Study on the sensitivity of disaster-breeding conditions for rainfall-induced cluster landslides in granite areas: Case study of Beiliu City in southeast Guangxi
-
摘要:
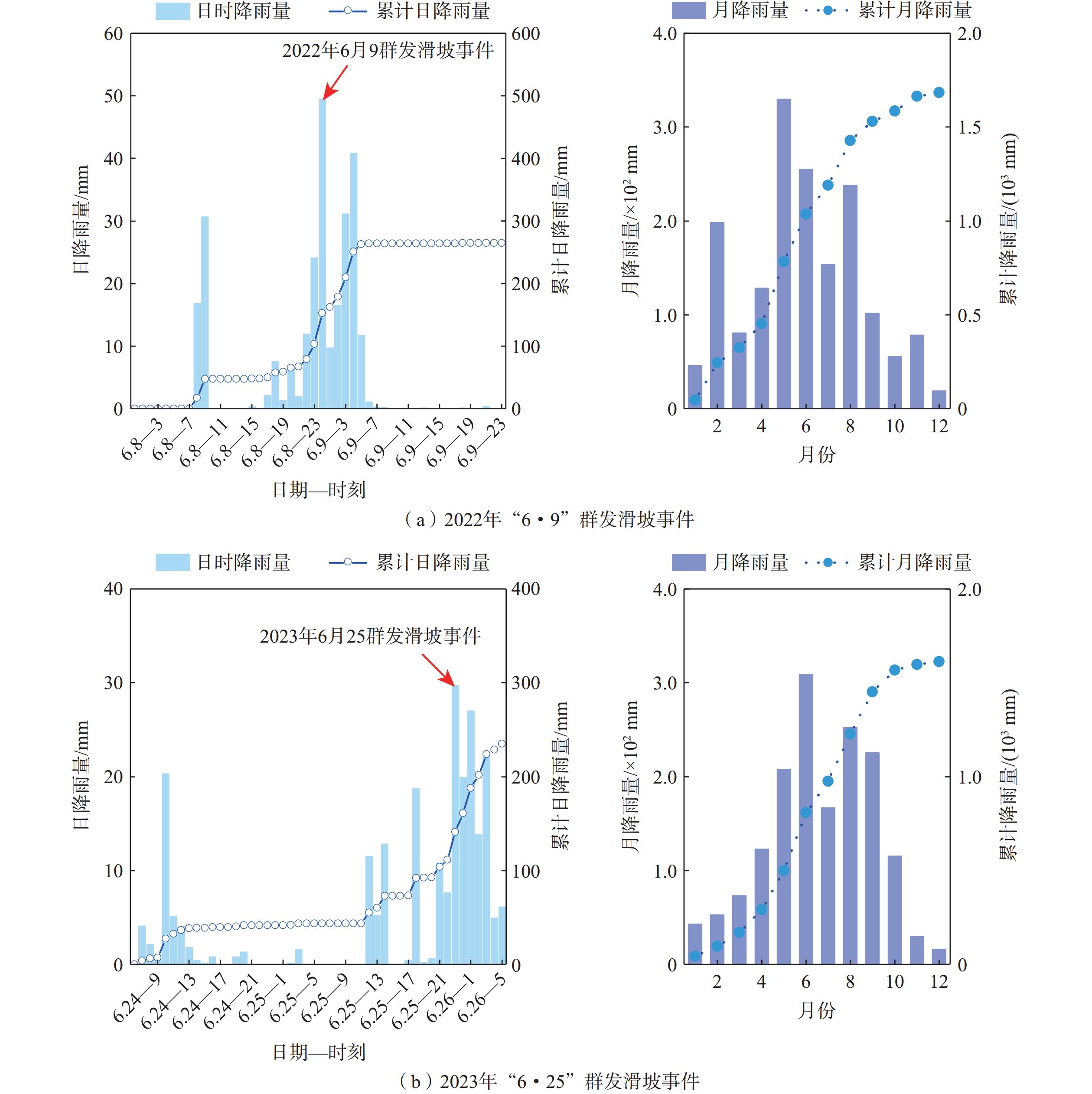
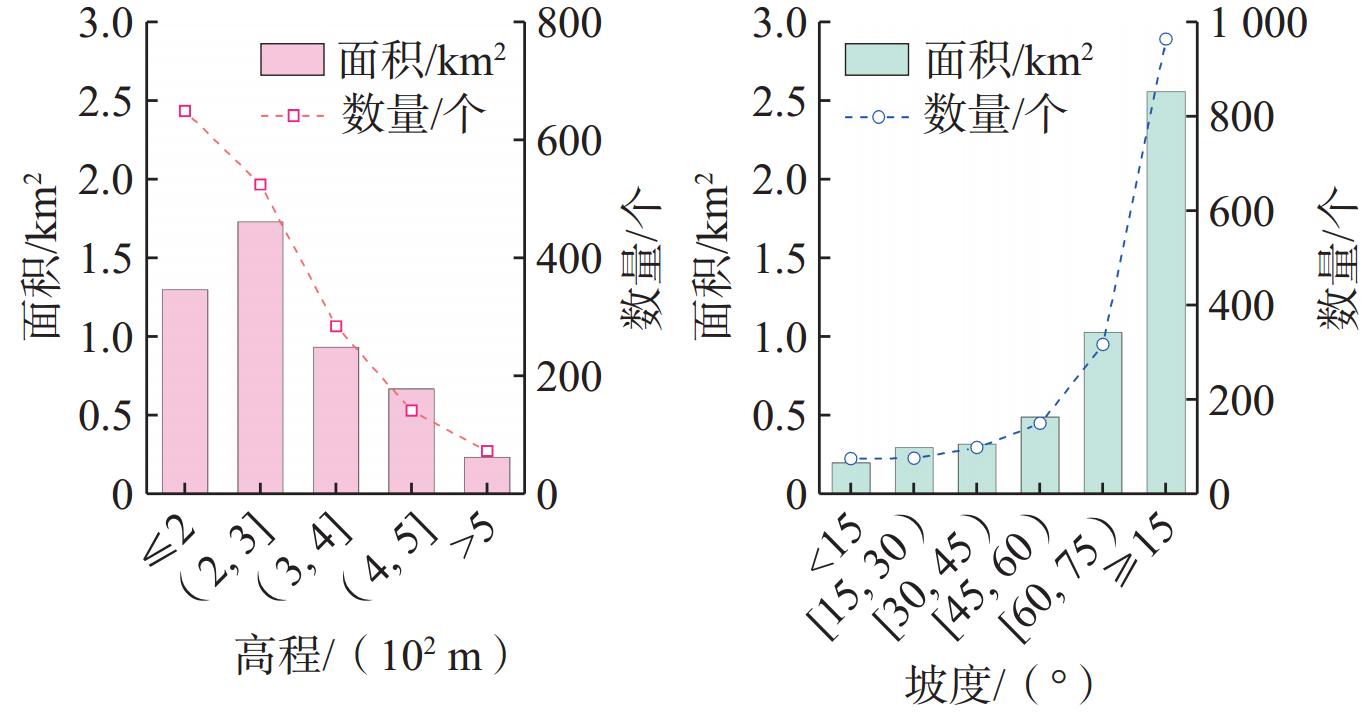
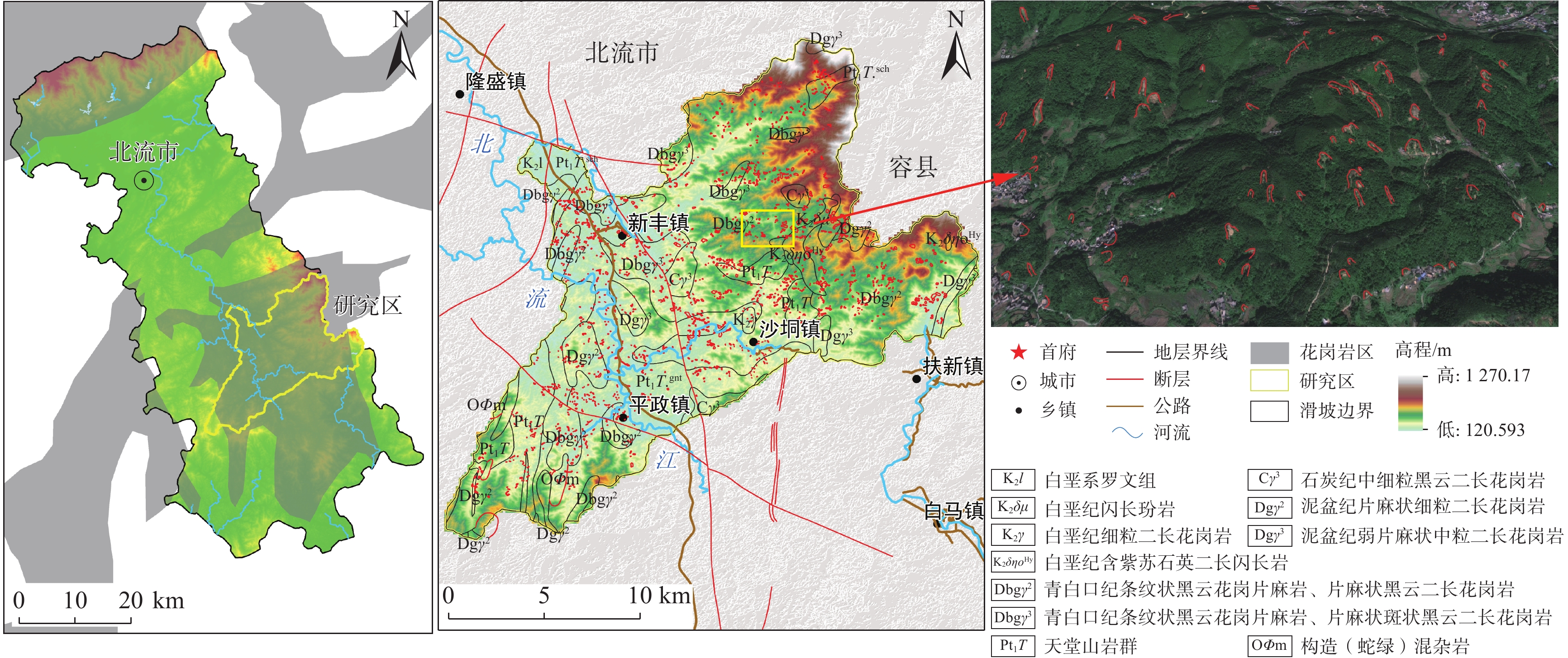
近年来,极端强降雨在我国南方全强风化花岗岩地区诱发了多起群发性滑坡事件,造成了严重的损失。由于区域性的极端气候、厚层风化花岗岩与不规范切坡等因素,群发滑坡频频发生。但滑坡发育特征及孕灾条件尚不明确,给地质灾害监测和防治带来挑战。文章以广西北流市花岗岩地区为研究区,采用现场调查、遥感解译与XG-boost模型,探讨了降雨型群发滑坡的发育特征、时空分布规律、破坏模式和孕灾条件敏感性。结果表明,区内两起暴雨事件共引发滑坡
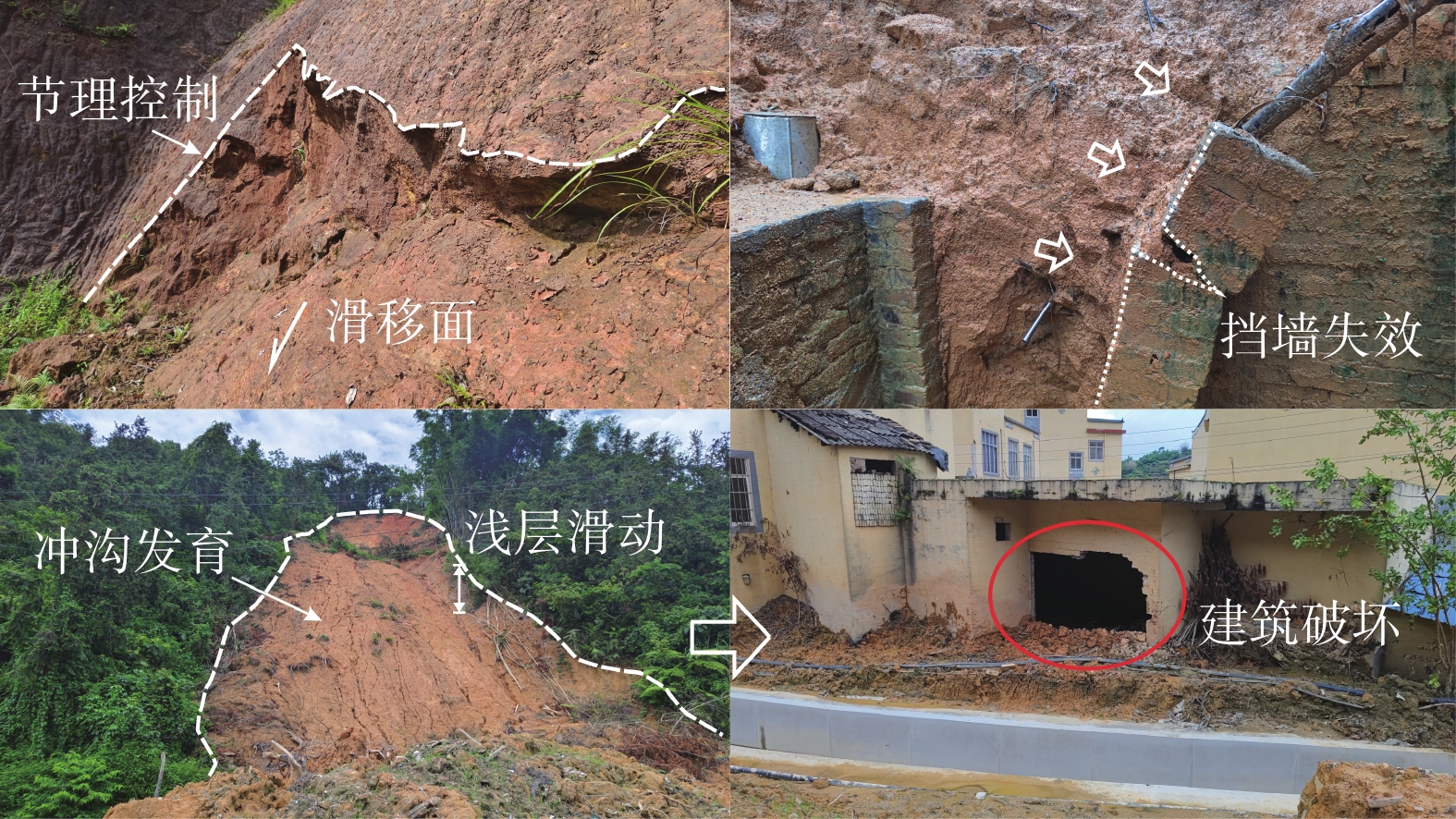
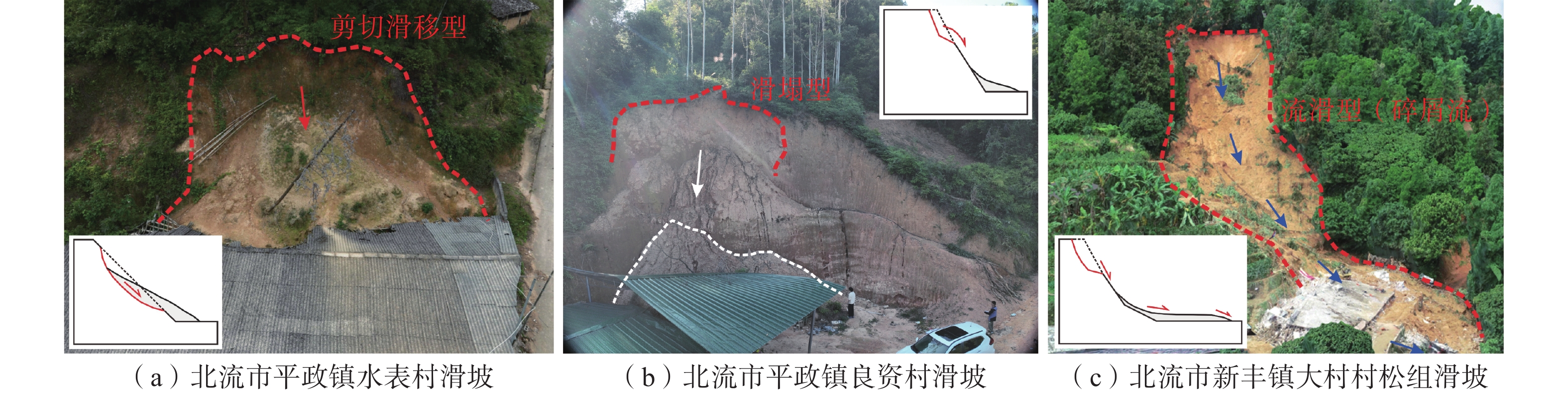
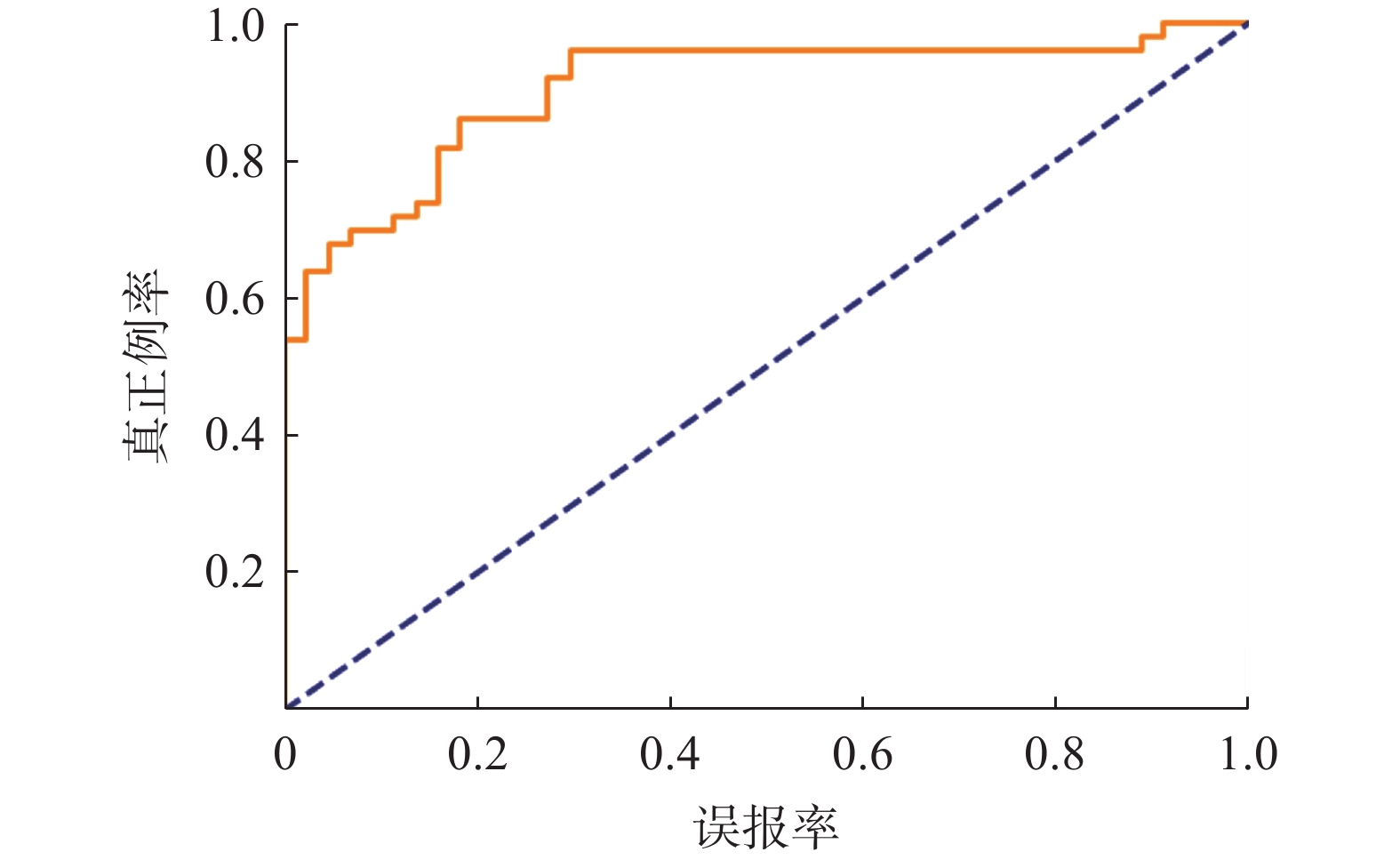
1670 处,以中小规模为主,占总数量的72.57%。群发滑坡集中发育于高程<300 m、坡度>75°的切坡地形下,表现出分布范围广、规模小、数量多、即雨即滑、爆发性强的特点,主要形成剪切滑移型、滑塌型及流滑型(碎屑流)三类破坏模式。距居民点距离(概率贡献为22.22%)、坡度(15.25%)、高程(14.47%)及植被覆盖度(12.01%)是诱发花岗岩地区降雨型群发滑坡的主要孕灾条件。本研究可为花岗岩地区降雨型群发滑坡的研究提供依据,在防控减灾方面具有重要意义。Abstract:In recent years, extreme heavy rainfall has triggered numerous cluster landslide events in the fully weathered granite areas of southern China, causing severe losses. Factors such as regional extreme weather, thick weathered granite layers, and non-standard slope cutting practices have led to frequent occurences of cluster landslides. However, the developmental characteristics and conditions conductive to these landslides are not well-understood, posing challenges to geological disaster monitoring and prevention. This paper focuses on the granite area of Beiliu City in Guangxi as the study area. The study discuss the developmental characteristics, spatiotemporal distribution patterns, failure modes, and sensitivity of disaster-breeding conditions of rainfall-induced cluster landslides through an integrated approach combining field investigations, remote sensing interpretation, and XG-boost modeling. The results show that two rainstorm events in the area triggered 1,670 landslides, mainly of small to medium scale, accounting for 72.57% of the total occurrences. The cluster landslides primarily developed in cut slopes with elevations less than 300 meters and slope angles greater than 75°, exhibiting characteristics of wide spatial distribution, small individual scale, high frequency, immediate response to rainfall, and strong explosiveness. Three main types of failure modes were identified: shear-sliding, toppling-sliding, and flow-sliding (debris flow). The primary disaster-breeding conditions were identified as distance to residential areas (proportion contribution of 22.22%), slope (15.25%), elevation (14.47%), and normalized difference vegetation index (12.01%) in the granite areas. This study provides a basis for the research of rainfall-induced cluster landslides in granite areas and is of great significance in disaster prevention and mitigation.
-
Key words:
- granite area /
- extreme rainfall /
- cluster landslides /
- failure modes /
- disaster-pregnant conditions
-

-
[1] 许强,徐繁树,蒲川豪,等. 2024年4月广东韶关江湾镇极端降雨诱发群发性滑坡初步分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2024,49(8):1264 − 1274. [XU Qiang,XU Fanshu,PU Chuanhao,et al. Preliminary analysis of extreme rainfall-induced cluster landslides in Jiangwan township,Shaoguan,Guangdong,April 2024[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2024,49(8):1264 − 1274. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XU Qiang, XU Fanshu, PU Chuanhao, et al. Preliminary analysis of extreme rainfall-induced cluster landslides in Jiangwan township, Shaoguan, Guangdong, April 2024[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2024, 49(8): 1264 − 1274. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 陈博,张灿灿,李振洪,等. 福建龙岩市2024年“6•16”特大暴雨诱发滑坡发育特征及其调控因子分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2024,49(11):2145 − 2155. [CHEN Bo,ZHANG Cancan,LI Zhenhong,et al. Developmental characteristics and controlling factors of landslides triggered by extreme rainfalls on 16 June 2024 in Longyan,Fujian Province[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2024,49(11):2145 − 2155. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Bo, ZHANG Cancan, LI Zhenhong, et al. Developmental characteristics and controlling factors of landslides triggered by extreme rainfalls on 16 June 2024 in Longyan, Fujian Province[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2024, 49(11): 2145 − 2155. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 何娜,潘宏坚,吴秋菊. 基于GIS的山地地质灾害气象预警研究——以广西陆川县为例[J]. 南方自然资源,2022(10):40 − 47. [HE Na,PAN Hongjian,WU Qiuju. Study on meteorological early warning of geological disasters in mountainous areas based on GIS:A case study of Luchuan County,Guangxi[J]. NanFang ZiRan ZiYuan,2022(10):40 − 47. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HE Na, PAN Hongjian, WU Qiuju. Study on meteorological early warning of geological disasters in mountainous areas based on GIS: A case study of Luchuan County, Guangxi[J]. NanFang ZiRan ZiYuan, 2022(10): 40 − 47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] YANG Hongjuan,YANG Taiqiang,ZHANG Shaojie,et al. Rainfall-induced landslides and debris flows in Mengdong Town,Yunnan Province,China[J]. Landslides,2020,17(4):931 − 941. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01336-y
[5] ROY P,MARTHA T R,VINOD KUMAR K,et al. Cluster landslides and associated damage in the Dima Hasao District of Assam,India due to heavy rainfall in May 2022[J]. Landslides,2023,20(1):97 − 109. doi: 10.1007/s10346-022-01977-6
[6] BENZ S A,BLUM P. Global detection of rainfall-triggered landslide clusters[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences,2019,19(7):1433 − 1444. doi: 10.5194/nhess-19-1433-2019
[7] 吴善百. 广西东南部花岗岩残积土降雨型滑坡的起动机理研究[D]. 南宁:广西大学,2020. [WU Shanbai. Study on starting mechanism of rainfall landslide in granite residual soil in southeast Guangxi[D]. Nanning:Guangxi University,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WU Shanbai. Study on starting mechanism of rainfall landslide in granite residual soil in southeast Guangxi[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 翁峻择. 桂东南地区压实花岗岩风化土崩解特性研究[D]. 桂林:桂林理工大学,2023. [WENG Junze. Study on disintegration characteristics of compacted granite weathered soil in southeast Guangxi[D]. Guilin:Guilin University of Technology,2023. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WENG Junze. Study on disintegration characteristics of compacted granite weathered soil in southeast Guangxi[D]. Guilin: Guilin University of Technology, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 白慧林. 花岗岩残积土滑坡降雨启动机理与预警模型研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2022. [BAI Huilin. Study on rainfall initiation mechanism and early warning model of granite residual soil landslide[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2022. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
BAI Huilin. Study on rainfall initiation mechanism and early warning model of granite residual soil landslide[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 陈立华,羊汉平,廖丽萍,等. 容县2010年6月滑坡灾害降雨阈值研究[J]. 自然灾害学报,2023,32(1):228 − 235. [CHEN Lihua,YANG Hanping,LIAO Liping,et al. Study on the rainfall threshold of the landslide disaster in Rong County in June 2010[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2023,32(1):228 − 235. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Lihua, YANG Hanping, LIAO Liping, et al. Study on the rainfall threshold of the landslide disaster in Rong County in June 2010[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2023, 32(1): 228 − 235. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] TAN Delin,XU Xiaoliang,WANG Lehua,et al. Deformation evolution and failure mechanism of rainfall-induced granite residual soil landsliding event in Northern Guangdong,China[J]. Landslides,2025,22(3):925 − 941. doi: 10.1007/s10346-024-02403-9
[12] 李荣华,江思义,李春玲,等. 基于GIS的北流市地质灾害气象预警研究[J]. 西部探矿工程,2024,36(7):13 − 15. [LI Ronghua,JIANG Siyi,LI Chunling,et al. Study on meteorological early warning of geological hazards in Beiliu City based on GIS[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering,2024,36(7):13 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2024.07.005
LI Ronghua, JIANG Siyi, LI Chunling, et al. Study on meteorological early warning of geological hazards in Beiliu City based on GIS[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2024, 36(7): 13 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2024.07.005
[13] 吴秋菊,江思义,李春玲,等. 基于GIS的北流市地质灾害危险性分区评价研究[J]. 贵州地质,2023,40(1):20 − 25. [WU Qiuju,JIANG Siyi,LI Chunling,et al. Evaluation research of geological hazard division based on GIS in Beiliu City[J]. Guizhou Geology,2023,40(1):20 − 25. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2023.01.003
WU Qiuju, JIANG Siyi, LI Chunling, et al. Evaluation research of geological hazard division based on GIS in Beiliu City[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2023, 40(1): 20 − 25. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2023.01.003
[14] 李振洪,朱武,余琛,等. 影像大地测量学发展现状与趋势[J]. 测绘学报,2023,52(11):1805 − 1834. [LI Zhenhong,ZHU Wu,YU Chen,et al. Development status and trends of imaging geodesy[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica,2023,52(11):1805 − 1834. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2023.20230003
LI Zhenhong, ZHU Wu, YU Chen, et al. Development status and trends of imaging geodesy[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2023, 52(11): 1805 − 1834. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2023.20230003
[15] LIU Haizhi,XU Hui,BAO Hongjun,et al. Application of machine learning classification algorithm to precipitation-induced landslides forecasting[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science,2022,33(3):282 − 292.
[16] 李立丰. 广西地区滑坡灾害的临界降雨量阈值研究[D]. 南宁:广西大学,2020. [LI Lifeng. Study on critical rainfall threshold of landslide disaster in Guangxi[D]. Nanning:Guangxi University,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Lifeng. Study on critical rainfall threshold of landslide disaster in Guangxi[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 梁柱. 机器学习在浅层滑坡敏感性评价中的综合应用与研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2021. [LIANG Zhu. Comprehensive application and research of machine learning in sensitivity evaluation of shallow landslide[D]. Changchun:Jilin University,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIANG Zhu. Comprehensive application and research of machine learning in sensitivity evaluation of shallow landslide[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 陈贺,付有旺. 贡山县进藏通道群发性滑坡地质特征与降雨阈值[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2024,43(增刊2):3861 − 3871. [CHEN He,FU Youwang. Geological feature and rainfall threshold of cluster landslides along roads toward Tibet in Gongshan County,Yunnan Province,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2024,43(Sup 2):3861 − 3871. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN He, FU Youwang. Geological feature and rainfall threshold of cluster landslides along roads toward Tibet in Gongshan County, Yunnan Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2024, 43(Sup 2): 3861 − 3871. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 刘帅,王涛,曹佳文,等. 基于优化随机森林模型的降雨群发滑坡易发性评价——以西秦岭极端降雨事件为例[J]. 地质通报,2024,43(6):958 − 970. [LIU Shuai,WANG Tao,CAO Jiawen,et al. Susceptibility assessment of precipitation-induced mass landslides based on optimal random forest model:Taking the extreme precipitation event in western Qinling mountains as an example[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2024,43(6):958 − 970. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.12097/gbc.2023.11.008
LIU Shuai, WANG Tao, CAO Jiawen, et al. Susceptibility assessment of precipitation-induced mass landslides based on optimal random forest model: Taking the extreme precipitation event in western Qinling mountains as an example[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2024, 43(6): 958 − 970. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12097/gbc.2023.11.008
[20] CHEN Tianqi,GUESTRIN C,CHEN Tianqi,et al. XGBoost[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. August 13 - 17,2016,San Francisco,California,USA. ACM,2016:785-794.
[21] 赵楠,卢毅敏. 中国地表臭氧浓度估算及健康影响评估[J]. 环境科学,2022,43(3):1235 − 1245. [ZHAO Nan,LU Yimin. Estimation of surface ozone concentration and health impact assessment in China[J]. Environmental Science,2022,43(3):1235 − 1245. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHAO Nan, LU Yimin. Estimation of surface ozone concentration and health impact assessment in China[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(3): 1235 − 1245. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 刘云,康卉君. 江西崩塌滑坡泥石流灾害空间时间分布特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(4):107 − 112. [LIU Yun,KANG Huijun. Spatial-temporal distribution of landslide,rockfall and debris flow hazards in Jiangxi Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(4):107 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Yun, KANG Huijun. Spatial-temporal distribution of landslide, rockfall and debris flow hazards in Jiangxi Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(4): 107 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 方宏宇. 广东龙川县“6•12” 群发型浅层滑坡发育特征及成因机理研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2021. [FANG Hongyu. Study on the development characteristics and genetic mechanism of “6•12” group-type shallow landslide in Longchuan County,Guangdong Province[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
FANG Hongyu. Study on the development characteristics and genetic mechanism of “6•12” group-type shallow landslide in Longchuan County, Guangdong Province[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 邓祖保,龚恩德. 山地公园群发地质灾害致灾因子分析及防治建议[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,2024,35(3):55 − 60. [DENG Zubao,GONG Ende. Analysis of the factors inducing group geological disasters in a mountain park and suggestions for control measures[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,2024,35(3):55 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2024.03.008
DENG Zubao, GONG Ende. Analysis of the factors inducing group geological disasters in a mountain park and suggestions for control measures[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 2024, 35(3): 55 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2024.03.008
[25] 穆启超,王万迁,王琦,等. 贵州松桃长冲组滑坡形成机理分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(3):40 − 47. [MU Qichao,WANG Wanqian,WANG Qi,et al. Analysis of the formation mechanism of landslide in Changchong group,Songtao,Guizhou[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(3):40 − 47. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
MU Qichao, WANG Wanqian, WANG Qi, et al. Analysis of the formation mechanism of landslide in Changchong group, Songtao, Guizhou[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(3): 40 − 47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 郭飞,王秀娟,陈玺,等. 基于不同模型的赣南地区小型削方滑坡易发性评价对比分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(6):125 − 133. [GUO Fei,WANG Xiujuan,CHEN Xi,et al. Comparative analyses on susceptibility of cutting slope landslides in southern Jiangxi using different models[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(6):125 − 133. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GUO Fei, WANG Xiujuan, CHEN Xi, et al. Comparative analyses on susceptibility of cutting slope landslides in southern Jiangxi using different models[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(6): 125 − 133. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: