Application of SBAS-InSAR technology to analyze the evolution characteristics and cause of ground subsidence in Sanhe City, Hebei Province
-
摘要:
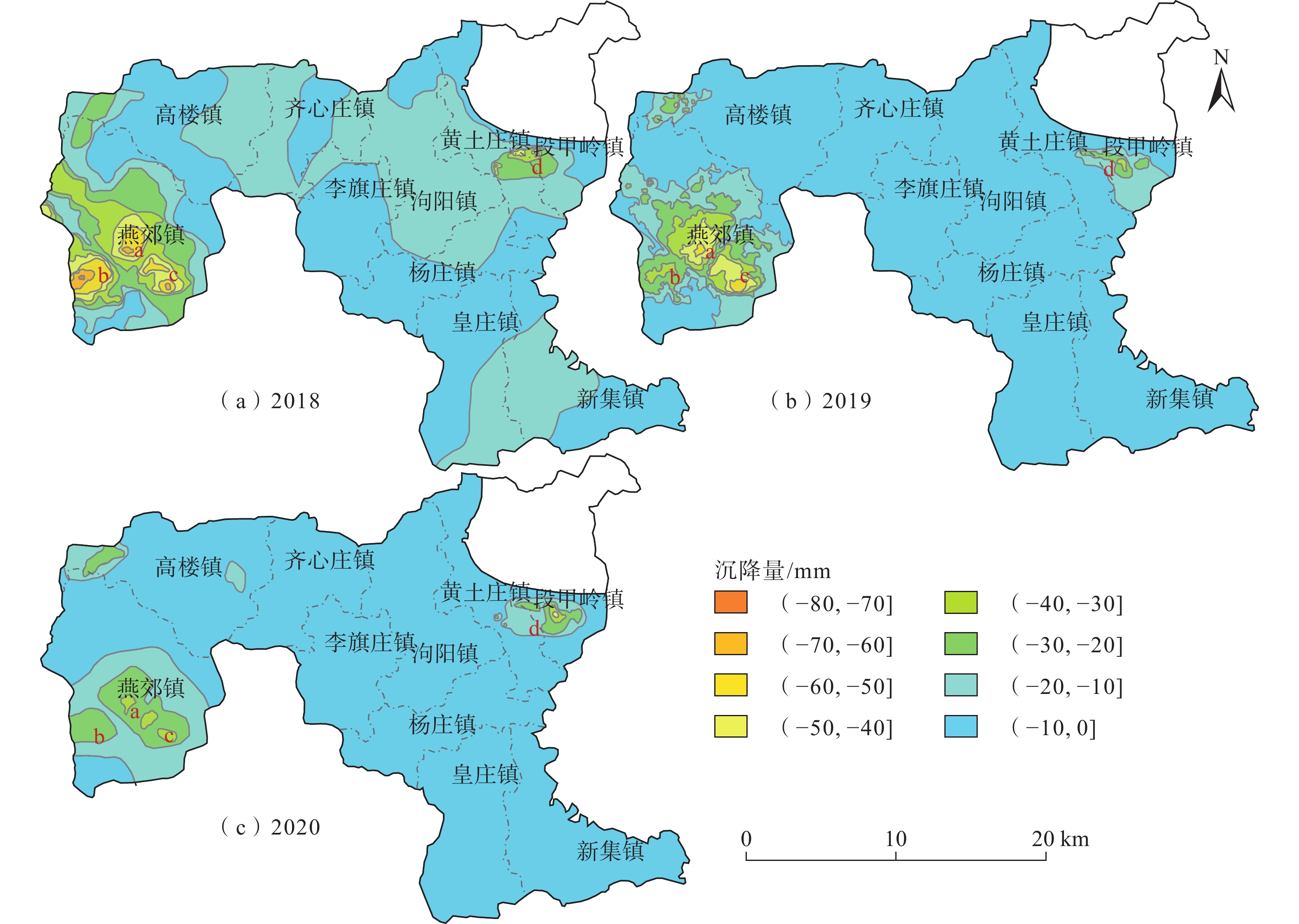
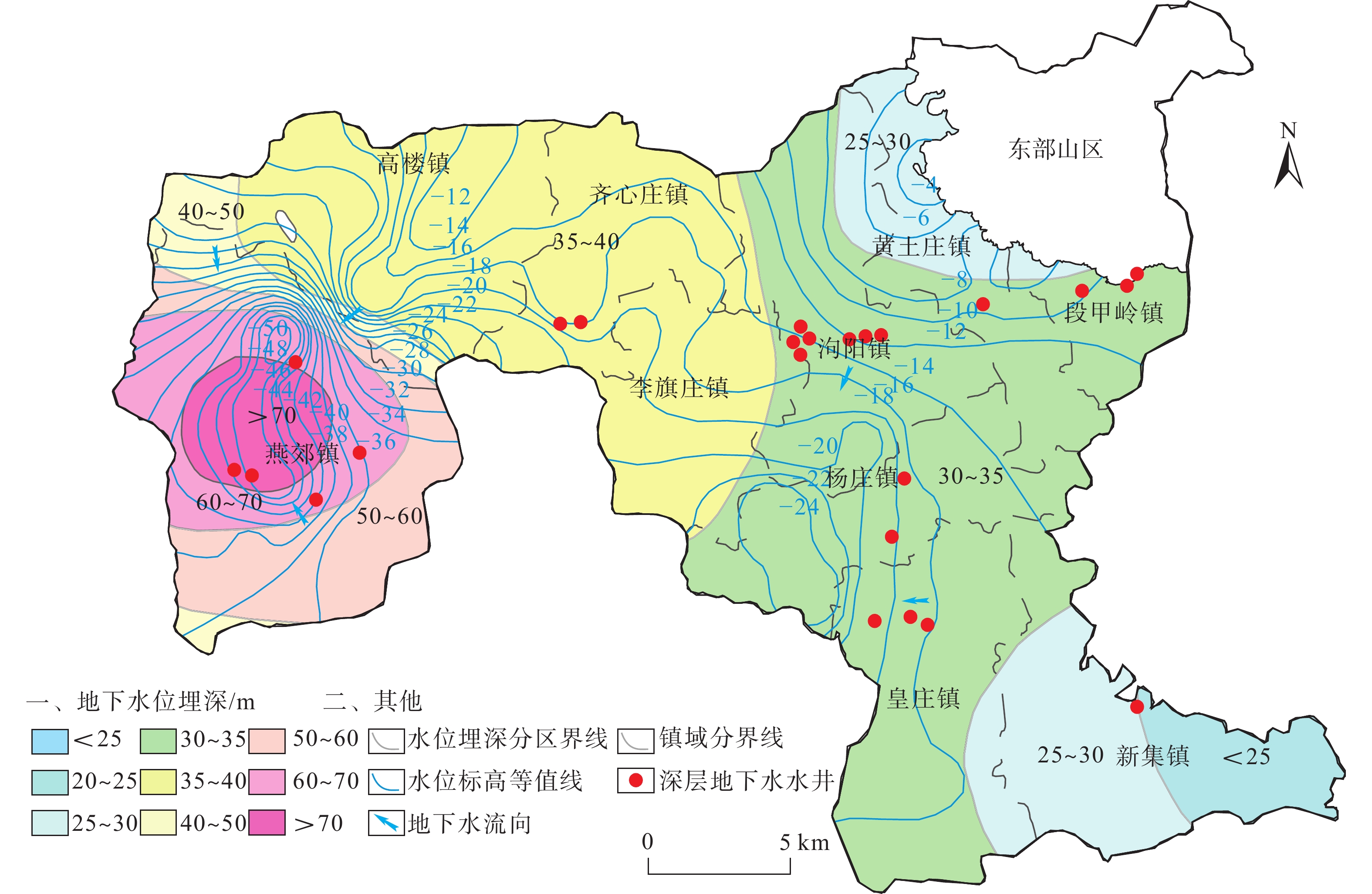
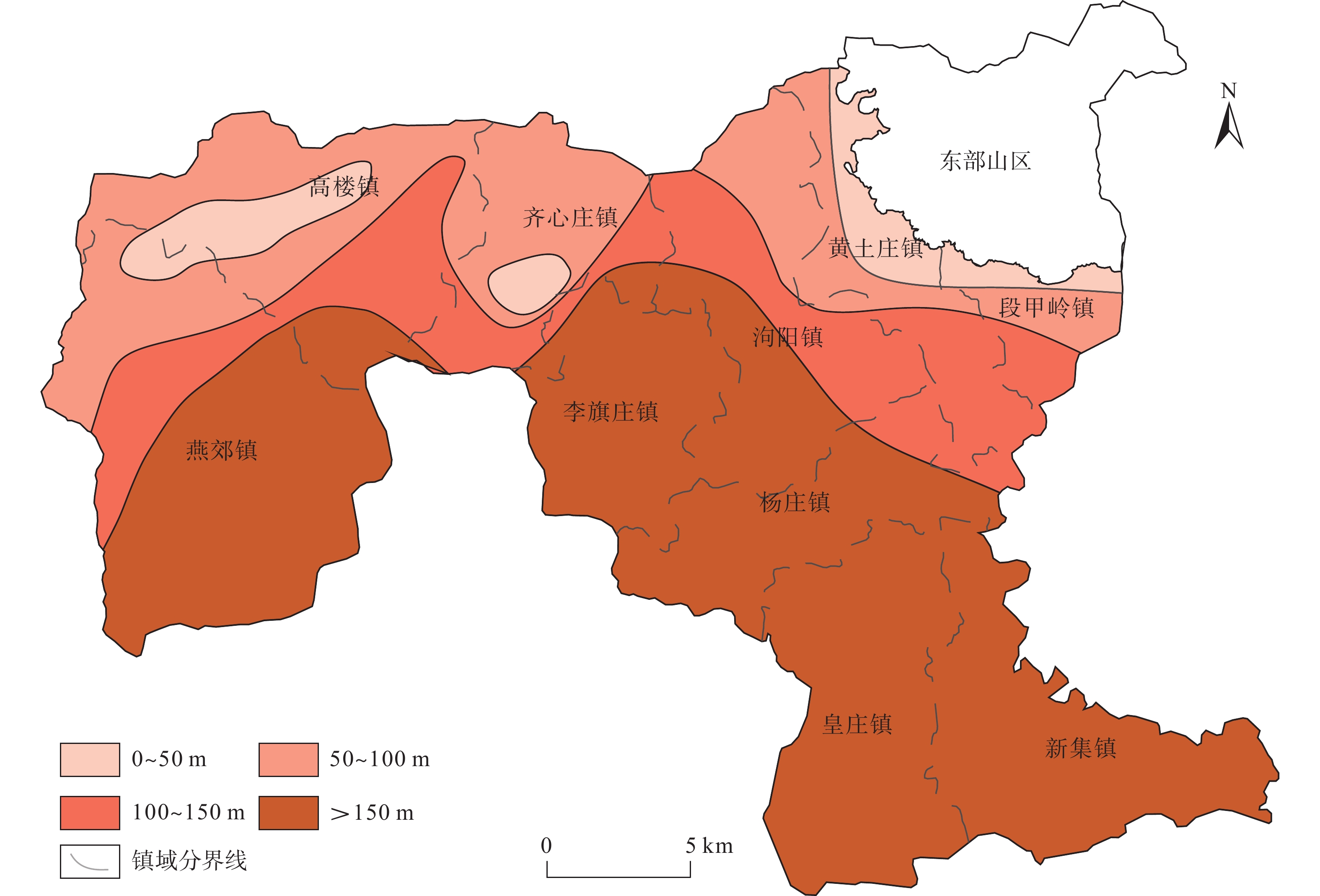
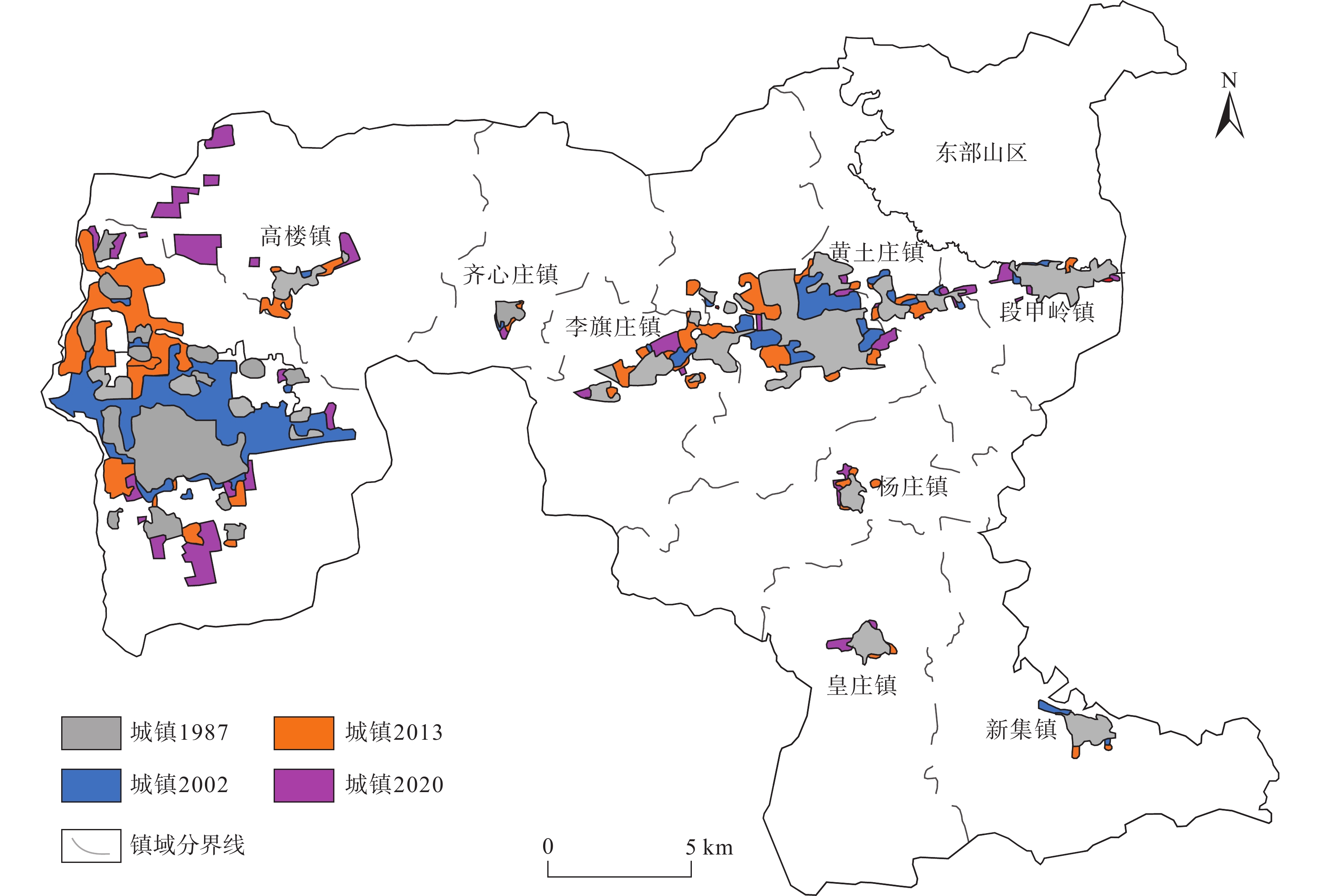
2003—2016年,三河市地面沉降速率逐步加大,其中燕郊地区地面沉降最严重,已和北京通州沉降区连成一片,2016年之后三河市地面沉降灾害的发展变化趋势尚不明确。随着京津冀一体化发展、北京城市副中心建设等国家政策的出台,查明三河市地面沉降灾害的发展演化特征并分析成因对保障三河市的城市安全和可持续发展至关重要。文章采用SBAS-InSAR技术解译三河市2018—2020年地面沉降发展演化特征,同时分析了导致三河市地面沉降的几个诱发因素,总结沉降原因。通过本次研究,掌握了三河市地面沉降灾害的空间分布及演化特征:三河市地面沉降在空间上呈现西部严重,东部较缓,发育重点沉降区的总体特征;主要发育有2个重点沉降区,分别为含3个沉降漏斗的燕郊镇沉降区和含1个沉降漏斗的段甲岭镇沉降区,其中燕郊镇沉降区为三河市地面沉降最为严重的区域;2018—2020年,三河市地面沉降灾害总体呈现减缓趋势。同时通过对比分析,三河市地下水的严重超采、土层性质、城镇化发展及人口激增是三河市地面沉降灾害发生及发展的主要因素。研究成果将为该区域地面沉降灾害的防治提供参考。
Abstract:According to studies by relevant scholars, the ground subsidence rate in Sanhe City, Hebei, increased gradually from 2003 to 2016, with the most severe subsidence observed in the Yanjiao area , which has become contiguous with the subsidence area in Tongzhou, Beijing. However, the development trend of ground subsidence disasters in Sanhe City after 2016 remains unclear. With the implementation of national policies such as the integration of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and the construction of Beijing’s sub-center, it is crucial to identify the development and evolution characteristics of land subsidence disasters in Sanhe City and analyze their causes to ensure the urban safety and sustainable development of Sanhe City. In this context, the authors used SBAS-InSAR technology to interpret the evolution characteristics of ground subsidence in Sanhe City from 2018 to 2020, and analyzed several inducing factors that led to land subsidence in Sanhe City, summarizing the main causes. Through this study, the spatial distribution and evolutionary characteristics of land subsidence disasters in Sanhe City were grasped: the western part of the city exhibits severe subsidence, while the eastern part is less affected, with a focus on the overall characteristics of key subsidence areas. Two main subsidence areas were identified, namely, the Yanjiao Town subsidence area with three subsidence funnels and the DuanJialing town subsidence area with one subsidence funnel, with the former being the most severely affected. From 2018 to 2020, the overall trend of ground subsidence disasters in Sanhe City showed a slowdown. Through comparative analysis, it was determined that severe overexploitation of groundwater, soil properties, urbanization development, and population growth are the main factors contributing to the occurrence and development of ground subsidence disasters in Sanhe City. The research results of this paper will provide reference for the prevention and control of ground subsidence disasters in the region.
-
Key words:
- Sanhe City /
- SBAS InSAR /
- ground subsidence /
- groundwater overexploitation /
- urbanization development /
- cause analysis.
-

-
表 1 2016年三河市各乡镇地下水开发利用简表
Table 1. Summary of groundwater development and utilization invarious townships of Sanhe City in the year 2016
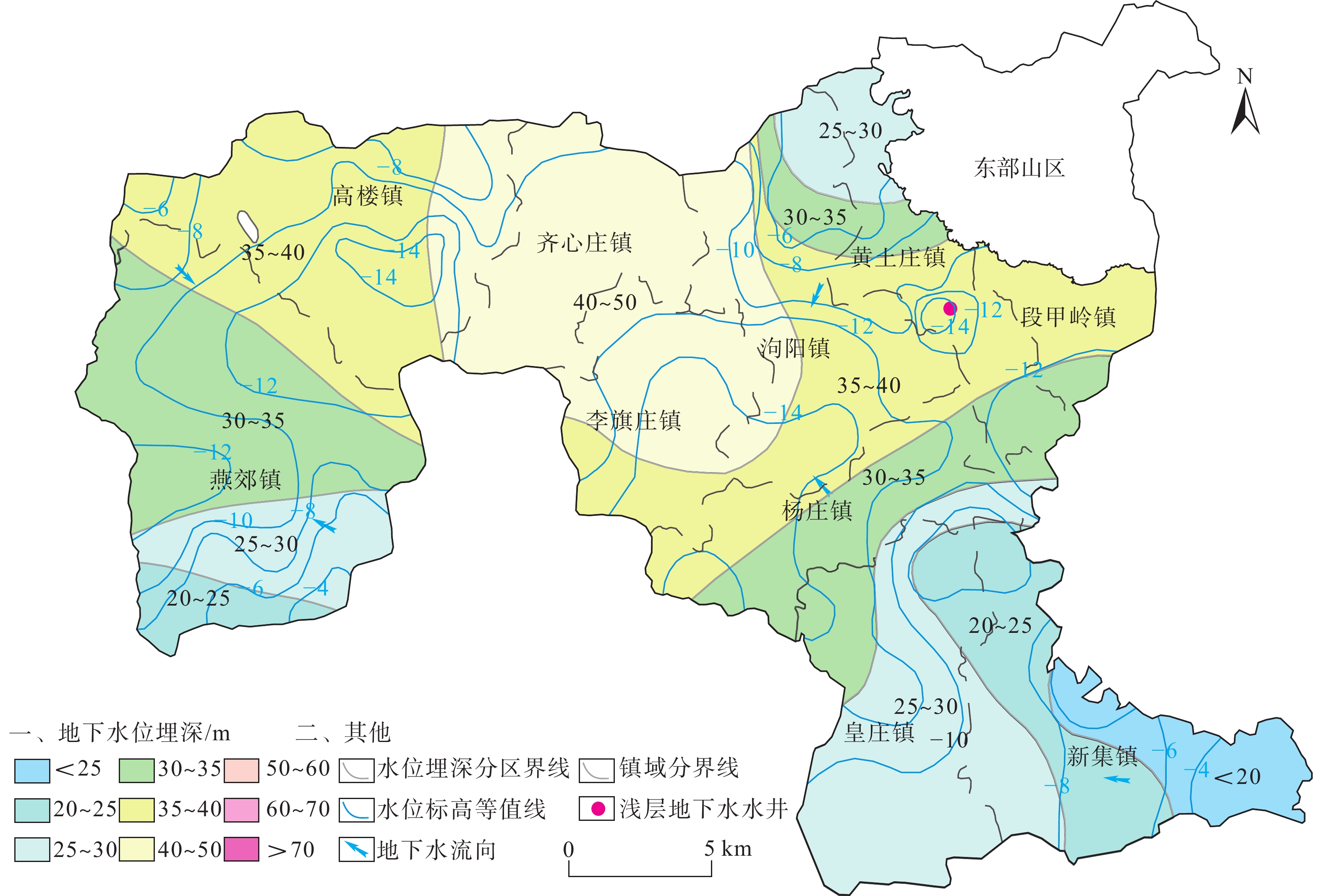
乡镇 生活用水 农业用水 工业用水 浅层开采量 深层开采量 基岩开采量 总开采量 深层 基岩 浅层 深层 基岩 燕郊镇 5123.94 0 480.06 1070.57 0 480.06 6194.51 0 6674.57 泃阳镇 513.12 0 961.84 266.94 0 961.84 780.06 0 1741.9 高楼镇 176.48 2945.04 914.79 0 0 914.79 176.48 2945.04 4036.31 齐心庄镇 120.67 18.03 688.09 0 330.46 688.09 120.67 348.49 1157.25 段甲岭镇 63.8 56.11 448.46 0 0 448.46 63.8 56.11 568.37 李旗庄镇 138.7 0 487.69 0 0 487.69 138.7 0 626.39 黄土庄镇 247.11 0 1072.13 0 0 1072.13 247.11 0 1319.24 杨庄镇 202.94 0 696.02 0 0 696.02 202.94 0 898.96 皇庄镇 268.22 0 964.47 0 0 964.47 268.22 0 1232.69 新集镇 328.83 0 1098.45 0 0 1098.45 328.83 0 1427.28 合计 10202.99 7812 1667.97 7812 8521.32 3349.64 19683 注:单位为104 m3。 -
[1] 张拴宏,纪占胜. 合成孔径雷达干涉测量(InSAR)在地面形变监测中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2004,15(1):112 − 117. [ZHANG Shuanhong,JI Zhansheng. A review on the application of interferometric synthetic aperture radar on surface deformation monitoring[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2004,15(1):112 − 117. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2004.01.024
ZHANG Shuanhong, JI Zhansheng. A review on the application of interferometric synthetic aperture radar on surface deformation monitoring[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2004, 15(1): 112 − 117. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2004.01.024
[2] 许文斌,李志伟,丁晓利,等. 利用InSAR短基线技术估计洛杉矶地区的地表时序形变和含水层参数[J]. 地球物理学报,2012,55(2):452 − 461. [XU Wenbin,LI Zhiwei,DING Xiaoli,et al. Application of small baseline subsets D-InSAR technology to estimate the time series land deformation and aquifer storage coefficients of LosAngeles area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2012,55(2):452 − 461. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.02.009
XU Wenbin, LI Zhiwei, DING Xiaoli, et al. Application of small baseline subsets D-InSAR technology to estimate the time series land deformation and aquifer storage coefficients of LosAngeles area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(2): 452 − 461. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.02.009
[3] GABRIEL A K,GOLDSTEIN R M,ZEBKER H A. Mapping small elevation changes over large areas:Differential radar interferometry[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,1989,94(B7):9183 − 9191. doi: 10.1029/JB094iB07p09183
[4] FERRETTI A,PRATI C,ROCCA F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2001,39(1):8 − 20. doi: 10.1109/36.898661
[5] BERARDINO P,FORNARO G,LANARI R,et al. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2002,40(11):2375 − 2383. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.803792
[6] 罗三明,杜凯夫,畅柳,等. 基于PS-InSAR方法反演北京地区地表沉降速率[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,2014,34(1):43 − 46. [LUO Sanming,DU Kaifu,CHANG Liu,et al. Ground subsidence rates of Beijing area inversed by PS-InSAR analysis[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,2014,34(1):43 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.14075/j.jgg.2014.01.024
LUO Sanming, DU Kaifu, CHANG Liu, et al. Ground subsidence rates of Beijing area inversed by PS-InSAR analysis[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2014, 34(1): 43 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.14075/j.jgg.2014.01.024
[7] 郭海朋,白晋斌,张有全,等. 华北平原典型地段地面沉降演化特征与机理研究[J]. 中国地质,2017,44(6):1115 − 1127. [GUO Haipeng,BAI Jinbin,ZHANG Youquan,et al. The evolution characteristics and mechanism of the land subsidence in typical areas of the north China Plain[J]. Geology in China,2017,44(6):1115 − 1127. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.12029/gc20170606
GUO Haipeng, BAI Jinbin, ZHANG Youquan, et al. The evolution characteristics and mechanism of the land subsidence in typical areas of the north China Plain[J]. Geology in China, 2017, 44(6): 1115 − 1127. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12029/gc20170606
[8] 周旭,许才军,温扬茂. 利用时序InSAR技术分析北京及河北廊坊地面沉降[J]. 测绘科学,2017,42(7):89 − 93. [ZHOU Xu,XU Caijun,WEN Yangmao. Land subsidence monitoring of Beijing and Langfang of Hebei Prouince by time series InSAR[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping,2017,42(7):89 − 93. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2017.07.015
ZHOU Xu, XU Caijun, WEN Yangmao. Land subsidence monitoring of Beijing and Langfang of Hebei Prouince by time series InSAR[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2017, 42(7): 89 − 93. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2017.07.015
[9] 李海君,张耀文,杨月巧,等. 廊坊北三县地区地面沉降时空分布特征与成因分析[J]. 科学技术与工程,2018,18(11):23 − 30. [LI Haijun,ZHANG Yaowen,YANG Yueqiao,et al. Spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and causation analysis of land subsidence in three northern counties area of Langfang[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2018,18(11):23 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.11.003
LI Haijun, ZHANG Yaowen, YANG Yueqiao, et al. Spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and causation analysis of land subsidence in three northern counties area of Langfang[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2018, 18(11): 23 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.11.003
[10] 李广宇,张瑞,刘国祥,等. Sentinel-1A TS-DInSAR京津冀地区沉降监测与分析[J]. 遥感学报,2018,22(4):633 − 646. [LI Guangyu,ZHANG Rui,LIU Guoxiang,et al. Land subsidence detection and analysis over Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei area based on Sentinel-1A TS-DInSAR[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing,2018,22(4):633 − 646. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Guangyu, ZHANG Rui, LIU Guoxiang, et al. Land subsidence detection and analysis over Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei area based on Sentinel-1A TS-DInSAR[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2018, 22(4): 633 − 646. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 刘毅. 地面沉降研究的新进展与面临的新问题[J]. 地学前缘,2001,8(2):273 − 278. [LIU Yi. Land subsidence research approaches and advent problems[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2001,8(2):273 − 278. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2001.02.009
LIU Yi. Land subsidence research approaches and advent problems[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2001, 8(2): 273 − 278. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2001.02.009
[12] 葛伟丽,李元杰,张春明,等. 基于InSAR技术的内蒙古巴彦淖尔市地面沉降演化特征及成因分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(4):198 − 206. [GE Weili, LI Yuanjie, ZHANG Chunming, et al. An attribution analysis of land subsidence features in the city of Bayannur in Inner Mongolia based on InSAR[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(4):198 − 206. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GE Weili, LI Yuanjie, ZHANG Chunming, et al. An attribution analysis of land subsidence features in the city of Bayannur in Inner Mongolia based on InSAR[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(4): 198 − 206. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 何庆成,刘文波,李志明. 华北平原地面沉降调查与监测[J]. 高校地质学报,2006,12(2):195 − 209. [HE Qingcheng,LIU Wenbo,LI Zhiming. Investigation and monitoring of land subsidence in north China Plain[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2006,12(2):195 − 209. (in Chinese)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2006.02.006
HE Qingcheng, LIU Wenbo, LI Zhiming. Investigation and monitoring of land subsidence in north China Plain[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2006, 12(2): 195 − 209. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2006.02.006
[14] 侯安业,张景发,刘斌,等. PS-InSAR与SBAS-InSAR监测地表沉降的比较研究[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,2012,32(4):125 − 128. [HOU Anye,ZHANG Jingfa,LIU Bin,et al. Comparative study on monitoring surface subsidence with PS-InSAR and SBAS-InSAR[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,2012,32(4):125 − 128. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5942.2012.04.029
HOU Anye, ZHANG Jingfa, LIU Bin, et al. Comparative study on monitoring surface subsidence with PS-InSAR and SBAS-InSAR[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2012, 32(4): 125 − 128. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5942.2012.04.029
[15] MASSONNET D,HOLZER T,VADON H. Land subsidence caused by the East Mesa Geothermal Field,California,observed using SAR interferometry[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,1997,24(8):901 − 904. doi: 10.1029/97GL00817
[16] 张凯翔,张占荣,于宪煜. SBAS-InSAR和PS-InSAR技术在鲁西南某线性工程沿线地面沉降成因分析中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(4):65 − 76. [ZHANG Kaixiang,ZHANG Zhanrong,YU Xianyu. Application of SBAS-InSAR and PS-InSAR technologies in analysis of landslide subsidence along a linear infrastructure in southwestern Shandong[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(4):65 − 76. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Kaixiang, ZHANG Zhanrong, YU Xianyu. Application of SBAS-InSAR and PS-InSAR technologies in analysis of landslide subsidence along a linear infrastructure in southwestern Shandong[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(4): 65 − 76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 张进才,沈荣辉,褚立峰. 河北平原地面沉降监测网络体系建设[R]. 中国地质学会,2006. [ZHANG Jincai,SHEN Ronghui,CHU Lifeng. Construction of land subsidence monitoring network system in Hebei Plain[R]. Geological Society of China,2006 .(in Chinese)]
ZHANG Jincai, SHEN Ronghui, CHU Lifeng. Construction of land subsidence monitoring network system in Hebei Plain[R]. Geological Society of China, 2006 .(in Chinese)
[18] 戴真印,刘岳霖,张丽平,等. 基于改进时序InSAR技术的东莞地面沉降时空演变特征[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(1):58 − 67. [DAI Zhenyin,LIU Yuelin,ZHANG Liping,et al. Spatial-temporal evolution characteristics of land subsidence in Dongguan City based on improved InSAR technology[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(1):58 − 67. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
DAI Zhenyin, LIU Yuelin, ZHANG Liping, et al. Spatial-temporal evolution characteristics of land subsidence in Dongguan City based on improved InSAR technology[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(1): 58 − 67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 刘贺, 罗勇, 雷坤超, 等. 北京新航城地区地面沉降演化规律及多源监测方法对比研究[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(1):398 − 406. [LIU He, LUO Yong, LEI Kunchao, et al. Evolution of land subsidence and comparative study on multi-source monitoring methods in New Airlines City of Beijing[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(1):398 − 406. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU He, LUO Yong, LEI Kunchao, et al. Evolution of land subsidence and comparative study on multi-source monitoring methods in New Airlines City of Beijing[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 398 − 406. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 程蕊, 朱琳, 周佳慧, 等. 北京潮白河冲洪积扇地面沉降时空异质性特征及驱动因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2021,51(4):1182 − 1192. [CHENG Rui, ZHU Lin, ZHOU Jiahui, et al. Spatio-temporal heterogeneity and driving factors of land subsidence in middle-lower part of Chaobai River alluvial fan[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition),2021,51(4):1182 − 1192. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHENG Rui, ZHU Lin, ZHOU Jiahui, et al. Spatio-temporal heterogeneity and driving factors of land subsidence in middle-lower part of Chaobai River alluvial fan[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1182 − 1192. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 成建梅, 柳璨, 李敏敏, 等. 城市化进程下北京平原渗流场与地面沉降发展演化模拟[J]. 地质科技通报,2020,39(1):43 − 52. [CHENG Jianmei, LIU Can, LI Minmin, et al. Numerical study on evolution of groundwater hydrodynamics and land subsidence under the process of metropolitan urbanization in Beijing Plain, China[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2020,39(1):43 − 52. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHENG Jianmei, LIU Can, LI Minmin, et al. Numerical study on evolution of groundwater hydrodynamics and land subsidence under the process of metropolitan urbanization in Beijing Plain, China[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 43 − 52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 狄胜同. 地下水开采导致地面沉降全过程宏细观演化机理及趋势预测研究[D]. 济南:山东大学,2020. [DI Shengtong. Study on macro-meso evolution mechanism and trend prediction of land subsidence caused by groundwater exploitation in the whole process[D]. Jinan:Shandong University,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
DI Shengtong. Study on macro-meso evolution mechanism and trend prediction of land subsidence caused by groundwater exploitation in the whole process[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 王云龙,陈晔,郭海朋,等. 沧州地区土层固结特征与地面沉降临界水位研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(4):185 − 192. [WANG Yunlong, CHEN Ye, GUO Haipeng, et al. A study of the critical groundwater level related to soil consolidation characteristics of land subsidence in Cangzhou[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(4):185 − 192. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Yunlong, CHEN Ye, GUO Haipeng, et al. A study of the critical groundwater level related to soil consolidation characteristics of land subsidence in Cangzhou[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(4): 185 − 192. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 殷跃平,张作辰,张开军. 我国地面沉降现状及防治对策研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2005,16(2):1 − 8. [YIN Yueping,ZHANG Zuochen,ZHANG Kaijun. Land subsidence and countermeasures for its prevention in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2005,16(2):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2005.02.001
YIN Yueping, ZHANG Zuochen, ZHANG Kaijun. Land subsidence and countermeasures for its prevention in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2005, 16(2): 1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2005.02.001
[25] 张田田, 杨为民, 万飞鹏. 浑河断裂带地质灾害发育特征及其成因机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2022,52(1):149 − 161. [ZHANG Tiantian, YANG Weimin, WAN Feipeng. Characteristics and formation mechanism of geohazards in Hunhe fault zone[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2022,52(1):149 − 161. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Tiantian, YANG Weimin, WAN Feipeng. Characteristics and formation mechanism of geohazards in Hunhe fault zone[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2022, 52(1): 149 − 161. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: