Basic characteristics of co-seismic geological hazards induced by Jishishan Ms 6.2 earthquake and suggestions for their risk control
-
摘要:
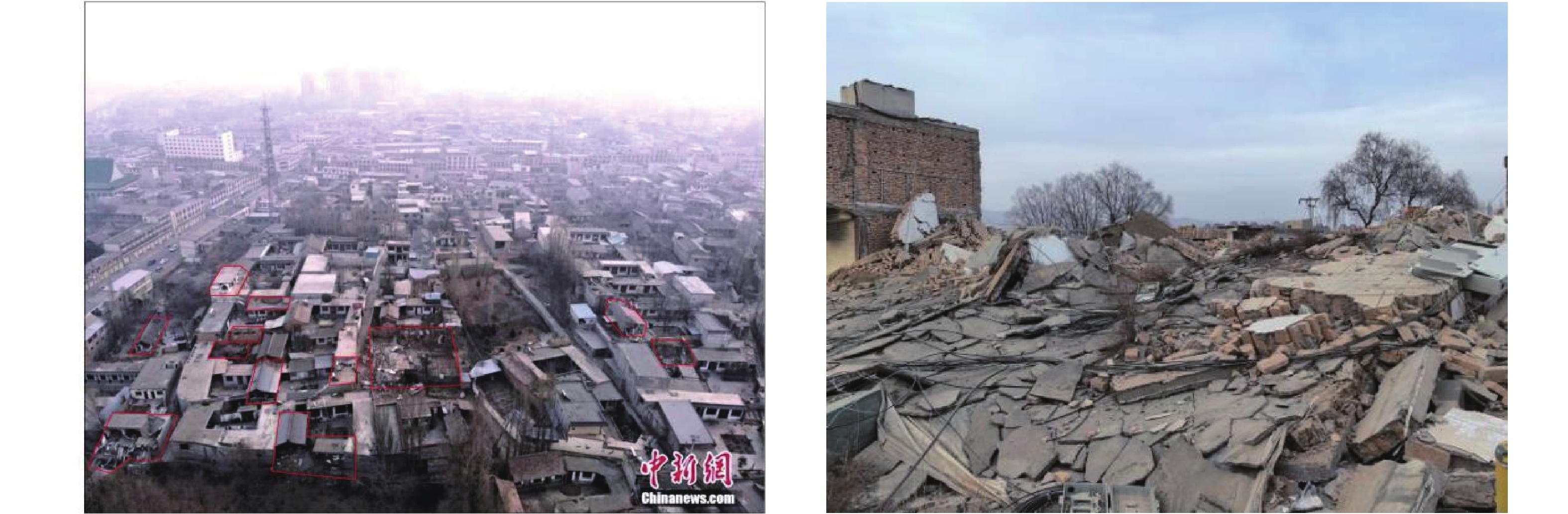
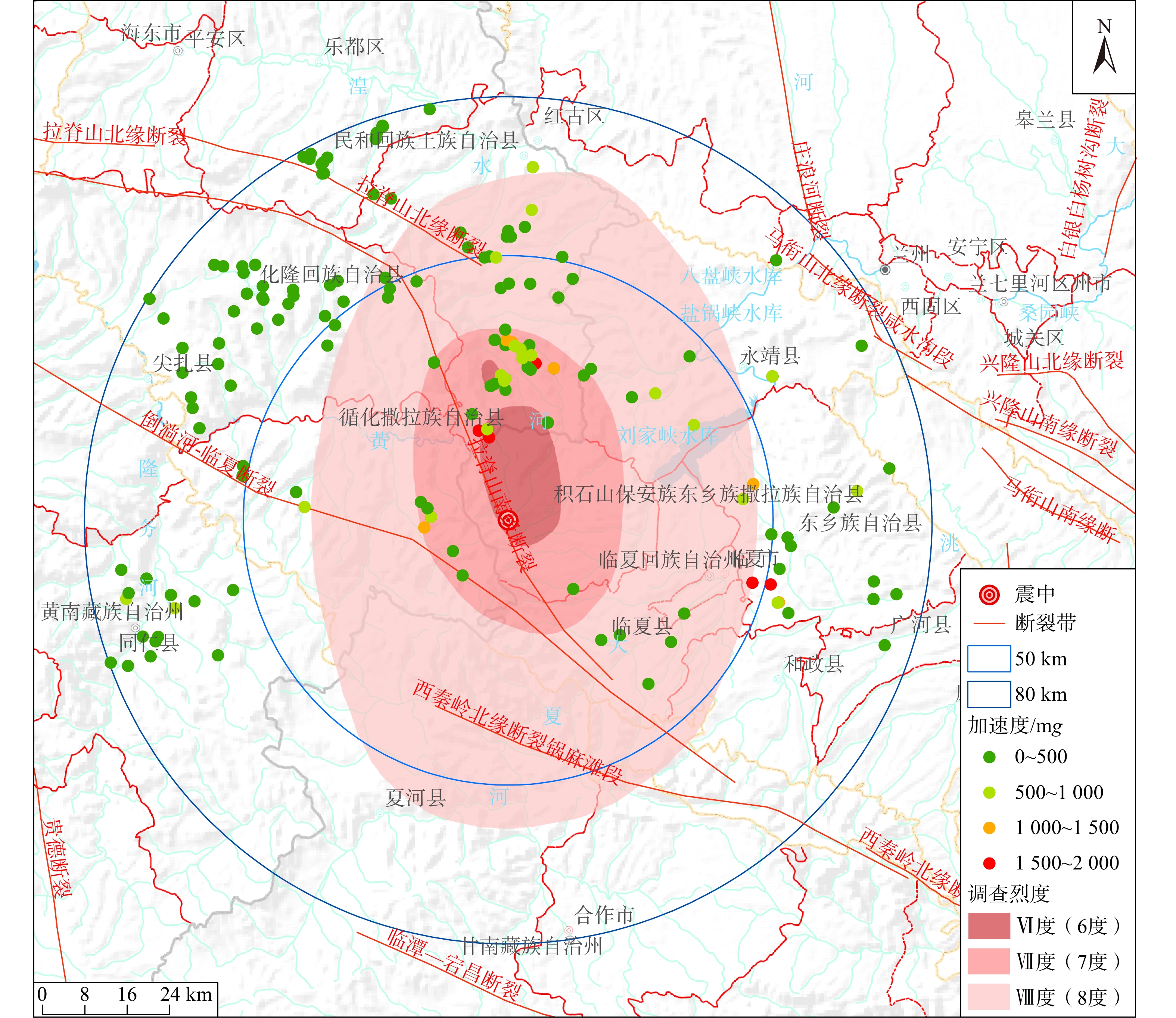
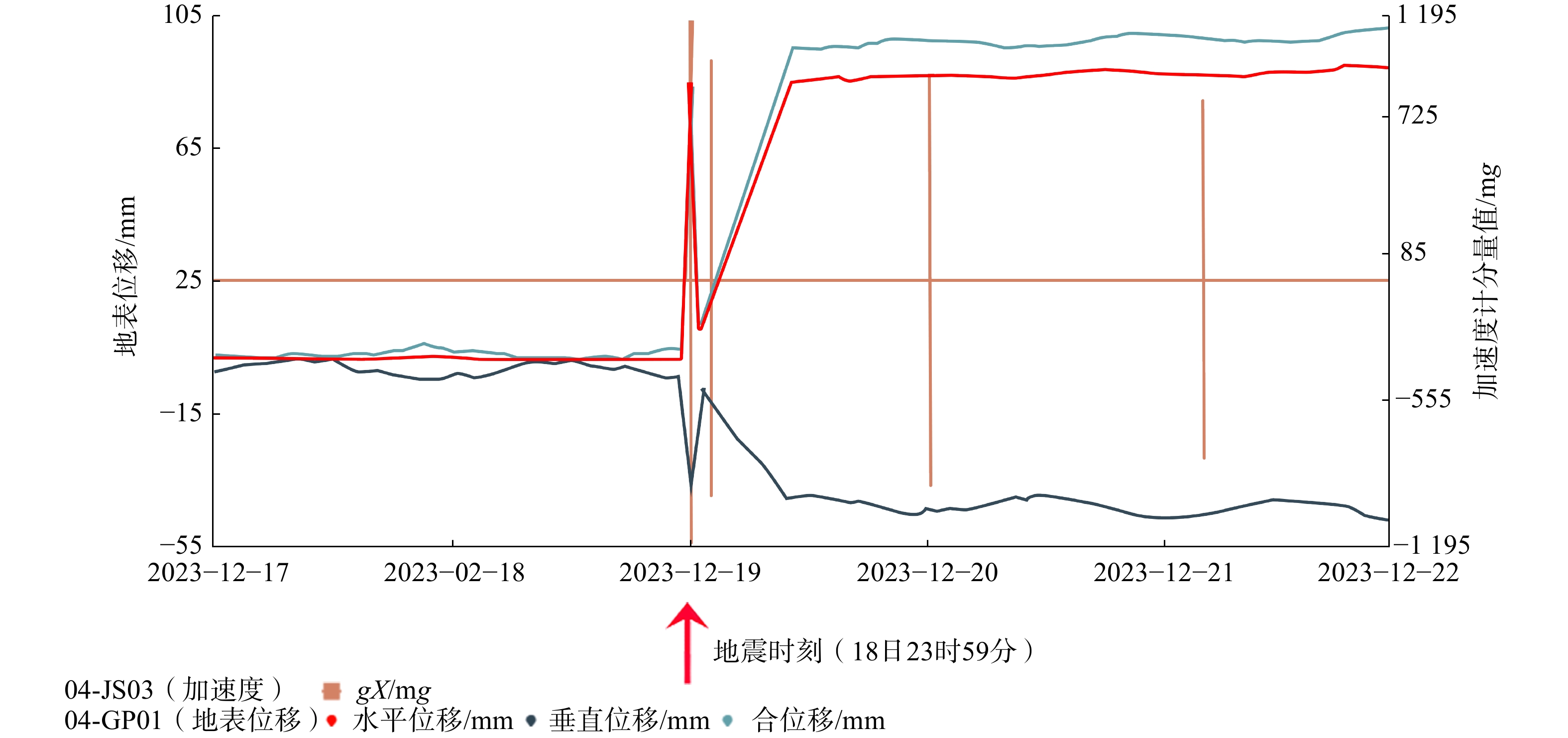
2023年12月18日甘肃省临夏州积石山县发生Ms 6.2级地震,引发了大量地质灾害,威胁人民生命与基础设施的安全。地震后,甘肃、青海两省迅速开展地质灾害隐患核查,文章基于这次地震地质灾害调查成果,对积石山地震诱发地质灾害的特征、控制因素、发展趋势进行了分析,提出防灾减灾措施建议。截至12月23日,共核查隐患点2044处,包括78处新增地质灾害隐患、88处地震加剧变形的在库隐患点和1878处无明显变形的在库隐患点。新增和变形加剧的隐患点数量以崩塌居多,占67.5%,滑坡次之,占31.9%;规模等级以小型居多,占84.9%,中型次之,占10.8%;成灾模式多为小型崩塌威胁房屋和道路。同震地质灾害密集分布于发震断层附近,发育密度随地震烈度增强而增大。国家地质安全监测台网震中50 km范围内206组加速度计数据显示,震区峰值加速度为30.4~1969.7 mg,并随与震中距离的增大呈对数衰减。此外,地表变形监测设备也记录了典型滑坡的同震位移曲线。分析认为,积石山地震地质灾害后效应与链式致灾效应将增强,建议尽快更新震区地质灾害隐患点数据库,有针对性地实施风险防控措施,深入开展综合遥感监测与同震地质灾害机理研究,完善气象预警模型及阈值,有效降低地质灾害风险。
Abstract:On December 18, 2023, an Ms 6.2earthquake occurred in Jishishan County, Linxia Prefecture, Gansu Province, causing a large number of geological disasters and threatening people's lives and the safety of infrastructure. After the earthquake, Gansu and Qinghai provincial governments quickly deployed hundreds of geology professionals to carried out the investigation and verification geological disasters in the earthquake area. Based on the results of the earthquake geohazard investigation and verification, this paper analyses the characteristics, control factors and development trend of the earthquake-induced geohazards, and puts forward suggestions on disaster prevention and risk mitigation measures. Till December 23, a total of 2044 geohazards have been checked, including 78 new geohazards, 88 existing geohazards with intensified deformation due to earthquake, and 1 878 existing geohazards without obvious different from before. Most of new and intensified deforming geohazards are collapse, accounting for 67.5%, followed by landslide, accounting for 31.9%. Most of new and intensified deforming geohazards are small in scale, accounting for 84.9%, followed by medium, accounting for 10.8%. Disaster mode of new and intensified deforming geohazards are mostly small collapse threatening houses and roads. The co-seismic geohazards are densely distributed along the seismic fault, and the spatial density increases with the enhancement of earthquake intensity. Data from 206 groups of accelerate-meters within 50 km from the epicenter of the National Geological Safety Monitoring Network showed that the peak acceleration of the earthquake area was 30.4~1969.7 mg. and decayed logarithm with the increase of the distance from the epicenter. In addition, the surface deformation monitoring equipment also recorded the co-seismic displacement curve of a typical landslide. Analysis shows, earthquake put a deteriorate effect to rock and soil, which decreased their integration and strength. There is a magnificent geohazard after-effect of earthquake; collapse, landslide and debris flow will be much often than before. So the authors suggest: (1) update earthquake geohazard database as soon as possible, (2) work out targeted prevention and control measures for the geohazards with large potential danger, (3) conduct comprehensive remote sensing monitoring and research of earthquake-induced geohazard mechanism, (4) improve the meteorological early warning model and threshold. By all this efforts the risk of geohazards after earthquake will be reduced and controlled.
-
Key words:
- geohazard /
- earthquake /
- Jishishan County of Gansu Province /
- loess /
- risk prevention and control
-

-
表 1 距震中10,30,50 km范围地质灾害隐患统计简表
Table 1. Table of geological hazards 10, 30, 50 km from epicentre
距震中距离/km 隐患点数/处 崩塌/处 滑坡/处 泥石流/处 其他/处 威胁人数/人 威胁财产/万元 10 49 3 23 3 20 2639 14833.00 30 472 50 214 91 117 33257 127086.90 50 1296 101 609 241 345 87623 326215.13 表 2 积石山震区地质灾害隐患排查点数
Table 2. Geological hazard investigation in the Jishishan earthquake area
省份 排查地质
灾害数量/处无明显变形的
已有隐患点
数量/处地震加剧变形
的已有隐患点
数量/处地震新引发的
地质灾害
数量/处甘肃省 1142 1015 63 64 青海省 902 863 25 14 合计 2044 1878 88 78 表 3 积石山地震期间变形加剧的地质灾害类型和规模等级
Table 3. Type and scale of geological hazards accelerated by the earthquake
省份 加剧变形
隐患点
数量/处类型 规模 崩塌/处 滑坡/处 特大型/处 大型/处 中型/处 小型/处 甘肃省 63 39 24 1 2 10 50 青海省 25 11 14 0 4 3 18 合计 88 50 38 1 6 13 68 表 4 积石山地震期间变形加剧的地质灾害空间分布与地震烈度关系表
Table 4. Earthquake intensity of geological hazards accelerated by the earthquake
地震烈度 变形加剧灾害点数量/处 占比/% Ⅷ度(8度) 29 33.0 Ⅶ度(7度) 51 57.9 Ⅵ度(6度) 6 6.8 V度(5度) 2 2.3 合计 88 100.00 表 5 积石山地震新引发的地质灾害类型和规模等级
Table 5. Type and scale of geological hazards newly generated by the earthquake
省份 地震新引发地质
灾害数量/处类型 规模 崩塌/处 滑坡/处 泥石流/处 中型/处 小型/处 甘肃省 64 51 12 1 5 59 青海省 14 11 3 0 0 14 合计 78 62 15 1 5 73 表 6 积石山地震新引发的地质灾害与地震烈度关系表
Table 6. Earthquake intensity of newly-generated geological hazards by the earthquake
地震烈度 地震新引发地质灾害数量/处 占比/% Ⅷ度(8度) 15 19.3 Ⅶ度(7度) 54 69.2 Ⅵ度(6度) 9 11.5 合计 78 100.00 表 7 不同地震烈度区新发和变形加剧地质灾害隐患点数量及密度
Table 7. Geological hazard amount and density of different seismic intensity zones
地震烈度区 隐患点数量/个 烈度区面积/km2 隐患点密度/(个·km−2) Ⅷ度(8度) 44 331 0.1329 Ⅶ度(7度) 105 1514 0.0694 Ⅵ度(6度) 15 6519 0.0023 V度(5度) 2 − − -
[1] 殷跃平. 汶川八级地震地质灾害研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2008,16(4):433 − 444. [YIN Yueping. Researches on the geo-hazards triggered by Wenchuan earthquake,Sichuan[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2008,16(4):433 − 444. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YIN Yueping. Researches on the geo-hazards triggered by Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2008, 16(4): 433 − 444. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 黄润秋. 汶川地震地质灾害后效应分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2011,19(2):145 − 151. [HUANG Runqiu. After effect of geohazards induced by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2011,19(2):145 − 151. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HUANG Runqiu. After effect of geohazards induced by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2011, 19(2): 145 − 151. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 裴向军,黄润秋. “4•20”芦山地震地质灾害特征分析[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2013,40(3):257 − 263. [PEI Xiangjun,HUANG Runqiu. Analysis of characteristics of geological hazards by “4•20” Lushan earthquake in Sichuan,China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition),2013,40(3):257 − 263. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2013.03.05
PEI Xiangjun, HUANG Runqiu. Analysis of characteristics of geological hazards by “4•20” Lushan earthquake in Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2013, 40(3): 257 − 263. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2013.03.05
[4] 殷跃平,张永双,马寅生,等. 青海玉树Ms 7.1级地震地质灾害主要特征[J]. 工程地质学报,2010,18(3):289 − 296. [YIN Yueping,ZHANG Yongshuang,MA Yinsheng,et al. Research on major characteristics of geohazards induced by the Yushu Ms 7.1 earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2010,18(3):289 − 296. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YIN Yueping, ZHANG Yongshuang, MA Yinsheng, et al. Research on major characteristics of geohazards induced by the Yushu Ms 7.1 earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2010, 18(3): 289 − 296. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 陈冠,孟兴民,乔良,等. “7•22”岷县漳县地震地质灾害分布、特征及与影响因子间关系分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2013,21(5):750 − 760. [CHEN Guan,MENG Xingmin,QIAO Liang,et al. Distribution,characteristics,and associated influencial factors of the geohazards induced by Minxian-Zhangxian earthquake on 22 July,2013,Gansu,China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2013,21(5):750 − 760. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Guan, MENG Xingmin, QIAO Liang, et al. Distribution, characteristics, and associated influencial factors of the geohazards induced by Minxian-Zhangxian earthquake on 22 July, 2013, Gansu, China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2013, 21(5): 750 − 760. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 殷志强,徐永强,陈红旗,等. 2013年甘肃岷县—漳县Ms 6.6级地震地质灾害展布特征及主控因素研究[J]. 第四纪研究,2015,35(1):88 − 99. [YIN Zhiqiang,XU Yongqiang,CHEN Hongqi,et al. Study on the distribution characteristics of geohazards and the causative tectonic of the Minxian-Zhangxian Ms 6.6 Earthquake on 22 July,2013,Gansu,China[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2015,35(1):88 − 99. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YIN Zhiqiang, XU Yongqiang, CHEN Hongqi, et al. Study on the distribution characteristics of geohazards and the causative tectonic of the Minxian-Zhangxian Ms 6.6 Earthquake on 22 July, 2013, Gansu, China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2015, 35(1): 88 − 99. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 范宣梅,王欣,戴岚欣,等. 2022年Ms 6.8级泸定地震诱发地质灾害特征与空间分布规律研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(5):1504 − 1516. [FAN Xuanmei,WANG Xin,DAI Lanxin,et al. Characteristics and spatial distribution pattern of Ms 6.8 Luding earthquake occurred on September 5,2022[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(5):1504 − 1516. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
FAN Xuanmei, WANG Xin, DAI Lanxin, et al. Characteristics and spatial distribution pattern of Ms 6.8 Luding earthquake occurred on September 5, 2022[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2022, 30(5): 1504 − 1516. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 铁永波,张宪政,卢佳燕,等. 四川省泸定县Ms 6.8级地震地质灾害发育规律与减灾对策[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(6):1 − 12. [TIE Yongbo,ZHANG Xianzheng,LU Jiayan,et al. Characteristics of geological hazards and it’s mitigations of the Ms 6.8 earthquake in Luding County,Sichuan Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(6):1 − 12. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
TIE Yongbo, ZHANG Xianzheng, LU Jiayan, et al. Characteristics of geological hazards and it’s mitigations of the Ms 6.8 earthquake in Luding County, Sichuan Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(6): 1 − 12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 刘甲美,王涛,杜建军,等. 四川泸定Ms 6.8级地震诱发崩滑灾害快速评估[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(2):84 − 94. [LIU Jiamei,WANG Tao,DU Jianjun,et al. Emergency rapid assessment of landslides induced by the Luding Ms 6.8 earthquake in Sichuan of China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(2):84 − 94. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Jiamei, WANG Tao, DU Jianjun, et al. Emergency rapid assessment of landslides induced by the Luding Ms 6.8 earthquake in Sichuan of China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(2): 84 − 94. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 孙东,杨涛,曹楠,等. 泸定Ms 6.8地震同震地质灾害特点及防控建议[J]. 地学前缘,2023,30(3):476 − 493. [SUN Dong,YANG Tao,CAO Nan,et al. Characteristics and mitigation of coseismic geohazards associated with the Luding Ms 6.8 earthquake[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2023,30(3):476 − 493. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SUN Dong, YANG Tao, CAO Nan, et al. Characteristics and mitigation of coseismic geohazards associated with the Luding Ms 6.8 earthquake[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(3): 476 − 493. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 武新宁,易俊梅,周淑丽,等. 尼泊尔Ms 8.1级地震活动构造及次生地质灾害研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(4):137 − 144. [WU Xinning,YI Junmei,ZHOU Shuli,et al. A study on the active faults structures and geohazards triggered by the Ms 8.1earthquake in Nepal[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(4):137 − 144. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WU Xinning, YI Junmei, ZHOU Shuli, et al. A study on the active faults structures and geohazards triggered by the Ms 8.1earthquake in Nepal[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2017, 44(4): 137 − 144. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] YUNUS A P,CHEN Xinyu,CATANI F,et al. Earthquake-induced soil landslides:volume estimates and uncertainties with the existing scaling exponents[J]. Scientific Reports,2023,13(1):8151. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-35088-6
[13] SØRENSEN M B,HAGA T,NESJE A. Earthquake-induced landslides in Norway[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences,2023,23(4):1577 − 1592. doi: 10.5194/nhess-23-1577-2023
[14] PYAKUREL A,DAHAL B K,GAUTAM D. Does machine learning adequately predict earthquake induced landslides?[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering,2023,171:107994. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2023.107994
[15] 廖勇,徐闯,陈军,等. 四川长宁“6•17”地震诱发的次生地质灾害类型及其发育特征[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(1):77 − 83. [LIAO Yong,XU Chuang,CHEN Jun,et al. Types and their characteristics of geological hazards triggered by “6•17” earthquake in Changning,Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(1):77 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIAO Yong, XU Chuang, CHEN Jun, et al. Types and their characteristics of geological hazards triggered by “6•17” earthquake in Changning, Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(1): 77 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 张永双. 我国地震地质灾害特点与监测防治进展[J]. 城市与减灾,2018(3):9 − 18. [ZHANG Yongshuang. Characteristics of earthquake induced geological disasters in China and their progress of monitoring,prevention and control [J]. City and disaster reduction. 2018(3):9 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Yongshuang. Characteristics of earthquake induced geological disasters in China and their progress of monitoring, prevention and control [J]. City and disaster reduction. 2018(3): 9 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 李智敏,李延京,田勤俭,等. 拉脊山断裂古地震与喇家遗址灾变事件关系研究[J]. 地震研究,2014,37(增刊1):109 − 115. [LI Zhimin,LI Yanjing,TIAN Qinjian,et al. Study on the relationship between Paleoseismic on Laji Mountain fault and Catastrophic event on Lajiashan site[J]. Journal of seismological research,2014,37(Sup 1):109 − 115. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Zhimin, LI Yanjing, TIAN Qinjian, et al. Study on the relationship between Paleoseismic on Laji Mountain fault and Catastrophic event on Lajiashan site[J]. Journal of seismological research, 2014, 37(Sup 1): 109 − 115. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 国家自然灾害防治研究院. 甘肃临夏州积石山县6.2级地震发震构造环境分析[Z/OL]. (2023-12-20) [2023-12-24] [National Institute of Natural Hazards. Analysis of the seismogenic tectonic environment of the Ms 6.2 earthquake in Jishishan County,Linxia Prefecture,Gansu Province[Z/OL]. (2023-12-20) [2023-12-24]. (in Chinese)]
National Institute of Natural Hazards. Analysis of the seismogenic tectonic environment of the Ms 6.2 earthquake in Jishishan County, Linxia Prefecture, Gansu Province[Z/OL]. (2023-12-20) [2023-12-24]. (in Chinese)
[19] 中华人民共和国应急管理部. 甘肃积石山6.2级地震烈度图[Z/OL]. (2023-12-22)[2023-12-24] [Ministry of Emergency Management of the People’s Republic of China. Gansu Jishishan Ms 6.2 earthquake intensity map[Z/OL]. (2023-12-22)[2023-12-24]. (in Chinese)]
Ministry of Emergency Management of the People’s Republic of China. Gansu Jishishan Ms 6.2 earthquake intensity map[Z/OL]. (2023-12-22)[2023-12-24]. (in Chinese)
[20] 中国地质环境监测院. 甘肃临夏州积石山县震区6.2级地震地质灾害监测预警智能速报[R]. 2023. [China Institute of Geo-Environment Mornitoring. Intelligent quick report on monitoring and early warning of 6.2 earthquake geological hazards in Jishishan County,Linxia Prefecture,Gansu Province[R]. 2023. (in Chinese)]
China Institute of Geo-Environment Mornitoring. Intelligent quick report on monitoring and early warning of 6.2 earthquake geological hazards in Jishishan County, Linxia Prefecture, Gansu Province[R]. 2023. (in Chinese)
[21] 甘肃工程地质研究院. 甘肃省临夏州积石山县地质灾害详细调查报告[R]. 2014. [Gansu Institute of Engineering Geology. Detailed investigation report on geological hazards in Jishishan County,Linxia Prefecture,Gansu Province[R]. 2014. (in Chinese)]
Gansu Institute of Engineering Geology. Detailed investigation report on geological hazards in Jishishan County, Linxia Prefecture, Gansu Province[R]. 2014. (in Chinese)
-




 下载:
下载: