Landslide geological hazard assessment based on the I-CF model of Dege County in Sichuan Province
-
摘要:
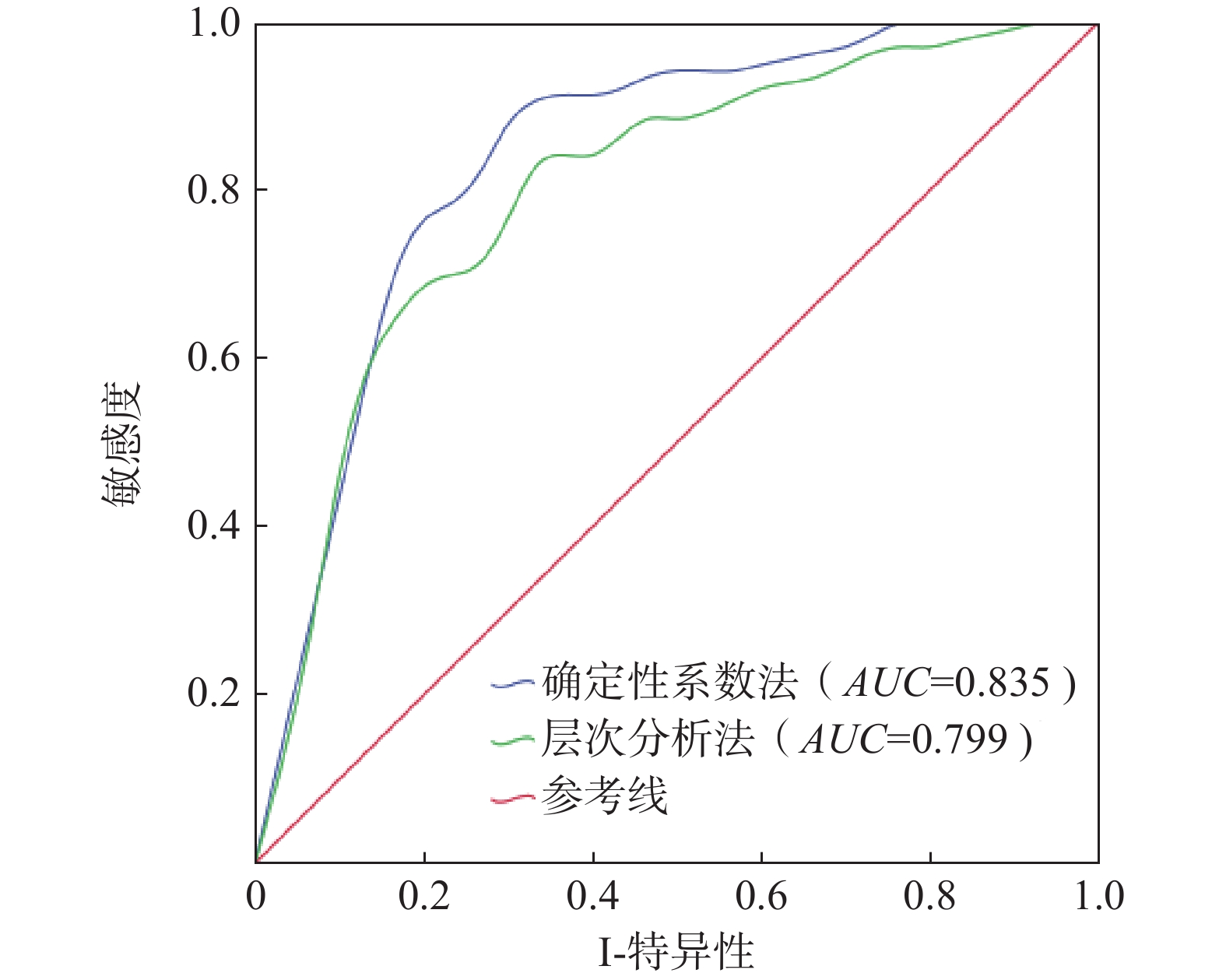
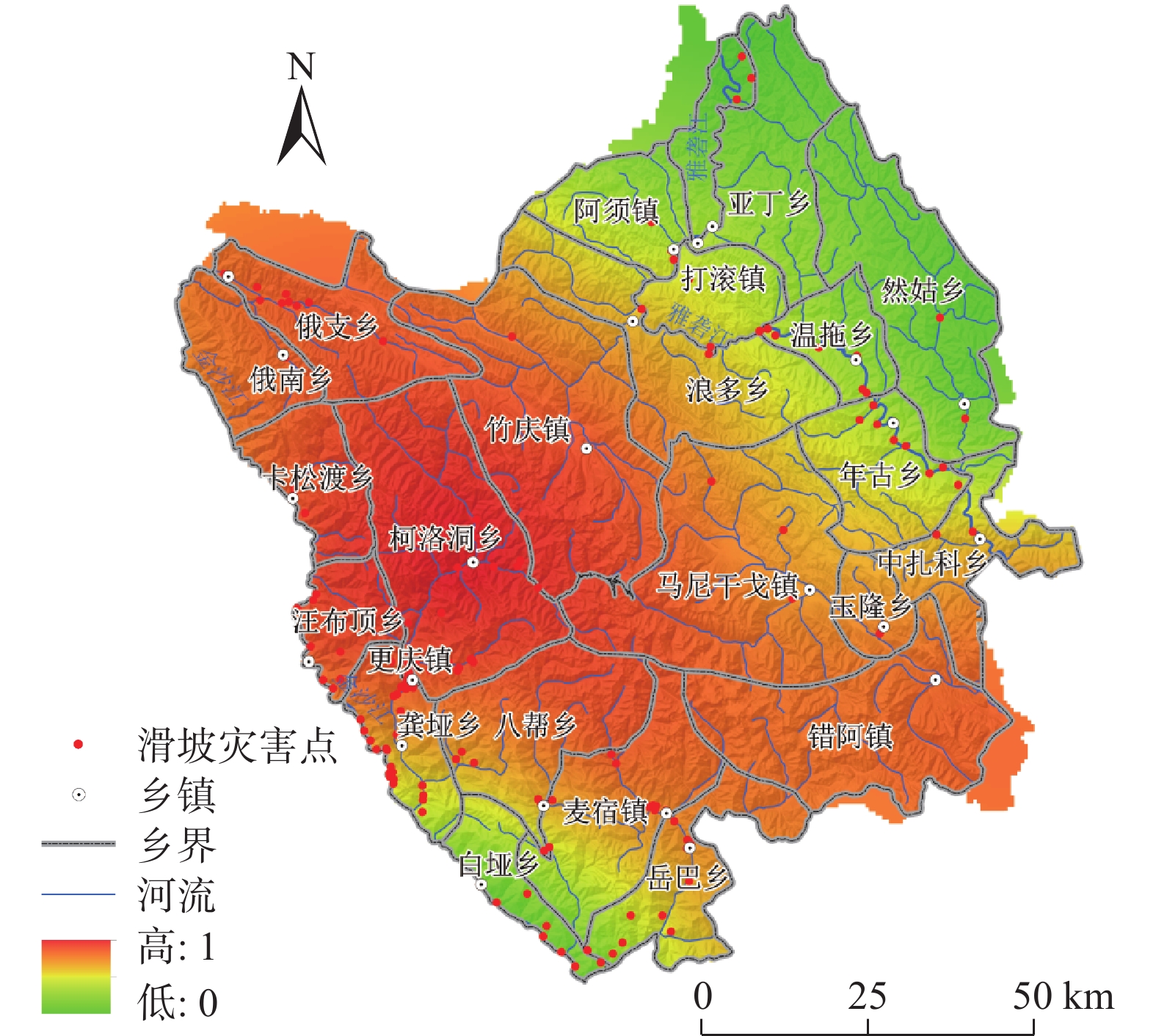
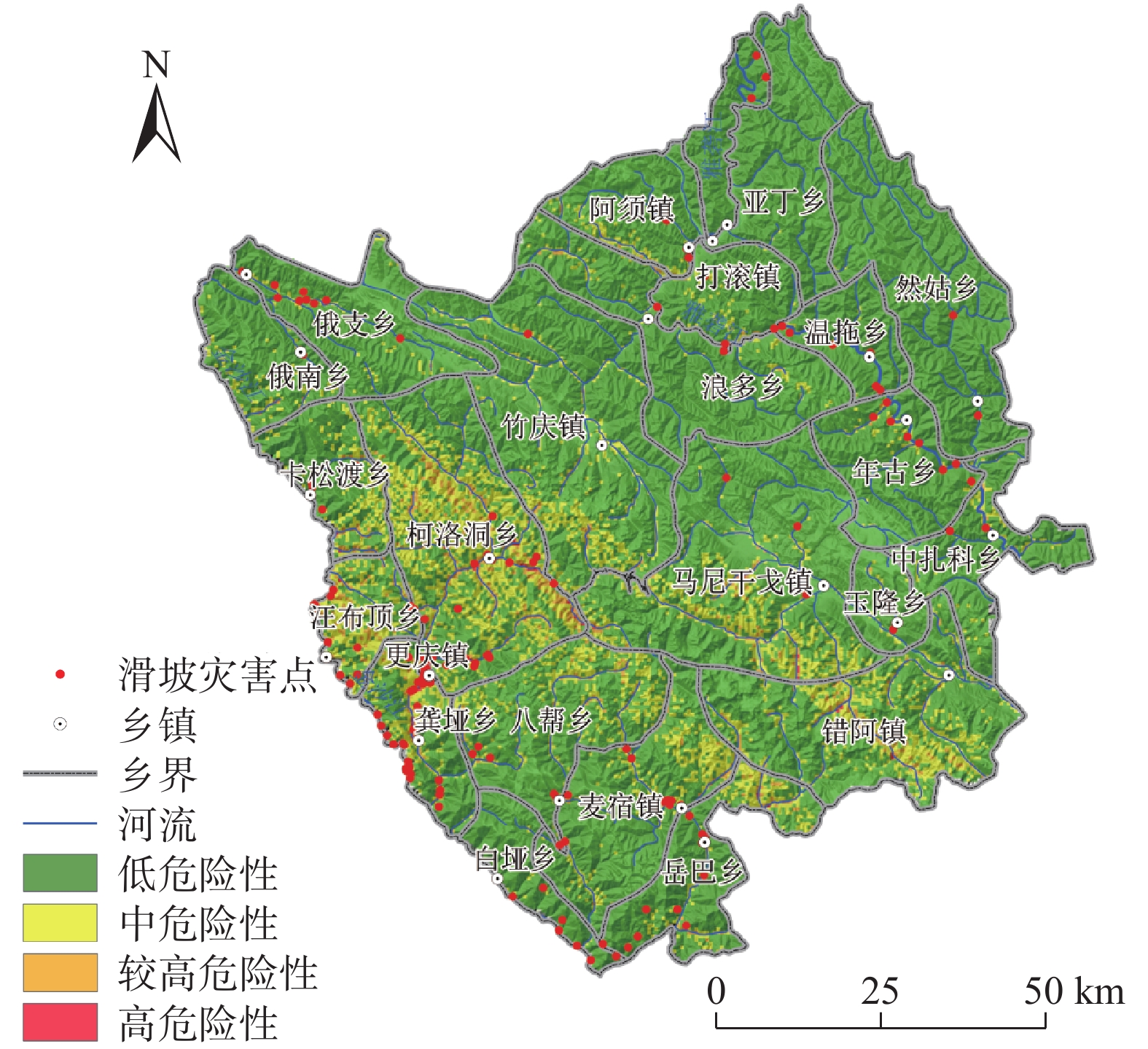
文章以德格县为研究区,以7 m DEM进行地形分析处理,并结合相关调查数据建立了德格县滑坡灾害数据库,通过选取的地震峰值加速度、断裂带、水系、坡度、坡向、高程、岩性等7个指标,在GIS技术支持下,利用信息量模型(I)、层次分析法模型(AHP)、确定性系数模型(CF)相互耦合对研究区灾害敏感性评价,再分析得到活动频率因素对研究区全县域进行危险性评价,将得到的结果分成4个区域,分别为高危险区、较高危险区、中危险区、低危险区,其中高、较高危险区占总面积2.23%。其中,滑坡灾害占总灾害的42%。评价结果与实际调查结果符合程度较高,能够为该地域未进行实地调查的地方进行相关滑坡灾害的预测预报,并对安全防治提供技术支持,亦可以为其他地区滑坡灾害危险性评价提供理论指导和技术参考。
Abstract:This study focuses on Dege County as the research area, and carries out terrain analysis and processing with 7m DEM. A landslide hazard database for Dege County is establishing using relevant survey data. With the support of GIS technology, this research employs the information quantity model (I), analytic hierarchy process model (AHP), and deterministic coefficient model (CF) coupling to evaluate the hazard sensitivity within the study area based on seven selected indicators: mic peak acceleration, fault zone, water system, slope, slope direction, elevation, and lithology. Subsequently, an assessment of hazard is conducted for the entire county domain by considering factors related to landslide activity frequency. The results are categorized into four zones: high risk, relatively high risk, moderate risk, and low risk. The high and relatively high-risk zones collectively cover 2.23% of the total area, with landslides accounting for 42% of the overall hazards. The evaluation results align well with the actual survey findings, providing technical support for predicting, forecasting, and implementing safety measures against landslide disasters in areas that without field investigation. Furthermore, it can serve as a theoretical guide and technical reference for the risk assessment of landslide hazard in other regions.
-
Key words:
- landslide /
- GIS /
- hazard assessment /
- certainty factor method /
- Dege County
-

-
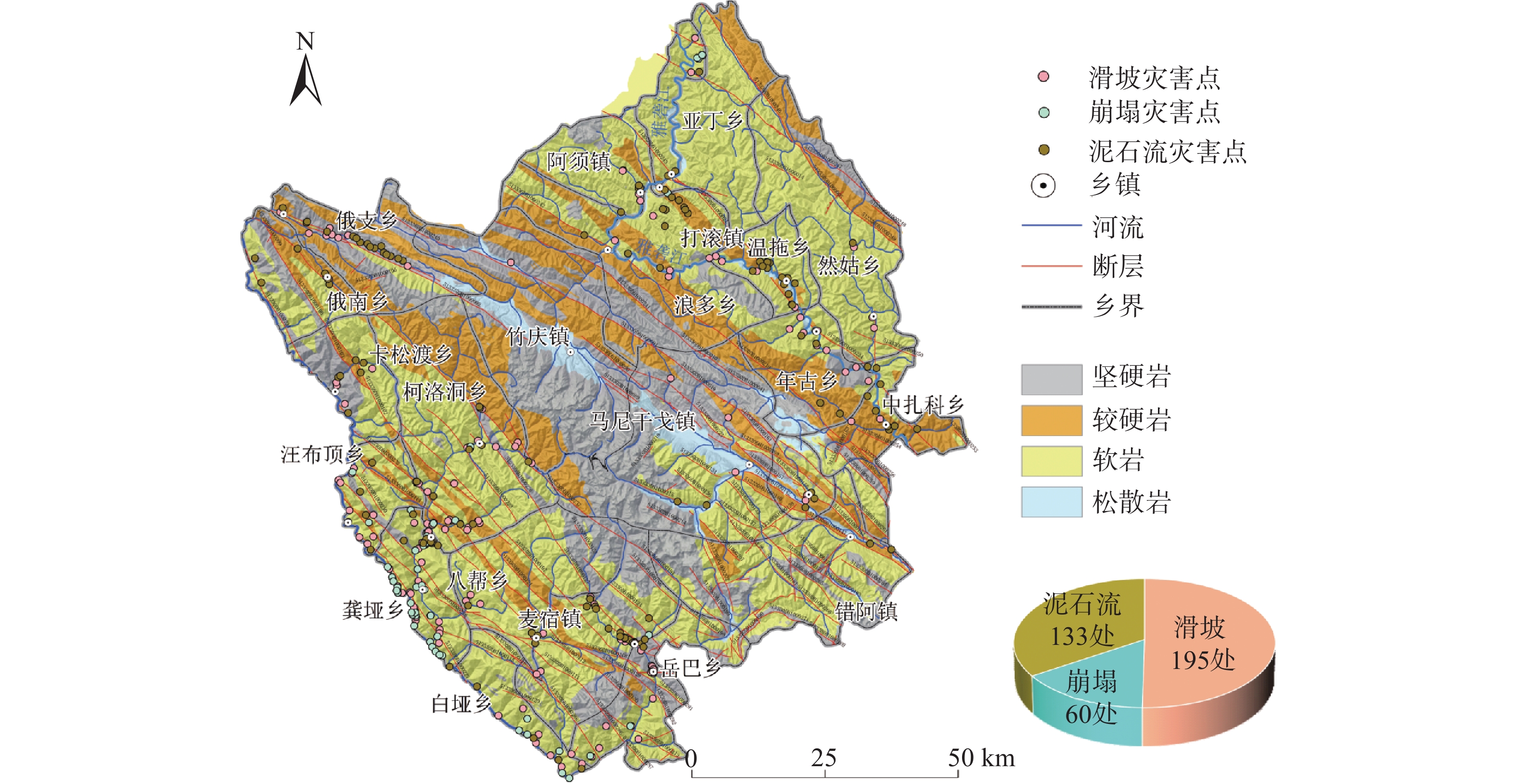
表 1 地质灾害隐患点分布表
Table 1. Distribution table of geological hazards hidden danger points
序号 乡镇 滑坡/处 崩塌/处 泥石流/处 合计 面积/
km2每百平方公里
灾害数/处1 阿须镇 5 1 6 12 365.19 3.29 2 八帮乡 8 1 4 13 562.71 2.31 3 白垭乡 8 6 4 18 200.69 8.97 4 错阿镇 0 0 2 2 498.33 0.40 5 打滚镇 3 3 4 10 461.77 2.17 6 俄南乡 3 0 6 9 299.07 3.01 7 俄支乡 8 0 16 24 439.17 5.46 8 更庆镇 58 13 14 85 427.51 19.88 9 龚垭乡 10 9 2 21 267.66 7.85 10 卡松渡乡 4 1 7 12 299.67 4.00 11 柯洛洞乡 8 2 5 15 963.76 1.56 12 浪多乡 3 0 4 7 619.74 1.13 13 马尼干戈镇 3 0 2 5 1075.43 0.46 14 麦宿镇 11 1 16 28 584.16 4.79 15 年古乡 10 0 3 13 397.21 3.27 16 然姑乡 3 0 1 4 481.87 0.83 17 汪布顶乡 25 21 4 50 226.63 22.06 18 温拖乡 7 0 12 19 274.14 6.93 19 亚丁乡 0 1 6 7 607.54 1.15 20 玉隆乡 2 0 3 5 202.83 2.47 21 岳巴乡 11 1 1 13 605.36 2.15 22 中扎科乡 4 0 11 15 447.74 3.35 23 竹庆镇 1 0 0 1 1131.09 0.09 表 2 使用数据详情表
Table 2. Data utilization details table
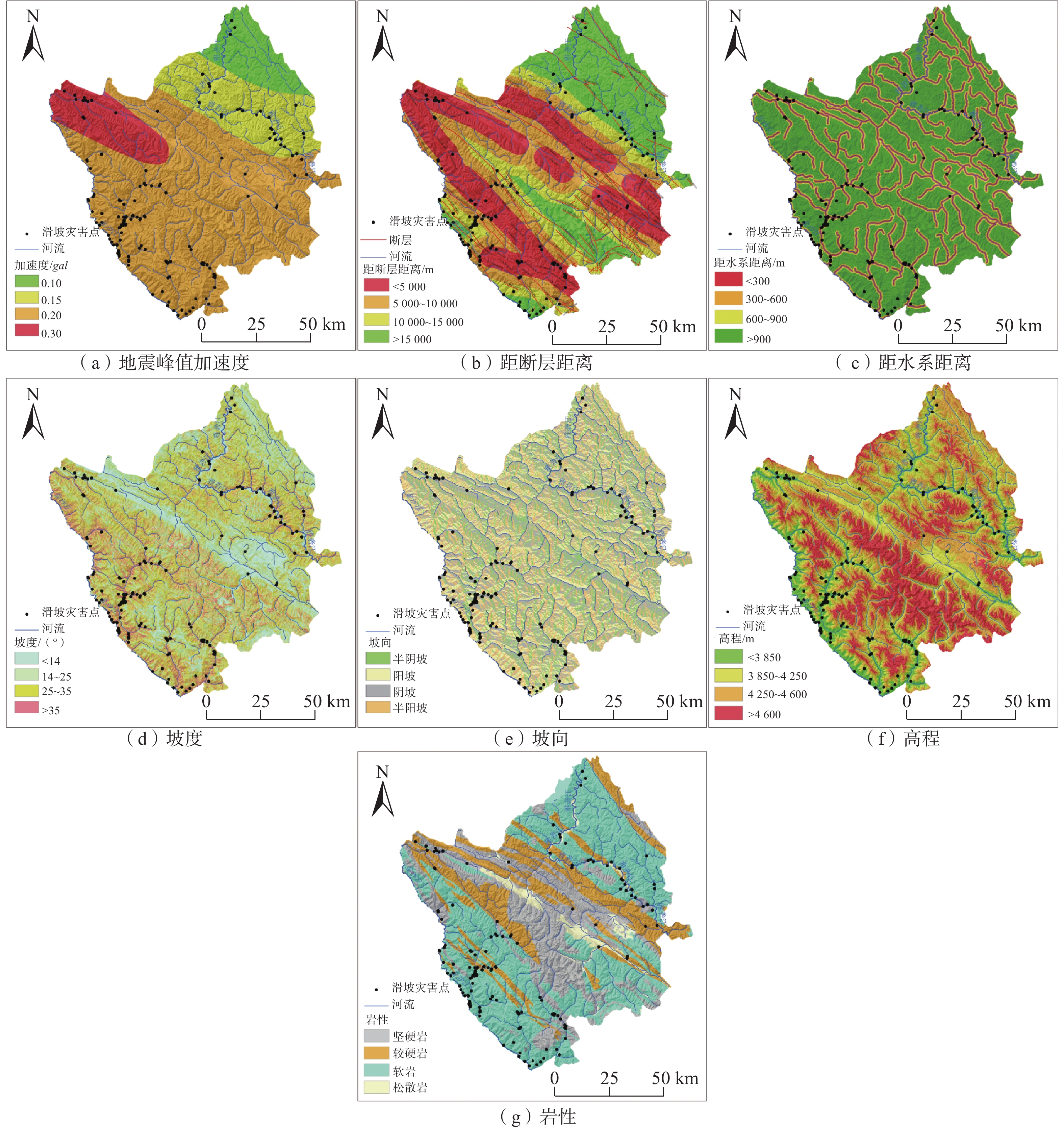
数据名称 数据精度(比例尺) 高分一号(GF1)高精度遥感影像 0.5 m 德格县DEM 7 m 德格县地形数据图 1∶50000 德格县地质数据图 1∶10 000 甘孜州年均降雨量数据 − 地震峰值加速度分布图 − 表 3 指标分级敏感性量化值
Table 3. Quantitative sensitivity values for indicator classification
指标 指标分级 灾害点个数 分区面积/km2 信息量 信息量归一化 地震峰值加速度/g 0.10 6 1131.6443 −1.317042484 0 0.15 30 1004.5774 −0.395084795 0.592148498 0.20 207 1997.8012 0.239927923 1 0.30 12 7304.9769 −0.743000070 0.368691923 地震断裂带缓冲区/m [0,5000) 52 3625.0082 −0.440847835 0 [5000,10000) 64 2940.5943 −0.023963605 0.34370709 [10000,15000) 87 1803.2948 0.772057694 1 [15000,56037) 52 3070.1025 −0.274702222 0.136981495 水系缓冲区/m [0,300) 170 1299.6380 1.76947768 1 [300,600) 27 1285.4982 −0.059544488 0.41368016 [600,900) 14 1239.9860 −0.680277809 0.214695004 [900,6924) 44 7613.8776 −1.35001793 0 坡度/(°) [0,14) 69 5075.3157 −0.494517212 0 [14,25) 92 3495.4392 0.166094562 0.551272903 [25,35) 56 2024.9770 0.215558335 0.592549851 [35,90) 38 843.2679 0.703821706 1 坡向 阴坡 67 2730.6483 0.095918567 0.892332366 半阴坡 50 2961.6391 −0.277954847 0 阳坡 63 2824.8389 0.000448382 0.664471457 半阳坡 75 2921.8690 0.141029635 1 高程/m [2980,3800) 59 1304.6405 0.707374888 1 [3800,4200) 67 3609.7618 −0.183184166 0.245339931 [4200,4600) 94 4005.7085 0.051339327 0.444075225 [4600,6 168) 35 2518.8890 −0.472704846 0 岩性 坚硬岩 31 2728.6819 −0.674066445 0.150627096 较硬岩 24 2558.4692 −0.865590279 0 较软岩 190 5679.5360 0.405919554 1 松散岩 10 472.3128 −0.051536121 0.640226396 表 4 判断矩阵及权重
Table 4. Decision matrix and weight
断层 水系 高程 坡度 坡向 岩性 峰值加速度 权重 峰值加速度 1 1/2 1/3 1/2 1 1/2 1/2 0.0734 距断层距离 1 1 1 2 2 1 0.1705 距水系距离 1 1 2 2 1/2 0.1681 坡度 1 4 3 2 0.2214 坡向 1 1/3 1 0.0655 高程 1 1/2 0.1190 岩性 1 0.1821 表 5 CF值及权重
Table 5. CF values and weights
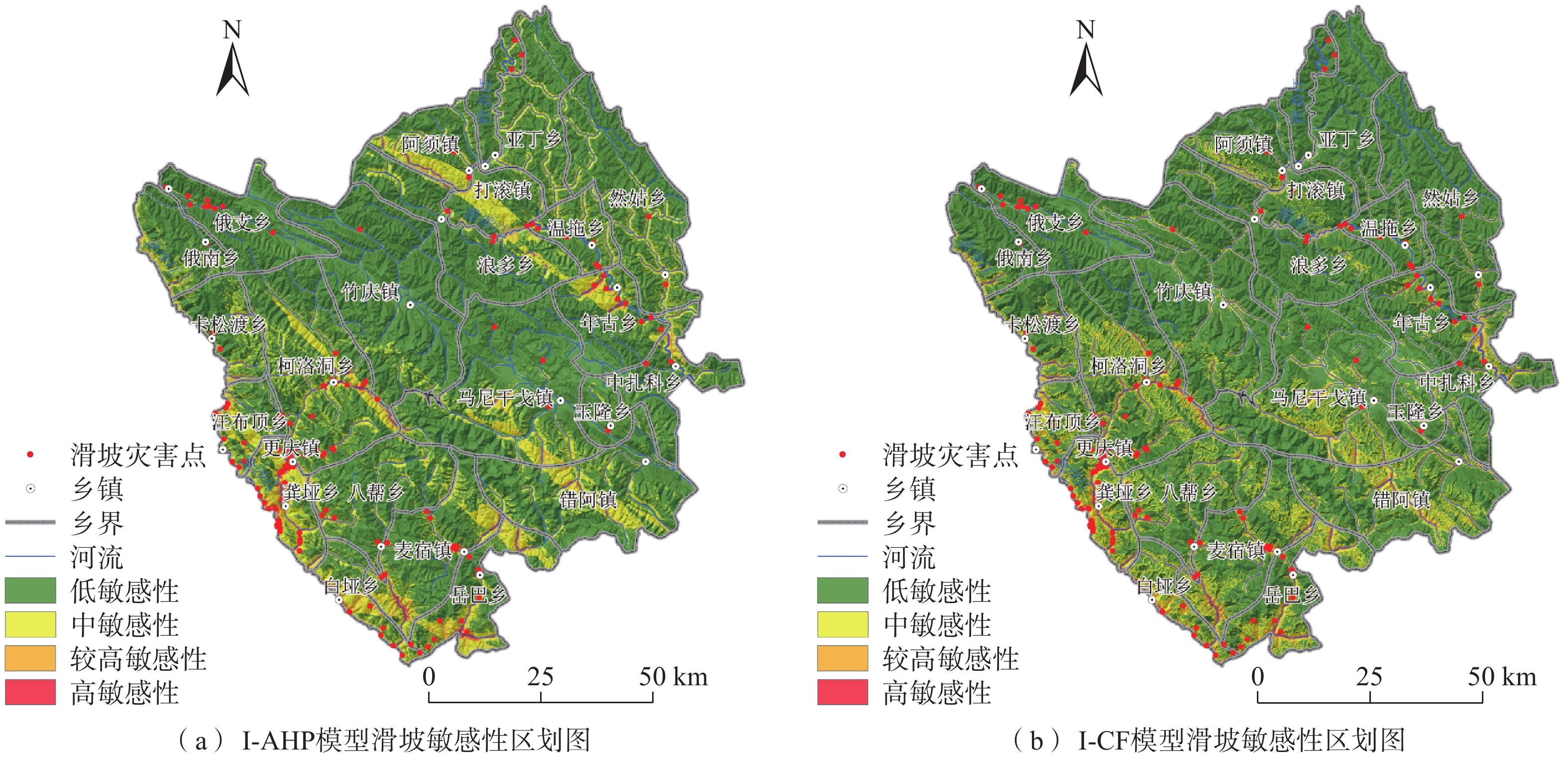
指标 CFmax CFmin 权重 峰值加速度 0.8027 −0.9278 1.7305 距断层距离 0.5502 −0.3616 0.9119 距水系距离 0.8484 −0.745 1.5935 坡度 0.5168 −0.3955 0.9123 坡向 0.1345 −0.2468 0.3813 高程 1.0773 −0.3819 1.4593 岩性 0.3412 −0.5846 0.9259 表 6 各危险区栅格统计表
Table 6. Grid statistics for various hazardous zones
危险性
等级面积/km2 面积
比例/%灾害
数量/个灾害密度/
(个·km−2)低 9525.590645 83.27 95 0.0100 中 1646.354741 14.39 56 0.0340 较高 251.629077 2.20 49 0.1947 高 15.425537 0.13 55 3.5655 -
[1] 李鹏岳,唐业旗,陈亮. 某厚层堆积体滑坡稳定性分析[J]. 工程建设与设计,2012 (8):148 − 150. [LI Pengyue,TANG Yeqi,CHEN Liang. Study on the stability of accumulation landslide[J]. Construction & Design for Project,2012 (8):148 − 150. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9467.2012.08.039
LI Pengyue, TANG Yeqi, CHEN Liang . Study on the stability of accumulation landslide[J]. Construction & Design for Project,2012 (8 ):148 −150 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[2] 潘桂棠,李兴振,王立全,等. 青藏高原及邻区大地构造单元初步划分[J]. 地质通报,2002,21(11):701 − 707. [PAN Guitang,LI Xingzhen,WANG Liquan,et al. Preliminary division of tectonic units of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau and its adjacent regions[J]. Regional Geology of China,2002,21(11):701 − 707. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.11.002
PAN Guitang, LI Xingzhen, WANG Liquan, et al . Preliminary division of tectonic units of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau and its adjacent regions[J]. Regional Geology of China,2002 ,21 (11 ):701 −707 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[3] 萧瑞良. 德格县生态承载力综合评价研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2013. [XIAO Ruiliang. Dege County comprehensive assessment of ecological carrying capacity[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XIAO Ruiliang. Dege County comprehensive assessment of ecological carrying capacity[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] 李萍,叶辉,谈树成. 基于层次分析法的永德县地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 水土保持研究,2021,28(5):394 − 399. [LI Ping,YE Hui,TAN Shucheng. Evaluation of geological hazards in Yongde County based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2021,28(5):394 − 399. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2021.05.045
LI Ping, YE Hui, TAN Shucheng . Evaluation of geological hazards in Yongde County based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2021 ,28 (5 ):394 −399 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[5] 张晓东,刘湘南,赵志鹏,等. 基于层次分析法的盐池县地质灾害危险性评价[J]. 国土资源遥感,2019,31(3):183 − 192. [ZHANG Xiaodong,LIU Xiangnan,ZHAO Zhipeng,et al. Geological disaster hazard assessment in Yanchi County based on AHP[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources,2019,31(3):183 − 192. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Xiaodong, LIU Xiangnan, ZHAO Zhipeng, et al . Geological disaster hazard assessment in Yanchi County based on AHP[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources,2019 ,31 (3 ):183 −192 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[6] 刘宇恒,邓辉,熊倩莹. 基于层次分析法的茂县斜坡地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 长江科学院院报,2017,34(5):31 − 35. [LIU Yuheng,DENG Hui,XIONG Qianying. AHP-based evaluation of slope geo-hazard susceptibility of Maoxian County,Sichuan,China[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2017,34(5):31 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20160155
LIU Yuheng, DENG Hui, XIONG Qianying . AHP-based evaluation of slope geo-hazard susceptibility of Maoxian County, Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2017 ,34 (5 ):31 −35 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[7] 李微,洪托,徐世光,等. 基于I法与CF法的榕江县地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,2022,33(3):42 − 48. [LI Wei,HONG Tuo,XU Shiguang,et al. Evaluation of geological hazard susceptibility based on i method and cf method[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,2022,33(3):42 − 48. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2022.03.007
LI Wei, HONG Tuo, XU Shiguang, et al . Evaluation of geological hazard susceptibility based on i method and cf method[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,2022 ,33 (3 ):42 −48 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[8] 乔德京,王念秦,郭有金,等. 加权确定性系数模型的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 西安科技大学学报,2020,40(2):259 − 267. [QIAO Dejing,WANG Nianqin,GUO Youjin,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on weighted certainty factor model[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology,2020,40(2):259 − 267. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13800/j.cnki.xakjdxxb.2020.0210
QIAO Dejing, WANG Nianqin, GUO Youjin, et al . Landslide susceptibility assessment based on weighted certainty factor model[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology,2020 ,40 (2 ):259 −267 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[9] 陈立华,李立丰,吴福,等. 基于GIS与信息量法的北流市地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 地球与环境,2020,48(4):471 − 479. [CHEN Lihua,LI Lifeng,WU Fu,et al. Evaluation of the geological hazard vulnerability in the Beiliu City based on GIS and information value model[J]. Earth and Environment,2020,48(4):471 − 479. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2020.48.060
CHEN Lihua, LI Lifeng, WU Fu, et al . Evaluation of the geological hazard vulnerability in the Beiliu City based on GIS and information value model[J]. Earth and Environment,2020 ,48 (4 ):471 −479 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[10] 周天伦,曾超,范晨,等. 基于快速聚类-信息量模型的汶川及周边两县滑坡易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(5):137 − 150. [ZHOU Tianlun,ZENG Chao,FAN Chen,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on K-means cluster information model in Wenchuan and two neighboring counties,China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(5):137 − 150. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHOU Tianlun, ZENG Chao, FAN Chen, et al . Landslide susceptibility assessment based on K-means cluster information model in Wenchuan and two neighboring counties, China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021 ,32 (5 ):137 −150 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[11] 谈树成,赵晓燕,李永平,等. 基于GIS与信息量模型的地质灾害危险性评价——以云南省丘北县为例[J]. 西北师范大学学报(自然科学版),2018,54(1):67 − 76. [TAN Shucheng,ZHAO Xiaoyan,LI Yongping,et al. Risk assessment on the geological disasters based on GIS and information content model:Taking Qiubei County,Yunnan Province as an example[J]. Journal of Northwest Normal University (Natural Science),2018,54(1):67 − 76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
TAN Shucheng, ZHAO Xiaoyan, LI Yongping, et al . Risk assessment on the geological disasters based on GIS and information content model: Taking Qiubei County, Yunnan Province as an example[J]. Journal of Northwest Normal University (Natural Science),2018 ,54 (1 ):67 −76 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[12] 李怡飞,刘延国,梁丽萍,等. 青藏高原高山峡谷地貌区地质灾害危险性评价——以雅江县为例[J]. 水土保持研究,2021,28(3):364 − 370. [LI Yifei,LIU Yanguo,LIANG Liping,et al. Assessment on hazard of geological disasters in alpine and canyon landforms of qinghai-Xizang plateau:A case study of Yajiang County[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2021,28(3):364 − 370. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2021.03.040
LI Yifei, LIU Yanguo, LIANG Liping, et al . Assessment on hazard of geological disasters in alpine and canyon landforms of qinghai-Xizang plateau: A case study of Yajiang County[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2021 ,28 (3 ):364 −370 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[13] 韩用顺,孙湘艳,刘通,等. 基于证据权-投影寻踪模型的藏东南地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 山地学报,2021,39(5):672 − 686. [HAN Yongshun,SUN Xiangyan,LIU Tong,et al. Susceptibility evaluation of geological hazards based on evidence weight-projection pursuit model in southeast Xizang,China[J]. Mountain Research,2021,39(5):672 − 686. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16089/j.cnki.1008-2786.000629
HAN Yongshun, SUN Xiangyan, LIU Tong, et al . Susceptibility evaluation of geological hazards based on evidence weight-projection pursuit model in southeast Xizang, China[J]. Mountain Research,2021 ,39 (5 ):672 −686 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[14] 沈迪,郭进京,陈俊合. 甘肃定西地区地质灾害危险性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(4):134 − 142. [SHEN Di,GUO Jinjing,CHEN Junhe. Risk assessment of geological hazards in Dingxi Region of Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(4):134 − 142. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.04-18
SHEN Di, GUO Jinjing, CHEN Junhe . Risk assessment of geological hazards in Dingxi Region of Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021 ,32 (4 ):134 −142 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[15] 张欣,王运生,梁瑞锋. 基于GIS的小江断裂中北段滑坡灾害危险性评价[J]. 地质与勘探,2018,54(3):623 − 633. [ZHANG Xin,WANG Yunsheng,LIANG Ruifeng. Assessment of landslide hazard in the middle and northern Xiaojiang fault zone based on GIS[J]. Geology and Exploration,2018,54(3):623 − 633. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2018.03.018
ZHANG Xin, WANG Yunsheng, LIANG Ruifeng . Assessment of landslide hazard in the middle and northern Xiaojiang fault zone based on GIS[J]. Geology and Exploration,2018 ,54 (3 ):623 −633 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[16] 李益敏,袁静,蒋德明,等. 基于GIS的高山峡谷区滑坡灾害危险性评价——以泸水市为例[J]. 水土保持研究,2021,28(3):355 − 363. [LI Yimin,YUAN Jing,JIANG Deming,et al. GIS-based risk assessment of landslide disaster in high mountain valley:Taking Lushui City as an example[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2021,28(3):355 − 363. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Yimin, YUAN Jing, JIANG Deming, et al . GIS-based risk assessment of landslide disaster in high mountain valley: Taking Lushui City as an example[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2021 ,28 (3 ):355 −363 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[17] 凌炳,余敏. 滑坡灾害坡度坡向敏感性分析研究——以云南大关县为例[J]. 城市地质,2015,10(3):66 − 68. [LING Bing,YU Min. Sensitivity factors of slope gradient and slope direction of landslides in Daguan County,Yunnan[J]. Urban Geology,2015,10(3):66 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2015.03.015
LING Bing, YU Min . Sensitivity factors of slope gradient and slope direction of landslides in Daguan County, Yunnan[J]. Urban Geology,2015 ,10 (3 ):66 −68 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[18] 王帅永,唐川,方群生,等. 研究强震区滑坡敏感性评价——以汶川县为例[J]. 地震研究,2016,39(2):279 − 287. [WANG Shuaiyong,TANG Chuan,FANG Qunsheng,et al. Research on landslide susceptibility assessment in strong seismic zone:Taking Wenchuan Country as an example[J]. Journal of Seismological Research,2016,39(2):279 − 287. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2016.02.014
WANG Shuaiyong, TANG Chuan, FANG Qunsheng, et al . Research on landslide susceptibility assessment in strong seismic zone: Taking Wenchuan Country as an example[J]. Journal of Seismological Research,2016 ,39 (2 ):279 −287 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[19] 周鑫. 金沙江上游茂顶河段滑坡成因机制及敏感性研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2019. [ZHOU Xin. The mechanism analysis and susceptibility mapping of the landslides along the Maoding River at the upstream of the Jinsha River[D]. Changchun:Jilin University,2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHOU Xin. The mechanism analysis and susceptibility mapping of the landslides along the Maoding River at the upstream of the Jinsha River[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) [20] 沈玲玲,刘连友,许冲,等. 基于多模型的滑坡易发性评价——以甘肃岷县地震滑坡为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2016,24(1):19 − 28. [SHEN Lingling,LIU Lianyou,XU Chong,et al. Multi-models based landslide susceptibility evaluation:Illustrated with landslides triggered by Minxian earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2016,24(1):19 − 28. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2016.01.003
SHEN Lingling, LIU Lianyou, XU Chong, et al . Multi-models based landslide susceptibility evaluation: Illustrated with landslides triggered by Minxian earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2016 ,24 (1 ):19 −28 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[21] 许冲,戴福初,徐锡伟. 基于GIS平台与证据权的地震滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地球科学,2011,36(6):1155 − 1164. [XU Chong,DAI Fuchu,XU Xiwei. Earthquake triggered landslide susceptibility evaluation based on GIS platform and weight-of-evidence modeling[J]. Earth Science,2011,36(6):1155 − 1164. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XU Chong, DAI Fuchu, XU Xiwei . Earthquake triggered landslide susceptibility evaluation based on GIS platform and weight-of-evidence modeling[J]. Earth Science,2011 ,36 (6 ):1155 −1164 . (in Chinese with English abstract) -




 下载:
下载: