Characteristics and causes analysis of Nandianzi landslide in Lingtai County, Gansu Province
-
摘要:
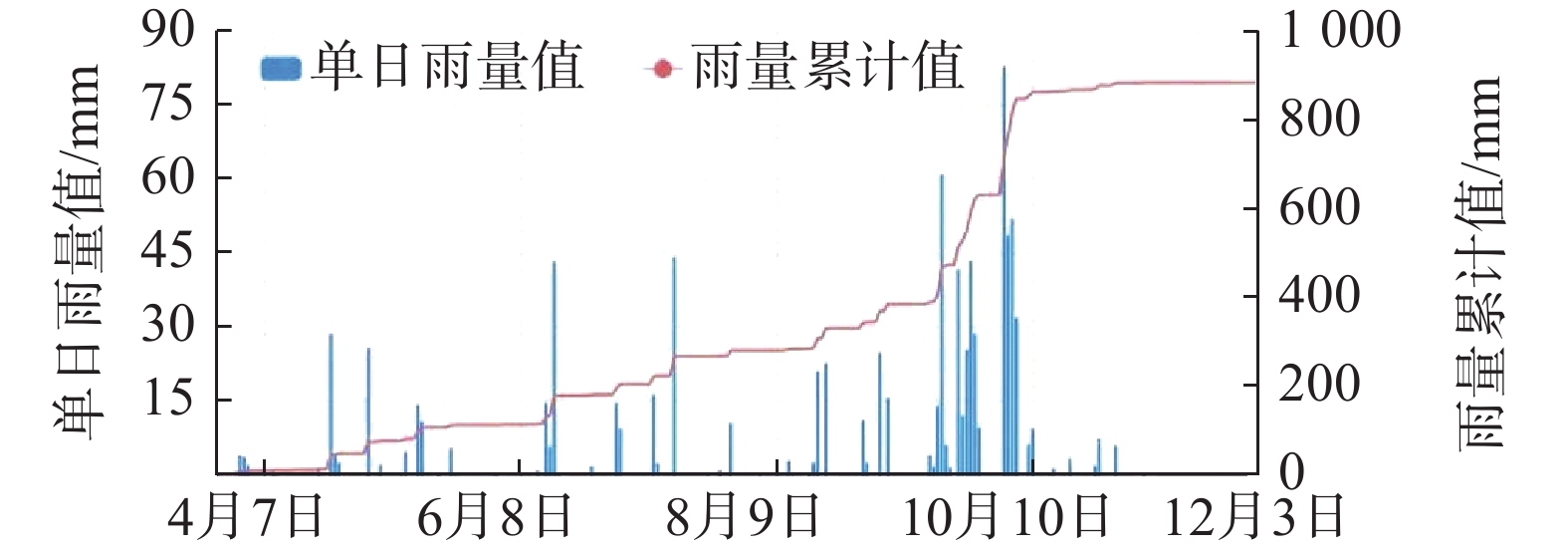
2021年10月3日甘肃灵台南店子发生大型推移式黄土—泥岩接触面滑坡,因成功预警而未造成人员伤亡。为探明南店子滑坡发生机理,对滑体地形地貌、地层岩性、水文地质条件以及人类工程活动等进行了基础调查,根据滑坡裂缝发育特征和差异,将该滑坡体分为5个滑块,并对每个滑体特征进行深入研究,定性定量分析了不同滑坡部位的具体滑动情况,并为滑坡分级分块的客观合理性和滑坡机理分析进一步提供证据。最终分析得出滑坡灾害的发生主要是:(1)斜坡中下部和坡脚抗滑段不合理的大规模挖坡取土等人为活动使斜坡变陡、抗滑力减小;(2)坡面洼坑,导致排水不畅,长期大量入渗软化了岩层接触面,降低了斜坡的稳定性;(3)长时间的强降雨。研究成果对于相似区域监测预警、风险评价和工程治理工作具有很好的借鉴意义。
Abstract:On October 3, 2021, a large landslide occurred at the loess-mudstone interface in Nandianzi, Lingtai, its successful early warning measures preventing casualties. In order to investigate the occurrence mechanism behind the Nandianzi landslide, a basic investigation was conducted, covering the topography, lithology, hydrogeological conditions, and human engineering activities related to the landslide. Based on the characteristics and differences of the crack development of the landslide, the landslide mass was divided into five blocks. The characteristics of each block were thoroughly analyzed through qualitative and quantitative analysis. The specific sliding situation of different parts of the landslide was analyzed, and further evidence was provided for the objective rationality of landslide classification and zoning, as well as the analysis of landslide mechanisms. Ultimately, it is concluded that the main causes of landslide disasters are as follows: (1) Large-scale excavation and earthwork activities at the lower and middle parts of the slope and the toe, leading to slope steepening and reduced resistance to sliding; (2) Formation of slope depressions, causing inadequate drainage and softening of the rock layer contact surface, thereby diminishing slope stability; and (3) Prolonged heavy rainfall that leads to instability and causes significant loss. While the Nandianzi landslide in Lintai county represents a successfully averted disaster, it serves as a noteworthy case study and a cautionary example for scientifically and standardizedly approaching urban construction and rural revitalization in China. This study holds significance value for monitoring, early warning,risk assessmen, and engineering treatment in comparable regions.
-

-
表 1 各滑体特征及相互关系
Table 1. Characteristics and interrelationships of sliding body
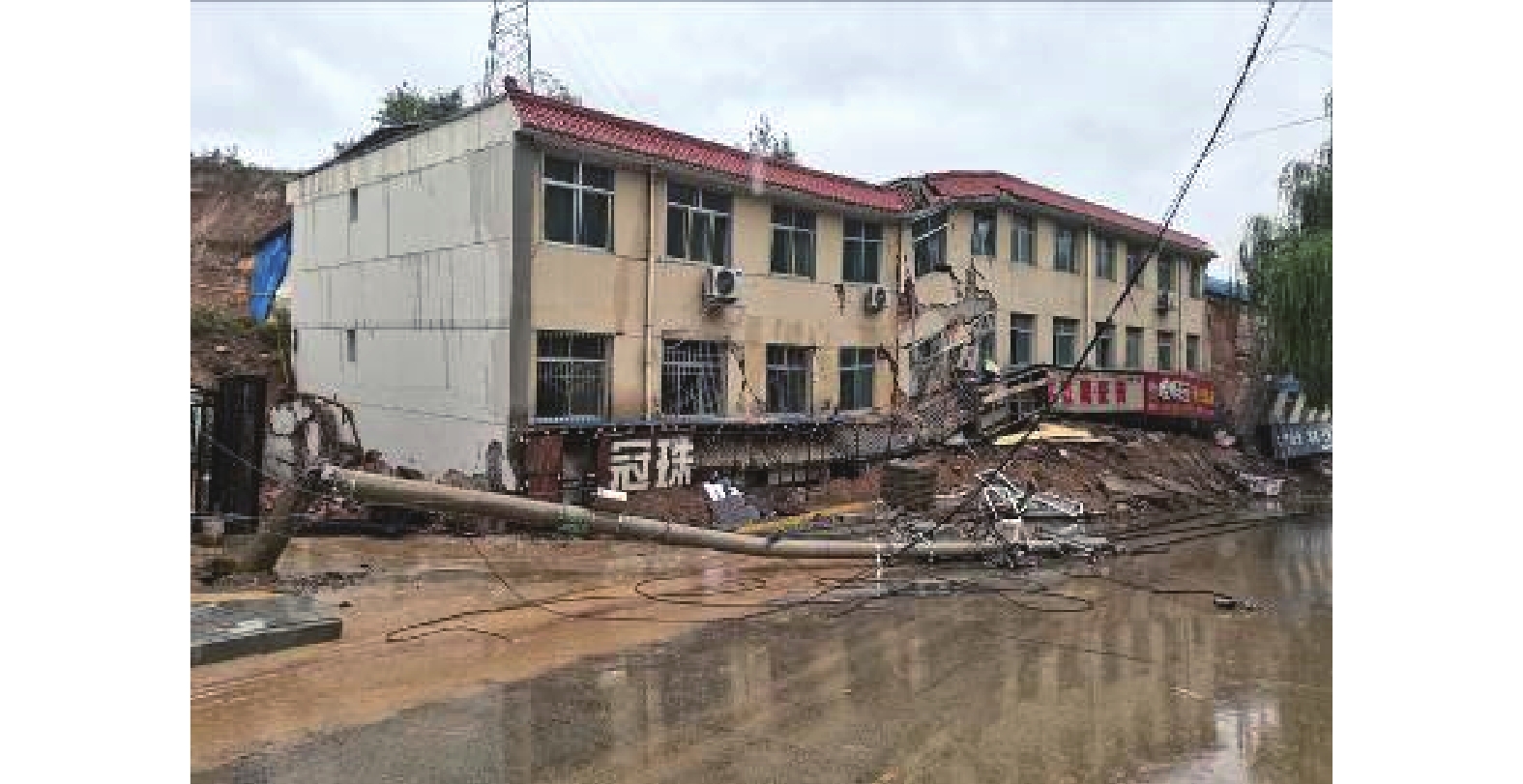
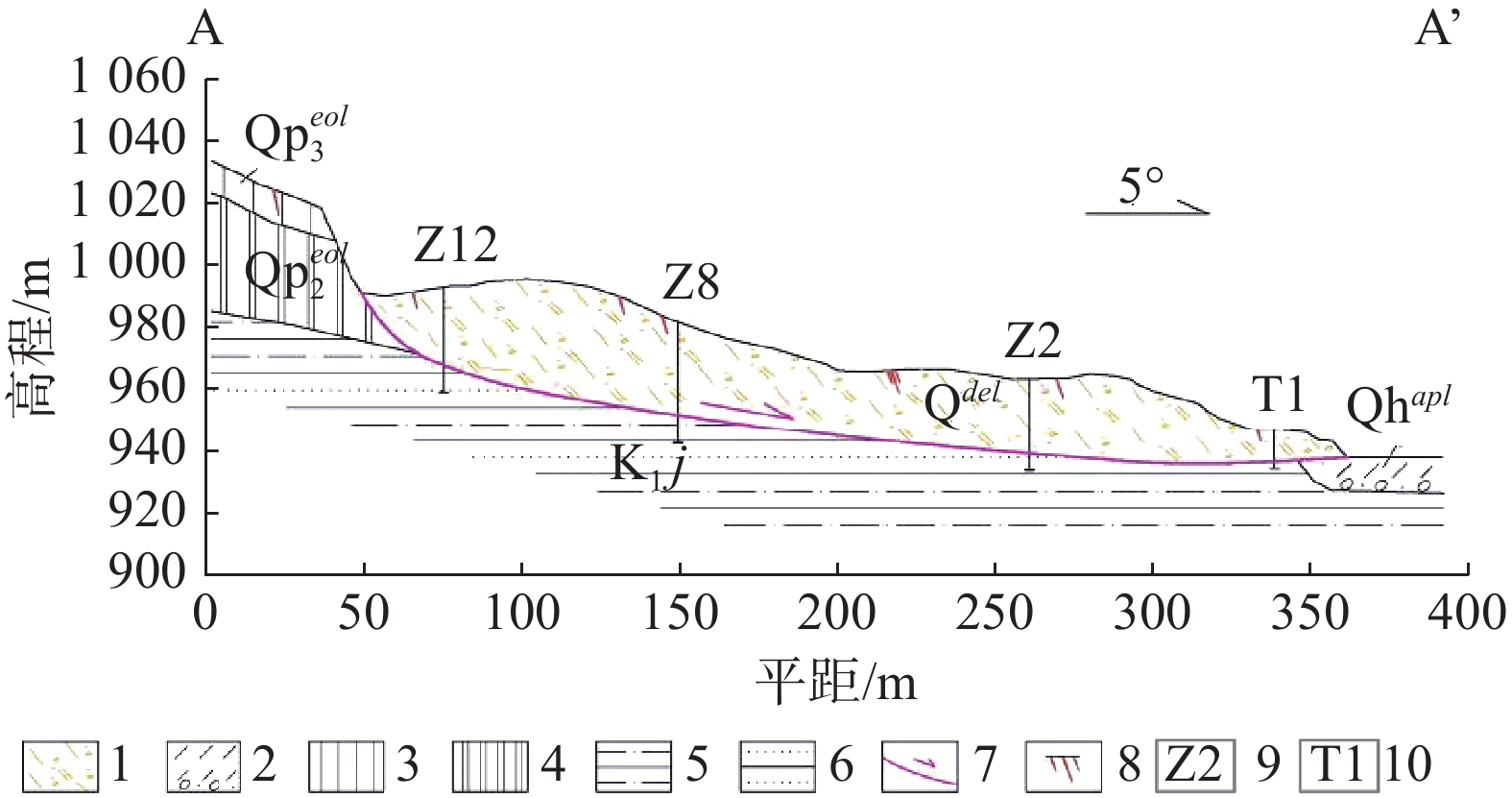
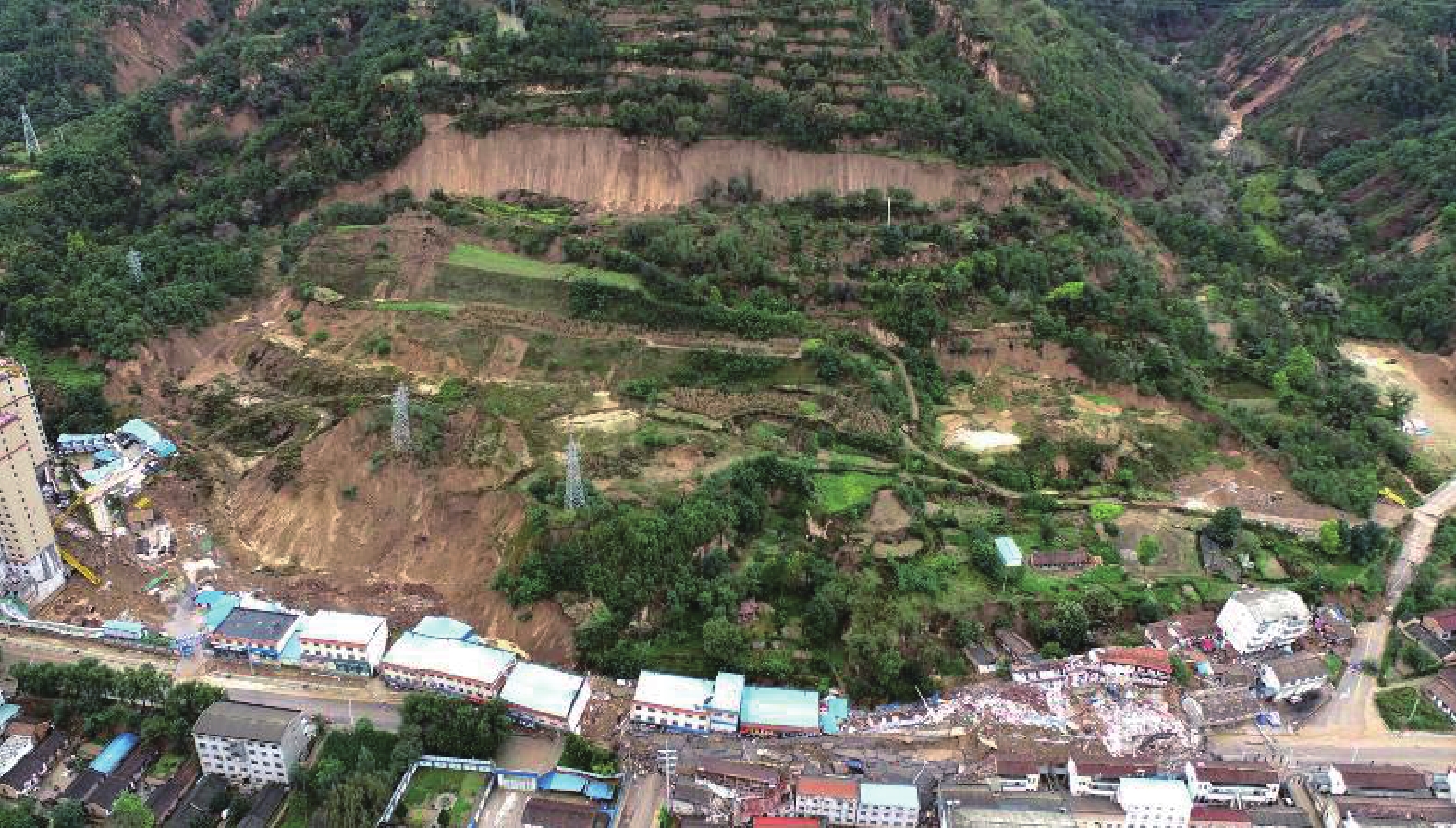
滑体编号 基本特征 各滑体特征 相互关系 1#滑块 体积约2.55×106 m3,滑动方向基本正北,裂缝延伸方向与滑动方向大体一致(图5) 为本次滑坡的主推滑体,后部与滑坡壁相接,中间为滑坡洼地,该滑块中前部发育平面呈弧形展布的放射状鼓胀裂缝带,反映出该滑块的前部受到后部滑体推挤变形的特点。前部东、西两侧为尖角状滑舌向前伸出 受前部2#滑块的阻挡,地形相对低洼且有积水,抗滑能力弱 2#滑块 近东西向展布,平均长度270 m,中间宽160 m、东西两侧宽50 m左右,体积约50×104 m3 与南部为1#滑块主体之间为挖方平台,发育一条基本连续的向南凸出的弧形裂缝带,长度280 m,宽度2~5 m(图6 − 7),裂缝表现出鼓胀的特点,这一带原近水平地面有鼓起和反翘10°的现象(图8),是挖坡取土和洼地渗水软化形成的薄弱部位 受1#滑块的推挤而滑动,为本次滑坡的前部被推动体,最前部鼓胀、剪张裂缝发育,变形强烈,破坏G244、商铺和居民住宅等,为本次滑坡破坏和损失最严重的部位(图9) 3#滑块 位于滑坡西侧后部,前缘临沟,平面呈不规则三角形,前缘北侧在小桥附近。滑块长度160 m,平均宽160 m,体积约25×104 m3 3#滑块位于滑坡西侧后部,前缘临沟,平面呈不规则三角形,前缘北侧在小桥附近。滑块中前部发育与沟道近于平行展布的放射状裂缝带,单条裂缝宽0.3 m左右。其滑坡后壁与主滑壁相连 主滑壁向西延伸部分实际上为3#滑块的北侧侧壁。该滑块后部受到1#滑块滑动时的侧向推挤作用,向西侧沟道临空方向滑动,其总体滑动方向约310°,与主滑差异较大,为一相对独特的滑块 4#滑块 滑块长度155 m,平均宽80 m,体积约25×104 m3 4#滑块位于滑坡东侧,与3#滑块基本呈对称状分布,平面为较规则等腰三角形,4#滑块为夹于两条小冲沟之间的高平台,西侧因人工开挖,使得4#滑块西侧地势呈陡崖状,高出1#滑块5~15 m,也是4#滑块的西侧界,近东西向拉张裂缝发育,单条裂缝宽1~2 m左右,东侧边缘地带也发育剪张裂缝。其滑动距离相对较小,前缘15 m高的黄土陡坡发生滑塌,摧毁挡土墙,滑体前缘堆压在前部天泰嘉苑2栋在建住宅楼外墙 该滑块后部受到西侧1#滑块滑动时的牵引和推挤作用,向西北临空方向滑动,滑动方向约30°,与主滑差异较大,说明为一相对独立的滑块。 5#滑块 平面形态呈簸箕状,滑块长度100 m,平均宽80 m,体积约10×104 m3 位于其上的输电线路铁塔滑移39 m,是本次滑坡滑动最远的一块特殊滑块,滑动方向约30°,其原因与坡脚大规模开挖和顶部洼坑积水下渗有关 5#滑块位于滑坡前部东侧,1#滑块与2#滑块之间,实为1#滑块中的滑动更剧烈的一块,为一相对独立的滑块 表 2 A-A′滑坡稳定性计算结果
Table 2. Calculation results of landslide stability
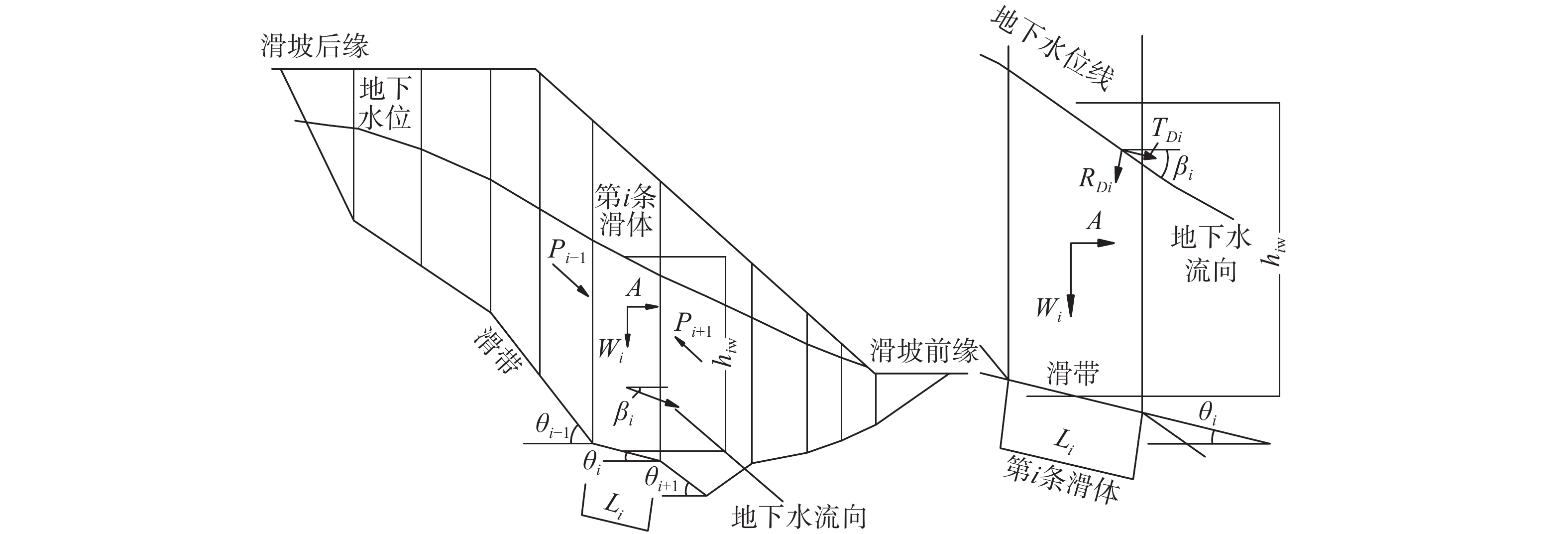
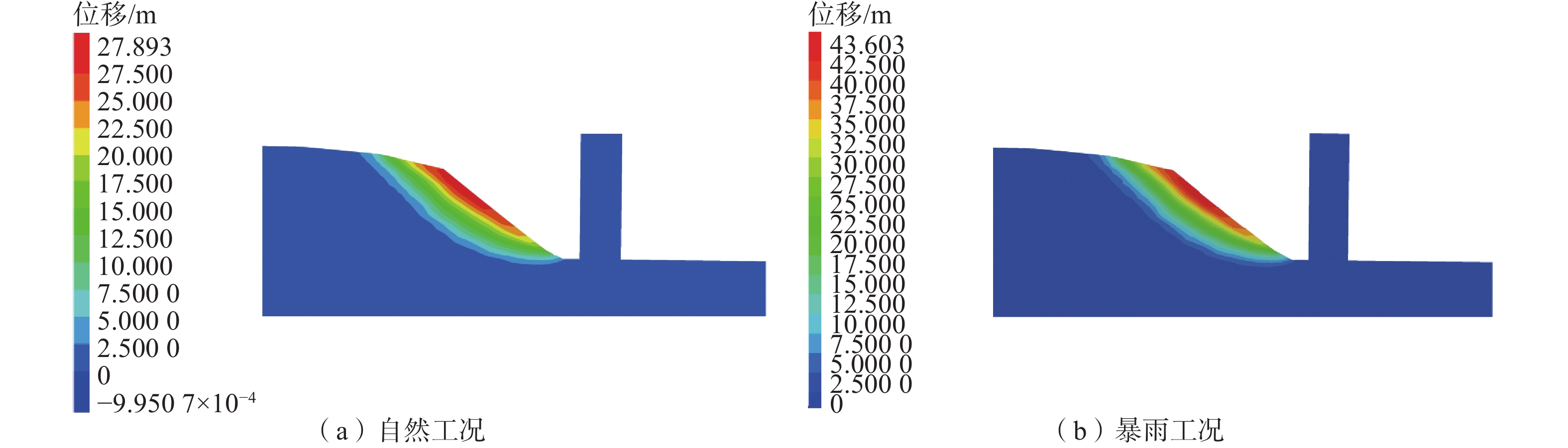
工况 稳定系数 自重 1.02 自重+持续强降雨 0.89 -
[1] 王磊, 李荣建, 杨正午, 等. 强降雨作用下黄土陡坡开裂特性测试[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2021,51(5):1338 − 1346. [WANG Lei, LI Rongjian, YANG Zhengwu, et al. Experimental study on cracking characteristics of loess steep slope under intensive rainfall[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2021,51(5):1338 − 1346. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Lei, LI Rongjian, YANG Zhengwu, et al . Experimental study on cracking characteristics of loess steep slope under intensive rainfall[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2021 ,51 (5 ):1338 −1346 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[2] 刘凡, 邓亚虹, 慕焕东, 等. 基于最大熵-无限边坡模型的降雨诱发浅层黄土滑坡稳定性评价方法研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(5):146 − 158. [LIU Fan, DENG Yahong, MU Huandong, et al. A study of the stability evaluation method of rainfall-induced shallow loess landslides based on the Maxent-Sinmap slope model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(5):146 − 158. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Fan, DENG Yahong, MU Huandong, et al . A study of the stability evaluation method of rainfall-induced shallow loess landslides based on the Maxent-Sinmap slope model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023 ,50 (5 ):146 −158 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[3] 郭富赟, 张龙生, 王信, 等. 甘肃黑方台罗家坡滑坡演化过程及运动机制分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(2):11 − 20. [GUO Fuyun, ZHANG Longsheng, WANG Xin, et al. Analysis on evolution process and movement mechanism of the Luojiapo landslide in Heifangtai, Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(2):11 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GUO Fuyun, ZHANG Longsheng, WANG Xin, et al . Analysis on evolution process and movement mechanism of the Luojiapo landslide in Heifangtai, Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023 ,34 (2 ):11 −20 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[4] 尹玉玲, 徐素宁, 王军, 等. 典型黄土丘陵区地质灾害隐患识别与时序监测[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(2):141 − 149. [YIN Yuling, XU Suning, WANG Jun, et al. Identification and time series monitoring of hidden dangers of geological hazards in the typical loess hilly regions[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(2):141 − 149. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YIN Yuling, XU Suning, WANG Jun, et al . Identification and time series monitoring of hidden dangers of geological hazards in the typical loess hilly regions[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023 ,50 (2 ):141 −149 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[5] 彭建兵,王启耀,庄建琦,等. 黄土高原滑坡灾害形成动力学机制[J]. 地质力学学报,2020,26(5):714 − 730. [PENG Jianbing,WANG Qiyao,ZHUANG Jianqi,et al. Dynamic formation mechanism of landslide disaster on the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2020,26(5):714 − 730. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.05.059
PENG Jianbing, WANG Qiyao, ZHUANG Jianqi, et al . Dynamic formation mechanism of landslide disaster on the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2020 ,26 (5 ):714 −730 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[6] 彭建兵,王启耀,门玉明. 黄土高原滑坡灾害[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2019. [PENG Jianbing,WANG Qiyao,MEN Yuming. Landslide disaster in loess plateau[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2019. (in Chinese)
PENG Jianbing, WANG Qiyao, MEN Yuming. Landslide disaster in loess plateau[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019. (in Chinese) [7] 吴玮江,王念秦. 甘肃滑坡灾害[M]. 兰州:兰州大学出版社,2006. [WU Weijiang,WANG Nianqin. Landslide hazards in Gansu[M]. Lanzhou:Lanzhou University Press,2006. (in Chinese)
WU Weijiang, WANG Nianqin. Landslide hazards in Gansu[M]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University Press, 2006. (in Chinese) [8] 吴玮江, 宿星, 冯乐涛, 等. 甘肃黑方台滑坡类型与活动特征研究[J]. 冰川冻土,2019,41(6):1483 − 1495. [WU Weijiang, SU Xing, FENG Letao, et al. The study on landslide types and activity characteristics in Heifangtai, Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2019,41(6):1483 − 1495. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WU Weijiang, SU Xing, FENG Letao, et al . The study on landslide types and activity characteristics in Heifangtai, Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2019 ,41 (6 ):1483 −1495 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[9] 吴玮江,宿星,刘伟,等. 黄土-泥岩接触面滑坡的特征与成因[J]. 冰川冻土,2014,36(5):1167 − 1175. [WU Weijiang,SU Xing,LIU Wei,et al. Loess-mudstone interface landslides:Characteristics and causes[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2014,36(5):1167 − 1175. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WU Weijiang, SU Xing, LIU Wei, et al . Loess-mudstone interface landslides: Characteristics and causes[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2014 ,36 (5 ):1167 −1175 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[10] 吴玮江, 宿星, 叶伟林, 等. 饱和黄土滑坡形成中的侧压力作用——以甘肃黑方台为例[J]. 岩土工程学报,2018,40(增刊1):135 − 140. [WU Weijiang, SU Xing, YE Weilin, et al. Lateral pressure in formation of saturated loess landslide—case study of Heifangtai, Gansu Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2018,40(Sup1):135 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WU Weijiang, SU Xing, YE Weilin, et al . Lateral pressure in formation of saturated loess landslide—case study of Heifangtai, Gansu Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2018 ,40 (Sup1 ):135 −140 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[11] 李同录,李颖喆,赵丹旗,等. 对水致黄土斜坡破坏模式及稳定性分析原则的思考[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):25 − 32. [LI Tonglu,LI Yingzhe,ZHAO Danqi,et al. Thoughts on modes of loess slope failure triggered by water infiltration and the principals for stability analysis[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):25 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Tonglu, LI Yingzhe, ZHAO Danqi, et al . Thoughts on modes of loess slope failure triggered by water infiltration and the principals for stability analysis[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022 ,33 (2 ):25 −32 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[12] 张国信, 周自强, 李高平, 等. 滑坡地质灾害风险防控与应急处置——以灵台县城南店子村滑坡地质灾害成功避险为例[J]. 甘肃科技,2023,39(5):20 − 25. [ZHANG Guoxin, ZHOU Ziqiang, LI Gaoping, et al. Risk prevention and emergency treatment of landslide geological disasters—taking the successful avoidance of landslide geological disasters in Dianzi Village, south of Lingtai County as an example[J]. Gansu Science and Technology,2023,39(5):20 − 25. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2009.04.001
ZHANG Guoxin, ZHOU Ziqiang, LI Gaoping, et al . Risk prevention and emergency treatment of landslide geological disasters—taking the successful avoidance of landslide geological disasters in Dianzi Village, south of Lingtai County as an example[J]. Gansu Science and Technology,2023 ,39 (5 ):20 −25 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[13] 孙秀娟,杨强,田运涛,等. 陇东某黄土滑坡地质灾害成因、特征分析及防治对策[J]. 勘察科学技术,2010(4):28 − 31. [SUN Xiujuan,YANG Qiang,TIAN Yuntao,et al. Cause of formation,characteristic analysis of loess landslides geological hazards in east of Gansu and its preventive countermeasures[J]. Site Investigation Science and Technology,2010(4):28 − 31. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SUN Xiujuan, YANG Qiang, TIAN Yuntao, et al . Cause of formation, characteristic analysis of loess landslides geological hazards in east of Gansu and its preventive countermeasures[J]. Site Investigation Science and Technology,2010 (4 ):28 −31 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[14] 杨秀元,田运涛,王爱军. 西塘湾滑坡成因分析及稳定性评价[J]. 山西建筑,2010,36(25):84 − 86. [YANG Xiuyuan,TIAN Yuntao,WANG Aijun. Causes analysis and stability assessment of Xitang Bay landslide[J]. Shanxi Architecture,2010,36(25):84 − 86. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2010.25.053
YANG Xiuyuan, TIAN Yuntao, WANG Aijun . Causes analysis and stability assessment of Xitang Bay landslide[J]. Shanxi Architecture,2010 ,36 (25 ):84 −86 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[15] 冉林, 马鹏辉, 彭建兵, 等. 甘肃黑方台“10·5”黄土滑坡启动及运动特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(6):1 − 9. [RAN Lin, MA Penghui, PENG Jianbing, et al. The initiation and motion characteristics of the“10·5”loess landslide in the Heifangtai platform, Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(6):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
RAN Lin, MA Penghui, PENG Jianbing, et al . The initiation and motion characteristics of the“10·5”loess landslide in the Heifangtai platform, Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022 ,33 (6 ):1 −9 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[16] 孙萍萍, 张茂省, 江睿君, 等. 降雨诱发浅层黄土滑坡变形破坏机制[J]. 地质通报,2021,40(10):1617 − 1625. [SUN Pingping, ZHANG Maosheng, JIANG Ruijun, et al. Deformation and failure mechanism of rainfall-induced shallow loess landslide[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2021,40(10):1617 − 1625. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SUN Pingping, ZHANG Maosheng, JIANG Ruijun, et al . Deformation and failure mechanism of rainfall-induced shallow loess landslide[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021 ,40 (10 ):1617 −1625 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[17] 毛正君, 张瑾鸽, 仲佳鑫, 等. 梯田型黄土滑坡隐患发育特征与成因分析——以宁夏南部黄土丘陵区为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(6):142 − 152. [MAO Zhengjun, ZHANG Jinge, ZHONG Jiaxin, et al. Analysis of basic characteristics and deformation mechanism of loess potential landslide of terrace: Taking loess hilly region in southern Ningxia as an example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(6):142 − 152. (in Chinese with English abstract)
MAO Zhengjun, ZHANG Jinge, ZHONG Jiaxin, et al . Analysis of basic characteristics and deformation mechanism of loess potential landslide of terrace: Taking loess hilly region in southern Ningxia as an example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022 ,33 (6 ):142 −152 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[18] 李拴虎,亓越,王晓荣,等. 黄土-泥岩滑坡渐进滑动失稳的模型试验研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2023,43(2):200 − 207. [LI Shuanhu,QI Yue,WANG Xiaorong,et al. Physical modelling of progressive sliding instability of loess-mudstone landslide[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2023,43(2):200 − 207. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Shuanhu, QI Yue, WANG Xiaorong, et al . Physical modelling of progressive sliding instability of loess-mudstone landslide[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2023 ,43 (2 ):200 −207 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[19] 冯海奎. 浅谈灵台县山洪地质灾害现状及成因分析[J]. 科技风,2020(35):122 − 123. [FENG Haikui. Discussion on the present situation and cause analysis of geological disasters of mountain torrents in Lingtai County[J]. Technology Wind,2020(35):122 − 123. (in Chinese with English abstract)
FENG Haikui . Discussion on the present situation and cause analysis of geological disasters of mountain torrents in Lingtai County[J]. Technology Wind,2020 (35 ):122 −123 . (in Chinese with English abstract) -




 下载:
下载: