Determination of regional landslide rainfall warning threshold based on susceptibility zoning: A case study in Longling County of Yunnan Province
-
摘要:
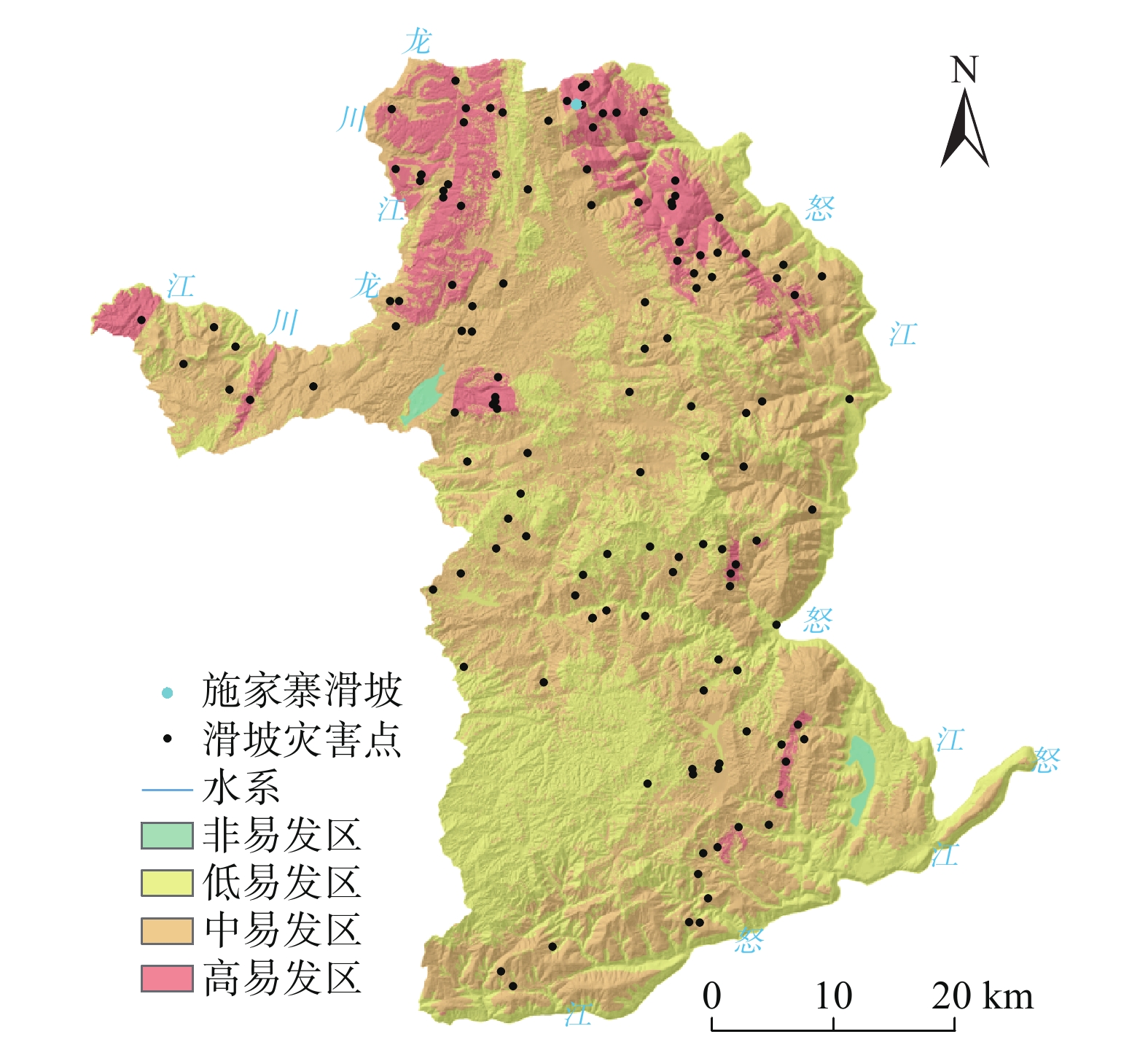
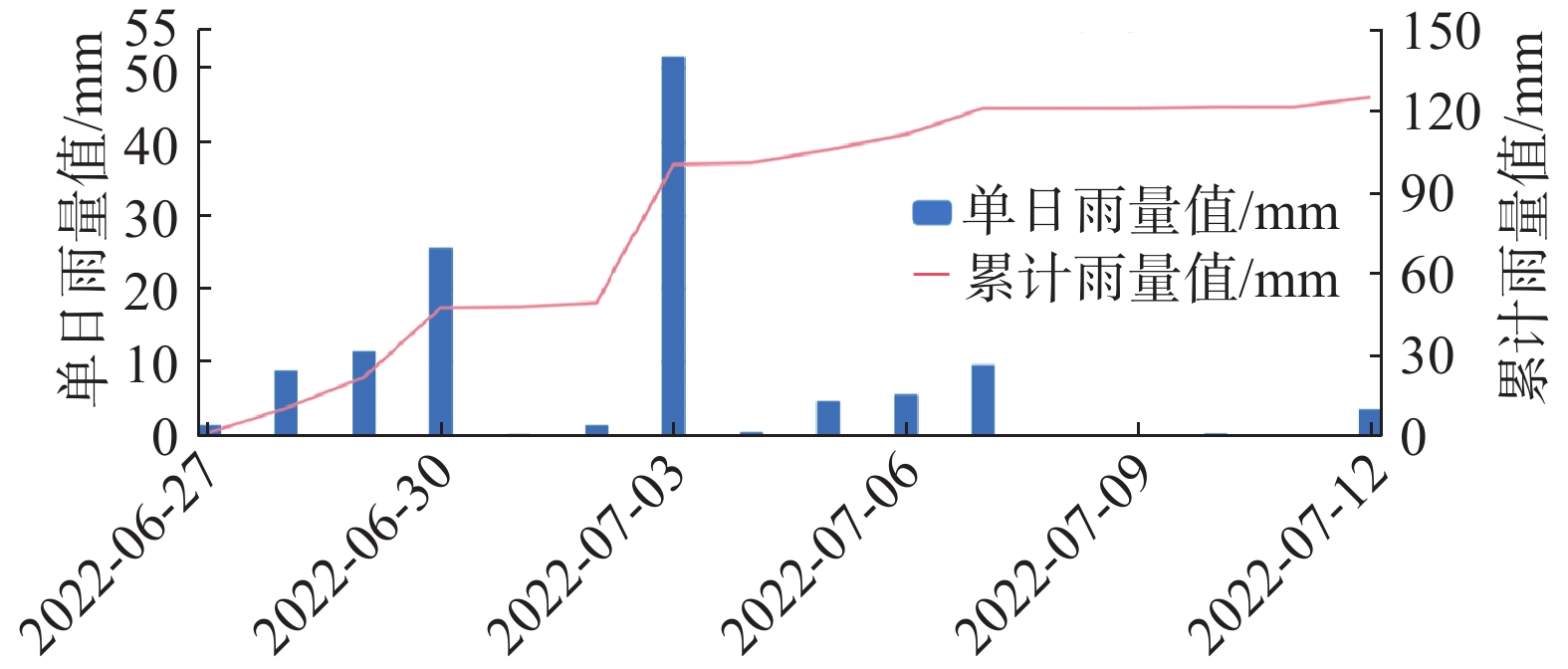
滑坡所处不同易发等级的区域,降雨预警阈值差别较大。为提高滑坡降雨预警的针对性和准确率,文章以野外地质调查和滑坡易发条件分析为基础,结合信息量模型和层次分析法开展滑坡易发性评价,再通过滑坡发生概率与前期累计降雨量的相关性分析,分区进行滑坡降雨预警阈值模型研究。结果表明:坡度、高程、距断层距离、工程地质岩组、水系是龙陵县滑坡的主要孕灾地质条件;龙陵县滑坡非易发区面积为14.33 km2,低易发区面积为1053.87 km2,中易发区面积为1471.65 km2,高易发区面积为254.73 km2;确定单日和前3日为降雨预警时间,分区分时细化了降雨预警阈值模型;对比降雨预警阈值模型应用于龙陵县滑坡监测预警中的前后,预警信息减少了70条,预警准确率提高了14.4%,并实现了镇安镇户帕村施家寨组滑坡的有效预警。文章为区域滑坡降雨预警阈值确定提供了一种较好的参考方法。
Abstract:Areas with different levels of susceptibility to landslides, rainfall warning thresholds vary widely, to improve the pertinence and accuracy of landslide monitoring and early warning. Based on field geological survey and landslide susceptibility condition analysis, this paper combines information quantity model and analytic hierarchy method to carry out susceptibility evaluation, and then analyzes the correlation between landslide occurrence probability and cumulative rainfall, and conducts landslide rainfall early warning threshold model research by zoning. The results showed that: Slope, elevation, geological structure, engineering rock group and water system are the main geological conditions of landslides in Longling County; The area of non-prone areas in Longling County was 14.33 km2, the area of low prone area was 1053.87 km2, the area of medium prone area was 1471.65 km2, and the area of high prone area was 254.73 km2; The rainfall warning time was determined for a single day and the previous 3 days, and the rainfall warning threshold was refined by district; Compared with the rainfall warning threshold model applied to the landslide monitoring and early warning in Longling County, the number of early warning information decreased by 70, the accuracy of early warning was increased by 14.4%, and the effective early warning of landslide in Shijiazhai Formation of Huba Village, Zhen’an Town was realized. This paper provides a good reference method for determining the regional landslide rainfall warning threshold.
-

-
表 1 不同孕灾地质环境条件的信息量
Table 1. Information of different disaster-induced geological environmental conditions
孕灾地质条件 分类区间 信息量 坡度/(°) [0, 8) −0.11678 [8, 16) 0.09139 [16, 21) 0.24305 [24, 32) 0.22223 [32, 90] −0.17598 高程/m [540, 1000) −1.87118 [1000, 1500) −0.01276 [1500, 2000) 0.36376 [2000, 2500) −0.35401 [2500, 3001] −0.92529 距断层距离/m [0,500) 0.55638 [500, 1000) 0.33742 [1000, 1500) −0.08659 [1500, 2000) −0.00810 [2000, 25805] −0.11811 工程地质岩组 松散岩土 −0.40000 较硬-硬层状碎屑岩 0.24766 硬质层状碳酸盐岩 −0.30988 岩浆岩 −0.16451 变质岩 0.17583 距水系距离/m [0,200) 0.03817 [200, 400) 0.23206 [400, 600) −0.16629 [600,800) −0.01517 [800, 6134] −0.05321 表 2 龙陵县滑坡灾害地质环境条件权重统计表
Table 2. Statistics of weights of geological and environmental conditions of landslide disaster in Longling County
地质环境条件 坡度 高程 距断层距离 工程地质岩组 距水系距离 权重 0.186 0.142 0.315 0.259 0.098 表 3 不同等级的易发区划与实际滑坡分布对比
Table 3. Comparison of the prone zoning of different grades with the actual landslide distribution
易发分区 灾点数量/个 灾点比例/% 面积/km2 面积比例/% 灾点密度/km2 滑坡面积/km2 占总滑坡面积比例/% 非易发区 0 0 14.33 0.51 0 0 0 低易发区 16 12.12 1053.87 37.46 0.02 0.13 6.11 中易发区 70 53.03 1471.65 52.96 0.05 0.98 46.71 高易发区 46 34.84 254.73 9.10 0.18 0.99 47.18 表 4 累计降雨量和滑坡相关性分析
Table 4. Correlation analysis of different times and landslides in the previous period
累计降雨量 相关系数 累计降雨量 相关系数 前1 d 0.819 前5 d 0.524 前2 d 0.785 前6 d 0.412 前3 d 0.808 前7 d 0.316 前4 d 0.615 前8 d 0.213 表 5 相关系数与相关强度对照表[16]
Table 5. Comparison of correlation coefficient and correlation intensity
相关系数的值 直线相关程度 |r|=0 完全不相关 |r|≤0.3 微弱相关 0.3<|r|≤0.5 低度相关 0.5<|r|≤0.8 显著相关 0.8<|r|<1 高度相关 |r|=1 完全相关 表 6 龙陵县滑坡四色预警降雨阈值
Table 6. Landslide four-color warning rainfall threshold of Longling County
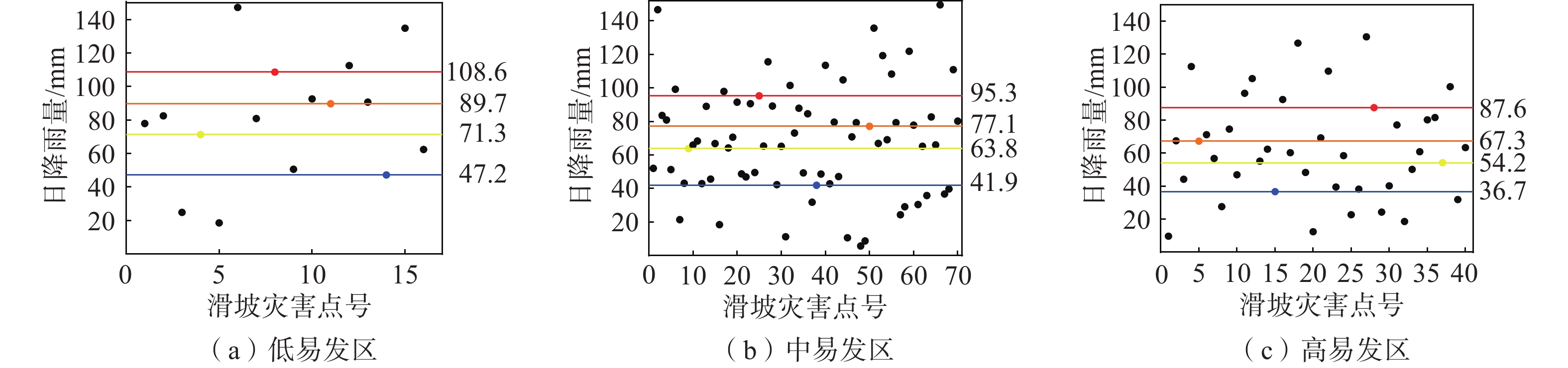
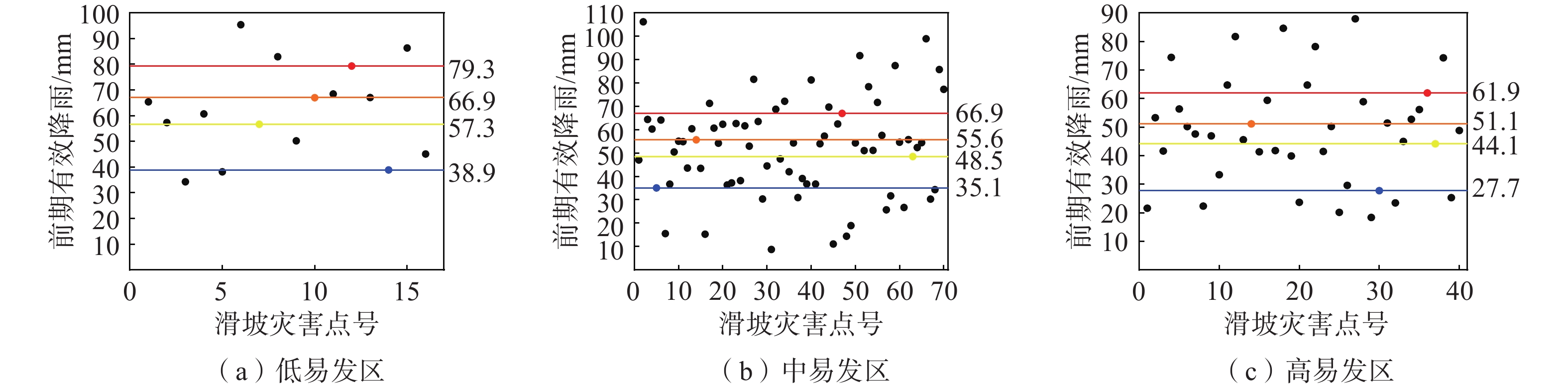
易发分区 降雨时段 不同等级预警阈值/mm 蓝色 黄色 橙色 红色 低易发区 单日 47.2 71.3 89.7 108.6 前3 d 38.9 57.3 66.9 79.3 中易发区 单日 41.9 63.8 77.1 95.3 前3 d 35.1 48.5 55.6 66.9 高易发区 单日 36.7 54.2 67.3 87.6 前3 d 27.1 44.1 51.1 61.9 -
[1] 李媛,杨旭东. 降雨诱发区域性滑坡预报预警方法研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2006,33(2):101 − 103. [LI Yuan,YANG Xudong. Research on the forecasting and early warning of the regional precipitation-induced landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2006,33(2):101 − 103. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2006.02.024
LI Yuan, YANG Xudong. Research on the forecasting and early warning of the regional precipitation-induced landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2006, 33(2): 101-103. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2006.02.024
[2] 温铭生,王连俊,李铁锋,等. 云南省新平县滑坡预警区划研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2010,37(4):103 − 106. [WEN Mingsheng,WANG Lianjun,LI Tiefeng,et al. Early-warning zoning studying of landslides in Xinping[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2010,37(4):103 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.04.021
WEN Mingsheng, WANG Lianjun, LI Tiefeng, et al. Early-warning zoning studying of landslides in Xinping[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2010, 37(4): 103-106. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.04.021
[3] 温智熊,蓝俊康,梁一敏. 广西龙胜县崩塌和滑坡地质灾害的气象预警预报[J]. 桂林理工大学学报,2018,38(3):464 − 468. [WEN Zhixiong,LAN Junkang,LIANG Yimin. Meteorological forecasting and alarming system against geological disasters in Longsheng of Guangxi[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology,2018,38(3):464 − 468. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2018.03.013
WEN Zhixiong, LAN Junkang, LIANG Yimin. Meteorological forecasting and alarming system against geological disasters in Longsheng of Guangxi[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2018, 38(3): 464-468. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2018.03.013
[4] 朱文慧,晏鄂川,邹浩,等. 湖北省黄冈市降雨型滑坡气象预警判据[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(6):45 − 53. [ZHU Wenhui,YAN Echuan,ZOU Hao,et al. Meteorological early warning criterion of rainfall landslide in Huanggang City,Hubei Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(6):45 − 53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHU Wenhui, YAN Echuan, ZOU Hao, et al. Meteorological early warning criterion of rainfall landslide in Huanggang City, Hubei Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(6): 45-53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 曹中山. 基于易发性和临界降雨阈值的滑坡危险性预警建模研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2020
CAO Zhongshan. Study on landslide risk early warning modeling based on susceptibility and critical rainfall threshold[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 孙德亮. 基于机器学习的滑坡易发性区划与降雨诱发滑坡预报预警研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2019
SUN Deliang. Study on landslide susceptibility zoning and rainfall-induced landslide prediction and early warning based on machine learning[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] ROSI A,SEGONI S,CATANI F,et al. Statistical and environmental analyses for the definition of a regional rainfall threshold system for landslide triggering in Tuscany (Italy)[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences,2012,22(4):617 − 629. doi: 10.1007/s11442-012-0951-0
[8] 朱昳橙,李益敏,魏苏杭. 怒江州滑坡地质灾害气象预警模型研究[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版),2016,38(4):610 − 619. [ZHU Yicheng,LI Yimin,WEI Suhang. A prediction model study on landslide in Nujiang State[J]. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Sciences Edition),2016,38(4):610 − 619. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHU Yicheng, LI Yimin, WEI Suhang. A prediction model study on landslide in Nujiang State[J]. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2016, 38(4): 610-619. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 夏辉,殷坤龙,梁鑫,等. 基于SVM-ANN模型的滑坡易发性评价—以三峡库区巫山县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(5):13 − 19. [XIA Hui,YIN Kunlong,LIANG Xin,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on SVM-ANN Models:A case stualy for Wushan County in the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(5):13 − 19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XIA Hui, YIN Kunlong, LIANG Xin, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on SVM-ANN Models: a case stualy for Wushan County in the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2018, 29(5): 13-19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 刘福臻,王灵,肖东升. 机器学习模型在滑坡易发性评价中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(6):98 − 106. [LIU Fuzhen,WANG Ling,XIAO Dongsheng. Application of machine learning model in landslide susceptibility evaluation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(6):98 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Fuzhen, WANG Ling, XIAO Dongsheng. Application of machine learning model in landslide susceptibility evaluation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(6): 98-106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 张玘恺,凌斯祥,李晓宁,等. 九寨沟县滑坡灾害易发性快速评估模型对比研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(8):1595 − 1610. [ZHANG Qikai,LING Sixiang,LI Xiaoning,et al. Comparison of landslide susceptibility mapping rapid assessment models in Jiuzhaigou County,Sichuan Province,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(8):1595 − 1610. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2020.0029
ZHANG Qikai, LING Sixiang, LI Xiaoning, et al. Comparison of landslide susceptibility mapping rapid assessment models in Jiuzhaigou County, Sichuan Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(8): 1595-1610. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2020.0029
[12] 郭子正,殷坤龙,黄发明,等. 基于滑坡分类和加权频率比模型的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2019,38(2):287 − 300. [GUO Zizheng,YIN Kunlong,HUANG Faming,et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on landslide classification and weighted frequency ratio model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2019,38(2):287 − 300. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GUO Zizheng, YIN Kunlong, HUANG Faming, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on landslide classification and weighted frequency ratio model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(2): 287-300. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 张勇,温智,程英建. 四川巴中市滑坡灾害与降雨雨型关系探讨[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(2):178 − 182. [ZHANG Yong,WEN Zhi,CHENG Yingjian. A discussion of the relationship between landslide disaster and rainfall types in Bazhong of Sichuan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(2):178 − 182. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.201906036
ZHANG Yong, WEN Zhi, CHENG Yingjian. A discussion of the relationship between landslide disaster and rainfall types in Bazhong of Sichuan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(2): 178-182. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.201906036
[14] 栗倩倩,史绪山,柴波,等. 台风-非台风降雨型滑坡的多时段临界雨量值预测模型[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(2):267 − 273. [LI Qianqian,SHI Xushan,CHAI Bo,et al. Multiduration critical rainfall prediction model for typhoons and non-typhoon rainfall landslides[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(2):267 − 273. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Qianqian, SHI Xushan, CHAI Bo, et al. Multiduration critical rainfall prediction model for typhoons and non-typhoon rainfall landslides[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 267-273. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 夏梦想,李远耀,吴吉民,等. 基于I-D统计模型的张家界市滑坡灾害降雨预警阀值研究[J]. 自然灾害学报,2021,30(4):203 − 212. [XIA Mengxiang,LI Yuanyao,WU Jimin,et al. Research on rainfall early warning threshold of landslide disaster in Zhangjiajie City based on I-D statistical model[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2021,30(4):203 − 212. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XIA Mengxiang, LI Yuanyao, WU Jimin, et al. Research on rainfall early warning threshold of landslide disaster in Zhangjiajie City based on I-D statistical model[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2021, 30(4): 203-212. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 卢纹岱. SPSS统计分析(第4版)[M]. 电子工业出版社, 2012
LU Wendai. SPSS Statistical Analysis (4th Edition) [M]. Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 林巍,李远耀,徐勇,等. 湖南慈利县滑坡灾害的临界降雨量阈值研究[J]. 长江科学院院报,2020,37(2):48 − 54. [LIN Wei,LI Yuanyao,XU Yong,et al. Rainfall thresholds of rainfall-triggered landslides in Cili County,Hunan Province[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2020,37(2):48 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20181125
LIN Wei, LI Yuanyao, XU Yong, et al. Rainfall thresholds of rainfall-triggered landslides in Cili County, Hunan Province[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2020, 37(2): 48-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20181125
[18] 刘谢攀, 殷坤龙, 肖常贵, 等. 基于 I-D-R 阈值模型的滑坡气象预警[J/OL]. 地球科学, 2022(2022-09-05)[2022-07-11]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20220708.1511.002.html.
LIU Xiepan, YIN Kunlong, XIAO Changgui, et al. Meteorological early warning of landslide based on I-D-R threshold model[J]. Earth Science, 1 − 15. [2023-05-24](in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 黄发明,曹中山,姚池,等. 基于决策树和有效降雨强度的滑坡危险性预警[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版),2021,55(3):472 − 482. [HUANG Faming,CAO Zhongshan,YAO Chi,et al. Landslides hazard warning based on decision tree and effective rainfall intensity[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science),2021,55(3):472 − 482. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HUANG Faming, CAO Zhongshan, YAO Chi, et al. Landslides hazard warning based on decision tree and effective rainfall intensity[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2021, 55(3): 472-482. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 中国气象局. 暴雨诱发的地质灾害气象风险预警等级: QX/T 487—2019[S]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2019
China Meteorological Bureau of the People's Republic of China. Meteorological risk early warning levels of geological disaster induced by torrential rain: QX/T 487—2019[S]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2019. (in Chinese)
[21] 赵衡,宋二祥. 诱发区域性滑坡的降雨阈值[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2011,41(5):1481 − 1487. [ZHAO Heng,SONG Erxiang. Rainfall thresholds for regional landslides[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2011,41(5):1481 − 1487. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHAO Heng, SONG Erxiang. Rainfall thresholds for regional landslides[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2011, 41(5): 1481-1487. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 戴丛蕊,黄玮,李蒙,等. 云南降雨型滑坡县级预警雨量阈值分析[J]. 气象科技,2015,43(4):675 − 680. [DAI Congrui,HUANG Wei,LI Meng,et al. County-level rainfall warning thresholds for rainfall-induced landslides in Yunnan[J]. Meteorological Science and Technology,2015,43(4):675 − 680. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6345.2015.04.019
DAI Congrui, HUANG Wei, LI Meng, et al. County-level rainfall warning thresholds for rainfall-induced landslides in Yunnan[J]. Meteorological Science and Technology, 2015, 43(4): 675-680. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6345.2015.04.019
-




 下载:
下载: