Hazard assessment of landslides in Lancang County, Yunnan Province based on weighted information value model
-
摘要:
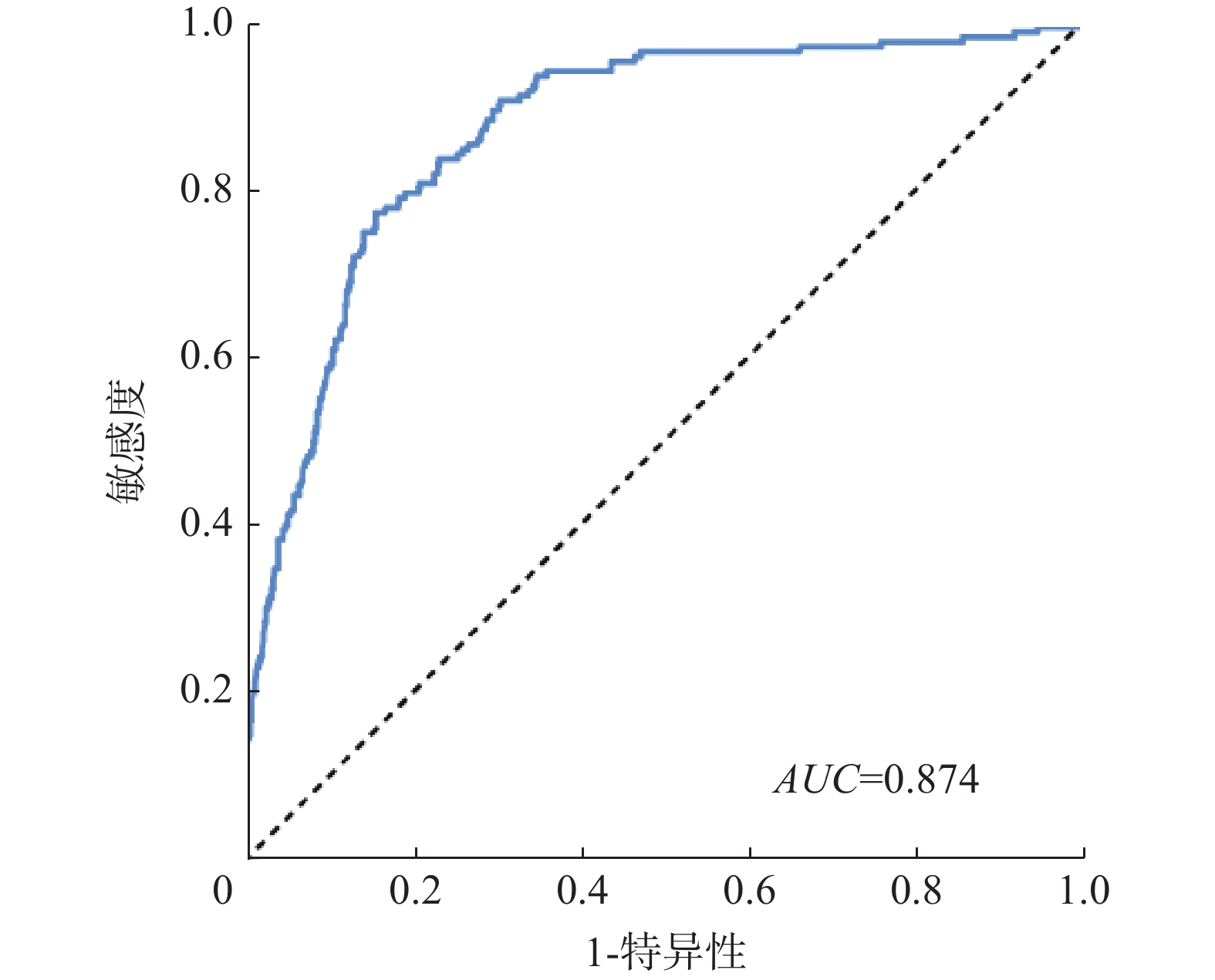
云南澜沧县位于滇西经向构造带中,在构造运动强烈,人类活动日益增加背景下,滑坡灾害发育,人民生命财产受到严重威胁,因此,对该区域进行滑坡危险性评价研究具有重要意义。以澜沧县滑坡数据为基础,选取高程、坡度、坡向、地层岩性、距断层距离、植被覆盖度、距道路距离、降雨量共8个评价因子,构建滑坡危险性评价指标体系。基于熵权法与信息量耦合模型,利用ArcGIS地理空间分析对研究区滑坡危险进行定性、定量评价并分区。结果显示:高危险区面积占17.91%,较高危险区占37.91%,中危险区占25.94%,低危险区占18.25%。经检验评价结果合理,加权信息量模型适用于滑坡危险性评价。
Abstract:Lancang County is located in the longitudinal tectonic zone of western Yunnan, where landslides are frequently developed by strong tectonic movement and increasing human activities, thus posing a significant threat to the safety and security of the local population. Therefore, it is of great significance to assess the landslide risk in this area. To construct a landslide risk evaluation index system, data on previous landslides in Lancang County was analyzed, and eight control factors were selected, including elevation, slope, slope direction, stratigraphic lithology, distance from fault, vegetation coverage, distance from road and rainfall. By using the entropy weight method and information coupling value model, the landslide risk in the study area was qualitatively and quantitatively evaluated, and ArcGIS geospatial analysis was used to partition the results. According to the assessment, high-risk areas accounted for 17.91% of the total area, relatively high-risk areas accounted for 37.91%, moderate-risk areas accounted for 25.94%, and low-risk areas accounted for 18.25%.The evaluation results were deemed reasonable, and the entropy weight method and information coupling value model were found to be appropriate for landslide hazard assessment in the region.
-
Key words:
- landslide /
- entropy weight method /
- information volume model /
- risk assessment /
- Lancang County
-

-
表 1 数据来源
Table 1. Summary of data source
数据名称 数据来源 数据名称 数据来源 滑坡灾害点 澜沧县地质灾害详查 DEM数据 地理空间数据云 地质图 全国地质资料馆 降雨量 中国气象数据网 道路数据 91卫图助手 植被覆盖数据 地理空间数据云 表 2 指标统计计算结果
Table 2. Statistical calculation results of indicators
因子 因子二级属性 滑坡点个数 栅格数量 信息量 相对点密度 归一化Xi Hi Wi 高程/m 492~1 099 20 1 224 511 −0.076 0.927 0.196 0.921 0.174 1 099~1 366 33 2 536 591 −0.303 0.738 0.156 1 366~1 623 54 2 684 074 0.133 1.142 0.241 1 623~1 910 58 1 991 079 0.503 1.653 0.350 1 910~2 530 6 1 268 180 −1.315 0.269 0.057 坡度/(°) 0~10 24 1 453 076 −0.065 0.937 0.171 0.984 0.034 10~20 75 3 730 552 0.132 1.141 0.208 20~30 47 3 223 642 −0.189 0.827 0.151 30~40 20 1 114 820 0.018 1.018 0.186 >40 5 182 345 0.442 1.556 0.284 坡向 北 18 1 267 813 −0.216 0.806 0.102 0.967 0.072 东北 38 1 404 853 0.429 1.535 0.195 东 9 1 199 159 −0.853 0.426 0.054 东南 14 1 116 898 −0.341 0.711 0.090 南 29 1 195 808 0.319 1.376 0.175 西南 25 1 283 120 0.101 1.106 0.140 西 14 1 112 242 −0.336 0.714 0.091 西北 24 1 124 542 0.192 1.211 0.154 地层岩性 松散岩(土)体 3 91 136 0.625 1.868 0.306 0.911 0.197 软弱岩层 7 197 943 0.697 2.007 0.329 较软弱岩层 30 2 174 744 −0.245 0.783 0.128 较坚硬岩层 128 6 776 327 0.070 1.072 0.176 坚硬岩层 3 464 285 −1.003 0.367 0.060 距断裂距离/m 0~1 000 44 1 912 260 0.267 1.306 0.282 0.971 0.065 1 000~2 000 29 1574 153 0.044 1.046 0.226 2 000~3 000 16 1 187 454 −0.268 0.765 0.165 3 000~4 000 8 917 368 −0.703 0.495 0.107 >4 000 74 4 113 200 0.021 1.021 0.220 植被覆盖度 0~0.19 33 900 995 0.732 2.079 0.329 0.897 0.228 0.19~0.45 45 1 291 011 0.682 1.978 0.313 0.45~0.66 38 1 846 666 0.155 1.168 0.185 0.66~0.84 41 2 895 125 −0.219 0.804 0.127 0.84~0.1 14 2 770 638 −1.249 0.287 0.045 距道路距离/m 0~500 19 480 354 0.809 2.245 0.358 0.950 0.111 500~1 000 11 458 280 0.309 1.362 0.217 1 000~1 500 7 433 124 −0.086 0.917 0.146 1 500~2 000 6 413 798 −0.195 0.823 0.131 >2 000 128 7 918 879 −0.086 0.917 0.146 降雨量/mm 1 212.3~1 313.2 41 1 166 233 0.691 1.995 0.356 0.947 0.119 1 313.2~1 382.0 35 1 524 128 0.265 1.303 0.233 1 382.0~1 435.2 27 1 962 908 −0.248 0.781 0.139 1 435.2~1 485.8 38 2 637 049 −0.201 0.818 0.146 1 485.8~1 545.5 30 2 414 117 −0.349 0.705 0.126 表 3 分区统计结果
Table 3. Statistical results of zoning
危险性等级 面积/km2 面积
比例/%滑坡点
/个滑坡点
比例/%滑坡相对
点密度高危险区 1549.72 17.91 84 49.12 2.74 较高危险区 3280.77 37.91 63 36.84 0.97 中危险区 2244.93 25.94 19 11.11 0.43 低危险区 1579.76 18.25 5 2.92 0.16 -
[1] 李益敏,袁静,蒋德明,等. 基于GIS的西南高山峡谷区滑坡风险性评价—以怒江州泸水市为例[J]. 西北师范大学学报(自然科学版),2021,57(6):94 − 102. [LI Yimin,YUAN Jing,JIANG Deming,et al. Risk assessment of landslide disasters in alpine canyon area based on GIS:Taking Lushui City,Nujiang Prefecture as an example[J]. Journal of Northwest Normal University (Natural Science),2021,57(6):94 − 102. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Yimin, YUAN Jing, JIANG Deming, et al. Risk assessment of landslide disasters in alpine canyon area based on GIS—taking Lushui City, Nujiang Prefecture as an example[J]. Journal of Northwest Normal University (Natural Science), 2021, 57(6): 94-102. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 屠水云,张钟远,付弘流,等. 基于CF与CF-LR模型的地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):96 − 104. [TU Shuiyun,ZHANG Zhongyuan,FU Hongliu,et al. Geological hazard susceptibility evaluation based on CF and CF-LR model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):96 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.02-12
TU Shuiyun, ZHANG Zhongyuan, FU Hongliu, et al. Geological hazard susceptibility evaluation based on CF and CF-LR model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(2): 96-104. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.02-12
[3] 杨华阳,许向宁,杨鸿发. 基于证据权法的九寨沟地震滑坡危险性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(3):20 − 29. [YANG Huayang,XU Xiangning,YANG Hongfa. The Jiuzhaigou co-seismic landslide hazard assessment based on weight of evidence method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(3):20 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.03.03
YANG Huayang, XU Xiangning, YANG Hongfa. The Jiuzhaigou co-seismic landslide hazard assessment based on weight of evidence method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(3): 20-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.03.03
[4] 管新邦. 云南省滑坡地质灾害危险性评价研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2018
GUAN Xinbang. Study on risk assessment of landslide geological hazards in Yunnan Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining & Technology, Beijing, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 孙长明,马润勇,尚合欣,等. 基于滑坡分类的西宁市滑坡易发性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):173 − 181. [SUN Changming,MA Runyong,SHANG Hexin,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment in Xining based on landslide classification[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):173 − 181. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SUN Changming, MA Runyong, SHANG Hexin, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment in Xining based on landslide classification[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(3): 173-181. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 温鑫,范宣梅,陈兰,等. 基于信息量模型的地质灾害易发性评价—以川东南古蔺县为例[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(2):290 − 299. [WEN Xin,FAN Xuanmei,CHEN Lan,et al. Susceptibility assessment of geological disasters based on an information value model:A case of Gulin County in southeast Sichuan[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(2):290 − 299. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WEN Xin, FAN Xuanmei, CHEN Lan, et al. Susceptibility assessment of geological disasters based on an information value model: a case of Gulin County in Southeast Sichuan[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 290-299. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 申怀飞,董雨,杨梅,等. 基于AHP与信息量法的甘肃省滑坡易发性评估[J]. 水土保持研究,2021,28(6):412 − 419. [SHEN Huaifei,DONG Yu,YANG Mei,et al. Assessment on landslide susceptibility in Gansu Province based on AHP and information quantity method[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2021,28(6):412 − 419. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2021.06.034
SHEN Huaifei, DONG Yu, YANG Mei, et al. Assessment on landslide susceptibility in Gansu Province based on AHP and information quantity method[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 28(6): 412-419. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2021.06.034
[8] 孙滨,祝传兵,康晓波,等. 基于信息量模型的云南东川泥石流易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(5):119 − 127. [SUN Bin,ZHU Chuanbing,KANG Xiaobo,et al. Susceptibility assessment of debris flows based on information model in Dongchuan,Yunnan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(5):119 − 127. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.202204003
SUN Bin, ZHU Chuanbing, KANG Xiaobo, et al. Susceptibility assessment of debris flows based on information model in Dongchuan, Yunnan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(5): 119-127. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.202204003
[9] 杜国梁,杨志华,袁颖,等. 基于逻辑回归-信息量的川藏交通廊道滑坡易发性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):102 − 111. [DU Guoliang,YANG Zhihua,YUAN Ying,et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Xizang traffic corridor using logistic regression-information value method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):102 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DU Guoliang, YANG Zhihua, YUAN Ying, et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Xizang traffic corridor using logistic regression-information value method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(5): 102-111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 王夏林,严宝文. 基于熵权的可拓理论在地灾危险性评价中的应用[J]. 人民长江,2012,43(21):70 − 74. [WANG Xialin,YAN Baowen. Application of entropy weight based extension theory in risk assessment of geological hazards[J]. Yangtze River,2012,43(21):70 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2012.21.019
WANG Xialin, YAN Baowen. Application of entropy weight based extension theory in risk assessment of geological hazards[J]. Yangtze River, 2012, 43(21): 70-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2012.21.019
[11] 周苏华,付宇航,徐智文,等. 基于主客观赋权法的福建省地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 安全与环境学报,2022,23(9):3204 − 3214. [ZHOU Suhua,FU Yuhang,XU Zhiwen,et al. Evaluation of geological disaster susceptibility in Fujian Province based on subjective and objective weighting method[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment,2022,23(9):3204 − 3214. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhou Suhua, Fu Yuhang, Xu Zhiwen, et al. Evaluation of geological disaster susceptibility in Fujian Province based on subjective and objective weighting method [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2022: 1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] KHATUN M,HOSSAIN A T M S,SAYEM H M,et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping using weighted-overlay approach in rangamati,Bangladesh[J]. Earth Systems and Environment,2023,7(1):223 − 235. doi: 10.1007/s41748-022-00312-2
[13] CHEN W,CHAI H C,SUN X Y,et al. A GIS-based comparative study of frequency ratio,statistical index and weights-of-evidence models in landslide susceptibility mapping[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2016,9(3):204. doi: 10.1007/s12517-015-2150-7
[14] 刘福臻,王灵,肖东升,等. 基于模糊综合评判法的宁南县滑坡易发性评价[J]. 自然灾害学报,2021,30(5):237 − 246. [LIU Fuzhen,WANG Ling,XIAO Dongsheng,et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility in Ningnan County based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2021,30(5):237 − 246. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Fuzhen, WANG Ling, XIAO Dongsheng, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility in Ningnan County based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2021, 30(5): 237-246. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 罗亮,宋国虎,唐良琴,等. 白龙江武都区段泥石流分布规律及其危险性评价[J]. 人民长江,2022,53(5):135 − 142. [LUO Liang,SONG Guohu,TANG Liangqin,et al. Debris flow distribution law and risk analysis in Wudu section of Bailong River[J]. Yangtze River,2022,53(5):135 − 142. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LUO Liang, SONG Guohu, TANG Liangqin, et al. Debris flow distribution law and risk analysis in Wudu section of Bailong River[J]. Yangtze River, 2022, 53(5): 135-142.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 崔阳阳. 基于不同评价单元的滑坡易发性评价方法研究—以陕西省洛南县为例[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2022
CUI Yangyang. Study on evaluation method of landslide susceptibility based on different evaluation units: A case study of Luonan County, Shaanxi Province[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 汤国安, 刘学军, 闾国年.数字高程模型及地学分析的原理与方法[M]. 科学出版社, 2005
TANG Guoan, LIU Xuejun, LU Guonian. Principles and methods of digital elevation model and geoscience analysis[M]. Science Press, 2005. (in Chinese )
[18] 朱晓霞,张力,杨树文. 降雨引发的兰州黄土滑坡时空规律分析和临界降雨量预测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(4):24 − 31. [ZHU Xiaoxia,ZHANG Li,YANG Shuwen. Characteristics of rainfall-induced loess landslides and their threshold rainfall in Lanzhou[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(4):24 − 31. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2019.04.04
ZHU Xiaoxia, ZHANG Li, YANG Shuwen. Characteristics of rainfall-induced loess landslides and their threshold rainfall in Lanzhou[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2019, 30(4): 24-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2019.04.04
[19] 韩玲,张庭瑜,张恒. 基于IOE和SVM模型的府谷镇滑坡易发性分区[J]. 水土保持研究,2019,26(3):367 − 372. [HAN Ling,ZHANG Tingyu,ZHANG Heng. Landslide susceptibility mapping based on IOE and SVM model in Fugu Town[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2019,26(3):367 − 372. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HAN Ling, ZHANG Tingyu, ZHANG Heng. Landslide susceptibility mapping based on IOE and SVM model in Fugu town[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 26(3): 367-372. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: