Comprehensive analysis of hazardous rock mass and simulation of potential rockfall processes using 3D terrain model: A case studyof the high cut slope near damsite of a hydropower stationin southern China
-
摘要:
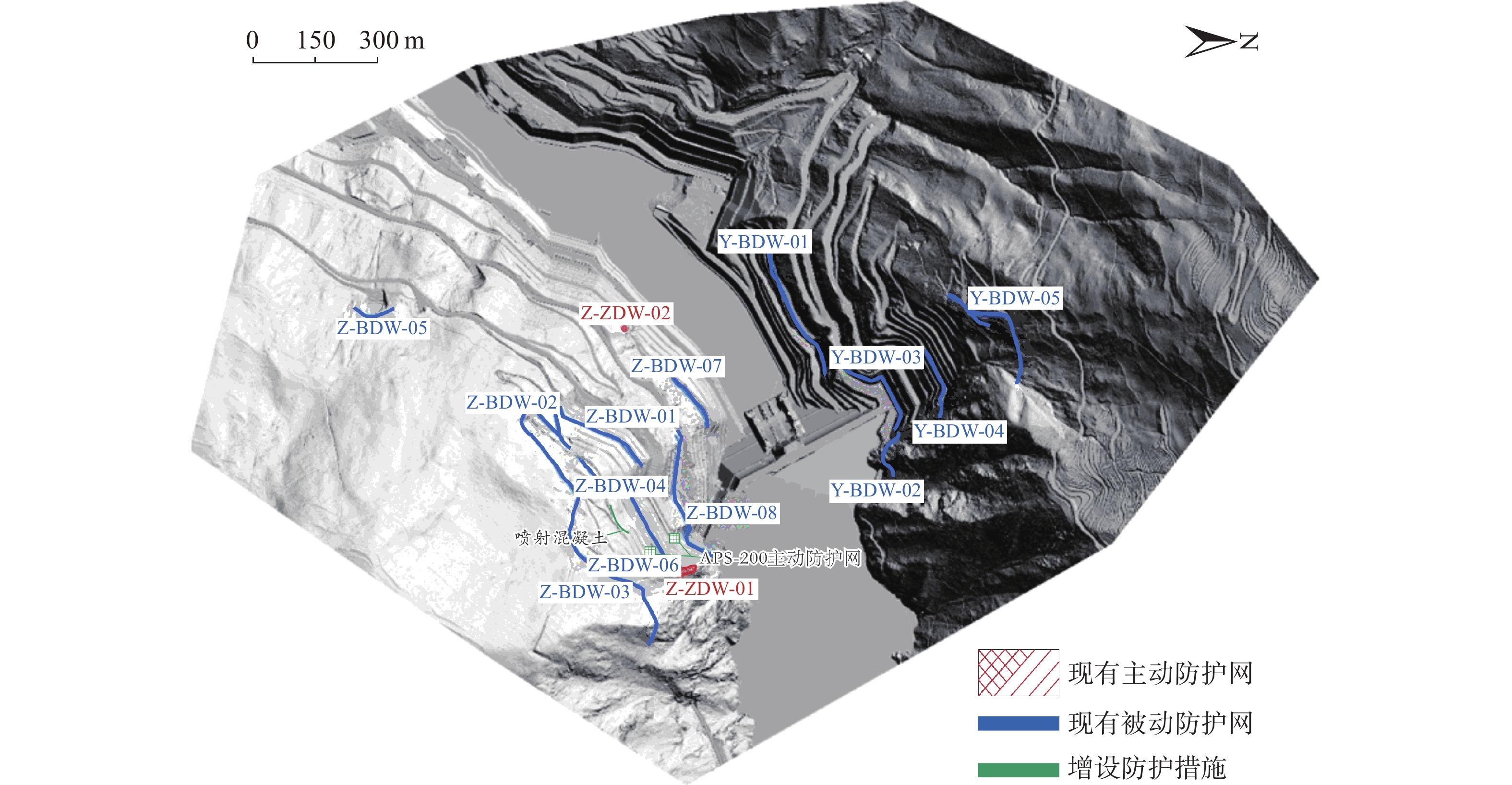
西南山区水电站两侧陡峻边坡发育有大量危岩体,危岩体滚动滑落、崩塌掉块等现象给电站的大坝、主要建筑物、厂房、道路、支护边坡等的正常运营带来了很大影响。现阶段针对危岩崩塌灾害的预测和防护多是忽略危岩体空间几何形状的二维Rockfall方法和人为截取优势剖面,但实际落石为三维运动,其威胁区域为一个地理上的三维空间。鉴于此,以西南某水电站危岩体隐患排查结果为基础,采用现场调查,机载LiDAR遥感测量技术和无人机倾斜摄影技术,获取研究区高精度的激光雷达点云数据,构建精细危岩体模型和真实三维实景模型,进行历史崩塌落石分布特征、岩体结构产状及崩塌源区危岩体特征和危岩体失稳模式的分析,结合Unity3D三维落石分析方法进行危岩崩落后的运动特征模拟,实现危岩崩落的运动路径及在不同位置上的弹跳高度、冲击能量和滚落区域等参数的获取。结果表明:水电站右岸危岩区块一典型危岩体的弹跳高度最大可达7.92 m,影响范围约145 m,多滚落至大坝,已设置多级被动防护网,不会对电厂内重要设施构成威胁,右岸危岩区块二发育的危岩体崩落后,落石影响范围约为120 m,部分落石会沿着公路护坡滚动到道路上,可能威胁交通要道;左岸危岩区块一发育典型危岩体体积巨大,稳定性差,其崩落后最大弹跳高度可达9.02 m,最终会落入水库蓄水区;左岸危岩区块二危岩分布密集,数量多,崩落后影响范围约为380 m,但受坡表植被茂密的影响,多数落石停积在坡表,对行人车辆有一定的威胁。相关研究成果可为类似水电设施危岩体隐患识别与落石运动模拟提供一定的参考。
Abstract:The steep slopes on both sides of the hydropower station in the southwestern mountainous region develop a multitude of dangerous rock formations. The rolling, collapsing and falling of these hazardous rocks have profound implications on the normal operation of the dam, main buildings, factories, roadways, and slope support systems. At present, the prediction and protection measures against rockfall disasters are predominantly reply on the two-dimensional Rockfall method, which ignores the spatial geometry of these dangerous rocks. In reality, falling rockfalls exhibit three-dimensional motion, and their threat zone extends throughout a three-dimensional geographical space. In view of this, this study is based on the hazard assessment results of the hidden danger investigation in a specific hydropower station of Yunnan Province. It employs field investigations, airborne LiDAR remote sensing measurement technology, and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) oblique photography technology to obtain high-precision laser radar point cloud data for the study area. This data is used to constrct detailed rock mass models and authentic three-dimensional scene models. The analysis includes historical rockfall distribution characteristics, rock mass structural characteristics, characteristics of hazardous rock masses in collapse source areas, and unstable modes. Furthermore, the study utilizes Unity3D three-dimensional rockfall analysis methods to simulate the motion characteristics of dangerous falling rocks after collapse. This enables the determination of the trajectory of dangerous falling rocks, as well as parameters such as bounce height, impact energy, and rolling area at different locations. The results indicate that for the right bank dangerous rock area of the hydropower station, a typical dangerous rock mass can achieve a maximum bounce height of up to 7.92 meters, with an impact range of approximately 145 meters. Most of these rocks roll towards the dam, which has multiple levels of passive protection nets and does not pose a threat to important facilities within the power plant. In the case of the right bank dangerous rock area two, after the collapse of dangerous rocks masses, the impact range of the falling rocks is approximately 120 meters, and some of the falling rocks may roll along the road embankment onto the road, potentially posing a threat to the main traffic artery. On the left bank, dangerous rock area one has a massive and unstable typical rock mass, with a maximum bounce height of up to 9.02 meters, ultimately falling into the reservoir storage area. Hazardous rock area two on the left bank has a dense distribution of hazardous rock masses, with a significant quantity, and after collapse, the impact range is approximately 380 meters. However, due to the dense vegetation cover on the slope, most of the falling rocks accumulate on the slope surface, posing a certain threat to pedestrians and vehicles. The related research results can provide valuable insights for the identification of hazardous rock masses and simulation of rockfall events in similar hydropower facilities.
-
Key words:
- dangerous rock mass /
- rock fall /
- motion simulation /
- UAV /
- Unity3D
-

-
表 1 坝址区室内岩石物理力学试验表
Table 1. Rock physical and mechanical test data for dam site area
岩石名称及风化程度 组数 抗压强度 静态变形试验 干抗压/MPa 湿抗压/MPa 软化系数 干 湿 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 变质火山角砾岩(弱−微) 11 95.9 72.8 0.76 68 0.17 59 0.19 表 2 危岩体特征参数设定
Table 2. Parameters for hazardous rock mass characteristics
特征参数 形状 d1/m d2/m d3/m 密度/(g·cm−3) 固定关节断裂力阈值/N 动摩擦系数 静摩擦系数 弹跳系数 取值 立方体 1.5~3 1.5~3 1.5~3 2.7 1000 0.3 0.3 0.6 表 3 水电站四区块危岩体分布特征表
Table 3. Confidence statistics for investigating characteristic hazardous rock bodies in the study area
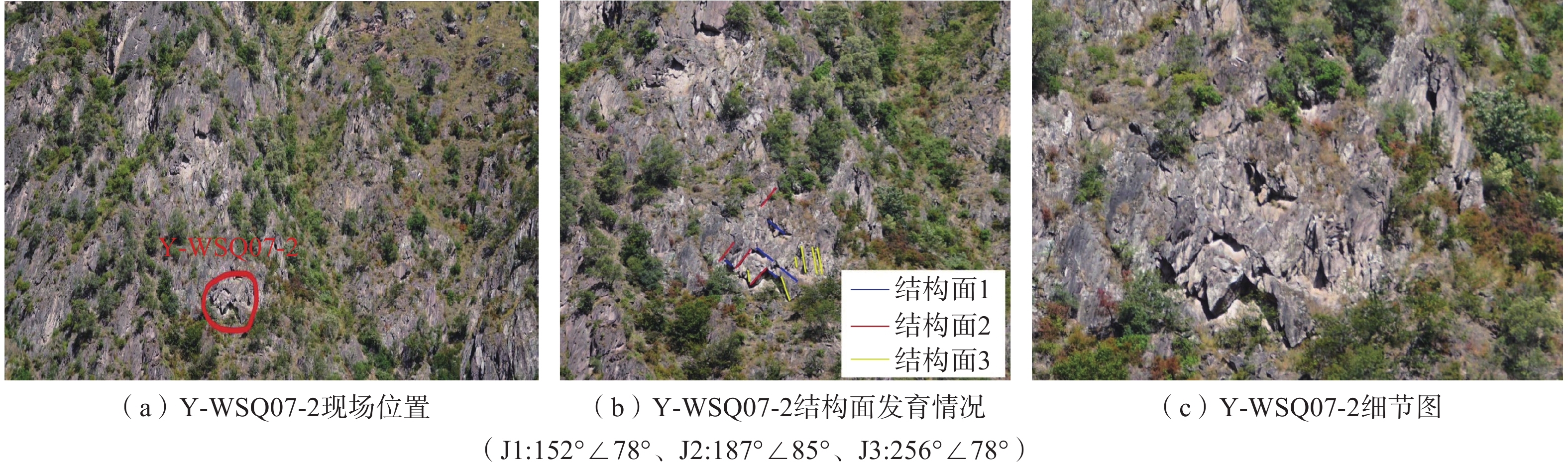
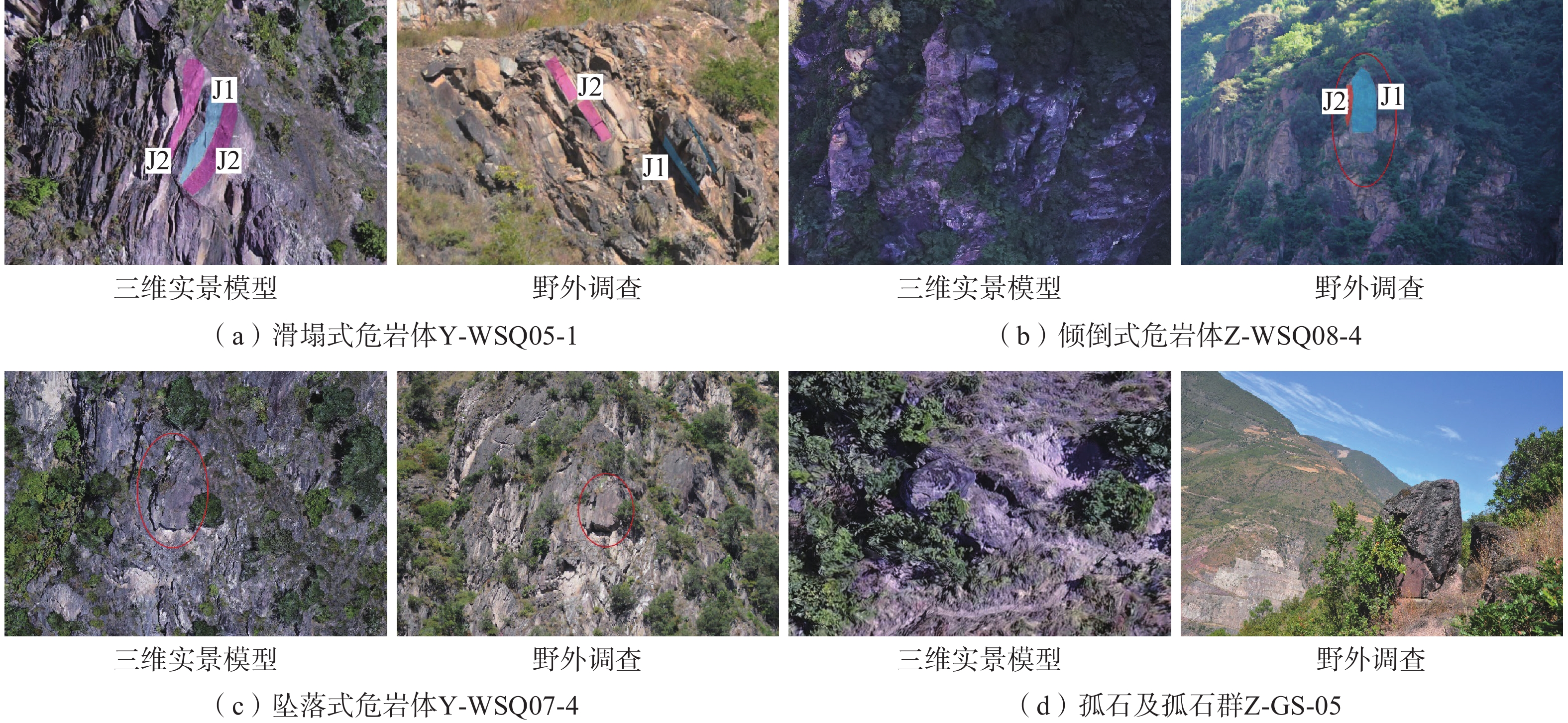
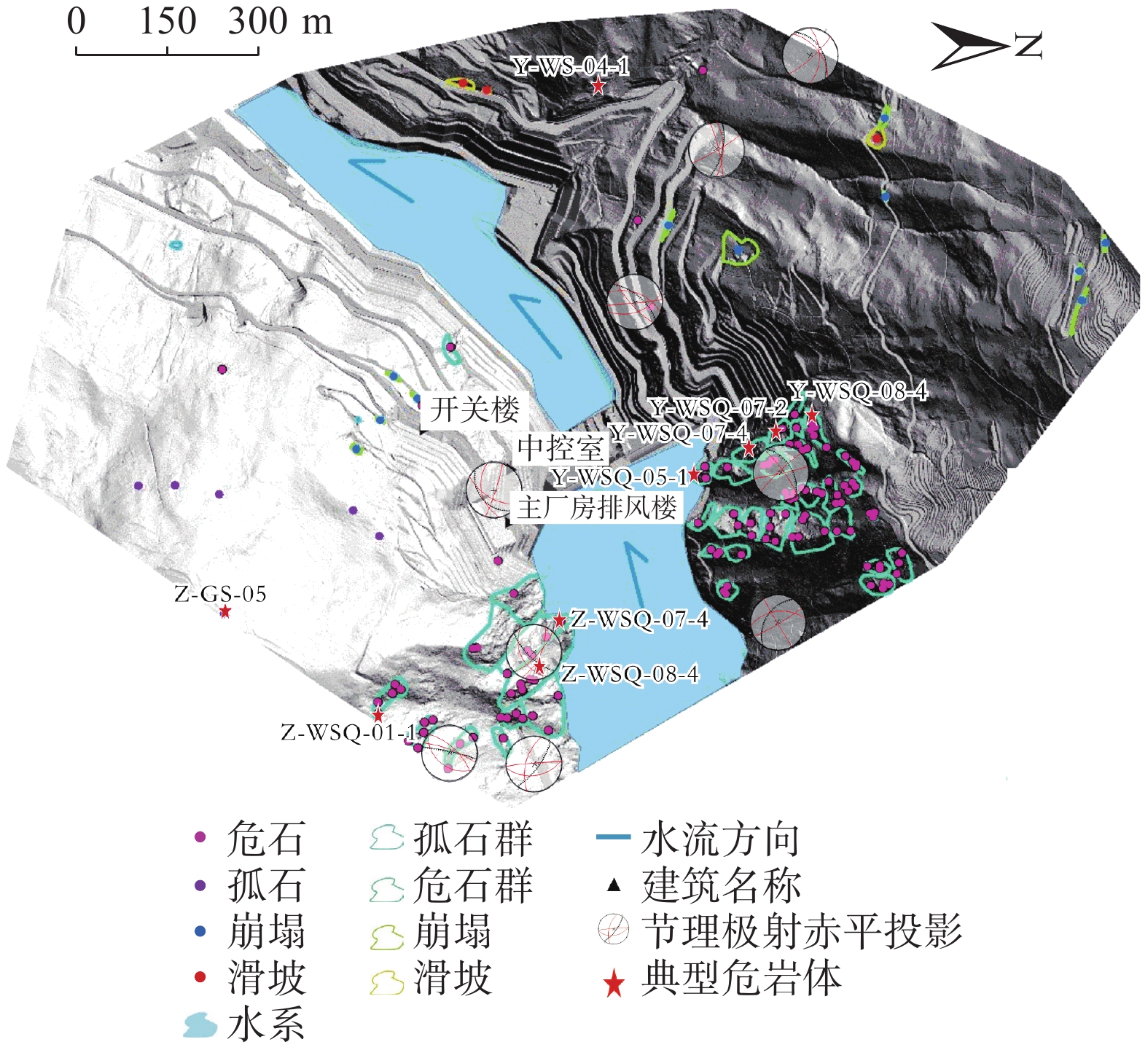
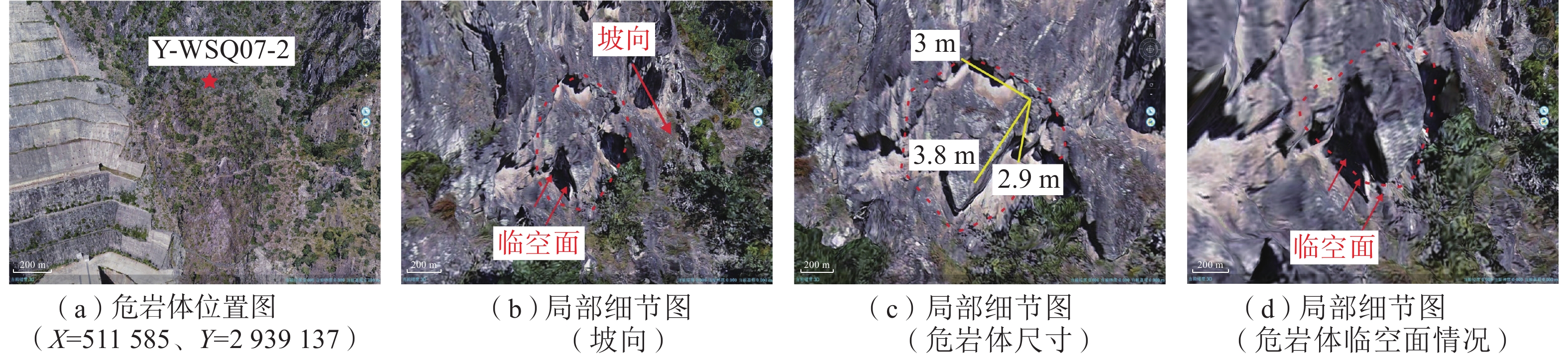
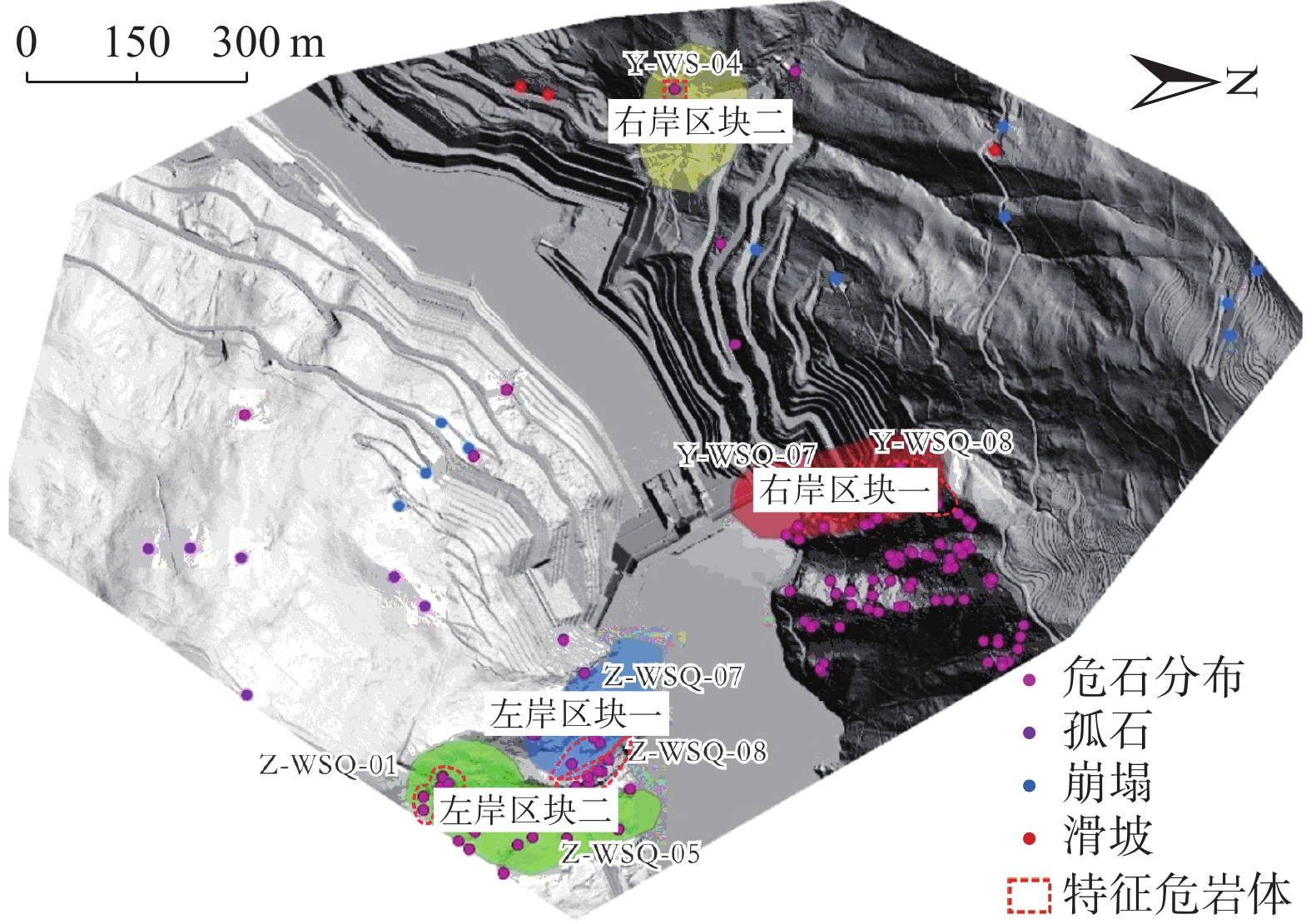
危岩区块 特征岩块 平面坐标 出露高程/m 危岩体规模 易发性 风险性 承灾体 体积/m3 规模 右岸区块一 Y-WSQ07-4 (511578.5,2939142.2) 1 766.1 60.20 小 极高 极高 坝体 右岸区块二 Y-WS-04-1 (510800.5,2938995.6) 1 586.2 57.90 小 高 低 道路 左岸区块一 Z-WSQ07-4 (512040.6,2938637.2) 1 719.3 909.66 中 高 中 电站设施 左岸区块二 Z-WSQ01-1 (512584.5,2932301.3) 1 944.2 2.94 小 高 低 道路 表 4 水电站四区块危岩体运动模拟结果
Table 4. Simulation results of hazardous rock mass motion in area four, Huangdengshui hydropower station
危岩区块 特征岩块 弹跳高度/m 冲击动能/kJ 距物源点的
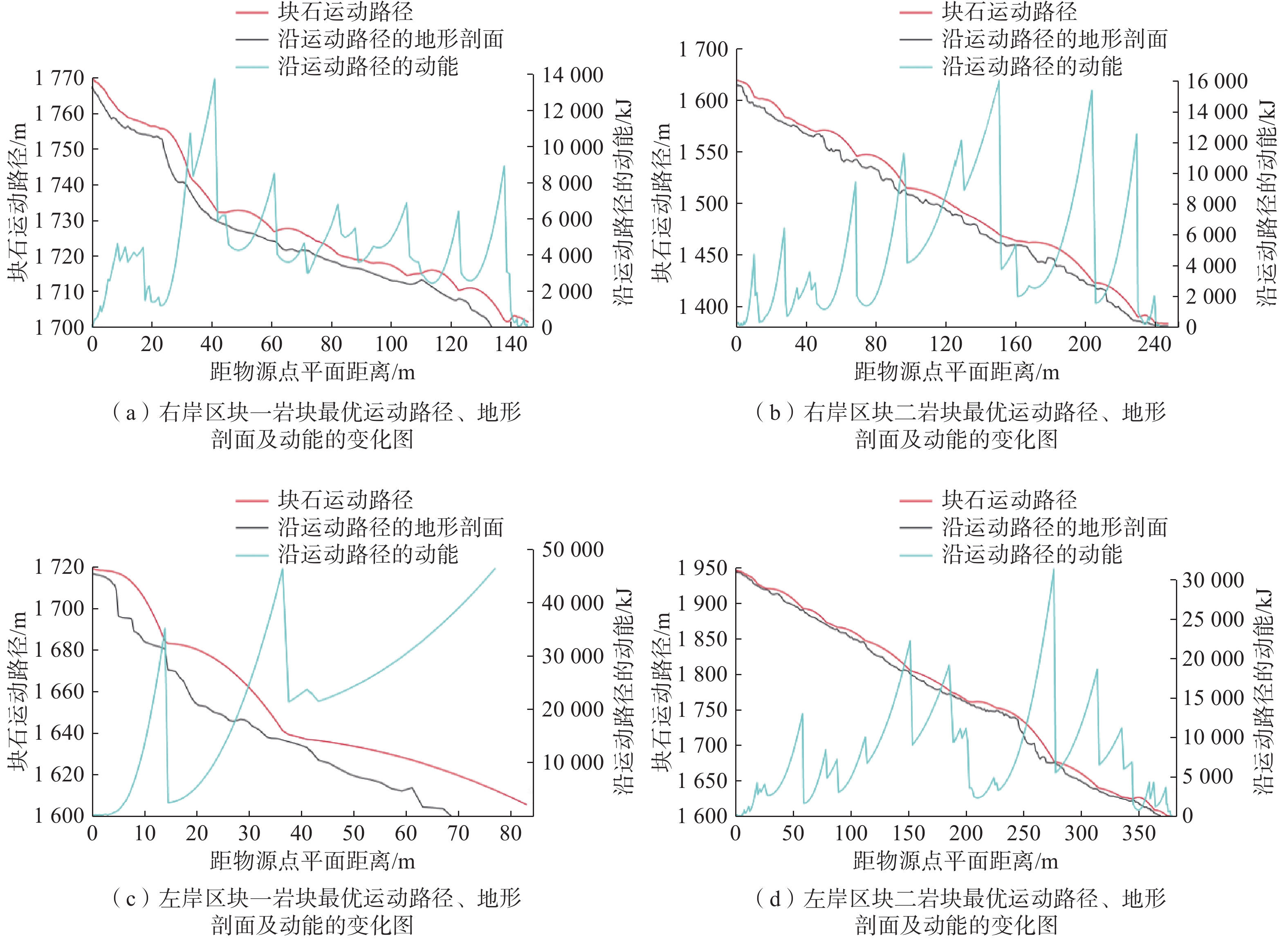
平面距离/m威胁对象 范围值 最大值 范围值 最大值 右岸区块一 Y-WSQ07-4 0.5~7.92 7.92 2000~13700 13700 146 大坝及场内人员 右岸区块二 Y-WS-04-1 1~6 6 4000~16000 16000 122 公路、行人及车辆 左岸区块一 Z-WSQ07-4 0.8~9.2 9.02 35000~45000 45000 83 电站设施 左岸区块二 Z-WSQ01-1 1~14.6 14.6 4000~30000 30000 379 公路、行人及车辆 -
[1] 黄海宁,黄健,周春宏,等. 无人机影像在高陡边坡危岩体调查中的应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(6):149 − 155. [HUANG Haining,HUANG Jian,ZHOU Chunhong,et al. Application of UAV images to rockfall investigation at the high and steep slope[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(6):149 − 155. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HUANG Haining, HUANG Jian, ZHOU Chunhong, et al . Application of UAV images to rockfall investigation at the high and steep slope[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019 ,46 (6 ):149 −155 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[2] 陈爱云,曾唯恐,王哲,等. 基于三维激光扫描技术的危岩体特征快速识别方法及稳定性评价[J]. 水利与建筑工程学报,2019,17(6):60 − 64. [CHEN Aiyun,ZENG Weikong,WANG Zhe,et al. Application of unstable rock investigation and stability evaluation based on 3D laser scanning technology[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering,2019,17(6):60 − 64. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHEN Aiyun, ZENG Weikong, WANG Zhe, et al . Application of unstable rock investigation and stability evaluation based on 3D laser scanning technology[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering,2019 ,17 (6 ):60 −64 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[3] 崔溦,谢恩发,张贵科,等. 利用无人机技术的高陡边坡孤立危岩体识别[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2021,46(6):836 − 843. [CUI Wei,XIE Enfa,ZHANG Guike,et al. Identification of isolated dangerous rock mass in high and steep slope using unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2021,46(6):836 − 843. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CUI Wei, XIE Enfa, ZHANG Guike, et al . Identification of isolated dangerous rock mass in high and steep slope using unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2021 ,46 (6 ):836 −843 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[4] 褚宏亮,殷跃平,曹峰,等. 大型崩滑灾害变形三维激光扫描监测技术研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(3):128 − 134. [CHU Hongliang,YIN Yueping,CAO Feng,et al. Research on deformation monitoring of large collapses and landslides based on 3D laser scanning technology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(3):128 − 134. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHU Hongliang, YIN Yueping, CAO Feng, et al . Research on deformation monitoring of large collapses and landslides based on 3D laser scanning technology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015 ,42 (3 ):128 −134 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[5] 黄润秋,刘卫华,周江平,等. 滚石运动特征试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2007,29(9):1296 − 1302. [HUANG Runqiu,LIU Weihua,ZHOU Jiangping,et al. Rolling tests on movement characteristics of rock blocks[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2007,29(9):1296 − 1302. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HUANG Runqiu, LIU Weihua, ZHOU Jiangping, et al . Rolling tests on movement characteristics of rock blocks[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2007 ,29 (9 ):1296 −1302 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[6] 陈宙翔,叶咸,张文波,等. 基于无人机倾斜摄影的强震区公路高位危岩崩塌形成机制及稳定性评价[J]. 地震工程学报,2019,41(1):257 − 267. [CHEN Zhouxiang,YE Xian,ZHANG Wenbo,et al. Formation mechanism analysis and stability evaluation of dangerous rock collapses based on the oblique photography by unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2019,41(1):257 − 267. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHEN Zhouxiang, YE Xian, ZHANG Wenbo, et al . Formation mechanism analysis and stability evaluation of dangerous rock collapses based on the oblique photography by unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2019 ,41 (1 ):257 −267 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[7] 谢金,杨根兰,覃乙根,等. 基于无人机与Rockfall的危岩体结构特征识别与运动规律模拟[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,40(1):55 − 64. [XIE Jin,YANG Genlan,QIN Yigen,et al. Structural feature recognition and motion law simulation of dangerous rock mass based on UAV and Rockfall[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Natural Science),2021,40(1):55 − 64. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XIE Jin, YANG Genlan, QIN Yigen, et al . Structural feature recognition and motion law simulation of dangerous rock mass based on UAV and Rockfall[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Natural Science),2021 ,40 (1 ):55 −64 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[8] 王栋,王剑锋,李天斌,等. 西南山区某铁路隧道口高位落石三维运动特征分析[J]. 地质力学学报,2021,27(1):96 − 104. [WANG Dong,WANG Jianfeng,LI Tianbin,et al. Analysis of three-dimensional movement characteristics of rockfall:A case study at a railway tunnel entrance in the southwestern mountainous area,China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2021,27(1):96 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.01.010
WANG Dong, WANG Jianfeng, LI Tianbin, et al . Analysis of three-dimensional movement characteristics of rockfall: A case study at a railway tunnel entrance in the southwestern mountainous area, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2021 ,27 (1 ):96 −104 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[9] 周月智,刘红岩,李俊峰,等. 地震荷载下危岩运动特征的模拟研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2021,29(5):1387 − 1400. [ZHOU Yuezhi,LIU Hongyan,LI Junfeng,et al. A study on motion characteristics of rockfall under seismic loadings by DDA[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021,29(5):1387 − 1400. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHOU Yuezhi, LIU Hongyan, LI Junfeng, et al . A study on motion characteristics of rockfall under seismic loadings by DDA[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021 ,29 (5 ):1387 −1400 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[10] 黎尤,何坤,胡卸文,等. 震裂山体崩塌形成特征及运动学三维模拟——以汶川县三官庙村崩塌为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(2):542 − 552. [LI You,HE Kun,HU Xiewen,et al. Formation characteristics and kinematics 3D simulation of rockfall evolved from shattered mountain:Case study of Sanguanmiao Village rockfall in Wenchuan County[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(2):542 − 552. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI You, HE Kun, HU Xiewen, et al . Formation characteristics and kinematics 3D simulation of rockfall evolved from shattered mountain: Case study of Sanguanmiao Village rockfall in Wenchuan County[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022 ,30 (2 ):542 −552 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[11] 柳万里,晏鄂川,魏鹏飞,等. 落石运动特征试验及影响因素敏感性分析[J]. 山地学报,2021,39(1):47 − 58. [LIU Wanli,YAN Echuan,WEI Pengfei,et al. Experimental study on rockfall and sensitivity analysis of influencing factors[J]. Mountain Research,2021,39(1):47 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Wanli, YAN Echuan, WEI Pengfei, et al . Experimental study on rockfall and sensitivity analysis of influencing factors[J]. Mountain Research,2021 ,39 (1 ):47 −58 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[12] 赵兴权,张迎宾,陈光齐,等. 非连续变形分析方法及其在灾害防治研究中的应用[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(2):300 − 312. [ZHAO Xingquan,ZHANG Yingbin,CHEN Guangqi,et al. Discontinuous deformation analysis method and its applications to disaster prevention[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University,2016,51(2):300 − 312. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHAO Xingquan, ZHANG Yingbin, CHEN Guangqi, et al . Discontinuous deformation analysis method and its applications to disaster prevention[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University,2016 ,51 (2 ):300 −312 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[13] 黄小福,张迎宾,赵兴权,等. 地震条件下危岩崩塌运动特性的初步探讨[J]. 岩土力学,2017,38(2):583 − 592. [HUANG Xiaofu,ZHANG Yingbin,ZHAO Xingquan,et al. A preliminary study of kinetic characteristic of rock-fall under seismic loading[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2017,38(2):583 − 592. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HUANG Xiaofu, ZHANG Yingbin, ZHAO Xingquan, et al . A preliminary study of kinetic characteristic of rock-fall under seismic loading[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2017 ,38 (2 ):583 −592 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[14] 刘国阳,孟海怡,宁宝宽,等. 基于三维非连续变形分析的巨石崩塌运动研究[J]. 岩土力学,2022,43(1):246 − 256. [LIU Guoyang,MENG Haiyi,NING Baokuan,et al. Study on collapse and movement of a boulder based on 3D discontinuous deformation analysis[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2022,43(1):246 − 256. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Guoyang, MENG Haiyi, NING Baokuan, et al . Study on collapse and movement of a boulder based on 3D discontinuous deformation analysis[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2022 ,43 (1 ):246 −256 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[15] 王军义,梁风,彭雄武,等. 基于GIS技术的单体崩塌危险范围评价方法研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2023,31(1):188 − 198. [WANG Junyi,LIANG Feng,PENG Xiongwu,et al. Study on assessment method of single collapse risk range based on GIS technology[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2023,31(1):188 − 198. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Junyi, LIANG Feng, PENG Xiongwu, et al . Study on assessment method of single collapse risk range based on GIS technology[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2023 ,31 (1 ):188 −198 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[16] 孙敬辉,石豫川. 重庆甑子岩崩塌落石动力学特征及危险性分区[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(3):6 − 11. [SUN Jinghui,SHI Yuchuan. Dynamics and hazard zoning of collapse and rockfall in Zengziyan,Chongqing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(3):6 − 11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SUN Jinghui, SHI Yuchuan . Dynamics and hazard zoning of collapse and rockfall in Zengziyan, Chongqing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019 ,30 (3 ):6 −11 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[17] 何宇航,裴向军,梁靖,等. 基于Rockfall的危岩体危险范围预测及风险评价——以九寨沟景区悬沟危岩体为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(4):24 − 33. [HE Yuhang,PEI Xiangjun,LIANG Jing,et al. Risk assessment and range prediction of dangerous rockmass based on rockfall:A case study of the Xuangou Collapse[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(4):24 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HE Yuhang, PEI Xiangjun, LIANG Jing, et al . Risk assessment and range prediction of dangerous rockmass based on rockfall: A case study of the Xuangou Collapse[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020 ,31 (4 ):24 −33 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[18] 王豪,黄健,黄祥,等. 一种利用Unity3D模拟崩塌三维运动全过程的方法[J/OL]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版):1 − 10[2022-04-27]. [WANG Hao,HUANG Jian,HUANG Xiang,et al. A method to simulate the whole process of collapse 3D motion using Unity3D[J/OL]. Journal of Wuhan University (Information Science Edition):1 − 10 [2022-04-27]. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Hao, HUANG Jian, HUANG Xiang, et al. A method to simulate the whole process of collapse 3D motion using Unity3D[J/OL]. Journal of Wuhan University (Information Science Edition): 1 − 10 [2022-04-27]. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] 夏雄彬,谯立家,许万忠. 基于机载LiDAR及无人机影像的高位危岩体调查和成因分析[J]. 长江科学院院报,2023,40(9):188 − 194. [XIA Xiongbin,QIAO Lijia,XU Wanzhong. Investigation and cause analysis of dangerous rock masses on high and steep slope based on airborne LiDAR and UAV imagery[J]. Journal of Changjiang River Scientific Research Institute,2023,40(9):188 − 194. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XIA Xiongbin, QIAO Lijia, XU Wanzhong . Investigation and cause analysis of dangerous rock masses on high and steep slope based on airborne LiDAR and UAV imagery[J]. Journal of Changjiang River Scientific Research Institute,2023 ,40 (9 ):188 −194 . (in Chinese with English abstract) -




 下载:
下载: