Analysis on factors controlling shallow failures of the cut slopes and its prevention by bio-engineering measures: A case study of the cut slopes along the highway from Shuangcheng to Dajiali
-
摘要:
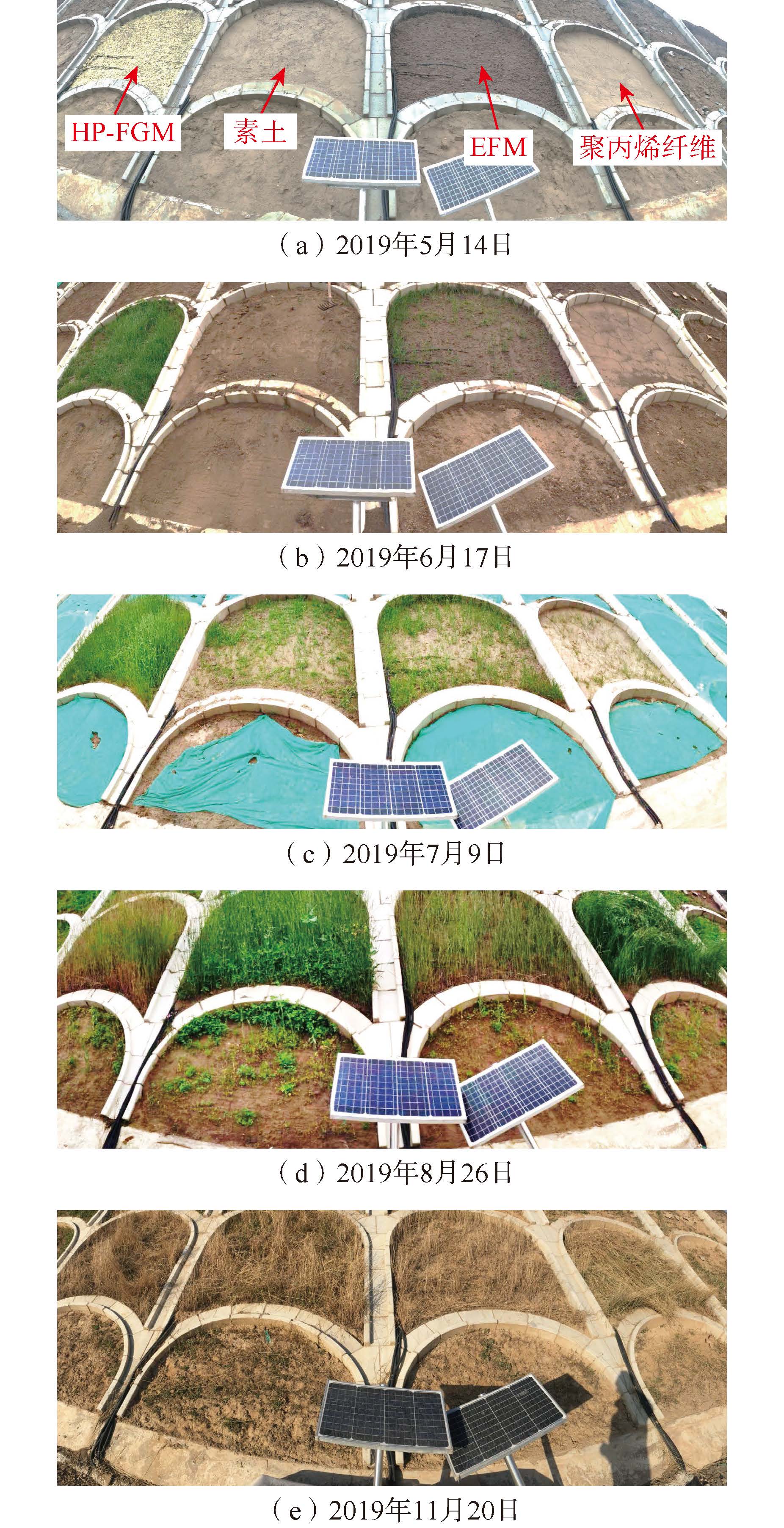
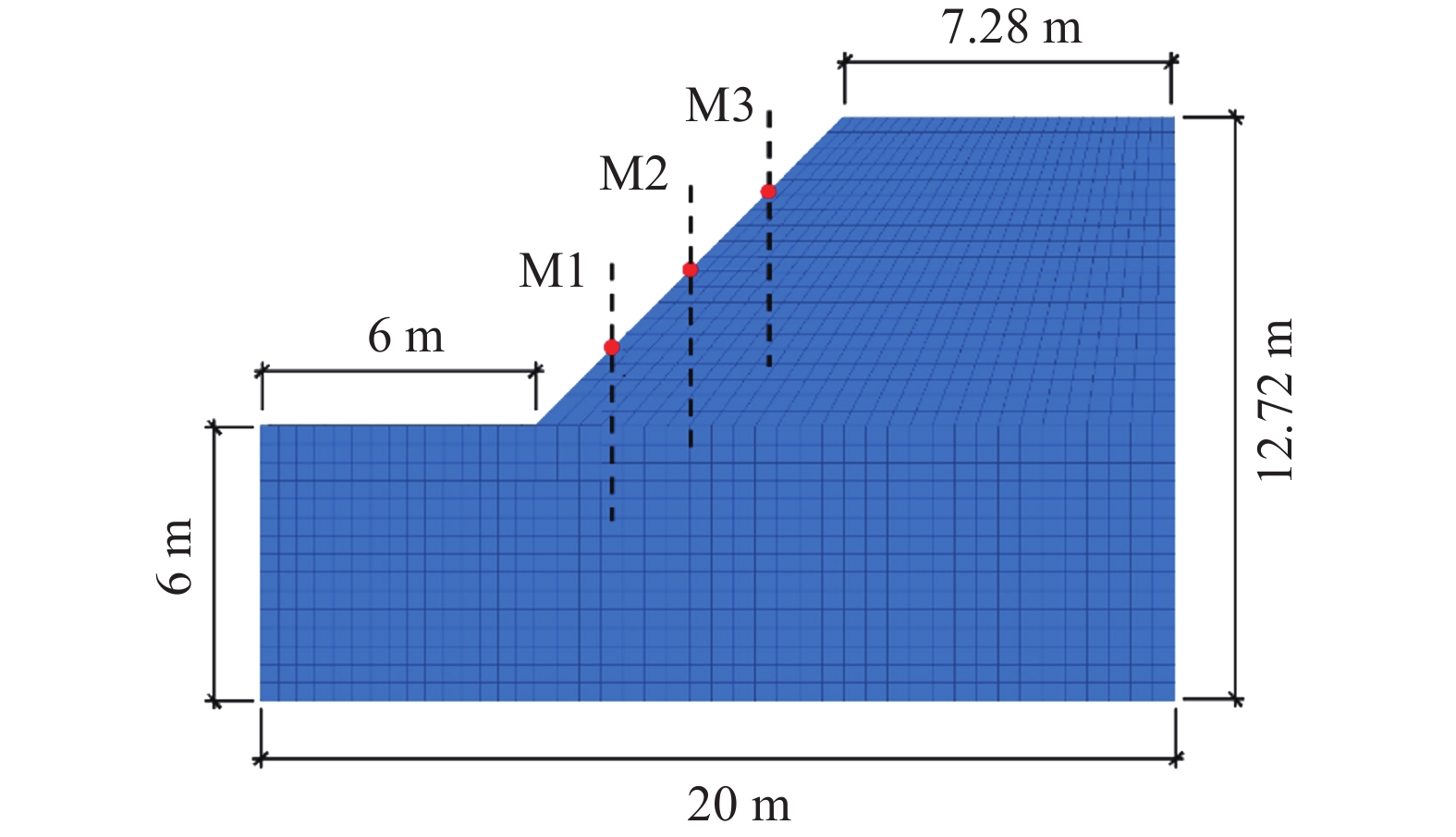
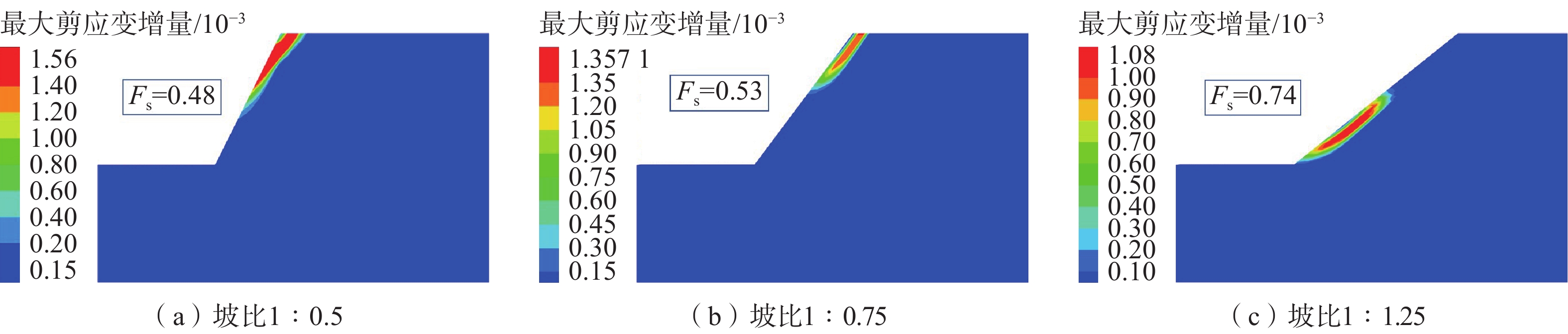
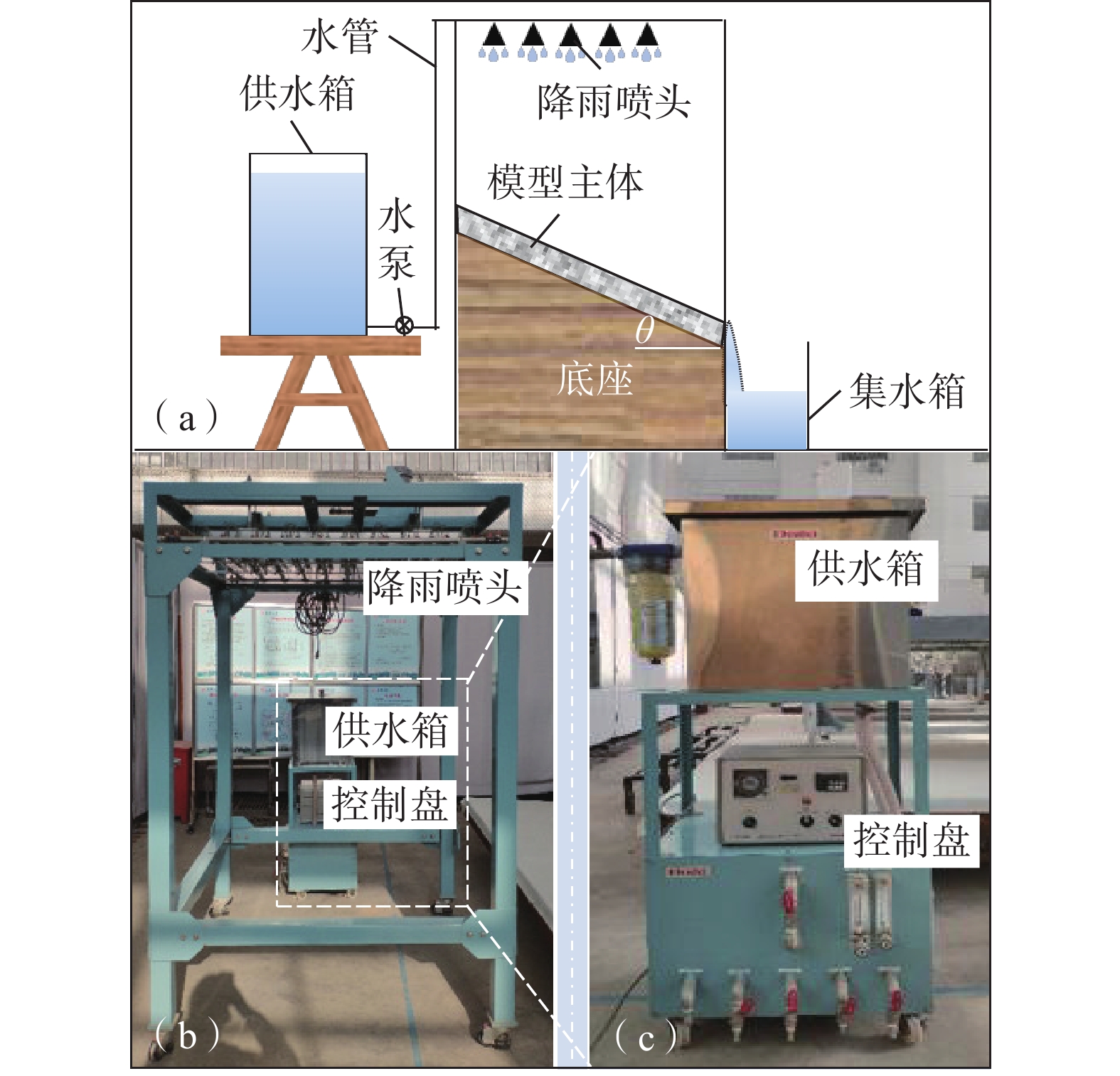
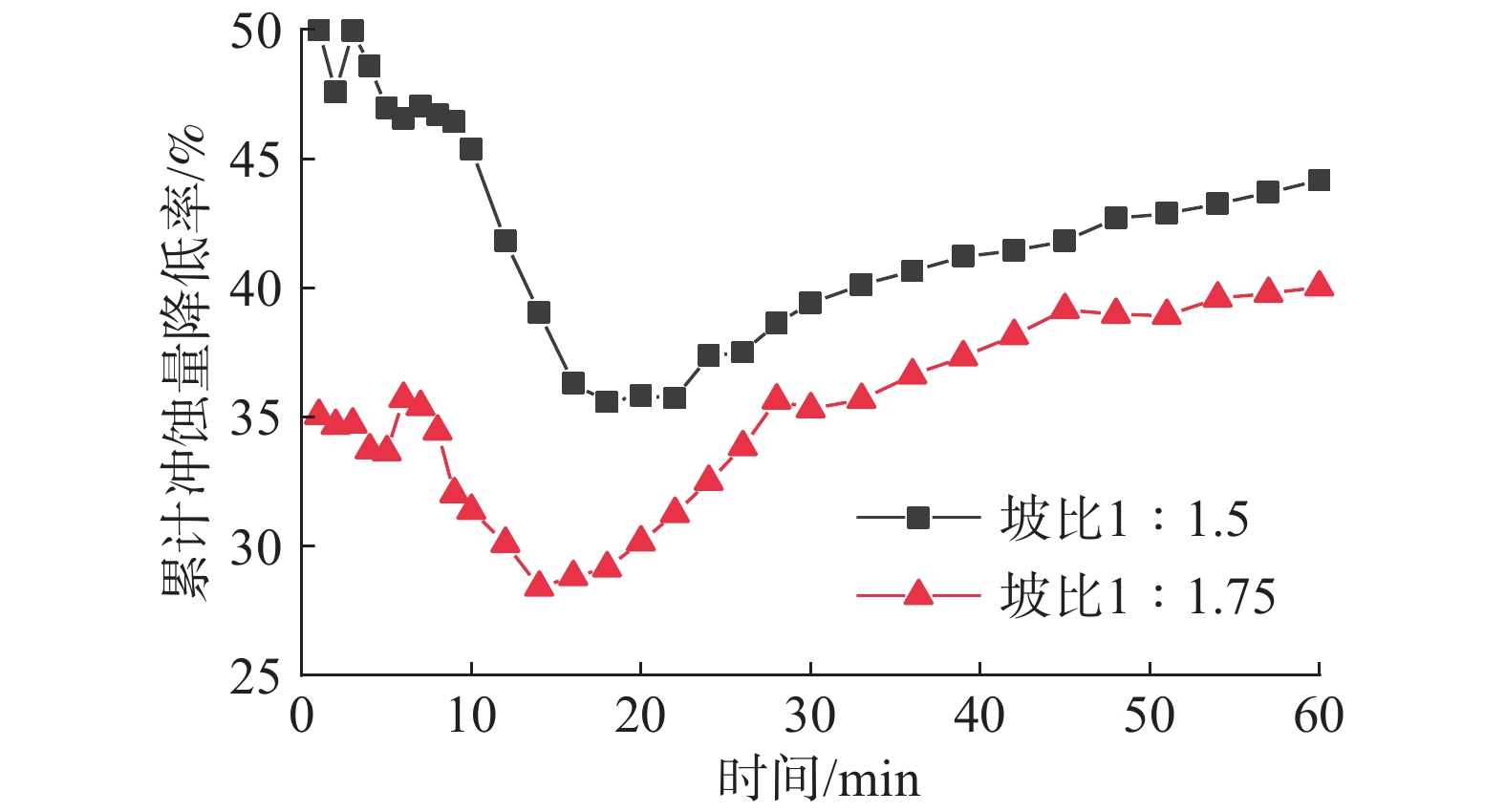
有效掌握边坡浅层塌滑机制及其影响因素的主次关系是开展路堑边坡变形预测及塌滑治理的重要前提。为此,以阵雨条件下甘肃省双达高速某路堑边坡为研究对象,首先通过FLAC3D有限元软件平台编写FISH语言,实现饱和度、重度和土体抗剪强度之间的动态关联,然后求解不同降雨强度、坡比和降雨历时条件下路堑边坡的安全系数,并基于灰色关联理论确定路堑边坡浅层塌滑主要外界因素的主次关系,最后通过室内降雨试验和现场生态防护试验总结出路堑边坡浅层塌滑机制,提出浅层塌滑生态防治措施。研究表明:降雨过程中,路堑边坡破坏模式由深层整体滑动向浅层局部滑动演化,且随坡比的降低,浅层塌滑区域由路堑边坡的坡肩部位向坡脚部位演化;相比降雨强度和降雨历时,坡比对路堑边坡浅层塌滑影响性最大;降雨过程中,路堑边坡浅层土体累计冲蚀率随时间呈现出先降低后增加的趋势,设置拱骨架和降低坡比均能提高路堑边坡浅层土体的抗塌滑能力;相比HP-FGM和EFM防护材料,聚丙烯纤维土防护材料时效性最理想,路堑边坡浅层塌滑生态治理效果最好。
Abstract:Understanding the primary and secondary relations of influencing factors is crucial for predicting deformation and controlling collapse in cutting slopes. Using a cutting slope along the Shuangcheng to Dalijia expressway in Gansu Province as the research object, this research utilized the FLAC3D finite element software platform to establish dynamic correlations between saturation, gravity, and soil shear strength through FISH language. Based on this, safety factors of the cutting slope were calculated under different rainfall intensities, slope ratios, and rainfall duration. Grey relational theory was applied to determine the primary and secondary relationships of key factors affecting shallow collapse of cutting slopes under rainfall conditions. Indoor rainfall experiments and on-site ecological protection tests were conducted to summarize the shallow collapse mechanism and propose the environmental control measures. The study revealed that the failure mode of cutting slopes transitioned from deep overall sliding to shallow local sliding during rainfall. As the slope ratio decreased, the shallow collapse area gradually shifted from the slope shoulder to the foot of the cutting slope. Cumulative erosion rates of shallow soil in cutting slopes decreased initially and then increased over time during rainfall. Installing arch skeletons and reducing the slope ratio enhanced the cutting slope's resistance against shallow collapses. Among with the protective materials, polypropylene fiber-reinforced soil protective materials exhibited the best timeliness and ecological control effect for shallow collapses of cutting slopes compared to HP-FGM and EFM materials.
-
Key words:
- cutting slope /
- safety factor /
- grey correlation theory /
- numerical simulation /
- shallow collapse
-

-
图 9 降雨60 min时坡面(据文献[14]修改)
Figure 9.
表 1 土体材料参数
Table 1. Basic physical parameters of undisturbed soil
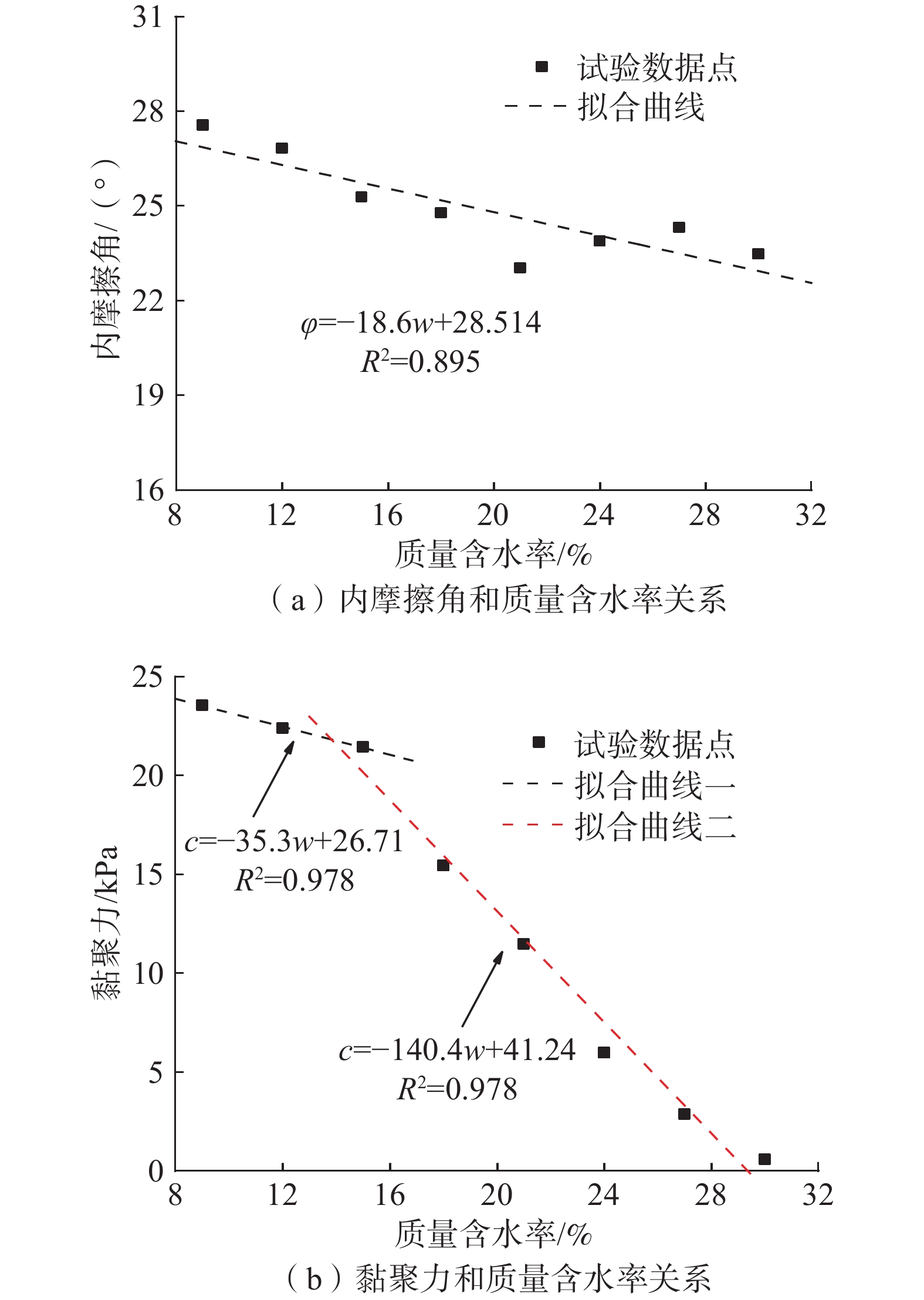
弹性模量
/MPa泊松比 密度
/(g·cm−3)渗透系数
/(cm·s−1)有效黏聚力
/kPa有效内摩擦
角/(°)12.00 0.3 1.88 4.5×10-5 26.7 28.5 表 2 VG模型参数
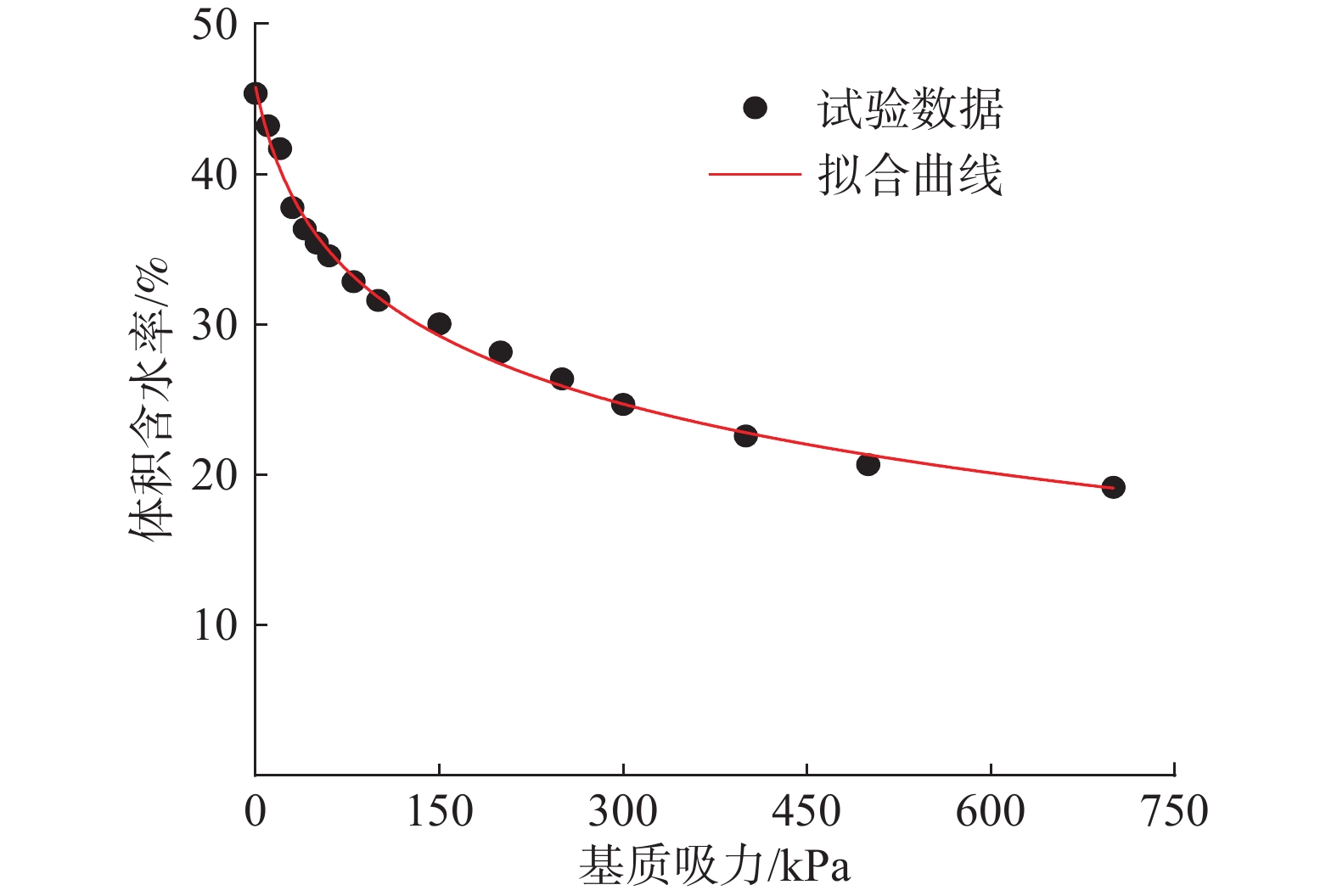
Table 2. Summary table of VG model parameters
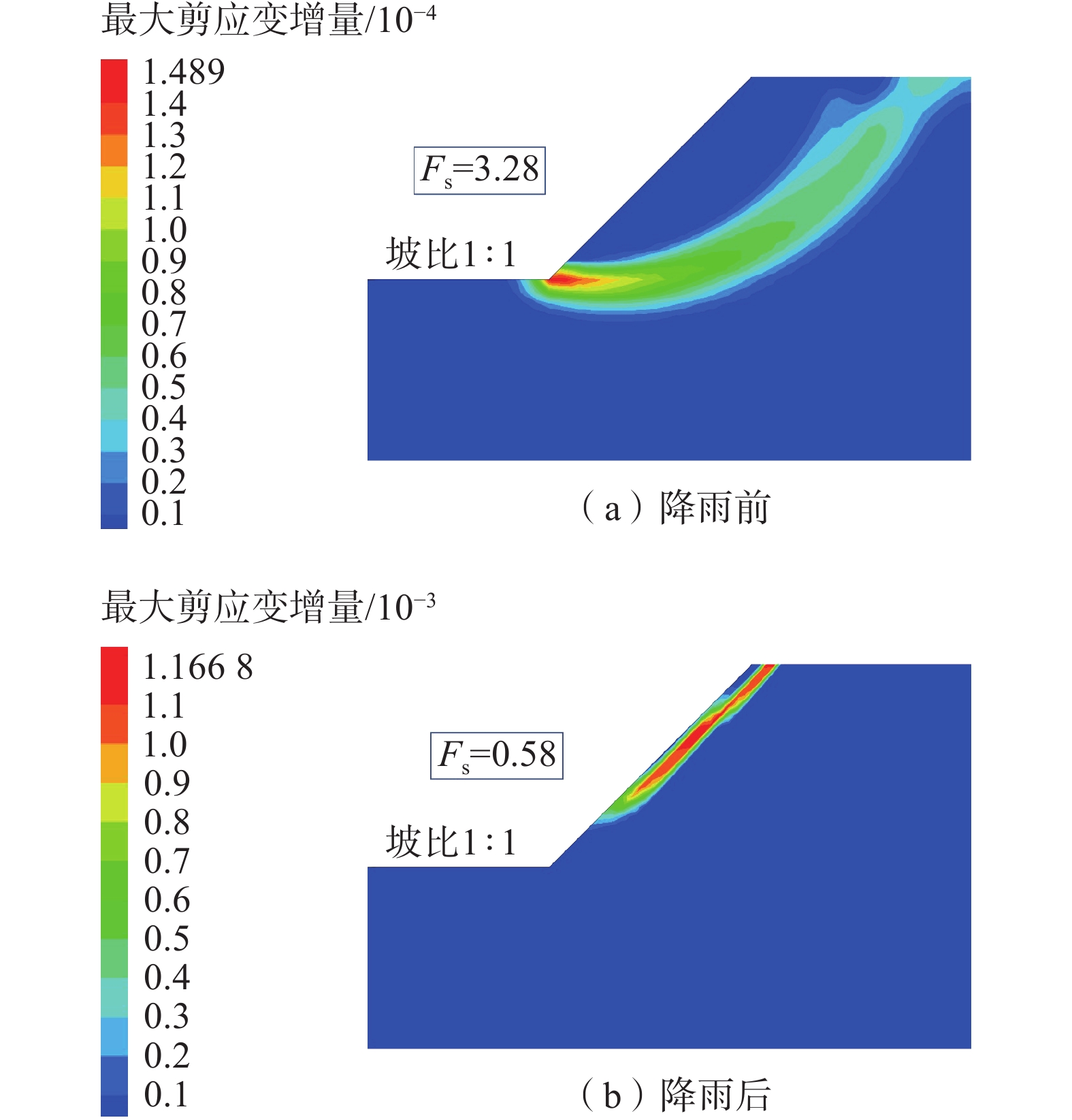
参数 θs θr α n R2 取值 0.4592 0.0837 0.0720 1.2661 0.9655 表 3 边坡降雨前后安全系数
Table 3. Safety factor of slope before and after rainfall
坡比 降雨
强度/
(mm·h−1)降雨
历时/h初始安全
系数降雨结束时
安全系数1∶0.5 5 24 2.68 2.490 1∶0.75 5 24 2.92 2.750 1∶1 5 24 3.28 3.120 1∶1.25 5 24 3.30 3.180 1∶1 2.5 24 3.28 3.230 1∶1 5 24 3.28 3.120 1∶1 7.5 24 3.28 1.250 1∶1 10 24 3.28 1.110 1∶1 5 12 3.28 3.210 1∶1 5 24 3.28 3.120 1∶1 5 32 3.28 1.575 1∶1 5 48 3.28 0.580 表 4 不同防护材料及防护效果对比
Table 4. Comparison of different protective materials and their effectiveness
防护材料名称 主要成分 质量配合比 草种添加量
/(g∙m−2)坡面防护层
厚度/mm路堑边坡浅层塌滑防治效果 HP-FGM
(灵活增长介质)卷曲纤维、木质纤维、
湿润剂和微孔颗粒16∶1∶2∶1 20 ≥30 坡面透气性和透水性最优,初期植被覆盖率最高,
短期内生态防治效果较优,长期应用表现一般素土 素土 — 20 ≥30 短期植被覆盖率一般,坡面透气性和透水性一般,
生态防治效果一般,长期应用表现一般EFM
(工程纤维基质)卷曲与木质纤维
和湿润剂8.1∶1 20 ≥30 坡面透气性和透水性良好,初期植被覆盖率较高,
短期内生态防治效果良好,长期应用表现一般聚丙烯纤维土 聚丙烯纤维
和素土0.003∶1 20 ≥30 坡面透气性和透水性最差,短期植被覆盖率最低,
短期生态防治效果较差,长期应用表现优良 -
[1] WANG Genlong,LI Tonglu,XING Xianli,et al. Research on loess flow-slides induced by rainfall in July 2013 in Yan’an,NW China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2014,73(12):7933 − 7944. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3951-9
[2] 李同录,李颖喆,赵丹旗,等. 对水致黄土斜坡破坏模式及稳定性分析原则的思考[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):25 − 32. [LI Tonglu,LI Yingzhe,ZHAO Danqi,et al. Thoughts on modes of loess slope failure triggered by water infiltration and the principals for stability analysis[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):25 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Tonglu, LI Yingzhe, ZHAO Danqi, et al. Thoughts on modes of loess slope failure triggered by water infiltration and the principals for stability analysis[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(2): 25-32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 石诚鋆,阮永芬,施炳军,等. 降雨入渗对边坡稳定性影响的敏感性分析[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2016,36(6):1002 − 1007. [SHI Cheng,RUAN Yongfen,SHI Bingjun,et al. The sensitivity analysis of influence of rainfall infiltration on landslide stability[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering,2016,36(6):1002 − 1007. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13409/j.cnki.jdpme.2016.06.022
SHI Cheng, RUAN Yongfen, SHI Bingjun, et al. The sensitivity analysis of influence of rainfall infiltration on landslide stability[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2016, 36(6): 1002-1007. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13409/j.cnki.jdpme.2016.06.022
[4] 蔡荣坤,戴自航,徐根连,等. 降雨对花岗岩风化层路堑边坡滑动模式影响—以福建云平高速云霄段为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(2):27 − 35. [CAI Rongkun,DAI Zihang,XU Genlian,et al. Influence of rainfall on sliding modes of cutting slope of weathered granite stratum:Taking Yunxiao section in the Yunping freeway in Fujian for example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(2):27 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CAI Rongkun, DAI Zihang, XU Genlian, et al. Influence of rainfall on sliding modes of cutting slope of weathered granite stratum: taking Yunxiao section in the Yunping freeway in Fujian for example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(2): 27-35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 孙萍萍,张茂省,江睿君,等. 降雨诱发浅层黄土滑坡变形破坏机制[J]. 地质通报,2021,40(10):1617 − 1625. [SUN Pingping,ZHANG Maosheng,JIANG Ruijun,et al. Deformation and failure mechanism of rainfall-induced shallow loess landslide[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2021,40(10):1617 − 1625. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2021.10.003
SUN Pingping, ZHANG Maosheng, JIANG Ruijun, et al. Deformation and failure mechanism of rainfall-induced shallow loess landslide[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(10): 1617-1625. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2021.10.003
[6] 胡华,吴轩,张越. 基于模拟试验的强降雨条件下花岗岩残积土斜坡滑塌破坏机理分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(5):92 − 97. [HU Hua,WU Xuan,ZHANG Yue. Experimental study on slope collapse characteristics of granite residual soil slope under heavy rainfall[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(5):92 − 97. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HU Hua, WU Xuan, ZHANG Yue. Experimental study on slope collapse characteristics of granite residual soil slope under heavy rainfall[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(5): 92-97. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 杜忠原,葛忻声,仝飞. 不同降雨条件下高边坡的稳定性分析[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021,21(30):13039 − 13045. [DU Zhongyuan,GE Xinsheng,TONG Fei. Stability analysis of high slope under different rainfall conditions[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2021,21(30):13039 − 13045. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.30.034
DU Zhongyuan, GE Xinsheng, TONG Fei. Stability analysis of high slope under different rainfall conditions[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(30): 13039-13045. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.30.034
[8] 李宁,赫建勇,许建聪,等. 降雨条件下抗滑桩边坡稳定性影响的数值分析[J]. 水利水电技术,2020,51(4):1 − 9. [LI Ning,HE Jianyong,XU Jiancong,et al. Numerical analysis on stability of anti-slide pile slope under rainfall condition[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,2020,51(4):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Ning, HE Jianyong, XU Jiancong, et al. Numerical analysis on stability of anti-slide pile slope under rainfall condition[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2020, 51(4): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 邓聚龙. 灰理论基础[M]. 武汉: 华中科技大学出版社, 2002
DENG Julong. Basis of grey theory[M]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press, 2002. (in Chinese)
[10] VAN GENUCHTEN M T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal,1980,44(5):892 − 898. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050002x
[11] FREDLUND D G,MORGENSTERN N R,WIDGER R A. The shear strength of unsaturated soils[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1978,15(3):313 − 321. doi: 10.1139/t78-029
[12] 饶鸿,王金淑,赵志明,等. 基于有限元软件自定义本构模型的膨胀土边坡降雨入渗分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):154 − 162. [RAO Hong,WANG Jinshu,ZHAO Zhiming,et al. An analysis of rainfall infiltration of expansive soil slope based on the finite element software custom constitutive model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):154 − 162. (in Chinese with English abstract)
RAO Hong, WANG Jinshu, ZHAO Zhiming, et al. An analysis of rainfall infiltration of expansive soil slope based on the finite element software custom constitutive model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(1): 154-162. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 黄明奎,马璐. 极端降雨对边坡土体强度的影响及其稳定性分析[J]. 灾害学,2021,36(3):6 − 9. [HUANG Mingkui,MA Lu. Stability and soil strength analysis of alope under extreme rainfall[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2021,36(3):6 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HUANG Mingkui, MA Lu. Stability and soil strength analysis of alope under extreme rainfall[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2021, 36(3): 6-9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 原泽,晏长根,陶悦,等. 骨架防护黄土边坡坡面冲蚀模型试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2023,31(6):1989 − 1998. [YUAN Ze,YAN Changgen,TAO Yue,et al. Erosion model test of loess slope with the framework protection[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2023,31(6):1989 − 1998. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YUAN Ze, YAN Changgen, TAO Yue, et. al. Erosion model test of loess slope with the framework protection[J].Journal of Engineering Geology.2023,31(6):1989-1998. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 晏长根,杨晓华,谢永利,等. 土工格室对黄土路堤边坡抗冲刷的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2005,26(8):1342 − 1344. [YAN Changgen,YANG Xiaohua,XIE Yongli,et al. Experimental research on anti-eroding effect of geocells in loess embankment[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2005,26(8):1342 − 1344. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2005.08.034
YAN Changgen, YANG Xiaohua, XIE Yongli, et al. Experimental research on anti-eroding effect of geocells in loess embankment[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2005, 26(8): 1342-1344. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2005.08.034
[16] 汪益敏,陶玥琛,程致远,等. 高速公路路堑边坡客土喷播的长期防护效果[J]. 生态环境学报,2021,30(8):1724 − 1731. [WANG Yimin,TAO Yuechen,CHENG Zhiyuan,et al. Long-term protective effect of external-soil spray seeding on highway cutting slope[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2021,30(8):1724 − 1731. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[WANG Yimin, TAO Yuechen, CHENG Zhiyuan, et al. Long-term protective effect of external-soil spray seeding on highway cutting slope[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(8): 1724-1731. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 谭明健,周春梅,孙东,等. 软硬互层顺层岩质边坡破坏试验[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(2):274 − 281, 324. [TAN Mingjian,ZHOU Chunmei,SUN Dong, et al. Failure experiment of soft-hard interlayer bedding rock slope[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(2):274 − 281, 324. (in Chinese with English abstract)
TAN Mingjian, ZHOU Chunmei, SUN Dong, et al. Failure experiment of soft-hard interlayer bedding rock slope[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 274-281, 324. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 罗晓娟, 寇桓嘉, 祝国强, 等. 断层破碎带条件下组合式圆截面抗滑桩加固边坡效果研究[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(6):253 − 261. [LUO Xiaojuan, KOU Huanjia, ZHU Guoqiang, et al. Effect of combined anti-slide piles with circular section to reinforce the slope containing the fault crushed zone[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(6):253 − 261. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LUO Xiaojuan, KOU Huanjia, ZHU Guoqiang, et al. Effect of combined anti-slide piles with circular section to reinforce the slope containing the fault crushed zone[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(6): 253-261. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 石爱红, 李国庆, 丁德民, 等. 考虑非饱和土基质吸力的丁家坡滑坡变形机制及稳定性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(6):141 − 151. [SHI Aihong, LI Guoqing, DING Demin, et al. Deformation mechanism and stability evaluation of Dingjiapo landslide considering the matric suction of unsaturated soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(6):141 − 151. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SHI Aihong, LI Guoqing, DING Demin, et al. Deformation mechanism and stability evaluation of Dingjiapo landslide considering the matric suction of unsaturated soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(6): 141-151.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 徐文刚, 余旭荣, 年廷凯, 等. 基于FLAC3D的三维边坡稳定性强度折减法计算效率改进算法及其应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2021,51(5):1347 − 1355. [XU Wengang, YU Xurong, NIAN Tingkai, et al. Optimization and application of FLAC3D strength-reduction computation in three-dimension slope stability analysis[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2021,51(5):1347 − 1355. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XU Wengang, YU Xurong, NIAN Tingkai, et al. Optimization and application of FLAC3D strength-reduction computation in three-dimension slope stability analysis[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1347-1355.(in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: