprehensive multi-hazard risk assessment of villages and towns in mountain areas based on GIS[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(1):102 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Jiajun, HE Yabo, YANG Lin, et al. Comprehensive multi-hazard risk assessment of villages and towns in mountain areas based on GIS[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2018, 29(1): 102-112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 刘传正. 论地质灾害风险识别问题[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(4):1 − 7. [LIU Chuanzheng. Research on the risk recognition of geological disasters[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(4):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Chuanzheng. Research on the risk recognition of geological disasters[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2017, 44(4): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 刘传正. 崩塌滑坡灾害风险识别方法初步研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(1):88 − 97. [LIU Chuanzheng. Analysis methods on the risk identification of landslide disasters[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(1):88 − 97. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Chuanzheng. Analysis methods on the risk identification of landslide disasters[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2019, 27(1): 88-97. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] ALEXANDER E D, Natural Disasters[M]. London: UCL Press Limited, 1993: 1 − 632.
-




 下载:
下载: